Uncovering Allele-Specific Expression Patterns Associated with Sea Lice (Caligus rogercresseyi) Burden in Atlantic Salmon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials & Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Transcriptome Sequencing
2.3. RNA-Seq Quality Control and Quantification
3. Results
3.1. RNA-Seq
3.2. Allele-Specific Expression Analysis
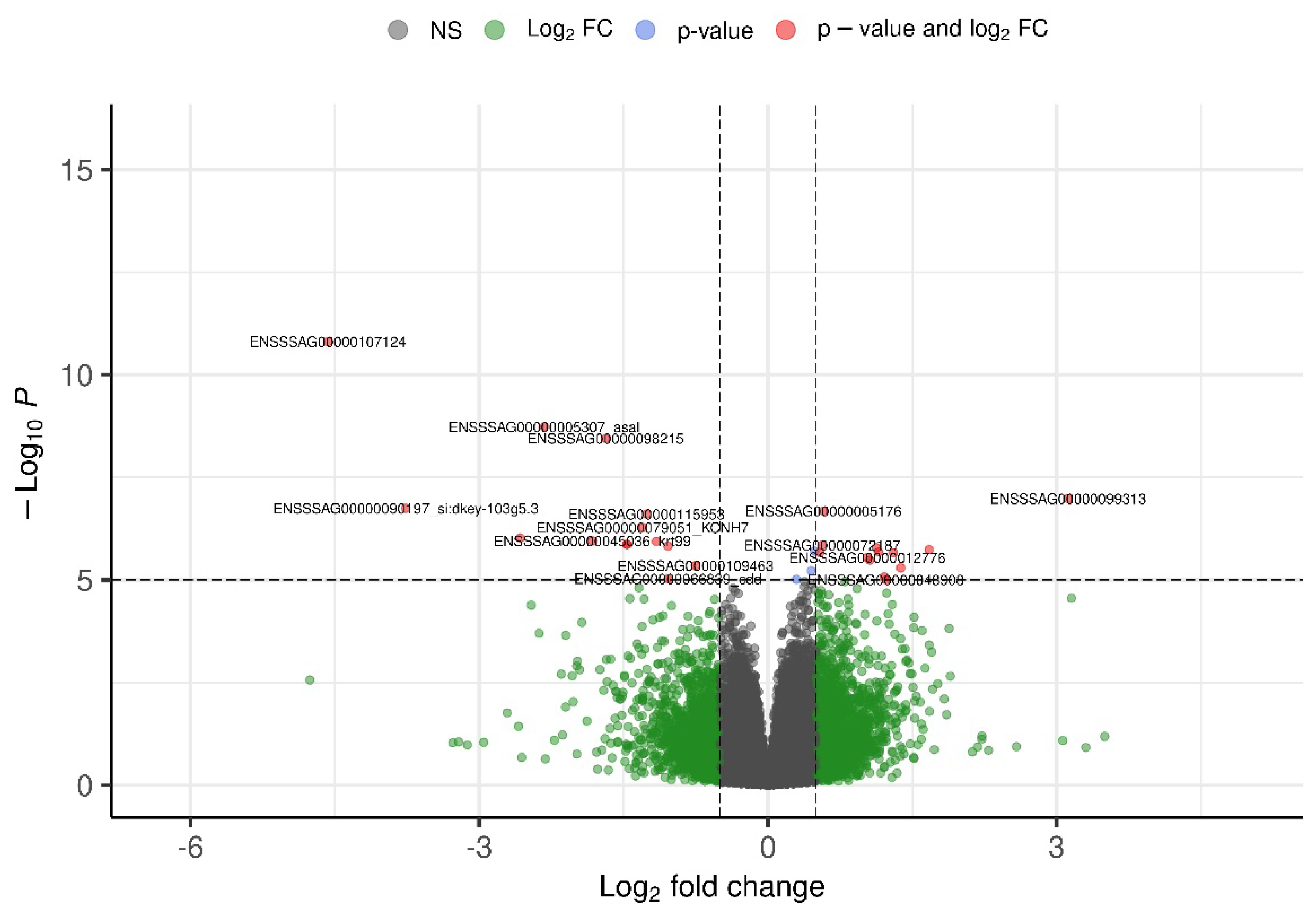
3.3. Candidate Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Lhorente, J.P.; Araneda, M.; Neira, R.; Yáñez, J.M. Advances in Genetic Improvement for Salmon and Trout Aquaculture: The Chilean Situation and Prospects. In Reviews in Aquaculture; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 11, pp. 340–353. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, S.; Silva, M.T.; Treasurer, J. Factors Affecting the Abundance of Caligus rogercresseyi (Boxshall and Bravo) on Farmed Salmonids in Chile in the Period 2006-2007. Aquaculture 2014, 434, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgesen, K.O.; Romstad, H.; Aaen, S.M.; Horsberg, T.E. First Report of Reduced Sensitivity towards Hydrogen Peroxide Found in the Salmon Louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis in Norway. Aquac. Rep. 2015, 1, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjedrem, T. Disease Resistant Fish and Shellfish Are within Reach: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2015, 3, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhorente, J.P.; Gallardo, J.A.; Villanueva, B.; Araya, A.M.; Torrealba, D.A.; Toledo, X.E.; Neira, R. Quantitative Genetic Basis for Resistance to Caligus rogercresseyi Sea Lice in a Breeding Population of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2012, 324–325, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez, J.M.; Lhorente, J.P.; Bassini, L.N.; Oyarzún, M.; Neira, R.; Newman, S. Genetic Co-Variation between Resistance against Both Caligus rogercresseyi and Piscirickettsia salmonis, and Body Weight in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Aquaculture 2014, 433, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, P.; Barría, A.; Christensen, K.A.; Bassini, L.N.; Correa, K.; Garcia, B.; Lhorente, J.P.; Yáñez, J.M. Genome-Scale Comparative Analysis for Host Resistance against Sea Lice between Atlantic Salmon and Rainbow Trout. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anacleto, O.; Cabaleiro, S.; Villanueva, B.; Saura, M.; Houston, R.D.; Woolliams, J.A.; Doeschl-Wilson, A.B. Genetic Differences in Host Infectivity Affect Disease Spread and Survival in Epidemics. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, S.C.; Woolliams, J.A. Genomics and Disease Resistance Studies in Livestock. Livest. Sci. 2014, 166, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, A.P.; Yáñ Ez, J.M.; Fukui, S.; Swift, B.; Davidson, W.S. Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) for Growth Rate and Age at Sexual Maturation in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.Y.; Hamilton, A.; Tinch, A.E.; Guy, D.R.; Bron, J.E.; Taggart, J.B.; Gharbi, K.; Stear, M.; Matika, O.; Pong-Wong, R.; et al. Genomic Prediction of Host Resistance to Sea Lice in Farmed Atlantic Salmon Populations. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2016, 48, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, G.M.; Lhorente, J.P.; Carvalheiro, R.; Yáñez, J.M. Bayesian Genome-Wide Association Analysis for Body Weight in Farmed Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.). Anim. Genet. 2017, 48, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerde, B.; Saltkjelvik, B.; Ødegård, J. Quantitative Genetics of Salmon Lice Resistance in Atlantic Salmon at Different Life Stages. In Proceedings of the 9th World Congress on Genetics Applied to Livestock Production (WCGALP), Leipzig, Germany, 1–6 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Correa, K.; Bangera, R.; Figueroa, R.; Lhorente, J.P.; Yáñez, J.M. The Use of Genomic Information Increases the Accuracy of Breeding Value Predictions for Sea Louse (Caligus rogercresseyi) Resistance in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Genet. Sel. Evol. 2017, 49, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robledo, D.; Gutiérrez, A.P.; Barría, A.; Lhorente, J.P.; Houston, R.D.; Yáñez, J.M. Discovery and Functional Annotation of Quantitative Trait Loci Affecting Resistance to Sea Lice in Atlantic Salmon. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, J.B.W. Principles of Transcriptome Analysis and Gene Expression Quantification: An RNA-Seq Tutorial. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braden, L.M.; Koop, B.F.; Jones, S.R.M. Signatures of Resistance to Lepeophtheirus salmonis Include a TH2-Type Response at the Louse-Salmon Interface. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2015, 48, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, M.D. Fish Immune Responses to Parasitic Copepod (Namely Sea Lice) Infection. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2014, 43, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, B.J.G.; Koczka, K.W.; Yasuike, M.; Jantzen, S.G.; Yazawa, R.; Koop, B.F.; Jones, S.R.M. Comparative Transcriptomics of Atlantic Salmo salar, Chum Oncorhynchus Keta and Pink Salmon O. Gorbuscha during Infections with Salmon Lice Lepeophtheirus salmonis. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, H.; Santi, N.; Kjøglum, S.; Perisic, N.; Skugor, S.; Evensen, Ø. Difference in Skin Immune Responses to Infection with Salmon Louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) of Families Selected for Resistance and Susceptibility. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2015, 42, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Huang, M.M.; Gan, Z.B.; Li, X.Z. Transcriptome Reveal Gene Regulation Mechanisms of the Barnacle Chthamalus Challengeri for Microhabitat Adaption in the Intertidal Zone. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ødegård, J.; Moen, T.; Santi, N.; Korsvoll, S.A.; Kjøglum, S.; Meuwisse, T.H.E. Genomic Prediction in an Admixed Population of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar). Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Dewey, C.N. RSEM: Accurate Transcript Quantification from RNA-Seq Data with or without a Reference Genome. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Auwera Geraldine, A.; O’Connor Brian, D. Genomics in the Cloud: Using Docker, GATK, and WDL in Terra (1st Edition), 1st ed.; O’Reilly Media, Inc.: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2020; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Hu, J.; Xue, C.; Zhang, H.; Susztak, K.; Reilly, M.P.; Reilly, M.P.; Xiao, R.; Li, M. ASEP: Gene-Based Detection of Allele-Specific Expression across Individuals in a Population by RNA Sequencing. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durinck, S.; Spellman, P.T.; Birney, E.; Huber, W. Mapping Identifiers for the Integration of Genomic Datasets with the R/ Bioconductor Package BiomaRt. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.N.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and Sequence Analysis Tools Services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W276–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsing, F.; Oppedal, F.; Johansson, D.; Bui, S.; Dempster, T. High Host Densities Dilute Sea Lice Lepeophtheirus salmonis Loads on Individual Atlantic Salmon, but Do Not Reduce Lice Infection Success. Aquac. Environ. Interact. 2014, 6, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfosse, C.; Pageat, P.; Lafont-Lecuelle, C.; Asproni, P.; Chabaud, C.; Cozzi, A.; Bienboire-Frosini, C. Effect of Handling and Crowding on the Susceptibility of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) to Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Krøyer) Copepodids. J. Fish Dis. 2021, 44, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easy, R.H.; Ross, N.W. Changes in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Epidermal Mucus Protein Composition Profiles Following Infection with Sea Lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2009, 4, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ødegård, J.; Kjøglum, S.; Medina, M.; Torgersen, J.S.; Korsvoll, S.A.; Deerenberg, R.; Yáñez, J.M.; Cichero, D.; López, P.; Moen, T. Genetics of Parasite Attraction in Atlantic Salmon: Potential for Group-Level Protection against Sea Lice; Wageningen Academic Publishers: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 2371–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Robledo, D.; Gutiérrez, A.P.; Barría, A.; Yáñez, J.M.; Houston, R.D. Gene Expression Response to Sea Lice in Atlantic Salmon Skin: RNA Sequencing Comparison between Resistant and Susceptible Animals. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, S.E.; Bricknell, I.R.; Covello, J.; Purcell, S.; Fast, M.D.; Wolters, W.; Bouchard, D.A.; Fujiwara, M. Sea lice, Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Krøyer 1837), infected Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) are more susceptible to infectious salmon anemia virus. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeBlanc, M.E.; Wang, W.; Caberoy, N.B.; Chen, X.; Guo, F.; Alvarado, G.; Shen, C.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Chen, R.; et al. Hepatoma-Derived Growth Factor-Related Protein-3 Is a Novel Angiogenic Factor. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skugor, S.; Glover, K.A.; Nilsen, F.; Krasnov, A. Local and Systemic Gene Expression Responses of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) to Infection with the Salmon Louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braden, L.M.; Monaghan, S.J.; Fast, M.D. Salmon Immunological Defence and Interplay with the Modulatory Capabilities of Its Ectoparasite Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Parasite Immunol. 2020, 42, e12731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, P.; Greis, K.D. Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor Receptor Signaling in Severe Congenital Neutropenia, Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia, and Related Malignancies. Exp. Hematol. 2017, 46, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Haq, S. Structure and Role of Neutrophil Cytosol Factor 1 (NCF1) Gene in Various Diseases. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 9286–9294. [Google Scholar]
| Trait | N | Mean | SD | Med. | Min | Max | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight Pre-challenge | 1126 | 168.6 | 24.4 | 165 | 108 | 271 | 14.5 |
| Length Pre-challenge | 1126 | 24.3 | 1.16 | 24.3 | 15.6 | 29.5 | 4.8 |
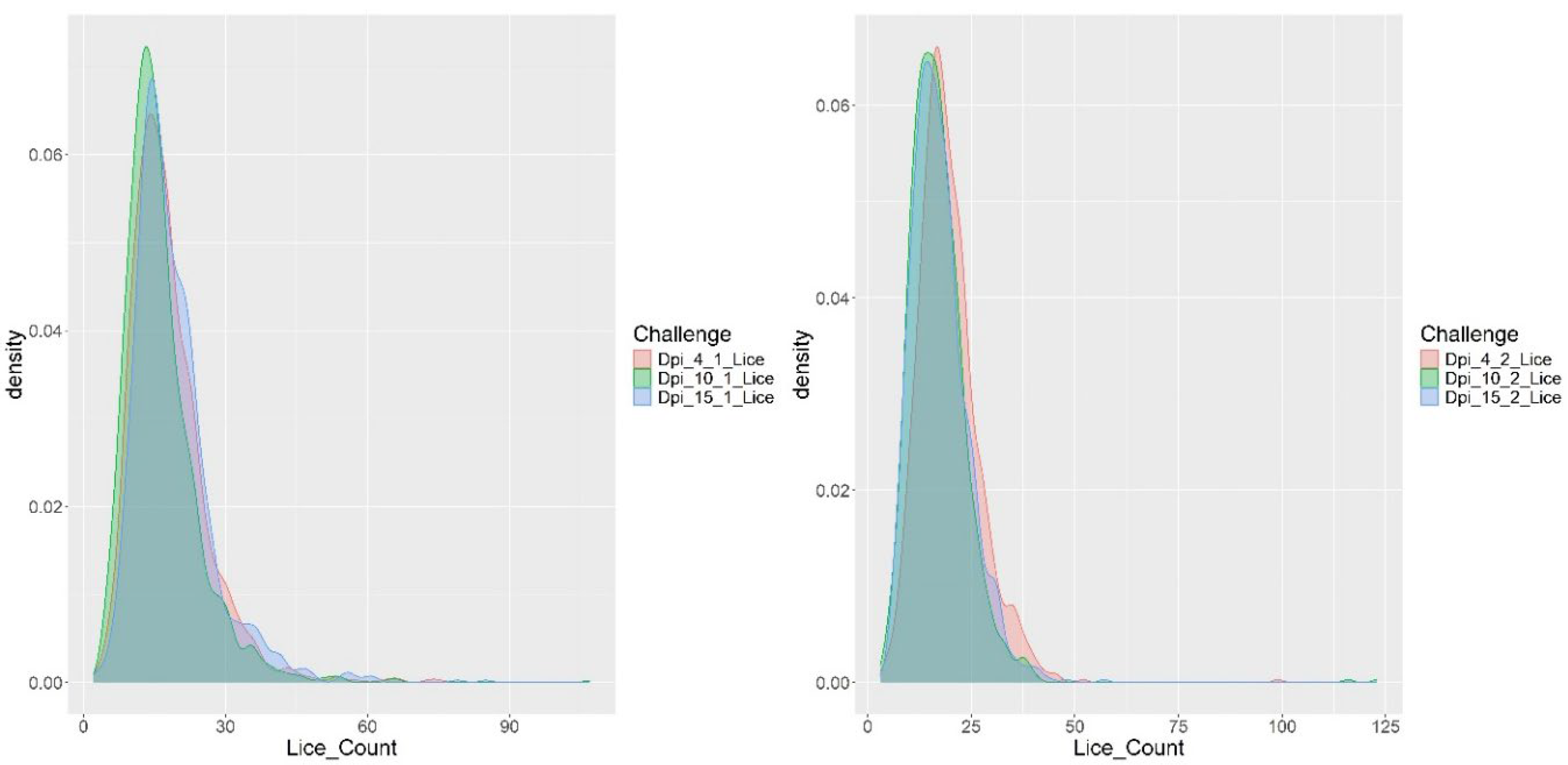
| DPI4_1 Parasites | 1127 | 18.0 | 8.2 | 17 | 2 | 75 | 45.8 |
| DPI10_1 Parasites | 1122 | 16.4 | 8.1 | 15 | 4 | 107 | 49.2 |
| DPI15_1 Parasites | 1019 | 19.0 | 8.7 | 17 | 2 | 85 | 45.7 |
| DPI4_1 Weight | 1127 | 169.1 | 24.1 | 167 | 108 | 278 | 14.3 |
