Characterization of Constitutional Ring Chromosomes over 37 Years of Experience at a Single-Site Institution
Abstract
1. Introduction
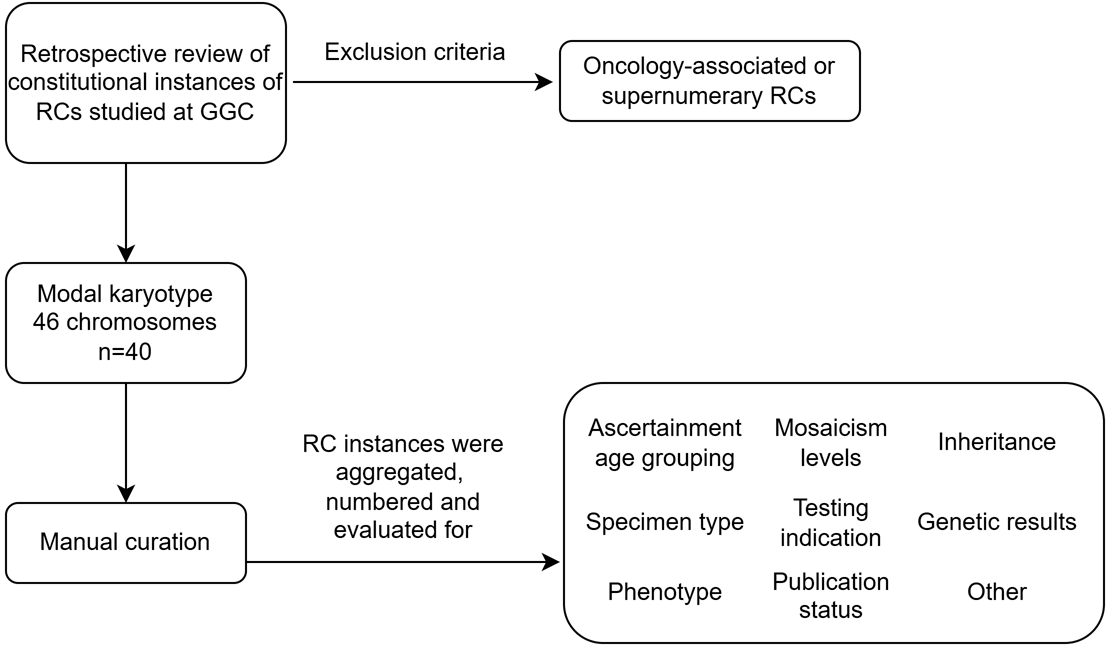
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Individuals
2.2. Methods
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Characteristics
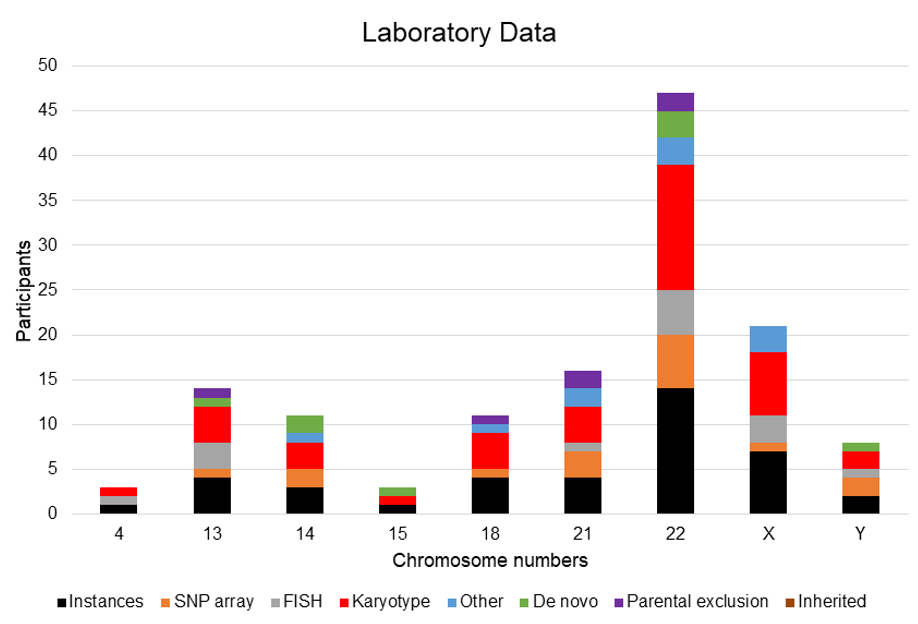
3.2. Ring Chromosome Summary
3.2.1. Ring Chromosome 4
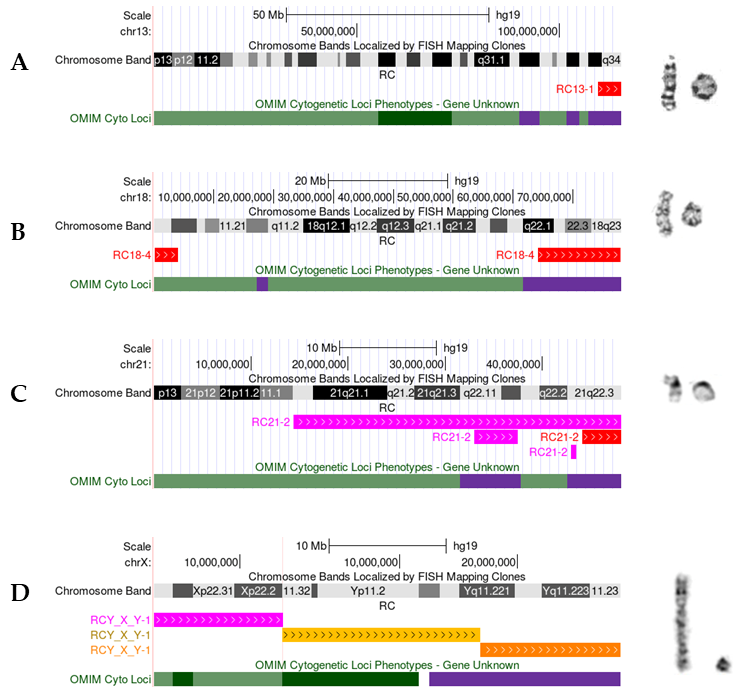
3.2.2. Ring Chromosome 13
3.2.3. Ring Chromosome 14
3.2.4. Ring Chromosome 15
3.2.5. Ring Chromosome 18
3.2.6. Ring Chromosome 21
3.2.7. Ring Chromosome 22
3.2.8. Ring Chromosome X
3.2.9. Ring Chromosome Y
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, P.; Dupont, B.; Hu, Q.; Crimi, M.; Shen, Y.; Lebedev, I.; Liehr, T. The Past, Present, and Future for Constitutional Ring Chromosomes: A Report of the International Consortium for Human Ring Chromosomes. HGG Adv. 2022, 3, 100139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsten, J.; Alvin, A.; Gustavson, K.H.; Fraccaro, M. Chromosomal Mosaic in a Girl with Some Features of Mongolism. Cytogenetics 1962, 1, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Liehr, T. Historical Perspective of Human Ring Chromosomes. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 3–15. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mostovoy, Y.; Boone, P.M.; Huang, Y.; Garimella, K.V.; Tan, K.-T.; Russell, B.E.; Salani, M.; de Esch, C.E.F.; Lemanski, J.; Curall, B.; et al. Resolution of Ring Chromosomes, Robertsonian Translocations, and Complex Structural Variants from Long-Read Sequencing and Telomere-to-Telomere Assembly. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 111, 2693–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Chai, H.; Shu, W.; Li, P. Human Ring Chromosome Registry for Cases in the Chinese Population: Re-Emphasizing Cytogenomic and Clinical Heterogeneity and Reviewing Diagnostic and Treatment Strategies. Mol. Cytogenet. 2018, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liehr, T.; Li, P. A New Database on Constitutional Human Ring Chromosomes, OBM Genetics; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bone, K.M.; Chernos, J.; Thomas, M.A. Ring Chromosome 4. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 93–112. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Chong, M.L. Ring Chromosome 13. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 201–214. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- Vaisfeld, A.; Crimi, M.; Rinaldi, B. Ring Chromosome 14. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 215–220. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- van Karnebeek, C.D.M.; Quik, S.; Sluijter, S.; Hulsbeek, M.M.F.; Hoovers, J.M.N.; Hennekam, R.C.M. Further Delineation of the Chromosome 14q Terminal Deletion Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2002, 110, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Guo, H.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Wu, W. Ring Chromosome 15. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 221–239. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- Cody, J.D. Ring Chromosome 18. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 261–270. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- Stankiewicz, P.; Brozek, I.; Hélias-Rodzewicz, Z.; Wierzba, J.; Pilch, J.; Bocian, E.; Balcerska, A.; Wozniak, A.; Kardaś, I.; Wirth, J.; et al. Clinical and Molecular-Cytogenetic Studies in Seven Patients with Ring Chromosome 18. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2001, 101, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yardin, C.; Esclaire, F.; Terro, F.; Baclet, M.C.; Barthe, D.; Laroche, C. First Familial Case of Ring Chromosome 18 and Monosomy 18 Mosaicism. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2001, 104, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chai, H. Ring Chromosome 21. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 287–300. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, T.; Downie, L.; Pertile, M.D.; Francis, D.; Glass, M.; Nouri, S.; Pszczola, R. Monosomy 21 Seen in Live Born Is Unlikely to Represent True Monosomy 21: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Case Rep. Genet. 2014, 2014, 965401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafabregue, E.; Chaby, G.; Vabres, P.; Carmi, E. Alopecia, deformed ear and mental retardation associated with terminal 21q deletion. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2019, 146, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Erez, A.; Nagamani, S.C.S.; Dhar, S.U.; Kołodziejska, K.E.; Dharmadhikari, A.V.; Cooper, M.L.; Wiszniewska, J.; Zhang, F.; Withers, M.A.; et al. Chromosome Catastrophes Involve Replication Mechanisms Generating Complex Genomic Rearrangements. Cell 2011, 146, 889–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, K. Ring Chromosome 22. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 301–335. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, C.M.; Betancur, C.; Boeckers, T.M.; Bockmann, J.; Chaste, P.; Fauchereau, F.; Nygren, G.; Rastam, M.; Gillberg, I.C.; Anckarsäter, H.; et al. Mutations in the Gene Encoding the Synaptic Scaffolding Protein SHANK3 Are Associated with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarasua, S.M.; Dwivedi, A.; Boccuto, L.; Rollins, J.D.; Chen, C.-F.; Rogers, R.C.; Phelan, K.; DuPont, B.R.; Collins, J.S. Association between Deletion Size and Important Phenotypes Expands the Genomic Region of Interest in Phelan-McDermid Syndrome (22q13 Deletion Syndrome). J. Med. Genet. 2011, 48, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahajpal, N.; DuPont, B.R. Ring Chromosome X. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 337–345. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- DuPont, B.R. Ring Chromosome Y. In Human Ring Chromosomes: A Practical Guide for Clinicians and Families; Li, P., Liehr, T., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 347–352. ISBN 978-3-031-47530-6. [Google Scholar]
