Genome-Wide Identification of CaPLATZ Family Members in Pepper and Their Expression Profiles in Response to Drought Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genomic Identification of CaPLATZ Genes in Pepper
2.2. Phylogenic Analysis
2.3. Analysis of Synteny and Homologous Gene Pairs
2.4. Analysis of CaPLATZ Gene Structures and Phylogenetics
2.5. Identification of Cis-Regulatory Elements in CaPLATZ Genes
2.6. Plant Materials and Stress Treatment Protocols
2.7. Expression Analysis for CaPLATZ Genes
3. Results
3.1. Identification of CaPLATZ Members in Pepper
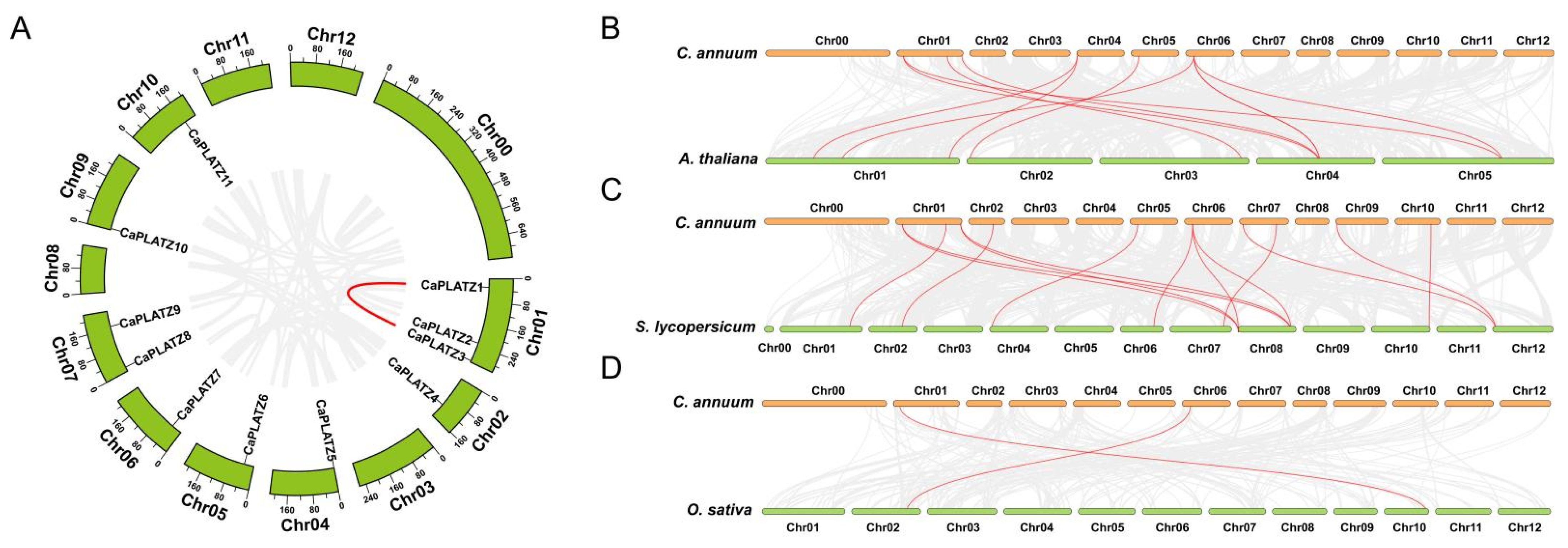
3.2. Duplication Modes and Collinearity Analysis of the CaPLATZ Gene Family in Pepper
3.3. Gene Structure Analysis of the CaPLATZ Genes in Pepper
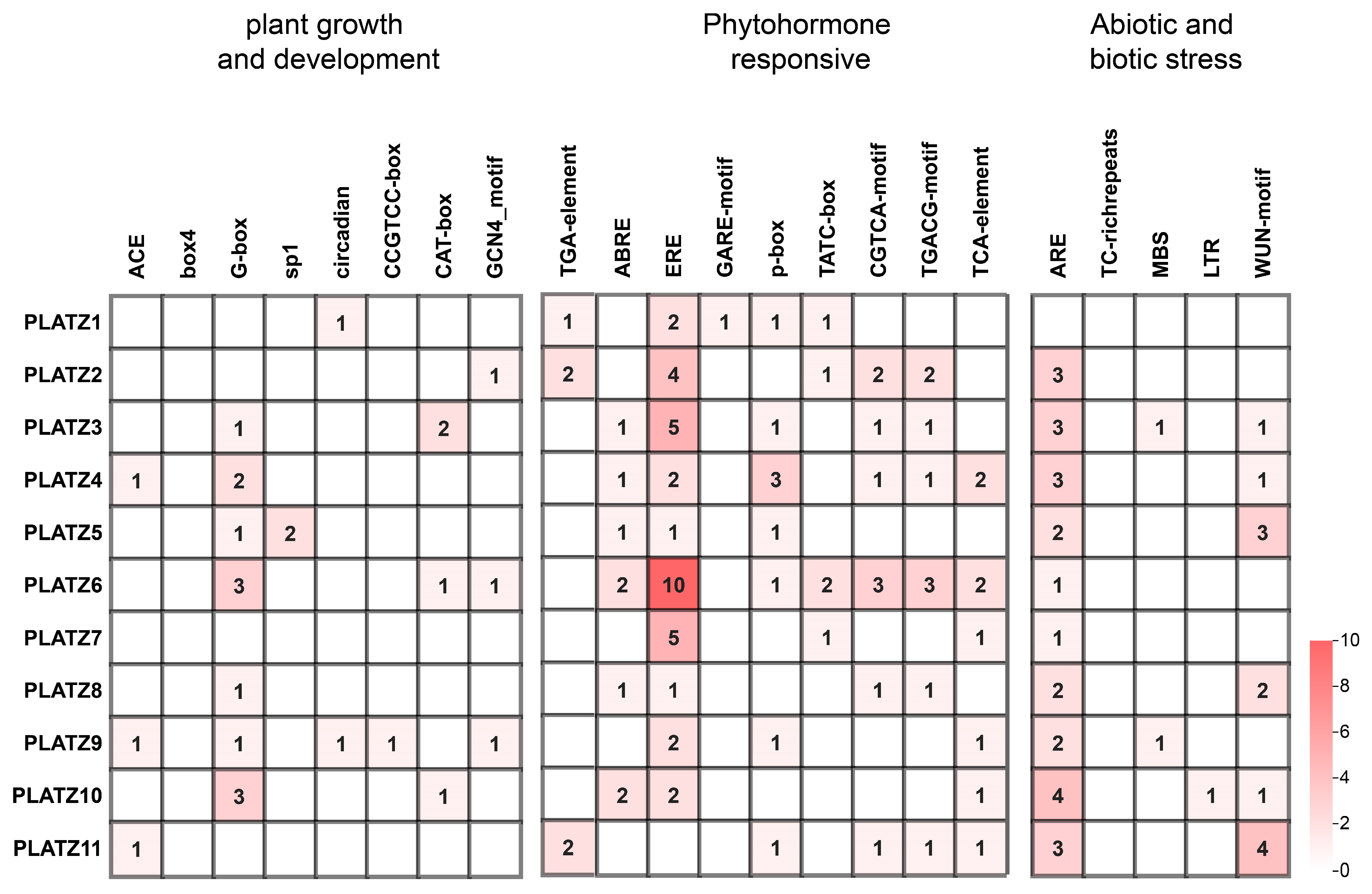
3.4. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements in CaPLATZ Promoter Regions in Pepper
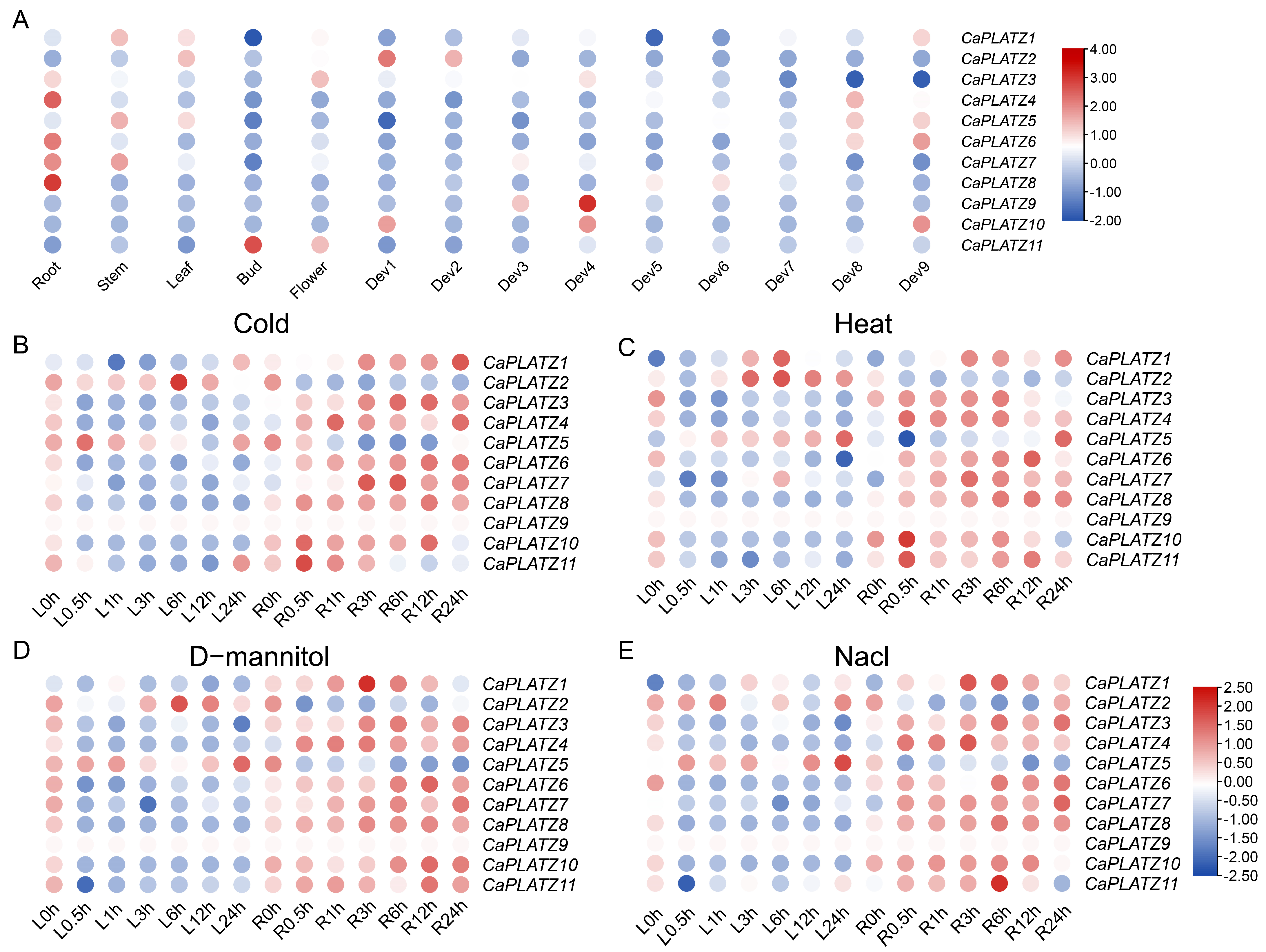
3.5. Expression Analysis of the CaPLATZ Genes in Pepper
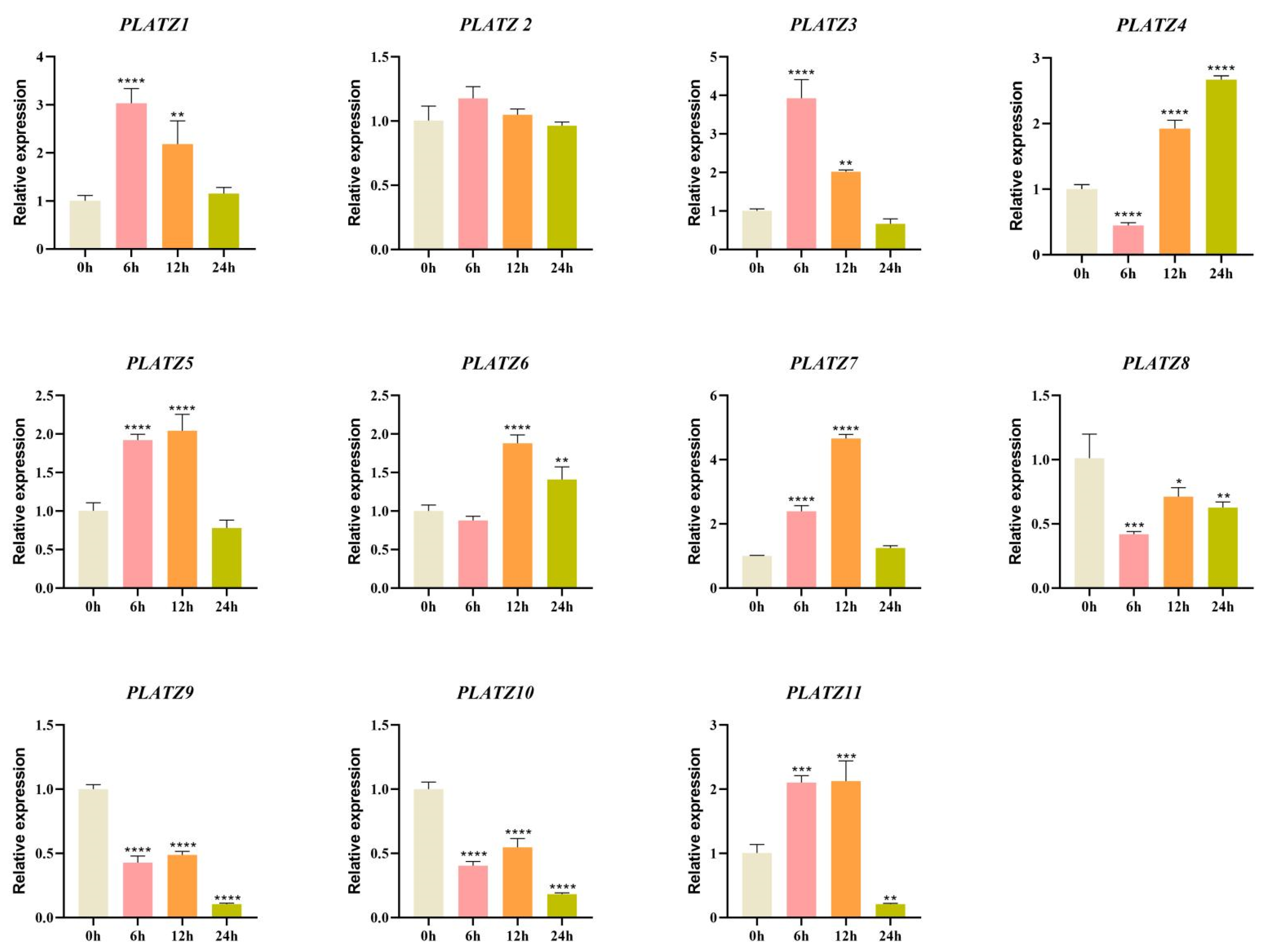
3.6. Expression Patterns of CaPLATZ Genes Under Drought Stress
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Tol, N.; Van der Zaal, B.J. Artificial transcription factor-mediated regulation of gene expression. Plant Sci. 2014, 225, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noman, A.; Aqeel, M.; Khalid, N.; Islam, W.; Sanaullah, T.; Anwar, M.; Khan, S.; Ye, W.; Lou, Y. Zinc finger protein transcription factors: Integrated line of action for plant antimicrobial activity. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samoluk, S.S.; Seijo, G. Genome-wide analysis of the PLATZ gene family provides insights into the genome evolution of cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea, Leguminosae). Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2025, 72, 4809–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azim, J.B.; Khan, M.F.H.; Hassan, L.; Robin, A.H.K. Genome-Wide Characterization and Expression Profiling of Plant-Specific PLATZ Transcription Factor Family Genes in Brassica rapa L. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 28–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Gao, Z.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Xu, X.; et al. Functional prediction of tomato PLATZ family members and functional verification of SlPLATZ17. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Liu, M.; Fang, Z.; Ma, D.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, J. Genome-wide Analysis of a Plant AT-rich Sequence and Zinc-binding Protein (PLATZ) in Triticum Aestivum. Phyton 2021, 90, 971–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liang, J.; Luo, J.; Yang, F.; Feng, P.; Wang, H.; Guo, B.; Ma, F.; Zhao, T. Identification of PLATZ genes in Malus and expression characteristics of MdPLATZs in response to drought and ABA stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1109784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Rong, H.; Tian, Y.; Qu, Y.; Xu, M.; Xu, L. Genome-Wide Identification of PLATZ Transcription Factors in Ginkgo biloba L. and their expression characteristics during seed development. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 946194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zheng, L.; Wei, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, F.; Ma, Y.; Xu, Z. The soybean PLATZ transcription factor GmPLATZ17 suppresses drought tolerance by interfering with stress-associated gene regulation of GmDREB5. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1014–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Jun, S.E.; Park, S.; Timilsina, R.; Kwon, D.S.; Kim, Y.; Park, S.; Hwang, J.Y.; Nam, H.G.; et al. ORESARA15, a PLATZ transcription factor, mediates leaf growth and senescence in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2018, 220, 609–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Han, X.; Benfey, P.N. RGF1 