Abstract
Background: Broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.), a drought-tolerant C4 crop, is crucial for agricultural resilience in arid regions. Lipoxygenases (LOXs), key enzymes in plant stress responses, have not been studied in broomcorn millet. This study aimed to identify LOX genes in broomcorn millet and elucidate their role in drought tolerance. Methods: We employed bioinformatics and physiological analyses to identify LOX genes in broomcorn millet. Expression profiles were assessed in different organs, and drought stress responses were evaluated in tolerant (HSZ, YXDHM) and sensitive (YS10) varieties. Antioxidant enzyme activities (SOD, POD, CAT) and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were measured. Results: Twelve LOX genes were identified, classified into three subfamilies, and mapped across seven chromosomes. These genes contained stress-responsive cis-elements and showed organ-specific expression, with PmLOX5 exhibiting no detectable expression. Under drought stress, tolerant varieties showed elevated antioxidant activities and reduced MDA accumulation. PmLOX2, a homolog of Arabidopsis AtLOX1/AtLOX5, was significantly induced in tolerant varieties, correlating with enhanced antioxidant capacity and reduced oxidative damage. Conclusions: PmLOX genes, particularly PmLOX2, play a pivotal role in drought tolerance by modulating ROS scavenging and membrane protection. This study provides a foundation for leveraging LOX genes to improve drought resilience in broomcorn millet and related crops.
1. Introduction
Global climate change has made drought a important factor that affects crop yield and quality in many regions. As an abiotic stressor, drought significantly hinders crop growth and development, and negatively affects productivity [1]. It disrupts the osmotic regulation system in plants, causing an imbalance in reactive oxygen species (ROS) metabolism within cell membranes. This imbalance can lead to excessive ROS accumulation, causing lipid peroxidation and cell membrane damage. Additionally, protein denaturation and inactivation disrupt key physiological and biochemical processes, weakens photosynthesis, inhibits growth, and increases plant mortality [2,3,4]. Consequently, developing high-yield, high-quality, and drought-resistant crop varieties coupled with water-saving cultivation practices has become a pressing challenge in agriculture owing to limited water resources.
Broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) is a short-day C4 crop belonging to the Gramineae genus, with a cultivation history in China dating back to 10,000 years [5]. Owing to its strong stress resistance, adaptability, drought tolerance, high water-use efficiency, short growth cycle, and alignment with the rainy season in arid and semi-arid regions, broomcorn millet thrives in various soils, particularly in dryland farming areas of the Loess Plateau. Its regional and production advantages make it a significant crop for disaster relief [6,7,8].
LOXs are oxidoreductases with non-heme iron as their active center and are widely distributed in both animals and plants [9]. In plants, LOXs contribute significantly to in physiological and biochemical processes and are present in various organs, including roots, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruits. As the key enzymes in the plant fatty acid metabolic pathway (LOX pathway), LOXs can significantly influence organ growth, development, fruit ripening, oil oxidation, and signal transduction processes related to abiotic and biotic stresses [10,11]. Moreover, LOXs regulate plant secondary metabolism, affecting the production of important compounds such as fruit flavors and flower aromas [12,13,14].
In plants, LOXs can catalyze the oxidation of linoleic acid (LA) and linolenic acid (LnA) at the C9 and C1 positions of the fatty acid carbon chain, respectively. LOXs can be categorized into two subfamilies according on the location of the bound carbon atom: 9-LOX and 13-LOX [15]. Based on similarities in sequence structure and whether chloroplast transit peptides are present, plant LOXs are categorized into type I and type II. Type I LOXs can share 5% sequence similarity and lack chloroplast transit peptides, while type II LOXs have lower sequence similarity but contain these peptides [16]. Currently, all 9-LOXs are type I, whereas 13-LOXs are classified into type I and type II subtypes [17].
Plant LOXs catalyze the production of hydroperoxides (HPOs), which serve as precursors for various bioactive substances through multiple downstream pathways. Jasmonates (JAs) synthesized via allene oxide synthase (AOS) and green leaf volatiles (GLVs) formed by hydroperoxide lyases (HPLs) play significant roles in plant responses to abiotic and biotic stressors [18,19]. GLVs contribute to plant defense by inducing the expression of defense-related genes and directly or indirectly suppressing pathogens and pests [20]. Similarly, JAs are major stress-signaling molecules, mediating plant responses to challenges, such as drought, salt stress, and pathogen invasion [21,22].
The LOX gene family has been identified and analyzed in several crops, including Arabidopsis (6 members), rice (14 members) [23], foxtail millet (12 members) [24], tomato (14 members) [25], and grape (18 members) [26]. In Arabidopsis, AtLOX2 is involved in JA biosynthesis [27], whereas AtLOX5 is essential for the development of lateral roots in plants and for resisting pathogens [28]. In rice, the overexpression and knockout studies have indicated that moderate inhibition of OsLOX2 under normal storage conditions can slow seed deterioration without affecting germination [29]. In foxtail millet, the expression of SiLOX7 increased in drought-resistant varieties under drought stress [24]. Despite these attributes, only a few drought-related gene families, such as YABBY [30], ASR [31], bZIP [32], and NAC [33], have been studied in broomcorn millet. However, the LOX gene family in this crop remains unexplored.
The study of LOXs in plants has provided valuable insights into their roles in various physiological processes and stress responses. However, the LOX gene family in broomcorn millet, a drought-tolerant C4 crop with significant agricultural importance in arid regions, remains largely unexplored. This study aims to fill this gap by systematically identifying and characterizing the LOX gene family in broomcorn millet. We investigate their evolutionary relationships, stress-responsive regulatory elements, and functional roles in drought tolerance through bioinformatic and physiological analyses. Our research contributes to a deeper understanding of the genetic basis of drought resistance in broomcorn millet and potentially facilitates the development of improved cultivars with enhanced drought resilience. We hypothesize that the LOX gene family in broomcorn millet plays a significant role in modulating drought tolerance by regulating ROS scavenging, membrane protection, and jasmonate signaling pathways.
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Identification and Retrieval of Broomcorn Millet LOX Family Member Sequences
Complete genome information, CDS sequences, protein sequences, and annotation files of broomcorn millet were obtained from the NCBI database [34]. Six AtLOX protein sequences from Arabidopsis were retrieved from the TAIR database [35], whereas twelve SiLOX protein sequences of foxtail millet were retrieved from the Phytozome v13 database [36]. Additionally, thirteen OsLOX protein sequences were downloaded from the National Rice Data Center. Using TBtools v2.152 software [37], a local BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi, accessed on 25 February 2025) search was performed with broomcorn millet protein sequences as the database and the six AtLOX sequences as the queries, setting an E-value threshold of <1 × 10−5 and removing duplicate genes to preliminarily identify the LOX gene family members of the broomcorn millet. The SMART online database was used to identify the structural domains of candidate PmLOX proteins. Sequences containing only the lipoxygenase or PLAT/LH2 domain were excluded, resulting in the final determination of broomcorn millet LOX gene family members.
