c‐Myc‐Induced Survivin Is Essential for Promoting the Notch‐Dependent T Cell Differentiation from Hematopoietic Stem Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Mice
2.2. HSC-T Cell Differentiation
2.3. Retroviral Transduction
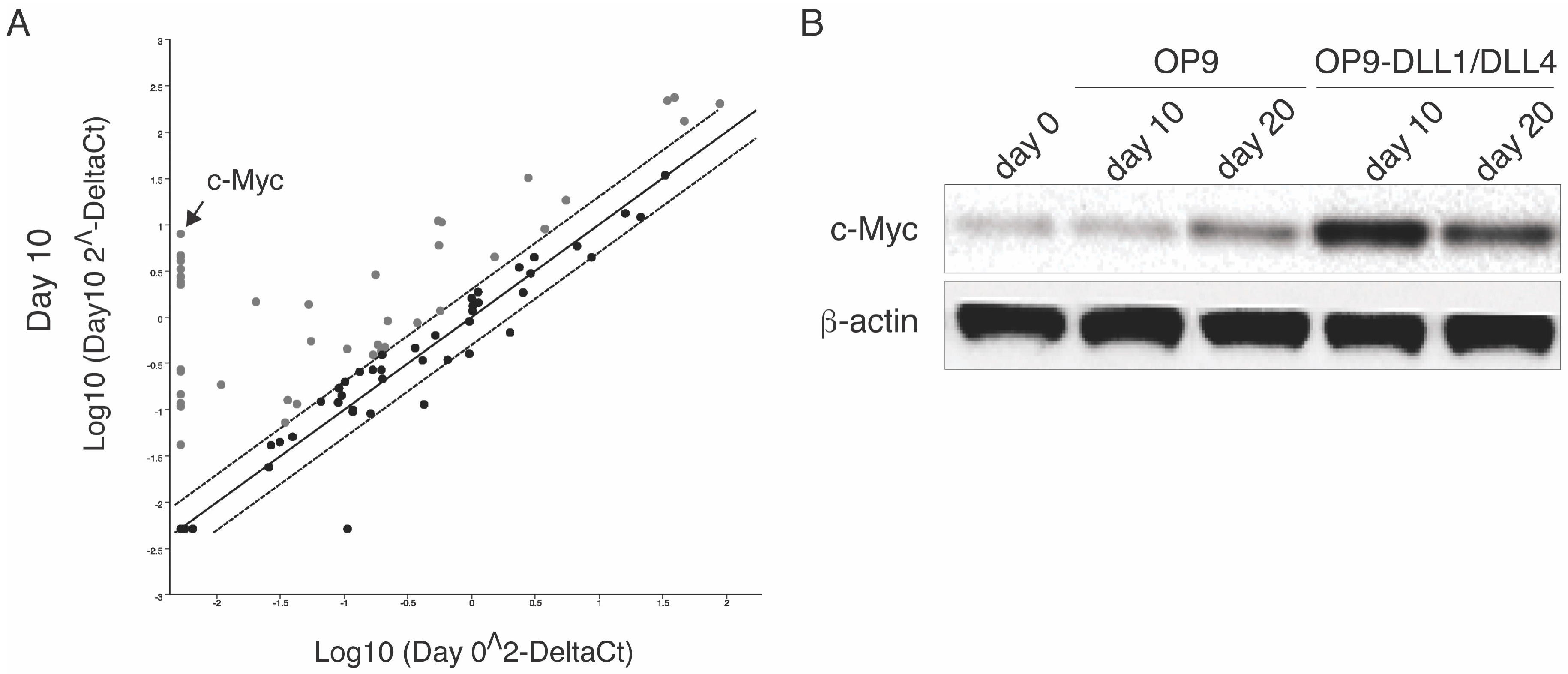
2.4. PCR-Based Array and RT-PCR
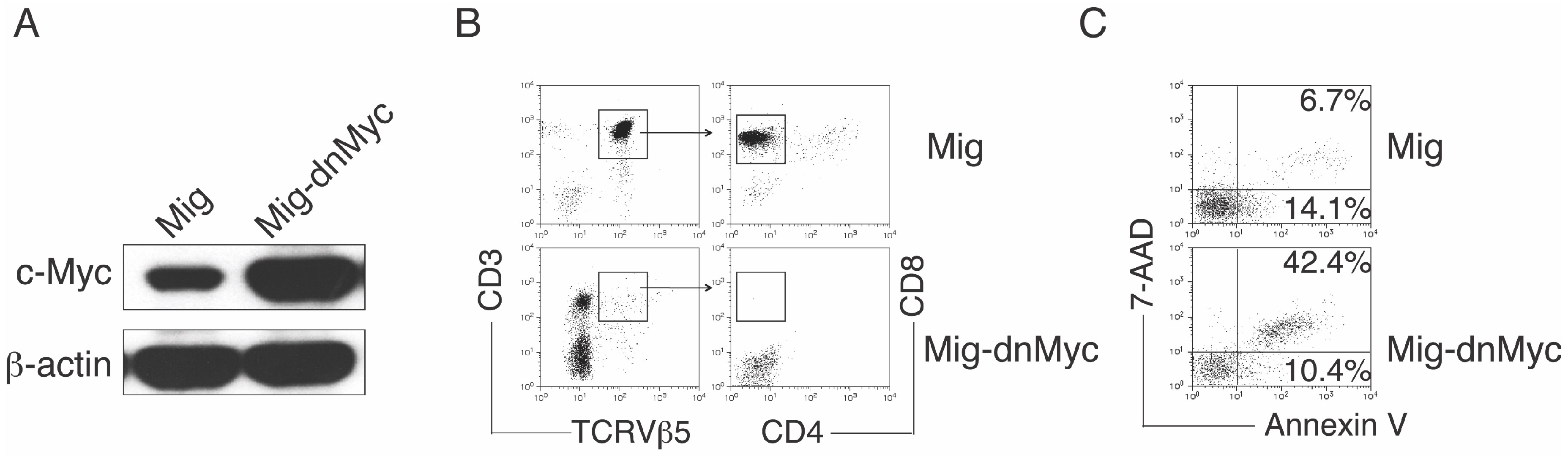
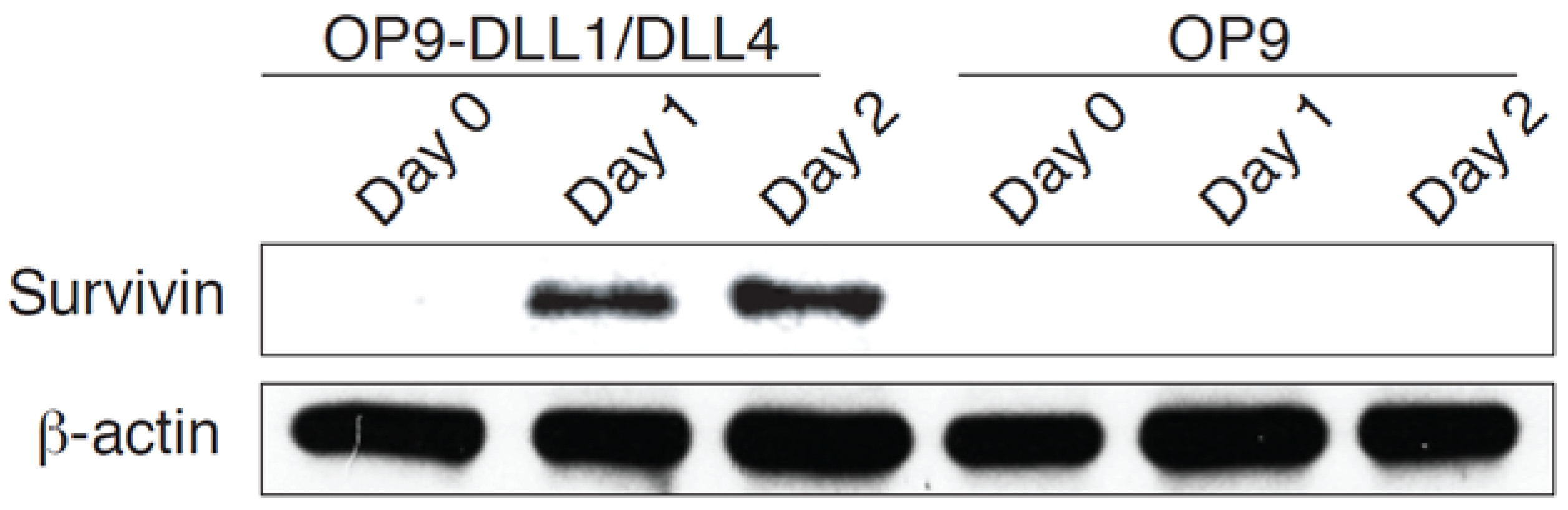
2.5. Western Blot
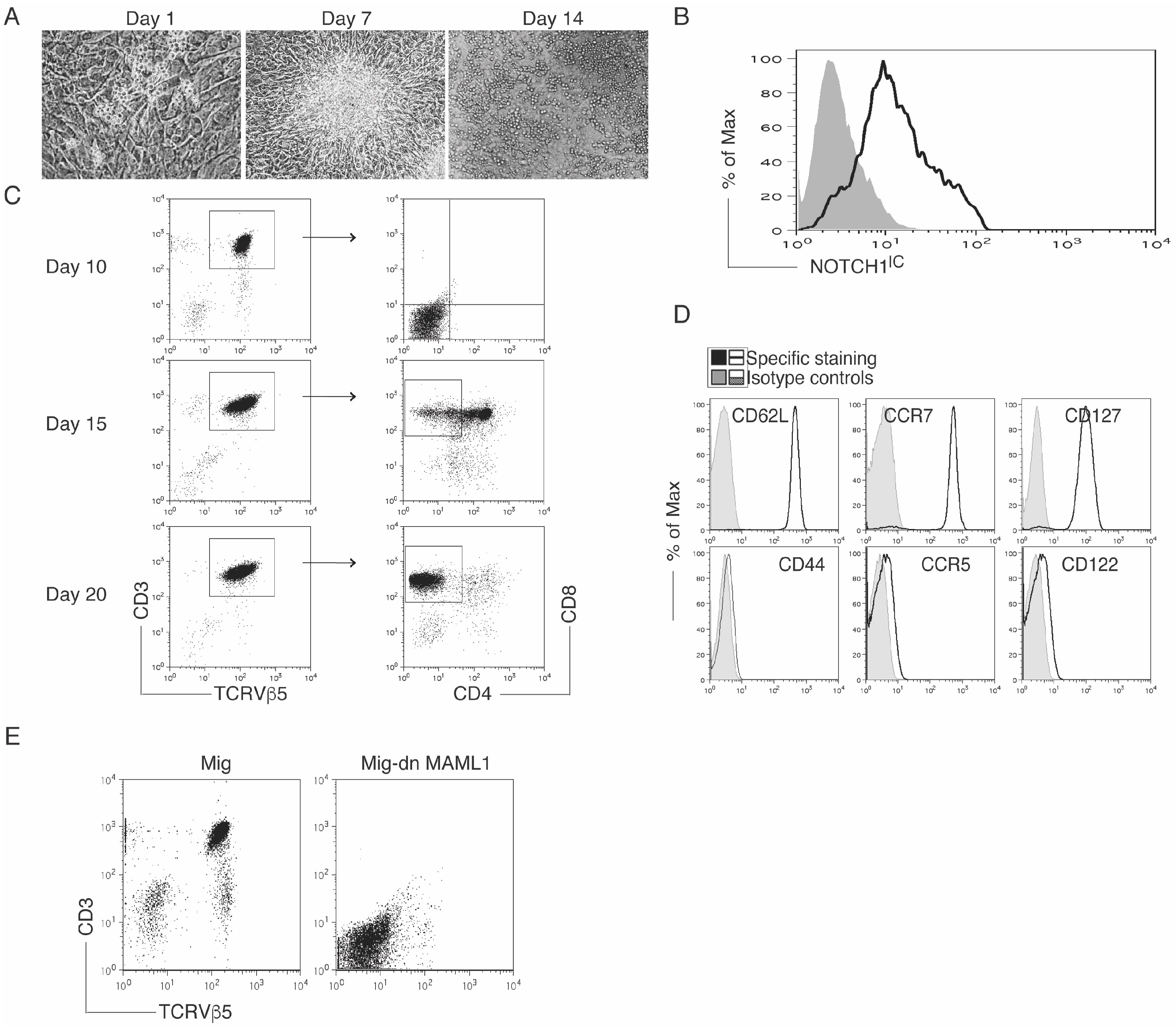
2.6. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.7. Antibodies
3. Results
3.1. Notch Signaling Induces HSC-T Cell Differentiation
3.2. Notch Signaling Regulates c-Myc Expression during Differentiation of HSC-T Cells
3.3. c-Myc Directs the Notch Signaling-Mediated Differentiation of HSC-T Cells
3.4. Notch Signaling Affects Survivin Expression during Differentiation of HSC-T Cells
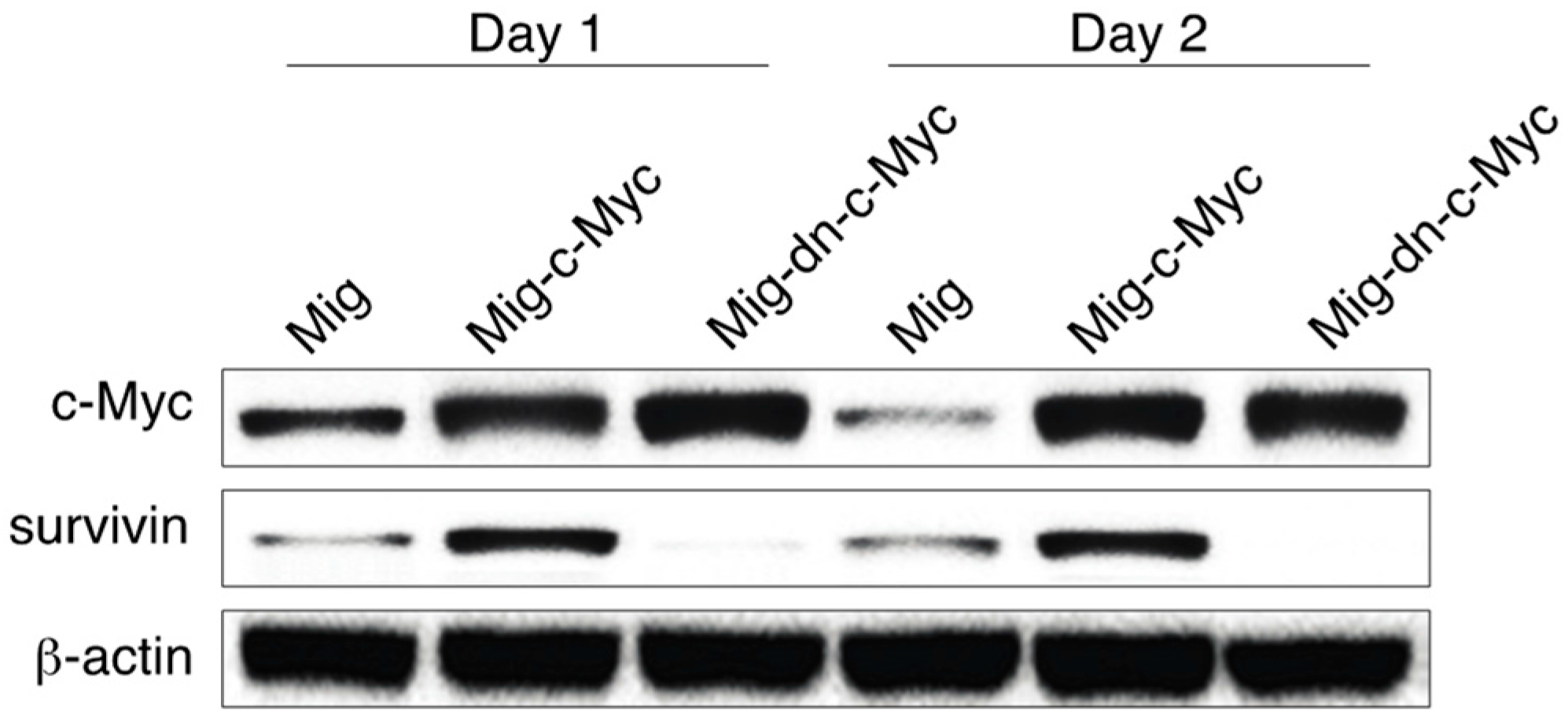
3.5. c-Myc Controls Survivin Expression in Notch-Activated Cells
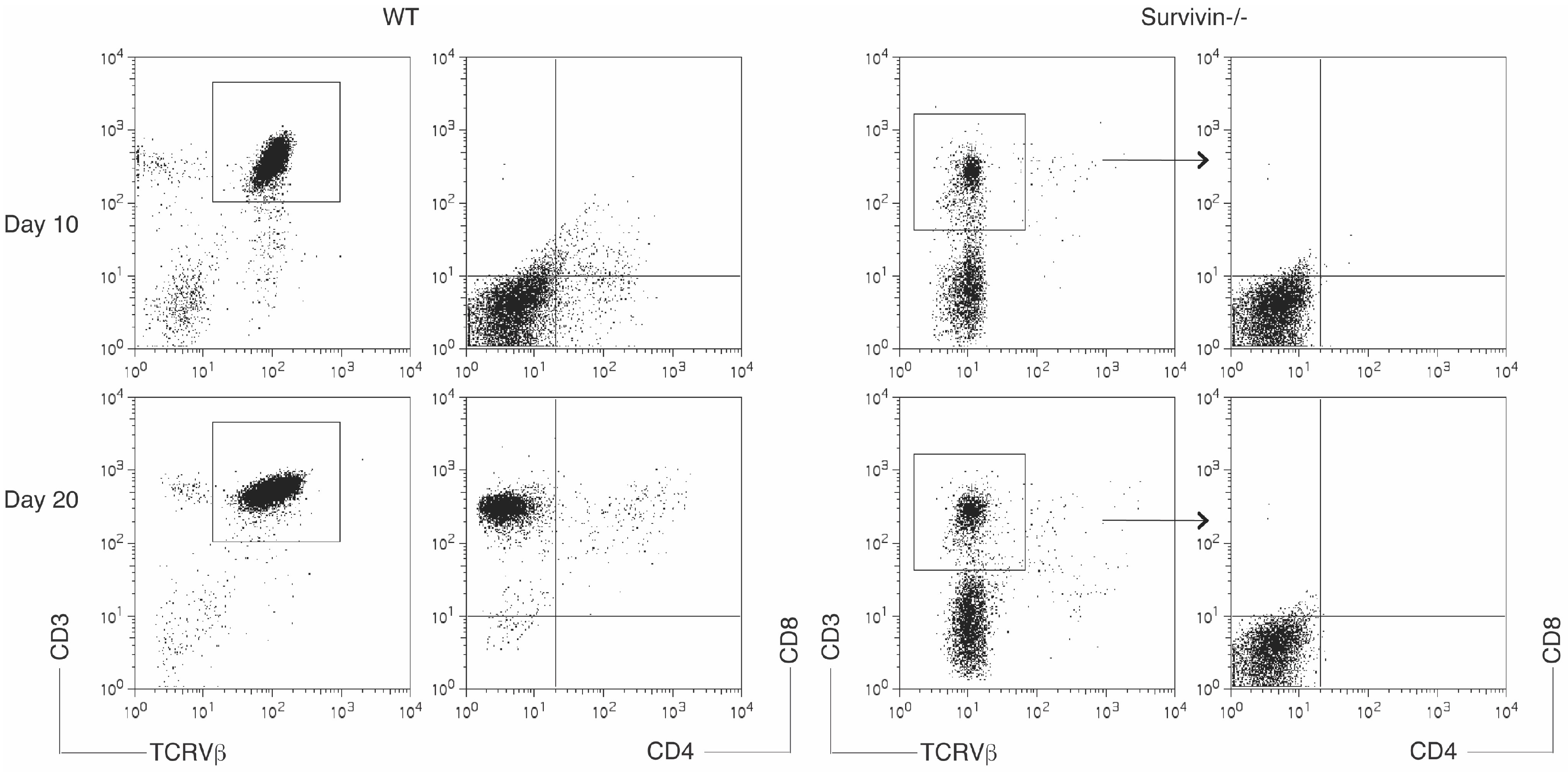
3.6. Survivin-Deficient HSCs Show Reduced Ability to Differentiate into T Cells in Response to Notch Signaling
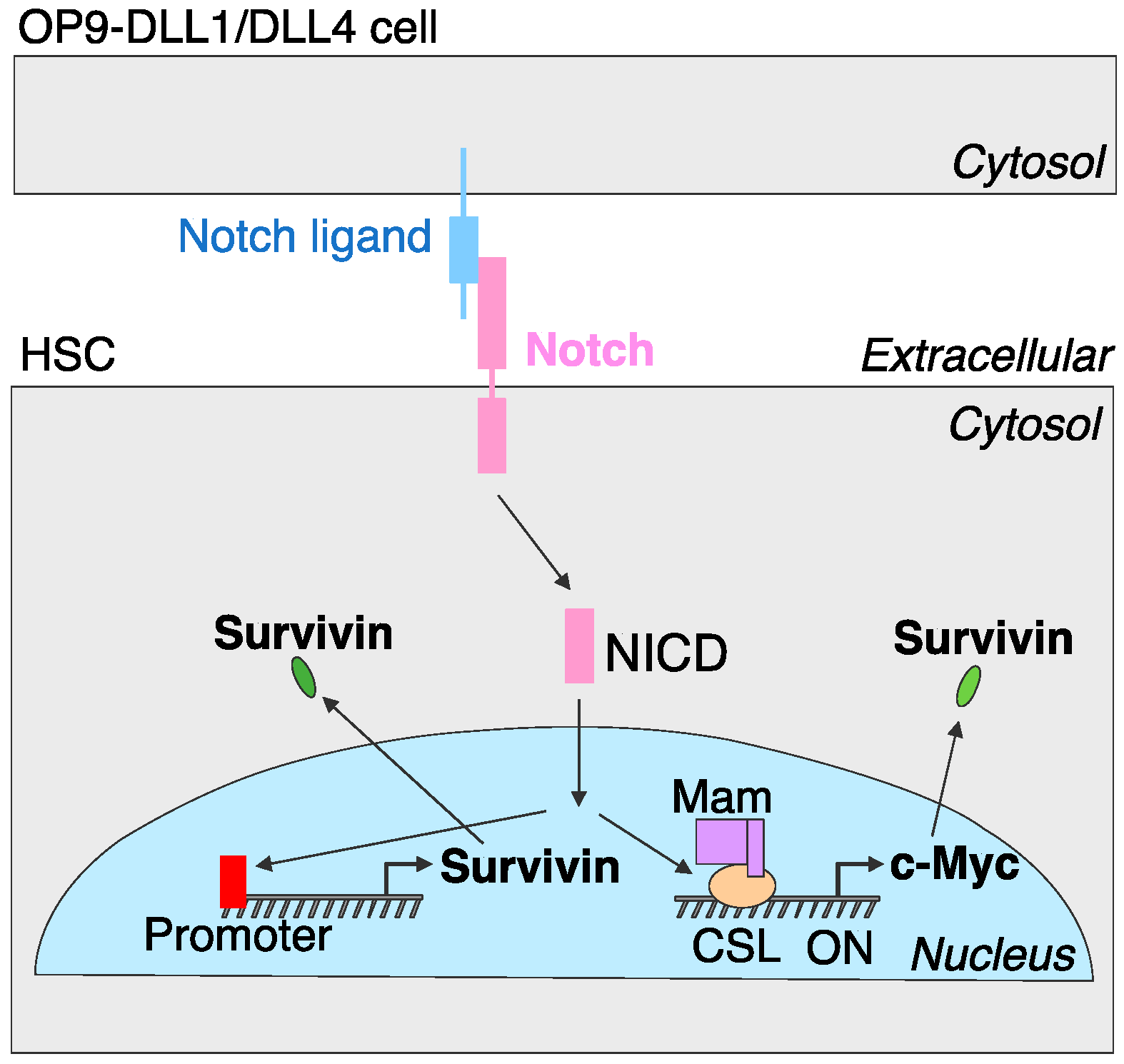
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perumalsamy, L.R.; Nagala, M.; Banerjee, P.; Sarin, A. A hierarchical cascade activated by non-canonical Notch signaling and the mTOR-Rictor complex regulates neglect-induced death in mammalian cells. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumalsamy, L.R.; Nagala, M.; Banerjee, P.; Sarin, A. Notch-activated signaling cascade interacts with mitochondrial remodeling proteins to regulate cell survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010, 107, 6882–6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.; Pongracz, J.; Parnell, S.; Jenkinson, E.J. Notch ligand-bearing thymic epithelial cells initiate and sustain Notch signaling in thymocytes independently of T cell receptor signaling. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 3349–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopan, R.; Ilagan, M.X. The canonical Notch signaling pathway: unfolding the activation mechanism. Cell 2009, 137, 216–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, S.J.; Mantei, N.; Dumortier, A.; Suter, U.; MacDonald, H.R.; Radtke, F. Jagged1-dependent Notch signaling is dispensable for hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Blood 2005, 105, 2340–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de La Coste, A.; Six, E.; Fazilleau, N.; Mascarell, L.; Legrand, N.; Mailhe, M.P.; Cumano, A.; Laabi, Y.; Freitas, A.A. In vivo and in absence of a thymus, the enforced expression of the Notch ligands delta-1 or delta-4 promotes T cell development with specific unique effects. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2730–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hozumi, K.; Negishi, N.; Suzuki, D.; Abe, N.; Sotomaru, Y.; Tamaoki, N.; Mailhos, C.; Ish-Horowicz, D.; Habu, S.; Owen, M.J. Delta-like 1 is necessary for the generation of marginal zone B cells but not T cells in vivo. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, U.; Fiorini, E.; Benedito, R.; Besseyrias, V.; Schuster-Gossler, K.; Pierres, M.; Manley, N.R.; Duarte, A.; Macdonald, H.R.; Radtke, F. Delta-like 4 is the essential, nonredundant ligand for Notch1 during thymic T cell lineage commitment. