Genome-Wide Identification of TPL/TPR Gene Family in Ten Cotton Species and Function Analysis of GhTPL3 Involved in Salt Stress Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of TPL/TPR Genes and Analysis of Related Protein Physicochemical Properties
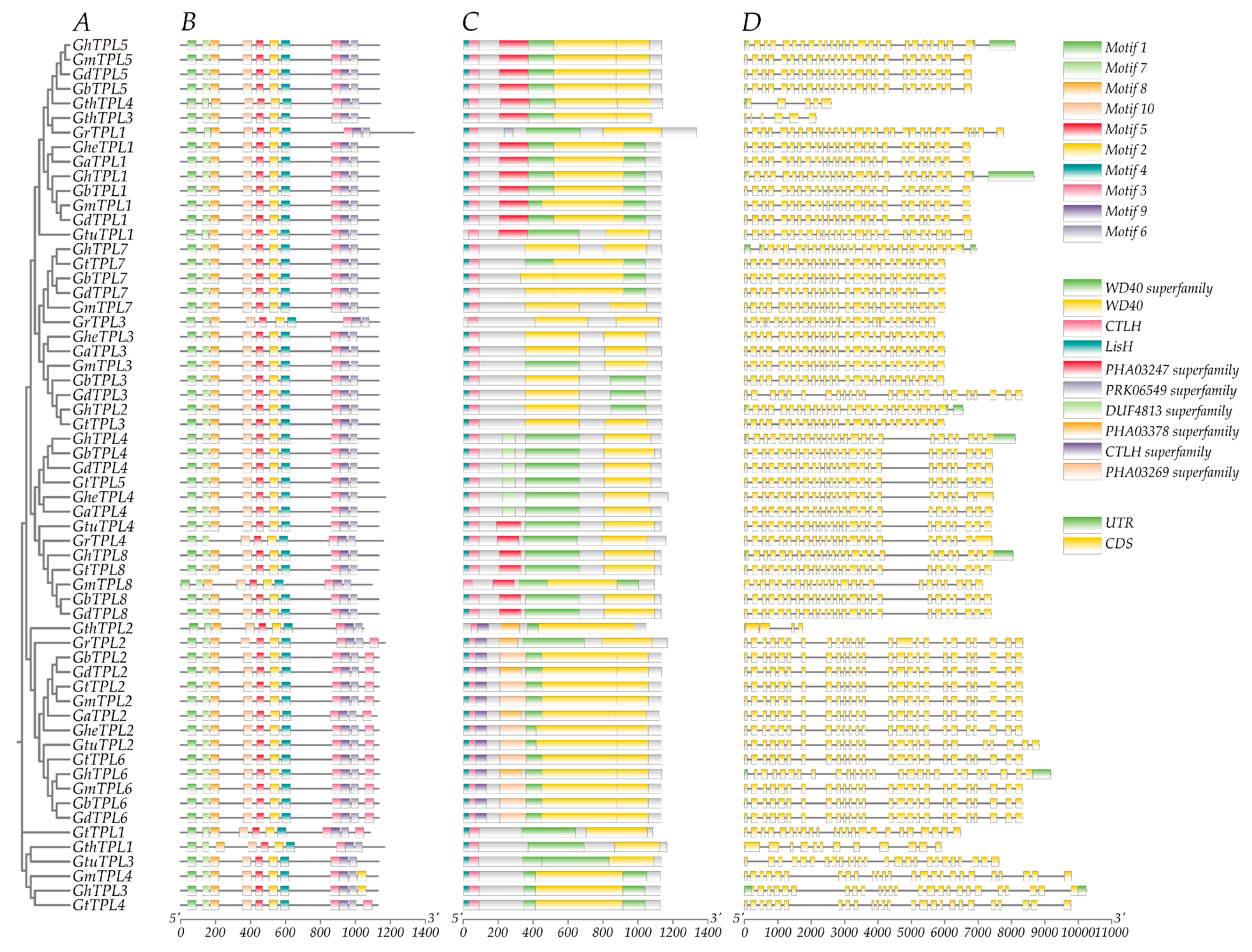
2.2. Analysis of TPL/TPR Gene Structure and Protein Conserved Motifs
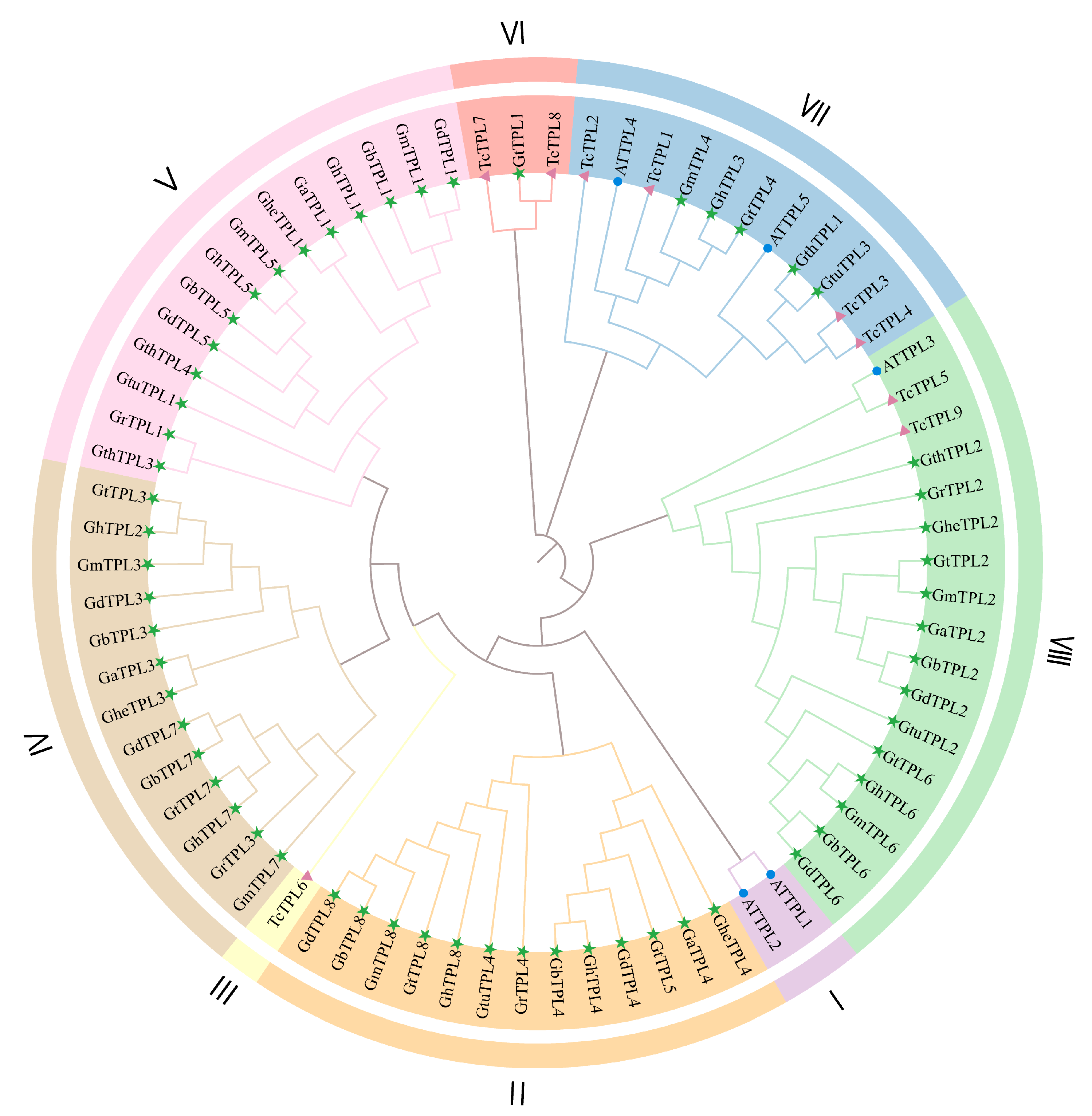
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of TPL/TPR Genes
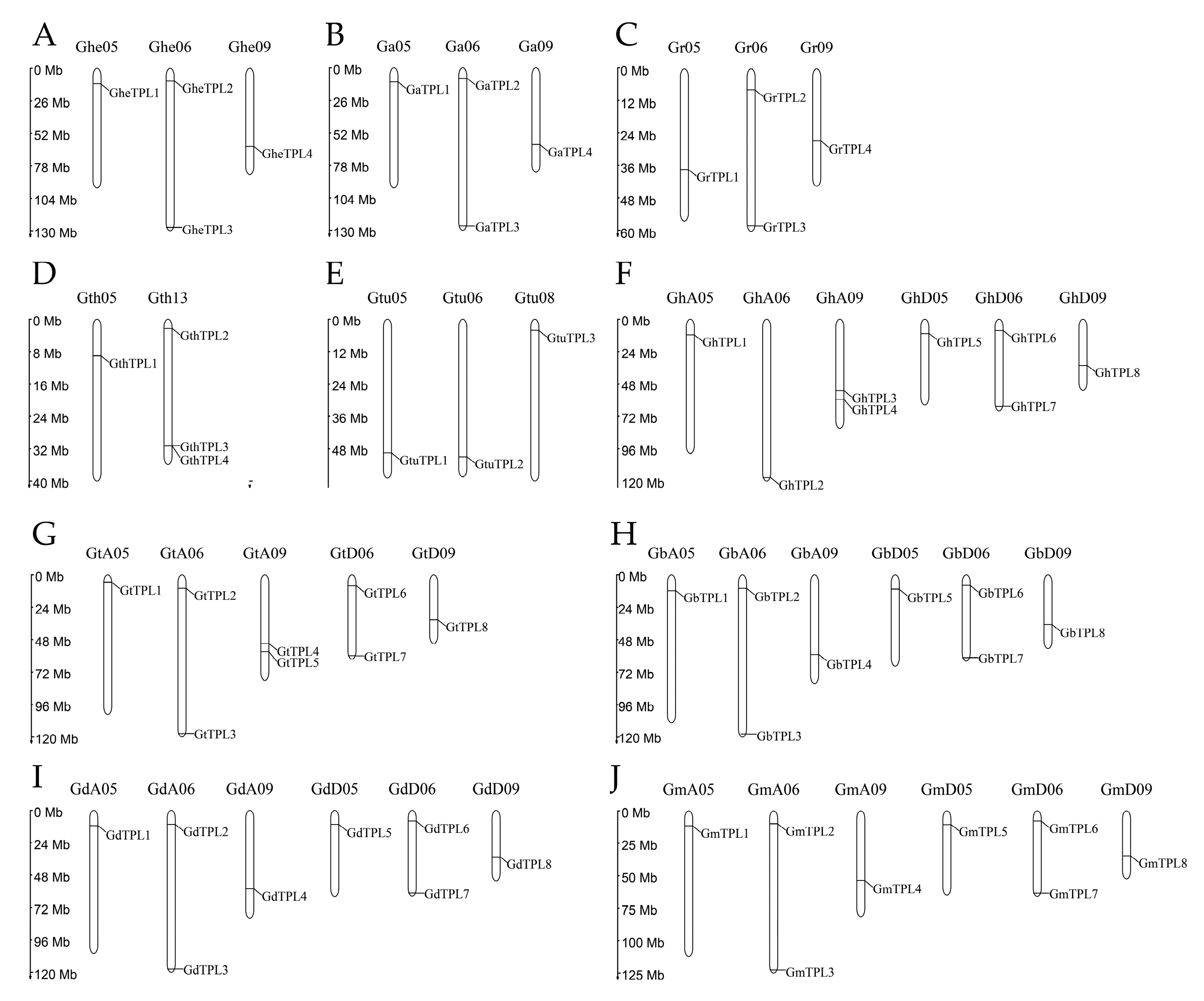
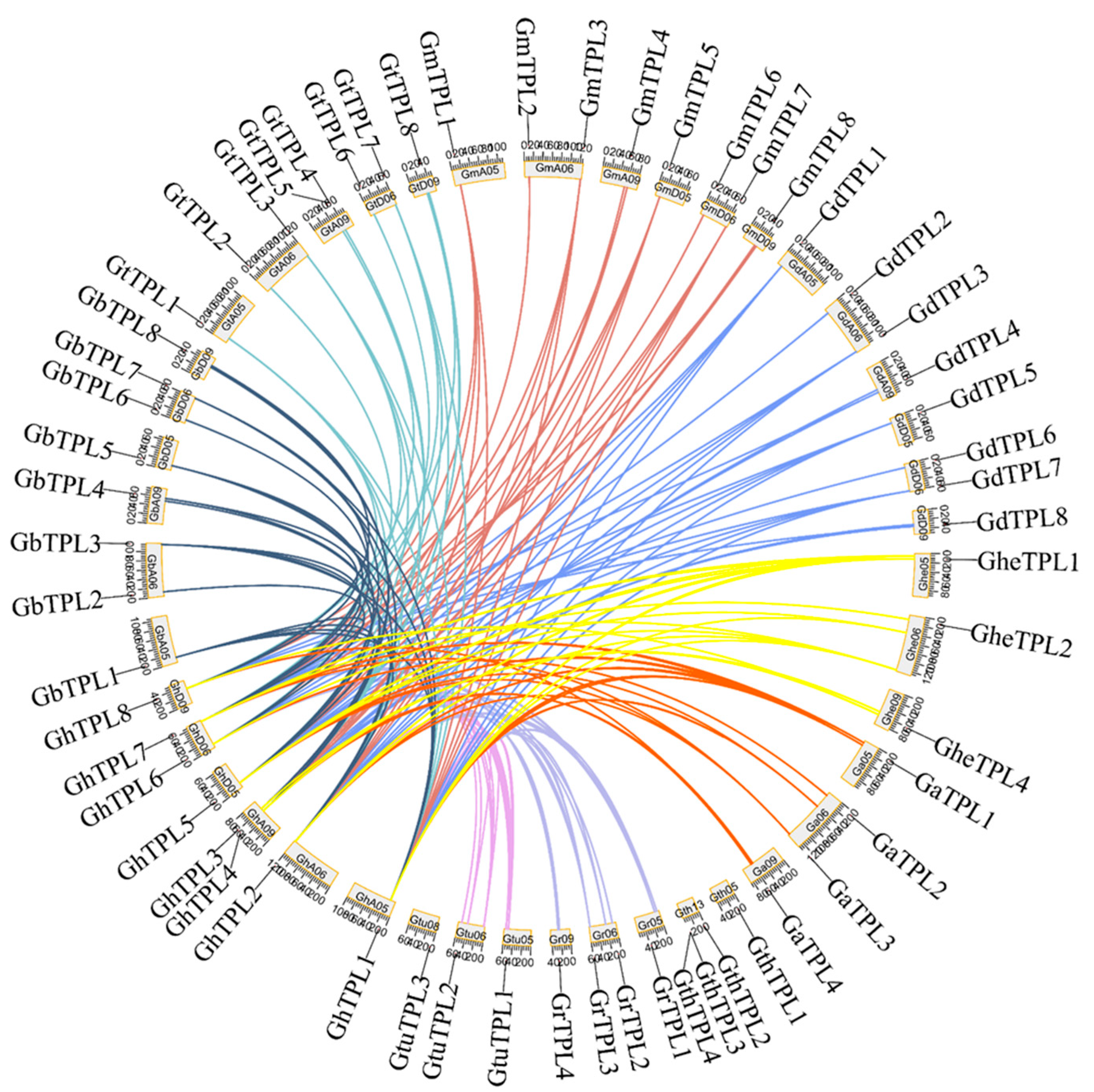
2.4. Chromosomal Localization and Interspecies Collinearity Analysis of TPL/TPR Genes
2.5. Cis-Regulatory Element Analysis of the TPL/TPR Gene Family
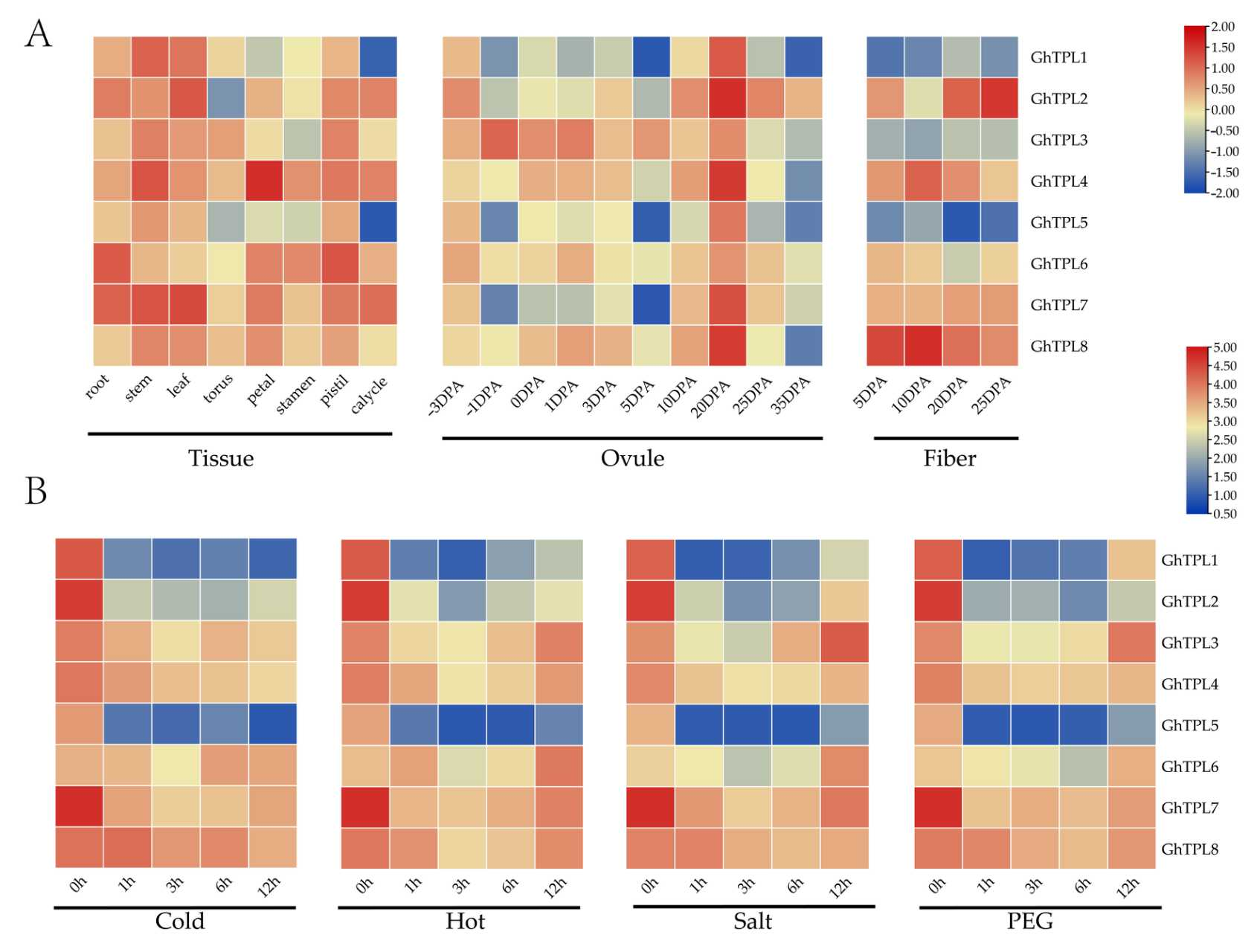
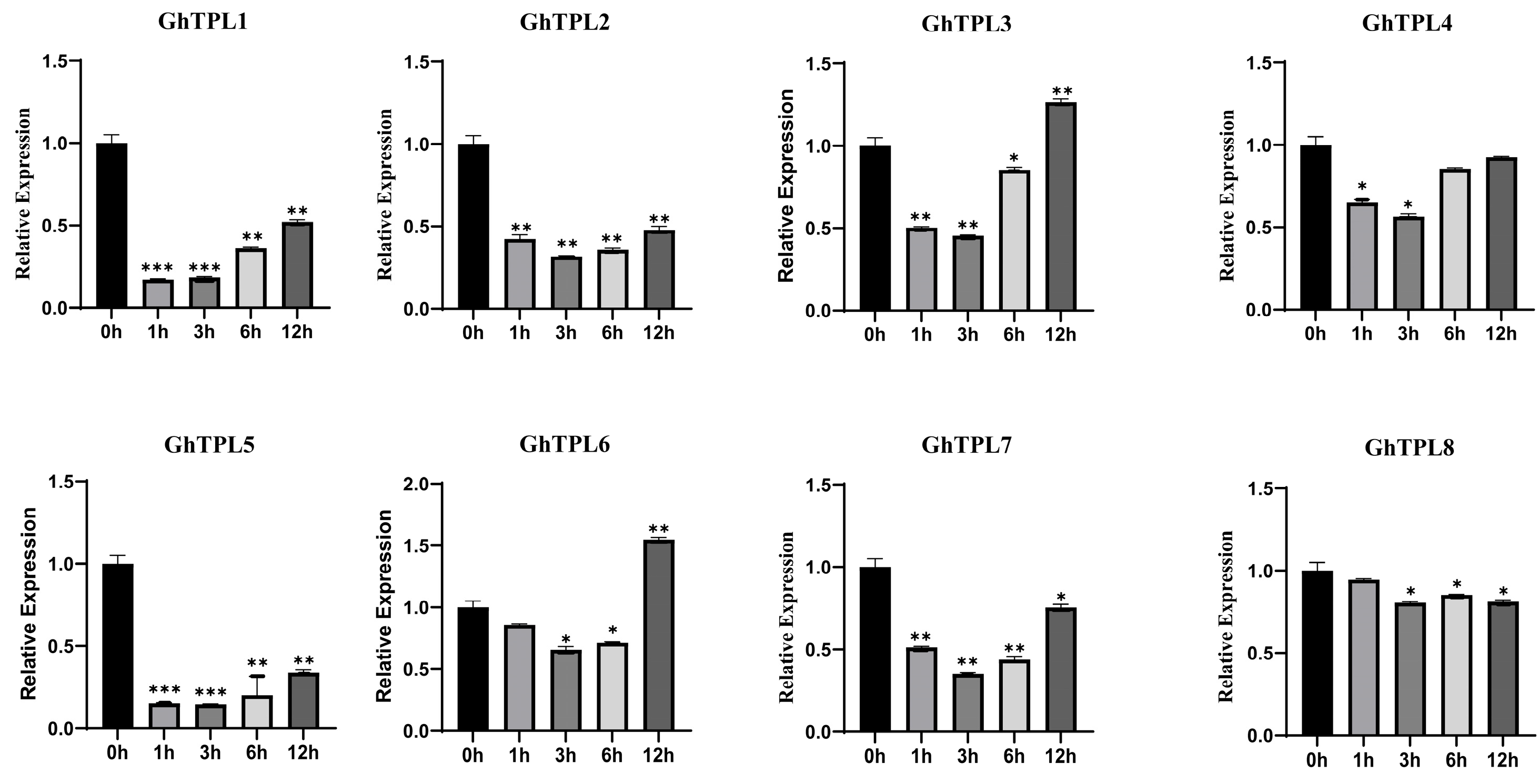
2.6. Expression Profiles of TPL/TPR Genes in Different Tissues and Under Abiotic Stresses
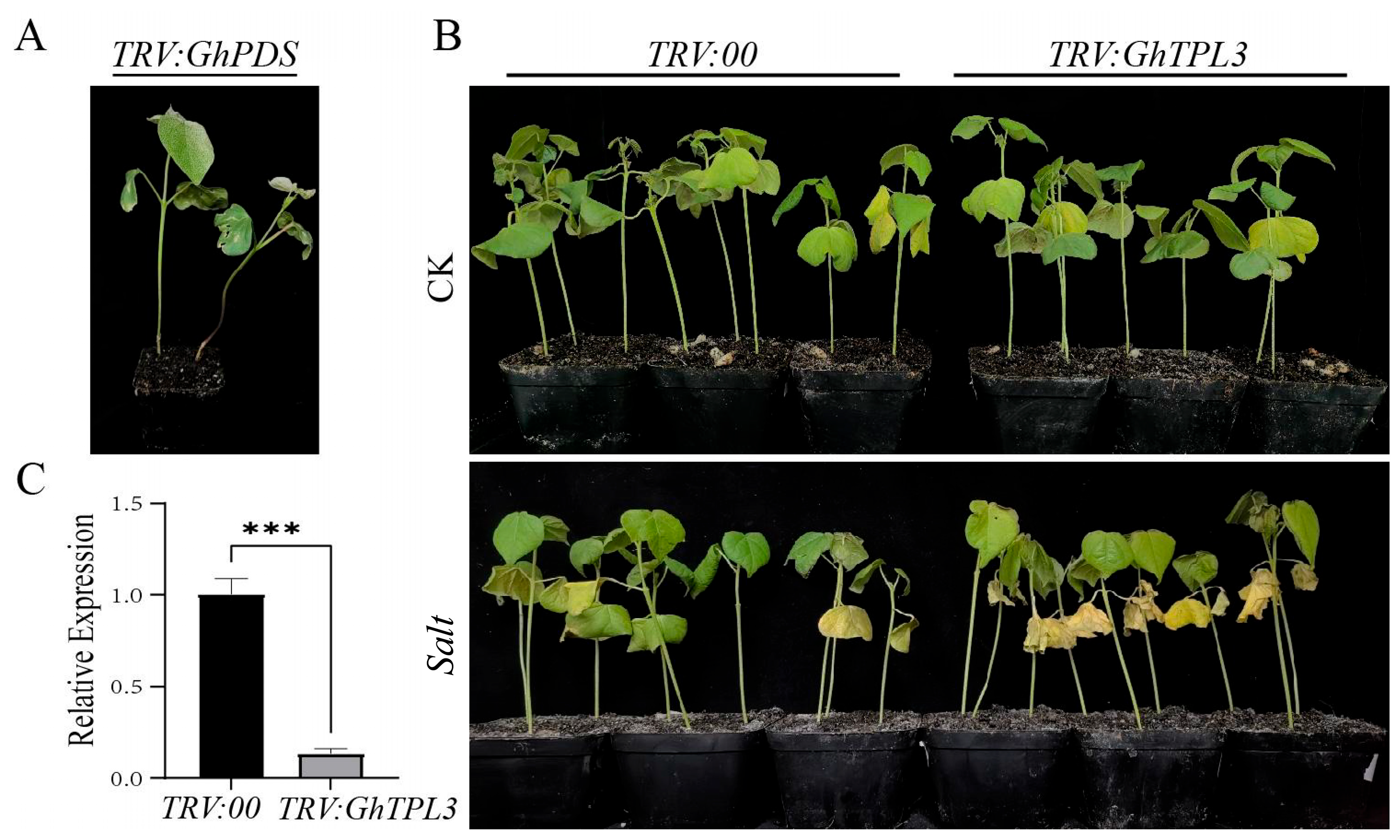
2.7. GhTPL3-Silenced Cotton Plants Showed High Sensitivity to Salt Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Experimental Treatments
4.2. The Identification Process Construction of Cotton TPL/TPR Genes and Subcellular Localization
4.3. Multiple Species TPL/TPR Protein Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Analysis
