Region-Based Analysis with Functional Annotation Identifies Genes Associated with Cognitive Function in South Asians from India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Whole-Genome Sequence Data
2.3. Principal Component Analysis and Genetic Relationship Matrix
2.4. Measures of Cognitive Function
2.5. Demographics and Lifestyle Factors
2.6. Gene Selection
2.7. Definition of Missense/LoF and Promoter/Enhancer SNVs
2.8. Annotation Selection
2.9. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Missense/Loss-of-Function (LoF) Analysis
3.2. High-Confidence Missense/LoF Analysis
3.3. Promoter/Enhancer Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| EA | European Ancestry |
| LASI-DAD | Harmonized Diagnostic Assessment of Dementia in the Longitudinal Aging Study of India |
| HMSE | Hindi Mental State Examination |
| LoF | Loss-of-Function |
| STAAR | variant-Set Test for Association using Annotation infoRmation |
| WGS | Whole Genome Sequencing |
| SNV | Single Nucleotide Variant |
| LASI | Longitudinal Aging Study of India |
| HCAP | Harmonized Cognitive Assessment Protocol |
| QC | Quality Control |
| GCAD | Genome Center for Alzheimer’s Disease |
| DP | Read Depth |
| GQ | Genotype Quality Score |
| VQSR | Variant Quality Score Recalibration |
| SNP | Single Nucleotide Polymorphism |
| PC | Principal Component |
| GRM | Genetic Relatedness Matrix |
| CHC | Cattell–Horn–Carroll |
| IRT | Item-Response Theory |
| GWAS | Genome-Wide Association Study |
| VEP | Variant Effect Predictor |
| ADD | AD and Dementia |
| WGSA | WGS Annotator |
| FDR | False-Discovery Rate |
| AF | Allele Frequency |
| MAF | Minor Allele Frequency |
References
- Wimo, A.; Seeher, K.; Cataldi, R.; Cyhlarova, E.; Dielemann, J.L.; Frisell, O.; Guerchet, M.; Jönsson, L.; Malaha, A.K.; Nichols, E.; et al. The Worldwide Costs of Dementia in 2019. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 2865–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.A.; Arvanitakis, Z.; Leurgans, S.E.; Bennett, D.A. The Neuropathology of Probable Alzheimer Disease and Mild Cognitive Impairment. Ann. Neurol. 2009, 66, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Comprehensive Review on Alzheimer’s Disease: Causes and Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, C.M.; Yee, C.; May, T.; Dhanala, A.; Mitchell, C.S. Cognitive Decline in Preclinical Alzheimer’s Disease: Amyloid-Beta versus Tauopathy. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 61, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Area-Gomez, E.; Schon, E.A. Alzheimer Disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 997, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, R.; Hill, M.; Williams, J. The Multiplex Model of the Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollon, J.; Knowles, E.E.M.; Mathias, S.R.; Gur, R.; Peralta, J.M.; Weiner, D.J.; Robinson, E.B.; Gur, R.E.; Blangero, J.; Almasy, L.; et al. Genetic Influence on Cognitive Development between Childhood and Adulthood. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Meijer, E.; Langa, K.M.; Ganguli, M.; Varghese, M.; Banerjee, J.; Khobragade, P.; Angrisani, M.; Kurup, R.; Chakrabarti, S.S.; et al. Prevalence of Dementia in India: National and State Estimates from a Nationwide Study. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2023, 19, 2898–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranath, V.; Sundarakumar, J.S. Changing Demography and the Challenge of Dementia in India. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuk, O.; Schaffner, S.F.; Samocha, K.; Do, R.; Hechter, E.; Kathiresan, S.; Daly, M.J.; Neale, B.M.; Sunyaev, S.R.; Lander, E.S. Searching for Missing Heritability: Designing Rare Variant Association Studies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E455–E464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perianayagam, A.; Bloom, D.; Lee, J.; Parasuraman, S.; Sekher, T.V.; Mohanty, S.K.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Govil, D.; Pedgaonkar, S.; Gupta, S.; et al. Cohort Profile: The Longitudinal Ageing Study in India (LASI). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, e167–e176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Khobragade, P.Y.; Banerjee, J.; Chien, S.; Angrisani, M.; Perianayagam, A.; Bloom, D.E.; Dey, A.B. Design and Methodology of the Longitudinal Aging Study in India-Diagnostic Assessment of Dementia (LASI-DAD). J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68 (Suppl. 3), S5–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Dey, A.B. Introduction to LASI-DAD: The Longitudinal Aging Study in India-Diagnostic Assessment of Dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68 (Suppl. 3), S3–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, Y.Y.; Valladares, O.; Chou, Y.F.; Lin, H.J.; Kuzma, A.B.; Cantwell, L.; Qu, L.; Gangadharan, P.; Salerno, W.J.; Schellenberg, G.D.; et al. VCPA: Genomic Variant Calling Pipeline and Data Management Tool for Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 1768–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgulis, A.; Gertz, E.M.; Schäffer, A.A.; Agarwala, R. A Fast and Symmetric DUST Implementation to Mask Low-Complexity DNA Sequences. J. Comput. Biol. 2006, 13, 1028–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogarten, S.M.; Sofer, T.; Chen, H.; Yu, C.; Brody, J.A.; Thornton, T.A.; Rice, K.M.; Conomos, M.P. Genetic Association Testing Using the GENESIS R/Bioconductor Package. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 5346–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Smith, J.A.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chintalapati, M.; Ammous, F.; Yu, M.; Moorjani, P.; Ganna, A.; Gross, A.; Dey, S.; et al. Polygenic Risk Scores for Alzheimer’s Disease and General Cognitive Function Are Associated with Measures of Cognition in Older South Asians. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2023, 78, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolaki, M.; Iakovidou, V.; Navrozidou, H.; Aminta, M.; Pantazi, T.; Kazis, A. Hindi Mental State Examination (HMSE) as a Screening Test for Illiterate Demented Patients. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2000, 15, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Khobragade, P.; Meijer, E.; Saxton, J. Measurement and Structure of Cognition in the Longitudinal Aging Study in India—Diagnostic Assessment of Dementia. Innov. Aging 2020, 4, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Küçükali, F.; Jansen, I.E.; Kleineidam, L.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Amin, N.; Naj, A.C.; Campos-Martin, R.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Andrade, V.; et al. New Insights into the Genetic Etiology of Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Dementias. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 412–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, D.P.; Jansen, I.E.; Savage, J.E.; Shadrin, A.A.; Bahrami, S.; Holland, D.; Rongve, A.; Børte, S.; Winsvold, B.S.; Drange, O.K.; et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study with 1,126,563 Individuals Identifies New Risk Loci for Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhao, F.; Lv, Z.P.; Zheng, C.G.; Zheng, W.D.; Sun, L.; Wang, N.N.; Pang, S.; De Andrade, F.M.; Fu, M.; et al. Association between APOC1 Polymorphism and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corder, E.H.; Saunders, A.M.; Strittmatter, W.J.; Schmechel, D.E.; Gaskell, P.C.; Small, G.W.; Roses, A.D.; Haines, J.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A. Gene Dose of Apolipoprotein E Type 4 Allele and the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease in Late Onset Families. Science 1993, 261, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, M.W.; Crenshaw, D.; Welsh-Bohmer, K.A.; Burns, D.K.; Roses, A.D. New Genetic Approaches to AD: Lessons from APOE-TOMM40 Phylogenetics. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 2016, 16, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, D.; Liao, X.; Gong, G.; Hu, J.; Fu, Y.; Cai, W. Association of Common Variants in TOMM40/APOE/APOC1 Region with Human Longevity in a Chinese Population. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 61, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkle, B.W.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Sims, R.; Bis, J.C.; Damotte, V.; Naj, A.C.; Boland, A.; Vronskaya, M.; van der Lee, S.J.; Amlie-Wolf, A.; et al. Genetic Meta-Analysis of Diagnosed Alzheimer’s Disease Identifies New Risk Loci and Implicates Aβ, Tau, Immunity and Lipid Processing. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 414–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, I.E.; Savage, J.E.; Watanabe, K.; Bryois, J.; Williams, D.M.; Steinberg, S.; Sealock, J.; Karlsson, I.K.; Hägg, S.; Athanasiu, L.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis Identifies New Loci and Functional Pathways Influencing Alzheimer’s Disease Risk. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.C.; Ibrahim-Verbaas, C.A.; Harold, D.; Naj, A.C.; Sims, R.; Bellenguez, C.; DeStafano, A.L.; Bis, J.C.; Beecham, G.W.; Grenier-Boley, B.; et al. Meta-Analysis of 74,046 Individuals Identifies 11 New Susceptibility Loci for Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1452–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Shi, B.; Peloso, G.M.; Wang, Y.; Heard-Costa, N.; Lin, H.; Pitsillides, A.N.; Sarnowski, C.; Boerwinkle, E.; De Jager, P.L.; et al. Functional Annotations-Informed Whole Genome Sequence Analysis Identifies Novel Rare Variants for AD in the Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2022, 18, e063968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, W.; Gil, L.; Hunt, S.E.; Riat, H.S.; Ritchie, G.R.S.; Thormann, A.; Flicek, P.; Cunningham, F. The Ensembl Variant Effect Predictor. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The Mutational Constraint Spectrum Quantified from Variation in 141,456 Humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; White, S.; Peng, B.; Johnson, A.D.; Brody, J.A.; Li, A.H.; Huang, Z.; Carroll, A.; Wei, P.; Gibbs, R.; et al. WGSA: An Annotation Pipeline for Human Genome Sequencing Studies. J. Med. Genet. 2015, 53, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rentzsch, P.; Witten, D.; Cooper, G.M.; Shendure, J.; Kircher, M. CADD: Predicting the Deleteriousness of Variants throughout the Human Genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D886–D894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davydov, E.V.; Goode, D.L.; Sirota, M.; Cooper, G.M.; Sidow, A.; Batzoglou, S. Identifying a High Fraction of the Human Genome to Be under Selective Constraint Using GERP++. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2010, 6, e1001025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita-Laza, I.; Mccallum, K.; Buxbaum, J. A Spectral Approach Integrating Functional Genomic Annotations for Coding and Noncoding Variants. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihab, H.A.; Rogers, M.F.; Gough, J.; Mort, M.; Cooper, D.N.; Day, I.N.M.; Gaunt, T.R.; Campbell, C. An Integrative Approach to Predicting the Functional Effects of Non-Coding and Coding Sequence Variation. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1536–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Sun, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cheung, K.H.; Zhao, H. A Statistical Framework to Predict Functional Non-Coding Regions in the Human Genome through Integrated Analysis of Annotation Data. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Levine, D.; Shen, J.; Gogarten, S.; Laurie, C.; Weir, B. A High-Performance Computing Toolset for Relatedness and Principal Component Analysis of SNP Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3326–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Gogarten, S.; Lawrence, M.; Stilp, A.; Conomos, M.; Weir, B.; Laurie, C.; Levine, D. SeqArray—A Storage-Efficient High-Performance Data Format for WGS Variant Calls. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2251–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Gaynor, S.M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, R.; Dey, R.; Arnett, D.K.; Aslibekyan, S.; et al. Dynamic Incorporation of Multiple in Silico Functional Annotations Empowers Rare Variant Association Analysis of Large Whole-Genome Sequencing Studies at Scale. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Francioli, L.C.; Goodrich, J.K.; Collins, R.L.; Kanai, M.; Wang, Q.; Alföldi, J.; Watts, N.A.; Vittal, C.; Gauthier, L.D.; et al. A Genome-Wide Mutational Constraint Map Quantified from Variation in 76,156 Human Genomes. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chételat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer Disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-C.; Liu, C.-C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer Disease: Risk, Mechanisms and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, C.A.R.; Oulhaj, A.; de Jager, C.A.; Williams, J.H. APOE Alleles Predict the Rate of Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer Disease. Neurology 2005, 65, 1888 LP–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, L.A.; Cupples, L.A.; Haines, J.L.; Hyman, B.; Kukull, W.A.; Mayeux, R.; Myers, R.H.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Risch, N.; van Duijn, C.M. Effects of Age, Sex, and Ethnicity on the Association Between Apolipoprotein E Genotype and Alzheimer Disease: A Meta-Analysis. JAMA 1997, 278, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulminski, A.M.; Shu, L.; Loika, Y.; Nazarian, A.; Arbeev, K.; Ukraintseva, S.; Yashin, A.; Culminskaya, I. APOE Region Molecular Signatures of Alzheimer’s Disease across Races/Ethnicities. Neurobiol. Aging 2020, 87, e1–e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Zhao, W.; Yu, M.; Rumfelt, K.E.; Moorjani, P.; Ganna, A.; Dey, A.B.; Lee, J.; Kardia, S.L.R. Association Between Episodic Memory and Genetic Risk Factors for Alzheimer’s Disease in South Asians from the Longitudinal Aging Study in India-Diagnostic Assessment of Dementia (LASI-DAD). J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2020, 68 (Suppl. 