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2515–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, F.; Zhao, B.; Haque, R.; Xiong, X.; Budgeon, L.; Christensen, N.D.; Wu, Y.; Song, J. In vivo programming of tumor antigen-specific T lymphocytes from pluripotent stem cells to promote cancer immunosurveillance. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4742–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, M.; Song, J.; Fino, K.; Wang, Y.; Sandhu, P.; Song, X.; Norbury, C.; Ni, B.; Fang, D.; Salek-Ardakani, S.; et al. C-Myc regulation by costimulatory signals modulates the generation of CD8+ memory T cells during viral infection. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 150208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, I.; Weng, A.P.; Carpenter, A.C.; Rodriguez, C.G.; Sai, H.; Xu, L.; Allman, D.; Aster, J.C.; Pear, W.S. Mastermind critically regulates Notch-mediated lymphoid cell fate decisions. Blood 2004, 104, 1696–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; So, T.; Cheng, M.; Tang, X.; Croft, M. Sustained survivin expression from OX40 costimulatory signals drives T cell clonal expansion. Immunity 2005, 22, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappell, J.; Sun, Y.; Singh, A.; Dalton, S. MYC/MAX control ERK signaling and pluripotency by regulation of dual-specificity phosphatases 2 and 7. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, N.C.; Jacobs, H.; Bothwell, A.L.; Hayday, A.C. Defining the specific physiological requirements for c-Myc in T cell development. Nat. Immunol. 