Long-Term Follow-Up of Acute Hepatitis B: New Insights in Its Natural History and Implications for Antiviral Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Virological Analyses and Viral Load Quantitation
2.3. DNA Extraction, Amplification and Sequencing
2.4. Worldwide HBV Sequence Selection and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
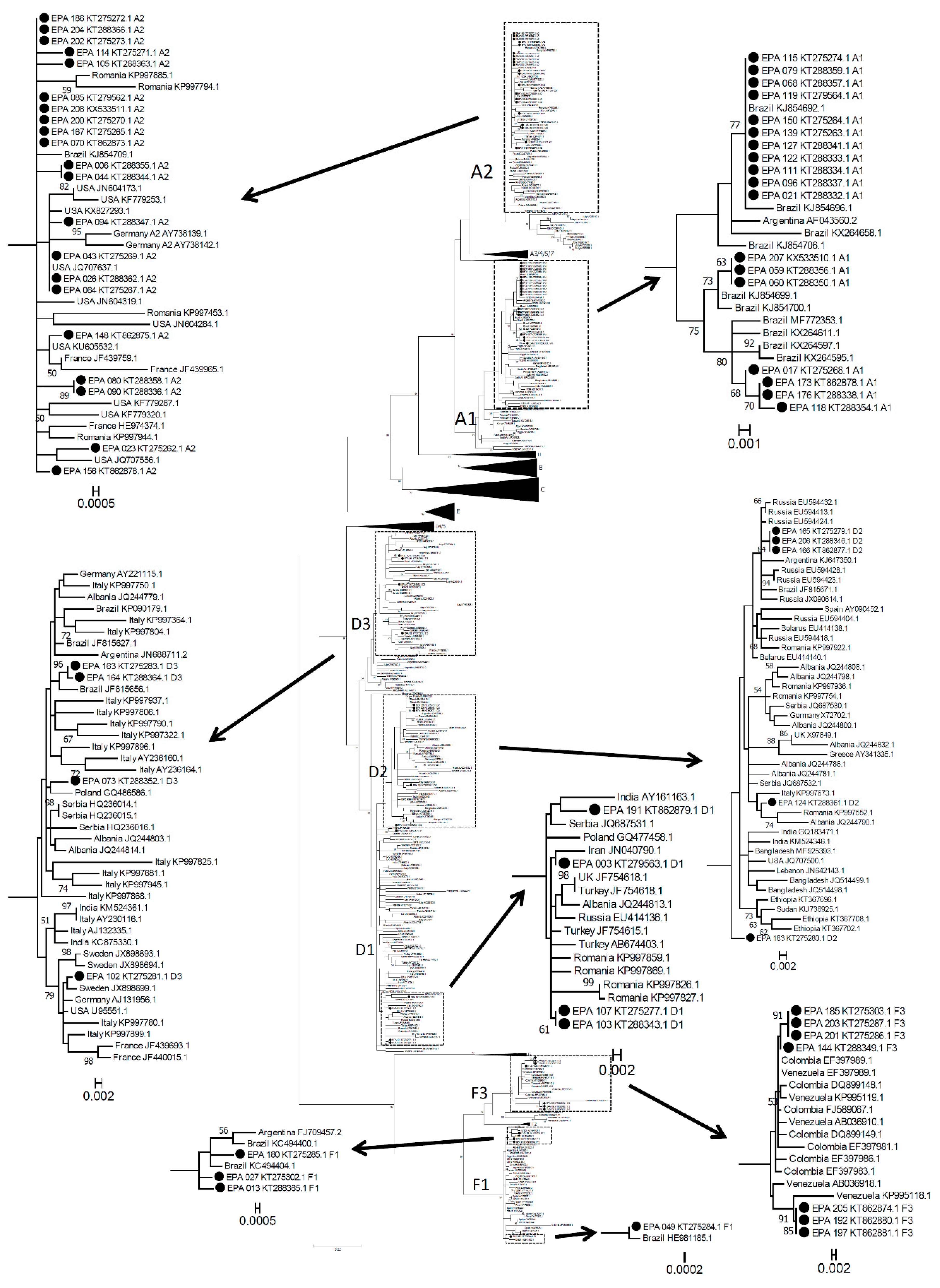
3.1. Molecular Epidemiology of Symptomatic Acute Hepatitis B Infection
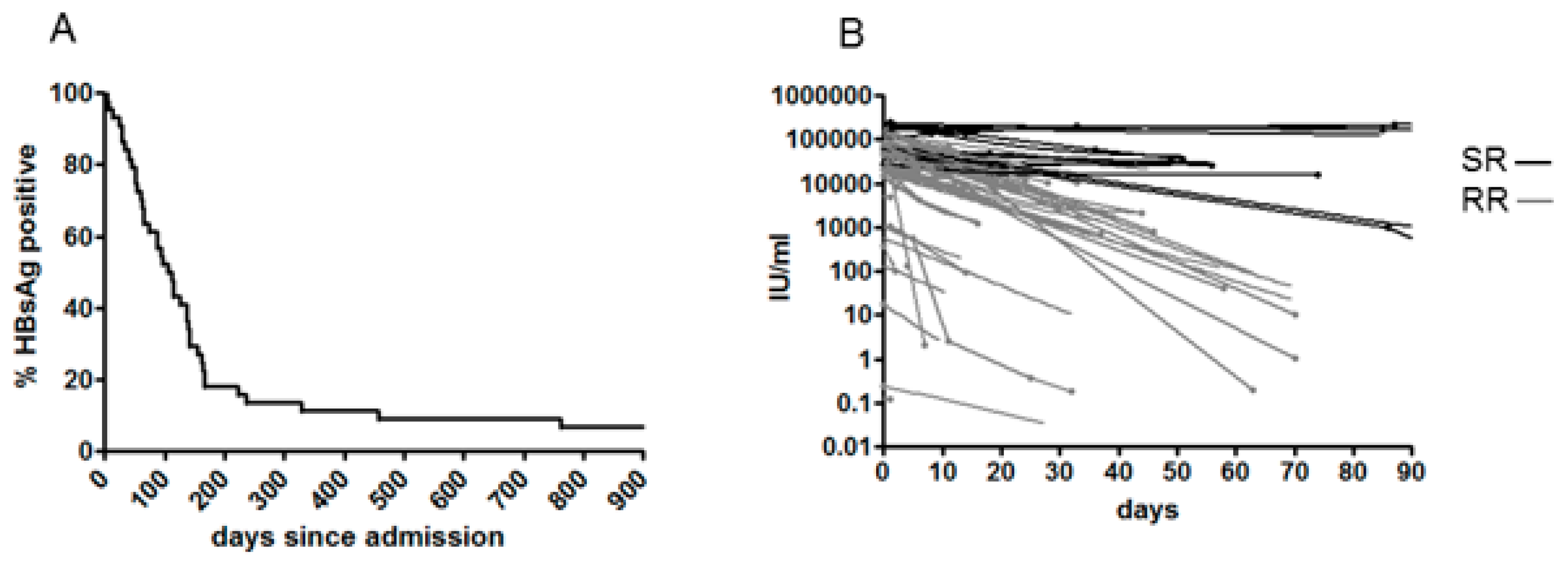
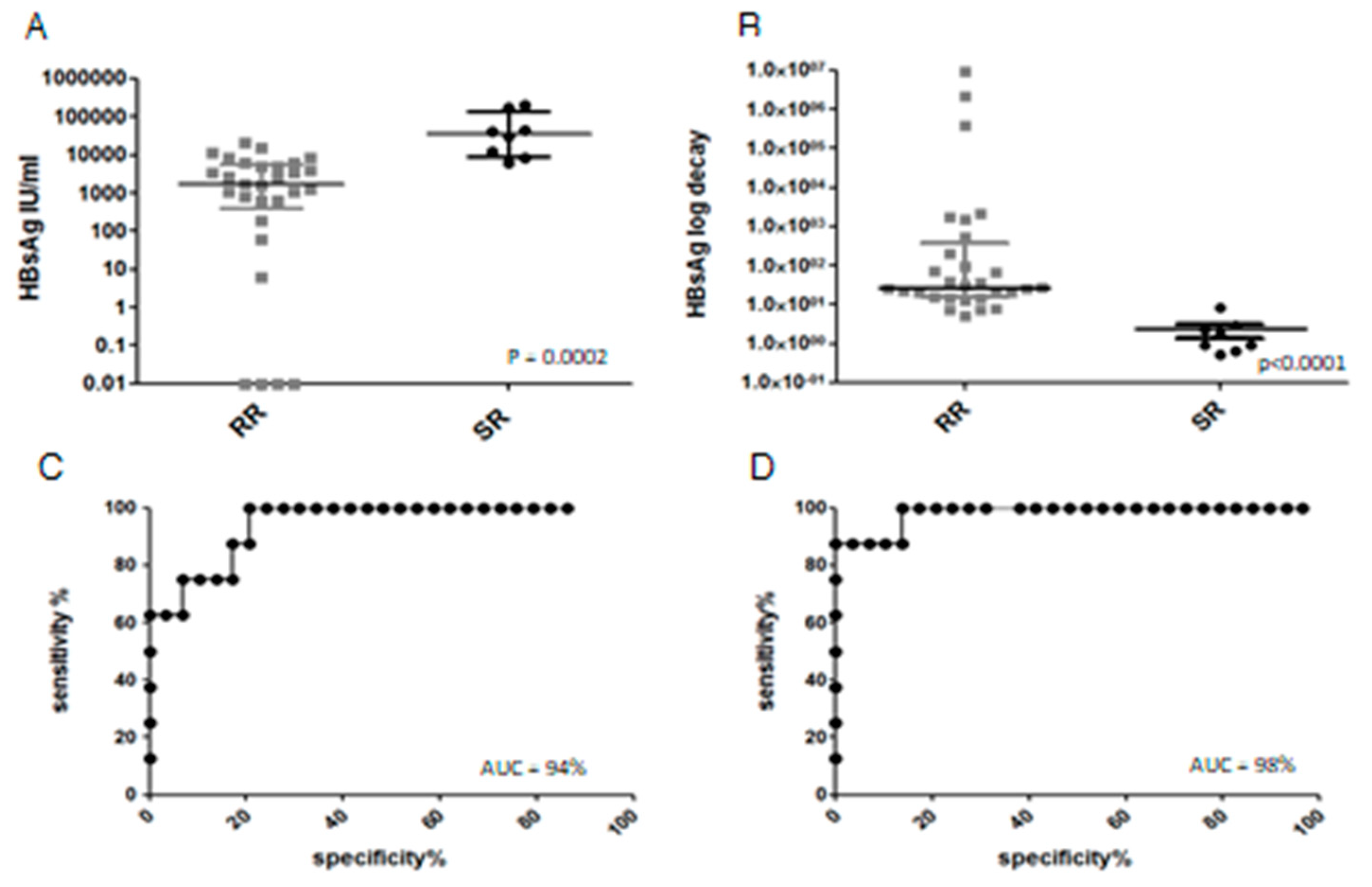
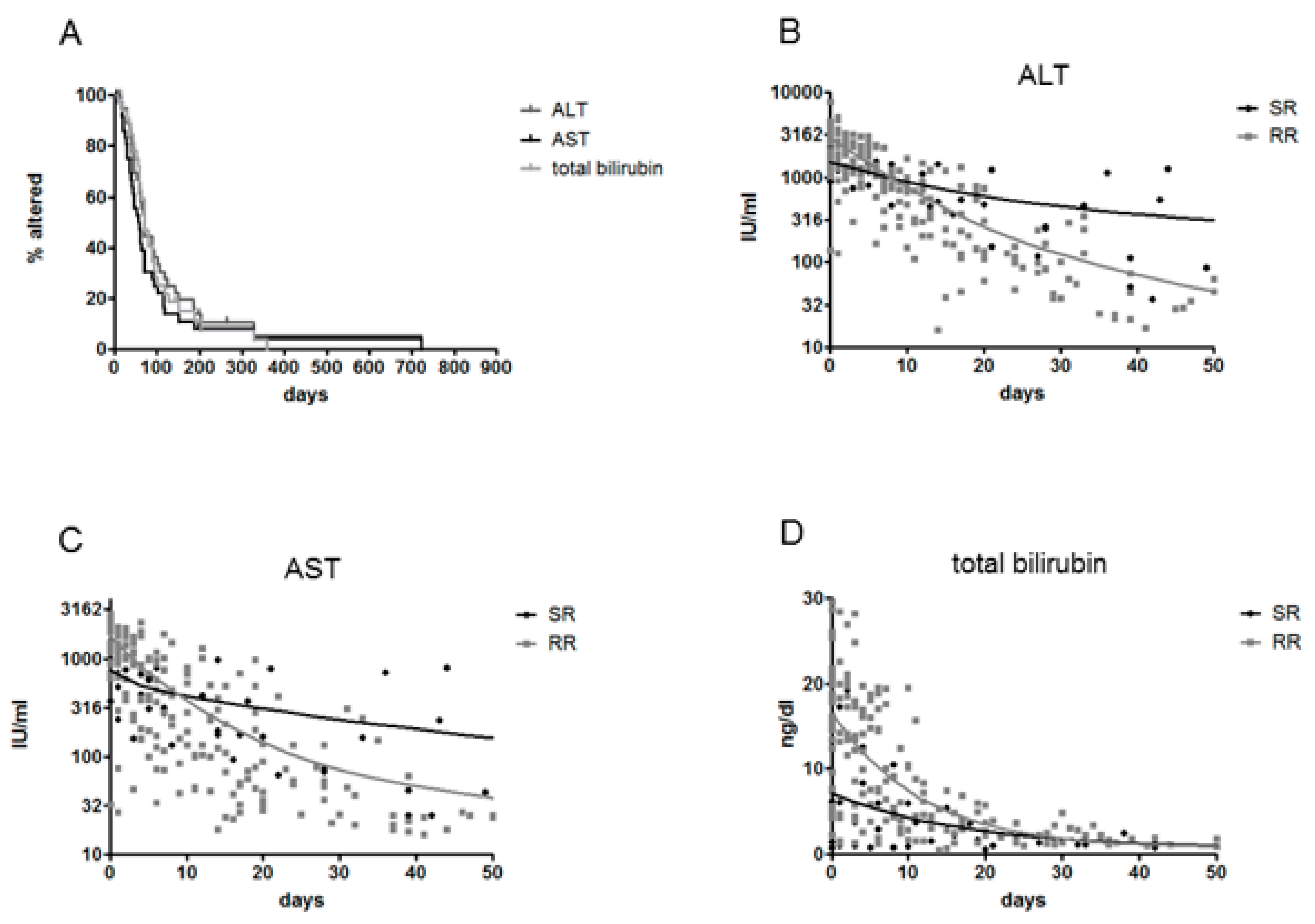
3.2. Clinical Outcome, Natural History and HBsAg Clearance
3.3. HBeAg/Anti-HBe Seroconversion and Evolution of the Precore Region
3.4. Mutations in the RT/HBsAg Region
4. Discussion
Author contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chotiyaputta, W.; Lok, A.S. Hepatitis B virus variants. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caligiuri, P.; Cerruti, R.; Icardi, G.; Bruzzone, B. Overview of hepatitis B virus mutations and their implications in the management of infection. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuma, P.; Pineda, J.A.; Labarga, P.; Vidal, F.; Rodriguez, C.; Poveda, E.; Santos, J.; Gonzalez-García, J.; Sobrino, P.; Tural, C.; et al. HBV primary drug resistance in newly diagnosed HIV-HBV-coinfected individuals in Spain. Antivir. Ther. 2011, 16, 585–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxa, D.M.; Thekdi, A.D.; Golembieski, A.; Krishnan, P.V.; Sharif, O.; Kizy, A.; Shetron-Rama, L.; Jovanovich, J.; Chappell, B.J.; Snow-Lampart, A.; et al. Evaluation of anti-HBV drug resistant mutations among patients with acute symptomatic hepatitis B in the United States. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, N.; Tonziello, G.; Colombatto, P.; Pisaturo, M.; Messina, V.; Moriconi, F.; Alessio, L.; Sagnelli, C.; Cavallone, D.; Brunetto, M.; et al. Lamivudine-resistant HBV strain rtM204V/I in acute hepatitis B. J. Infect. 2013, 67, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, L.; Si, L.; Wang, Y.; Ren, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, D. Acute hepatitis B infection associated with drug-resistant hepatitis B virus. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 48, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, F.; Dai, J.; Yang, S.; Jiang, X.; Cui, X.; Ning, H.; Li, J.; Huang, M. Prevalence and types of drug-resistant variants in Chinese patients with acute hepatitis B. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 1527–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, N.; Alessio, L.; Pisaturo, M.; Macera, M.; Sagnelli, C.; Zampino, R.; Sagnelli, E. Hepatitis B virus infection in immigrant populations. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2955–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassopoulos, N.C.; Papaevangelou, G.J.; Sjogren, M.H.; Roumeliotou-Karayannis, A.; Gerin, J.L.; Purcell, R.H. Natural history of acute hepatitis B surface antigen-positive hepatitis in Greek adults. Gastroenterology 1987, 92, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, C.T.; Fontana, R.J.; Polson, J.; Hussain, M.; Shakil, A.O.; Han, S.H.; Davern, T.J.; Lee, W.M.; Lok, A.S.-F.; The US Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Clinical outcome and virological characteristics of hepatitis B-related acute liver failure in the United States. J. Viral Hepat. 2005, 12, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 21, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccaro, O.; Romano, L.; Mele, A.; Mariano, A.; Clementi, M.; Tosti, M.E.; Taliani, G.; Galli, C.; Zanetti, A.R.; Spada, E.; et al. Clinical, epidemiological and virological features of acute hepatitis B in Italy. Infection 2015, 43, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, N.; Masiello, A.; Tonziello, G.; Pisapia, R.; Pisaturo, M.; Sagnelli, C.; Messina, V.; Iodice, V.; Sagnelli, E. Factors affecting the changes in molecular epidemiology of acute hepatitis B in a Southern Italian area. J. Viral Hepat. 2010, 17, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urone, N.; Di Marco, V.; Cacopardo, B.; Craxi, A.; Ferraro, D. Impact of HBV genotypes A and D genetic variability on infection evolution. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 33, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Ikeda, K.; Suzuki, F.; Arfase, Y.; Akuta, N.; Hosaka, T.; Saitoh, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Someya, T.; et al. Persistence of acute infection with hepatitis B virus genotype A and treatment in Japan. J. Med. Virol. 