3), S45–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirova, A.-M.; Bays, R.B.; Lagalwar, S. Working Memory and Executive Function Decline across Normal Aging, Mild Cognitive Impairment, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 748212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.-T. The Role of PICALM in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengel-From, J.; Christensen, K.; McGue, M.; Christiansen, L. Genetic Variations in the CLU and PICALM Genes Are Associated with Cognitive Function in the Oldest Old. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, e7–e554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Reich, D.; Thangaraj, K.; Patterson, N.; Price, A.L.; Singh, L. Reconstructing Indian Population History. Nature 2009, 461, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Feng, R.; Jiang, Q. PICALM Rs3851179 Variant Confers Susceptibility to Alzheimer’s Disease in Chinese Population. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 3131–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankarappa, B.M.; Kota, L.N.; Purushottam, M.; Nagpal, K.; Mukherjee, O.; Viswanath, B.; Varghese, M.; Bharath, S.; Jain, S. Effect of CLU and PICALM Polymorphisms on AD Risk: A Study from South India. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2017, 27, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mencacci, N.E.; Brockmann, M.M.; Dai, J.; Pajusalu, S.; Atasu, B.; Campos, J.; Pino, G.; Gonzalez-Latapi, P.; Patzke, C.; Schwake, M.; et al. Biallelic Variants in TSPOAP1, Encoding the Active-Zone Protein RIMBP1, Cause Autosomal Recessive Dystonia. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suthar, S.K.; Alam, M.M.; Lee, J.; Monga, J.; Joseph, A.; Lee, S.-Y. Bioinformatic Analyses of Canonical Pathways of TSPOAP1 and Its Roles in Human Diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 667947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Jia, X.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Bai, S.; Rampes, S.; Vizcaychipi, M.P.; Wu, C.; Wang, K.; et al. Inflammation Disrupts the Brain Network of Executive Function after Cardiac Surgery. Ann. Surg. 2021, 277, e689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, G.R.; Chung, J.; Mez, J.; Barber, R.; Beecham, G.W.; Bennett, D.A.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Byrd, G.S.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Crane, P.K.; et al. Transethnic Genome-Wide Scan Identifies Novel Alzheimer’s Disease Loci. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017, 13, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dib, S.; Pahnke, J.; Gosselet, F. Role of ABCA7 in Human Health and in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltschmidt, B.; Helweg, L.P.; Greiner, J.F.W.; Kaltschmidt, C. NF-ΚB in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Recent Evidence from Human Genetics. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 954541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Yoon, S.Y.; Leung, L.; Knoferle, J.; Huang, Y. Cellular Source-Specific Effects of Apolipoprotein (Apo) E4 on Dendrite Arborization and Dendritic Spine Development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Sung, B.H.; Cho, I.H.; Kim, S.M.; Song, W.K. NESH Regulates Dendritic Spine Morphology and Synapse Formation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karahan, H.; Smith, D.C.; Kim, B.; Dabin, L.C.; Al-Amin, M.M.; Sagara Wijeratne, H.R.; Pennington, T.; Prisco, G.V.d.; McCord, B.; Lin, P.B.C.; et al. Deletion of Abi3 Gene Locus Exacerbates Neuropathological Features of Alzheimer’s Disease in a Mouse Model of Aβ Amyloidosis. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogelgsang, J.; Vukovich, R.; Wedekind, D.; Wiltfang, J. Higher Level of Mismatch in APOE E4 Carriers for Amyloid-Beta Peptide Alzheimer’s Disease Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid. ASN Neuro 2019, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, H.I.L.; Gronenschild, E.H.B.M.; Evers, E.A.T.; Ramakers, I.H.G.B.; Hofman, P.A.M.; Backes, W.H.; Jolles, J.; Verhey, F.R.J.; Van Boxtel, M.P.J. Visuospatial Processing in Early Alzheimer’s Disease: A Multimodal Neuroimaging Study. Cortex 2015, 64, 394–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J. The Immune-Modulatory Role of Apolipoprotein E with Emphasis on Multiple Sclerosis and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2010, 2010, 186813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, J.T.; Mulazzani, E.; Nutt, S.L.; Masters, S.L. The Role of PLCγ2 in Immunological Disorders, Cancer, and Neurodegeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Bokil, N.J.; Wall, A.A.; Kapetanovic, R.; Lansdaal, N.M.; Marceline, F.; Burgess, B.J.; Tong, S.J.; Guo, Z.; Alexandrov, K.; et al. SCIMP Is a Transmembrane Non-TIR TLR Adaptor That Promotes Proinflammatory Cytokine Production from Macrophages. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Turck, C.W.; Kurosaki, T.; Chan, A.C. BLNK: A Central Linker Protein in B Cell Activation. Immunity 1998, 9, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, D.P.; Savage, J.E.; de Leeuw, C.A.; Jansen, I.E.; Posthuma, D. Rare Variant Aggregation in 148,508 Exomes Identifies Genes Associated with Proxy Dementia. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenguez, C.; Charbonnier, C.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Quenez, O.; Le Guennec, K.; Nicolas, G.; Chauhan, G.; Wallon, D.; Rousseau, S.; Richard, A.C.; et al. Contribution to Alzheimer’s Disease Risk of Rare Variants in TREM2, SORL1, and ABCA7 in 1779 Cases and 1273 Controls. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 59, e1–e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorman, S.M.; Carr, K.; Greenfield, E.A. Childhood Socioeconomic Status and Genetic Risk for Poorer Cognition in Later Life. Soc. Sci. Med. 2018, 212, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulick, E.R.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Boehme, A.K.; Joyce, N.R.; Schupf, N.; Kaufman, J.D.; Mayeux, R.; Manly, J.J.; Wellenius, G.A. Long-Term Exposure to Ambient Air Pollution, APOE-Ε4 Status, and Cognitive Decline in a Cohort of Older Adults in Northern Manhattan. Environ. Int. 2020, 136, 105440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifan, A.; Schelke, M.; Obeng-Aduasare, Y.; Isaacson, R. Early Life Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s Disease—A Critical Review. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 45, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.H.; Manczak, M.; Yin, X.; Grady, M.C.; Mitchell, A.; Tonk, S.; Kuruva, C.S.; Bhatti, J.S.; Kandimalla, R.; Vijayan, M.; et al. Protective Effects of Indian Spice Curcumin Against Amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 61, 843–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.; Ee, N.; Peters, J.; Booth, A.; Mudway, I.; Anstey, K.J. Air Pollution and Dementia: A Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 70, S145–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambhir, I.S.; Khurana, V.; Kishore, D.; Sinha, A.K.; Mohapatra, S.C. A Clinico-Epidemiological Study of Cognitive Function Status of Community-Dwelling Elderly. Indian J. Psychiatry 2014, 56, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Ostbye, T.; Vorderstrasse, A.A.; Dupre, M.E.; Wu, B. Place of Residence and Cognitive Function among the Adult Population in India. Neuroepidemiology 2018, 50, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belessiotis-Richards, C.; Livingston, G.; Marston, L.; Mukadam, N. A Cross-Sectional Study of Potentially Modifiable Risk Factors for Dementia and Cognitive Function in India: A Secondary Analysis of 10/66, LASI, and SAGE Data. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2022, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhao, W.; Moorjani, P.; Gross, A.L.; Zhou, X.; Dey, A.B.; Lee, J.; Smith, J.A.; Kardia, S.L.R. Effect of Apolipoprotein E Ε4 and Its Modification by Sociodemographic Characteristics on Cognitive Measures in South Asians from LASI-DAD. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2024, 20, 4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, J.; Jain, U.; Khobragade, P.; Weerman, B.; Hu, P.; Chien, S.; Dey, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Saxton, J.; Keller, B.; et al. Methodological Considerations in Designing and Implementing the Harmonized Diagnostic Assessment of Dementia for Longitudinal Aging Study in India (LASI-DAD). Biodemography Soc. Biol. 2020, 65, 189–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, D.; Choudhury, A.; Basu, A.; Ramsay, M. Population Stratification and Underrepresentation of Indian Subcontinent Genetic Diversity in the 1000 Genomes Project Dataset. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsuka, N.; Moorjani, P.; Rai, N.; Sarkar, B.; Tandon, A.; Patterson, N.; Bhavani, G.S.; Girisha, K.M.; Mustak, M.S.; Srinivasan, S.; et al. The Promise of Discovering Population-Specific Disease-Associated Genes in South Asia. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Covariate | Count (%) or Mean (SD) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 69.6 (7.3) |
| Sex (female) | 1408 (52.5) |
| Literacy (cannot read or write) | 1511 (56.4) |
| Location | |
| Rural | 1697 (63.3) |
| Urban | 983 (36.7) |
| Education | |
| Less than lower secondary | 2004 (75) |
| Upper secondary and vocational training | 578 (22) |
| Tertiary | 98 (4) |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) * | |
| Underweight (<18 kg/m2) | 401 (16.2) |
| Normal weight (18 to <23 kg/m2) | 1002 (40.5) |
| Overweight (23 to <25 kg/m2) | 370 (15.0) |
| Obese (≥25 kg/m2) | 701 (28.3) |
| Alcohol consumption * | |
| No | 2482 (92.6) |
| Yes | 183 (6.8) |
| Smoking * | |
| Never | 2062 (76.9) |
| Former | 175 (6.5) |
| Current | 427 (15.9) |
| Physical activity * | |
| No | 2231 (83.2) |
| Yes | 433 (16.2) |
| Psychiatric medication use * | |
| No | 2664 (99.4) |
| Yes | 6 (0.2) |
| AD/dementia medication use * | |
| No | 2661 (99.3) |
| Yes | 8 (0.3) |
| HMSE score | 22.7 (5.4) |
| Analysis | Minimum | Q1 | Median | Q3 | Maximum | Number of Genes | Number of SNVs with MAF > 0 | Total Number of SNVs Analyzed * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Missense/LoF | 3 | 15 | 23 | 40 | 178 | 77 | 2510 | 2507 |
| Missense | 3 | 14 | 21 | 38 | 167 | 77 | 2442 | 2439 |
| LoF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 11 | 36 | 68 | 68 |
