Differential Gene Expression in Response to Salinity and Temperature in a Haloarcula Strain from Great Salt Lake, Utah
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Salt-Temperature Optima Study of NA6-27
2.2. Antibiotic Sensitivity, Biochemical Tests and Lipid Analysis
2.3. Thin Layer Chromatography
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Amplification
2.5. Inoculum Preparation and Growth of NA6-27 at Different Conditions
2.6. Arbitrary Primer Design
2.7. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription PCR
2.8. RNA Arbitrarily Primed PCR
2.9. Confirmation of RNA Arbitrarily Primed PCR Fragments
2.10. Accession Numbers
3. Results
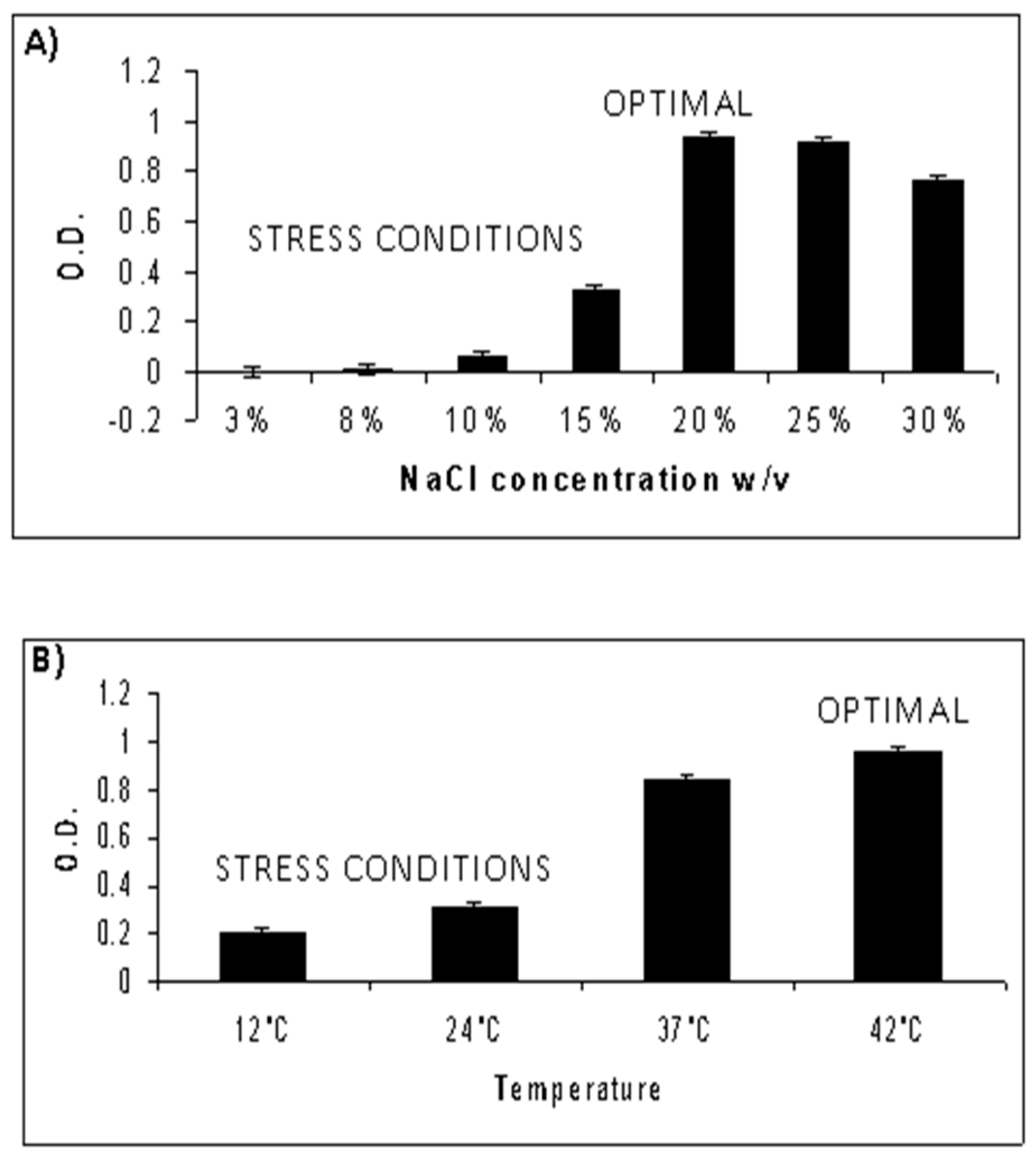
3.1. Characterization of Optimal Growth Conditions for NA6-27
3.2. Nutrient Utilization and Antibiotic Sensitivity for NA6-27
3.3. Lipid Analysis of NA6-27
3.4. Genetic Analysis of NA6-27
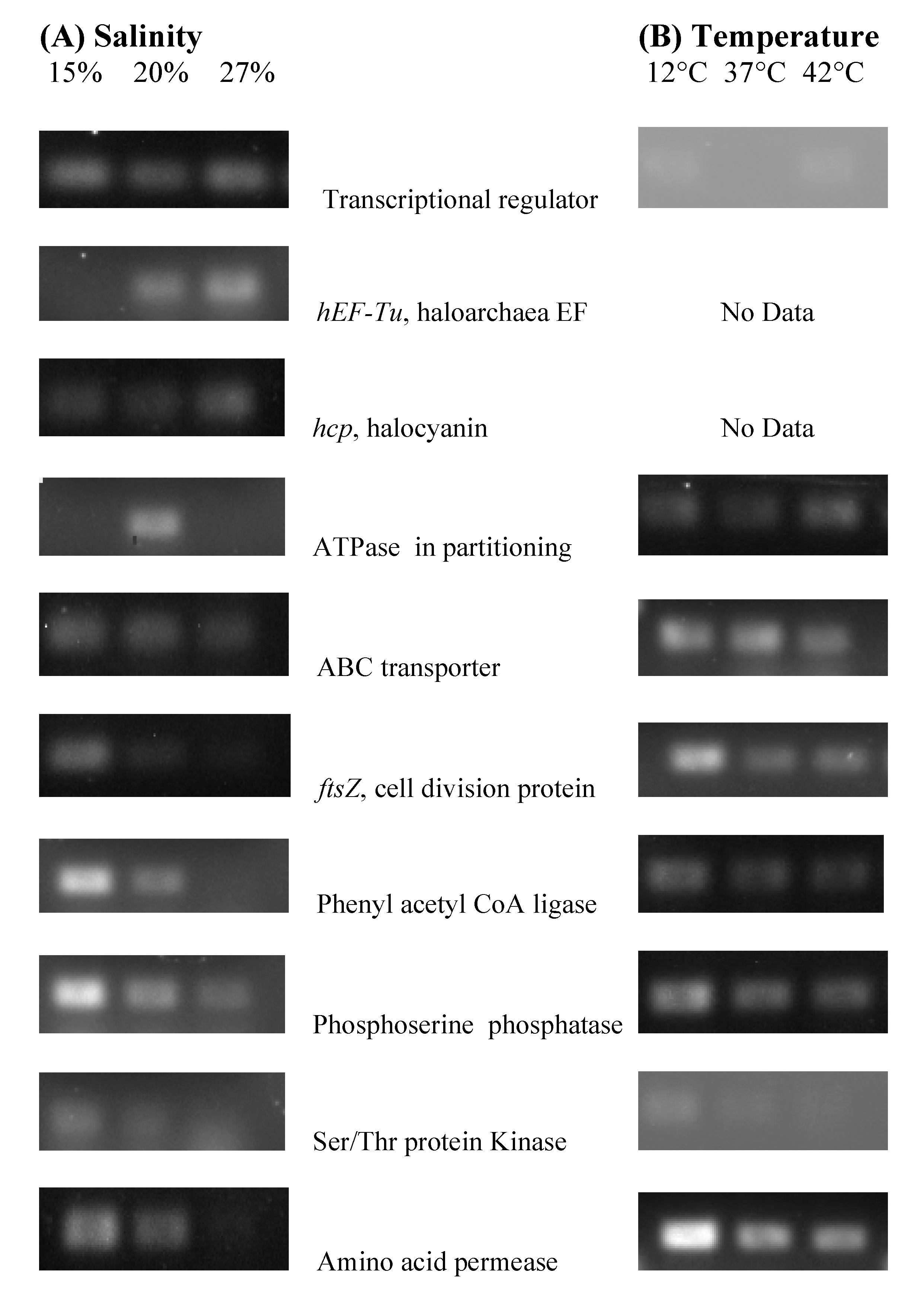
3.5. NA6-27 Gene Expression under Salinity and Temperature Stress
3.6. Identification of Genes in Stress Experiments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keck, W.G.; Hassibe, W.R. The Great Salt Lake; U.S. Geological Survey Pamphlet; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1979; pp. 1–16.
