An Analytic Approach Using Candidate Gene Selection and Logic Forest to Identify Gene by Environment Interactions (G × E) for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in African Americans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
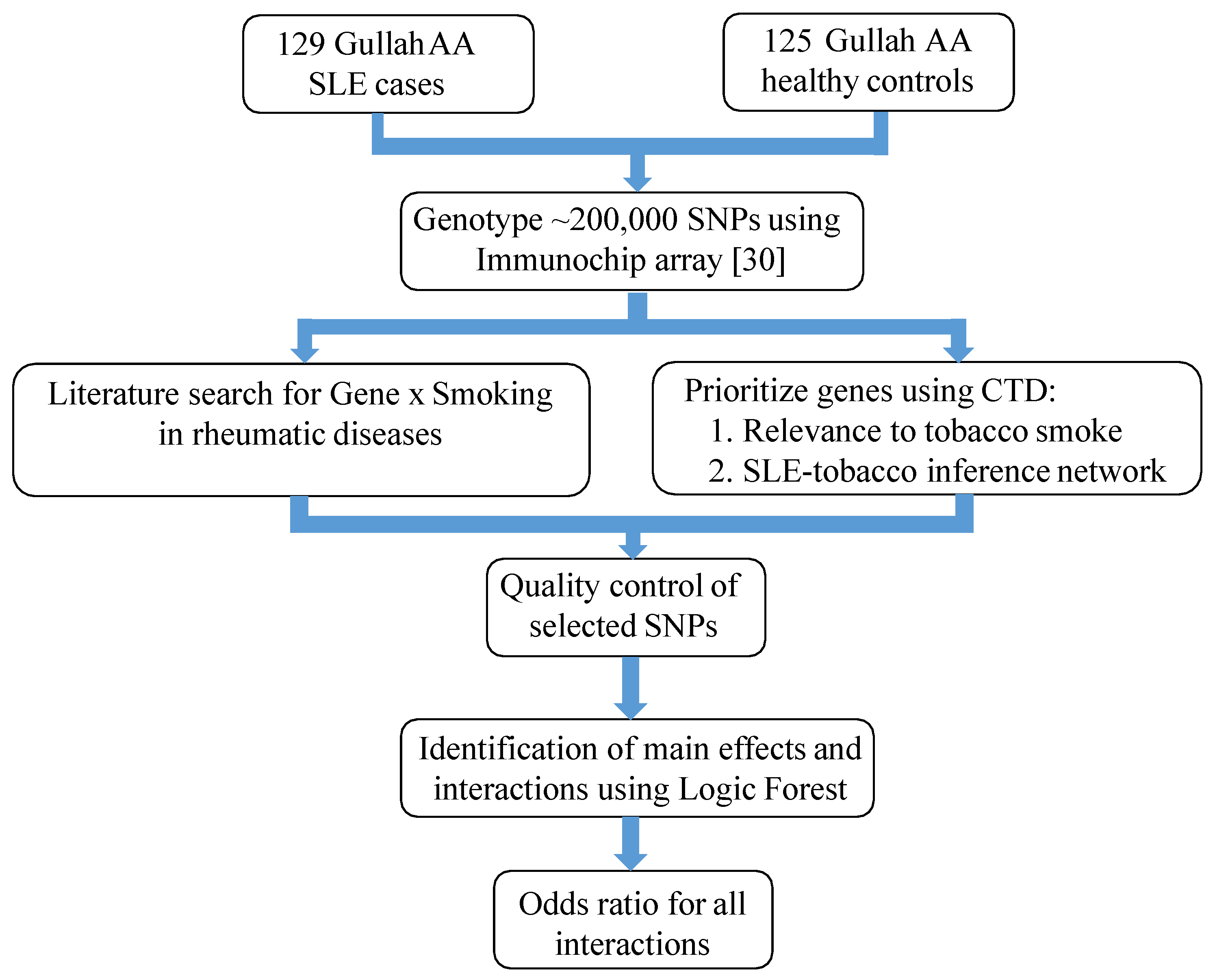
2.1. Study Subjects and Design
2.2. Prioritization of SNPs
2.2.1. Gene Selection
2.2.2. Genotypic Dataset and Quality Control
2.3. Identification of Important Main Effects and Interactions
2.3.1. Logic Forest
2.3.2. Validation of Main Effects and Interactions
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carlborg, O.; Haley, C.S. Epistasis: Too often neglected in complex trait studies? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton-Wells, T.A.; Moore, J.H.; Haines, J.L. Genetics, statistics and human disease: Analytical retooling for complexity. Trends Genet. 2004, 20, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Castro, J.M.; Carlborg, O. A unified model for functional and statistical epistasis and its application in quantitative trait Loci analysis. Genetics 2007, 176, 1151–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, D.J.; Kraft, P.; Jacobs, K.B.; Cox, D.G.; Yeager, M.; Hankinson, S.E.; Wacholder, S.; Wang, Z.; Welch, R.; Hutchinson, A.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies alleles in FGFR2 associated with risk of sporadic postmenopausal breast cancer. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kotti, S.; Bickeboller, H.; Clerget-Darpoux, F. Strategy for detecting susceptibility genes with weak or no marginal effects. Hum. Hered. 2007, 63, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempfle, A.; Scherag, A.; Hein, R.; Beckmann, L.; Chang-Claude, J.; Schäfer, H. Gene–environment interactions for complex traits: Definitions, methodological requirements and challenges. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2008, 16, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, R.G.; Olden, K. Gene-environment interactions in the development of complex disease phenotypes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2008, 5, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert-Diamond, D.; Moore, J.H. Analysis of gene-gene interactions. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2011, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.H.; Hemani, G.; Haley, C.S. Detecting epistasis in human complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordell, H.J. Detecting gene–gene interactions that underlie human diseases. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, M.J.; Flanders, W.D. Nontraditional epidemiologic approaches in the analysis of gene environment interaction: Case-control studies with no controls! Am. J. Epidemiol. 1996, 144, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.; Schaid, D.J. Potential misinterpretation of the case-only study to assess gene-environment interaction. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 150, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Khoury, M.J.; Sun, F.; Flanders, W.D. Case-only design to measure gene-gene interaction. Epidemiology 1999, 10, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, P.S.; Ratnasinghe, D.; Tangrea, J.; Wacholder, S. Limitations of the case-only design for identifying gene-environment interactions. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 154, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanderWeele, T.J.; Hernandez-Diaz, S.H.M. Case-only gene-environment interaction studies: When does association imply mechanistic interaction? Genet. Epidemiol. 2010, 34, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, N.M.; Campbell, U.B.; Rundle, A.G.; Ahsan, H. Further development of the case-only design for assessing gene–environment interaction: Evaluation of and adjustment for bias. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 33, 1014–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doniger, S.; Hofmann, T.; Yeh, J. Predicting CNS permeability of drug molecules: Comparison of neural network and support vector machine algorithms. J. Comput. Biol. 2002, 9, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, L.W.; Ritchie, M.D.; Moore, J.H. Multifactor dimensionality reduction software for detecting gene-gene and gene-environment interactions. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, J.H.; Ritchie, M.D. The challenges of whole-genome approaches to common diseases. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 291, 1642–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction, 2nd ed.; Springer Series in Statistics: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, B.J.; Hill, E.G.; Slate, E.H. Logic Forest: An ensemble classifier for discovering logical combinations of binary markers. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, M.N.; Ziegler, A.; König, I.R. Do little interactions get lost in dark random forests? BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opala, J. The Gullah: Rice, Slavery and the Sierra Leone-American Connection; US Information Service (Fort Sumter National Monument): Sullivans Island, SC, USA, 1987.