- Milenkovic, T.; Guc-Scekic, M.; Zdravkovic, D.; Topic, V.; Liehr, T.; Joksic, G.; Radivojevic, D.; Lakic, N. Molecular Analysis of Ring y Chromosome in a 10-Year-Old Boy with Mixed Gonadal Dysgenesis and Growth Hormone Deficiency. Balk. J. Med. Genet. BJMG 2011, 14, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertini, V.; Canale, D.; Bicocchi, M.P.; Simi, P.; Valetto, A. Mosaic Ring Y Chromosome in Two Normal Healthy Men with Azoospermia. Fertil. Steril. 2005, 84, 1744.e1–1744.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grass, F.S.; Brown, C.A.; Backeljauw, P.F.; Lucas, A.; Brasington, C.; Gazak, J.M.; Nakano, S.; Ostrowski, R.S.; Spence, J.E. Novel Ring Chromosome Composed of X- and Y-Derived Material in a Girl with Manifestations of Ullrich-Turner Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 93, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| RC | Type | Age | Gender | Sample | Features | Assay | Mosaic (K) | Inheritance | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RC4-1 | CCR | P | F | PB | micrognathia, thin lips, slanted palpebral fissures down, helix abn, nasal tip abn, prematurity, congenital heart defect, advanced bone age, preauricular appendage, short philtrum (absent), microcephaly, midface hypoplasia, ID-severe | K, FISH | N | Unk | F;U |
| RC13-1 | S | P | M | PB | DD, speech delay, microcephaly, café au lait spots, involuntary gait/movement, sloping forehead, dysmorphic facies, clinodactyly-fifth finger | K, FISH, CMA 13q33.3q34 loss (5.7 Mb) | N | Maternal exclusion | |
| RC13-2 | S | A | F | PB | ID-mild, tonic-clonic (grand mal) seizure, depression | K, FISH | N | Unk | |
| RC13-3 | S | P | M | PB | Hypotonia and microcephaly | K | 93% | Unk | unstable RC |
| RC13-4 | S | Fetus-stillborn | F | AF/Placental biopsy | Abn U/S (not NTD), cystic hygroma AF-AFP at risk AChE negative, triple screen negative, 2nd pregnancy, 17.4 weeks, affected by holoprosencephaly and MCA 23 weeks GA, TOF, hypoplastic external genitalia, cystic hygroma, thumb a/hypoplasia, renal a/hypogenesis, choanal atresia, lung a/hypoplasia, ectopic anus | K, FISH | 6.67~13% | De novo | F;U |
| RC14-1 | S | A | F | PB | ID-moderate and seizures, palpebral fissure abn, seizures, hyperpigmented macule | K, CMA 14q32.33 loss (4.7 Mb) | 86% | Unk | |
| RC14-2 | S | Fetus-POC | F | POC | K | 63% | De novo | ||
| RC14-3 | S | P | F | PB | seizure disorder | K, CMA 14q32.33 loss (2.6 Mb) | N | De novo | |
| RC15-1 | S | Fetus-POC | F | Fetal tissue | K | N | De novo | ||
| RC18-1 | S | P | F | PB | DD, affected by ring autosomes, ID-moderate, flat midface, slanted palpebral fissures-up, low nasal bridge depressed, hypoplastic alae nasi, flat midface, attached earlobes, heart murmur, short stature, telecanthus | K | N | Unk | |
| RC18-2 | S | P | F | PB | ptosis of eyelid, eye, slanted palpebral fissures (up), protruding ears (lop ears), oral/mouth anomaly/saliva, hearing loss/impairment, DD | K, MLPA | 52% | Unk | |
