Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals Gene Expression Changes in Mouse Liver Tissue During Alveolar Echinococcosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasites and Experimental Animals
2.2. Establishment of Alveolar Echinococcosis Infected Mouse Model
2.3. Collection and HE Staining of Liver Tissue
2.4. RNA-Seq
2.5. Differentially Expressed Gene (DEG) Analysis
2.6. Gene Ontology (GO) Annotation and KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis
2.7. Weighted Coexpression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
2.8. qRT-PCR Analysis
3. Results
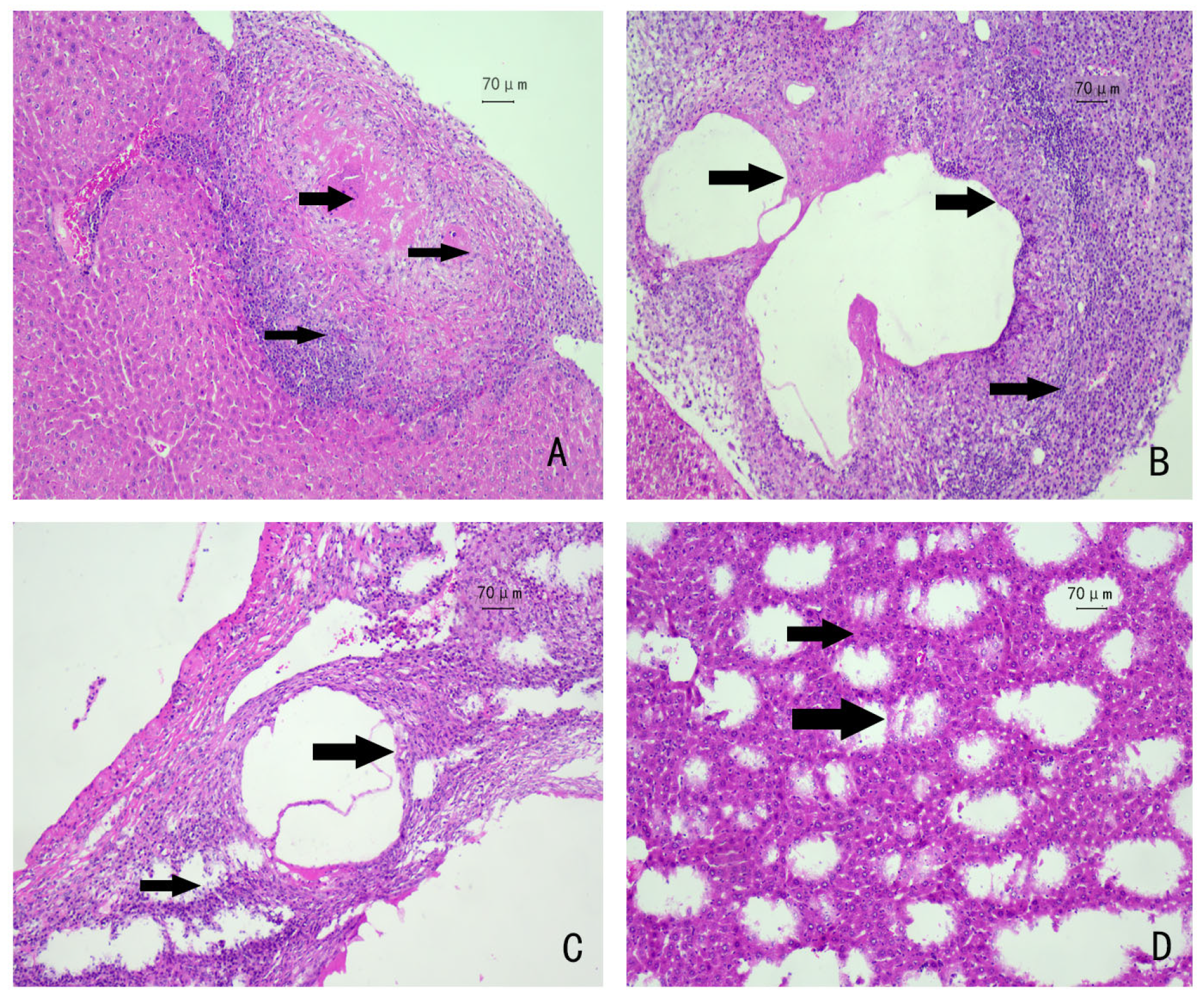
3.1. Autopsies of Mice and HE Staining of Liver Tissues
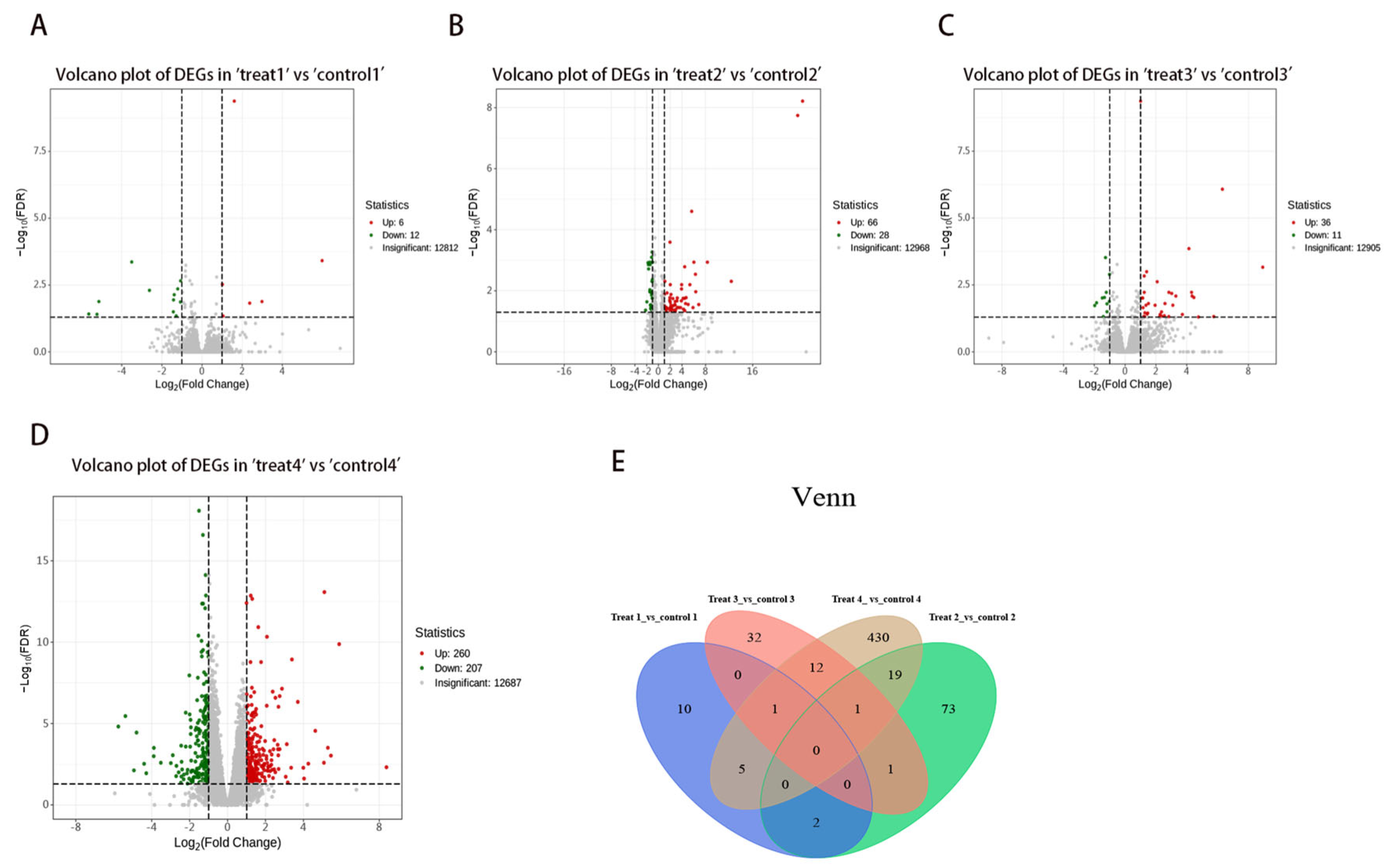
3.2. Identification of DEGs in Liver Tissues at Various Stages of Hepatic Alveolar Hydatid Disease Development
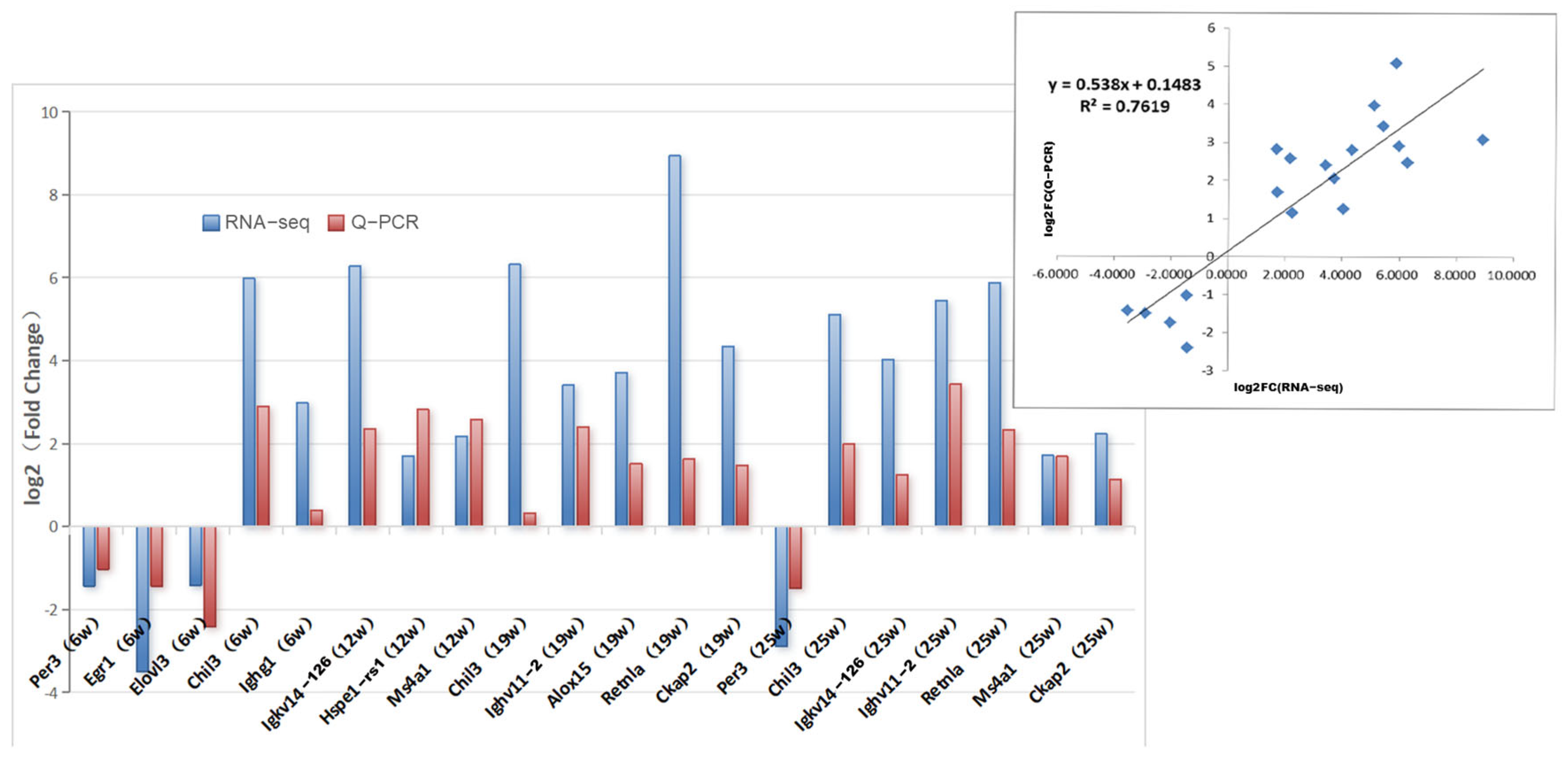
3.3. Validation of Differential Genes by qRT-PCR
3.4. Function and Pathway Outcomes of GO Enrichment
3.5. Function and Pathway Results of KEGG Analysis
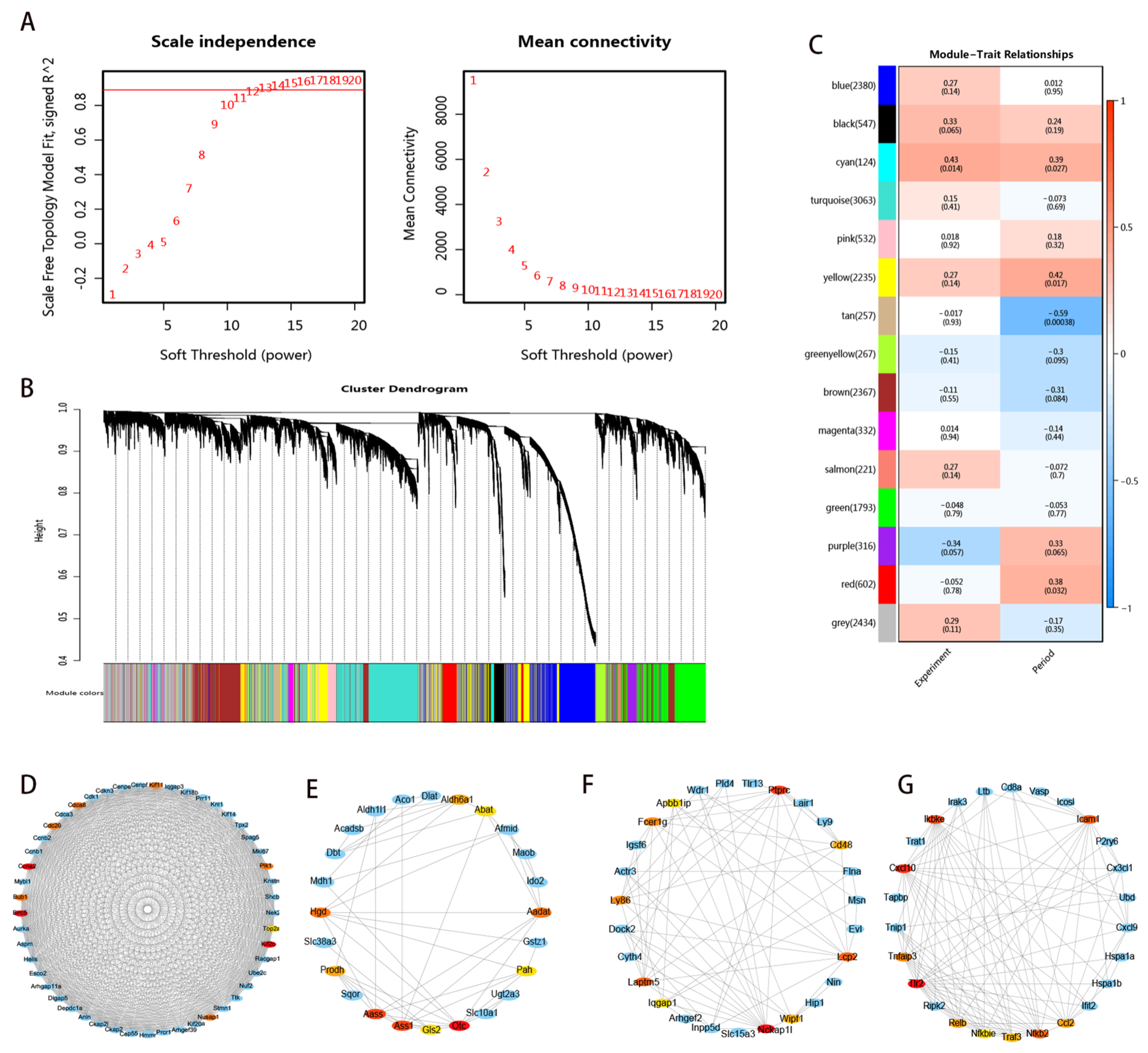
3.6. Coexpression Network-Related Modules and Hub Genes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | Alveolar echinococcosis |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| BIRC5 | Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing 5 |
| CCNA2 | Cyclin A2 |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| EDTA | Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid |
| FPKM | Fragments per kilobase million |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| HEM1 | Hematopoietic protein 1 |
| HSCs | Hepatic stellate cells |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| KIF2C | Kinase family member 2C |
| M2 | Macrophages 2 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| NCKAP1L | NCK-associated protein1-like |
| OTC | Ornithine transcarbamylase |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| RNA-Seq | RNA sequencing |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor-beta |
| TLR2 | Toll-like receptor 2 |
| WGCNA | Weighted gene co-expression network analysis |