Chromosomal location information of the broomcorn millet LOX gene family members was extracted from the genome annotation file using the Sequence Toolkit option in TBtools. Subsequently, Gene Location Visualization from the GTF/GFF plugin in TBtools was utilized to construct a chromosomal location map.
2.2. Prediction of Amino Acids and Physicochemical Properties of LOX Family Members in Broomcorn Millet
The physicochemical properties of the LOX family of proteins in broomcorn millet, including the amino acid count, the isoelectric point, the molecular weight, and other characteristics, were analyzed and predicted using the ExPASy-ProtParam online tool [38].
2.3. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Tree Construction
Multiple sequence alignments of the amino acid sequences of 12 SiLOX proteins from foxtail millet, 12 OsLOX proteins from rice, and 6 AtLOX proteins from Arabidopsis were performed using the MUSCLE program in MEGA7.0. A phylogenetic evolutionary tree (NJ tree) was constructed from the aligned sequences using the neighbor-joining method in MEGA7.0, with the model set to p-distance, bootstrap value set to 1000, and default settings for other parameters. iTOL was used to edit and visually enhance the resulting phylogenetic tree.
2.4. Prediction and Analysis of Conserved Motifs, Protein Secondary Structure, and Subcellular Localization
The MEME online tool was used to analyze and predict conserved motifs within the amino acid sequences of broomcorn millet LOX proteins [39]. TBtools was used for visualization [37]. WebLogo was used to create sequence logos for the conserved domains. The secondary structure of broomcorn millet LOX proteins was predicted with the SOPMA online tool. The subcellular localization of the identified PmLOX proteins was predicted using the Plant-mPLoc online platform.
2.5. Analysis of Cis-Acting Components in the Promoter Region of LOX Family in Broomcorn Millet
The 2000 bp promoter sequences upstream of the 12 LOX genes were extracted from the genome annotation information of broomcorn millet using the TBtools software. These sequences were submitted to the PlantCARE online platform for cis-acting element predictions.
2.6. Plant Growth Conditions
Three kinds of broomcorn millet were used as varieties with varying drought tolerances in this study: drought-resistant varieties HSZ and YXDHM and drought-sensitive variety YS10 after evaluation [40]. Seeds of three broomcorn millet varieties (HSZ, YXDHM, YS10) were planted in pots with a 2:1 nutrient soil-to-vermiculite ratio. Plants were grown in an artificial climate chamber of at the Agricultural College of Shanxi Agricultural University under controlled conditions: light intensity 14,000 lx, temperature 28 °C/22 °C (day/night), 16 h/8 h light/dark cycle, and 80% humidity. Seedlings were maintained until the four-leaf stage before drought treatment.
2.7. Drought Stress Treatment
Drought stress was imposed on four-leaf-stage broomcorn millet seedlings by completely withholding irrigation to simulate natural drought conditions. Control plants were maintained under well-watered conditions throughout the experiment. Soil water content (SWC) was monitored gravimetrically using the formula:
where Fresh weight and Dry weight represent the mass of soil samples before and after oven-drying at 105 °C for 48 h, respectively. Drought stress initiation was defined when SWC dropped below 30% of field capacity (FC), reflecting moderate-to-severe drought conditions in arid agroecosystems.
The penultimate leaves of aboveground seedlings were collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 days post-drought treatment for physiological characterization and qRT-PCR profiling. Three biological replicates were harvested per time point and variety. The gathered samples were placed in an ultra-low-temperature freezer set at −80 °C after being rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen.
2.8. Relevant Physiological Indexes Were Measured
Malondialdehyde (MDA) content was determined using the thiobarbituric acid (TBA) method [41]. Superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity was measured using the nitroblue tetrazolium (NBT) method [42], whereas peroxidase (POD) activity was assessed using the guaiacol method [43]. The catalase (CAT) activity was determined using the ultraviolet absorption method, as described by Abei [44]. For sample preparation, 0.1 g of leaves were placed in a 2 mL centrifuge tube, frozen with liquid nitrogen after adding steel balls, and ground into powder at 1500 rpm for 30 s using a tissue grinding instrument. For MDA content measurement, 1.5 mL of 0.1% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) was added as the extraction solution. For SOD, POD, and CAT activity measurements, 1 mL of 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.8) was used as the extract. The samples were shaken, mixed, and centrifuged at 12,000 rpm at 4 °C for 15 min, and the supernatant was collected as the crude enzyme solution for subsequent enzyme activity and content analysis.
2.9. Analysis of Expression Pattern of LOX Gene Family in Broomcorn Millet
The leaves, roots, stems, and grains of broomcorn millet seedlings frozen at low temperatures were ground into powder using a plant tissue grinding instrument. The RNaiso Plus reagent (Takara Biotechnology, Beijing, China) was used to extract total RNA from every sample. An ultra-low-volume spectrophotometer (BioDrop, Cambridge, UK) was used to measure the A260/A280 ratio and RNA concentration in order to evaluate the quality of the RNA. For reverse transcription into cDNA, samples with an A260/A280 ratio between 1.8 and 2.1 were chosen.
Reverse transcription was performed using the PrimeScriptTM RT Reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser (Perfect Real Time) (Takara Biotechnology, Beijing, China) following the manufacturer’s protocol, and the resulting cDNA was diluted fivefold for qRT-PCR analysis. qRT-PCR analysis was performed on a Bio-Rad CFX96 real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR system using a TB Green® Premix Ex TaqTM II (Tli RNaseH Plus) kit (Takara Biotechnology, Dalian, China).
The qRT-PCR protocol was configured as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 5 s and annealing and extension at 60 °C for 30 s. A stepwise temperature transition from 60 °C to 95 °C with 0.5 °C increment for 5 s was applied to generate the melting curve. Relative gene expression levels were calculated using the ΔΔCq method using Bio-Rad Manager 3.1 software [45]. Real-time fluorescent quantitative primers were designed using Primer Premier 5 software based on the CDS sequence of the broomcorn millet LOX gene, with ACT2 as a drought-stress-stable gene from switchgrass used as an internal reference for broomcorn millet [31].
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Characterization of the LOX Gene Family in Broomcorn Millet
The conserved domains of the identified proteins were confirmed by comparing their sequences with the LOX protein sequences in Arabidopsis. Sequences lacking both the lipoxygenase domain and PLAT/LH2 domain were excluded. Consequently, 12 LOX family members were identified in broomcorn millet and designated as PmLOX1-PmLOX12 (Table 1). These genes were dispersed irregularly throughout the seven chromosomes of broomcorn millet (Figure 1). Chr2 contained the highest number of members (3), whereas Chr1, Chr11, and Chr15 each contained two members. Chr7, Chr13, and Chr16 had only one LOX gene each.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties and subcellular localization predictions of LOX family members in broomcorn millet.