2005, 76, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Hige, S.; Yamada, G.; Murawaki, Y.; Komatsu, M.; Kuramitsu, T.; Kawata, S.; Tanaka, E.; Izumi, N.; et al. Distribution of hepatitis B virus genotypes among patients with chronic infection in Japan shifting toward an increase of genotype A. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayerat, C.; Mantegani, A.; Frei, P.C. Does hepatitis B virus (HBV) genotype influence the clinical outcome of HBV infection? J. Viral Hepat. 1999, 6, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Yotsuyanagi, H.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Karino, Y.; Takikawa, Y.; Saito, T.; Arase, Y.; Imazeki, F.; Kurosaki, M.; Umemura, T.; et al. Risk factors for long-term persistence of serum hepatitis B surface antigen following acute hepatitis B virus infection in Japanese adults. Hepatology 2014, 59, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Ferrari, C. Adaptive immunity in HBV infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64 (Suppl. 1), S71–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, C.; Penna, A.; Bertoletti, A.; Valli, A.; Antoni, A.D.; Giuberti, T.; Cavalli, A.; Petit, M.A.; Fiaccadori, F. Cellular immune response to hepatitis B virus-encoded antigens in acute and chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 3442–3449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maini, M.K.; Boni, C.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.S.; Reignat, S.; Lee, C.K.; Larrubia, J.R.; Webster, G.J.M.; McMichael, A.J.; Ferrari, C.; et al. Direct ex vivo analysis of hepatitis B virus-specific CD8+ T cells associated with the control of infection. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimme, R.; Wieland, S.; Steiger, C.; Ghrayeb, J.; Reimann, K.A.; Purcell, R.H.; Chisari, F.V. CD8+ T cells mediate viral clearance and disease pathogenesis during acute hepatitis B virus infection. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Ishikawa, T.; Hobbs, M.V.; Matzke, B.; Schreiber, R.; Chisari, F.V. Intracellular inactivation of the hepatitis B virus by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Immunity 1996, 4, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, G.J.; Reignat, S.; Maini, M.K.; Whalley, S.A.