- Parra, E.J.; Marcini, A.; Akey, J.; Martinson, J.; Batzer, M.A.; Cooper, R.; Forrester, T.; Allison, D.B.; Deka, R.; Ferrell, R.E.; et al. Estimating African American admixture proportions by use of population-specific alleles. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 63, 1839–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, E.J.; Kittles, R.A.; Argyropoulos, G.; Pfaff, C.; Hiester, K.; Bonilla, C.; Sylvester, N.; Parrish-Gause, D.; Garvey, W.; Jin, L.; et al. Ancestral proportions and admixture dynamics in geographically defined African Americans living in South Carolina. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2001, 114, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, D.C., Jr.; Spruill, I.; Gevao, S.; Morrison, E.Y.; Bernard, O.S.; Argyropoulos, G.; Garvey, W.T. Three novel mtDNA restriction site polymorphisms allow exploration of population affinities of African Americans. Hum. Biol. 2003, 75, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, B.A.; Wilson, J.L.; Kirbah, S.; Sidney, S.S.; Rosenberger, J.; Bassie, L.; Alie, J.A.; McLean, D.C.; Garvey, W.T.; Ely, B. Mitochondrial DNA genetic diversity among four ethnic groups in Sierra Leone. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2005, 128, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean, D.C.; Spruill, I.; Argyropoulos, G.; Page, G.P.; Shriver, M.D.; Garvey, W.T. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplotypes reveal maternal population genetic affinities of Sea Island Gullah-speaking African Americans. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 2005, 127, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, S. A brief history of twins. Lupus 2006, 15, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deafen, D.; Escalante, A.; Weinrib, L.; Horwitz, D.; Bachman, B.; Roy-Burman, P.; Walker, A.; Mack, T.M. A revised estimate of twin concordance in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 1992, 35, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alarcón-Segovia, D.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Cardiel, M.H.; Caeiro, F.; Massardo, L.; Villa, A.R.; Pons-Estel, B.A. Familial aggregation of systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune diseases in 1,177 lupus patients from the GLADEL cohort. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2005, 52, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Tsao, B.P. Genetic susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus in the genomic era. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra, S.G.; Vyse, T.J.; Graham, D.S.C. The genetics of lupus: A functional perspective. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, S.E.; Kottyan, L.C.; Munroe, M.E.; Harley, J.B. Genetic susceptibility to lupus: The biological basis of genetic risk found in B cell signaling pathways. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2012, 92, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wu, H.; Khosravi, M.; Cui, H.; Qian, X.; Kelly, J.A.; Kaufman, K.M.; Langefeld, C.D.; Williams, A.H.; Comeau, M.E.; et al. Association of genetic variants in complement factor H and factor H-related genes with systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Cho, S.K.; Sestak, A.; Namjou, B.; Kang, C.; Bae, S.C. Interferon-gamma gene polymorphisms associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, C.O.; Zhu, J.; Armstrong, D.L.; Yan, M.; Han, J.; Zhou, X.J.; Thomas, J.A.; Reiff, A.; Myones, B.L.; Ojwang, J.O.; et al. Identification of IRAK1 as a risk gene with critical role in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6256–6261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandman-Goddard, G.; Solomon, M.; Rosman, Z.; Peeva, E.; Shoenfeld, Y. Environment and lupus-related diseases. Lupus 2012, 21, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyohara, C.; Washio, M.; Horiuchi, T.; Tada, Y.; Asami, T.; Ide, S.; Takahashi, H.; Kobashi, G.; Kyushu Sapporo SLE (KYSS) Study Group. Cigarette smoking, N-acetyltransferase 2 polymorphisms and systemic lupus erythematosus in a Japanese population. Lupus 2009, 18, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilkeson, G.; James, J.; Kamen, D.; Knackstedt, T.; Maggi, D.; Meyer, A.; Ruth, N. The United States to Africa lupus prevalence gradient revisited. Lupus 2011, 20, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamen, D.L.; Barron, M.; Parker, T.M.; Shaftman, S.R.; Bruner, G.R.; Aberle, T.; James, J.A.; Scofield, R.H.; Harley, J.B.; Gilkeson, G.S. Autoantibody prevalence and lupus characteristics in a unique African American population. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2008, 58, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hochberg, M.C. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spruill, I.J.; Leite, R.S.; Fernandes, J.K.; Kamen, D.L.; Ford, M.E.; Jenkins, C.; Hunt, K.J.; Andrews, J.O. Successes, challenges and lessons learned: Community-engaged research with South Carolina’s Gullah population. Gatew. Int. J. Community Res. Engagem. 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langefeld, C.D.; Ainsworth, H.C.; Graham, D.S.C.; Kelly, J.A.; Comeau, M.E.; Marion, M.C.; Howard, T.D.; Ramos, P.S.; Croker, J.A.; Morris, D.L.; et al. Transancestral mapping and genetic load in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karlson, E.W.; Chang, S.C.; Cui, J.; Chibnik, L.B.; Fraser, P.A.; De Vivo, I.; Costenbader, K.H. Gene–environment interaction between HLA-DRB1 shared epitope and heavy cigarette smoking in predicting incident rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Chang, S.C.; De Vivo, I.; Plenge, R.; Karlson, E.W. Genetic polymorphisms in PTPN22, PADI-4, and CTLA-4 and risk for rheumatoid arthritis in two longitudinal cohort studies: Evidence of gene-environment interactions with heavy cigarette smoking. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keenan, B.T.; Chibnik, L.B.; Cui, J.; Ding, B.; Padyukov, L.; Kallberg, H.; Bengtsson, C.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L.; Karlson, E.W. Effect of interactions of glutathione S-transferase T1, M1, and P1 and HMOX1 gene promoter polymorphisms with heavy smoking on the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010, 62, 3196–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, A.P.; Grondin, C.J.; Lennon-Hopkins, K.; Saraceni-Richards, C.; Sciaky, D.; King, B.L.; Wiegers, T.C.; Mattingly, C.J. The comparative toxicogenomics database: Update 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D972–D978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2016; Available online: http://www.R-project.org (accessed on 15 October 2016).