| RC18-3 | S | P | M | PB | FTT, cleft palate | K | 44% | Unk | |
| RC18-4 | S | P | F | PB | DD, short stature, balance and coordination problems, large lobes, low-set ears, sloping forehead, upslanted palpebral fissures, brachydactyly, camptodactyly, long facies, midface hypoplasia, retrognathia, downturned corners of mouth | K, CMA 18p11.32p11.31 (3.8 Mb) and 18q22.1q23 (13.9 Mb) losses | 85% | Maternal exclusion | |
| RC21-1 | S | P | M | PB | dolichocephaly, ID-mild, attention problems, small earlobes, pes planus, midface hypoplasia, family history of ID, high arched palate, large nose, affected by ring autosome | K | N | Unk | |
| RC21-2 | CCR | P | M | PB | holoprosencephaly, pulmonary hypertension | K, CMA 21q11.2q22.3 mosaic loss with mosaic gains of 21q22.11 (4.5 Mb) and 21q22.3 (589 Kb), and 21q22.3 loss (4 Mb) | 70% | Maternal exclusion | |
| RC21-3 | S | P | M | PB | Speech delay and hearing impairment, hyperactivity, DD, expressive speech delay/disorder, epicanthal folds, slanted palpebral fissures up, midface hypoplasia, thin nails | K, MLPA, FISH, qPCR, CMA 21q22.13q22.3 gain (10.2 Mb) | N | Maternal exclusion | |
| RC21-4 | S | P | M | PB | Dysmorphic features, DD. Findings: coloboma, protruding ears (lop ears), cupped ears, microcephaly, ID-moderate, thin underweight, hyperreflexia, hypertonia | K, CMA 21q22.13 loss (9.6 Mb) | N | Unk | |
| RC22-1 | S | A | F | PB | ID and seizure disorder | K, FISH | N | Unk | |
| RC22-2 | S | A | F | PB | ID-profound, dysmorphic facies, obesity, microcephaly, Madelung deformity, sloping forehead, midface hypoplasia, slanted palpebral fissures up, sparse (absent) eyebrows, cataract | K | N | Unk | |
| RC22-3 | S | A | F | PB | ID-severe, affected by neurofibromatosis (AD), flat midface, micrognathia, attached earlobes | K, FISH | N | Unk | |
| RC22-4 | S | P | F | PB | Midface hypoplasia, fine and gross motor incoordination, thin finger nails, significant speech hard to understand, DiGeorge | K, FISH | 61% | Paternal exclusion | |
| RC22-5 | S | A | M | PB | K, CMA (negative) | 8% | De novo | ||
| RC22-6 | S | P | F | PB | DD, syndactyly, hooded eyelids | K, CMA 22q13.33 loss (1.6 Mb) | N | De novo | |
| RC22-7 | S | A | F | PB | Nose, ID, sunken/recessed eyes, small palpebral fissures, synophrys, macrotia, camptodactyly | K, FISH | N | Unk | |
| RC22-8 | S | P | F | PB | K, CMA 22q13.31 (3.8 Mb) loss | N | De novo | ||
| RC22-9 | S | A | F | PB | hypopigmented macule, heart murmur, asymmetric facies, ID-moderate | K | N | Unk | |
| RC22-10 | S | Fetus | F | CVS | AMA, AFP normal, 16.1 weeks, prior pregnancy normal male | K | N | Unk | |
| RC22-11 | S | A | F | PB | K, CMA 22q13.2 loss (7.6 Mb) | N | Unk | ||
| RC22-12 | S | Fetus AND P | F | AF AND PB | quad screen negative, prenatal screen risk of Down syndrome, AF-AFP/MCA at birth | K, FISH | 24% prenatal K and absent postnatal K | Unk | F;U |
| RC22-13 | S | P | M | PB | K, CMA 22q13.2q13.31 gain (2.34 Mb) and 22q13.31qter loss (6.1 Mb) | N | Paternal exclusion | ||
