Comparative Genomics and Functional Profiling Reveal Lineage-Specific Metabolic Adaptations in Globally Emerging Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Salmonella Kentucky ST198
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Selection and Growth
2.2. Comparative Metabolic Profiling of ST152 and FluR ST198
2.3. Benchtop Growth Assay
2.4. Comparative Genomics Analysis
2.5. RT-qPCR
3. Results and Discussion
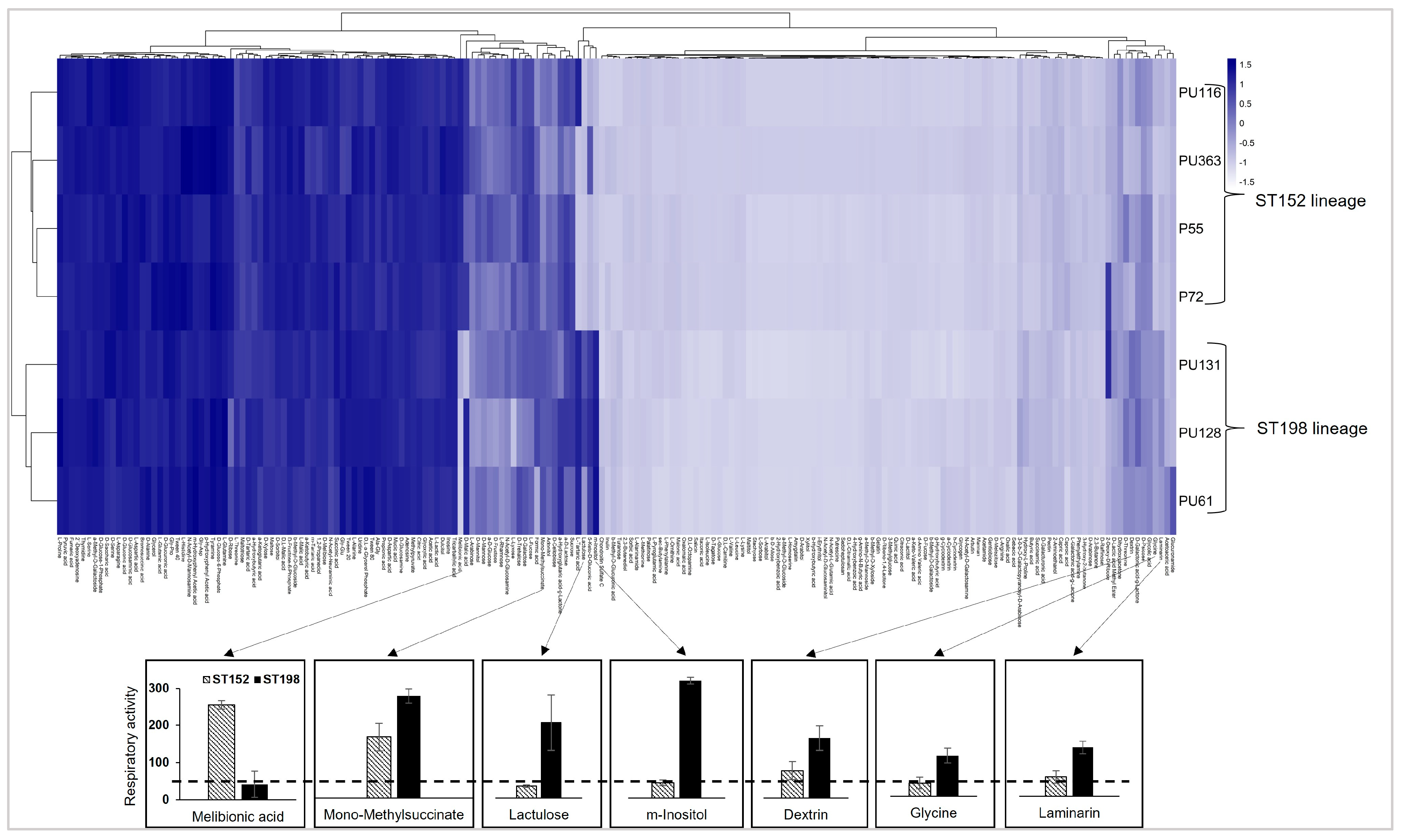
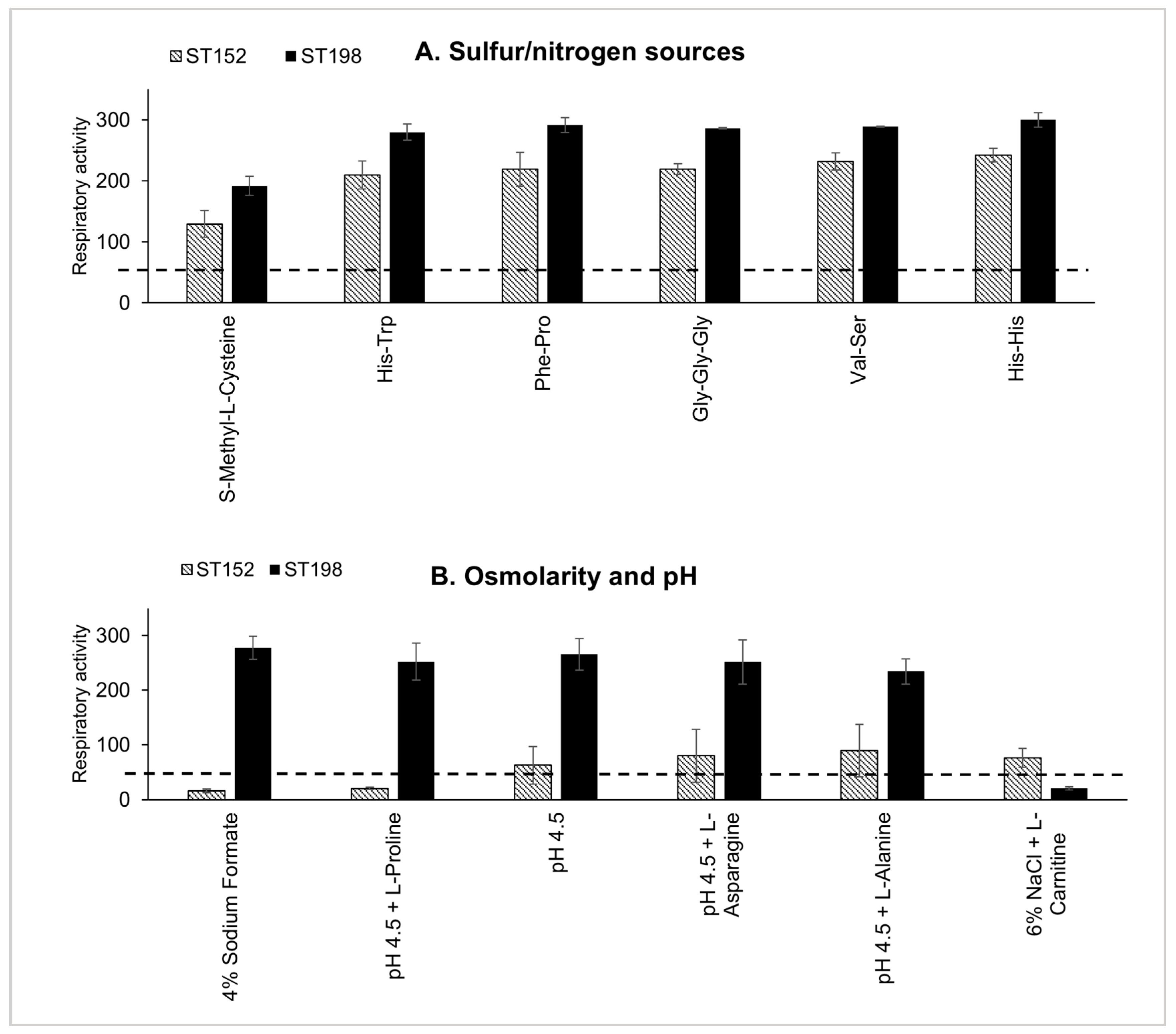
3.1. Differences in Metabolic Fitness Between ST152 and FluR ST198 Lineages
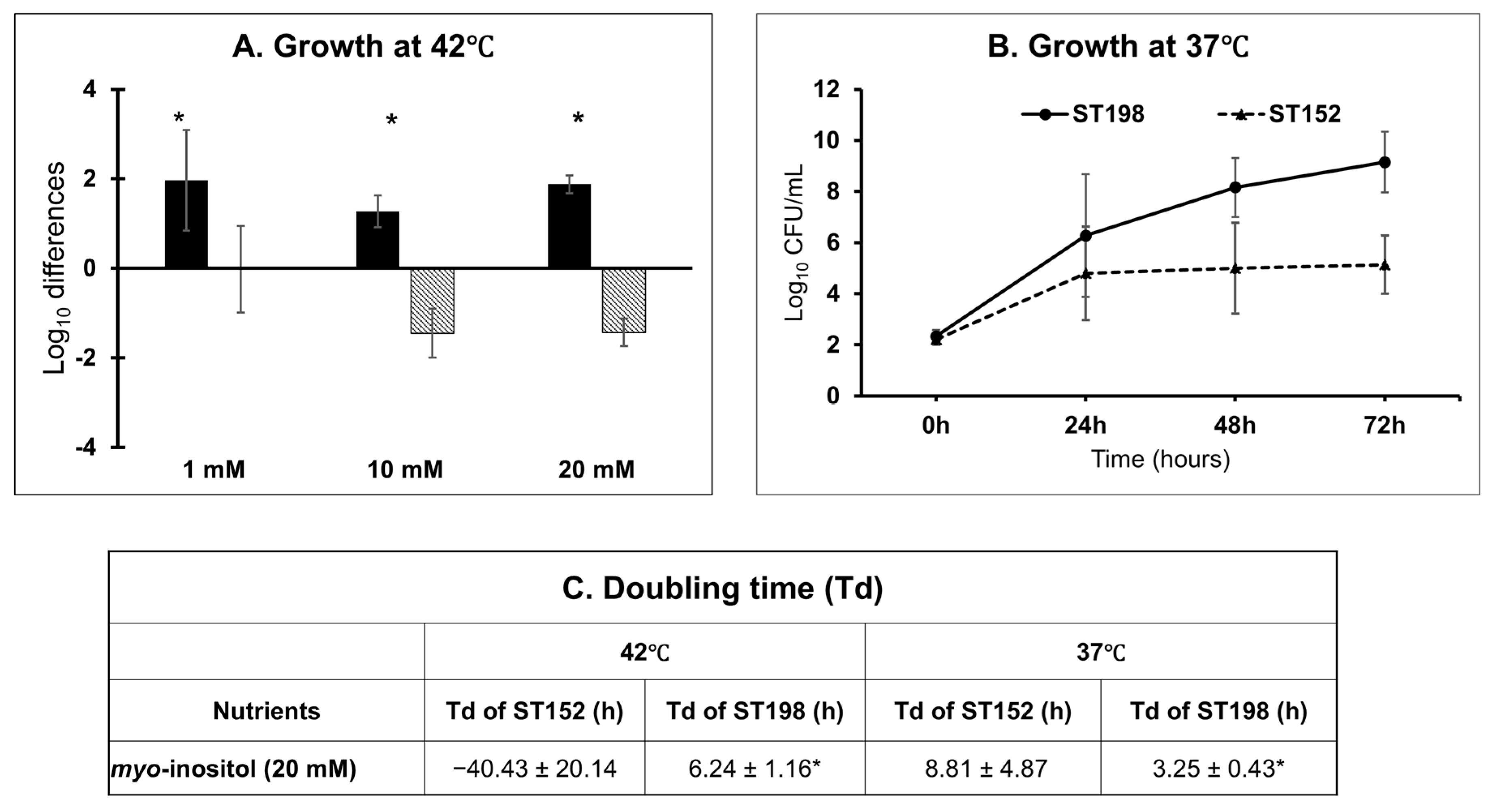
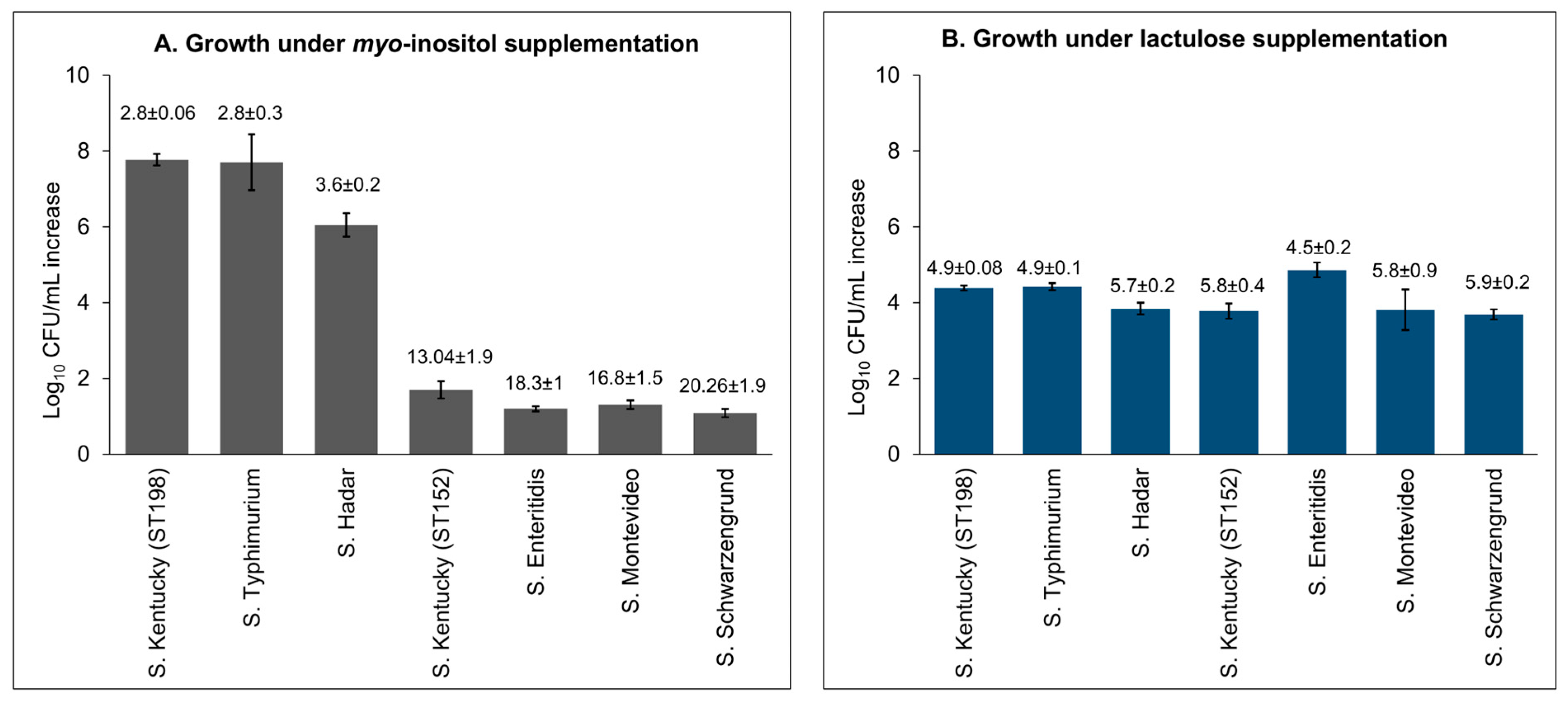
3.2. Lineage- and Temperature-Dependent Differences in Myo-Inositol Utilization by ST152 and FluR ST198 Strains
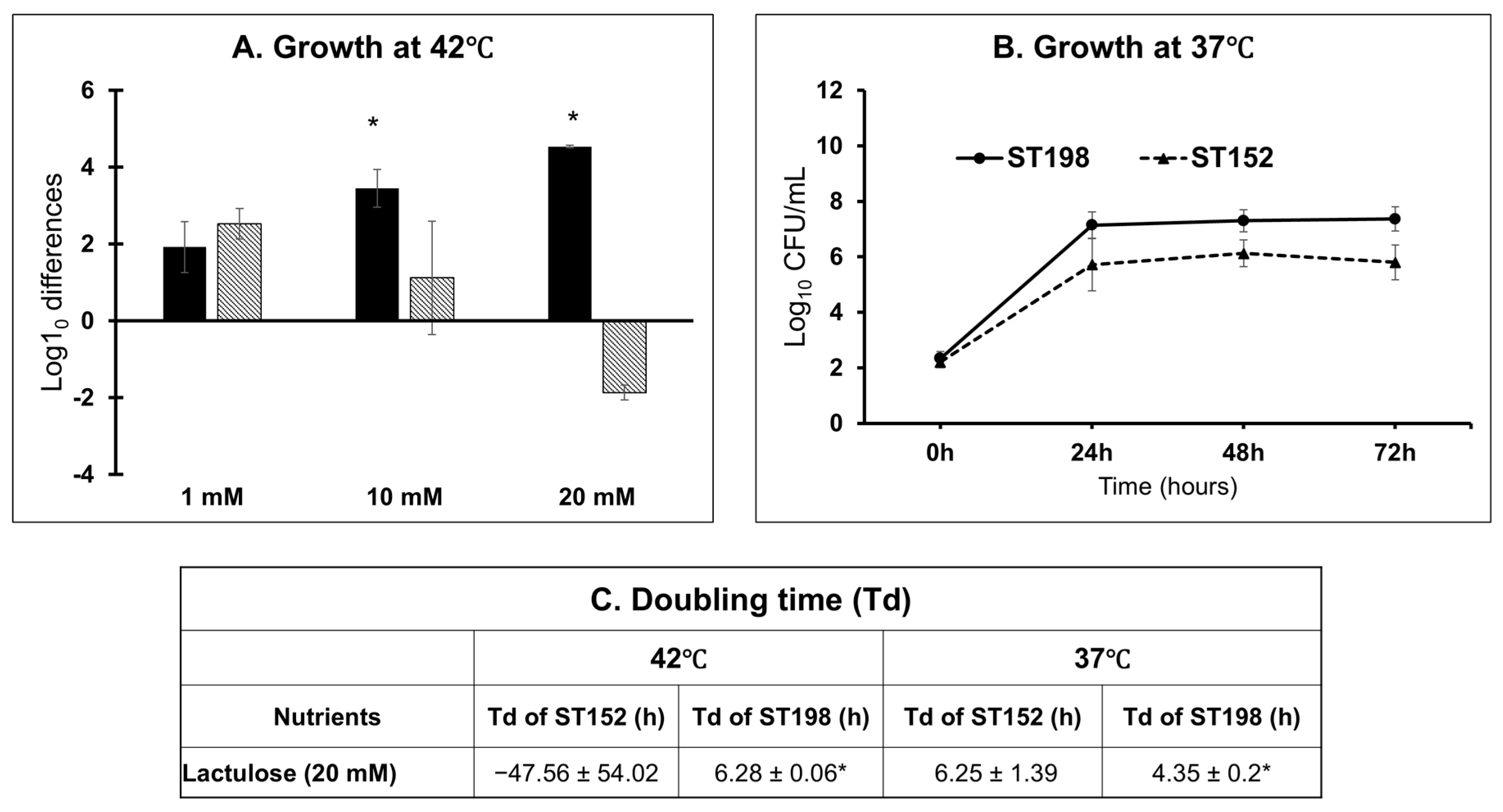
3.3. Lineage- and Temperature-Dependent Differences in Lactulose Utilization by ST152 and FluR ST198 Strains
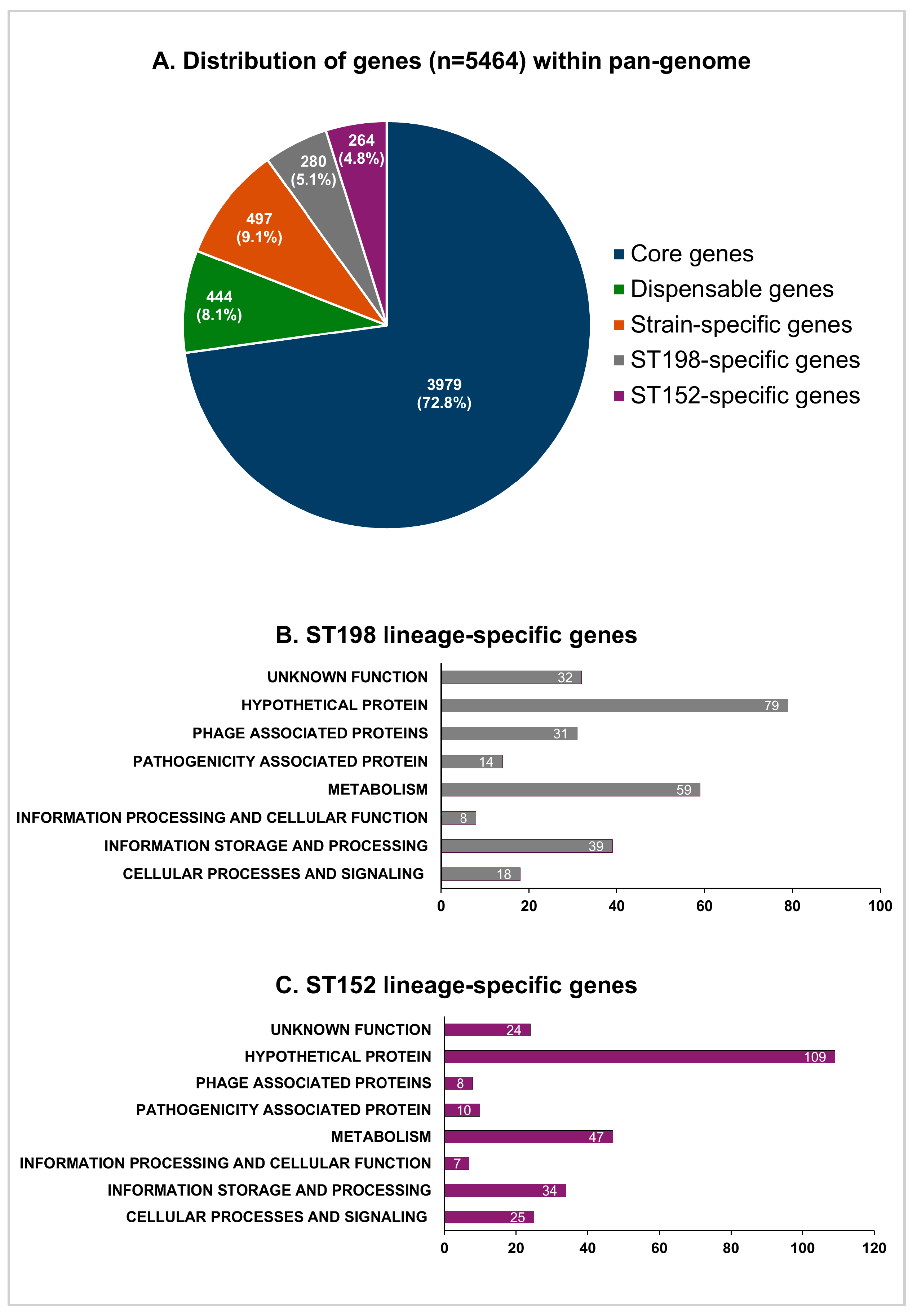
3.4. Pan-Genome and Comparative Gene Functional Analysis of ST152 and FluR ST198 Strains
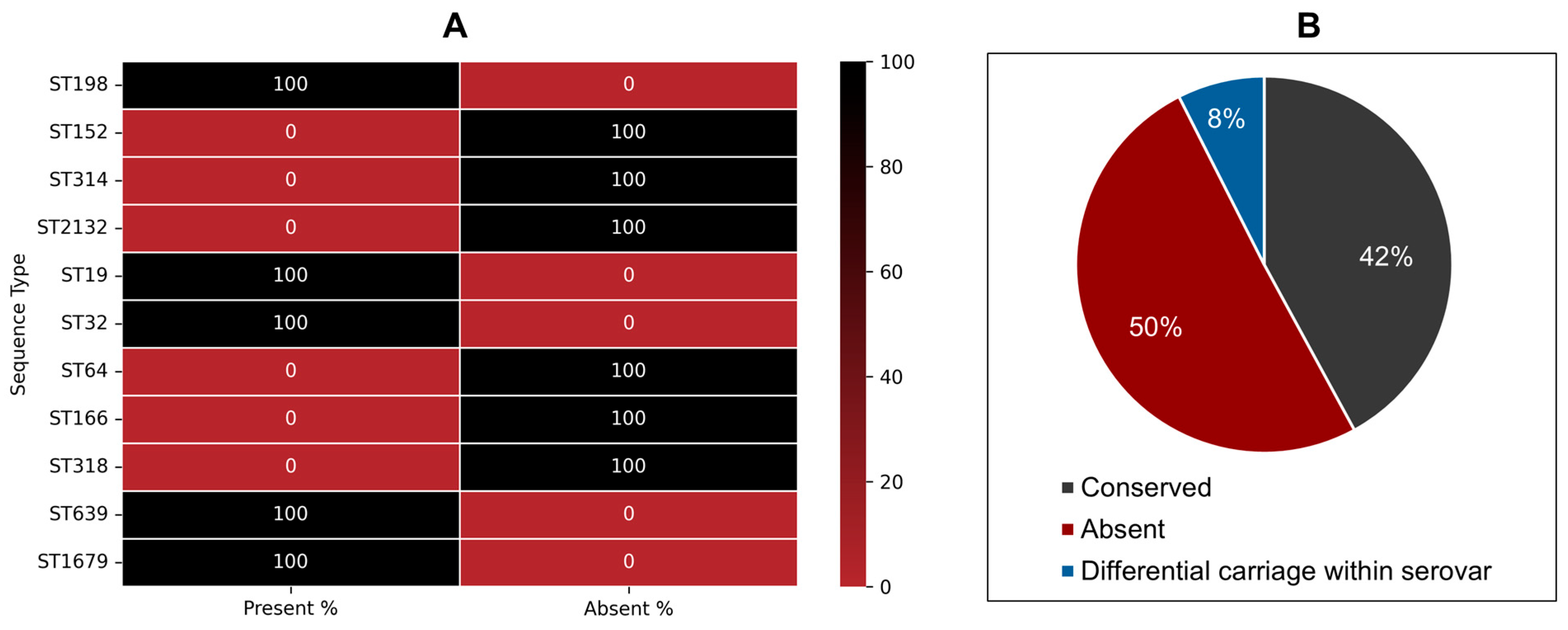
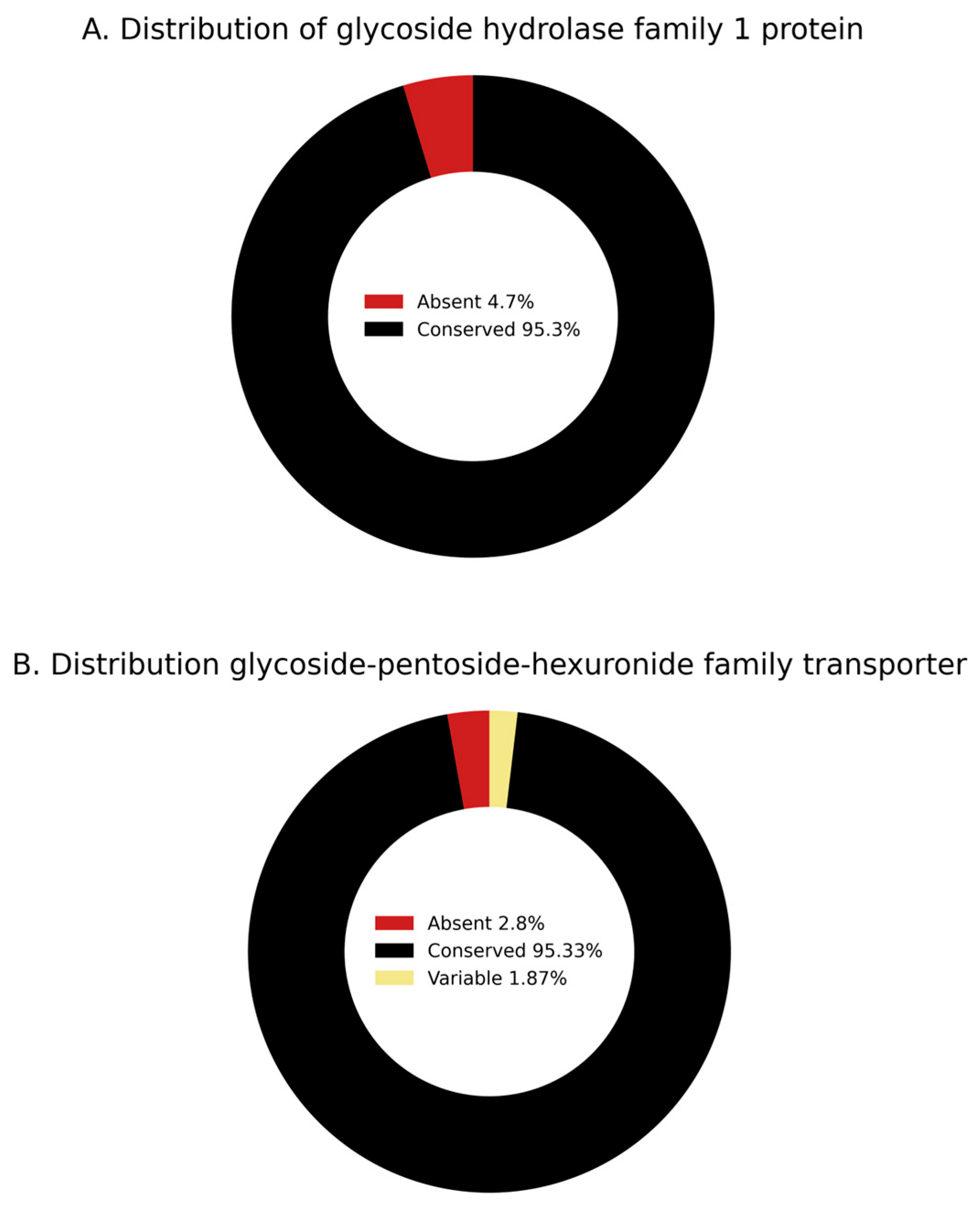
3.4.1. Phenotype-to-Genotype Association for Myo-Inositol Metabolism in S. Kentucky ST198 and ST152 Lineages and Across NTS
3.4.2. Phenotype-to-Genotype Association for Lactulose Metabolism in S. Kentucky ST198 and ST152 Lineages and Across NTS
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Majowicz, S.E.; Musto, J.; Scallan, E.; Angulo, F.J.; Kirk, M.; O’Brien, S.J.; Jones, T.F.; Fazil, A.; Hoekstra, R.M.; for the International Collaboration on Enteric Disease “Burden of Illness” Studies. The Global Burden of Nontyphoidal Salmonella Gastroenteritis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, B.J.; Kim, S.W.; Haendiges, J.; Keller, E.; Torpey, D.; Kim, A.; Crocker, K.; Myers, R.A.; Van Kessel, J.A.S. Salmonella Enterica Serovar Kentucky Recovered from Human Clinical Cases in Maryland, USA (2011–2015). Zoonoses Public Health 2019, 66, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, A.K.; Kue, S.; Norris, C.G.; Shariat, N.W. Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization of Salmonella Enterica Serovar Kentucky. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 001089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, H.; Hsu, C.-H.; Chen, J.C.; Han, J.; Foley, S.L.; Folster, J.P.; Francois Watkins, L.K.; Reynolds, J.; Tillman, G.E.; Nyirabahizi, E.; et al. Genomic Diversity, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Virulence Gene Profiles of Salmonella Serovar Kentucky Isolated from Humans, Food, and Animal Ceca Content Sources in the United States. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2022, 19, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggel, M.; Horlbog, J.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M.; Chattaway, M.A.; Stephan, R. Epidemiological Links and Antimicrobial Resistance of Clinical Salmonella Enterica ST198 Isolates: A Nationwide Microbial Population Genomic Study in Switzerland. Microb. Genom. 2022, 8, 000877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hello, S.L.; Harrois, D.; Bouchrif, B.; Sontag, L.; Elhani, D.; Guibert, V.; Zerouali, K.; Weill, F.-X. Highly Drug-Resistant Salmonella Enterica Serotype Kentucky ST198-X1: A Microbiological Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashe, T.; Thilliez, G.; Chaibva, B.V.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Bawn, M.; Nyanzunda, M.; Robertson, V.; Tarupiwa, A.; Al-Khanaq, H.; Baker, D.; et al. Highly Drug Resistant Clone of Salmonella Kentucky ST198 in Clinical Infections and Poultry in Zimbabwe. Npj Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowey, R.; Kim, S.W.; Prendergast, D.; Madigan, G.; Van Kessel, J.A.S.; Haley, B.J. Genomic Diversity and Resistome Profiles of Salmonella Enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Kentucky Isolated from Food and Animal Sources in Ireland. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltys, R.C.; Sakomoto, C.K.; Oltean, H.N.; Guard, J.; Haley, B.J.; Shah, D.H. High-Resolution Comparative Genomics of Salmonella Kentucky Aids Source Tracing and Detection of ST198 and ST152 Lineage-Specific Mutations. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 695368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, B.J.; Kim, S.W.; Pettengill, J.; Luo, Y.; Karns, J.S.; Kessel, J.A.S.V. Genomic and Evolutionary Analysis of Two Salmonella Enterica Serovar Kentucky Sequence Types Isolated from Bovine and Poultry Sources in North America. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, H.; Jiao, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Q. Poultry Production as the Main Reservoir of Ciprofloxacin- and Tigecycline-Resistant Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase (ESBL)-Producing Salmonella Enterica Serovar Kentucky ST198.2-2 Causing Human Infections in China. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e00944-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Song, J.; Zeng, X.; Chen, D.; Chen, R.; Qiu, C.; Zhou, K. National Prevalence of Salmonella Enterica Serotype Kentucky ST198 with High-Level Resistance to Ciprofloxacin and Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporins in China, 2013 to 2017. mSystems 2021, 6, e00935-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, X.; Fernández, J.; Bances, M.; Lumbreras, P.; Alkorta, M.; Hernáez, S.; Prieto, E.; de la Iglesia, P.; de Toro, M.; Rodicio, M.R.; et al. Genomic Analysis of Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Salmonella Enterica Serovar Kentucky ST198 From Spanish Hospitals. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 720449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołkowicz, T.; Zacharczuk, K.; Gierczyński, R.; Nowakowska, M.; Piekarska, K. Antimicrobial Resistance and Whole-Genome Characterisation of High-Level Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Salmonella Enterica Serovar Kentucky ST 198 Strains Isolated from Human in Poland. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.H.; Paul, N.C.; Guard, J. Complete Genome Sequence of a Ciprofloxacin-Resistant Salmonella Enterica Subsp. Enterica Serovar Kentucky Sequence Type 198 Strain, PU131, Isolated from a Human Patient in Washington State. Genome Announc. 2018, 6, e00125-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, K.J.; Siler, J.D.; Goodman, L.B.; Childs-Sanford, S.E. Ciprofloxacin-Resistant ST198 Salmonella Kentucky in a Hospitalized American Black Bear (Ursus americanus), with Evidence of Subsequent Nosocomial Transmission. Zoonoses Public Health 2023, 70, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoro, C.K.; Barquist, L.; Connor, T.R.; Harris, S.R.; Clare, S.; Stevens, M.P.; Arends, M.J.; Hale, C.; Kane, L.; Pickard, D.J.; et al. Signatures of Adaptation in Human Invasive Salmonella Typhimurium ST313 Populations from Sub-Saharan Africa. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Fujarte, I.; Calva, E.; García-Domínguez, J.; Ortiz-Jiménez, S.; Puente, J.L. Population Structure and Ongoing Microevolution of the Emerging Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Typhimurium ST213. Npj Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, J.R.; Kingsley, R.A. Evolution of Salmonella within Hosts. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burin, R.; Shah, D.H. Phenelzine and Amoxapine Inhibit Tyramine and D-Glucuronic Acid Catabolism in Clinically Significant Salmonella in A Serotype-Independent Manner. Pathogens 2021, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiok, K.L.; Addwebi, T.; Guard, J.; Shah, D.H. Dimethyl Adenosine Transferase (KsgA) Deficiency in Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis Confers Susceptibility to High Osmolarity and Virulence Attenuation in Chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 7857–7866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, J.R.; Paul, N.C.; Burin, R.; Guard, J.; Shah, D.H. Genomic Organization and Role of SPI-13 in Nutritional Fitness of Salmonella. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2018, 308, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guard-Bouldin, J.; Morales, C.A.; Frye, J.G.; Gast, R.K.; Musgrove, M. Detection of Salmonella Enterica Subpopulations by Phenotype Microarray Antibiotic Resistance Patterns. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7753–7756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R Package, version 1.0.12. 2019. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Dereeper, A.; Summo, M.; Meyer, D.F. PanExplorer: A Web-Based Tool for Exploratory Analysis and Visualization of Bacterial Pan-Genomes. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 4412–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröger, C.; Rothhardt, J.E.; Brokatzky, D.; Felsl, A.; Kary, S.C.; Heermann, R.; Fuchs, T.M. The Small RNA RssR Regulates Myo-Inositol Degradation by Salmonella Enterica. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Fuchs, T.M. Metabolism in the Niche: A Large-Scale Genome-Based Survey Reveals Inositol Utilization To Be Widespread among Soil, Commensal, and Pathogenic Bacteria. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02013-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medema, M.H.; Takano, E.; Breitling, R. Detecting Sequence Homology at the Gene Cluster Level with MultiGeneBlast. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, R.D.; Assaf, R.; Brettin, T.; Conrad, N.; Cucinell, C.; Davis, J.J.; Dempsey, D.M.; Dickerman, A.; Dietrich, E.M.; Kenyon, R.W.; et al. Introducing the Bacterial and Viral Bioinformatics Resource Center (BV-BRC): A Resource Combining PATRIC, IRD and ViPR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D678–D689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baramee, S.; Siriatcharanon, A.-K.; Waeonukul, R.; Pason, P.; Tachaapaikoon, C.; Ratanakhanokchai, K. A Novel β-Galactosidase from Anaerobic Thermophilic Caldicellulosiruptor Saccharolyticus DSM 8903 with High Potential for Lactulose Production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2025, 105, 6781–6789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Panesar, P.S.; Panwar, D.; Singla, G. Lactulose. In Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 338–360. ISBN 978-1-119-70216-0. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, B.; Li, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Gu, Z.; Chen, Y.Q.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. In Vitro Fermentation of Lactulose by Human Gut Bacteria. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 10970–10977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahota, S.S.; Bramley, P.M.; Menzies, I.S. The Fermentation of Lactulose by Colonic Bacteria. Microbiology 1982, 128, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vičič, V.; Pandel Mikuš, R.; Ferjančič, B. Review of History and Mechanisms of Action of Lactulose (4-O-β-D-Galactopyranosyl-β-D-Fructofuranose): Present and Future Applications in Food. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 61, 2036–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aung, K.T.; Khor, W.C.; Ong, K.H.; Tan, W.L.; Wong, Z.N.; Oh, J.Q.; Wong, W.K.; Tan, B.Z.Y.; Maiwald, M.; Tee, N.W.S.; et al. Characterisation of Salmonella Enteritidis ST11 and ST1925 Associated with Human Intestinal and Extra-Intestinal Infections in Singapore. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulford, C.V.; Perez-Sepulveda, B.M.; Canals, R.; Bevington, J.A.; Bengtsson, R.J.; Wenner, N.; Rodwell, E.V.; Kumwenda, B.; Zhu, X.; Bennett, R.J.; et al. Stepwise Evolution of Salmonella Typhimurium ST313 Causing Bloodstream Infection in Africa. Nat. Microbiol. 2021, 6, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boas Lichty, K.E.; Loughran, R.M.; Ushijima, B.; Richards, G.P.; Boyd, E.F. Osmotic Stress Response of the Coral and Oyster Pathogen Vibrio Coralliilyticus: Acquisition of Catabolism Gene Clusters for the Compatible Solute and Signaling Molecule Myo-Inositol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e00920-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manske, C.; Schell, U.; Hilbi, H. Metabolism of Myo-Inositol by Legionella Pneumophila Promotes Infection of Amoebae and Macrophages. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 5000–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsl, A.; Brokatzky, D.; Kröger, C.; Heermann, R.; Fuchs, T.M. Hierarchic Regulation of a Metabolic Pathway: H-NS, CRP, and SsrB Control Myo-Inositol Utilization by Salmonella Enterica. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 12, e02724-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothhardt, J.E.; Kröger, C.; Broadley, S.P.; Fuchs, T.M. The Orphan Regulator ReiD of Salmonella Enterica Is Essential for Myo-Inositol Utilization. Mol. Microbiol. 