Detection of Clinically Significant BRCA Large Genomic Rearrangements in FFPE Ovarian Cancer Samples: A Comparative NGS Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. NGS Methods Used for CNV Calling
2.4. BRCA Testing with Myriapod® NGS BRCA1/2 Panel Kit and Primary Sequencing Strategy
2.5. Re-Evaluation of CNV Calling Using Diatech Software by Simulating a Diagnostic Setting
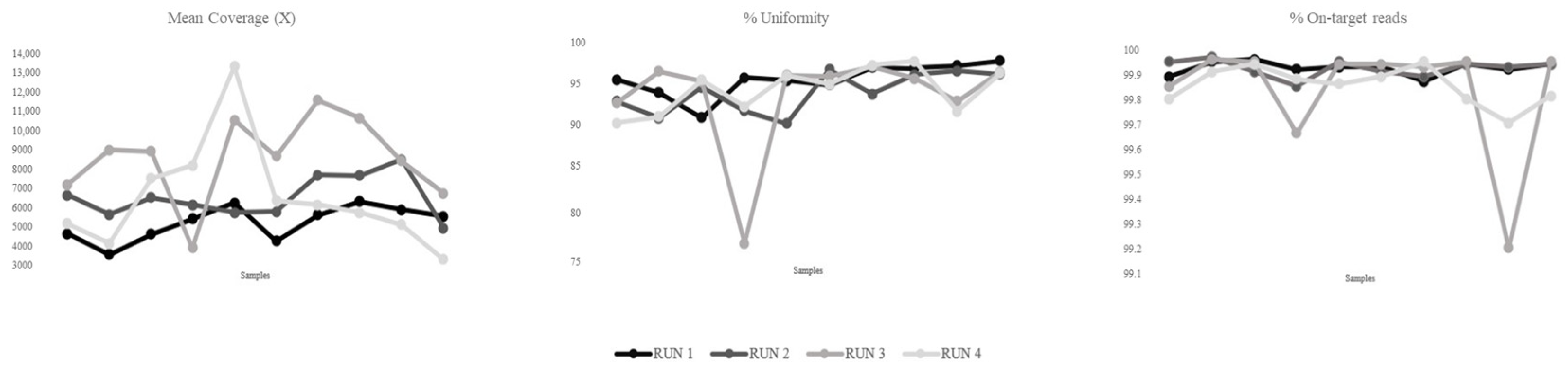
2.6. Read Coverage and Comparative Analyses
2.7. Data Analysis
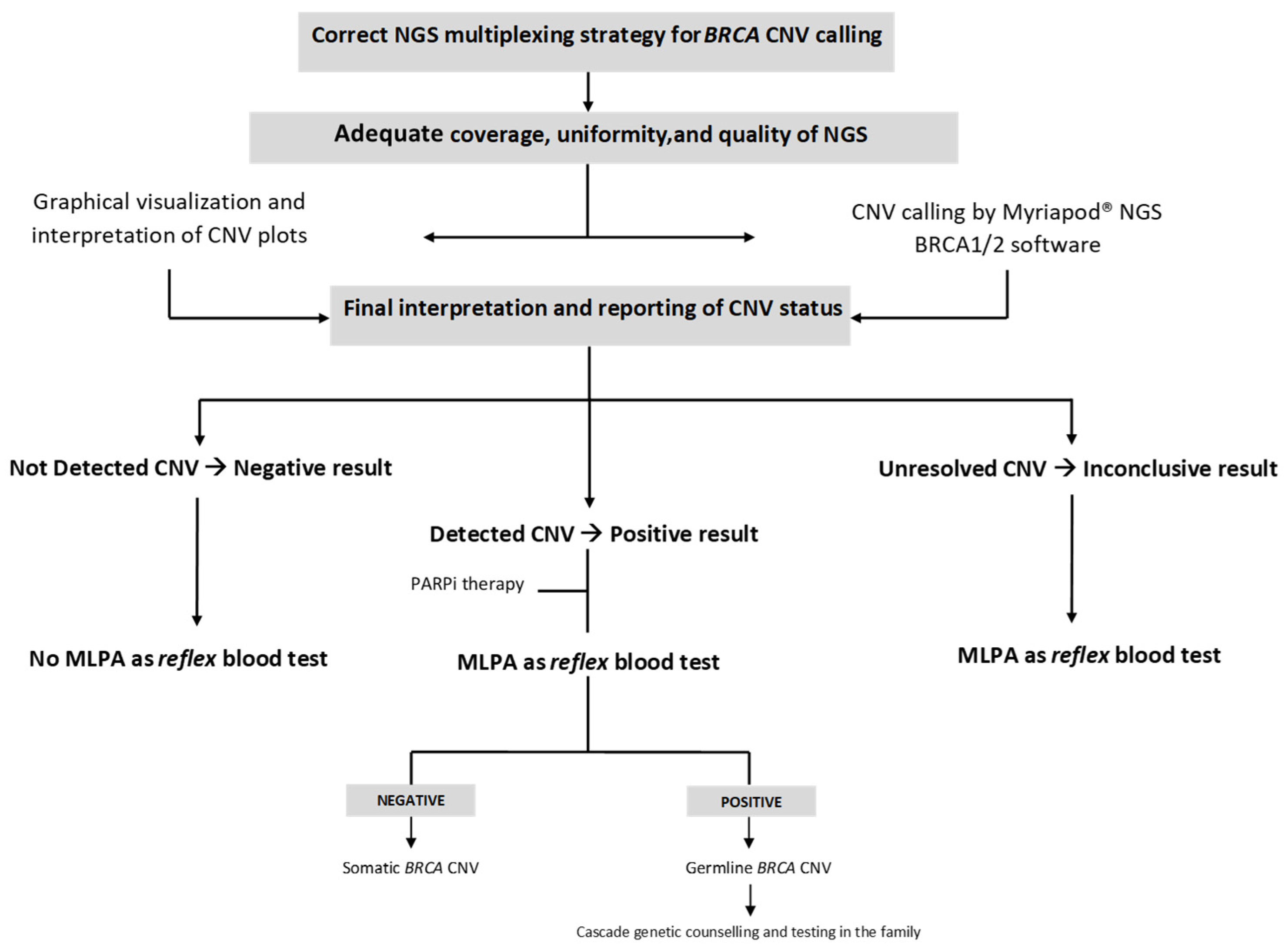
3. Results
- (a)
- Graphical visualization and interpretation of CNV plots;
- (b)
- CNV calling by the Myriapod® NGS data analysis software (v 5.0.11);
- (c)
- Final interpretation and reporting of CNV status, as a decision-making result integrating the two previous analysis levels.
3.1. Myriapod® NGS Data Results
3.1.1. BRCA CNV-Negative Samples
3.1.2. BRCA CNV-Positive Samples
3.2. CNV Calling in a Simulated Diagnostic Scenario (One BRCA CNV-Positive vs. Nine BRCA CNV-Negative Samples in the Same NGS Run)
3.2.1. BRCA CNV-Negative Samples
3.2.2. BRCA CNV-Positive Samples
3.3. Sequencing Metrics and Performance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Marmolejo, D.H.; Wong, M.Y.Z. Overview of Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Guidelines across Europe. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 64, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Ledermann, J.A.; Kohn, E.C. PARP Inhibitors for BRCA1/2 Mutation-Associated and BRCA-Like Malignancies. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewani, D.; Jaiswal, A.; Karwade, P.C. Poly (Adenosine Diphosphate Ribose) Polymerase (PARP) Inhibitors in the Treatment of Advanced Ovarian Cancer: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2024, 16, e68463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guffanti, F.; Mengoli, I.; Damia, G. Current HRD Assays in Ovarian Cancer: Differences, Pitfalls, Limitations, and Novel Approaches. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1405361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnaparkhi, R.; Javellana, M.; Jewell, A.; Spoozak, L. Evaluation of Homologous Recombination Deficiency in Ovarian Cancer. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2024, 25, 237–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcieri, M.; Tius, V.; Andreetta, C.; Restaino, S.; Biasioli, A.; Poletto, E.; Damante, G.; Ercoli, A.; Driul, L.; Fagotti, A.; et al. How BRCA and Homologous Recombination Deficiency Change Therapeutic Strategies in Ovarian Cancer: A Review of Literature. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1335196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mafficini, A.; Simbolo, M.; Parisi, A.; Rusev, B.; Luchini, C.; Cataldo, I.; Piazzola, E.; Sperandio, N.; Turri, G.; Franchi, M.; et al. BRCA Somatic and Germline Mutation Detection in Paraffin-Embedded Ovarian Cancers by Next-Generation Sequencing. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewald, I.P.; Ribeiro, P.L.; Palmero, E.I.; Cossio, S.L.; Giugliani, R.; Ashton-Prolla, P. Genomic Rearrangements in BRCA1 and BRCA2: A Literature Review. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2009, 32, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concolino, P.; Mello, E.; Minucci, A.; Santonocito, C.; Scambia, G.; Giardina, B.; Capoluongo, E. Advanced Tools for BRCA1/2 Mutational Screening: Comparison between Two Methods for Large Genomic Rearrangements (LGRs) Detection. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enyedi, J.; Pintér, L.; Sükösd, F.; Gyuris, Z.; Hajdu, A.; Határvölgyi, E.; Priskin, K.; Haracska, L. Simultaneous Detection of BRCA Mutations and Large Genomic Rearrangements in Germline DNA and FFPE Tumor Samples. Oncotarget 2016, 20, 61845–61859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.Y.; Hansen, T.V.O.; Ahlborn, L.B.; Jønson, L.; Yde, C.W.; Nielsen, F.C. Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Detection of Germline Copy Number Variations in BRCA1/BRCA2: Validation of a One-Step Diagnostic Workflow. J. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 19, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, D.; Paudice, M.; Gismondi, V.; Anselmi, G.; Vellone, V.G.; Varesco, L.; Ligurian BRCA Working Group. Implementing NGS-based BRCA tumour tissue testing in FFPE ovarian carcinoma specimens: Hints from a real-life experience within the framework of expert recommendations. J. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 74, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nero, C.; Duranti, S.; Giacomini, F.; Minucci, A.; Giacò, L.; Piermattei, A.; Genuardi, M.; Pasciuto, T.; Urbani, A.; Daniele, G.; et al. Integrating a Comprehensive Cancer Genome Profiling into Clinical Practice: A Blueprint in an Italian Referral Center. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczerba, E.; Kamińska, K.; Mierzwa, T.; Misiek, M.; Kowalewski, J.; Lewandowska, M.A. BRCA1/2 Mutation Detection in the Tumor Tissue from Selected Polish Patients with Breast Cancer Using Next Generation Sequencing. Genes 2021, 12, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishio, S.Y.; Moteki, H.; Usami, S.I. Simple and efficient germline copy number variant visualization method for the Ion AmpliSeq™ custom panel. Mol. Genet. Genomic. Med. 2018, 12, 678–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barili, V.; Ambrosini, E.; Bortesi, B.; Minari, R.; De Sensi, E.; Cannizzaro, I.R.; Taiani, A.; Michiara, M.; Sikokis, A.; Boggiani, D.; et al. Genetic Basis of Breast and Ovarian Cancer: Approaches and Lessons Learnt from Three Decades of Inherited Predisposition Testing. Genes 2024, 15, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ID | Disease | Timing | Age of the Sample | TC (%) | Reference Assay | CNV Status | Detected CNVs * | CNV Status | OncoKB Database Classification *** | Clinical Implication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 90 | TSO500HT | Positive | BRCA2 exon 2–3 deletion | Somatic | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment |
| 2 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 90 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 19 deletion | Somatic | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment |
| 3 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 60 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 8–11 deletion | Germline ** | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment; cascade screening |
| 4 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 70 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 20 deletion | Germline ** | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment; Cascade screening |
| 5 | HGSC | RELAPSE | 2023 | 90 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 2 deletion | Germline ** | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment; cascade screening |
| 6 | HGSC | RELAPSE | 2024 | 90 | SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 16–17 deletion | Germline ** | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment; cascade screening |
| 7 | HGSC | RELAPSE | 2024 | 70 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 4–7 deletion | Germline ** | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment; cascade screening |
| 8 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2023 | 90 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA2 exon 9–21 deletion | Somatic | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment |
| 9 | ENOC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 90 | TSO500HT | Positive | BRCA1 exon 11 deletion | Somatic | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment |
| 10 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 95 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 2–3 deletion | Somatic | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment |
| 11 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 60 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 19 deletion | Germline * | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment; cascade screening |