controls root meristem size through ROS signalling. Nature 2020, 577, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iocco-corena, P.; Chaïb, J.; Torregrosa, L.; Mackenzie, D.; Thomas, M.R.; Smith, H.M. VviPLATZ1 is a major factor that controls female flower morphology determination in grapevine. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Hou, Q.; Si, L.; Huang, X.; Luo, J.; Lu, D.; Zhu, J.; Shangguan, Y.; Miao, J.; Xie, Y.; et al. The PLATZ Transcription Factor GL6 Affects Grain Length and Number in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2019, 180, 2077–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, L.; Tao, J.; Cheng, T.; Jin, M.; Wang, Z.; Wei, J.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, W.; et al. Global analysis of seed transcriptomes reveals a novel PLATZ regulator for seed size and weight control in soybean. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 2436–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-morales, S.I.; Chávez-montes, R.A.; Hayano-kanashiro, C.; Alejo-jacuinde, G.; Rico-cambron, T.Y.; De folter, S.; Herrera-estrella, L. Regulatory network analysis reveals novel regulators of seed desiccation tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E5232–E5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Ji, Z.; Lu, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Huang, J.; Yang, G.; Yan, K.; Zhang, S.; et al. Regulation of drought tolerance in Arabidopsis involves the PLATZ4-mediated transcriptional repression of plasma membrane aquaporin PIP2;8. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 115, 434–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lan, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, H.; Xiang, Y. PhePLATZ1, a PLATZ transcription factor in moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis), improves drought resistance of transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 186, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, R.; Huo, Y.; Liu, S.; Yang, G.; Huang, J.; Zheng, C.; Wu, C. Expression of cotton PLATZ1 in transgenic Arabidopsis reduces sensitivity to osmotic and salt stress for germination and seedling establishment associated with modification of the abscisic acid, gibberellin, and ethylene signalling pathways. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Chang, Y.; Han, K.; Gao, Y.; Xie, J. Characterization of GPX Gene Family in Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) under Abiotic Stress and ABA Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Yu, C.; Shen, Y.; Fang, X.; Chen, L.; Min, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, S.; Xu, M.; Luo, Y.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of cultivated and wild peppers provides insights into Capsicum domestication and specialization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 40–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A one for all, all for one bioinformatics platform for biological. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 7–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yu, H.; Deng, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, M.; Ou, L.; Yang, B.; Dai, X.; Ma, Y.; Feng, S.; et al. PepperHub, an Informatics Hub for the Chili Pepper Research Community. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1129–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianyang, L.; Fei, H.; Guoqing, Z.; Mingna, L.; Ruicai, L.; Junmei, K.; Qingchuan, Y.; Lin, C. Genome-Wide Identification and Phylogenetic and Expression Analyses of the PLATZ Gene Family in Medicago sativa L. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2388. [Google Scholar]
