Association Study of SPARCL1 Gene Polymorphisms in Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Estimation of Biochemical Factors Concentration
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Ischemic Stroke Patients and Control Groups
3.2. Genotype Frequencies of Four SPARCL1 Polymorphisms in Ischemic Stroke Patients and Controls
3.3. Genotype Frequencies of Four SPARCL1 Polymorphisms in Ischemic Stroke Subtypes and Controls
3.4. Analysis of SPARCL1 Haplotypes in Ischemic Stroke Patients and Controls
3.5. Combined Genotype Analysis of SPARCL1 Polymorphisms in Ischemic Stroke Patients and Controls
3.6. Comparison of Clinical Variables Stratified by SPARCL1 Polymorphism Status in Ischemic Stroke Patients and Controls
3.7. Stratified Analysis of SPARCL1 Genotype Frequencies by Clinical Parameters
3.8. Interaction Analysis Between SPARCL1 Polymorphisms and Clinical Factors Affecting Ischemic Stroke Prevalence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pappachan, J.; Kirkham, F.J. Cerebrovascular disease and stroke. Arch. Dis. Child. 2008, 93, 890–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The World Health Report 2002: Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Chugh, C. Acute ischemic stroke: Management approach. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 23 (Suppl. S2), S140–S146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GBD 2019 Stroke Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 795–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feske, S.K. Ischemic stroke. Am. J. Med. 2021, 134, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea National Statistical Office. Changes in Leading Causes of Death in Korea, 1999–2009; Korea National Statistical Office: Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Arboix, A. Cardiovascular risk factors for acute stroke: Risk profiles in the different subtypes of ischemic stroke. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 418–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubow, J.; Fink, M.E. Impact of hypertension on stroke. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2011, 13, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Xavier, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Chin, S.L.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Rangarajan, S.; Islam, S.; Pais, P.; McQueen, M.J.; et al. Risk factors for ischaemic and intracerebral haemorrhagic stroke in 22 countries (the INTERSTROKE study): A case-control study. Lancet 2010, 376, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloubani, A.; Nimer, R.; Samara, R. Relationship between hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease and stroke: A systematic review. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2021, 17, e051121189015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.H.; Lew, J.; Borschmann, K.; Thijs, V.; Ekinci, E.I. Prevalence of diabetes and its effects on stroke outcomes: A meta-analysis and literature review. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao Kondapally Seshasai, S.; Kaptoge, S.; Thompson, A.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Gao, P.; Sarwar, N.; Whincup, P.H.; Mukamal, K.J.; Gillum, R.F.; Holme, I.; et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.S.; Cole, J.W. Smoking and stroke: The more you smoke the more you stroke. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2010, 8, 917–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marklund, N.; Bellander, B.M.; Godbolt, A.K.; Levin, H.; McCrory, P.; Thelin, E.P. Treatments and rehabilitation in the acute and chronic state of traumatic brain injury. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 285, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Jung, H.G.; Kim, A.; Shim, H.S.; Hyeon, S.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Han, J.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, J.; Ryu, H.; et al. Hevin–calcyon interaction promotes synaptic reorganization after brain injury. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2571–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukdereli, H.; Allen, N.J.; Lee, A.T.; Feng, A.; Ozlu, M.I.; Conatser, L.M.; Chakraborty, C.; Workman, G.; Weaver, M.; Sage, E.H.; et al. Control of excitatory CNS synaptogenesis by astrocyte-secreted proteins Hevin and SPARC. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E440–E449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Stogsdill, J.A.; Pulimood, N.S.; Dingsdale, H.; Kim, Y.H.; Pilaz, L.J.; Kim, I.H.; Manhaes, A.C.; Rodrigues, W.S., Jr.; Pamukcu, A.; et al. Astrocytes assemble thalamocortical synapses by bridging NRX1α and NL1 via Hevin. Cell 2016, 164, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, X.; Yang, A.; Fu, W.; Yin, F.; Zeng, X. Associations of tumor suppressor SPARCL1 with cancer progression and prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the human tissue-specific expression by genome-wide integration of transcriptomics and antibody-based proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingler, A.; Regensburger, D.; Tenkerian, C.; Britzen-Laurent, N.; Hartmann, A.; Stürzl, M.; Naschberger, E. Species-, organ- and cell-type-dependent expression of SPARCL1 in human and mouse tissues. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0233422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneiderova, M.; Naccarati, A.; Pardini, B.; Rosa, F.; Gaetano, C.D.; Jiraskova, K.; Opattova, A.; Levy, M.; Veskrna, K.; Veskrnova, V.; et al. MicroRNA-binding site polymorphisms in genes involved in colorectal cancer etiopathogenesis and their impact on disease prognosis. Mutagenesis 2017, 32, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.O.; Park, H.S.; Ko, E.J.; Sung, J.H.; Kim, J.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, O.J.; Kim, N.K. The 3’-UTR polymorphisms in the thymidylate synthase (TS) gene associated with the risk of ischemic stroke and silent brain infarction. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.O.; Ryu, C.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Ko, E.J.; Ha, Y.H.; Sung, J.H.; Hwang, T.S.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, N.K. Association of thymidylate synthase (TS) gene polymorphisms with incidence and prognosis of coronary artery disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, C.S.; Bae, J.; Kim, I.J.; Kim, J.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, O.J.; Kim, N.K. MPG and NPRL3 polymorphisms are associated with ischemic stroke susceptibility and post-stroke mortality. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddighi, S.; Varma, V.R.; An, Y.; Varma, S.; Beason-Held, L.L.; Tanaka, T.; Kitner-Triolo, M.H.; Kraut, M.A.; Davatzikos, C.; Thambisetty, M. SPARCL1 Accelerates Symptom Onset in Alzheimer’s Disease and Influences Brain Structure and Function During Aging. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 61, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalabrini, D.; Fenoglio, C.; Scarpini, E.; De Riz, M.; Comi, C.; Venturelli, E.; Cortini, F.; Piola, M.; Villa, C.; Naldi, P.; et al. Candidate gene analysis of SPARCL1 gene in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 425, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Xu, J.; Cai, W.; Huang, Y.; Bai, R.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Y.; et al. SPARCL1 exhibits different expressions in left- and right-sided colon cancer and is downregulated via DNA methylation. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 1269–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, I.; Kayed, H.; Keleg, S.; Giese, T.; Sage, E.H.; Schirmacher, P.; Friess, H.; Kleeff, J. Tumor-suppressor function of SPARC-like protein 1/Hevin in pancreatic cancer. Neoplasia 2007, 9, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xu, J.; Luo, H.; Luo, X.; Singh, S.K.; Ramirez, J.J.; James, M.L.; Mathew, J.P.; Berger, M.; Eroglu, C.; et al. Hevin/SPARCL1 drives pathological pain through spinal cord astrocyte and NMDA receptor signaling. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e161028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, H.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Ko, E.J.; Kim, Y.R.; Cho, H.Y.; Lee, W.S.; Ahn, E.H.; Kim, N.K. Association Study between Mucin 4 (MUC4) Polymorphisms and Idiopathic Recurrent Pregnancy Loss in a Korean Population. Genes 2022, 13, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

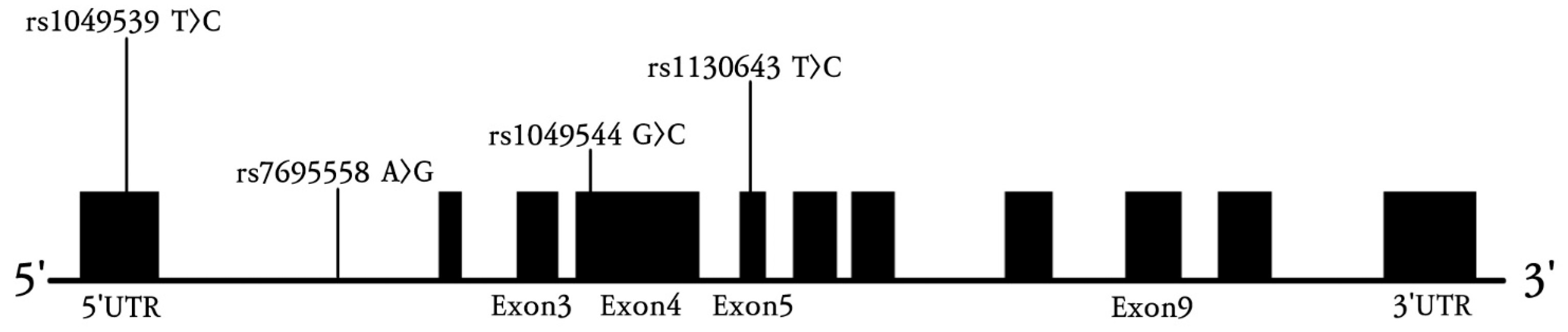
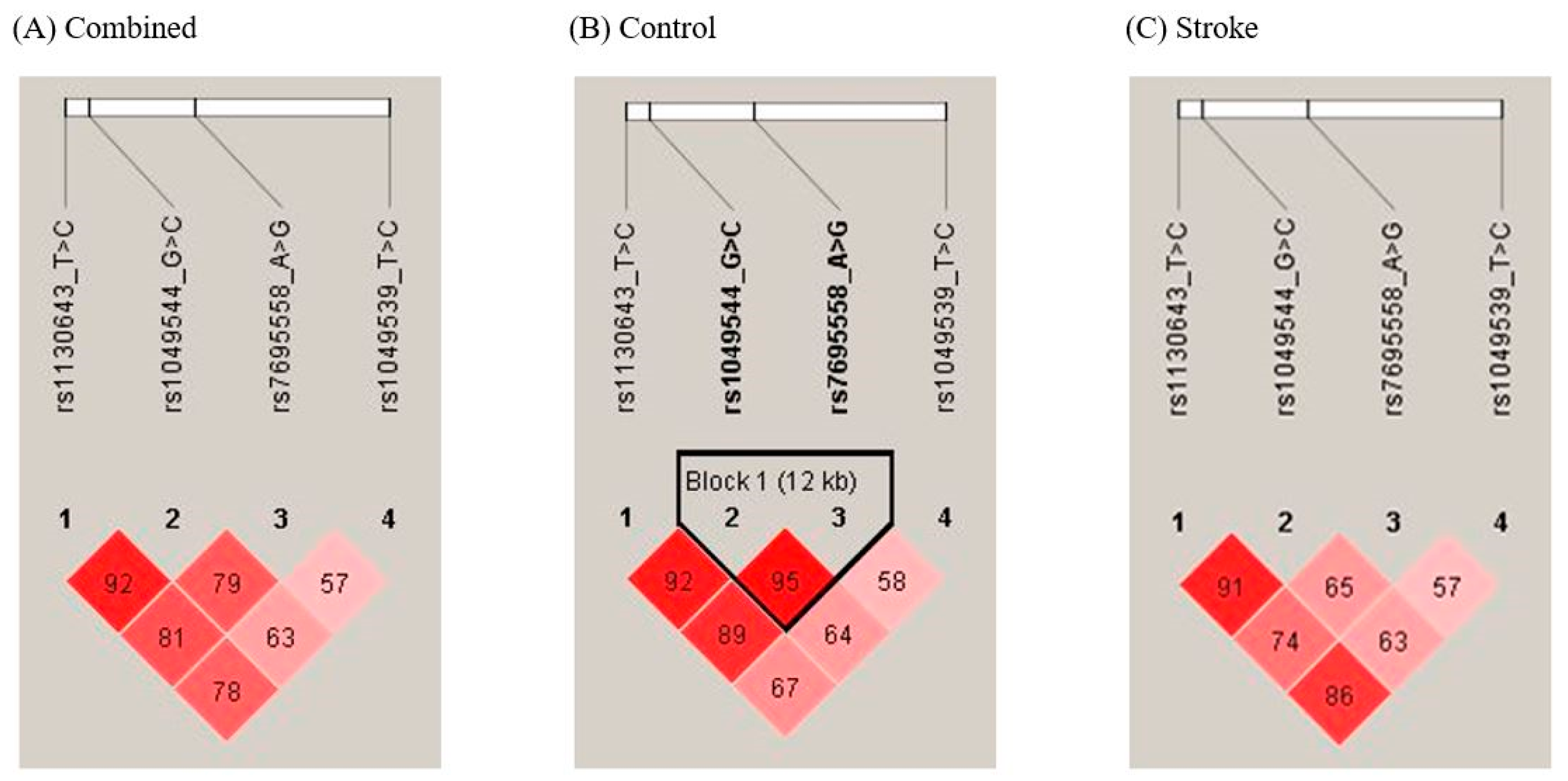
| Characteristic | Controls (n = 387) | Stroke Patients (n = 509) | p a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male (%) | 168 (43.41) | 232 (45.58) | 0.734 |
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 62.81 ± 10.69 | 64.00 ± 11.13 | 0.110 |
| Smoking (%) | 129 (33.33) | 203 (39.88) | 0.193 |
| Hypertension (%) | 162 (41.86) | 327 (64.24) | 0.0003 |
| Diabetes mellitus (%) | 55 (14.21) | 141 (27.70) | 0.0001 |
| Hyperlipidemia (%) | 88 (22.74) | 150 (29.47) | 0.098 |
| BMI (kg/m2, mean ± SD) | 24.25 ± 3.21 | 24.21 ± 3.82 | 0.877 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL, mean ± SD) | 46.48 ± 13.86 | 44.80 ± 15.65 | 0.222 |
| Homocysteine (μmol/L, mean ± SD) | 10.05 ± 4.09 | 11.21 ± 6.60 | 0.003 |
| Folate (nmol/L, mean ± SD) | 8.93 ± 8.11 | 6.83 ± 4.94 | <0.0001 |
| Vitamin B12 (pg/mL, mean ± SD) | 687.18 ± 277.40 | 690.66 ± 322.64 | 0.867 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL, mean ± SD) | 193.04 ± 37.78 | 189.89 ± 40.91 | 0.244 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL, mean ±SD) | 145.78 ± 87.56 | 151.09 ± 111.27 | 0.445 |
| PLT (103/μL, mean ± SD) | 244.12 ± 65.63 | 244.76 ± 87.56 | 0.905 |
| PT (s, mean ± SD) | 11.78 ± 0.78 | 11.93 ± 3.31 | 0.469 |
| aPTT (s, mean ± SD) | 32.32 ± 9.09 | 30.56 ± 4.44 | 0.0003 |
| Fibrinogen (mg/dL, mean ± SD) | 396.92 ± 121.97 | 427.92 ± 130.48 | 0.014 |
| Antithrombin (%, mean ± SD) | 94.48 ± 44.58 | 92.57 ± 16.77 | 0.446 |
| BUN (mg/dL, mean ± SD) | 16.02 ± 5.01 | 16.19 ± 6.25 | 0.667 |
| Uric acid (mg/dL, mean ± SD) | 4.72 ± 1.46 | 4.64 ± 1.53 | 0.466 |
| Genotypes | Controls (n = 387) | Stroke Patients (n = 509) | COR (95% CI) | p | FDR-P | AOR (95% CI) a | p | FDR-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C | ||||||||
| TT | 194 (50.13) | 247 (48.53) | 1.000 (reference) | 1.000 (reference) | ||||