4.4. Construction of Cotton TPL/TPR Gene Chromosome Map and Intraspecific Collinearity Visualization Analysis
4.5. Cotton TPL/TPR Gene Promoter Sequence Extraction and PlantCARE Cis-Element Prediction Analysis
4.6. TPL/TPR Expression Pattern Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Yang, Z.E.; Chen, E.Y.; Zhang, C.J.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, F.G. Genome-wide analysis of GRAS transcription factor gene family in Gossypium hirsutum L. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mistry, J.; Chuguransky, S.; Williams, L.; Qureshi, M.; Salazar, G.A.; Sonnhammer, E.L.L.; Tosatto, S.C.; Paladin, L.; Raj, S.; Richardson, L.J.; et al. Pfam: The protein families database in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D412–D419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leydon, A.R.; Wang, W.; Gala, H.P.; Gilmour, S.; Juarez-Solis, S.; Zahler, M.L.; Zemke, J.E.; Zheng, N.; Nemhauser, J.L. Repression by the Arabidopsis TOPLESS corepressor requires association with the core mediator complex. Elife 2021, 10, e66739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, R.; Nandi, A.K. TOPLESS in the regulation of plant immunity. Plant Mol. Biol. 2022, 109, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, K.; Matsuzaki, K.; Hayashi, H. Plant sesquiterpenes induce