A Comprehensive Analysis Examining the Role of Genetic Influences on Psychotropic Medication Response in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
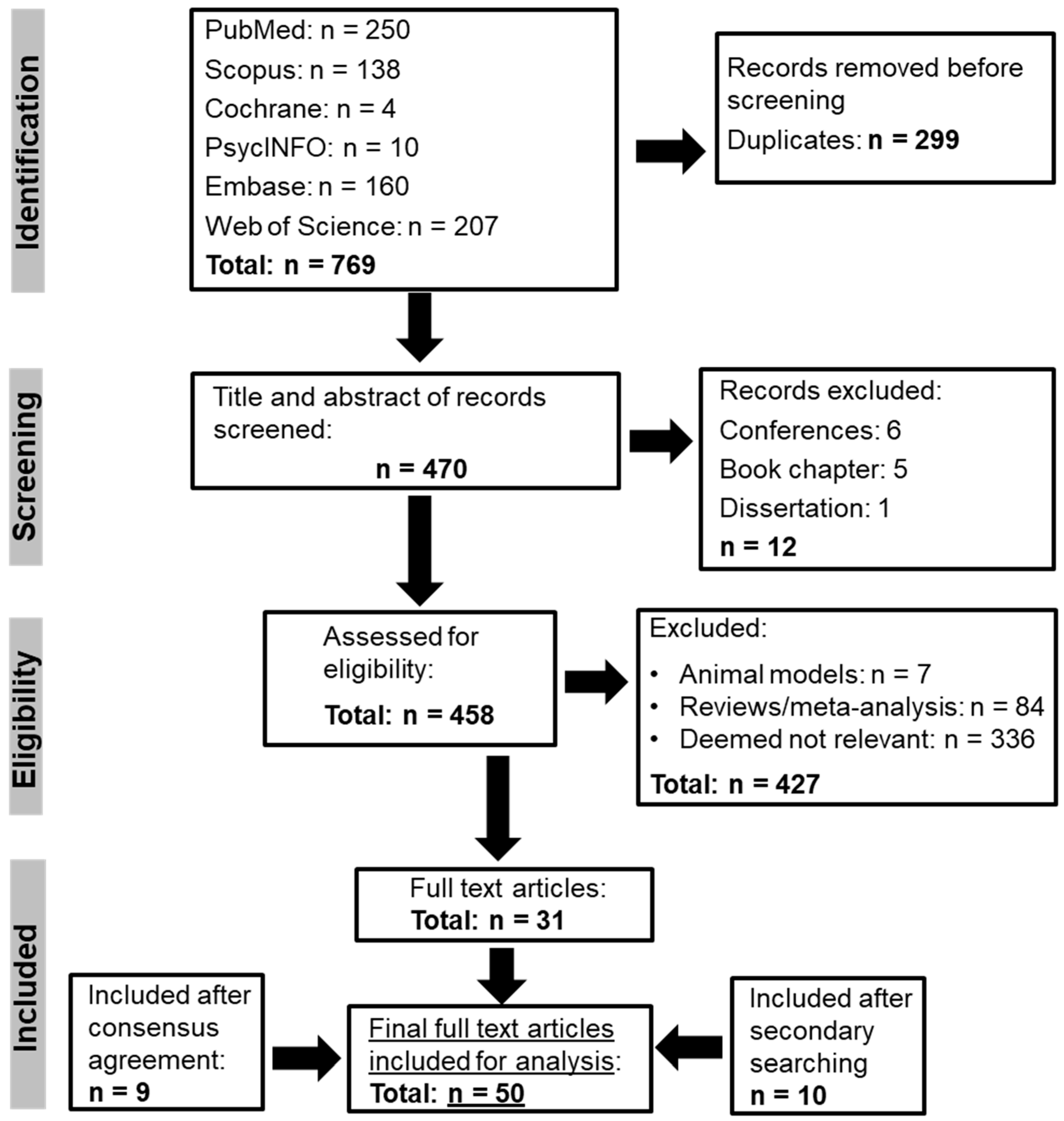
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Search Terms
2.3. Population Characteristics
2.4. Intervention
2.5. Eligibility Criteria
- ➢
- Records in full-text peer-reviewed journal articles.
- ➢
- All information is for the paediatric population.
- ➢
- Records are not available in the English language.
- ➢
- Studies performed in pre-clinical animal models.
- ➢
- The following literature was excluded: reviews (all types), meta-analyses, preprints, letters, conference proceedings, clinical trial protocols and books.
2.6. Extraction of Data
2.7. Thematic Analysis
2.8. Quality Appraisal
2.9. Health Economic Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Article Characteristics
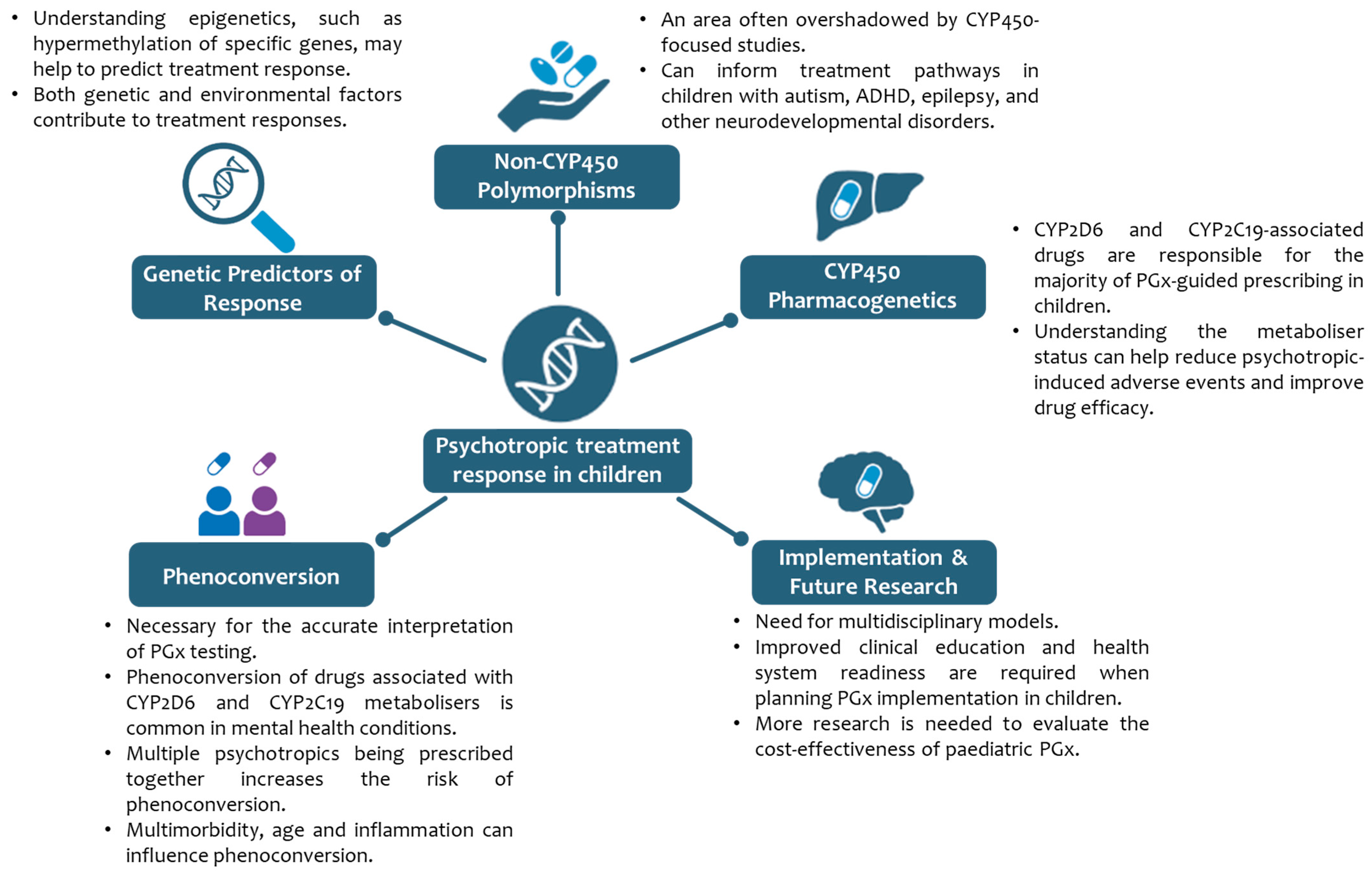
3.2. Thematic Analysis of the Analysed Studies
- Theme 1: Implications of non-CYP450 polymorphisms
- Sub-theme: Disorder-Specific Associations
- I, Neurodevelopmental Disorders
- Epilepsy
- ASD
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
- II, Mental Health Disorders
- Anxiety and/or Major Depressive Disorder
- Bipolar Disorder
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
- Acute Psychosis
- III, Oncology
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
- Brain Tumours
- Sub-theme: Treatment Response and Efficacy
- Theme 1—Broader Literature Context
- Theme 2: Paediatric CYP450 PGx
- Sub-theme: Treatment Response and Efficacy
- Sub-theme: CYP450 substrates and gene–drug pairs
- Sub-theme: Disorder-Specific Associations
- Theme 2—Broader Literature Context
- Theme 3: Genetic Predictors of Response
- Theme 3—Broader Literature Context
- Theme 4: Insights for Implementation and Future Research
- Theme 4—Broader Literature Context
- Theme 5: Phenoconversion
- Theme 5—Broader Literature Context
3.3. Quality Appraisal and Health Economic Evaluation
- Quality Appraisal
- Health Economic Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Developmental Considerations
4.2. Heterogeneity in Studies
4.3. Health Economics and Quality Appraisal
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
International Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Barker, C.I.S.; Groeneweg, G.; Maitland-van der Zee, A.H.; Rieder, M.J.; Hawcutt, D.B.; Hubbard, T.J.; Swen, J.J.; Carleton, B.C. Pharmacogenomic testing in paediatrics: Clinical implementation strategies. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 4297–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshitsuki, K.; Fernandez, C.A.; Yang, J.J. Pharmacogenomics for Drug Dosing in Children: Current Use, Knowledge, and Gaps. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61 (Suppl. S1), S188–S192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawn, J.R.; Dobson, E.T.; Giles, L.L. Primary Pediatric Care Psychopharmacology: Focus on Medications for ADHD, Depression, and Anxiety. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2017, 47, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaadawi, A.Z.; Patel, R.; Almaaitah, Y.; Logsdon, M.G. Effect of pharmacogenomic testing on pediatric mental health outcome: A 6-month follow-up. Pharmacogenomics 2023, 24, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Nagano, N.; Tsuji, Y.; Noto, N.; Ayusawa, M.; Morioka, I. Challenges of pediatric pharmacotherapy: A narrative review of pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacogenetics. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2024, 80, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wildt, S.N.; Tibboel, D.; Leeder, J.S. Drug metabolism for the paediatrician. Arch. Dis. Child 2014, 99, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, L.B.; Ong, H.H.; Schildcrout, J.S.; Shi, Y.; Tang, L.A.; Hicks, J.K.; El Rouby, N.; Cavallari, L.H.; Tuteja, S.; Aquilante, C.L.; et al. IGNITE Pharmacogenetics Working Group. Prescribing Prevalence of Medications With Potential Genotype-Guided Dosing in Pediatric Patients. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2029411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudle, K.E.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Relling, M.V.; Hoffman, J.M.; Donnelly, R.S.; Haidar, C.E.; Bourque, M.S.; Frear, S.; Gong, L.; Sangkuhl, K.; et al. Advancing Clinical Pharmacogenomics Worldwide Through the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC). Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousman, C.A.; Al Maruf, A.; Marques, D.F.; Brown, L.C.; Müller, D.J. The emergence, implementation, and future growth of pharmacogenomics in psychiatry: A narrative review. Psychol. Med. 2023, 53, 7983–7993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.A.; Wagner, J.A.; Sandritter, T.; Black, B.T.; Gaedigk, A.; Stancil, S.L. Retrospective Review of Pharmacogenetic Testing at an Academic Children’s Hospital. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maagdenberg, H.; Vijverberg, S.J.; Bierings, M.B.; Carleton, B.C.; Arets, H.G.; de Boer, A.; der Zee, A.H.M.-V. Pharmacogenomics in Pediatric Patients: Towards Personalized Medicine. Paediatr. Drugs 2016, 18, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnone, D.; Omar, O.; Arora, T.; Östlundh, L.; Ramaraj, R.; Javaid, S.; Govender, R.D.; Ali, B.R.; Patrinos, G.P.; Young, A.H.; et al. Effectiveness of pharmacogenomic tests including CYP2D6 and CYP2C19 genomic variants for guiding the treatment of depressive disorders: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 144, 104965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.C.; Stanton, J.D.; Bharthi, K.; Maruf, A.A.; Müller, D.J.; Bousman, C.A. Pharmacogenomic Testing and Depressive Symptom Remission: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective, Controlled Clinical Trials. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 112, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodieux, F.; Daali, Y.; Rollason, V.; Samer, C.F.; Ing Lorenzini, K. Practice of CYP450 genotyping and phenotyping in children in a real-life setting. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1130100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosu, C.; Klauser, P.; Dwir, D.; Khadimallah, I.; Alemán-Gómez, Y.; Laaboub, N.; Piras, M.; Fournier, M.; Preisig, M.; Conus, P.; et al. Associations between antipsychotics-induced weight gain and brain networks of impulsivity. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanu, A.A.; Johnston, M.M.; Poweleit, E.A.; Vaughn, S.E.; Strawn, J.R.; Ramsey, L.B. Influence of CYP2D6 Metabolizer Status on Risperidone and Paliperidone Tolerability in Children and Adolescents. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2024, 34, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strawn, J.R.; Poweleit, E.A.; Ramsey, L.B. CYP2C19-Guided Escitalopram and Sertraline Dosing in Pediatric Patients: A Pharmacokinetic Modeling Study. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poweleit, E.A.; Taylor, Z.L.; Mizuno, T.; Vaughn, S.E.; Desta, Z.; Strawn, J.R.; Ramsey, L.B. Escitalopram and Sertraline Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis in Pediatric Patients. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2023, 62, 1621–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.R.; Najjar, F.; Rubin, L.H.; Guter, S.J.; Owley, T.; Mosconi, M.W.; Jacob, S.; Cook, E.H. Escitalopram pharmacogenetics: CYP2C19 relationships with dosing and clinical outcomes in autism spectrum disorder. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2015, 25, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Al-Kofahi, M.; Leeder, J.S.; Brown, J.T. Population Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Atomoxetine and its Metabolites in Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2024, 115, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Koyama, E.; Zai, C.C.; Beitchman, J.H.; Kennedy, J.L.; Lunsky, Y.; Desarkar, P.; Müller, D.J. Pharmacogenomic Studies in Intellectual Disabilities and Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review. Can. J. Psychiatry 2021, 66, 1019–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Wilkins, G.; Goodman-Vincent, E.; Chishti, S.; Bonilla Guerrero, R.; McFadden, L.; Zahavi, Z.; Santosh, P. Co-Occurring Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) rs1801133 and rs1801131 Genotypes as Associative Genetic Modifiers of Clinical Severity in Rett Syndrome. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahawi, S.; Naik, H.; Blake, K.V.; Owusu Obeng, A.; Wasserman, R.M.; Seki, Y.; Funanage, V.L.; Oishi, K.; Scott, S.A. Knowledge and attitudes on pharmacogenetics among pediatricians. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 65, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soda, T.; Merner, A.R.; Small, B.J.; Torgerson, L.N.; Muñoz, K.; Austin, J.; Storch, E.A.; Pereira, S.; Lázaro-Muñoz, G. Child and adolescent psychiatrists’ use, attitudes, and understanding of genetic testing and pharmacogenetics in clinical practice. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 325, 115246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi, I.; Crinson, I.; Dawes, M.; Rafi, D.; Pirmohamed, M.; Walter, F.M. The implementation of pharmacogenomics into UK general practice: A qualitative study exploring barriers, challenges and opportunities. J. Community Genet. 2020, 11, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, C.W.; Sridhar, S.B.; Karattuthodi, M.S.; Ganesan, P.M.; Shareef, J.; Lee, E.L.; Armani, K. Scoping review of enablers and challenges of implementing pharmacogenomics testing in the primary care settings. BMJ Open 2024, 14, e087064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzón-Espinosa, J.; van der Horst, M.; Zinkstok, J.; Austin, J.; Aalfs, C.; Batalla, A.; Sullivan, P.; Vorstman, J.; Luykx, J.J. Barriers to genetic testing in clinical psychiatry and ways to overcome them: From clinicians’ attitudes to sociocultural differences between patients across the globe. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousman, C.A.; Stevenson, J.M.; Ramsey, L.B.; Sangkuhl, K.; Hicks, J.K.; Strawn, J.R.; Singh, A.B.; Ruaño, G.; Mueller, D.J.; Tsermpini, E.E.; et al. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) Guideline for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2B6, SLC6A4, and HTR2A Genotypes and Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor Antidepressants. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 114, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, A.P.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Petrone, J.R.; Igelström, K.; George, C.D.; Garrett, T.J.; Orešič, M.; Triplett, E.W.; Ludvigsson, J. Infant microbes and metabolites point to childhood neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell 2024, 187, 1853–1873.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, J.L.; Cui, J.Y. Microbiome is a functional modifier of P450 drug metabolism. Curr. Pharmacol. Rep. 2019, 5, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Tu, H.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Jing, L.; Zhang, K. Association analysis of gut microbiota and efficacy of SSRIs antidepressants in patients with major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 330, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, J.; Kang, Y.; Pang, L.; Zhang, P.; Li, A.; Lv, L.; Andreassen, O.A.; et al. Gut microbial biomarkers for the treatment response in first-episode, drug-naïve schizophrenia: A 24-week follow-up study. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, D.S.; Fu, C.; Gandhi, T.; Fowler, J.C.; Frueh, B.C.; Weinstein, B.L.; Petrosino, J.; Hadden, J.K.; Carlson, M.; Coarfa, C.; et al. Differential co-expression networks of the gut microbiota are associated with depression and anxiety treatment resistance among psychiatric inpatients. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 120, 110638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.T.; Eum, S.; Cook, E.H.; Bishop, J.R. Pharmacogenomics of autism spectrum disorder. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Hao, S.; Williamson, T.; McMorris, C.A.; Bousman, C.A. Psychotropic prescribing rates and pharmacogenomic testing implications for autism in the Canadian primary care sentinel surveillance network. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2022, 32, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, A.E. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Lanzarini, E.; Santosh, P. Autonomic dysfunction and sudden death in patients with Rett syndrome: A systematic review. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2020, 45, 150–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzzani, M.; Hammady, H.; Fedorowicz, Z.; Elmagarmid, A. Rayyan-a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Leary, Z. The Essential Guide to Doing Your Research Project, 2nd ed.; Sage: London, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, S.H.; Black, N. The feasibility of creating a checklist for the assessment of the methodological quality both of randomised and non-randomised studies of health care interventions. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1998, 52, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadullah Khani, N.; Hudson, G.; Mills, G.; Ramesh, S.; Varney, L.; Cotic, M.; Abidoph, R.; Richards-Belle, A.; Carrascal-Laso, L.; Franco-Martin, M.; et al. A systematic review of pharmacogenetic testing to guide antipsychotic treatment. Nat. Ment. Health 2024, 2, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husereau, D.; Drummond, M.; Petrou, S.; Carswell, C.; Moher, D.; Greenberg, D.; Augustovski, F.; Briggs, A.H.; Mauskopf, J.; Loder, E. ISPOR Health Economic Evaluation Publication Guidelines-CHEERS Good Reporting Practices Task Force. Consolidated Health Economic Evaluation Reporting Standards (CHEERS)—explanation and elaboration: A report of the ISPOR Health Economic Evaluation Publication Guidelines Good Reporting Practices Task Force. Value Health 2013, 16, 231–250. [Google Scholar]
- Kalla, P.; Namerow, L.B.; Walker, S.A.; Ruaño, G.; Malik, S. Contrasting ABCB1 pharmacogenetics and psychotropic responses in child and adolescent psychiatry: A case comparison. Pharmacogenomics 2023, 24, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha, J.; Sangüesa, E.; Peña, J.L.; Ribate, M.P.; García, C.B. Retrospective pharmacogenetic study in a cohort of pediatric tuberous sclerosis complex patients using everolimus. Pharmacogenomics 2023, 24, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhazmi, S.; Alzahrani, M.; Farsi, R.; Alharbi, M.; Algothmi, K.; Alburae, N.; Ganash, M.; Azhari, S.; Basingab, F.; Almuhammadi, A.; et al. Multiple Recurrent Copy Number Variations (CNVs) in Chromosome 22 Including 22q11.2 Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pharmgenomics Pers. Med. 2022, 15, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyoubi, R.; Althomali, A.; Magadmi, R.; Abdel Kawy, H.S.; Al Mahdi, H.B.; Kamel, F.O.; Bakhshwin, D.M.; Jamal, M.; Alsieni, M. Association of Polymorphism of the Methyl Tetrahydrofolate Reductase (MTHFR) Gene with Anti-Seizure Medication Response in Pediatric Patients in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Medicina 2022, 58, 1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, N.; Ghazanfari, N.; Shoushtari, A.A.; Firouzabadi, D.; Haem, E. Angiotensin-converting enzyme genetic variants does not influence response to risperidone in autistic children. Trends Pharm. Sci. 2022, 8, 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Wolking, S.; Moreau, C.; Nies, A.T.; Schaeffeler, E.; McCormack, M.; Auce, P.; Avbersek, A.; Becker, F.; Krenn, M.; Møller, R.S.; et al. Testing association of rare genetic variants with resistance to three common antiseizure medications. Epilepsia 2020, 61, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukasem, C.; Vanwong, N.; Srisawasdi, P.; Ngamsamut, N.; Nuntamool, N.; Hongkaew, Y.; Puangpetch, A.; Chamkrachangpada, B.; Limsila, P. Pharmacogenetics of Risperidone-Induced Insulin Resistance in Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2018, 123, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukasem, C.; Hongkaew, Y.; Ngamsamut, N.; Puangpetch, A.; Vanwong, N.; Chamnanphon, M.; Chamkrachchangpada, B.; Sinrachatanant, A.; Limsila, P. Impact of Pharmacogenetic Markers of CYP2D6 and DRD2 on Prolactin Response in Risperidone-Treated Thai Children and Adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorders. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 36, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firouzabadi, N.; Ghazanfari, N.; Alavi Shoushtari, A.; Erfani, N.; Fathi, F.; Bazrafkan, M.; Bahramali, E. Genetic Variants of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Are Linked to Autism: A Case-Control Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, S.; Yanagimachi, M.; Tanoshima, R.; Urayama, K.Y.; Tanaka, F.; Aida, N.; Goto, H.; Ito, S. Influence of ADORA2A gene polymorphism on leukoencephalopathy risk in MTX-treated pediatric patients affected by hematological malignancies. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1983–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouget, J.G.; Bryushkova, L.; Koyama, E.; Zai, C.C.; Fonseka, T.M.; Mueller, D.; Kennedy, J.L.; Beitchman, J.H. Exploring the association of interleukin polymorphisms with aggression and internalizing behaviors in children and adolescents. Brain Behav. 