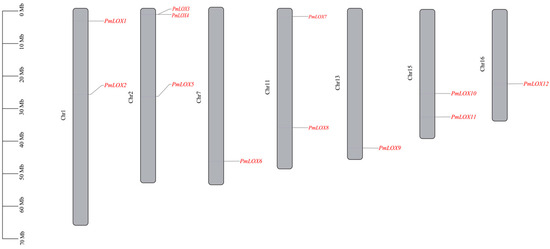
Figure 1.
Chromosome localization of LOX family members of broomcorn millet.
The physicochemical properties and subcellular localization predictions for the 12 PmLOX proteins are summarized in Table 1. The coding sequences (CDS) of PmLOX genes ranged from 2253 bp (PmLOX4) to 2856 bp (PmLOX12), with the corresponding protein lengths varying from 750 (PmLOX4) to 951 (PmLOX12) amino acids. The protein molecular weights ranged from 83,630.97 (PmLOX12) to 105,900.23, and the isoelectric points (pI) spanned between 5.65 (PmLOX4) and 8.49 (PmLOX9). Notably, only PmLOX1, PmLOX8, and PmLOX9 had pI values above 7, indicating that they were basic proteins, whereas the remaining nine members had pI values below 7, classifying them as acidic proteins. The average hydrophilicity coefficients of broomcorn millet LOX proteins were negative, indicating that they were hydrophilic proteins. The subcellular localization predictions revealed that PmLOX proteins were primarily localized in the cytoplasm and chloroplasts. Specifically, there were six proteins localized to the cytoplasm, including PmLOX1, PmLOX5, PmLOX6, PmLOX8, PmLOX10, and PmLOX12, and six proteins localized to the chloroplasts, including PmLOX2, PmLOX3, PmLOX4, PmLOX7, PmLOX9, and PmLOX11.
3.2. Systematic Evolutionary Analysis of the LOX Gene Family in Broomcorn Millet
To examine the evolutionary relationships of broomcorn millet LOX genes, the 12 identified broomcorn millet LOX protein sequences, along with 6 AtLOX (Arabidopsis), 12 OsLOX (Oryza sativa), and 12 SiLOX (Setaria italica) protein sequences, were aligned using MEGA7.0, and a phylogenetic tree was created (Figure 2). A phylogenetic tree was constructed to classify the LOX genes of broomcorn millet into three subfamilies. Six PmLOX members (PmLOX2, PmLOX3, PmLOX4, PmLOX5, PmLOX6, and PmLOX8) were assigned to the 9-LOX subfamily, and the remaining six members were grouped into the 13-LOX subfamily. Based on previously established LOX classification criteria [16], the type I 13-LOX subfamily included three PmLOX genes (PmLOX1, PmLOX10, and PmLOX12), and the type II 13-LOX subfamily included three PmLOX genes (PmLOX7, PmLOX9, and PmLOX11). Notably, type I 13-LOX members can be present only in rice, foxtail millet, and broomcorn millet and can be absent in Arabidopsis [46].
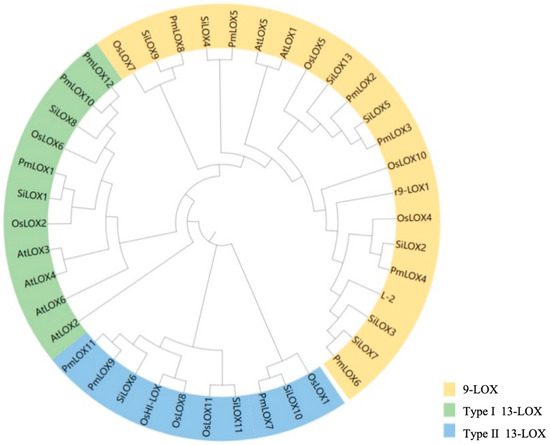
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree of the LOX gene family in broomcorn millet.
3.3. Protein Secondary Structure Prediction, Motif Analysis, and Conserved Domain Analysis of Members of the LOX Gene Family Members in Broomcorn Millet
Analysis of the protein sequences of the broomcorn millet LOX gene family revealed two characteristic domains: PLAT/LH2 and Lipoxygenase (Table 2). The members (PmLOX1 to PmLOX12) contained both domains, demonstrating typical features of the LOX gene family.

Table 2.
Conserved domains of LOX family members in broomcorn millet.
Conserved motif analysis of the amino acid sequences of the 12 PmLOX family members identified 10 motifs. Based on the classification of PmLOX members in Section 3.2, all 13-LOX members were observed to contain all 10 motifs, whereas most 9-LOX members also contained nearly all motifs, except PmLOX8, which lacked motif 5, as well as PmLOX5 lacking motifs 7, 8, and 10. Motif 1 contains the characteristic lipoxygenase domain of the LOX family, and is highly conserved across all broomcorn millet LOX family members, including a histidine-rich segment [His-(X)4-His-(X)4-His-(X)17-His-(X)8-His]. This domain, consisting of 38 amino acids, is important for maintaining the structural stability of LOXs. Notably, in PmLOX5, the first histidine (H) in this segment is replaced by asparagine (N) (Figure 3).
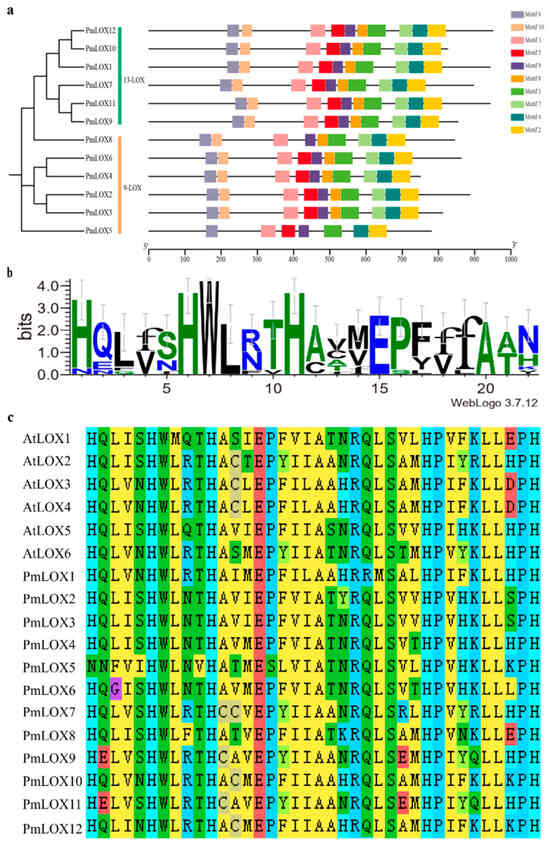
Figure 3.