2001, 2, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.H.; Dong, C.L.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, B.; Liu, N.; Lan, H.F.; Liang, L.; Liao, W.B.; Zhang, L.; Han, Z.C. Transcriptional regulation of survivin by c-Myc in BCR/ABL-transformed cells: implications in anti-leukaemic strategy. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 2039–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrave, N.; Hill, A.D.; Young, L.S. Growth factor-dependent regulation of survivin by c-myc in human breast cancer. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 37, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, H.; Bakal, C.; Shahinian, A.; Elia, A.; Wakeham, A.; Suh, W.K.; Duncan, G.S.; Ciofani, M.; Rottapel, R.; Zuniga-Pflucker, J.C.; et al. Survivin loss in thymocytes triggers p53-mediated growth arrest and p53-independent cell death. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallas, M.H.; Varnum-Finney, B.; Delaney, C.; Kato, K.; Bernstein, I.D. Density of the Notch ligand Delta1 determines generation of B and T cell precursors from hematopoietic stem cells. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohtashami, M.; Shah, D.K.; Nakase, H.; Kianizad, K.; Petrie, H.T.; Zuniga-Pflucker, J.C. Direct comparison of Dll1- and Dll4-mediated Notch activation levels shows differential lymphomyeloid lineage commitment outcomes. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 867–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, T.M.; de Pooter, R.F.; Gronski, M.A.; Cho, S.K.; Ohashi, P.S.; Zuniga-Pflucker, J.C. Induction of T cell development and establishment of T cell competence from embryonic stem cells differentiated in vitro. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awong, G.; Herer, E.; Surh, C.D.; Dick, J.E.; La Motte-Mohs, R.N.; Zuniga-Pflucker, J.C. Characterization in vitro and engraftment potential in vivo of human progenitor T cells generated from hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 2009, 114, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, F.; Haque, R.; Weiler, L.; Vrana, K.E.; Song, J. T lineage differentiation from induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Immunol. 2009, 260, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, F.; Haque, R.; Xiong, X.; Song, J. Directed differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells towards T lymphocytes. JoVE 2012, 14, e3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, R.; Lei, F.; Xiong, X.; Bian, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Y.; Song, J. Programming of regulatory T cells from pluripotent stem cells and prevention of autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.G.; Xu, Y.; Mularski, B.; Liu, H.; Gurbuxani, S.; Crispino, J.D. Requirements for survivin in terminal differentiation of erythroid cells and maintenance of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Z.; Conway, E.M.; Kang, C.; Winoto, A. Essential role of survivin, an inhibitor of apoptosis protein, in T cell development, maturation, and homeostasis. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Song, A.; Haque, R.; Lei, F.; Weiler, L.; Xiong, X.; Wu, Y.; Croft, M.; Song, J. Cooperation between molecular targets of costimulation in promoting T cell persistence and tumor regression. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 6744–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Salek-Ardakani, S.; So, T.; Croft, M. The kinases aurora B and mTOR regulate the G1-S cell cycle progression of T lymphocytes. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mingueneau, M.; Kreslavsky, T.; Gray, D.; Heng, T.; Cruse, R.; Ericson, J.; Bendall, S.; Spitzer, M.H.; Nolan, G.P.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. The transcriptional landscape of alphabeta T cell differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 619–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Will, B.; Vogler, T.O.; Bartholdy, B.; Garrett-Bakelman, F.; Mayer, J.; Barreyro, L.; Pandolfi, A.; Todorova, T.I.; Okoye-Okafor, U.C.; Stanley, R.F.; et al. Satb1 regulates the self-renewal of hematopoietic stem cells by promoting quiescence and repressing differentiation commitment. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Dillon, C.P.; Shi, L.Z.; Milasta, S.; Carter, R.; Finkelstein, D.; McCormick, L.L.; Fitzgerald, P.; Chi, H.; Munger, J.; et al. The transcription factor Myc controls metabolic reprogramming upon T lymphocyte activation. Immunity 2011, 35, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trumpp, A.; Refaeli, Y.; Oskarsson, T.; Gasser, S.; Murphy, M.; Martin, G.R.; Bishop, J.M. c-Myc regulates mammalian body size by controlling cell number but not cell