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.; Brown, D.; Amlot, P.L.; Williams, R.; Vergani, D.; et al. Incubation phase of acute hepatitis B in man: Dynamic of cellular immune mechanisms. Hepatology 2000, 32, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.; Chokshi, S.; Riva, A.; Evans, A.; Williams, R.; Naoumov, N.V. CD8+ T cell control of hepatitis B virus replication: Direct comparison between cytolytic and noncytolytic functions. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 287–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.L.; Althage, A.; Chung, J.; Maier, H.; Wieland, S.; Isogawa, M.; Chisari, F.V. Immune effectors required for hepatitis B virus clearance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Stadler, D.; Lucifora, J.; Reisinger, F.; Webb, D.; Hosel, M.; Michler, T.; Wisskirchen, K.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, K.; et al. Interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α produced by T cells reduce the HBV persistence form, cccDNA, without cytolysis. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozasa, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Orito, E.; Sugiyama, M.; Kang, J.H.; Hige, S.; Kuramitsu, T.; Suzuki, K.; Tanaka, E.; Okada, S.; et al. Influence of genotypes and precore mutations on fulminant or chronic outcome of acute hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2006, 44, 326–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Li, B.; Ren, X.; Bai, S.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Dai, J.; et al. Features and clinical implications of hepatitis B virus genotypes and mutations in basal core promoter/precore region in 507 Chinese patients with acute and chronic hepatitis B. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 47, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, H.; Evans, A.A.; London, W.T.; Block, T.M.; Ren, X.D. Quantitative dynamics of hepatitis B basal core promoter and precore mutants before and after HBeAg seroconversion. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Guindon, S.; Rodrigo, A.; Lim, S.G. Increased viral quasispecies evolution in HBeAg seroconverter patients treated with oral nucleoside therapy. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mphahlele, M.J.; Shattock, A.G.; Boner, W.; Quinn, J.; McCormick, P.A.; Carman, W.F. Transmission of a homogenous hepatitis B virus population of A1896-containing strains leading to mild resolving acute hepatitis and seroconversion to hepatitis B e antigen antibodies in an adult. Hepatology 1997, 26, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Arase, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Tsubota, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, F.; Akuta, N.; Hosaka, T.; et al. Precore wild-type hepatitis B virus with G1896 in the resolution of persistent hepatitis B virus infection. Intervirology 2003, 46, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Cai, B.; Tang, J.; Ying, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, L. Precore mutation of hepatitis B virus may contribute to hepatocellular carcinoma risk: Evidence from an updated meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michitaka, K.; Horiike, N.; Chen, Y.; Yatsuhashi, H.; Yano, M.; Kojima, N.; Ohkubo, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamamoto, K.; Ohno, N.; et al. Infectious source factors affecting the severity of sexually transmitted acute hepatitis due to hepatitis B virus genotype C. Intervirology 2005, 48, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, L.; Welkers, M.R.A.; van Dort, K.A.; Takkenberg, R.B.; Lopatin, U.; Zaaijer, H.L.; de Jong, M.D.; Reesink, H.W.; Kootstra, N.A. Viral minority variants in the core promoter and precore region identified by deep sequencing are associated with response to peginterferon and adefovir in HBeAg negative chronic hepatitis B patients. Antivir. Res. 2017, 145, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homs, M.; Buti, M.; Quer, J.; Jardi, R.; Schaper, M.; Tabernero, D.; Ortega, I.; Sanchez, A.; Esteban, R.; Rodriguez-Frias, F. Ultra-deep pyrosequencing analysis of the hepatitis B virus preCore region and main catalytic motif of the viral polymerase in the same viral genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 8457–8471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inuzuka, T.; Ueda, Y.; Morimura, H.; Fujii, Y.; Umeda, M.; Kou, T.; Osaki, Y.; Uemoto, S.; Chiba, T.; Marusawa, H. Reactivation from occult HBV carrier status is characterized by low genetic heterogeneity with the wild-type or G1896A variant prevalence. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisotti, A.; Azzaroli, F.; Buonfiglioli, F.; Montagnani, M.; Alessandrelli, F.; Mazzella, G. Lamivudine treatment for severe acute HBV hepatitis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 5, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.W.; Sun, L.J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Kang, P.; Li, S.C. The study of efficacy of lamivudine in patients with severe acute hepatitis B. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Arase, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Tsubota, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Saitoh, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, F.; Akuta, N.; Someya, T.; et al. Viral genotypes and response to interferon in patients with acute prolonged hepatitis B virus infection of adulthood in Japan. J. Med. Virol. 2002, 68, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tassopoulos, N.C.; Koutelou, M.G.; Polychronaki, H.; Paraloglou-Ioannides, M.; Hadziyannis, S.J. Recombinant interferon-α therapy for acute hepatitis B: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Viral Hepat. 1997, 4, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Satapathy, S.; Monga, R.; Das, K.; Hissar, S.; Pande, C.; Sharma, B.C.; Sarin, S.K. A randomized controlled trial of lamivudine to treat acute hepatitis B. Hepatology 2007, 45, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainokami, S.; Abe, K.; Sato, A.; Endo, R.; Takikawa, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Okamoto, H. Initial load of hepatitis B virus (HBV), its changing profile, and precore/core promoter mutations correlate with the severity and outcome of acute HBV infection. J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 42, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Genotype | A | D | F |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 42.8 ± 13.1 | 41.2 ± 1.5 | 40.9 ± 10.5 |
| Gender (f/m) | 8/36 | 4/16 | 2/9 |
| AST, IU/mL | 2358 ± 684 a | 3234 ± 677 b | 1264 ± 885 |
| ALT, IU/mL | 1491 ± 914 c,d | 1865 ± 1773 e | 757 ± 916 |
| Total bilirubin, ng/dl | 14.8 ± 8.7 f | 17.6 ± 8.9 g | 10.3 ± 11.4 |
| HBsAg, logIU/mL | 4.64 ± 0.57 h | 3.66 ± 1.70 | 4.28 ± 1.12 |
| HBeAg (−/+ at admission) | 4/40 | 7/13 | 1/10 |
| HIV (−/+ at admission) | 43/1 | 20/0 | 11/0 |
| HCV RNA (−/+ at admission) | 43/1 | 20/0 | 11/0 |