Motifs and conserved domains of the broomcorn millet LOX family members. (a) Phylogenetic tree constructed based on the protein sequences of PmLOX and motif analysis; (b) identification of the conserved domain sequence of 38 residues in motif 1; (c) alignment of the conserved sequence of 38 residues in AtLOX and PmLOX protein sequences.
To further characterize PmLOX proteins, their secondary structures were predicted (Table 3). The analysis revealed that the PmLOX proteins primarily consisted of α helices, which accounted for the highest proportion, ranging from 42.04% to 46.06%. This was followed by α-helices at 34.79% to 39.87%, extending the strands at 12.62% to 14.42%, and β-turns at the lowest proportion, ranging from 3.24% to 5.73%.

Table 3.
Secondary structure of the LOX protein in broomcorn millet.
3.4. Analysis of Cis-Acting Elements of LOX Gene Family Promoter in Broomcorn Millet
To investigate the regulatory expression patterns of PmLOX genes in broomcorn millet, 2000 bp upstream sequences from their transcription start sites were analyzed using the PlantCARE online tool to identify the cis-acting elements in the promoters of the 12 PmLOX genes. A total of 41 cis-acting elements were identified, including 21 light-responsive elements, 9 hormone-responsive elements, 5 stress-responsive elements, and 6 elements related to plant growth and development (Figure 4). These findings suggest that PmLOX expression is regulated by multiple factors.
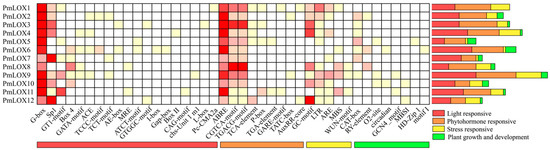
Figure 4.
Cis-acting elements statistics in the upstream promoter of LOX gene in broomcorn millet.
Analysis of the 12 PmLOX genes revealed that 10 contained low-temperature stress-related elements (LTR), while 9 contained tissue-specific or growth and development-responsive elements, such as CAT-box, GCN4_motif, and RY-element. Eight genes included anaerobic induction elements (ARE) and hypoxia-specific induction elements (GC-motif), while five contained MYB-binding sites involved in drought induction (MBS). Additionally, two genes had diurnal rhythm regulation elements (CAT-box and circadian), and one gene contained a mechanical injury response element (WUN-motif). All PmLOX genes exhibited numerous light-responsive regulatory elements, with the G-box, Sp1, and GT1-motif being the most common. Each PmLOX gene contains at least seven hormone-responsive cis-acting elements, including those related to abscisic acid (ABA) and methyl jasmonate (MeJA). ABA-responsive elements (ABREs) were the most abundant, followed by MeJA-responsive elements (CGTCA-motif- and TGACG-motifs). Some genes also included elements responsive to gibberellic acid (GARE-motif, P-box, TATC-box), auxin (AuxRR core, TGA-element), and salicylic acid (TCA-element). These findings suggest that most of the PmLOX genes play a role in the responses of broomcorn millet to abiotic stress.
3.5. Physiological Response of Broomcorn Millet Seedlings to Drought Stress at Seedling Stage
Three broomcorn millet samples with varying drought tolerance were subjected to natural drought stress, and changes in physiological indices, including POD, SOD, CAT, and MDA, were measured. The results (Figure 5) indicated significant differences in the physiological response patterns among the varieties under drought stress, which correlated markedly with their respective drought tolerance levels.
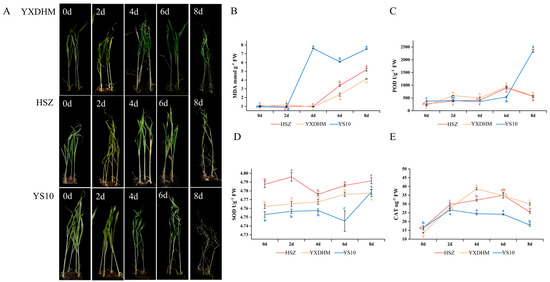
Figure 5.
Physiological response of HSZ, YXDHM, and YS10 under drought stress. (A) Phenotypic changes in leaves, stems. (B) MDA content. (C) POD activity. (D) SOD activity. (E) CAT activity. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference between drought stress at different times in the same variety (p < 0.05). MDA: malondialdehyde; POD: peroxidase; SOD: superoxide dismutase; CAT: catalase.
Observations of the apparent morphology under drought stress revealed that the drought-tolerant varieties HSZ and YXDHM exhibited delayed wilting symptoms compared to the drought-sensitive YS10. While YS10 displayed initial leaf wilting on day 4 post-drought, HSZ and YXDHM maintained turgor until day 6 (Figure 5A). After eight days of treatment, YS10 exhibited severe dehydration, with some plants dying, whereas HSZ and YXDHM exhibited increased wilting and inhibited growth but remained viable. Phenotypic analysis confirmed that HSZ and YXDHM possessed stronger drought resistance than YS10.
Physiological indicator responses were analyzed to validate epigenetic findings (Figure 5). The MDA content in YS10 was substantially greater than that in HSZ and YXDHM, as seen in Figure 5B. During the first two days of drought stress, the MDA content of all three kinds of varieties remained similar. However, YS10 exhibited a sharp increase in MDA levels between days 2 and 4, which remained consistently high thereafter. The MDA content in HSZ and YXDHM increased steadily between days 4 and 8 of drought stress, with HSZ showing slightly higher levels than YXDHM. However, both remained consistently lower than YS10 from day 2 onward. MDA can be a key indicator of membrane lipid peroxidation and stress intensity, as drought stress can induce its accumulation, exacerbating lipid peroxidation in plant cell membranes and causing cellular damage [47,48]. These findings indicated that compared to HSZ and YXDHM, YS10 seedlings accumulated more MDA under drought stress, resulting in greater membrane damage and weaker antioxidant capacity.
Under drought stress, the activity of the antioxidant enzyme system (POD, SOD, and CAT) in plants can be enhanced to eliminate reactive oxygen free radicals, reduce cellular damage, and increase drought resistance [49,50,51]. As shown in Figure 5C, the POD activity of the drought-resistant varieties HSZ and YXDHM initially increased and then declined, with levels higher than those of the sensitive variety YS10 on days 4 and 6. Between days 2 and 6, YXDHM displayed higher POD activity than HSZ. In contrast, YS10 showed minimal changes in POD activity in the early stages, with a significant increase after 6–8 d of drought treatment. Figure 5D illustrates that the SOD activities of HSZ and YXDHM were significantly higher than that of YS10, whereas the activity in HSZ initially decreased before increasing. YXDHM showed a continuous increase. In YS10, SOD activity mirrored the trend in POD activity, presenting a marked increase after 6–8 d of drought treatment. As shown in Figure 5E, CAT activity of the three experimental varieties initially increased and then decreased under drought stress. YS10 exhibited significantly lower CAT activity than HSZ and YXDHM. These results were consistent with the observed morphological changes under drought stress, confirming that HSZ and YXDHM possess stronger drought resistance than YS10.