| TC | 162 (41.86) | 227 (44.60) | 1.100 (0.835–1.550) | 0.496 | 0.661 | 1.069 (0.801–1.425) | 0.652 | 0.652 |
| CC | 31 (8.01) | 35 (6.88) | 0.887 (0.528–1.490) | 0.650 | 0.650 | 0.923 (0.535–1.593) | 0.774 | 0.774 |
| Dominant (TT vs. TC + CC) | 1.066 (0.819–1.390) | 0.635 | 0.635 | 1.045 (0.792–1.378) | 0.756 | 0.756 | ||
| Recessive (TT + TC vs. CC) | 0.848 (0.513–1.402) | 0.521 | 0.679 | 0.893 (0.526–1.515) | 0.675 | 0.819 | ||
| HWE P | 0.727 | 0.074 | ||||||
| SPARCL1 rs7695558 A>G | ||||||||
| AA | 289 (74.68) | 401 (78.78) | 1.000 (reference) | 1.000 (reference) | ||||
| AG | 88 (22.74) | 97 (19.06) | 0.794 (0.574–1.100) | 0.166 | 0.332 | 0.816 (0.579–1.149) | 0.244 | 0.489 |
| GG | 10 (2.58) | 11 (2.16) | 0.793 (0.332–1.892) | 0.601 | 0.601 | 0.874 (0.354–2.156) | 0.770 | 0.774 |
| Dominant (AA vs. AG + GG) | 0.794 (0.581–1.086) | 0.149 | 0.298 | 0.822 (0.592–1.141) | 0.240 | 0.343 | ||
| Recessive (AA + AG vs. GG) | 0.833 (0.350–1.981) | 0.679 | 0.679 | 0.900 (0.366–2.216) | 0.819 | 0.819 | ||
| HWE P | 0.297 | 0.082 | ||||||
| SPARCL1 rs1049544 G>C | ||||||||
| GG | 134 (34.63) | 193 (37.92) | 1.000 (reference) | 1.000 (reference) | ||||
| GC | 184 (47.55) | 254 (49.90) | 0.958 (0.717–1.282) | 0.775 | 0.775 | 0.922 (0.680–1.250) | 0.600 | 0.652 |
| CC | 69 (17.83) | 62 (12.18) | 0.624 (0.415–0.938) | 0.023 | 0.023 | 0.642 (0.418–0.986) | 0.043 | 0.171 |
| Dominant (GG vs. GC + CC) | 0.867 (0.658–1.142) | 0.311 | 0.415 | 0.846 (0.634–1.130) | 0.257 | 0.343 | ||
| Recessive (GG + GC vs. CC) | 0.639 (0.441–0.927) | 0.018 | 0.072 | 0.672 (0.455–0.993) | 0.046 | 0.184 | ||
| HWE P | 0.764 | 0.120 | ||||||
| SPARCL1 rs1130643 T>C | ||||||||
| TT | 296 (76.49) | 413 (81.14) | 1.000 (reference) | 1.000 (reference) | ||||
| TC | 83 (21.45) | 88 (17.29) | 0.760 (0.544–1.062) | 0.108 | 0.332 | 0.786 (0.553–1.116) | 0.178 | 0.489 |
| CC | 8 (2.07) | 8 (1.57) | 0.717 (0.266–1.931) | 0.510 | 0.510 | 0.790 (0.282–2.214) | 0.654 | 0.774 |
| Dominant (TT vs. TC + CC) | 0.756 (0.547–1.045) | 0.090 | 0.298 | 0.786 (0.560–1.103) | 0.163 | 0.343 | ||
| Recessive (TT + TC vs. CC) | 0.757 (0.281–2.034) | 0.580 | 0.679 | 0.834 (0.298–2.336) | 0.729 | 0.819 | ||
| HWE P | 0.447 | 0.194 |
| Genotypes | Controls (n = 387) | LAD (n = 184) | AOR (95% CI) a | p | FDR-P | SVD (n = 136) | AOR (95% CI) a | p | FDR-P | CE (n = 55) | AOR (95% CI) a | p | FDR-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C | |||||||||||||
| TT | 194 (50.13) | 84 (45.65) | 1.000 (reference) | 76 (55.88) | 1.000 (reference) | 20 (36.36) | 1.000 (reference) | ||||||
| TC | 162 (41.86) | 86 (46.74) | 1.153 (0.785–1.694) | 0.467 | 0.846 | 56 (41.18) | 0.889 (0.585–1.351) | 0.582 | 0.846 | 29 (52.73) | 1.849 (0.993–3.442) | 0.053 | 0.427 |