| RC22-14 | S | P | F | PB | studied for 22q13 deletion | K, CMA 22q13.31 loss (4.4 Mb) | N | Unk |
| RC | Type | Age | Gender | Sample | Features | Assay | Mosaic (K) | Inheritance | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCX-1 | S | P | F | PB | possible TS, short stature, hyperconvex nails, sacral dimple, unfurled helices, epicanthal folds, upslanted palpebral fissures, cubitus valgus, metacarpal hypoplasia, acanthosis nigricans, growth hormone supplementation, which was discontinued. Mild vision issues, bilateral knee dislocations, Tanner stage IV pubic hair | K | 4% | Unk | |
| RCX-2 | S | A | F | PB | rule out mosaicism 45,X/46,XX or XY, diagnosed with mosaic TS at a young age, aberrant right subclavian artery CT scan discovered incidentally, hyperlipidemia, insomnia, premature menopause in early 20s due to TS | K | 9.30% | Unk | |
| RCX-3 | S | P | F | PB | ID, epicanthal folds, fifth finger a/hypoplasia, palmar line, short stature, DD, slanted palpebral fissure-up, ptosis of eyelid | K, FISH, DNA studies | 8~11% | Unk | F;U; unstable RC |
| RCX-4 | S | P | F | PB | TS, short stature, hypothyroidism, intellectual disability-unk, everted eyelid, palpebral fissure long, synophrys, arched eyebrows | K | 33~40% | Unk | F;U |
| RCX-5 | S | P | F | PB | short stature, FTT, undergrowth, SGA, TS | K, CMA (inconclusive) | 28% | Unk | |
| RCX-6 | S | P | F | PB | concern for 45,X mosaicism, abn sex chromosomes | K, CMA Xp11.22p11.21 mosaic gain (911 Kb) and Xp21q21.1 mosaic loss (25 Mb) | 56% | Unk | |
| RCX-7 | S | P | F | PB | rule out chromosomal abnormality | K, FISH | 66% | Unk | |
| RCY-1 | S | P | M | PB | bifid uvula, submucous cleft palate, ring chromosome Y syndrome | K, CMA Yp11.32 loss (1.7 Mb) and Yq12 loss (302 Kb), and Yq11.21q12 loss (15 Mb) | 90% | De novo | |
| RCX;Y-1 | CCR | Fetus | F | AF | AFP not elevated. NIPT high risk for monosomy X. GA 16 weeks | K, FISH, CMA Yp11.32q11.221 mosaic loss (17 Mb) and Yq11.221q11.23 loss (11.9 Mb) with Xp22.33p22.2 mosaic gain (11 Mb) | 54% | Unk |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Murry, J.B.; DuPont, B.R. Characterization of Constitutional Ring Chromosomes over 37 Years of Experience at a Single-Site Institution. Genes 2025, 16, 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070736
Murry JB, DuPont BR. Characterization of Constitutional Ring Chromosomes over 37 Years of Experience at a Single-Site Institution. Genes. 2025; 16(7):736. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070736
Chicago/Turabian StyleMurry, Jaclyn B., and Barbara R. DuPont. 2025. "Characterization of Constitutional Ring Chromosomes over 37 Years of Experience at a Single-Site Institution" Genes 16, no. 7: 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070736
APA StyleMurry, J. B., & DuPont, B. R. (2025). Characterization of Constitutional Ring Chromosomes over 37 Years of Experience at a Single-Site Institution. Genes, 16(7), 736. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16070736