3.6. Organ-Specific Expression of PmLOX Family Members
Organ-specific expression analysis (Figure 6) revealed that PmLOX5 was not detected in the roots, stems, leaves, seedlings, or grains. This suggests that PmLOX5 may be expressed only at specific developmental stages or exhibit extremely low expression levels. The expression levels of the majority of broomcorn millet LOX genes were higher in stems than in other organs, with notably low expression in seedlings and grains. However, PmLOX4, PmLOX6, PmLOX8, and PmLOX12 exhibited higher expression levels in roots than the other LOX genes.
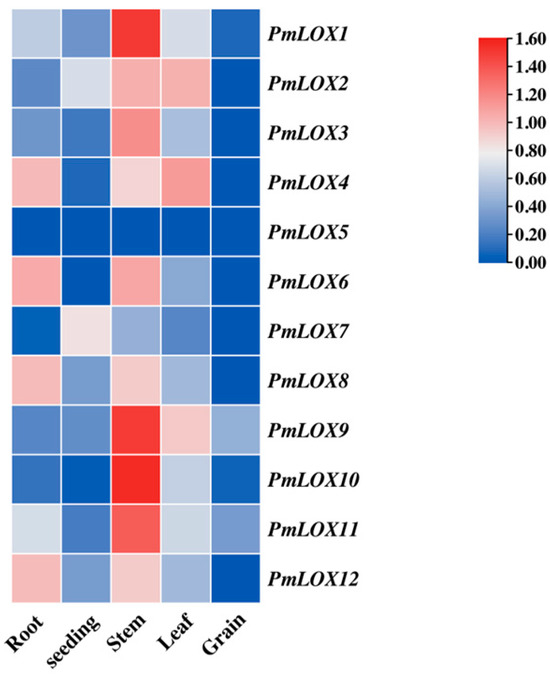
Figure 6.
Organ-specific expression of LOX family in broomcorn millet.
3.7. Expression Analysis of PmLOX Family Members in Leaves of Five-Leaf-Stage Seedlings Under Drought Stress
To explore the role of LOX gene family members in drought stress in broomcorn millet, qRT-PCR was used to analyze their expression patterns across the varieties of three broomcorn millet (Figure 7). Among the 12 PmLOX genes, PmLOX5 was not expressed at any of the four drought sampling time points. The remaining 11 PmLOX genes responded to the drought stress. PmLOX1 and PmLOX10 in HSZ and YS10 exhibited similar expression patterns, with the levels initially increasing and then decreasing as drought duration progressed. In YXDHM, the expression of PmLOX1 and PmLOX10 was downregulated under drought stress, with PmLOX1 remaining low after 4 d and PmLOX10 after 2 d. PmLOX6 showed the highest expression in drought-sensitive variety YS10, whereas its expression decreased significantly after 4 d of drought. In YXDHM, PmLOX7, PmLOX9, and PmLOX11 displayed an “up–down–up” expression pattern under prolonged drought stress, whereas in YS10, PmLOX9 and PmLOX11 followed a similar trend, peaking on day 6. However, PmLOX7 was inhibited and its expression declined as drought stress intensified.
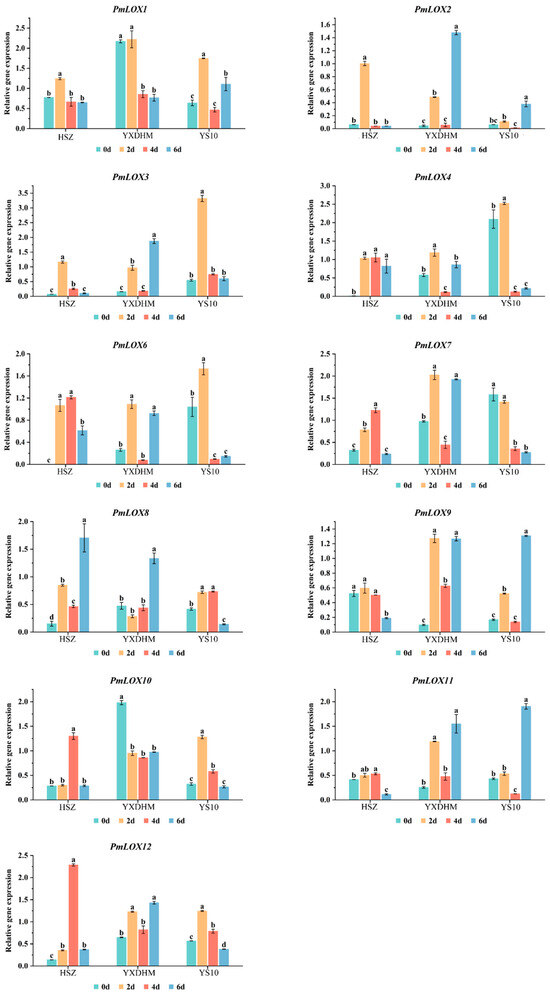
Figure 7.
qRT-PCR analysis of the expression patterns of LOX genes family members in broomcorn millet under drought stress. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) based on one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.
Compared to YXDHM and YS10, HSZ had substantially decreased expression levels of PmLOX7, PmLOX9, and PmLOX11. Under drought conditions, PmLOX9 was downregulated, although the other two genes’ expression levels first rose and subsequently fell. In the drought-sensitive variety YS10, PmLOX3 and PmLOX4 expression levels were noticeably greater in the drought-tolerant varieties HSZ and YXDHM, peaking at day 2 of drought treatment. Conversely, PmLOX8 in drought-tolerant plants displayed an overall upward trend, with expression levels higher than those in YS10.
The expression of PmLOX2 in the drought-tolerant varieties HSZ and YXDHM followed distinct patterns, showing a “first increase and then decrease” trend in HSZ and an “increase–decrease–increase” trend in YXDHM, with peaks at day 2 and day 6 under drought stress, respectively. The expression levels were 2.6 and 3.8 times higher than those in drought-sensitive variety YS10. The PmLOX12 expression in YXDHM and YS10 was similar, whereas in HSZ, PmLOX12 gradually increased, peaking at day 4, significantly exceeding the levels in YS10. PmLOX8 in the drought-tolerant plants exhibited an overall upward trend, with expression levels higher than those in YS10. A comprehensive analysis of the correlation between LOX gene expression and physiological indices under drought stress suggests that PmLOX2, PmLOX12, and PmLOX8 are probably involved in the drought stress response of broomcorn millet.