References
- Fu, M.H.; Wang, X.; Han, S.; Guan, Y.Y.; Bergquist, R.; Wu, W.P. Advances in research on echinococcoses epidemiology in China. Acta Trop. 2021, 219, 105921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, Y.; Ogul, H.; Topdagi, O.; Ulas, A.B.; Sade, R.; Ozturk, G.; Korkut, E.; Aksungur, N.; Sener, E.; Can, F.K.; et al. Relevance of Pulmonary Alveolar Echinococcosis. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2020, 56, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Dai, G.; Li, M.; Jia, W.; Guo, Z.; Lu, J. Prevalence of human alveolar echinococcosis in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Vuitton, L.; Tuxun, T.; Li, J.; Vuitton, D.A.; Zhang, W.; McManus, D.P. Echinococcosis: Advances in the 21st Century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00075-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresson-Hadni, S.; Spahr, L.; Chappuis, F. Hepatic Alveolar Echinococcosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D.H. The liver. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R1147–R1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martyniuk, C.J. Perspectives on transcriptomics in animal physiology studies. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 250, 110490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoni, C.; Kia, D.A.; Vandrovcova, J.; Hardy, J.; Wood, N.W.; Lewis, P.A.; Ferrari, R. Genome, transcriptome and proteome: The rise of omics data and their integration in biomedical sciences. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varet, H.; Brillet-Guéguen, L.; Coppée, J.Y.; Dillies, M.A. SARTools: A DESeq2- and EdgeR-Based R Pipeline for Comprehensive Differential Analysis of RNA-Seq Data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Araki, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Hirakawa, M.; Itoh, M.; Katayama, T.; Kawashima, S.; Okuda, S.; Tokimatsu, T.; et al. KEGG for linking genomes to life and the environment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D480–D484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 29, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nian, X.; Li, L.; Ma, X.