- Cannon, J.S.; Canon, M.A. The Southern Pacific Railroad Trestle—Past and present. In Great Salt Lake, an Overview of Change; Gwynn, J.W., Ed.; Special Publication of the Utah Department of Natural Resources: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2002; pp. 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- Baxter, B.K.; Litchfield, C.D.; Sowers, K.; Griffith, J.D.; Dassarma, P.A.; Dassarma, S. Microbial diversity of Great Salt Lake. In Adaptation to Life at High Salt Concentrations in Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya; Gunde-Cimerman, N., Oren, A., Plemenitas, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 9–26. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida-Dalmet, S.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M.; Litchfield, C.D.; Baxter, B.K. Temporal study of the microbial diversity of the north arm of Great Salt Lake, Utah, U.S. Microorganisms 2015, 3, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meuser, J.E.; Baxter, B.K.; Spear, J.R.; Peters, J.W.; Posewitz, M.C.; Boyd, E.S. Contrasting patterns of community assembly in the stratified water column of Great Salt Lake, Utah. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, E.S.; Hamilton, T.L.; Swanson, K.D.; Howells, A.E.; Baxter, B.K.; Meuser, J.E.; Posewitz, M.C.; Peters, J.W. [Fe]-hydrogenase abundance and diversity along a vertical redox gradient in Great Salt Lake, USA. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 21947–21966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida-Dalmet, S. A Study of the Microbial Diversity in the North Arm of Great Salt Lake. Ph. D. Thesis, George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Crosman, E.T.; Horel, J.D. MODIS-derived surface temperature of the Great Salt Lake. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, F.J. The microbial ecology of the Great Salt Lake. Microb. Ecol. 1977, 3, 143–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norais, C.; Hawkins, M.; Hartman, A.L.; Eisen, J.A.; Myllykallio, H.; Allers, T. Genetic and physical mapping of DNA replication origins in Haloferax volcanii. PLoS Genet. 2007, 3, e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, P.; Chandel, A.K.; Singh, O.V. Extremophiles and Their Applications in Medical Processes; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-12808-5. [Google Scholar]
- Schubert, B.A.; Timofeeff, M.N.; Lowenstein, T.K.; Polle, J.E. Dunaliella cells in fluid inclusions in halite: Significance for long-term survival of prokaryotes. Geomicrobiol. J. 2010, 27, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerulla, K.; Soppa, J. Polyploidy in haloarchaea: Advantages for growth and survival. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerulla, K.; Chimileski, S.; Näther, D.; Gophna, U.; Papke, R.T.; Soppa, J. DNA as a phosphate storage polymer and the alternative advantages of polyploidy for growth or survival. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevack, A.; Gewitz, H.; Hennemann, B.; Yonath, A.; Wittmann, H. Characterization and crystallization of ribosomal particles from Halobacterium marismortui. FEBS Lett. 1985, 184, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.; Zaigler, A.; Hammelmann, M.; Twellmeyer, J.; Raddatz, G.; Schuster, S.C.; Oesterhelt, D.; Soppa, J. Genome-wide analysis of growth phase-dependent translational and transcriptional regulation in halophilic archaea. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soppa, J. From genomes to function: Haloarchaea as model organisms. Microbiology 2006, 152, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, J.; Brenneis, M.; Jellen-Ritter, A.; Heyer, R.; Soppa, J.; Marchfelder, A. Small RNAs in haloarchaea: Identification, differential expression and biological function. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coker, J.A.; DasSarma, P.; Kumar, J.; Müller, J.A.; DasSarma, S. Transcriptional profiling of the model archaeon Halobacterium sp. NRC-1: Responses to changes in salinity and temperature. Saline Syst. 2007, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leuko, S.; Raftery, M.J.; Burns, B.P.; Walter, M.R.; Neilan, B.A. Global protein-level responses of Halobacterium salinarum NRC-1 to prolonged changes in external sodium chloride concentrations. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 2218–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidle, K.A. Differential expression of genes influenced by changing salinity using RNA arbitrarily primed PCR in the archaeal halophile Haloferax volcanii. Extremophiles 2003, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bidle, K.A.; Bartlett, D.H. RNA arbitrarily primed PCR survey of genes regulated by ToxR in the deep-sea bacterium Photobacterium profundum str. SS9. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1688–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Souza, S.E.; Altekar, W.; D’Souza, S. Adaptive response of Haloferax mediterranei to low concentrations of NaCl (<20%) in the growth medium. Arch. Microbiol. 1997, 168, 68–71. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, J.; Haque, F.N.; Paul, A. Carotenogenesis in Haloferax sp. str. BKW301, a halophilic archaeon from Indian solar salterns. J. Adv. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LoBasso, S.; LoPalco, P.; Mascolo, G.; Corcelli, A. Lipids of the ultra-thin square halophilic archaeon Haloquadratum walsbyi. Archaea 2008, 2, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-López, A.; Benlloch, S.; Bonfá, M.; Rodríguez-Valera, F.; Mira, A. Intragenomic 16S rDNA divergence in Haloarcula marismortui is an adaptation to different temperatures. J. Mol. Evol. 2007, 65, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thombre, R.S.; Shinde, V.D.; Oke, R.S.; Dhar, S.K.; Shouche, Y.S. Biology and survival of extremely halophilic archaeon Haloarcula marismortui RR12 isolated from Mumbai salterns, India in response to salinity stress. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Gutiérrez, M.C.; Kamekura, M. Haloarcula quadrata sp. nov., a square, motile archaeon isolated from a brine pool in Sinai (Egypt). Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1999, 49, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Grant, W. Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1997, 47, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A.; Litchfield, C.D. A procedure for the enrichment and isolation of Halobacterium. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1999, 173, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litchfield, C.D.; Gillevet, P.M. Microbial diversity and complexity in hypersaline environments: A preliminary assessment. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 28, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litchfield, C.D.; Oren, A. Polar lipids and pigments as biomarkers for the study of the microbial community structure of solar salterns. In Saline Lakes. Developments in Hydrobiology; Melack, J.M., Jellison, R., Herbst, D.B., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 162, pp. 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield, C.D.; Sikaroodi, M.; Gillevet, P.M. Characterization of natural communities of halophilic microorganisms. Methods Microbiol. 2006, 35, 513–533. [Google Scholar]
- Litchfield, C.D.; (George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA). Personal communication, 2007.