4. Discussion
LOXs are key enzymes in the fatty acid metabolic pathway of plants and play a important role in growth, development, and stress responses. The LOX gene family has been extensively studied in various crops, with 6 LOXs identified in Arabidopsis [23], 14 in rice [23], 12 in foxtail millet [24], 14 in tomato [25], 18 in grape [26], and 23 in cucumber [52]. However, the LOX gene family in broomcorn millet is largely unknown. Based on the six LOX members found in Arabidopsis, twelve members of the LOX gene family were identified in the genome of broomcorn millet in this study. According to chromosome localization studies, these genes were dispersed irregularly across seven chromosomes, with a total count double that of Arabidopsis, potentially reflecting the polyploidy and evolutionary history of broomcorn millet.
Phylogenetic tree analysis classified the broomcorn millet LOX gene family into three subfamilies, which is consistent with the findings of Feussner and Wasternack [16]. PmLOX2, PmLOX3, PmLOX4, PmLOX5, PmLOX6, and PmLOX8 are assigned to the 9-LOX subfamily. The six 13-LOX members were further divided into type I and type II 13-LOX subfamilies, based on the presence of a chloroplast transit peptide in the N-terminal sequence of type II LOX proteins. PmLOX1, PmLOX10, and PmLOX12 are classified as type I 13-LOX, whereas PmLOX7, PmLOX9, and PmLOX11 are classified as type II 13-LOX. Notably, type I 13-LOX subfamily members were identified exclusively in rice, foxtail millet, and broomcorn millet and were absent in Arabidopsis, consistent with the classification results for Arabidopsis and rice [23,46].
Conserved motif analysis of broomcorn millet LOX proteins identified 10 motifs, most of which were highly conserved across the PmLOX members. However, PmLOX8 lacked motif 5, and PmLOX5 lacked motifs 7, 8, and 10, suggesting that these proteins may have additional or unique functions. All broomcorn millet LOX proteins contain a highly conserved lipoxygenase domain within motif 1, composed of 38 amino acid residues, consistent with the findings in foxtail millet and cotton [24,53]. Notably, in PmLOX5, the first histidine (H) in the lipoxygenase domain was replaced with asparagine (N) (Figure 3b,c), coinciding with the absence of conserved motifs. To further understand the regulatory expression patterns of PmLOX genes under various conditions, their promoter cis-acting elements were predicted and analyzed, revealing four categories: light response, hormone response, stress response, and plant growth and development. These elements include those related to abscisic acid, MeJA, low-temperature stress, drought induction, and tissue-specific expression. This diversity of cis-acting elements aligned with the studies highlighting the functional versatility of plant LOX genes [54,55]. Notably, MeJA, a hormone involved in plant signal transduction, has been extensively explored in crops such as wheat [56], rice [57], pepper [58], and tomato [59]. By inducing the expression of defense-related genes, research has demonstrated significant positive effects of MeJA on plant resistance to biotic stresses, such as pest infestations, and abiotic stresses like drought and low temperatures [60]. In broomcorn millet, all LOX genes were found to contain the MeJA-responsive CGTCA-motif and TGACG-motif, suggesting that the PmLOX gene family may enhance plant resistance to both abiotic and biotic stresses.
To investigate the potential functions of LOX family members in broomcorn millet growth and development, three kinds of varieties with varying levels of drought resistance were subjected to drought stress, and their roles were analyzed by integrating physiological indices and PmLOX gene expression patterns. ROS in plants are maintained in a dynamic balance under typical environmental circumstances. However, drought stress disrupts this balance, which leads to disordered ROS production and metabolism. ROS-mediated oxidative stress induces harmful cellular effects, including lipid peroxidation of biological membranes and obstruction of photosynthesis [47,48,49,50,51]. As a product of membrane lipid peroxidation, MDA can severely damage the biofilm system, and its accumulation can indicate the extent of plant injury [47,48]. In response to drought stress, the activity of the antioxidant enzyme system (POD, SOD, and CAT) increases to remove ROS, mitigate plant damage, and enhance drought resistance [49,50,51]. In this study, HSZ and YXDHM exhibited lower MDA levels than YS10, indicating a stronger antioxidant activity and reduced cellular damage. Additionally, the activities of SOD, POD, and CAT were significantly higher in HSZ and YXDHM than in YS10, further confirming their superior drought resistance (Figure 5).
Organ-specific expression analysis of PmLOX genes demonstrated that most LOX genes were not expressed in grains, while all were expressed in other organs, with particularly high expression levels in stems. Notably, PmLOX5 was not expressed in the roots, stems, leaves, seedlings, or grains, consistent with its absence under drought stress. This suggests that PmLOX5 may exhibit extremely low expression levels or be expressed exclusively during specific developmental stages, which requires further experimental validation.
Expression pattern analysis revealed that most LOX genes in broomcorn millet exhibited increased expression levels under drought stress, which was consistent with the LOX response to drought stress observed in cotton, radish, and foxtail millet [24,53,61]. Broomcorn millet employs various tolerance mechanisms to mitigate abiotic stresses. Under drought conditions, most PmLOX genes were upregulated at different expression levels. Notably, PmLOX1 and PmLOX10 were downregulated in YXDHM, whereas PmLOX3, PmLOX4, PmLOX9, and PmLOX11 demonstrated higher expression levels in the drought-sensitive variety YS10 than in the drought-tolerant varieties HSZ and YXDHM. Compared to other LOX genes, PmLOX4, PmLOX6, PmLOX8, and PmLOX12 have greater expression levels in the roots.
In foxtail millet, Zhang et al. [24] identified 12 LOX genes and demonstrated that SiLOX7 was significantly upregulated under drought stress, particularly in drought-resistant varieties. Similarly, our study identified 12 LOX genes in broomcorn millet, with PmLOX2 showing marked upregulation in drought-tolerant genotypes. However, unlike SiLOX7 with root-specific expression, PmLOX2 exhibited higher expression levels in both leaves and stems, suggesting tissue-specific functional diversification between these two closely related species. This divergence highlights the potential for species-specific adaptation mechanisms within the LOX gene family.