- Wolf, B. LogicForest: Logic Forest; R package Version 2.1.0; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L.; Friedman, J.; Olshen, R.; Stone, C. Classification and Regression Tees; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Ruczinski, I.; Kooperberg, C.; LeBlanc, M. Logic regression. J. Comput. Graph. Stat. 2003, 12, 475–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svetnik, V.; Liaw, A.; Tong, C.; Culberson, J.C.; Sheridan, R.P.; Feuston, B.P. Random forest: A classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwender, H.; Ickstadt, K. Identification of SNP interactions using logic regression. Biostatistics 2008, 9, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Bagging Predictors; Technical Report 421; Department of Statistics, University of California at Berkley: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1994; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Dietterich, T.G. An experimental comparison of three methods for constructing ensembles of decision trees: Bagging, boosting, and randomization. Mach. Learn. 2000, 40, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Control (n = 104) | SLE (n = 100) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Mean ± Std Dev) | 42.6 ± 11.7 | 38.6 ± 13.4 | 0.022 |
| Female (n, %) | 87 (83.6) | 88 (88.0) | 0.491 |
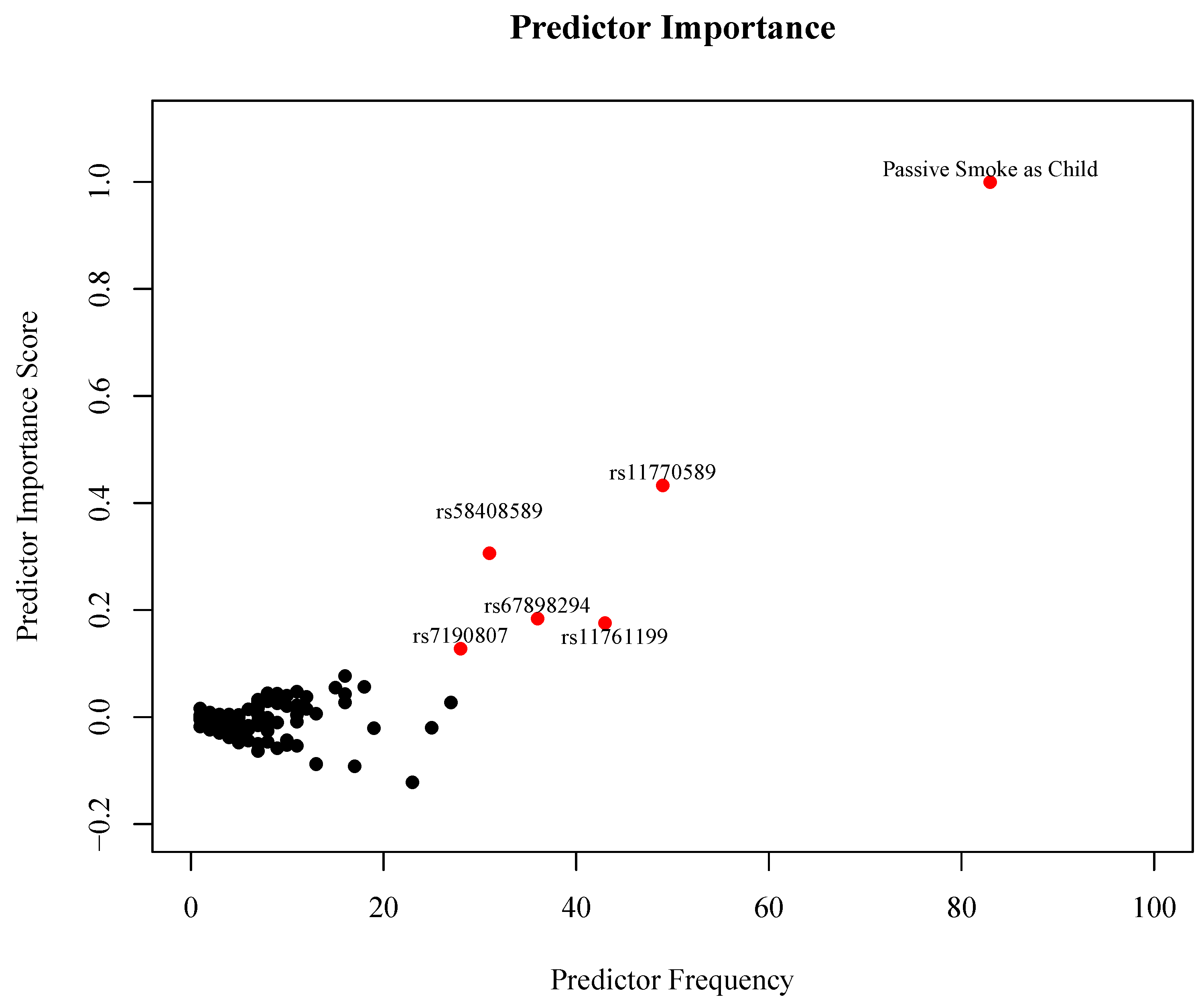
| Passive Smoke Exposure as a Child (n, %) | 28 (26.9) | 41 (41.0) | 0.048 |
| Passive Smoke Exposure as an Adult (n, %) | 18 (17.3) | 20 (20.0) | 0.754 |
| Ever Smoker (n, %) | 24 (23.1) | 24 (24.0) | 1.000 |
| Current Smoker (n, %) | 13 (12.5) | 17 (17.0) | 0.478 |
| Effect | Gene | Odds Ratio (95% CI) | Unadjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
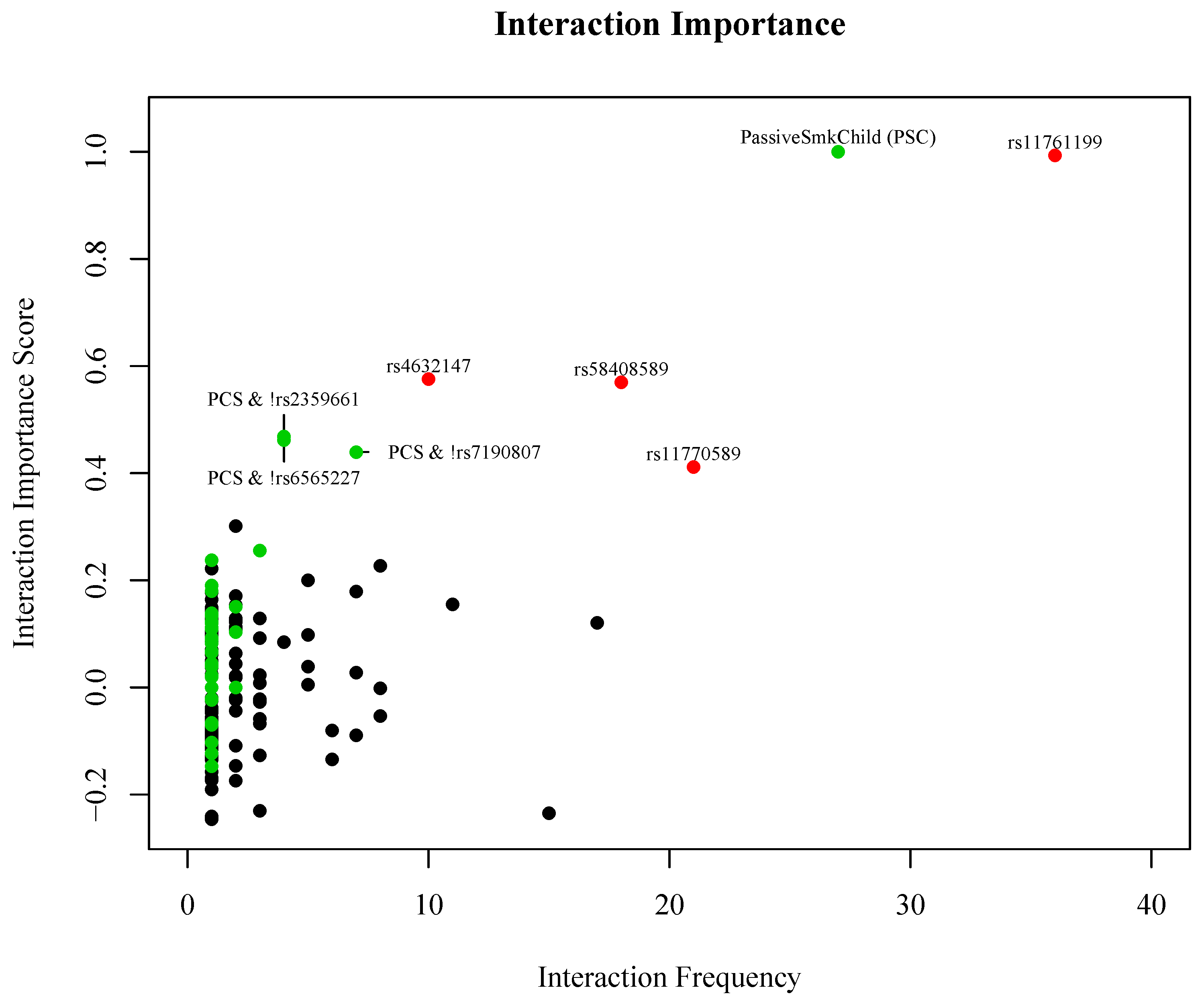
| Passive Smoke Exposure as Child (PSC) | 1.88 (1.01, 3.55) | 0.039 | |
| 2 copies of the minor allele of rs4632147 (T) | ITGAX | 3.09 (1.09, 10.1) | 0.023 |
| 2 copies of the minor allele of rs58408589 (C) | ITGAX | 2.96 (1.23, 7.75) | 0.011 |
| 2 copies of the minor allele of rs11761199 (G) | IRF5 | 7.69 (1.01, 352) | 0.033 |