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, N.; Ohiolei, J.A.; Li, L.; Dai, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Understanding pathogen-host interplay by expression profiles of lncRNA and mRNA in the liver of Echinococcus multilocularis-infected mice. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022, 16, e0010435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Lü, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Xie, W.; Lu, X.; Mantion, G.; Martin, H.; Richert, L.; Vuitton, D.A.; et al. Time course of gene expression profiling in the liver of experimental mice infected with Echinococcus multilocularis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Lü, G.; Li, J.; Lu, X.; Mantion, G.; Vuitton, D.A.; Wen, H.; Lin, R. Hepatocyte proliferation/growth arrest balance in the liver of mice during E. multilocularis infection: A coordinated 3-stage course. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wuren, T.; Wu, B.; Cheng, S.; Fan, H. The expression of CTLA-4 in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis patients and blocking CTLA-4 to reverse T cell exhaustion in Echinococcus multilocularis-infected mice. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1358361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abulizi, A.; Tuergan, T.; Shalayiadang, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, R.; Jiang, T.; Guo, Q.; Wang, H.; Li, L.; Lin, R.; et al. Hepatic alveolar echinococcosis infection induces a decrease in NK cell function through high expression of NKG2A in patients. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1563248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Huo, L.; Mo, X.; Jiang, B.; Luo, Y.; Xu, B.; Li, J.; Ma, X.; Jing, T.; Feng, Z.; et al. Suppressive effect of pseudolaric acid B on Echinococcus multilocularis involving regulation of TGF-β1 signaling in vitro and in vivo. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1008274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuitton, D.A.; Gottstein, B. Echinococcus multilocularis and its intermediate host: A model of parasite-host interplay. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 923193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottstein, B.; Soboslay, P.; Ortona, E.; Wang, J.; Siracusano, A.; Vuitton, D.A. Immunology of Alveolar and Cystic Echinococcosis (AE and CE). Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 96, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Fan, H. Activation of the Wnt signaling pathway and its role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and hepatic fibrosis in alveolar echinococcosis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1583802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuitton, D.A.; Zhang, S.L.; Yang, Y.; Godot, V.; Beurton, I.; Mantion, G.; Bresson-Hadni, S. Survival strategy of Echinococcus multilocularis in the human host. Parasitol. Int. 2006, 55, S51–S55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hübner, M.P.; Manfras, B.J.; Margos, M.C.; Eiffler, D.; Hoffmann, W.H.; Schulz-Key, H.; Kern, P.; Soboslay, P.T. Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes modulate cellular cytokine and chemokine release by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in alveolar echinococcosis patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2006, 145, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, W.F.; Xu, S.; Dang, Z.S.; Zhao, Y.M. In Vitro and in Vivo Effect of MAPK Signal Transduction Pathway Inhibitors on Echinococcus multilocularis. J. Parasitol. 2019, 105, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Gui, W.; Niu, F.; Chong, S. The MAPK Signaling Pathways as a Novel Way in Regulation and Treatment of Parasitic Diseases. Diseases 2019, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, S.; Chen, G.; Dang, Z.; Niu, F.; Zhang, L.; Ma, H.; Zhao, Y. Echinococcus multilocularis drives the polarization of macrophages by regulating the RhoA-MAPK signaling pathway and thus affects liver fibrosis. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 8747–8758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.P.; Cunningham, R.P.; Davis, R.A.H.; Deemer, S.E.; Roberts, B.M.; Plaisance, E.P.; Rector, R.S. A dietary ketone ester mitigates histological outcomes of NAFLD and markers of fibrosis in high-fat diet fed mice. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 320, G564–G572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.-Z.; Ke, F.; Chai, J.-P.; A, J.-D.; Tan, Q.-L. Progress on the HIF-1α/VEGF/VEGFR2 signal pathway in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. Front. Oncol. 2025, 15, 1553125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.-S.; Fang, B.-B.; Hou, J.; Li, W.-D.; Li, Z.-D.; Li, L.; Bi, X.-J.; Abulizi, A.; Shao, Y.-M.; et al. Dual Role of Hepatic Macrophages in the Establishment of the Echinococcus multilocularis Metacestode in Mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 600635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christofides, A.; Konstantinidou, E.; Jani, C.; Boussiotis, V.A. The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) in immune responses. Metabolism 2021, 114, 154338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.G.; Wen, X.; Bailey, S.T.; Jiang, W.; Rangwala, S.M.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Flanigan, A.; Murthy, S.; Lazar, M.A.; Wu, G.D. A novel therapy for colitis utilizing PPAR-gamma ligands to inhibit the epithelial inflammatory response. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 104, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, R.; Zuo, X.; Jaoude, J.; Mao, F.; Colby, J.; Shureiqi, I. ALOX15 as a suppressor of inflammation and cancer: Lost in the link. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2017, 132, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, X.; Wu, Y.; Morris, J.S.; Stimmel, J.B.; Leesnitzer, L.M.; Fischer, S.M.; Lippman, S.M.; Shureiqi, I. Oxidative metabolism of linoleic acid modulates PPAR-beta/delta suppression of PPAR-gamma activity. Oncogene 2006, 25, 1225–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, X.; Xu, M.; Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Moussalli, M.J.; Manyam, G.C.; Lee, S.I.; Liang, S.; Gagea, M.; Morris, J.S.; et al. Potentiation of colon cancer susceptibility in mice by colonic epithelial PPAR-δ/β overexpression. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyaz, S.; Mana, M.D.; Roper, J.; Kedrin, D.; Saadatpour, A.; Hong, S.-J.; Bauer-Rowe, K.E.; Xifaras, M.E.; Akkad, A.; Arias, E.; et al. High-fat diet enhances stemness and tumorigenicity of intestinal progenitors. Nature 2016, 531, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballav, S.; Biswas, B.; Sahu, V.K.; Ranjan, A.; Basu, S. PPAR-γ Partial Agonists in Disease-Fate Decision with Special Reference to Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Su, F.; Yang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Su, H.; Zhang, T.; Bai, Y.; Ling, X. E2F1 transcriptionally regulates CCNA2 expression to promote triple negative breast cancer tumorigenicity. Cancer Biomark. 2022, 33, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreis, N.N.; Moon, H.H.; Wordeman, L.; Louwen, F.; Solbach, C.; Yuan, J.; Ritter, A. KIF2C/MCAK a prognostic biomarker and its oncogenic potential in malignant progression, and prognosis of cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis as biomarker. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2024, 61, 404–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avalos, A.; Tietsort, J.T.; Suwankitwat, N.; Woods, J.D.; Jackson, S.W.; Christodoulou, A.; Morrill, C.; Liggitt, H.D.; Zhu, C.; Li, Q.-Z.; et al. Hem-1 regulates protective humoral immunity and limits autoantibody production in a B cell-specific manner. JCI Insight 2022, 7, e153597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuxun, T.; Ma, H.Z.; Apaer, S.; Zhang, H.; Aierken, A.; Li, Y.P.; Lin, R.Y.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhang, J.H.; Wen, H. Expression of Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 4 and Related Cytokines in Patients with Hepatic Cystic and Alveolar Echinococcosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 632760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, S. Exogenous or endogenous Toll-like receptor ligands: Which is the MVP in tumorigenesis? Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 69, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Xu, H.-W.; Hao, W.-T.; Sun, F.-F.; Qin, Y.-F.; Hao, S.-S.; Liu, H.; Cao, J.-P.; Shen, Y.-J.; Zheng, K.-Y. The excretory-secretory products of Echinococcus granulosus protoscoleces stimulated IL-10 production in B cells via TLR-2 signaling. BMC Immunol. 2018, 19, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhtiar, N.M.; Spotin, A.; Mahami-Oskouei, M.; Ahmadpour, E.; Rostami, A. Recent advances on innate immune pathways related to host-parasite cross-talk in cystic and alveolar echinococcosis. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, N.; Liu, J.; Cai, H.; Zhao, C.; Shi, K.; Lei, W.; Ma, W.; Guo, S.; et al. Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals Gene Expression Changes in Mouse Liver Tissue During Alveolar Echinococcosis. Genes 2025, 16, 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070839
Zhang X, Zhang Q, Liu N, Liu J, Cai H, Zhao C, Shi K, Lei W, Ma W, Guo S, et al. Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals Gene Expression Changes in Mouse Liver Tissue During Alveolar Echinococcosis. Genes. 2025; 16(7):839. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070839
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiongying, Qing Zhang, Na Liu, Jia Liu, Huixia Cai, Cunzhe Zhao, Kemei Shi, Wen Lei, Wanli Ma, Shuai Guo, and et al. 2025. "Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals Gene Expression Changes in Mouse Liver Tissue During Alveolar Echinococcosis" Genes 16, no. 7: 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070839
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhang, Q., Liu, N., Liu, J., Cai, H., Zhao, C., Shi, K., Lei, W., Ma, W., Guo, S., Wang, W., Ma, X., & Wang, M. (2025). Transcriptomic Profiling Reveals Gene Expression Changes in Mouse Liver Tissue During Alveolar Echinococcosis. Genes, 16(7), 839. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070839