| 12 | HGSC | RELAPSE | 2024 | 80 | SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 2 deletion | Germline ** | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment; cascade screening |
| 13 | HGSC | RELAPSE | 2024 | 80 | SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 exon 2–19 deletion | Somatic | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment |
| 14 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 80 | TSO500HT | Positive | BRCA1 exon 15 deletion | Somatic | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment |
| 15 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 55 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA1 whole gene deletion | Germline ** | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment; cascade screening |
| 16 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2025 | 30 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Positive | BRCA2 exon 11–27 deletion | Somatic | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment |
| 17 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 80 | TSO500HT | Positive | BRCA1 exon 3–23 deletion | Somatic | Oncogenic (loss of function) | PARPi treatment |
| 18 | OCS | RELAPSE | 2024 | 60 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 19 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 80 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 20 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2025 | 20 | TSO500HT | Negative | - | - | - | |
| 21 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 80 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 22 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 80 | TSO500HT | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 23 | CCOC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 80 | TSO500HT | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 24 | ENOC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 90 | TSO500HT | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 25 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 25 | TSO500HT | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 26 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 80 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 27 | HSGC | RELAPSE | 2024 | 95 | SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 28 | ENOC | RELAPSE | 2024 | 30 | SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 29 | HSGC | RELAPSE | 2024 | 30 | SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 30 | HSGC | RELAPSE | 2024 | 35 | SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 31 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2023 | 70 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 32 | CCOC | PRIMARY | 2023 | 80 | TSO500HT | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 33 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 40 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 34 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2024 | 36 | SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 35 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2023 | 80 | SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 36 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2025 | 70 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 37 | CCOC | PRIMARY | 2025 | 20 | TSO500HT | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 38 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2025 | 30 | TSO500HT; SOPHiA DDM HRD | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 39 | CCOC | PRIMARY | 2025 | 70 | TSO500HT | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| 40 | HGSC | PRIMARY | 2025 | 25 | TSO500HT | Negative | - | - | - | - |
| ID Samples | Graphical Visualization and Interpretation of CNV Plots | CNV Calling by Myriapod® NGS Data Analysis Software | Final Interpretation and Reporting CNV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRCA1 | BRCA2 | BRCA1 | BRCA2 | BRCA1 | BRCA2 | |
| BRCA CNV-negative samples | ||||||
| 18 | cCNV | oCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Negative | oCNV |