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liang, P. Global analysis of gene expression by differential display. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004, 27, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.D.; Umayam, L.A.; Dickinson, T.; Hickey, E.K.; White, O. The comprehensive microbial resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fislage, R.; Berceanu, M.; Humboldt, Y.; Wendt, M.; Oberender, H. Primer design for a prokaryotic differential display RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 1830–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; O’Connell, R.P.; Averboukh, L.; Wang, F.; Pardee, A.B. Differential display using one-base anchored oligo-dT primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, P.; Meade, J.D.; Pardee, A.B. A protocol for differential display of mRNA expression using either fluorescent or radioactive labeling. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, N.R.; Wong, R.M.-Y.; McClelland, M. Analysis of the SOS response in Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium using RNA fingerprinting by arbitrarily primed PCR. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 3490–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Untergasser, A.; Nijveen, H.; Rao, X.; Bisseling, T.; Geurts, R. Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W71–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takashina, T.; Hamamoto, T.; Otozai, K.; Grant, W.D.; Horikoshi, K. Haloarcula japonica sp. nov., a new triangular halophilic archaebacterium. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1990, 13, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindall, B.J. The family Halobacteriaceae. In The Prokaryotes: A Handbook on the Biology of Bacteria: Ecophysiology, Identification, Applications; Balows, A., Trüper, H.G., Dworkin, M., Harder, W., Schleifer, K.H., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1991; Volume 1, pp. 768–808. [Google Scholar]
- Kamekura, M. Lipids of extreme halophiles. In The Biology of Halophilic Bacteria; Vreeland, R.H., Hochstein, L.I., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 135–161. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xiao, X.; Li, J.; Luo, J.; Wang, F. Identification of genes regulated by changing salinity in the deep-sea bacterium Shewanella sp. WP3 using RNA arbitrarily primed PCR. Extremophiles 2006, 10, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturtevant, J. Applications of differential-display reverse transcription-PCR to molecular pathogenesis and medical mycology. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 408–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.L.; Baxter, B.K. An Analysis of Bipyrimidine Limitations as Photoprotective Genome Strategies in Halophilic Archaea; Utah State University: Logan, UT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Spiess, A.-N.; Ivell, R. A highly efficient method for long-chain cDNA synthesis using trehalose and betaine. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 301, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagel, A.C.; Fleming, J.T.; Sayler, G.S.; Beattie, K.L. Screening for ribosomal-based false positives following prokaryotic mRNA differential display. BioTechniques 2001, 30, 988–990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naftz, D.; Angeroth, C.; Kenney, T.; Waddell, B.; Darnall, N.; Silva, S.; Perschon, C.; Whitehead, J. Anthropogenic influences on the input and biogeochemical cycling of nutrients and mercury in Great Salt Lake, Utah, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2008, 23, 1731–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, B.I.; Ault, T.R.; Smerdon, J.E. Unprecedented 21st century drought risk in the American Southwest and Central Plains. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1400082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; DeRose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world’s saline lakes. Nat. Geosci. 2017, 10, 816–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyyssölä, A.; Kerovuo, J.; Kaukinen, P.; von Weymarn, N.; Reinikainen, T. Extreme halophiles synthesize betaine from glycine by methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 22196–22201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, B.; Bremer, E. Uptake and synthesis of compatible solutes as microbial stress responses to high-osmolality environments. Arch. Microbiol. 1998, 170, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.F. Osmoadaptation and osmoregulation in archaea. Front. Biosci. 2000, 5, D796–D812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.F. Organic compatible solutes of halotolerant and halophilic microorganisms. Saline Syst. 2005, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedwell, D.B. Effect of low temperature on microbial growth: Lowered affinity for substrates limits growth at low temperature. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1999, 30, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macario, A.J.; Lange, M.; Ahring, B.K.; De Macario, E.C. Stress genes and proteins in the archaea. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1999, 63, 923–967. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Toone, W.M.; Mata, J.; Lyne, R.; Burns, G.; Kivinen, K.; Brazma, A.; Jones, N.; Bähler, J. Global transcriptional responses of fission yeast to environmental stress. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Maury, L.; Marguerat, S.; Bähler, J. Tuning gene expression to changing environments: From rapid responses to evolutionary adaptation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, T.J.; Liao, Y.; Ye, J.; Kuchel, R.P.; Poljak, A.; Raftery, M.J.; Cavicchioli, R. Cold adaptation of the Antarctic haloarchaea Halohasta litchfieldiae and Halorubrum lacusprofundi. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2210–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldas, T.D.; El Yaagoubi, A.; Richarme, G. Chaperone properties of bacterial elongation factor EF-Tu. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 11478–11482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerdes, K.; Møller-Jensen, J.; Jensen, R.B. Plasmid and chromosome partitioning: Surprises from phylogeny. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 37, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, H.P. FtsZ, a tubulin homologue in prokaryote cell division. Trends Cell Biol. 1997, 7, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kültz, D. Molecular and evolutionary basis of the cellular stress response. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2005, 67, 225–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattar, S.; Scharf, B.; Kent, S.; Rodewald, K.; Oesterhelt, D.; Engelhard, M. The primary structure of halocyanin, an archaeal blue copper protein, predicts a lipid anchor for membrane fixation. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 14939–14945. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scharf, B.; Engelhard, M. Halocyanin, an archaebacterial blue copper protein (type I) from Natronobacterium pharaonis. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 12894–12900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, F.; Schuster, S.; Broicher, A.; Falb, M.; Palm, P.; Rodewald, K.; Ruepp, A.; Soppa, J.; Tittor, J.; Oesterhelt, D. Evolution in the laboratory: The genome of Halobacterium salinarum str. R1 compared to that of strain NRC-1. Genomics 2008, 91, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattar, S.; Engelhard, M. Cytochrome ba3 from Natronobacterium pharaonis. FEBS J. 1997, 250, 332–341. [Google Scholar]
- Baliga, N.S.; Bonneau, R.; Facciotti, M.T.; Pan, M.; Glusman, G.; Deutsch, E.W.; Shannon, P.; Chiu, Y.; Weng, R.S.; Gan, R.R. Genome sequence of Haloarcula marismortui: A halophilic archaeon from the Dead Sea. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 2221–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corton, J.M.; Gillespie, J.G.; Hardie, D.G. Role of the AMP-activated protein kinase in the cellular stress response. Curr. Biol. 1994, 4, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Blanco, H.; Reglero, A.; Rodriguez-Aparicio, L.B.; Luengo, J. Purification and biochemical characterization of phenylacetyl-CoA ligase from Pseudomonas putida. A specific enzyme for the catabolism of phenylacetic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 7084–7090. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Müller, V.; Spanheimer, R.; Santos, H. Stress response by solute accumulation in archaea. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2005, 8, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collet, J.F.; Stroobant, V.; Van Schaftingen, E. Mechanistic studies of phosphoserine phosphatase, an enzyme related to P-type ATPases. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33985–33990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, M.; Hu, C.; Zhang, J.; Shen, P.; Chen, X. Effects of salinity on the cellular physiological responses of Natrinema sp. J7-2. PloS One 2017, 12, e0184974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, I.B.; Blight, M.A. ABC-ATPases, adaptable energy generators fuelling transmembrane movement of a variety of molecules in organisms from bacteria to humans. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 293, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campanaro, S.; Williams, T.J.; Burg, D.W.; De Francisci, D.; Treu, L.; Lauro, F.M.; Cavicchioli, R. Temperature-dependent global gene expression in the Antarctic archaeon Methanococcoides burtonii. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2018–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakermans, C.; Tollaksen, S.L.; Giometti, C.S.; Wilkerson, C.; Tiedje, J.M.; Thomashow, M.F. Proteomic analysis of Psychrobacter cryohalolentis K5 during growth at subzero temperatures. Extremophiles 2007, 11, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, M.; Völker, U. Non-specific, general and multiple stress resistance of growth-restricted Bacillus subtilis cells by the expression of the σB regulon. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 29, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias-Lopez, J.; Shi, Y.; Tyson, G.W.; Coleman, M.L.; Schuster, S.C.; Chisholm, S.W.; DeLong, E.F. Microbial community gene expression in ocean surface waters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3805–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Nitrogen Source Positive for NA6-27 Growth | Nitrogen Source Negative for NA6-27 Growth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| biuret | l-methionine | ammonia | adenosine |
| l-alanine | l-phenylalanine | l-aspargine | uric acid |
| l-arginine | l-valine | l-aspartic acid | Ala-gln |
| l-proline | d-asparagine | l-cysteine | Ala-glu |
| Gly-met | d-lysine | l-glutamic acid | Ala-thr |
| nitrate | d-valine | l-threonine | Met-ala |
| urea | ethanolamine | l-putrescine | l-valine |
| l-glutamine | uracil | agmatine | acetamide |
| glycine | Gly-asn | N-acetyl-d-glucosamine | guanosine |
| l-histidine | Gly-gln | N-acetyl-d-galactosamine | thymine |
| l-isoleucine | d-aspartic acid | uridine | xanthosine |
| l-leucine | Ala-gly | inosine | allontoin |
| l-lysine | Gly-glu | nitrite | amino-n-valeric ac |
| Gly-met | l-serine | l-tryptophan | |
| l-ornithine | l-tyrosine | ||
| ethelenediamine | l-citrulline | ||
| formamide | xanthine | ||
| d-galactosamine | l-citrulline | ||
| d-mannosamine | |||
| Carbon Source Positive for NA6-27 Growth | Carbon Source Negative for NA6-27 Growth |
|---|---|
| d-glucose | 2-amino ethanol |
| d-fructose | inosine |
| d-galactose | ketobutyric acid |
| d-mannose | maltose |
| acetoacetic acid | glyoxylic acid |
| pyruvic acid | uridine |
| glucuronamide | sucrose |
| l-malic acid | mallotriose |
| d-lactose | d,l-glycerol phosphate |
| Primer Pairs | Product Size (bp) | Gene Match | Accession number | From Species | Alignment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 39, 1 | 352 | hEF-Tu, halophilic archaea elongation factor | KT793932 | Halobacterium marismortui | 100% |
| 39, 3 | 434 | Amino acid permease associated region | KT793929 | Haloarcula hispanica ATCC 33960 chromosome II | 99% |
| 39, 6 | 229 | Halocyanin precursor like | KT793937 | Haloarcula marismortui ATCC 43049 chromosome I | 86% |
| 39, 28 | 330 | ATPase involved in chromosome partitioning | KT793930 | Natrinema pellirubrum DSM 15624 plasmid pNATPE01 | 98% |
| 7, 30 | 494 | ftsZ, cell division protein | KT793931 | Haloarcula japonica ftsZ2 gene for cell division protein ftsZ2 | 99% |
| 7, 12 | 233 | Transcriptional regulator | KT793936 | Haloarcula sp. CBA1115 | 100% |
| 38, 35 | 283 | Phenyl acetyl coenzyme A ligase | KT793933 | Haloarcula sp. CBA1115/Haloarcula hispanica N601 chromosome 2 | 99% |
| 39, 38 | 342 | Phosphoserine phosphotase | KT793934 | Haloarcula sp. CBA1115 | 99% |
| 39, 10 | 433 | Iron ABC transporter ATP binding protein | KT793928 | Haloarcula sp. CBA1115 | 99% |
| 39, 38 | 430 | Oxidoreductase aldo/keto reductase family | No accession number; PCR not comfirmedafter first trial | Haloarcula marismortui ATCC 43049 chromosome I | 90% |
| 39, 37 | 320 | Serine/threonine protein kinase | KT793935 | Haloarcula sp. CBA1115 | 100% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almeida-Dalmet, S.; Litchfield, C.D.; Gillevet, P.; Baxter, B.K. Differential Gene Expression in Response to Salinity and Temperature in a Haloarcula Strain from Great Salt Lake, Utah. Genes 2018, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9010052
Almeida-Dalmet S, Litchfield CD, Gillevet P, Baxter BK. Differential Gene Expression in Response to Salinity and Temperature in a Haloarcula Strain from Great Salt Lake, Utah. Genes. 2018; 9(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmeida-Dalmet, Swati, Carol D. Litchfield, Patrick Gillevet, and Bonnie K. Baxter. 2018. "Differential Gene Expression in Response to Salinity and Temperature in a Haloarcula Strain from Great Salt Lake, Utah" Genes 9, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9010052
APA StyleAlmeida-Dalmet, S., Litchfield, C. D., Gillevet, P., & Baxter, B. K. (2018). Differential Gene Expression in Response to Salinity and Temperature in a Haloarcula Strain from Great Salt Lake, Utah. Genes, 9(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9010052