Previous studies have indicated that AtLOX6 can be significant for the buildup of jasmonic acid (JA) in Arabidopsis roots under drought stress, significantly contributing to the plant response to abiotic and biotic stresses [60]. Under drought stress, the expression levels of PmLOX8 and PmLOX12 in drought-resistant plants were slightly higher than those in YS10, suggesting that their role in the drought stress response of broomcorn millet may primarily involve the accumulation of root derivatives. PmLOX2, a member of the 9-LOX subfamily, was upregulated in the drought-resistant varieties HSZ and YXDHM, whereas its expression in YS10 remained relatively unchanged. PmLOX2 is homologous to AtLOX1 and AtLOX5 in Arabidopsis. Previous studies have shown that the Arabidopsis mutants lox1 and lox5 exhibited increased membrane lipid peroxidation, higher MDA accumulation, and reduced stress resistance compared to the wild type [62]. In this study, HSZ and YXDHM, which exhibited high PmLOX2 expression, had significantly higher SOD and CAT activities and lower MDA accumulation than YS10, which is consistent with previous findings [62]. The increased activity of antioxidant enzymes (POD, SOD, and CAT) in the drought-resistant varieties HSZ and YXDHM resulted in lower MDA accumulation and reduced cellular oxidation. This response is likely linked to the upregulation of LOX genes, including PmLOX2, which correlates with improved drought adaptation and reduced cellular damage.
Our study identified 12 LOX gene family members in broomcorn millet, classified into three subfamilies, and revealed their potential roles in drought tolerance. Notably, PmLOX2 was strongly induced in drought-tolerant varieties, correlating with enhanced antioxidant capacity and reduced oxidative damage.
However, our study has some limitations. The absence of growth and yield data under drought conditions restricts direct correlations between PmLOX expression and physiological responses. Subcellular localizations predictions require experimental validation. Additionally, the use of a single reference gene (ACT2) may introduce technical bias; future studies should incorporate multiple reference genes to enhance reliability. To advance these findings, functional validation of PmLOX2 via CRISPR/Cas9 knockout and its interaction with jasmonate signaling under drought should be prioritized. Such data would elucidate the mechanistic role of LOX genes in drought adaptation and their potential for improving stress-resilient crops.
5. Conclusions
This study identified 12 LOX gene family members in broomcorn millet using bioinformatic methods and categorized them into three subfamilies, each exhibiting distinct structural features and conserved motifs, and were unevenly distributed across seven chromosomes. Promoter analysis revealed the presence of stress-responsive cis-elements, such as ABA, MeJA, and drought-inducible motifs, suggesting their potential involvement in stress signaling pathways. Organ-specific expression profiles indicated that most PmLOX genes were predominantly expressed in stems, while PmLOX5 showed no detectable expression, implying its potential role in specific developmental stages or extremely low expression levels. The response of PmLOX genes to drought stress was examined, revealing notable similarities and specificities in gene expression patterns among different drought-resistant varieties in broomcorn millet. Notably, PmLOX2 expression correlated with improved drought adaptation, suggesting its potential role in regulating ROS scavenging and membrane protection mechanisms. These findings establish a basis for further exploration of the functional role of LOX in broomcorn millet.
Author Contributions
J.W., H.L. and Y.H. designed the study; L.C. and L.D. wrote the manuscript; Y.Z. and L.D. performed the bioinformatics analysis; H.Y., L.C. and L.D. performed the experiment; Y.H., B.Z. and H.W. revised the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by Key Research Project of Shanxi Province (grant number 202302140601003), Science and Technology Special Project in Shanxi Province (202101140601027), CGGL Technology Development Fund (YDZJSX2022B007), and Key Research and Development Program of Shanxi Province (2022ZDYF110).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LOXs | Lipoxygenases |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| POD | Peroxidase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| ABA | Abscisic Acid |
| MeJA | Methyl Jasmonate |
| JA | Jasmonic Acid |
| SWC | Soil Water Content |
References
- Wahab, A.; Abdi, G.; Saleem, M.H.; Ali, B.; Ullah, S.; Shah, W.; Mumtaz, S.; Yasin, G.; Muresan, C.C.; Marc, R.A. Plants’ Physio-Biochemical and Phyto-Hormonal Responses to Alleviate the Adverse Effects of Drought Stress: A Comprehensive Review. Plants 2022, 11, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, M.; Sarkar, S.; Era, F.M.; Islam, A.K.M.M.; Anwar, M.P.; Fahad, S.; Datta, R.; Islam, A.K.M.A. Drought Stress in Grain Legumes: Effects, Tolerance Mechanisms and Management. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Wahid, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Fujita, D.; Basra, S.M.A. Plant Drought Stress: Effects, Mechanisms and Management. In Sustainable Agriculture; Lichtfouse, E., Navarrete, M., Debaeke, P., Véronique, S., Alberola, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, H.; Khattak, J.Z.K.; Ksiksi, T.S.; Saleem, M.H.; Fahad, S.; Sohail, H.; Ali, Q.; Zamin, M.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Saud, S.; et al. Negative impact of long-term exposure of salinity and drought stress on native Tetraena mandavillei L. Physiol. Plant 2021, 72, 1336–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, K.B.; Wu, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, K.; Ye, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; et al. Earliest domestication of common millet (Panicum miliaceum) in East Asia extended to 10,000 years ago. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7367–7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Gong, X.; Feng, B.; Xue, Z.; Yang, P. Effects of ridging and mulching combined practices on proso millet growth and yield in semi-arid regions of China. Field Crops Res. 2017, 213, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Hunt, H.V.; Qiao, Z.; Wang, L.; Han, Y. Diversity and Cultivation of Broomcorn Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) in China: A Review. Econ. Bot. 2016, 70, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Dang, K.; Lv, S.; Zhao, G.; Tian, L.; Luo, Y.; Feng, B. Interspecific root interactions and water-use efficiency of intercropped proso millet and mung bean. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 115, 126034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Arif, Y.; Miszczuk, E.; Bajguz, A.; Hayat, S. Specific Roles of Lipoxygenases in Development and Responses to Stress in Plants. Plants 2022, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Mattoo, A.K. Genome-wide identification of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) lipoxygenases coupled with expression profiles during plant development and in response to methyl-jasmonate and wounding. J. Plant Physiol. 2018, 231, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczko, R.; Csiszar, K. Lysyl Oxidase (LOX): Functional Contributions to Signaling Pathways. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Li, D.; Li, S.; Yang, H.; Zhao, Z. GC-MS Metabolite and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal the Differences of Volatile Synthesis and Gene Expression Profiling between Two Apple Varieties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Jin, B. Floral Scents and Fruit Aromas: Functions, Compositions, Biosynthesis, and Regulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 860157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Li, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Li, G.; Yan, Y.; Wu, Q.; Luo, Z. FaLEC2 repressing FaLOX2 promoter involved in the metabolism of LOX-derived volatiles during strawberry ripening. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 303, 111188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, P.O.; Calzado, N.F.; Budzinski, I.G.F.; Domingues, D.S. Genome-Wide Analysis of Lipoxygenase (LOX) Genes in Angiosperms. Plants 2023, 12, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feussner, I.; Wasternack, C. The lipoxygenase pathway. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 53, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yuan, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Yan, C.; Li, C.; Shan, S. Identification of the LOX Gene Family in Peanut and Functional Characterization of AhLOX29 in Drought Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 832785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, F.; Schaller, A.; Stintzi, A. Biosynthesis and Metabolism of Jasmonates. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2004, 23, 179–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, K.; Koeduka, T. Green Leaf Volatiles in Plant Signaling and Response. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 2016, 86, 427–443. [Google Scholar]