hyphal branching in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Nature 2005, 435, 824–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besserer, A.; Puech-Pagès, V.; Kiefer, P.; Gomez-Roldan, V.; Jauneau, A.; Roy, S.; Portais, J.C.; Roux, C.; Bécard, G.; Séjalon-Delmas, N. Strigolactones stimulate arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi by activating mitochondria. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Yu, H.; Guo, H.; Lin, T.; Kou, L.; Wang, A.; Shao, N.; Ma, H.; Xiong, G.; et al. Transcriptional regulation of strigolactone signalling in Arabidopsis. Nature 2020, 583, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szemenyei, H.; Hannon, M.; Long, J.A. TOPLESS mediates auxindependent transcriptional repression during Arabidopsis embryogenesis. Science 2008, 319, 1384–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Ma, H.; Gu, X.; Thelen, A.; Brunzelle, J.S.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K. Structural basis for recognition of diverse transcriptional repressors by the TOPLESS family of corepressors. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Arevalillo, R.; Nanao, M.H.; Larrieu, A.; Vinos-Poyo, T.; Mast, D.; Galvan-Ampudia, C.; Brunoud, G.; Vernoux, T.; Dumas, R.; Parcy, F. Structure of the Arabidopsis TOPLESS corepressor provides insight into the evolution of transcriptional repression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.; O’Rady, K.; Chen, S.; Gurley, W. The C-terminal WD40 repeats on the TOPLESS co-repressor function as a protein–protein interaction surface. Plant Mol. Biol. 2019, 100, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.A.; Ohno, C.; Smith, Z.R.; Meyerowitz, E.M. TOPLESS regulates apical embryonic fate in Arabidopsis. Science 2006, 312, 1520–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Causier, B.; Ashworth, M.; Guo, W.; Davies, B. The TOPLESS interactome: A framework for gene repression in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 158, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Bassa, C.; Mila, I.; Audran, C.; Maza, E.; Li, Z.; Bouzayen, M.; van der Rest, B.; et al. Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic analysis, expression profiling, and protein–protein interaction properties of TOPLESS gene family members in tomato. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Ruiz, A.; Martínez, C.; de Lucas, M.; Fàbregas, N.; Bosch, N.; Caño-Delgado, A.I.; Prat, S. TOPLESS mediates brassinosteroid control of shoot boundaries and root meristem development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 