| Promoter/Enhancer | 6 | 61 | 93 | 127 | 265 | 77 | 7402 | 7370 |
| Promoter | 6 | 59 | 91 | 125 | 231 | 77 | 7108 | 7077 |
| Enhancer | 29 | 37.25 | 48 | 62 | 88 | 10 | 509 | 508 |
| Gene | Model | Number of SNVs Analyzed | p-Value (Without Annotation Weights) | p-Value (with Annotation Weights) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMSE Score | ||||
| APOE | Model 1 | 20 | 9.5 × 10−4 * | 0.001 * |
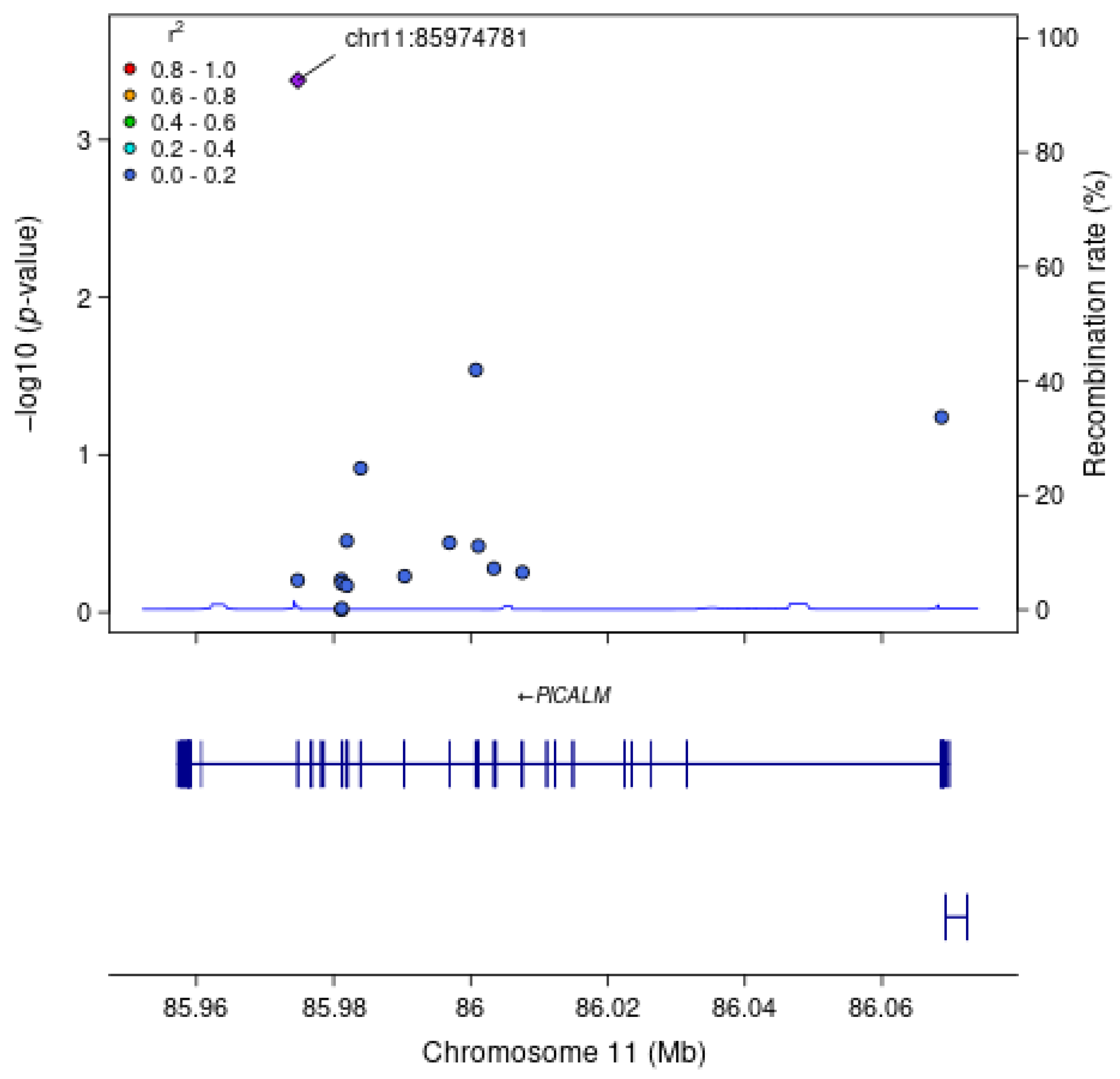
| PICALM | Model 1 | 16 | 0.002 * | 0.002 * |
| PICALM | Model 2 | 16 | 0.001 * | 0.001 * |
| General Cognitive Function | ||||
| APOE | Model 1 | 20 | 5.6 × 10−4 * | 7.8 × 10−4 * |
| Executive Function | ||||
| APOE | Model 1 | 20 | 0.002 * | 0.002 |
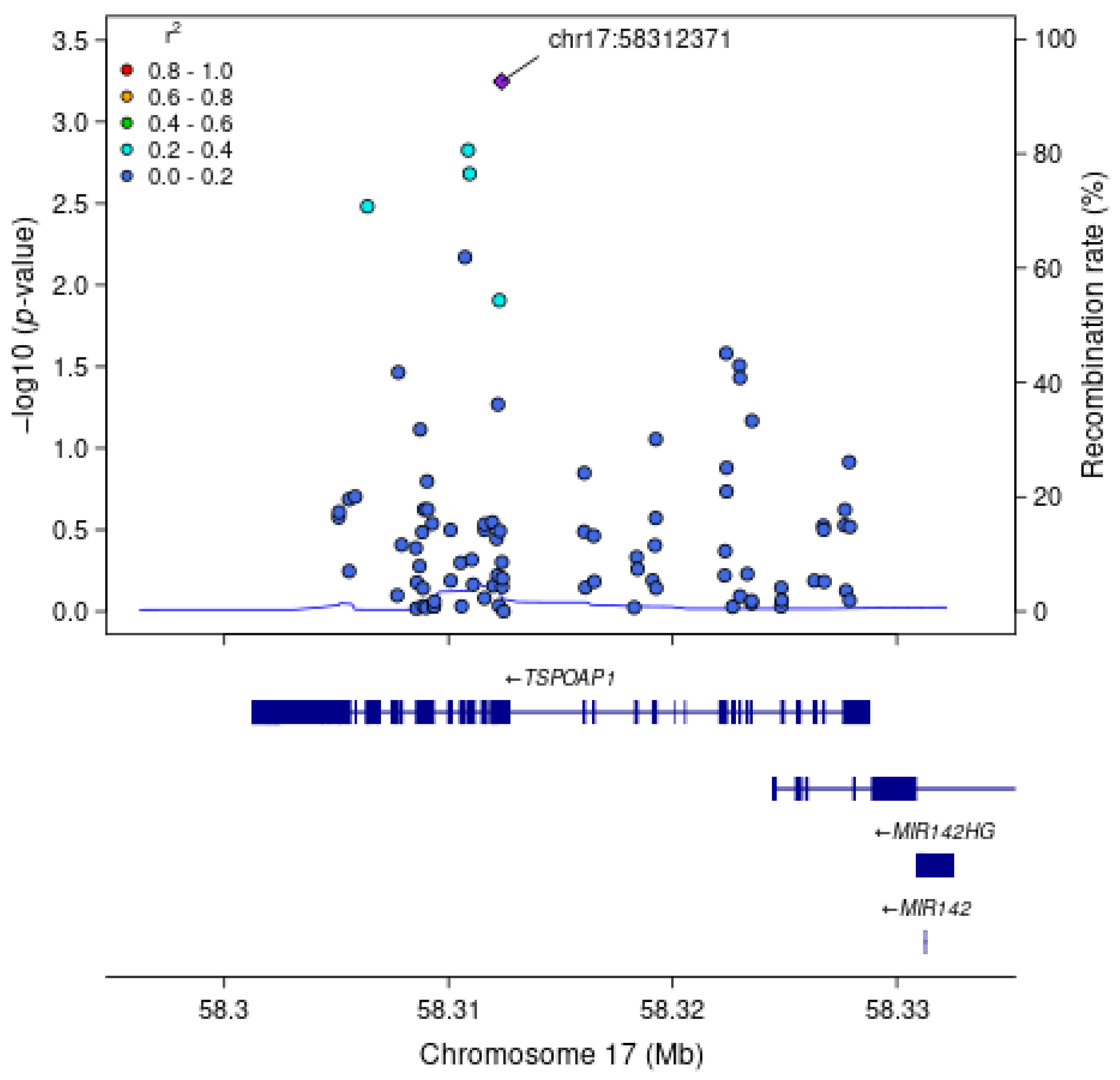
| TSPOAP1 | Model 1 | 89 | 0.002 * | 0.004 |
| Orientation | ||||
| APOE | Model 1 | 20 | 9.3 × 10−4 * | 0.001 * |
| Cognitive Function | Model | rsID | ID | Gene | Allele (Effect Direction) | AF in LASI-DAD | AF in EA gnomAD | SNV Functional Annotation | Position in Gene | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMSE Score | Model 1 | rs429358 | 19:44908684:T:C | APOE | C (−) | 0.11 | 0.15 | Missense | Exon 4 | 2.9 × 10−4 |
| HMSE Score | Model 1 | rs779406084 | 11:85974781:G:A | PICALM | A (−) | 0.00075 | 0.000015 | Missense | Exon 19 | 4.2 × 10−4 |
| HMSE Score | Model 2 | rs779406084 | 11:85974781:G:A | PICALM | A (−) | 0.00075 | 0.000015 | Missense | Exon 19 | 1.6 × 10−4 |
| General Cognitive Function | Model 1 | rs429358 | 19:44908684:T:C | APOE | C (−) | 0.11 | 0.15 | Missense | Exon 4 | 1.4 × 10−4 |
| Executive Function | Model 1 | rs429358 | 19:44908684:T:C | APOE | C (−) | 0.11 | 0.15 | Missense | Exon 4 | 4.1 × 10−4 |
| Executive Function | Model 1 | rs9913145 | 17:58312371:T:C | TSPOAP1 | C (+) | 0.15 | 0.12 | Missense | Exon 17 | 5.7 × 10−4 |
| Orientation | Model 1 | rs429358 | 19:44908684:T:C | APOE | C (−) | 0.11 | 0.15 | Missense | Exon 4 | 2.4 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu-Amara, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Leung, Y.Y.; Schellenberg, G.D.; Wang, L.-S.; Moorjani, P.; Dey, A.B.; Dey, S.; Zhou, X.; et al. Region-Based Analysis with Functional Annotation Identifies Genes Associated with Cognitive Function in South Asians from India. Genes 2025, 16, 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060640
Abu-Amara H, Zhao W, Li Z, Leung YY, Schellenberg GD, Wang L-S, Moorjani P, Dey AB, Dey S, Zhou X, et al. Region-Based Analysis with Functional Annotation Identifies Genes Associated with Cognitive Function in South Asians from India. Genes. 2025; 16(6):640. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060640
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu-Amara, Hasan, Wei Zhao, Zheng Li, Yuk Yee Leung, Gerard D. Schellenberg, Li-San Wang, Priya Moorjani, Aparajit B. Dey, Sharmistha Dey, Xiang Zhou, and et al. 2025. "Region-Based Analysis with Functional Annotation Identifies Genes Associated with Cognitive Function in South Asians from India" Genes 16, no. 6: 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060640
APA StyleAbu-Amara, H., Zhao, W., Li, Z., Leung, Y. Y., Schellenberg, G. D., Wang, L.-S., Moorjani, P., Dey, A. B., Dey, S., Zhou, X., Gross, A. L., Lee, J., Kardia, S. L. R., & Smith, J. A. (2025). Region-Based Analysis with Functional Annotation Identifies Genes Associated with Cognitive Function in South Asians from India. Genes, 16(6), 640. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060640