- Jiahui, Q.; Hui, W.; Xinyi, W.; Muhammad, N.; Ya, W.; Dayong, L.; Fengming, S. Genome-wide characterization of the PLATZ gene family in watermelon (Citrullus lanatus L.) with putative functions in biotic and abiotic stress response. Plant Physiol. Biochem. PPB 2023, 201, 107854. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Zhu, G.; Meng, Q.; Zeng, J.; He, X.; Liu, W. Comprehensive analysis of PLATZ family genes and their responses to abiotic stresses in Barley. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; He, W.; Dai, Z.; Xie, D.; Sun, J. Genome-Wide Analysis of the PLATZ Gene Family and Identification of Seed Development-Related Genes in Flax [Linum usitatissimum L.]. J. Nat. Fibers 2024, 21, 2321534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Du, H.; Chen, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhu, F.; Chen, H.; Meng, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, P.; Zheng, L.; et al. The Chromosome-Level Genome Sequence of the Autotetraploid Alfalfa and Resequencing of Core Germplasms Provide Genomic Resources for Alfalfa Research. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1250–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hobson, N.; Galindo, L.; Zhu, S.; Shi, D.; Mcdill, J.; Yang, L.; Hawkins, S.; Neutelings, G.; Datla, R.; et al. The genome of flax (Linum usitatissimum) assembled de novo from short shotgun sequence reads. Plant J. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 72, 73–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, N.; Jiang, W. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the PLATZ Transcription Factor in Tomato. Plants 2023, 12, 2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, P.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. Genome-wide analysis of the LBD family in rice: Gene functions, structure and evolution. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 153, 106452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi-shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Organization of cis-acting regulatory elements in osmotic- and cold-stress-responsive promoters. Trends. Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhao, X.; Bürger, M.; Chory, J.; Wang, X. The role of ethylene in plant temperature stress response. Trends. Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 808–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghunath, A.; Sundarraj, K.; Nagarajan, R.; Arfuso, F.; Bian, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Perumal, E. Antioxidant response elements: Discovery, classes, regulation and potential applications. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, O.; Singh, P.C.; Bhatia, R. A review on drought stress in plants: Implications, mitigation and the role of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 5, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Number | Gene ID | Gene Name | Chr | Start | Stop | Strand | Size (aa) | MWs (Da) | pI | Loc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CaPLATZ1 | Capana01g001082 | 1 | 29,898,510 | 29,900,326 | − | 231 | 25,991.48 | 9.30 | nucl |
| 2 | CaPLATZ2 | Capana01g003577 | 1 | 229,778,174 | 229,780,086 | − | 241 | 27,134.36 | 8.93 | nucl |
| 3 | CaPLATZ3 | Capana01g004338 | 1 | 296,584,241 | 296,586,323 | − | 182 | 20,484.66 | 9.73 | nucl |
| 4 | CaPLATZ4 | Capana02g001147 | 2 | 111,660,814 | 111,663,906 | − | 240 | 27,282.98 | 6.16 | nucl |
| 5 | CaPLATZ5 | Capana04g000021 | 4 | 366,427 | 367,644 | − | 242 | 27,830.56 | 8.25 | nucl |
| 6 | CaPLATZ6 | Capana05g000900 | 5 | 34,861,705 | 34,865,244 | + | 174 | 20,057.15 | 8.84 | nucl |
| 7 | CaPLATZ7 | Capana06g001532 | 6 | 36,555,377 | 36,556,697 | − | 245 | 27,769.75 | 9.30 | nucl |
| 8 | CaPLATZ8 | Capana07g000312 | 7 | 15,338,566 | 15,340,312 | − | 204 | 23,382.8 | 7.05 | chlo |
| 9 | CaPLATZ9 | Capana07g001262 | 7 | 168,116,678 | 168,126,780 | + | 189 | 21,752.29 | 8.75 | cyto |
| 10 | CaPLATZ10 | Capana09g000109 | 9 | 4,956,382 | 4,957,541 | − | 247 | 28,113.13 | 8.30 | nucl |
| 11 | CaPLATZ11 | Capana10g001532 | 10 | 163,187,426 | 163,189,479 | + | 204 | 22,819.09 | 8.97 | nucl |