2017, 144, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, E.; Zhu, J.Y.; Ryu, H.; Hwang, I.; Wang, Z.Y. TOPLESS mediates brassinosteroid-induced transcriptional repression through interaction with BZR1. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauwels, L.; Barbero, G.F.; Geerinck, J.; Tilleman, S.; Grunewald, W.; Prez, A.C.; Chico, J.M.; Bossche, R.V.; Sewell, J.; Gil, E.; et al. NINJA connects the co-repressor TOPLESS to jasmonatesignalling. Nature 2020, 464, 788–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; et al. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D222–D226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, P.; Park, K.J.; Obayashi, T.; Fujita, N.; Harada, H.; Adams-Collier, C.J.; Nakai, K. WoLF PSORT: Protein localization predictor. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W585–W587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whelan, S.; Goldman, N. A general empirical model of protein evolution derived from multiple protein families using a maximum-likelihood approach. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton-Rauh, A. Evolutionary dynamics of duplicated genes in plants. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2003, 29, 396–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, L.; Huang, J.; Weidig, S.; Yang, Z.; Heidersberger, C.; Genty, B.; Falter-Braun, P.; Christmann, A.; Grill, E. The temperature sensor TWA1 is required for thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Nature 2024, 629, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.C.; Purugganan, M.D. The early stages of duplicate gene evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15682–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhong, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, C.; Liu, J.; Lin, Z. The tin1 gene retains the function of promoting tillering in maize. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, A.R.; Larrieu, A.; Causier, B. Repressor for hire! The vital roles of TOPLESS-mediated transcriptional repression in plants. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Guo, C.; Su, X.; Mu, T.; Feng, B.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of TOPLESS/TOPLESS-RELATED co-repressors and functional characterization of BnaA9.TPL regulating the embryogenesis and leaf morphology in rapeseed. Plant Sci. 2024, 346, 112149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, F.; Gallei, M.; Kornienko, A.E.; Saado, I.; Khan, M.; Chia, K.S.; Darino, M.A.; Bindics, J.; Djamei, A. TOPLESS promotes plant immunity by repressing auxin signaling and is targeted by the fungal effector Naked1. Plant Commun. 