Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Pyrrhalta aenescens Fairmaire in Response to 20-Hydroxyecdysone Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing
2.2. 20E Treatment and Sample Collection
2.3. RNA Sequencing
2.4. Small RNA Analyses and miRNA Identification
2.5. Differential miRNA Expression Analyses
2.6. Target Gene Prediction and Functional Analyses
2.7. miRNA Expression Profile Validation
3. Results
3.1. Small RNA-Seq Data Analyses
3.2. DEM Identificaiton
3.3. Prediction and Functional Analyses of DEM Targets
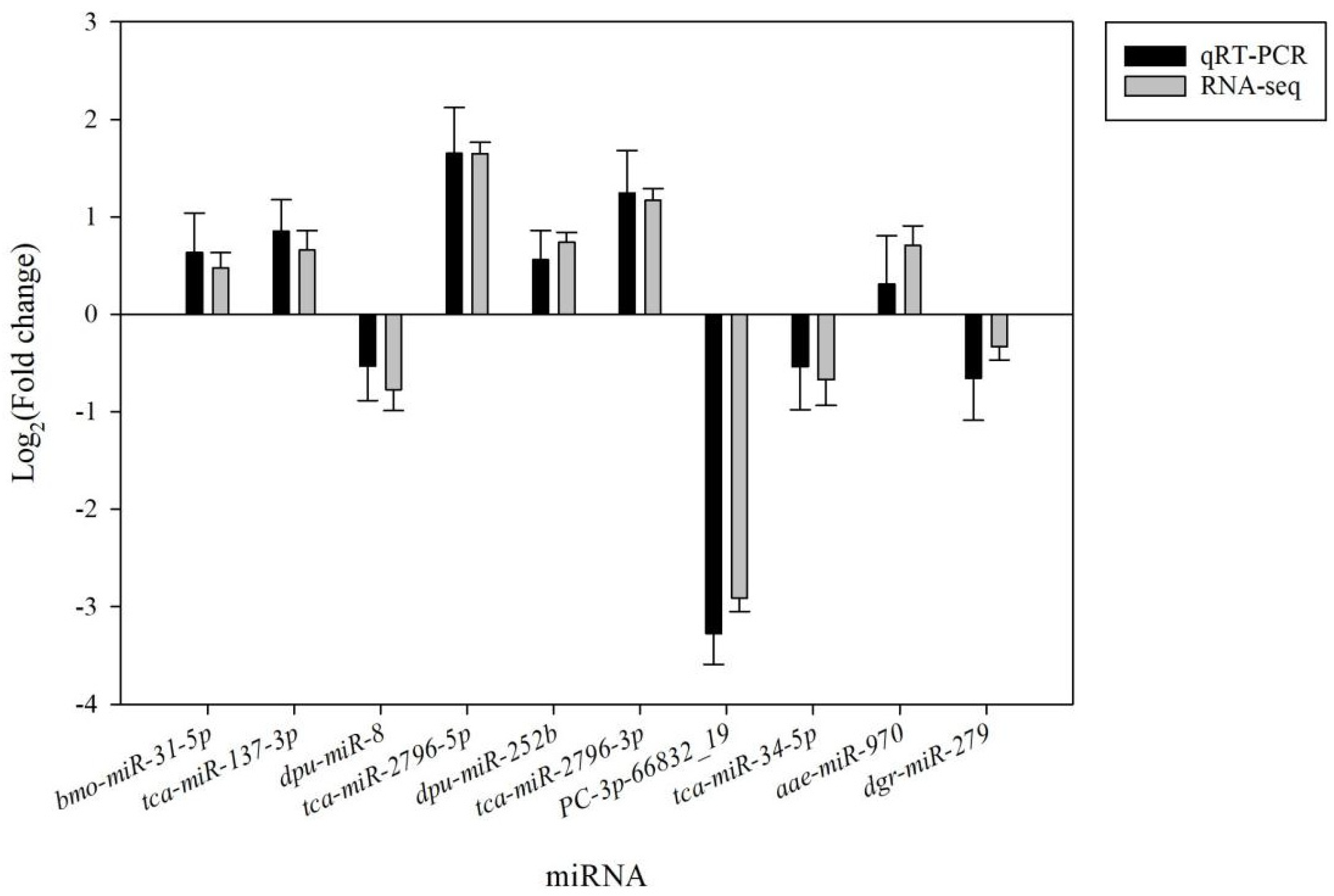
3.4. Validation of Small RNA-Seq Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, W.Q.; Wang, S.J.; Zhao, J.Q.; Duan, J.P. Observation of biological characteristics and prevention methods in Pyrrhalta aenescens. J. Inner Mong. For. 2015, 9, 14–15. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.J.; Si, Q.; Zhang, L.Y.; Hua, P.C.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, Y.Y. Laboratory toxicity and field efficacy of four insecticides against Pyrrhalta aenescens larva in Hohhot. Plant Prot. 2023, 49, 369–372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Humujiletu, L.; Xi, W.; Li, N.; Wu, X.H.; Wei, C.G.; Zhang, Y. Research progress on characteristics and biological control of two elm leaf beetles. J. Inner Mong. For. Sci. Technol. 2019, 45, 51–55. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shen, T.T.; Shen, T. Integrated control techniques of Pyrrhalta aenescens. Modern Horti. 2025, 48, 80–81, 84. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Wang, S.J.; Tian, X. Plant Diseases and Pests in Hohhot Gardens; China Forestry Press: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 115–116. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, W.; Nie, R.E.; Li, W.Z.; Segraves, K.A.; Yang, X.K.; Xue, H.J. Comparative transcriptome analysis of chemosensory genes in two sister leaf beetles provides insights into chemosensory speciation. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 79, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.P.; Forman, B.M.; Jiang, Z.; Cherbas, L.; Chen, J.D.; McKeown, M.; Cherbas, P.; Evans, R.M. Functional ecdysone receptor is the product of EcR and ultraspiracle genes. Nature 1993, 366, 476–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Rewitz, K.F.; O’Connor, M.B. Ecdysone control of developmental transitions: Lessons from drosophila research. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N. Ecdysteroid signalling in insects—From biosynthesis to gene expression regulation. Adv. Insect Physiol. 2021, 60, 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cáceres, L.; Necakov, A.S.; Schwartz, C.; Kimber, S.; Roberts, I.J.H.; Krause, H.M. Nitric oxide coordinates metabolism, growth, and development via the nuclear receptor E75. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1476–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayukawa, T.; Nagamine, K.; Ito, Y.; Nishita, Y.; Ishikawa, Y.; Shinoda, T. Krüppel Homolog 1 Inhibits Insect Metamorphosis via Direct Transcriptional Repression of Broad-Complex, a Pupal Specifier Gene. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierceall, W.E.; Li, C.; Biran, A.; Miura, K.; Raikhel, A.S.; Segraves, W.A. E75 expression in mosquito ovary and fat body suggests reiterative use of ecdysone-regulated hierarchies in development and reproduction. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 1999, 150, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beachum, A.N.; Whitehead, K.M.; McDonald, S.I.; Phipps, D.N.; Berghout, H.E.; Ables, E.T. Orphan nuclear receptor ftz-f1 (NR5A3) promotes egg chamber survival in the Drosophila ovary. G3 Bethesda 2021, 11, jkab003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, K.; Tian, L.; Li, S. 20-Hydroxyecdysone-induced transcriptional activity of FoxO upregulates brummer and acid lipase-1 and promotes lipolysis in Bombyx fat body. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.H.; Zhang, N.; Jiang, H.; Meng, X.K.; Ge, H.C.; Yang, X.M.; Xu, X.; Qian, K.; Park, Y.; Zheng, Y.; et al. 20-hydroxyecdysone regulates expression of methioninesulfoxide reductases through transcription factor FOXO in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 131, 103546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Yang, H.H.; Chen, X.X.; Zhang, J.Y.; Huang, L.Q. Genomic transcriptional response to 20-hydroxyecdysone in the fat body of silkworm, Bombyx mori. Gene Rep. 2018, 13, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Carthew, R.W.; Sontheimer, E.J. Origins and mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, M.; de Horna, A.; Belles, X. MicroRNAs in metamorphic and nonmetamorphic transitions in hemimetabolan insect metamorphosis. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Kim, V.N.; Hyun, S. Conserved microRNA miR-8 controls body size in response to steroid signaling in drosophila. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Xiao, H.M.; Sun, Y.; Situ, G.; Xi, Y.; Li, F. microRNA-14 as an efficient suppressor to switch off ecdysone production after ecdysis in insects. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.L.; Wu, X.Y.; Zhou, L.T.; He, T.; Yin, Q.; Liu, S.P. 20-hydroxyecdysone-responsive microRNAs of insects. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 1454–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Tian, Z.; Wu, Q.W.; King-Jones, K.; Liu, W.; Zhu, F.; Wang, X.P. Steroid hormone ecdysone deficiency stimulates preparation for photoperiodic reproductive diapause. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1009352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.C.; Han, H.B.; Duan, T.F.; Li, L.; Pang, B.P. Transcriptome-wide identification of microRNAs in response to 20-hydroxyecdysone in Galeruca daurica. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2022, 42, 100981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Ling, L.; Luo, X.; Yang, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. miR-34 regulates larval growth and wing morphogenesis by directly modulating ecdysone signalling and cuticle protein in Bombyx mori. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 1342–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Bai, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Noel, S.W.; Yan, Q.S.; Thi, H.P.; Sun, X.G.; Wei, W.; Ma, J.; Zheng, F. Plasma exosomal miRNAs involved in endothelial injury in microscopic polyangiitis patients. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 6215–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Jin, M.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, S. Population genomics provide insights into the evolution and adaptation of the Asia corn borer. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2023, 40, masd112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Integrating microRNA annotation and deep-sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D152–D157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B. Aligning short sequencing reads with Bowtie. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2010, 32, 11.7.1–11.7.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofacker, L.L.; Bernhart, S.H.F.; Stadler, P.F. Alignment of RNA base pairing probability matrices. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2222–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambady, S.; Wu, Z.Y.; Dominko, T. Identification of novel microRNAs in Xenopus laevis metaphase II arrested eggs. Genesis 2012, 50, 286–299. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shahid, M.Q.; Wu, J.W.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.D.; Lu, Y.G. Comparative small RNA analysis of pollen development in autotetraploid and diploid rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, J.H.; Li, Z.Z.; Li, X.X.; Hu, X.D.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.K.; Liang, C.Z.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; et al. Integrated profiling of microRNAs and mRNAs: MicroRNAs located on Xq27.3 associate with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar]
- Young, M.D.; Wakefield, M.J.; Smyth, G.K.; Oshlack, A. Goseq: Gene Ontology Testing for RNA-seq Datasets. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages//2.13/bioc/vignettes/goseq/inst/doc/goseq.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2012).