2014, 94, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröger, C.; Stolz, J.; Fuchs, T.M. Myo-Inositol Transport by Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium. Microbiology 2010, 156, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhetri, D.R. Myo-Inositol and Its Derivatives: Their Emerging Role in the Treatment of Human Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croze, M.L.; Soulage, C.O. Potential Role and Therapeutic Interests of Myo-Inositol in Metabolic Diseases. Biochimie 2013, 95, 1811–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.G.; Corrado, F.; Caruso, S.; Di Benedetto, A.; Giunta, L.; Cianci, A.; D’Anna, R. Myo-Inositol Supplementation to Prevent Gestational Diabetes in Overweight Non-Obese Women: Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis, Metabolic Aspects, Obstetric and Neonatal Outcomes—A Randomized and Open-Label, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 670–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Phytates, 1st ed.; Reddy, N.R., Sathe, S.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlemmer, U.; Frølich, W.; Prieto, R.M.; Grases, F. Phytate in Foods and Significance for Humans: Food Sources, Intake, Processing, Bioavailability, Protective Role and Analysis. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, S330–S375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.; McWilliams, A.; LeRiche, J.; MacAulay, C.; Wattenberg, L.; Szabo, E. A Phase I Study of Myo-Inositol for Lung Cancer Chemoprevention. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2006, 15, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regidor, P.-A.; Schindler, A.E. Myoinositol as a Safe and Alternative Approach in the Treatment of Infertile PCOS Women: A German Observational Study. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 2016, 9537632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, F.A.; Wilson, M.P.; Wallis, T.S.; Galyov, E.E.; Majerus, P.W. SopB, a Protein Required for Virulence of Salmonella Dublin, Is an Inositol Phosphate Phosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14057–14059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Chen, L.M.; Hernandez, L.; Shears, S.B.; Galán, J.E. A Salmonella Inositol Polyphosphatase Acts in Conjunction with Other Bacterial Effectors to Promote Host Cell Actin Cytoskeleton Rearrangements and Bacterial Internalization. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlemont, R.; Martiny, A.C. Glycoside Hydrolases across Environmental Microbial Communities. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1005300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mouali, Y.; Gaviria-Cantin, T.; Sánchez-Romero, M.A.; Gibert, M.; Westermann, A.J.; Vogel, J.; Balsalobre, C. CRP-cAMP Mediates Silencing of Salmonella Virulence at the Post-Transcriptional Level. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.-C.; Garner, C.D.; Slauch, J.M.; Dwyer, Z.W.; Lawhon, S.D.; Frye, J.G.; McClelland, M.; Ahmer, B.M.M.; Altier, C. The Intestinal Fatty Acid Propionate Inhibits Salmonella Invasion through the Post-Translational Control of HilD. Mol. Microbiol. 