size. Nature 2001, 414, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.; Murphy, M.J.; Oskarsson, T.; Kaloulis, K.; Bettess, M.D.; Oser, G.M.; Pasche, A.C.; Knabenhans, C.; Macdonald, H.R.; Trumpp, A. c-Myc controls the balance between hematopoietic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 2747–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Li, Q.; O’Neal, J.; Kreisel, F.; Le Beau, M.M.; Tomasson, M.H. c-Myc rapidly induces acute myeloid leukemia in mice without evidence of lymphoma-associated antiapoptotic mutations. Blood 2005, 106, 2452–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomero, T.; Lim, W.K.; Odom, D.T.; Sulis, M.L.; Real, P.J.; Margolin, A.; Barnes, K.C.; O’Neil, J.; Neuberg, D.; Weng, A.P.; et al. NOTCH1 directly regulates c-MYC and activates a feed-forward-loop transcriptional network promoting leukemic cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18261–18266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, A.P.; Millholland, J.M.; Yashiro-Ohtani, Y.; Arcangeli, M.L.; Lau, A.; Wai, C.; Del Bianco, C.; Rodriguez, C.G.; Sai, H.; Tobias, J.; et al. c-Myc is an important direct target of Notch1 in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2096–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demarest, R.M.; Dahmane, N.; Capobianco, A.J. Notch is oncogenic dominant in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 2901–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herranz, D.; Ambesi-Impiombato, A.; Palomero, T.; Schnell, S.A.; Belver, L.; Wendorff, A.A.; Xu, L.; Castillo-Martin, M.; Llobet-Navas, D.