2022, 12, e2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukec, E.; Goričar, K.; Dolžan, V.; Rener-Primec, Z. HIF1A polymorphisms do not modify the risk of epilepsy nor cerebral palsy after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Brain Res. 2021, 1757, 147281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasiołek, M.; Romanowicz, H.; Połatyńska, K.; Chamielec, M.; Skalski, D.; Makowska, M.; Smolarz, B. Association between C3435T polymorphism of MDR1 gene and the incidence of drug-resistant epilepsy in the population of Polish children. Behav. Brain Funct. 2016, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, S.; Maruf, A.A.; Shaheen, S.M.; McCloud, R.; Heintz, M.; McAusland, L.; Arnold, P.D.; Bousman, C.A. Prevalence Estimates of Cytochrome P450 Phenoconversion in Youth Receiving Pharmacotherapy for Mental Health Conditions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2025, 117, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharthi, K.; Zuberi, R.; Maruf, A.A.; Shaheen, S.M.; McCloud, R.; Heintz, M.; McAusland, L.; Arnold, P.D.; Bousman, C.A. Impact of Cytochrome P450 Genetic Variation on Patient-Reported Symptom Improvement and Side Effects Among Children and Adolescents Treated with Fluoxetine. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2024, 34, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, S.; Maruf, A.A.; Shaheen, S.M.; McCloud, R.; Heintz, M.; McAusland, L.; Arnold, P.D.; Bousman, C.A. Bousman CA. Effect of CYP2D6 genetic variation on patient-reported symptom improvement and side effects among children and adolescents treated with amphetamines. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2024, 34, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attia, Z.R.; Labib, M.E.; Kelany, A.K.; Alnefaie, R.M.; Twab, H.A.; Wahsh, E.; El Azeem, R.A.A.; Shaaban, E.I.A.; Elsaid, A.M.; Alalawy, A.I.; et al. Pharmacogenetic insights into ABCB1, ABCC2, CYP1A2, and CYP2B6 variants with epilepsy susceptibility among Egyptian Children: A retrospective case-control study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 142, 113073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P.S.; Elchynski, A.L.; Porter-Gill, P.A.; Goodson, B.G.; Scott, M.A.; Lipinski, D.; Seay, A.; Kehn, C.; Balmakund, T.; Schaefer, G.B. Multidisciplinary Consulting Team for Complicated Cases of Neurodevelopmental and Neurobehavioral Disorders: Assessing the Opportunities and Challenges of Integrating Pharmacogenomics into a Team Setting. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Grigorian, A.; Kennedy, K.G.; Zai, C.C.; Shao, S.; Kennedy, J.L.; Andreazza, A.C.; Ameis, S.H.; Heyn, C.; Maclntosh, B.J.; et al. Differential association of antioxidative defense genes with white matter integrity in youth bipolar disorder. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nussbaum, L.; Hogea, L.M.; Calina, D.; Andreescu, N.; Gradinaru, R.; Stefanescu RPuiu, M. Modern treatment approaches in psychoses. Pharmacogenetic, neuroimagistic and clinical implications. Farmacia 2017, 65, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaum, L.A.; Hogea, L.M.; Andreescu, N.I.; Grădinaru, R.C.; Puiu, M.; Todica, A. The prognostic and clinical significance of neuroimagistic and neurobiological vulnerability markers in correlation with the molecular pharmacogenetic testing in psychoses and ultra high-risk categories. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2016, 57, 959–967. [Google Scholar]
- Gassó, P.; Ortiz, A.E.; Mas, S.; Morer, A.; Calvo, A.; Bargalló, N.; Lafuente, A.; Lázaro, L. Association between genetic variants related to glutamatergic, dopaminergic and neurodevelopment pathways and white matter microstructure in child and adolescent patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 186, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, W.J.; Wu, Y.; Tian, X.X.; Zhang, Y.W. Synaptosomal-Associated Protein 25 Gene Polymorphisms Affect Treatment Efficiency of Methylphenidate in Children with Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: An fNIRS Study. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 793643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruxel, E.M.; Salatino-Oliveira, A.; Akutagava-Martins, G.C.; Tovo-Rodrigues, L.; Genro, J.P.; Zeni, C.P.; Polanczyk, G.V.; Chazan, R.; Schmitz, M.; Arcos-Burgos, M.; et al. LPHN3 and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A susceptibility and pharmacogenetic study. Genes Brain Behav. 2015, 14, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poweleit, E.A.; Aldrich, S.L.; Martin, L.J.; Hahn, D.; Strawn, J.R.; Ramsey, L.B. Pharmacogenetics of Sertraline Tolerability and Response in Pediatric Anxiety and Depressive Disorders. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zai, G.; Zai, C.C.; Arnold, P.D.; Richter, M.A.; Hanna, G.L.; Rosenberg, D.; Kennedy, J.L. White matter volume and myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) microsatellites in pediatric obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatr. Genet. 2023, 33, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashchenko, D.V.; Khoang, S.Z.; Tazagulova, M.K.h.; Makhmudova, B.V.; Buromskaya, N.I.; Shimanov, P.V.; Deitch, R.V.; Dorina, I.V.; Nastovich, M.I.; Akmalova, K.A.; et al. The polymorphic variants DRD2 rs1800497 and ABCB1 3435C>T are associated with antipsychotic safety parameters in adolescents with an acute psychotic episode: The results of a pilot study. Neurol. Neuropsychiatry Psychosom. 