| 2 copies of the minor allele of rs11770589 (A) | IRF5 | 1.65 (0.81, 3.42) | 0.179 |
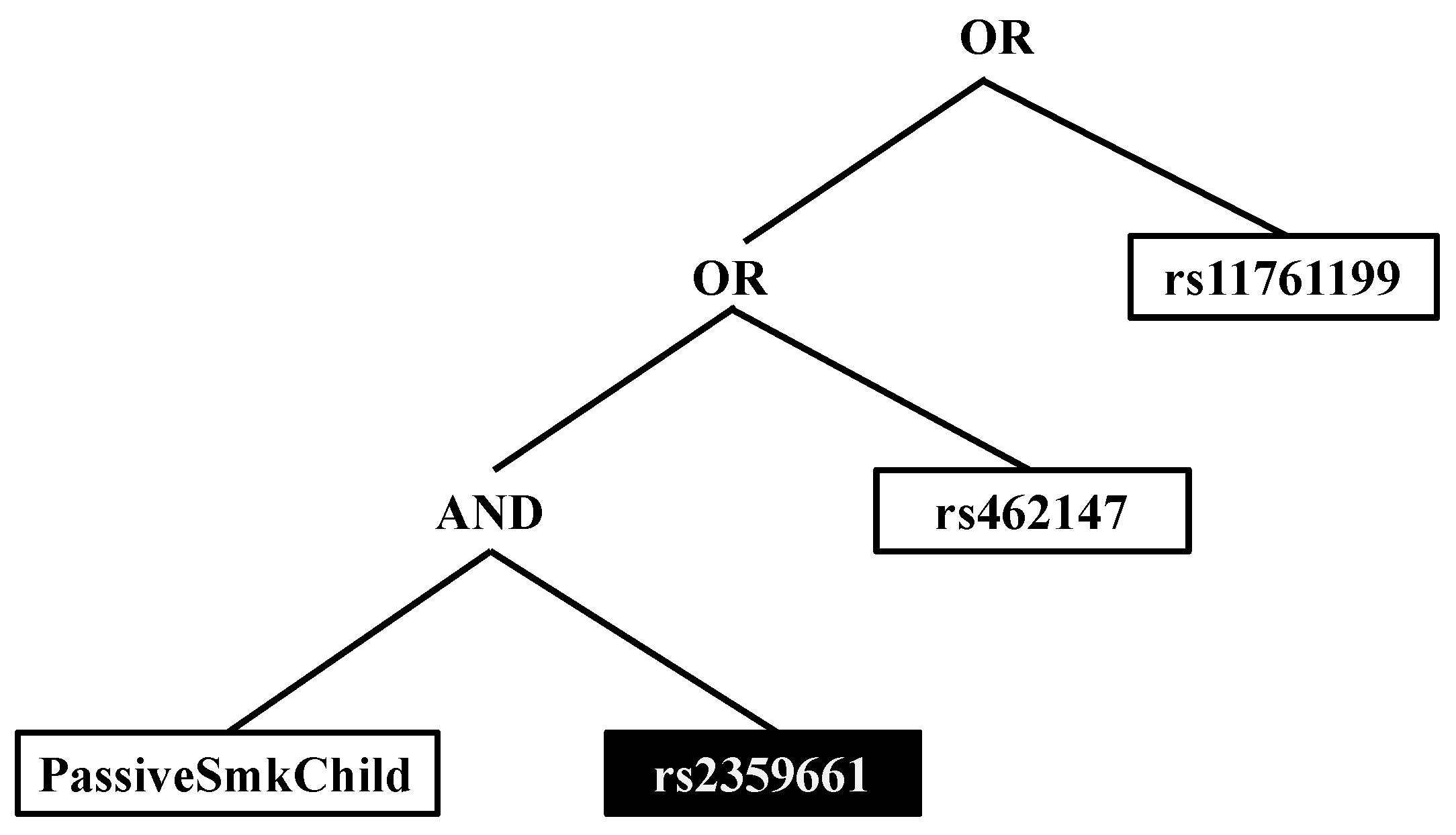
| PSC & copy of the major allele of rs2359661 (A) | ITGAM | 2.28 (1.18, 4.48) | 0.009 |
| PSC & copy of the major allele of rs7190807 (G) | ITGAM | 2.46 (1.25, 4.92) | 0.005 |
| PSC & copy of the major allele of rs6565227 (T) | ITGAM | 2.37 (1.23, 4.66) | 0.006 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wolf, B.J.; Ramos, P.S.; Hyer, J.M.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Hardiman, G.; Nietert, P.J.; Kamen, D.L. An Analytic Approach Using Candidate Gene Selection and Logic Forest to Identify Gene by Environment Interactions (G × E) for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in African Americans. Genes 2018, 9, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9100496
Wolf BJ, Ramos PS, Hyer JM, Ramakrishnan V, Gilkeson GS, Hardiman G, Nietert PJ, Kamen DL. An Analytic Approach Using Candidate Gene Selection and Logic Forest to Identify Gene by Environment Interactions (G × E) for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in African Americans. Genes. 2018; 9(10):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9100496
Chicago/Turabian StyleWolf, Bethany J., Paula S. Ramos, J. Madison Hyer, Viswanathan Ramakrishnan, Gary S. Gilkeson, Gary Hardiman, Paul J. Nietert, and Diane L. Kamen. 2018. "An Analytic Approach Using Candidate Gene Selection and Logic Forest to Identify Gene by Environment Interactions (G × E) for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in African Americans" Genes 9, no. 10: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9100496
APA StyleWolf, B. J., Ramos, P. S., Hyer, J. M., Ramakrishnan, V., Gilkeson, G. S., Hardiman, G., Nietert, P. J., & Kamen, D. L. (2018). An Analytic Approach Using Candidate Gene Selection and Logic Forest to Identify Gene by Environment Interactions (G × E) for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in African Americans. Genes, 9(10), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9100496