2021, 3, 100269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; He, F.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Shou, H.; Zheng, L. OsbHLH062 regulates iron homeostasis by inhibiting iron deficiency responses in rice. aBIOTECH 2025, 6, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, X.; Guan, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Song, A.; Chen, S.; Ding, L.; Chen, F. Heterologous expression of chrysanthemum TOPLESS corepressor CmTPL1-1 alters meristem maintenance and organ development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 157, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma., S.; Guo., H. Bioinformatics Analysis of VOZ Gene Family in Populus trichocarpa. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 23, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, D. Identification and characterization of a VOZ transcription factor in Syntrichia caninervis using profile HMM method. Chin. J. Bioinform. 2014, 2, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Loudet, O.; Hasegawa, P.M. Abiotic stress, stress combinations and crop improvement potential. Plant J. 2017, 90, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Gao, J.; Zhu, F.; Chen, K.; Fan, J.; Meng, L.; Li, Z.; Shi, S.; Li, H. Genome-Wide Identification of TPL/TPR Gene Family in Ten Cotton Species and Function Analysis of GhTPL3 Involved in Salt Stress Response. Genes 2025, 16, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091072
Zhang G, Gao J, Zhu F, Chen K, Fan J, Meng L, Li Z, Shi S, Li H. Genome-Wide Identification of TPL/TPR Gene Family in Ten Cotton Species and Function Analysis of GhTPL3 Involved in Salt Stress Response. Genes. 2025; 16(9):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091072
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ganggang, Jianguo Gao, Faren Zhu, Kailu Chen, Jiliang Fan, Lu Meng, Zihan Li, Shandang Shi, and Hongbin Li. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification of TPL/TPR Gene Family in Ten Cotton Species and Function Analysis of GhTPL3 Involved in Salt Stress Response" Genes 16, no. 9: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091072
APA StyleZhang, G., Gao, J., Zhu, F., Chen, K., Fan, J., Meng, L., Li, Z., Shi, S., & Li, H. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification of TPL/TPR Gene Family in Ten Cotton Species and Function Analysis of GhTPL3 Involved in Salt Stress Response. Genes, 16(9), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091072