- Mao, X.Z.; Cai, T.; Olyarchuk, J.G.; Wei, L.P. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3787–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆Ct method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar]
- Bryant, B.; Macdonald, W.; Raikhel, A.S. microRNA miR-275 is indispensable for blood digestion and egg development in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22391–22398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulan, L.; Martin, D.; Milan, M. Bantam miRNA promotes systemic growth by connecting insulin signaling and ecdysone production. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, J.; Montanez, R.; Belles, X. MiR-2 family regulates insect metamorphosis by controlling the juvenile hormone signaling pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3740–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz, H.; Cohen, S.M. MicroRNAs and gene regulatory networks: Managing the impact of noise in biological systems. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carthew, R.W.; Agbu, P.; Giri, R. MicroRNA function in Drosophila melanogaster. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 65, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Q.Q.; Long, G.Y.; Yang, H.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.B.; Yan, Y.; Yan, X. Conserved microRNAs miR-8-3p and miR-2a-3 targeting chitin biosynthesis to regulate the molting process of Sogatella furcifera (Horváth) (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2024, 117, 1675–1685. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wen, D.; Li, E.Y.; Palli, S.R.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.N. MicroRNA miR-8 promotes cell growth of corpus allatum and juvenile hormone biosynthesis independent of insulin/IGF signaling in Drosophila melanogaster. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 136, 103611. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Zhai, M.; Li, C.; Yu, X.; Song, X.; Gao, S.; Li, B. Multiple functions of miR-8-3p in the development and metamorphosis of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Insect Mol. Biol. 2019, 28, 208–221. [Google Scholar]
- Ekoka, E.; Maharaj, S.; Nardini, L.; Dahan-Moss, Y.; Koekemoer, L.L. 20-Hydroxyecdysone (20E) signaling as a promising target for the chemical control of malaria vectors. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, B.; Kim, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Shen, W.P.; Jang, J.S.; Stein, S.N.; Cormier, O.; Pereira, L.; Shih, C.R.Y.; Krieger, C.; et al. 20-hydroxyecdysone (20E) signaling regulates amnioserosa morphogenesis during Drosophila dorsal closure: EcR modulates gene expression in a complex with the AP-1 subunit, Jun. Biol. Open 2021, 10, bio058605. [Google Scholar]
- Carney, G.E.; Bender, M. The Drosophila ecdysone receptor (EcR) gene is required maternally for normal oogenesis. Genetics 2000, 154, 1203–1211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ables, E.T.; Drummond-Barbosa, D. The steroid hormone ecdysone functions with intrinsic chromatin remodeling factors to control female germline stem cells in Drosophila. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 7, 581–592. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Liang, Z.K.; Liang, Y.K.; Pang, R.; Zhang, W.Q. Conserved micrornas mir-8-5p and mir-2a-3p modulate chitin biosynthesis in response to 20-hydroxyecdysone signaling in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 839–848. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, T.C.; Pang, R.; Yue, X.Z.; Hu, J.; Zhang, W.Q. Genome-wide screening and functional analysis reveal that the specifc microRNA nlu-miR-173 regulates molting by targeting Ftz-F1 in Nilaparvata lugens. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1854. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.S.; Zhou, S.T. Post-transcriptional regulation of insect metamorphosis and oogenesis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1893–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sempere, L.F.; Sokol, N.S.; Dubrovsky, E.B.; Berger, E.M.; Ambros, V. Temporal regulation of microRNA expression in Drosophila melanogaster mediated by hormonal signals and broad-Complex gene activity. Dev. Biol. 2003, 259, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Su, J.Y. Research advances in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in insects. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2016, 59, 906–916. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.; Chen, W.W.; Kang, K.; Pang, R.; Dong, Y.P.; Liu, K.; Zhang, W.Q. FoxO directly regulates the expression of TOR/S6K and vitellogenin to modulate the fecundity of the brown planthopper. Sci. China Life Sci. 2021, 64, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, M.; Frentiu, F.D.; Moreira, L.A.; O’Neill, S.L.; Asgari, S. Wolbachia uses host microRNAs to manipulate host gene expression and facilitate colonization of the dengue vector Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 9250–9255. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.Y.; Chen, S.; Yang, P.C.; Ma, Z.Y.; Kang, L. Characterization and comparative profiling of the small RNA transcriptomes in two phases of locust. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R6. [Google Scholar]
- Asgari, S. MicroRNA functions in insects. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, J.A.; Nachman, R.J.; Denlinger, D.L. Distinct microRNA and mRNA responses elicited by ecdysone, diapause hormone and a diapause hormone analog at diapause termination in pupae of the corn earworm, Helicoverpa zea. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2019, 278, 68–78. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, L.; Kokoza, V.A.; Zhang, C.Y.; Aksoy, E.; Raikhel, A.S. MicroRNA-277 targets insulin-like peptides 7 and 8 to control lipid metabolism and reproduction in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8017–E8024. [Google Scholar]
- Asl, E.R.; Amini, M.; Najafi, S.; Mansoori, B.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Mohammadi, A.; Lotfinejad, P.; Bagheri, M.; Shirjang, S.; Lotfi, Z.; et al. Interplay between MAPK/ERK signaling pathway and microRNAs: A crucial mechanism regulating cancer cell metabolism and tumor progression. Life Sci. 2021, 278, 119499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, T.F.; Li, L.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Pang, B.P. Identification and functional analysis of microRNAs in the regulation of summer diapause in Galeruca daurica. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2021, 37, 100786. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.J.; Si, F.L.; Fu, D.Y.; He, Z.B.; Chen, B. Insight into the possible mechanism of the summer diapause of Delia antiqua (Diptera: Anthomyiidae) through digital gene expression analysis. Insect Sci. 2016, 23, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, X.B.; Wang, J.; Hao, K.; Whitman, D.W.; Fan, Y.L.; Cao, G.C.; Zhang, Z.H. Transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of pre-diapause and nondiapause eggs of migratory locust, Locusta migratoria L. (Orthoptera: Acridoidea). Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Gao, L.; Du, C.; Duan, T.; Liu, L. Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Pyrrhalta aenescens Fairmaire in Response to 20-Hydroxyecdysone Treatment. Genes 2025, 16, 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040435
Liu J, Gao L, Du C, Duan T, Liu L. Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Pyrrhalta aenescens Fairmaire in Response to 20-Hydroxyecdysone Treatment. Genes. 2025; 16(4):435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040435
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jie, Li Gao, Chao Du, Tianfeng Duan, and Li Liu. 2025. "Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Pyrrhalta aenescens Fairmaire in Response to 20-Hydroxyecdysone Treatment" Genes 16, no. 4: 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040435
APA StyleLiu, J., Gao, L., Du, C., Duan, T., & Liu, L. (2025). Transcriptomic Characterization of miRNAs in Pyrrhalta aenescens Fairmaire in Response to 20-Hydroxyecdysone Treatment. Genes, 16(4), 435. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16040435