2020, 12, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sági, J.C.; Gézsi, A.; Egyed, B.; Jakab, Z.; Benedek, N.; Attarbaschi, A.; Köhrer, S.; Sipek, J.; Winkowska, L.; Zaliova, M.; et al. Pharmacogenetics of the Central Nervous System-Toxicity and Relapse Affecting the CNS in Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagne, O.; Huang, J.; Lin, T.; Reddick, W.E.; Selvo, N.S.; Onar-Thomas, A.; Ward, D.; Robinson, G.; Gajjar, A.; Stewart, C.F. Population pharmacokinetics of methotrexate and 7-hydroxymethotrexate and delayed excretion in infants and young children with brain tumors. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 193, 106669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilbayeh, S.A.R.; Adeen, I.S.; Ghanem, E.H.; Aljurayb, H.; Aldilaijan, K.E.; AlDosari, F.; Fadda, A. Exploratory focused pharmacogenetic testing reveals novel markers associated with risperidone pharmacokinetics in Saudi children with autism. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1356763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honeycutt, D.C.; Blom, T.J.; Ramsey, L.B.; Strawn, J.R.; Bruns, K.M.; Welge, J.A.; Patino, L.R.; Singh, M.K.; DelBello, M.P. Pharmacogenetic Factors Influence Escitalopram Pharmacokinetics and Adverse Events in Youth with a Family History of Bipolar Disorder: A Preliminary Study. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2024, 34, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, S.L.; Poweleit, E.A.; Prows, C.A.; Martin, L.J.; Strawn, J.R.; Ramsey, L.B. Influence of CYP2C19 Metabolizer Status on Escitalopram/Citalopram Tolerability and Response in Youth with Anxiety and Depressive Disorders. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.J.; Ryckman, K.K.; Bahr, T.M.; Dagle, J.M. Polymorphisms in CYP2C9 are associated with response to indomethacin among neonates with patent ductus arteriosus. Pediatr. Res. 2017, 82, 776–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Yarema, M.C.; Box, A.; Hume, S.; Aitchison, K.J.; Bousman, C.A. Identification of high-impact gene-drug pairs for pharmacogenetic testing in Alberta, Canada. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2021, 31, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.; Martinez-Pinteño, A.; Blázquez, A.; Ortiz, A.E.; Moreno, E.; Gassó, P.; Lafuente, A.; Lazaro, L.; Mas, S. Integrative DNA Methylation and Gene Expression Analysis of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Response in Children and Adolescents with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder; a Pilot Study. Pharmgenomics Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassó, P.; Rodríguez, N.; Boloc, D.; Blázquez, A.; Torres, T.; Gortat, A.; Plana, M.T.; Lafuente, A.; Mas, S.; Arnaiz, J.A.; et al. Association of regulatory TPH2 polymorphisms with higher reduction in depressive symptoms in children and adolescents treated with fluoxetine. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2017, 77, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garfunkel, D.; Anagnostou, E.A.; Aman, M.G.; Handen, B.L.; Sanders, K.B.; Macklin, E.A.; Chan, J.; Veenstra-VanderWeele, J. Pharmacogenetics of Metformin for Medication-Induced Weight Gain in Autism Spectrum Disorder. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 29, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidambaran, V.; Mavi, J.; Esslinger, H.; Pilipenko, V.; Martin, L.J.; Zhang, K.; Sadhasivam, S. Association of OPRM1 A118G variant with risk of morphine-induced respiratory depression following spine fusion in adolescents. Pharmacogenom. J. 2015, 15, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhasivam, S.; Chidambaran, V.; Zhang, X.; Meller, J.; Esslinger, H.; Zhang, K.; Martin, L.J.; McAuliffe, J. Opioid-induced respiratory depression: ABCB1 transporter pharmacogenetics. Pharmacogenom. J. 2015, 15, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vande Voort, J.L.; Orth, S.S.; Shekunov, J.; Romanowicz, M.; Geske, J.R. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Combinatorial Pharmacogenetics Testing in Adolescent Depression. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 61, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nooraeen, S.; Croarkin, P.E.; Geske, J.R.; Shekunov, J.; Orth, S.S.; Romanowicz, M.; Frye, M.A.; Vande Voort, J.L. High Probability of Gene-Drug Interactions Associated with Medication Side Effects in Adolescent Depression: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial of Pharmacogenetic Testing. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2024, 34, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liko, I.; Lee, Y.M.; Stutzman, D.L.; Blackmer, A.B.; Deininger, K.M.; Reynolds, A.M.; Aquilante, C.L. Providers’ perspectives on the clinical utility of pharmacogenomic testing in pediatric patients. Pharmacogenomics 2021, 22, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, I.; Manshaei, R.; Liston, E.; Okello, J.B.A.; Khan, R.; Curtis, M.R.; Krupski, A.J.; Jobling, R.K.; Kalbfleisch, K.; Paton, T.A.; et al. Assessment of the Implementation of Pharmacogenomic Testing in a Pediatric Tertiary Care Setting. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.H.; Beasley, T.M.; Amaral, M.; Szaflarski, J.P.; Gaston, T.; Curtis, M.R.; Krupski, A.J.; Jobling, R.K.; Kalbfleisch, K.; Paton, T.A.; et al. UAB CBD Study Group (includes all the investigators involved in the UAB EAP CBD program). Pharmacogenetic Predictors of Cannabidiol Response and Tolerability in Treatment-Resistant Epilepsy. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gota, V.; Chinnaswamy, G.; Vora, T.; Rath, S.; Yadav, A.; Gurjar, M.; Veal, G.; Kurkure, P. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacogenetics of 13-cis retinoic acid in Indian high-risk neuroblastoma patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hallik, M.; Soeorg, H.; Kahre, T.; Murumets, Ü.; Ilmoja, M.L.; Kipper, K.; Metsvaht, T. Pharmacogenetics may explain part of the interindividual variability of dobutamine pharmacodynamics in neonates. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 4155–4162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.O.; Chia, R.; Miller, D.E.; Li, R.; Kumaran, R.; Abramzon, Y.; Alahmady, N.; Renton, A.E.; Top, S.D.; Gibbs, J.R.; et al. Association of Variants in the SPTLC1 Gene with Juvenile Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 1236–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, M.; Petersen, T.S.; Dalhoff, K.P. Clinical Implications of P-Glycoprotein Modulation in Drug-Drug Interactions. Drugs 2017, 77, 859–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenstein, B.; Brückl, T.M.; Ising, M.; Müller-Myhsok, B.; Holsboer, F.; Czamara, D. ABCB1 gene variants and antidepressant treatment outcome: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2015, 168, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brückl, T.M.; Uhr, M. ABCB1 genotyping in the treatment of depression. Pharmacogenomics 2016, 17, 2039–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, L.M.; Markova, S.M.; Chinn, L.W.; Gow, J.M.; Kroetz, D.L.; Klein, T.E.; Altman, R.B. Very important pharmacogene summary: ABCB1 (MDR1, P-glycoprotein). Pharmacogenet. Genomics. 2011, 21, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corradini, I.; Verderio, C.; Sala, M.; Wilson, M.C.; Matteoli, M. SNAP-25 in neuropsychiatric disorders. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1152, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, K.S.; Koromina, M.; van der Veen, T.; Boltz, T.; David, F.S.; Yang, J.M.K.; Lin, K.-H.; Wang, X.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Mitchell, B.L.; et al. Bipolar Disorder Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Genomics yields biological and phenotypic insights into bipolar disorder. Nature 2025, 639, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiao, C.; Wang, K.; Yuan, N. DNA Methylation and Psychiatric Disorders. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2018, 157, 175–232. [Google Scholar]
- Herrera, M.L.; Paraíso-Luna, J.; Bustos-Martínez, I.; Barco, Á. Targeting epigenetic dysregulation in autism spectrum disorders. Trends Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 1028–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastergiou, J.; Quilty, L.C.; Li, W.; Thiruchselvam, T.; Jain, E.; Gove, P.; Mandlsohn, L.; Van Den Bemt, B.; Pojskic, N. Pharmacogenomics guided versus standard antidepressant treatment in a community pharmacy setting: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2021, 14, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greden, J.F.; Parikh, S.V.; Rothschild, A.J.; Thase, M.E.; Dunlop, B.W.; DeBattista, C.; Conway, C.R.; Forester, B.P.; Mondimore, F.M.; Shelton, R.C.; et al. Impact of pharmacogenomics on clinical outcomes in major depressive disorder in the GUIDED trial: A large, patient- and rater-blinded, randomized, controlled study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2019, 111, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thase, M.E.; Parikh, S.V.; Rothschild, A.J.; Dunlop, B.W.; DeBattista, C.; Conway, C.R.; Forester, B.P.; Mondimore, F.M.; Shelton, R.C.; Macaluso, M.; et al. Impact of Pharmacogenomics on Clinical Outcomes for Patients Taking Medications with Gene-Drug Interactions in a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2019, 80, 22039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraballo, P.J.; Hodge, L.S.; Bielinski, S.J.; Stewart, A.K.; Farrugia, G.; Schultz, C.G.; Rohrer-Vitek, C.R.; Olson, J.E.; Sauver, J.L.S.; Roger, V.L.; et al. Multidisciplinary model to implement pharmacogenomics at the point of care. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnenberger, H.M.; Biszewski, M.; Bell, G.C.; Sereika, A.; May, H.; Johnson, S.G.; Hulick, P.J.; Khandekar, J. Implementation of a multidisciplinary pharmacogenomics clinic in a community health system. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1956–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulana, Y.; Toro Jimenez, R.; Twesigomwe, D.; Sani, L.; Irwanto, A.; Bertin, N.; Gonzalez-Porta, M. The variation landscape of CYP2D6 in a multi-ethnic Asian population. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahid, N.A.; Johnson, J.A. CYP2D6 pharmacogenetics and phenoconversion in personalized medicine. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2022, 18, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klomp, S.D.; Manson, M.L.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Swen, J.J. Phenoconversion of Cytochrome P450 Metabolism: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicali, E.J.; Elchynski, A.L.; Cook, K.J.; Houder, J.T.; Thomas, C.D.; Smith, D.M.; Elsey, A.; Johnson, J.A.; Cavallari, L.H.; Wiisanen, K. How to Integrate CYP2D6 Phenoconversion Into Clinical Pharmacogenetics: A Tutorial. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upreti, V.V.; Wahlstrom, J.L. Meta-analysis of hepatic cytochrome P450 ontogeny to underwrite the prediction of pediatric pharmacokinetics using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koukouritaki, S.B.; Manro, J.R.; Marsh, S.A.; Stevens, J.C.; Rettie, A.E.; McCarver, D.G.; Hines, R.N. Developmental expression of human hepatic CYP2C9 and CYP2C19. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeder, J.S.; Gaedigk, A.; Wright, K.J.; Staggs, V.S.; Soden, S.E.; Lin, Y.S.; Pearce, R.E. A longitudinal study of cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) activity during adolescence. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2022, 15, 2514–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapron, B.D.; Chapron, A.; Leeder, J.S. Recent advances in the ontogeny of drug disposition. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 88, 4267–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.R.; Smith, R.L. Inflammation-induced phenoconversion of polymorphic drug metabolizing enzymes: Hypothesis with implications for personalized medicine. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.M.; Cowan, M.; Moonah, S.N.; Petri, W.A., Jr. The Impact of Systemic Inflammation on Neurodevelopment. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Wen, M.S.; Cheng, C.K.; Sheen, Y.J.; Yao, T.C.; Lee, S.-L.; Wu, J.-Y.; Li, L.-H.; Fann, C.S.-J.; Yang, H.-C.; et al. Clinical impact of pharmacogenetic risk variants in a large chinese cohort. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.D.; Do, L.A.; Synnott, P.G.; Lavelle, T.A.; Prosser, L.A.; Wong, J.B.; Neumann, P.J. Developing Criteria for Health Economic Quality Evaluation Tool. Value Health 2023, 26, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virelli, C.R.; Mohiuddin, A.G.; Kennedy, J.L. Barriers to clinical adoption of pharmacogenomic testing in psychiatry: A critical analysis. Transl. Psychiatry 2021, 11, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Role of Genetic Testing in Mental Health Settings (Royal College of Psychiatrists, 2023). Available online: https://www.rcpsych.ac.uk/docs/default-source/improving-care/better-mh-policy/college-reports/College-report-CR237---Genetic-testing-in-mental-health-settings.pdf (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- O’Connor, S.R.; Tully, M.A.; Ryan, B.; Bradley, J.M.; Baxter, G.D.; McDonough, S.M. Failure of a numerical quality assessment scale to identify potential risk of bias in a systematic review: A comparison study. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousman, C.A.; Dunlop, B.W. Genotype, phenotype, and medication recommendation agreement among commercial pharmacogenetic-based decision support tools. Pharmacogenom. J. 2018, 18, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, C.; Joffe, H. Intercoder reliability in qualitative research: Debates and practical guidelines. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2020, 19, 1609406919899220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, V.; Salavert, A.; Espadaler, J.; Tuson, M.; Saiz-Ruiz, J.; Sáez-Navarro, C.; Bobes, J.; Baca-García, E.; Vieta, E.; Olivares, J.M.; et al. Efficacy of prospective pharmacogenetic testing in the treatment of major depressive disorder: Results of a randomized, double-blind clinical trial. BMC Psychiatry 2017, 17, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessel, C.D.; Al Maruf, A.; Oomen, A.; Arnold, P.D.; Bousman, C.A. Pharmacogenetic Testing Knowledge and Attitudes among Pediatric Psychiatrists and Pediatricians in Alberta, Canada. J. Can. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2022, 31, 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Kabbani, D.; Akika, R.; Wahid, A.; Daly, A.K.; Cascorbi, I.; Zgheib, N.K. Pharmacogenomics in practice: A review and implementation guide. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1189976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Source | Region | Ethnicity Reported (Yes/No) | Study Design | Sample Characteristics | Assessment Methods | Relevant Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ramsey et al. (2020) [7] | a United States—IGNITE Pharmacogenetics Working Group | Yes | Cross-sectional study of prescribing data from 16 healthcare systems |
| The main outcome measure was the frequency of level A prescribing and actionability. |
|
| Singh et al. (2024) [22] | United Kingdom | Yes | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Ahmed et al. (2022) [35] | Canada | Yes | Observational study | Prescribing data were reviewed in 787 (n = 613 males) cases with ASD (mean age [range]: 15.4 years [2–87 years]) during 2012 and 2014 |
|
|
| Kalla et al. (2023) [44] | United States | Yes | Case comparison report to investigate ABCB1 polymorphisms and blood–brain barrier (BBB) access to psychotropic medications. |
|
|
|
| Concha et al. (2023) [45] | Spain | No | Retrospective observational study |
|
|
|
| Alhazmi et al. (2022) [46] | Saudi Arabia | Yes ¥ | Observational study |
| Samples of DNA were analysed using DNA sequencing and genomic hybridisation. |
|
| Alyoubi et al. (2022) [47] | Saudi Arabia | Yes | Multicentre case-controlled retrospective study |
| Genotyping for MTHFR (rs180133) SNP |
|
| Firouzabadi et al. (2022) [48] | Iran | No | Cross-sectional study |
|
|
|
| Wolking et al. (2020) [49] | b European consortium | No | Case-controlled study |
|
|
|
| Sukasem et al. (2018) [50] | Thailand | No | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Sukasem et al. (2016) [51] | Thailand | No | Retrospective cross-sectional study |
|
|
|
| Firouzabadi et al. (2016) [52] | Iran | No | Case-controlled study |
| Genotyping of two polymorphisms (rs4291 and rs4343) within the ACE gene |
|
| Tsujimoto et al. (2016) [53] | Japan | No | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Pouget et al. (2021) [54] | Canada | Yes | Hypothesis-driven genetic study |
|
|
|
| Kukec et al. (2021) [55] | Slovenia | Yes | Observational study | The study consisted of:
|
|
|
| Stasiołek et al. (2016) [56] | Poland | Yes | Observational study |
| Genotyping and allele distributions of the MDR1 gene (rs1045642 polymorphism) |
|
| Gerlach et al. (2025) [57] | Canada | Yes | c PGx-SParK clinical trial |
|
|
|
| Bharthi et al. (2024) [58] | Canada | Yes | c PGx-SParK clinical trial Mirror Image Trial of PGx testing implementation |
| Participants had DNA extracted from saliva samples and genotyped for CYP2D6, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. |
|
| Gerlach et al. (2024) [59] | Canada | Yes | c PGx-SParK clinical trial |
|
|
|
| Attia et al. (2024) [60] | Egypt | No | Retrospective case–control study |