| 19 | oCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 20 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Negative |
| 21 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Negative | Negative |
| 22 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 23 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 24 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 25 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 26 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 27 | oCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | oCNV | Negative |
| 28 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 29 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 30 | oCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | oCNV | Negative |
| 31 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 32 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 33 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 34 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 35 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Negative |
| 36 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Negative |
| 37 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 38 | iCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 39 | cCNV | iCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | iCNV |
| 40 | oCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | oCNV | Negative |
| BRCA CNV-positive samples | ||||||
| 1 | oCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Positive | Positive |
| 2 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 3 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 4 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Positive | Negative |
| 5 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Positive | Negative |
| 6 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 7 | cCNV | oCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | iCNV |
| 8 | oCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | oCNV | Positive |
| 9 | fCNV | fCNV | CNV Failed | CNV Failed | fCNV | fCNV |
| 10 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 11 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Positive | Negative |
| 12 | cCNV | iCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Positive | iCNV |
| 13 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 14 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Positive | Positive |
| 15 | ntCNV | iCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | iCNV |
| 16 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Positive |
| 17 | ntCNV | iCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | iCNV | iCNV |
| (A) Primary CNV calling strategy and concordance analysis | ||
| Diatech Myriapod® NGS CNVs final interpretation | TSO500HT/SOPHiA DDM™ HRD | |
| CNV-Positive | CNV-Negative | |
| BRCA CNV-Positive | 13 | 5 |
| BRCA CNV-Negative | 3 | 18 |
| Inconclusive | 1 | |
| Analytical Performance | Value (%) | |
| Sensitivity | 81.25 | |
| Specificity | 78.26 | |
| Positive predictive value | 72.22 | |
| Negative predictive value | 85.71 | |
| Accuracy | 79.49 | |
| (B) CNV calling in a simulated BRCA diagnostic setting | ||
| Diatech Myriapod® NGS CNVs final interpretation | TSO500HT/SOPHiA DDM™ HRD | |
| CNV-Positive | CNV-Negative | |
| BRCA CNV-Positive | 15 | 1 |
| BRCA CNV-Negative | 1 | 22 |
| Inconclusive | 1 | |
| Analytical Performance | Value (%) | |
| Sensitivity | 93.75 | |
| Specificity | 95.65 | |
| Positive predictive value | 94.87 | |
| Negative predictive value | 93.75 | |
| Accuracy | 95.65 | |
| ID Samples | Graphical Visualization and Interpretation of CNV Plots | CNV Calling By Myriapod® NGS Data Analysis Software | Final Interpretation and Reporting CNV | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRCA1 | BRCA2 | BRCA1 | BRCA2 | BRCA1 | BRCA2 | |
| BRCA CNV-negative samples | ||||||
| 18 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Negative |
| 19 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Negative |
| 20 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 21 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Negative |