| Motif | Length (aa) | Best Possible Match |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 41 | HKDHRLJQIRRYVYHDVVRLNEIZKYJDCSSVQTYIINSAK |
| 2 | 35 | KPPWLKPLLKEKFFVACKIHEDAKKNEKNMYCLDC |
| 3 | 29 | KGVTNTCEICERSLLDSFRFCSLGCKVVG |
| 4 | 17 | NYKTMKRRKGIPHRAPL |
| 5 | 11 | VVFLNERPQPR |
| 6 | 41 | FLRRCTTLQLGPDFFIPNDMGDDDMANETAHSTIVDSDEPW |
| 7 | 14 | NKIQSFSPSTPPPT |
| 8 | 11 | NLALCPHCLSS |
| 9 | 21 | VMSFPCTEFVRKKRSGLHVCG |
| 10 | 17 | TSKNFVKKPKQSPEKKR |
| 1 | 41 | HKDHRLJQIRRYVYHDVVRLNEIZKYJDCSSVQTYIINSAK |
| 2 | 35 | KPPWLKPLLKEKFFVACKIHEDAKKNEKNMYCLDC |
| 3 | 29 | KGVTNTCEICERSLLDSFRFCSLGCKVVG |
| 4 | 17 | NYKTMKRRKGIPHRAPL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Yang, N.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H. Genome-Wide Identification of CaPLATZ Family Members in Pepper and Their Expression Profiles in Response to Drought Stress. Genes 2025, 16, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060632
Wang X, Huang Y, Yang N, Wang X, Wang Y, Ma W, Zhang H. Genome-Wide Identification of CaPLATZ Family Members in Pepper and Their Expression Profiles in Response to Drought Stress. Genes. 2025; 16(6):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060632
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xingliang, Yue Huang, Na Yang, Xue Wang, Yuanqian Wang, Wenyao Ma, and Hui Zhang. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification of CaPLATZ Family Members in Pepper and Their Expression Profiles in Response to Drought Stress" Genes 16, no. 6: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060632
APA StyleWang, X., Huang, Y., Yang, N., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Ma, W., & Zhang, H. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification of CaPLATZ Family Members in Pepper and Their Expression Profiles in Response to Drought Stress. Genes, 16(6), 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16060632