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; et al. A NOTCH1-driven MYC enhancer promotes T cell development, transformation and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1130–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haque, R.; Song, J.; Haque, M.; Lei, F.; Sandhu, P.; Ni, B.; Zheng, S.; Fang, D.; Yang, J.; Song, J. c‐Myc‐Induced Survivin Is Essential for Promoting the Notch‐Dependent T Cell Differentiation from Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Genes 2017, 8, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8030097
Haque R, Song J, Haque M, Lei F, Sandhu P, Ni B, Zheng S, Fang D, Yang J, Song J. c‐Myc‐Induced Survivin Is Essential for Promoting the Notch‐Dependent T Cell Differentiation from Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Genes. 2017; 8(3):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8030097
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaque, Rizwanul, Jianyong Song, Mohammad Haque, Fengyang Lei, Praneet Sandhu, Bing Ni, Songguo Zheng, Deyu Fang, Jin‐Ming Yang, and Jianxun Song. 2017. "c‐Myc‐Induced Survivin Is Essential for Promoting the Notch‐Dependent T Cell Differentiation from Hematopoietic Stem Cells" Genes 8, no. 3: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8030097
APA StyleHaque, R., Song, J., Haque, M., Lei, F., Sandhu, P., Ni, B., Zheng, S., Fang, D., Yang, J., & Song, J. (2017). c‐Myc‐Induced Survivin Is Essential for Promoting the Notch‐Dependent T Cell Differentiation from Hematopoietic Stem Cells. Genes, 8(3), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes8030097