| 22 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 23 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 24 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 25 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 26 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 27 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 28 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 29 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 30 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 31 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 32 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 33 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 34 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 35 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 36 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Negative |
| 37 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 38 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Negative | Negative |
| 39 | oCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | oCNV | Negative |
| 40 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Negative | Negative |
| BRCA CNV-positive samples | ||||||
| 1 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Positive |
| 2 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Positive | Negative |
| 3 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 4 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Positive | Negative |
| 5 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Positive | Negative |
| 6 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Positive | Negative |
| 7 | cCNV | iCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Positive | iCNV |
| 8 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Negative | Positive |
| 9 | fCNV | fCNV | CNV failed | CNV failed | fCNV | fCNV |
| 10 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Positive | Negative |
| 11 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | CNV Not Positive | Positive | Negative |
| 12 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 13 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 14 | cCNV | cCNV | Potential CNV | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 15 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Positive | Negative |
| 16 | cCNV | cCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | Positive |
| 17 | ntCNV | iCNV | CNV Not Positive | Potential CNV | Negative | iCNV |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perrucci, A.; De Bonis, M.; Maneri, G.; Ricciardi Tenore, C.; Concolino, P.; Corsi, M.; Conca, A.; Evangelista, J.; Piermattei, A.; Nero, C.; et al. Detection of Clinically Significant BRCA Large Genomic Rearrangements in FFPE Ovarian Cancer Samples: A Comparative NGS Study. Genes 2025, 16, 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091052
Perrucci A, De Bonis M, Maneri G, Ricciardi Tenore C, Concolino P, Corsi M, Conca A, Evangelista J, Piermattei A, Nero C, et al. Detection of Clinically Significant BRCA Large Genomic Rearrangements in FFPE Ovarian Cancer Samples: A Comparative NGS Study. Genes. 2025; 16(9):1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091052
Chicago/Turabian StylePerrucci, Alessia, Maria De Bonis, Giulia Maneri, Claudio Ricciardi Tenore, Paola Concolino, Matteo Corsi, Alessandra Conca, Jessica Evangelista, Alessia Piermattei, Camilla Nero, and et al. 2025. "Detection of Clinically Significant BRCA Large Genomic Rearrangements in FFPE Ovarian Cancer Samples: A Comparative NGS Study" Genes 16, no. 9: 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091052
APA StylePerrucci, A., De Bonis, M., Maneri, G., Ricciardi Tenore, C., Concolino, P., Corsi, M., Conca, A., Evangelista, J., Piermattei, A., Nero, C., Giacò, L., De Paolis, E., Fagotti, A., & Minucci, A. (2025). Detection of Clinically Significant BRCA Large Genomic Rearrangements in FFPE Ovarian Cancer Samples: A Comparative NGS Study. Genes, 16(9), 1052. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091052







