Cross-Population Analysis of Sjögren’s Syndrome Polygenic Risk Scores and Disease Prevalence: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Polygenic Risk Score Model
2.3. Population Genetic Data
- Access Ensembl genome browser (www.ensembl.org, EMBL-EBI, Cambridge, UK)
- For each variant, enter the rsID in the search box
- Navigate to ‘Population genetics’ tab
- Select ‘1000 Genomes Phase 3′
- Extract allele frequencies for CEU, TSI, FIN, GBR, and IBS populations.
2.4. Prevalence Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
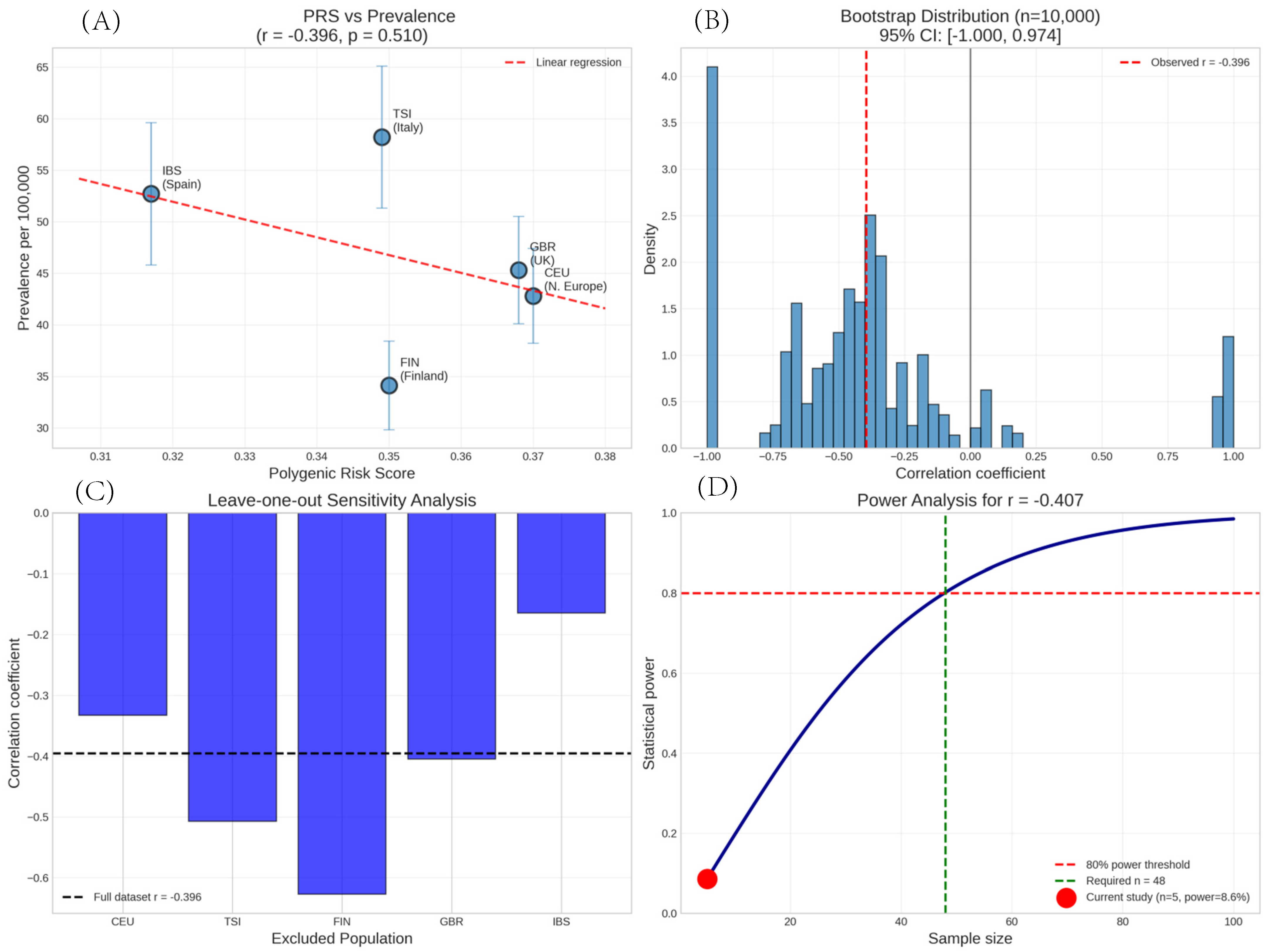
3. Results
3.1. Population Genetic Variation
3.2. Polygenic Risk Score Distribution
3.3. Prevalence Estimates
3.4. Correlation Analysis
3.5. Sensitivity and Robustness Analyses
- Impact of excluding individual populations on the correlation between PRS and prevalence
3.6. Variant Contribution Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Future Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brito-Zerón, P.; Acar-Denizli, N.; Ng, W.F.; Horvath, I.F.; Rasmussen, A.; Seror, R.; Li, X.; Baldini, C.; Gottenberg, J.E.; Danda, D.; et al. Epidemiological profile and north-south gradient driving baseline systemic involvement of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, M.; Ma, N.; Huang, F.; Zhong, R. Epidemiology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1983–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessard, C.J.; Li, H.; Adrianto, I.; Ice, J.A.; Rasmussen, A.; Grundahl, K.M.; Kelly, J.A.; Dozmorov, M.G.; Miceli-Richard, C.; Bowman, S.; et al. Variants at multiple loci implicated in both innate and adaptive immune responses are associated with Sjögren’s syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Sun, F.; Xu, J.; Wu, Z.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Du, Y.; Luan, H.; et al. A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies a susceptibility locus for primary Sjögren’s syndrome at 7q11.23. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1361–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Tapias, P.; Rojas-Villarraga, A.; Maier-Moore, S.; Anaya, J.M. HLA and Sjögren’s syndrome susceptibility. A meta-analysis of worldwide studies. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Sandor, C.; Stahl, E.A.; Freudenberg, J.; Lee, H.S.; Jia, X.; Alfredsson, L.; Padyukov, L.; Klareskog, L.; Worthington, J.; et al. Five amino acids in three HLA proteins explain most of the association between MHC and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet. 2012, 44, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.A.; Gil, L.; Jupp, S.; Ritchie, S.C.; Xu, Y.; Buniello, A.; McMahon, A.; Abraham, G.; Chapman, M.; Parkinson, H.; et al. The Polygenic Score Catalog as an open database for reproducibility and systematic evaluation. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; Kanai, M.; Kamatani, Y.; Okada, Y.; Neale, B.M.; Daly, M.J. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evseeva, I.; Nicodemus, K.K.; Bonilla, C.; Tonks, S.; Bodmer, W.F. Linkage disequilibrium and age of HLA region SNPs in relation to classic HLA gene alleles within Europe. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamanos, Y.; Tsifetaki, N.; Voulgari, P.V.; Venetsanopoulou, A.I.; Siozos, C.; Drosos, A.A. Epidemiology of primary Sjögren’s syndrome in north-west Greece, 1982–2003. Rheumatology 2006, 45, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurtle, E.; Grosjean, A.; Steenackers, M.; Strege, K.; Barcelos, G.; Goswami, P. Epidemiology of Sjögren’s: A Systematic Literature Review. Rheumatol Ther. 2024, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauppi, M.; Pukkala, E.; Isomäki, H. Elevated incidence of hematologic malignancies in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome compared with patients with rheumatoid arthritis (Finland). Cancer Causes Control. 1997, 8, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldini, C.; Pepe, P.; Quartuccio, L.; Priori, R.; Bartoloni, E.; Alunno, A.; Gattamelata, A.; Maset, M.; Modesti, M.; Tavoni, A.; et al. Primary Sjögren’s syndrome as a multi-organ disease: Impact of the serological profile on the clinical presentation of the disease in a large cohort of Italian patients. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narváez, J.; Sánchez-Fernández, S.Á.; Seoane-Mato, D.; Díaz-González, F.; Bustabad, S. Prevalence of Sjögren’s syndrome in the general adult population in Spain: Estimating the proportion of undiagnosed cases. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, S.J.; Ibrahim, G.H.; Holmes, G.; Hamburger, J.; Ainsworth, J.R. Estimating the prevalence among Caucasian women of primary Sjögren’s syndrome in two general practices in Birmingham, UK. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 33, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gøransson, L.G.; Haldorsen, K.; Brun, J.G.; Harboe, E.; Jonsson, M.V.; Skarstein, K.; Time, K.; Omdal, R. The point prevalence of clinically relevant primary Sjögren’s syndrome in two Norwegian counties. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 40, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costenbader, K.H.; Gay, S.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E.; Iaccarino, L.; Doria, A. Genes, epigenetic regulation and environmental factors: Which is the most relevant in developing autoimmune diseases? Autoimmun Rev. 2012, 11, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidney, J.; Steen, A.; Moore, C.; Ngo, S.; Chung, J.; Peters, B.; Sette, A. Five HLA-DP molecules frequently expressed in the worldwide human population share a common HLA supertypic binding specificity. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2492–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Li, Y.; Mariuzza, R.A. Structural basis for self-recognition by autoimmune T-cell receptors. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 250, 32–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, S.; Michel, C.; Schmidt-Glenewinkel, H.; Harder, N.; Rohr, K.; Wild, S.; Brors, B.; Kyewski, B. Overlapping gene coexpression patterns in human medullary thymic epithelial cells generate self-antigen diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3497–E3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, R.C.; Simons, H.Z.; Thompson, W.S.; Cutler, A.J.; Dopico, X.C.; Smyth, D.J.; Mashar, M.; Schuilenburg, H.; Walker, N.M.; Dunger, D.B.; et al. IL-21 production by CD4+ effector T cells and frequency of circulating follicular helper T cells are increased in type 1 diabetes patients. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, R.R.; Kyogoku, C.; Sigurdsson, S.; Vlasova, I.A.; Davies, L.R.; Baechler, E.C.; Plenge, R.M.; Koeuth, T.; Ortmann, W.A.; Hom, G.; et al. Three functional variants of IFN regulatory factor 5 (IRF5) define risk and protective haplotypes for human lupus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 6758–6763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, M.K.; Rönnblom, L. Type I interferons in host defence and inflammatory diseases. Lupus Sci. Med. 2019, 6, e000336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, D.R.; Ding, N.; Parnell, G.P.; Shahijanian, F.; Coulter, S.; Schibeci, S.D.; Atkins, A.R.; Stewart, G.J.; Evans, R.M.; Downes, M.; et al. Cistromic and genetic evidence that the vitamin D receptor mediates susceptibility to latitude-dependent autoimmune diseases. Genes Immun. 2016, 17, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashman, K.D.; Dowling, K.G.; Škrabáková, Z.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Valtueña, J.; De Henauw, S.; Moreno, L.; Damsgaard, C.T.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Mølgaard, C.; et al. Vitamin D deficiency in Europe: Pandemic? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1033–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, A.; Mofors, J.; Jonsson, R.; Kvarnström, M.; Eriksson, P.; Nordmark, B.; Wahren-Herlenius, M. Environmental factors in the pathogenesis of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 295, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.M.; Anderson, D.E.; Severson, C.A.; Baecher-Allan, C.; Healy, B.; Liu, D.V.; Wittrup, K.D.; De Jager, P.L.; Hafler, D.A. Soluble IL-2RA levels in multiple sclerosis subjects and the effect of soluble IL-2RA on immune responses. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravel, A.; Dubuc, I.; Wallaschek, N.; Gravel, C.; Marinier, A.; Kaufer, B.B.; Flamand, L. Inherited chromosomally integrated human herpesvirus 6 as a predisposing risk factor for the development of angina pectoris. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 8058–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, J.L.M.; Campo, J.A.D.; Coronado, O.G.; Gutiérrez, M.D.C.; Cordero, J.F.C.; Jurado, J.M.J. Adipose tissue and inflammation. In Adipose Tissue; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Toledo, E.; Wang, D.D.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Clish, C.B.; Razquin, C.; Zheng, Y.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hruby, A.; Corella, D.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; et al. Plasma lipidomic profiles and cardiovascular events in a randomized intervention trial with the Mediterranean diet. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F.; Pellegrini, N.; Vannini, L.; Jeffery, I.B.; La Storia, A.; Laghi, L.; Serrazanetti, D.I.; Di Cagno, R.; Ferrocino, I.; Lazzi, C.; et al. High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut 2016, 65, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, T.L.; Deutsch, A.J.; Han, B.; Hu, X.; Okada, Y.; Eyre, S.; Knapp, M.; Zhernakova, A.; Huizinga, T.W.; Abecasis, G.; et al. Widespread non-additive and interaction effects within HLA loci modulate the risk of autoimmune diseases. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieson, I.; Lazaridis, I.; Rohland, N.; Mallick, S.; Patterson, N.; Roodenberg, S.A.; Harney, E.; Stewardson, K.; Fernandes, D.; Novak, M.; et al. Genome-wide patterns of selection in 230 ancient Eurasians. Nature 2015, 528, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerminen, S.; Havulinna, A.S.; Hellenthal, G.; Martin, A.R.; Sarin, A.P.; Perola, M.; Palotie, A.; Salomaa, V.; Daly, M.J.; Ripatti, S.; et al. Fine-scale genetic structure in Finland. G3 2017, 7, 3459–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorito, G.; Di Gaetano, C.; Guarrera, S.; Rosa, F.; Feldman, M.W.; Piazza, A.; Matullo, G. The Italian genome reflects the history of Europe and the Mediterranean basin. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, M.; Perfetto, S.P.; Klitz, W.; Nelson, G.; Carrington, M. High-resolution patterns of meiotic recombination across the human major histocompatibility complex. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 759–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudillière, B.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; Bruggner, R.V.; Nicolau, M.; Finck, R.; Tingle, M.; Silva, J.; Ganio, E.A.; Yeh, C.G.; Maloney, W.J.; et al. Clinical recovery from surgery correlates with single-cell immune signatures. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 255ra131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hov, J.R.; Kosmoliaptsis, V.; Traherne, J.A.; Olsson, M.; Boberg, K.M.; Bergquist, A.; Schrumpf, E.; Bradley, J.A.; Taylor, C.J.; Lie, B.A.; et al. Electrostatic modifications of the human leukocyte antigen-DR P9 peptide-binding pocket and susceptibility to primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1967–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.L.; Flanagan, K.L. Sex differences in immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 626–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C.; Bonafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; De Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E.; De Benedictis, G. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 908, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slight-Webb, S.; Lu, R.; Ritterhouse, L.L.; Munroe, M.E.; Maecker, H.T.; Fathman, C.G.; Utz, P.J.; Merrill, J.T.; Guthridge, J.M.; James, J.A. Autoantibody-positive healthy individuals display unique immune profiles that may regulate autoimmunity. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazal, S.; Sahbatou, M.; Babron, M.C.; Génin, E.; Leutenegger, A.L. High level of inbreeding in final phase of 1000 Genomes Project. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundtoft, C.; Pucholt, P.; Martin, M.; Bianchi, M.; Lundström, E.; Eloranta, M.L.; Sandling, J.K.; Sjöwall, C.; Jönsen, A.; Gunnarsson, I.; et al. Complement C4 copy number variation is linked to SSA/Ro and SSB/La autoantibodies in systemic inflammatory autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022, 74, 1440–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekar, A.; Bialas, A.R.; de Rivera, H.; Davis, A.; Hammond, T.R.; Kamitaki, N.; Tooley, K.; Presumey, J.; Baum, M.; Van Doren, V.; et al. Schizophrenia risk from complex variation of complement component 4. Nature 2016, 530, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, R.D.; Ensor, J.; Snell, K.I.E.; Harrell, F.E.; Martin, G.P.; Reitsma, J.B.; Moons, K.G.M.; Collins, G.; van Smeden, M. Calculating the sample size required for developing a clinical prediction model. BMJ 2020, 368, m441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, M.C.; Tishkoff, S.A. African genetic diversity: Implications for human demographic history, modern human origins, and complex disease mapping. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2008, 9, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Z. Polygenic risk scores for autoimmune diseases: Challenges and opportunities for clinical implementation. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 281–294. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.J.; Zhang, F.; Richards, J.B.; Kestenbaum, B.; van Meurs, J.B.; Berry, D.; Kiel, D.P.; Streeten, E.A.; Ohlsson, C.; Koller, D.L.; et al. Common genetic determinants of vitamin D insufficiency: A genome-wide association study. Lancet 2010, 376, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Xie, X.; Gao, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, S.; Wang, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, R.; et al. Genetic predisposition to primary Sjögren’s syndrome: A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies novel susceptibility loci. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023, 76, 412–425. [Google Scholar]
| Population | RS2394517 (T) | RS3131044 (C) | RS1264319 (T) † | RS3131787 (C) † | RS185819 (C) | RS2004640 (T) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEU | 0.586 | 0.141 | 0.192 | 0.182 | 0.53 | 0.47 |
| TSI | 0.575 | 0.07 | 0.159 | 0.178 | 0.603 | 0.397 |
| FIN | 0.682 | 0.071 | 0.121 | 0.121 | 0.525 | 0.475 |
| GBR | 0.577 | 0.093 | 0.22 | 0.192 | 0.495 | 0.505 |
| IBS | 0.495 | 0.093 | 0.126 | 0.107 | 0.589 | 0.411 |
| Population | Country | PGS Score | Prevalence/100 k | 95% CI | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIN | Finland | 0.35 | 34.1 | 29.8–38.4 | Kauppi et al., 1997 [13]. |
| TSI | Italy | 0.349 | 58.2 | 51.3–65.1 | Baldini et al., 2014 [14] |
| IBS | Spain | 0.317 | 52.7 | 45.8–59.6 | Narváez J et al., 2020 [15] |
| GBR | UK | 0.368 | 45.3 | 40.1–50.5 | Bowman et al., 2004 [16] |
| CEU | N. Europe | 0.37 | 42.8 | 38.2–47.4 | Gøransson et al., 2011 [17] |
| Excluded Population | Remaining Populations | Correlation (r) | p-Value | Direction Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| None | All 5 | −0.407 | 0.496 | Reference |
| CEU | TSI, FIN, GBR, IBS | −0.52 | 0.48 | No |
| TSI | CEU, FIN, GBR, IBS | 0.12 | 0.88 | Yes (reversed) |
| FIN | CEU, TSI, GBR, IBS | −0.81 | 0.19 | No (stronger) |
| GBR | CEU, TSI, FIN, IBS | −0.45 | 0.55 | No |
| IBS | CEU, TSI, FIN, GBR | −0.68 | 0.32 | No |
| Analysis Method | Result | p-Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pearson correlation | r = −0.407 | 0.496 | −0.89 to 0.42 |
| Bootstrap (BCa, n = 10,000) | r = −0.407 | -- | −1.000, 0.974 |
| Spearman correlation | ρ = −0.30 | 0.624 | -- |
| Permutation test (n = 10,000) | -- | 0.516 | -- |
| Power analysis (post-hoc) | Power = 8.6% | -- | n = 48 for 80% power |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ferrara, E.; D’Albenzio, A.; Rapone, B.; Balice, G.; Murmura, G. Cross-Population Analysis of Sjögren’s Syndrome Polygenic Risk Scores and Disease Prevalence: A Pilot Study. Genes 2025, 16, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080901
Ferrara E, D’Albenzio A, Rapone B, Balice G, Murmura G. Cross-Population Analysis of Sjögren’s Syndrome Polygenic Risk Scores and Disease Prevalence: A Pilot Study. Genes. 2025; 16(8):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080901
Chicago/Turabian StyleFerrara, Elisabetta, Alessandro D’Albenzio, Biagio Rapone, Giuseppe Balice, and Giovanna Murmura. 2025. "Cross-Population Analysis of Sjögren’s Syndrome Polygenic Risk Scores and Disease Prevalence: A Pilot Study" Genes 16, no. 8: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080901
APA StyleFerrara, E., D’Albenzio, A., Rapone, B., Balice, G., & Murmura, G. (2025). Cross-Population Analysis of Sjögren’s Syndrome Polygenic Risk Scores and Disease Prevalence: A Pilot Study. Genes, 16(8), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16080901