| CC | 31 (8.01) | 14 (7.61) | 1.097 (0.534–2.255) | 0.802 | 0.913 | 4 (2.94) | 0.355 (0.117–1.080) | 0.068 | 0.427 | 6 (10.91) | 2.449 (0.861–6.971) | 0.093 | 0.498 |
| Dominant (TT vs. TC + CC) | 1.146 (0.791–1.660) | 0.472 | 0.846 | 0.804 (0.534–1.209) | 0.295 | 0.846 | 1.883 (1.037–3.418) | 0.038 | 0.427 | ||||
| Recessive (TT + TC vs. CC) | 1.049 (0.523–2.105) | 0.893 | 0.953 | 0.368 (0.125–1.082) | 0.069 | 0.427 | 1.720 (0.665–4.452) | 0.264 | 0.846 | ||||
| SPARCL1 rs7695558 A>G | |||||||||||||
| AA | 289 (74.68) | 146 (79.35) | 1.000 (reference) | 101 (74.26) | 1.000 (reference) | 44 (80.00) | 1.000 (reference) | ||||||
| AG | 88 (22.74) | 36 (19.57) | 0.911 (0.575–1.443) | 0.690 | 0.913 | 30 (22.06) | 0.943 (0.574–1.551) | 0.818 | 0.913 | 9 (16.36) | 0.667 (0.309–1.441) | 0.303 | 0.846 |
| GG | 10 (2.58) | 2 (1.09) | 0.427 (0.087–2.091) | 0.293 | 0.846 | 5 (3.68) | 1.669 (0.534–5.217) | 0.379 | 0.846 | 2 (3.64) | 1.263 (0.255–6.255) | 0.775 | 0.913 |
| Dominant (AA vs. AG + GG) | 0.859 (0.550–1.343) | 0.505 | 0.846 | 1.012 (0.633–1.618) | 0.962 | 0.982 | 0.727 (0.356–1.486) | 0.382 | 0.846 | ||||
| Recessive (AA + AG vs. GG) | 0.431 (0.088–2.106) | 0.299 | 0.846 | 1.666 (0.535–5.191) | 0.379 | 0.846 | 1.386 (0.282–6.822) | 0.688 | 0.913 | ||||
| SPARCL1 rs1049544 G>C | |||||||||||||
| GG | 134 (34.63) | 70 (38.04) | 1.000 (reference) | 50 (36.76) | 1.000 (reference) | 18 (32.73) | 1.000 (reference) | ||||||
| GC | 185 (47.80) | 97 (52.72) | 0.928 (0.620–1.389) | 0.716 | 0.913 | 65 (47.79) | 0.995 (0.637–1.555) | 0.982 | 0.982 | 25 (45.45) | 1.016 (0.528–1.957) | 0.962 | 0.982 |
| CC | 68 (17.57) | 17 (9.24) | 0.486 (0.257–0.920) | 0.027 | 0.427 | 21 (15.44) | 0.800 (0.426–1.502) | 0.488 | 0.846 | 12 (21.82) | 1.323 (0.587–2.978) | 0.500 | 0.846 |
| Dominant (GG vs. GC + CC) | 0.834 (0.568–1.224) | 0.353 | 0.846 | 0.939 (0.614–1.437) | 0.773 | 0.913 | 1.101 (0.598–2.026) | 0.758 | 0.913 | ||||
| Recessive (GG + GC vs. CC) | 0.529 (0.294–0.953) | 0.034 | 0.427 | 0.848 (0.487–1.476) | 0.560 | 0.846 | 1.287 (0.636–2.604) | 0.483 | 0.846 | ||||
| SPARCL1 rs1130643 T>C | |||||||||||||
| TT | 296 (76.49) | 155 (84.24) | 1.000 (reference) | 102 (75.00) | 1.000 (reference) | 48 (87.27) | 1.000 (reference) | ||||||
| TC | 83 (21.45) | 27 (14.67) | 0.688 (0.418–1.133) | 0.142 | 0.620 | 32 (23.53) | 1.150 (0.708–1.869) | 0.572 | 0.846 | 5 (9.09) | 0.362 (0.138–0.949) | 0.039 | 0.427 |
| CC | 8 (2.07) | 2 (1.09) | 0.549 (0.106–2.850) | 0.475 | 0.846 | 2 (1.47) | 0.858 (0.170–4.335) | 0.853 | 0.930 | 2 (3.64) | 1.588 (0.307–8.220) | 0.582 | 0.846 |