2013, 87, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, V.; Golaconda Ramulu, H.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The Carbohydrate-Active Enzymes Database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D490–D495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakan, T.; Tuohy, K.M.; Janssen-van Solingen, G. Low-Dose Lactulose as a Prebiotic for Improved Gut Health and Enhanced Mineral Absorption. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 672925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, A.L.; Mahmud, N.; Chaudhry, S.; Cao, J.Y.; Branigan, G.P.; Lee, J.; Theiller, E.; Roggiani, M.; Friedman, E.S.; Herman, L.; et al. Carbohydrate Consumption Drives Adaptive Mutations in Escherichia Coli Associated with Increased Risk for Systemic Infection. BioRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovee-Oudenhoven, I.M.J.; ten Bruggencate, S.J.M.; Lettink-Wissink, M.L.G.; Meer, R. van der Dietary Fructo-Oligosaccharides and Lactulose Inhibit Intestinal Colonisation but Stimulate Translocation of Salmonella in Rats. Gut 2003, 52, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotzka, S.Y.; Kreuzer, M.; Maier, L.; Zünd, M.; Schlumberger, M.; Nguyen, B.; Fox, M.; Pohl, D.; Heinrich, H.; Rogler, G.; et al. Microbiota Stability in Healthy Individuals after Single-Dose Lactulose Challenge—A Randomized Controlled Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, A.; Hara, H.; Kataoka, M.; Mitsuoka, T. Effect of Lactulose on the Composition and Metabolic Activity of the Human Faecal Flora. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 1992, 5, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuohy, K.M.; Ziemer, C.J.; Klinder, A.; Knöbel, Y.; Pool-Zobel, B.L.; Gibson, G.R. A Human Volunteer Study to Determine the Prebiotic Effects of Lactulose Powder on Human Colonic Microbiota. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2002, 14, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi Gheisar, M.; Nyachoti, C.M.; Hancock, J.D.; Kim, I.H. Effects of Lactulose on Growth, Carcass Characteristics, Faecal Microbiota, and Blood Constituents in Broilers. Veterinární Medicína 2016, 61, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Peláez, S.; Costabile, A.; Hoyles, L.; Rastall, R.A.; Gibson, G.R.; La Ragione, R.M.; Woodward, M.J.; Mateu, E.; Martín-Orúe, S.M. Evaluation of the Inclusion of a Mixture of Organic Acids or Lactulose into the Feed of Pigs Experimentally Challenged with Salmonella Typhimurium. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Serovar | ST Type | Strain ID | Source | Resistance | Isolation Year | Travel History | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S. Kentucky | ST198 | PU61 | Human | FluR | 2004 | Egypt, the Middle East, India, Tanzania, Ethiopia, Ivory Coast, or Morocco | Soltys et al., 2021 [9] |