| DPI10_1 Weight | 1122 | 166.9 | 23.8 | 165 | 104 | 276 | 14.3 |
| DPI15_1 Weight | 1019 | 170.6 | 28.5 | 169 | 16.3 | 402 | 16.7 |
| DPI4_2 Parasites | 992 | 19.6 | 7.5 | 19 | 4 | 99 | 38.2 |
| DPI10_2 Parasites | 978 | 17.0 | 7.8 | 16 | 3 | 123 | 45.5 |
| DPI15_2 Parasites | 952 | 17.4 | 6.8 | 16 | 4 | 57 | 38.8 |
| DPI4_2 Weight | 992 | 179.1 | 29.9 | 178 | 85 | 312 | 16.7 |
| DPI10_2 Weight | 978 | 188.1 | 32.8 | 186 | 94 | 340 | 17.4 |
| DPI15_2 Weight | 952 | 184.0 | 31.7 | 184 | 5 | 320 | 17.2 |
| Gene | p-Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ENSSSAG00000008223 | 0 | Fibronectin type III domain containing 1 |
| ENSSSAG00000012776 | 0.005 | Angiopoietin-1-like |
| ENSSSAG00000035308 | 0 | Membrane-associated ring-CH-type finger 3 |
| ENSSSAG00000045136 | 0.003 | Keratin 15 |
| ENSSSAG00000048512 | 0.003 | Keratin 15 |
| ENSSSAG00000054925 | 0 | Myristoylated alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate |
| ENSSSAG00000056022 | 0.045 | Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2a |
| ENSSSAG00000063640 | 0 | D-amino acid oxidase |
| ENSSSAG00000064326 | 0 | GULP PTB domain-containing engulfment adaptor 1a |
| ENSSSAG00000064378 | 0 | novel |
| ENSSSAG00000064682 | 0 | Collagen type IV alpha 5 |
| ENSSSAG00000065229 | 0.005 | Novel gene |
| ENSSSAG00000069698 | 0 | Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor A3 |
| ENSSSAG00000070277 | 0 | Beta 3-glucosyltransferase a |
| ENSSSAG00000070579 | 0 | Disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 12 |
| ENSSSAG00000073657 | 0.001 | LOC106569355 |
| ENSSSAG00000076502 | 0.035 | Matrix metallopeptidase 28 |
| ENSSSAG00000076511 | 0.004 | EGF-like domain multiple 6 |
| ENSSSAG00000083329 | 0 | LOC106612420 |
| ENSSSAG00000085545 | 0 | Novel gene |
| ENSSSAG00000087971 | 0.003 | Synaptotagmin XII |
| ENSSSAG00000090709 | 0.001 | Collagen type V alpha 3a |
| ENSSSAG00000094685 | 0.002 | Sperm acrosome-associated 4-like |
| ENSSSAG00000097547 | 0 | Novel gene |
| ENSSSAG00000102125 | 0 | Osteoglycin |
| ENSSSAG00000104092 | 0.008 | Novel gene |
| ENSSSAG00000104872 | 0 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 16-like |
| ENSSSAG00000104937 | 0 | Iodothyronine deiodinase 1 |
| ENSSSAG00000109080 | 0 | CD248 molecule, endosialin a |
| ENSSSAG00000111485 | 0 | Novel gene |
| ENSSSAG00000118058 | 0 | Myosin-7 |
| ENSSSAG00000119277 | 0 | Serine protease 35 |
| ENSSSAG00000122110 | 0.01 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21-like |
| Gene | p-Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ENSSSAG00000000392 | 0 | RNA exonuclease 5 |
| ENSSSAG00000002452 | 0 | NOP14 nucleolar protein homolog (yeast) |
| ENSSSAG00000003919 | 0.016 | Novel gene |