| Dominant (TT vs. TC + CC) | 0.678 (0.418–1.098) | 0.114 | 0.548 | 1.127 (0.702–1.809) | 0.621 | 0.876 | 0.461 (0.198–1.069) | 0.071 | 0.427 | ||||
| Recessive (TT + TC vs. CC) | 0.597 (0.116–3.081) | 0.538 | 0.846 | 0.814 (0.160–4.134) | 0.804 | 0.913 | 1.918 (0.374–9.846) | 0.435 | 0.846 |
| Haplotype | Stroke Controls (2n = 774) | Stroke Patients (2n = 1018) | OR (95% CI) | p a | FDR-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C/rs7695558 A>G/rs1049544 G>C/rs1130643 T>C | |||||
| T-A-G-T | 402 (51.94) | 544 (53.44) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| T-A-C-C | 3 (0.39) | 18 (1.77) | 4.434 (1.297–15.160) | 0.012 | 0.056 |
| T-G-G-T | 0 (0) | 24 (2.36) | 36.220 (2.195–597.800) | <0.0001 | 0.001 |
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C/rs7695558 A>G/rs1049544 G>C | |||||
| T-A-G | 401 (51.81) | 550 (54.03) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| T-G-G | 2 (0.26) | 21 (2.06) | 7.655 (1.784–32.850) | 0.001 | 0.007 |
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C/rs7695558 A>G/rs1130643 T>C | |||||
| T-A-T | 454 (58.66) | 597 (58.64) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| T-A-C | 4 (0.52) | 24 (2.36) | 4.563 (1.572–13.250) | 0.002 | 0.014 |
| T-G-T | 6 (0.78) | 24 (2.36) | 3.042 (1.233–7.505) | 0.011 | 0.035 |
| SPARCL1 rs7695558 A>G/rs1049544 G>C/rs1130643 T>C | |||||
| A-G-T | 447 (57.75) | 606 (59.53) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| G-G-T | 1 (0.13) | 29 (2.85) | 21.390 (2.902–157.700) | <0.0001 | 0.001 |
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C/rs1049544 G>C | |||||
| T-G | 406 (52.45) | 571 (56.09) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| T-C | 144 (18.60) | 150 (14.73) | 0.741 (0.570–0.962) | 0.024 | 0.072 |
| SPARCL1 rs7695558 A>G/rs1049544 G>C | |||||
| A-G | 449 (58.01) | 614 (60.31) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| G-G | 3 (0.39) | 26 (2.55) | 6.338 (1.906–21.070) | 0.0004 | 0.001 |
| SPARCL1 rs1049544 G>C/rs1130643 T>C | |||||
| G-T | 448 (57.88) | 634 (62.28) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| C-C | 95 (12.27) | 98 (9.63) | 0.729 (0.536–0.991) | 0.043 | 0.129 |
| Genotype | Stroke Controls (n = 387) | Stroke Patients (n = 509) | AOR (95% CI) a | p | FDR-P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C/rs7695558 A>G/rs1049544 G>C | |||||
| TT/AA/GG | 106 (27.39) | 143 (28.09) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| TT/AG/CC | 8 (2.07) | 2 (0.39) | 0.117 (0.021–0.634) | 0.013 | 0.208 |
| TT/GG/CC | 9 (2.33) | 4 (0.79) | 0.276 (0.077–0.993) | 0.049 | 0.261 |