| Genotyping of rs2032582, rs717620, rs2273697, rs762551 and rs3745274 polymorphisms | When compared to healthy controls, the study showed:
|
| Gill et al. (2022) [61] | United States | Yes | Retrospective chart review study |
|
|
|
| Zou et al. (2022) [62] | Canada | Yes | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Nussbaum et al. (2017) [63] | Romania | No | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Nussbaum et al. (2016) [64] | Romania | No | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Gassó et al. (2015) [65] | Spain | No | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Li et al. (2022) [66] | China | No | fNIRS observational study |
|
|
|
| Bruxel et al. (2015) [67] | Brazil | Yes | Observational PGx study |
|
|
|
| Poweleit et al. (2019) [68] | United States | Yes | Retrospective analysis of electronic medical data |
| Retrospective review of electronic medical record data including CYP2C19, HTR2A, SLC6A4 and GRIK4 variant genotyping |
|
| Zai et al. (2023) [69] | d United States | Yes Y | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Ivashchenko et al. (2020) [70] | Russia | No | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Sági et al. (2021) [71] | e Europe | No | Retrospective study |
|
| The study showed that gene polymorphisms ABCB1, ABCG2 and GSTP are associated with chemotherapy-related CNS adverse events such as seizures and relapse. |
| Campagne et al. (2024) [72] | United States | No | Multicentre clinical trial |
|
| The study showed that MTHFR, ABC and SLC polymorphisms only had a modest influence on MTX metabolism but were not deemed to be clinically relevant. |
| Shilbayeh et al. (2024) [73] | Saudi Arabia | Yes | Prospective cohort study | The sample consisted of 89 children (mean age [SD]: 9.0 [4.1] years) with ASD treated with Risperidone |
| The study showed that:
|
| Honeycutt et al. (2024) [74] | United States | Yes | Clinical trial |
|
|
|
| Aldrich et al. (2019) [75] | United States | Yes | Retrospective analysis of electronic medical data |
| Retrospective review of electronic medical record data, including routine CYP2C19 genotyping |
|
| Smith et al. (2017) [76] | United States | Yes | Case control study |
| Genotyping of six polymorphisms rs4918758, rs1799853, rs2253635, rs4086116, rs1505 and rs2153628) located in CYP2C9 |
|
| Fan et al. (2021) [77] | Canada | Yes | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Rodriguez et al. (2021) [78] | Spain | No | Genome-wide methylation analysis study |
|
|
|
| Gassó et al. (2017) [79] | Spain | No | Observational PGx study |
|
|
|
| Garfunkel et al. (2019) [80] | United States | Yes | Randomised controlled trial |
|
|
|
| Chidambaran et al. (2015) [81] | United States | Yes | Prospective observational study |
|
|
|
| Sadhasivam et al. (2015) [82] | United States | Yes | Observational study |
|
|
|
| Vande Voort et al. (2022) [83] | United States | Yes | Randomised controlled trial |
|
|
|
| Nooraeen et al. (2024) [84] | United States | Yes | Randomised Controlled Clinical Trial—post hoc analysis |
|
|
|
| Liko et al. (2021) [85] | United States | Yes | Cross-sectional study |
|
|
|
| Cohn et al. (2021) [86] | Canada | No | Cohort study consisting of two patient cohorts: 1, Point-of-care (reactive—based on targeted drug–guided testing) 2, Pre-emptive (whole-genome sequencing–guide testing) |
|
|
|
| Davis et al. (2021) [87] | United States | Yes | Open-label CBD study |
|
|
|
| Gota et al. (2016) [88] | India | No | Observational study |
| Genotyping of UGT2B7, CYP3A5, CYP3A7 and CYP2C8 polymorphisms | The study showed that genetic variation in CYP and UGT polymorphisms does not modify the metabolism of 13-cis retinoic acid in patients being treated for neuroblastoma |
| Hallik et al. (2022) [89] | Estonia | No | Clinical trial |
| Genotyping of SNPs: β1, β2 adrenoceptor (AR) and Gs protein α-subunit gene (GNAS) Assessment of heart rate parameters | The study showed that β1-AR Arg389Gly and GNAS c.393C > T polymorphisms were associated with the haemodynamic response to dobutamine in severely ill neonates. |
| Johnson et al. (2021) [90] | f Consortium | Yes µ | Multicentre genetic study |
| Clinical history and assessment Next-generation sequencing Mitochondrial assays and sphingolipid measurements |
|
| Theme | Sub-theme | Count * |
|---|---|---|
| Implications of non-CYP450 polymorphisms | Disorder-Specific Associations | 19 |
| Treatment Response and Efficacy | 3 | |
| Paediatric CYP450 PGx | Treatment Response and Efficacy | 5 |
| CYP450 Substrates and Gene–drug Pairs | 3 | |
| Disorder-Specific Associations | 3 | |
| Genetic predictors of response | 8 | |
| Insights for implementation and future research | 7 | |
| Phenoconversion | 4 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, J.; Manginas, A.; Wilkins, G.; Santosh, P. A Comprehensive Analysis Examining the Role of Genetic Influences on Psychotropic Medication Response in Children. Genes 2025, 16, 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091055
Singh J, Manginas A, Wilkins G, Santosh P. A Comprehensive Analysis Examining the Role of Genetic Influences on Psychotropic Medication Response in Children. Genes. 2025; 16(9):1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091055
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Jatinder, Athina Manginas, Georgina Wilkins, and Paramala Santosh. 2025. "A Comprehensive Analysis Examining the Role of Genetic Influences on Psychotropic Medication Response in Children" Genes 16, no. 9: 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091055
APA StyleSingh, J., Manginas, A., Wilkins, G., & Santosh, P. (2025). A Comprehensive Analysis Examining the Role of Genetic Influences on Psychotropic Medication Response in Children. Genes, 16(9), 1055. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091055