| HDV (−/+ at admission) | 43/1 | 20/0 | 11/0 |
| AHB | CHB | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 19 (28.8%) | 23 (6%) | <0.0001 |
| A2 | 21 (31.8%) | 59 (14%) | 0.0005 |
| B | 1 (1.7%) | 0 (0%) | ns |
| C | 1 (1.7%) | 0 (0%) | ns |
| D1 | 5 (7.7%) | 50 (13%) | ns |
| D2 | 4 (6.1%) | 45 (11%) | ns |
| D3 | 4 (6.1%) | 227 (52%) | <0.0001 |
| D4 | 0 (0%) | 4 (1%) | ns |
| F | 11 (16.7%) | 7 (2%) | <0.0001 |
| G | 0 (0%) | 4 (1%) | ns |
| H | 0 (0%) | 1 (0%) | ns |
| A, n = 37 | D, n = 19 | p (Fisher) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HBeAg—at admission | 3 (8%) | 7 (37%) | 0.01 |
| chronic infection | 2 (6%) | 0 | >0.1 |
| G1896A | 0 | 6 (32%) | 0.0006 |
| C1653T | 0 | 1 (5%) | >0.1 |
| T1753A | 1 (3%) | 1 (5%) | >0.1 |
| A1762T | 0 | 1 (5%) | >0.1 |
| G1764A | 1 (3%) | 3 (16%) | 0.09 |
| T1846A | 0 | 2 (11%) | >0.1 |
| G1899A | 2 (6%) | 1 (5%) | >0.1 |
| any mutation | 4 (11%) | 8 (42%) | 0.0075 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menzo, S.; Minosse, C.; Vincenti, D.; Vincenzi, L.; Iacomi, F.; Zaccaro, P.; D’Offizi, G.; Capobianchi, M.R. Long-Term Follow-Up of Acute Hepatitis B: New Insights in Its Natural History and Implications for Antiviral Treatment. Genes 2018, 9, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060293
Menzo S, Minosse C, Vincenti D, Vincenzi L, Iacomi F, Zaccaro P, D’Offizi G, Capobianchi MR. Long-Term Follow-Up of Acute Hepatitis B: New Insights in Its Natural History and Implications for Antiviral Treatment. Genes. 2018; 9(6):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060293
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenzo, Stefano, Claudia Minosse, Donatella Vincenti, Laura Vincenzi, Fabio Iacomi, Paola Zaccaro, Gianpiero D’Offizi, and Maria R. Capobianchi. 2018. "Long-Term Follow-Up of Acute Hepatitis B: New Insights in Its Natural History and Implications for Antiviral Treatment" Genes 9, no. 6: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060293
APA StyleMenzo, S., Minosse, C., Vincenti, D., Vincenzi, L., Iacomi, F., Zaccaro, P., D’Offizi, G., & Capobianchi, M. R. (2018). Long-Term Follow-Up of Acute Hepatitis B: New Insights in Its Natural History and Implications for Antiviral Treatment. Genes, 9(6), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9060293