| TC/AG/CC | 19 (4.91) | 12 (2.36) | 0.425 (0.187–0.968) | 0.042 | 0.261 |
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C/rs7695558 A>G/rs1130643 T>C | |||||
| TT/AA/TT | 133 (34.37) | 168 (33.01) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| TT/AG/TT | 2 (0.52) | 11 (2.16) | 4.836 (1.009–23.173) | 0.049 | 0.366 |
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C/rs1049544 G>C/rs1130643 T>C | |||||
| TT/GG/TT | 105 (27.13) | 150 (29.47) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| TT/CC/TC | 10 (2.58) | 3 (0.59) | 0.149 (0.036–0.610) | 0.008 | 0.120 |
| SPARCL1 rs7695558 A>G/rs1049544 G>C/rs1130643 T>C | |||||
| AA/GG/TT | 131 (33.85) | 176 (34.58) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| AG/CC/TC | 25 (6.46) | 14 (2.75) | 0.348 (0.161–0.749) | 0.007 | 0.091 |
| SPARCL1 rs1049539 T>C/rs1049544 G>C | |||||
| TT/GG | 107 (27.65) | 152 (29.86) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| TT/CC | 19 (4.91) | 14 (2.75) | 0.455 (0.211–0.980) | 0.044 | 0.352 |
| SPARCL1 rs7695558 A>G/rs1049544 G>C | |||||
| AA/GG | 133 (34.37) | 179 (35.17) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| AG/GG | 1 (0.26) | 13 (2.55) | 10.995 (1.370–88.261) | 0.024 | 0.084 |
| AG/CC | 28 (7.24) | 15 (2.95) | 0.328 (0.158–0.683) | 0.003 | 0.021 |
| SPARCL1 rs1049544 G>C/rs1130643 T>C | |||||
| GG/TT | 131 (33.85) | 190 (37.33) | 1.000 (reference) | ||
| CC/TC | 28 (7.24) | 19 (3.73) | 0.421 (0.214–0.826) | 0.012 | 0.072 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwak, S.S.; Lee, K.O.; Ryu, C.S.; Ko, E.J.; Park, H.W.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, O.J.; Kim, N.K. Association Study of SPARCL1 Gene Polymorphisms in Ischemic Stroke. Genes 2025, 16, 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091007
Kwak SS, Lee KO, Ryu CS, Ko EJ, Park HW, Lee JH, Kim OJ, Kim NK. Association Study of SPARCL1 Gene Polymorphisms in Ischemic Stroke. Genes. 2025; 16(9):1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091007
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwak, Seong Shin, Ki Ook Lee, Chang Soo Ryu, Eun Ju Ko, Hyeon Woo Park, Jae Hyun Lee, Ok Joon Kim, and Nam Keun Kim. 2025. "Association Study of SPARCL1 Gene Polymorphisms in Ischemic Stroke" Genes 16, no. 9: 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091007
APA StyleKwak, S. S., Lee, K. O., Ryu, C. S., Ko, E. J., Park, H. W., Lee, J. H., Kim, O. J., & Kim, N. K. (2025). Association Study of SPARCL1 Gene Polymorphisms in Ischemic Stroke. Genes, 16(9), 1007. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16091007