| S. Kentucky | ST198 | PU128 | Human | FluR | 2013 | ||
| S. Kentucky | ST198 | PU131 | Human | FluR | 2013 | ||
| S. Kentucky | ST152 | P55 | Poultry | FluS | 2012 | Not available | |
| S. Kentucky | ST152 | P72 | Poultry | FluS | 2012 | Not available | |
| S. Kentucky | ST152 | PU116 | Human | FluS | 2012 | No travel outside North America | |
| S. Kentucky | ST152 | PU363 | Poultry | FluS | 2005 | Not available | |
| S. Typhimurium | Unknown | 21611 | Unknown | Not tested | Unknown | Not available | Burin and Shah, 2021 [20] |
| S. Hadar | Unknown | 27032 | Human | Not tested | 2014 | Not available | |
| S. Enteritidis | Unknown | MD15 | Human | Not tested | 2010 | Not available | |
| S. Montevideo | Unknown | DHS-R6 | Unknown | Not tested | Unknown | Not available | |
| S. Schwarzengrund | Unknown | 26682 | Human | Not tested | 2014 | Not available |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, J.; Soltys, R.C.; Shringi, S.; Guard, J.; Haley, B.J.; Shah, D.H. Comparative Genomics and Functional Profiling Reveal Lineage-Specific Metabolic Adaptations in Globally Emerging Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Salmonella Kentucky ST198. Genes 2025, 16, 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091051
Ahmed J, Soltys RC, Shringi S, Guard J, Haley BJ, Shah DH. Comparative Genomics and Functional Profiling Reveal Lineage-Specific Metabolic Adaptations in Globally Emerging Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Salmonella Kentucky ST198. Genes. 2025; 16(9):1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091051
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Juned, Rachel C. Soltys, Smriti Shringi, Jean Guard, Bradd J. Haley, and Devendra H. Shah. 2025. "Comparative Genomics and Functional Profiling Reveal Lineage-Specific Metabolic Adaptations in Globally Emerging Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Salmonella Kentucky ST198" Genes 16, no. 9: 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091051
APA StyleAhmed, J., Soltys, R. C., Shringi, S., Guard, J., Haley, B. J., & Shah, D. H. (2025). Comparative Genomics and Functional Profiling Reveal Lineage-Specific Metabolic Adaptations in Globally Emerging Fluoroquinolone-Resistant Salmonella Kentucky ST198. Genes, 16(9), 1051. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091051