| ENSSSAG00000004485 | 0 | Immunoglobulin-like and fibronectin type III domain-containing 1 |
| ENSSSAG00000008409 | 0.001 | Cell death-inducing DFFA like effector b |
| ENSSSAG00000010799 | 0 | Novel gene |
| ENSSSAG00000015527 | 0 | Palmitoyltransferase |
| ENSSSAG00000018923 | 0 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase ABCA1 |
| ENSSSAG00000041926 | 0 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase ABCA1 |
| ENSSSAG00000045036 | 0 | Keratin 99 |
| ENSSSAG00000049698 | 0 | RNA binding motif protein 34 |
| ENSSSAG00000060839 | 0 | Nucleolar protein 8 |
| ENSSSAG00000064522 | 0 | Nucleolar protein 11 |
| ENSSSAG00000066839 | 0.001 | Cytidine deaminase |
| ENSSSAG00000067044 | 0 | Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 |
| ENSSSAG00000068370 | 0 | Nucleolar protein with MIF4G domain 1 |
| ENSSSAG00000068818 | 0 | TRNA methyltransferase 2 homolog A |
| ENSSSAG00000069874 | 0.016 | Matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| ENSSSAG00000070332 | 0 | AMP-activated alpha 1 catalytic subunit |
| ENSSSAG00000070495 | 0 | Collagenase 3 |
| ENSSSAG00000071944 | 0 | Nle1 |
| ENSSSAG00000072535 | 0.024 | Colony-stimulating factor 3 receptor (granulocyte) |
| ENSSSAG00000079794 | 0 | Novel gene |
| ENSSSAG00000079828 | 0 | Neutrophil cytosolic factor |
| ENSSSAG00000080634 | 0 | Deoxynucleotidyltransferase, terminal, interacting protein 2 |
| ENSSSAG00000090197 | 0.039 | Zona pellucida-like domain-containing protein 1 |
| ENSSSAG00000117724 | 0 | Guanine deaminase |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cáceres, P.; López, P.; Araya, C.; Cichero, D.; Bassini, L.N.; Yáñez, J.M. Uncovering Allele-Specific Expression Patterns Associated with Sea Lice (Caligus rogercresseyi) Burden in Atlantic Salmon. Genes 2025, 16, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070841
Cáceres P, López P, Araya C, Cichero D, Bassini LN, Yáñez JM. Uncovering Allele-Specific Expression Patterns Associated with Sea Lice (Caligus rogercresseyi) Burden in Atlantic Salmon. Genes. 2025; 16(7):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070841
Chicago/Turabian StyleCáceres, Pablo, Paulina López, Carolina Araya, Daniela Cichero, Liane N. Bassini, and José M. Yáñez. 2025. "Uncovering Allele-Specific Expression Patterns Associated with Sea Lice (Caligus rogercresseyi) Burden in Atlantic Salmon" Genes 16, no. 7: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070841
APA StyleCáceres, P., López, P., Araya, C., Cichero, D., Bassini, L. N., & Yáñez, J. M. (2025). Uncovering Allele-Specific Expression Patterns Associated with Sea Lice (Caligus rogercresseyi) Burden in Atlantic Salmon. Genes, 16(7), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070841