- Prost, I.; Dhondt, S.; Rothe, G.; Vicente, J.; Rodriguez, M.J.; Kift, N.; Carbonne, F.; Griffiths, G.; Esquerré-Tugayé, M.T.; Rosahl, S.; et al. Evaluation of the antimicrobial activities of plant oxylipins supports their involvement in defense against pathogens. Plant Physiol. 2005, 139, 1902–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, J.; Schiller, D.; Ulrich, D.; Schwab, W.; Dunemann, F. Identification of lipoxygenase (LOX) genes putatively involved in fruit flavour formation in apple (Malus × domestica). Tree Genet. Genomes 2013, 9, 1493–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liao, B.; He, W.; Liu, Q.; Shen, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, S. Genome-Wide Identification, Characterization and Expression Analysis of Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Artemisia annua L. Plants 2022, 11, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umate, P. Genome-wide analysis of lipoxygenase gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Signal. Behav. 2011, 6, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Ma, F.; Duan, M.; Zhang, B.; Li, H. The Responses of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family to Salt and Drought Stress in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica). Life 2021, 11, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.K.; Handa, A.K.; Mattoo, A.K. Transcript Abundance Patterns of 9- and 13-Lipoxygenase Subfamily Gene Members in Response to Abiotic Stresses (Heat, Cold, Drought or Salt) in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Highlights Member-Specific Dynamics Relevant to Each Stress. Genes 2019, 10, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriy, P.; Jackie, W.; Brian, J.; Chris, W. Identification of the lipoxygenase gene family from Vitis vinifera and biochemical characterisation of two 13-lipoxygenases expressed in grape berries of Sauvignon Blanc. Funct. Plant Biol. 2010, 37, 767–784. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, D.; Dorion, S.; Jmii, S.; Cappadocia, L.; Bede, J.C.; Rivoal, J. Pseudophosphorylation of Arabidopsis jasmonate biosynthesis enzyme lipoxygenase 2 via mutation of Ser(600) inhibits enzyme activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2023, 299, 102898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellosillo, T.; Martínez, M.; López, M.A.; Vicente, J.; Cascón, T.; Dolan, L.; Hamberg, M.; Castresana, C. Oxylipins produced by the 9-lipoxygenase pathway in Arabidopsis regulate lateral root development and defense responses through a specific signaling cascade. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 831–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cai, M.; Long, Q.; Liu, L.; Lin, Q.; Jiang, L.; Chen, S.; Wan, J. OsLOX2, a rice type I lipoxygenase, confers opposite effects on seed germination and longevity. Transgenic Res. 2014, 23, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Liu, T.; He, J.; Dong, K.; Ren, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, T. Genome-wide Identification and Expression Characteristics of the YABBY Gene Family under Hypertonic Solution Stress in Broomcorn Millet (Panicum miliaceum L.). Genom. Appl. Biol. 2022, 41, 1067–1078. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.N.; Shen, L.H.; Song, J.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, H.G.; Chen, L.; Pei, Y.X.; Liu, S.C.; Qiao, Z.J. Analysis of cloned sequences and expression of ASR gene family in millet. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2021, 31, 1309–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, T.; He, J.; Dong, K.; Ren, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, T. Genome-wide identification of bZIP gene family in broomcorn millet and analysis of its expression characteristics under polyethylene glycol treatment in seedling stage. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2022, 28, 920–930. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.; Guo, J.; Dong, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G. Genome-wide analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in broomcorn millet (Panicum miliaceum L.) and expression analysis under drought stress. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.; Li, L.; Miki, D.; Li, D.; Tang, Q.; Xiao, L.; Rajput, S.; Deng, P.; Peng, L.; Jia, W.; et al. The genome of broomcorn millet. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huala, E.; Dickerman, A.W.; Garcia-Hernandez, M.; Weems, D.; Reiser, L.; LaFond, F.; Hanley, D.; Kiphart, D.; Zhuang, M.; Huang, W.; et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): A comprehensive database and web-based information retrieval, analysis, and visualization system for a model plant. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodstein, D.M.; Shu, S.; Howson, R.; Neupane, R.; Hayes, R.D.; Fazo, J.; Mitros, T.; Dirks, W.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; et al. Phytozome: A comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1178–D1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Williams, N.; Misleh, C.; Li, W.W. MEME: Discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W369–W373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, W.; Qiao, Z.; Feng, M.; Wang, G.; Duan, Y.; Chen, L. Resistance Evaluation and Response of 16 Millet Varieties at Germination Stage to Drought Stress. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2013, 21, 302. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Kirkham, M.B. Antioxidant responses to drought in sunflower and sorghum seedlings. New Phytol. 1996, 132, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, A.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Yang, F.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, A.; Chen, L.; et al. Genetic Diversity, Rather than Cultivar Type, Determines Relative Grain Cd Accumulation in Hybrid Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 7, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abei, H. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1984, 105, 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi, A.; Nakamura, K.; Sakata, K.; Sato-Fukuda, N.; Ishigaki, T.; Mano, J.; Takabatak, R.; Kitta, K.; Teshima, R.; Kondo, K.; et al. Development and Interlaboratory Validation of a Simple Screening Method for Genetically Modified Maize Using a ΔΔC(q)-Based Multiplex Real-Time PCR Assay. Anal. Chem. 2015, 88, 4285–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannenberg, G.; Martínez, M.; Hamberg, M.; Castresana, C. Diversity of the enzymatic activity in the lipoxygenase gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana. Lipids 2009, 44, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y. Physiological and proteomic changes of Castanopsis fissa in response to drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, C.; Hu, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, W.; Zhen, J. Photosynthetic, antioxidant activities, and osmoregulatory responses in winter wheat differ during the stress and recovery periods under heat, drought, and combined stress. Plant Sci. 2023, 327, 111557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadarajah, K.K. ROS Homeostasis in Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandurska, H. Drought Stress Responses: Coping Strategy and Resistance. Plants 2022, 11, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarma, B.; Kashtoh, H.; Lama Tamang, T.; Bhattacharyya, P.N.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Baek, K.-H. Abiotic Stress in Rice: Visiting the Physiological Response and Its Tolerance Mechanisms. Plants 2023, 12, 3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.Q.; Liu, X.H.; Jiang, L.W. Genome-wide identification, phylogeny and expression analysis of the lipoxygenase gene family in cucumber. Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 2613–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaban, M.; Ahmed, M.; Sun, H.; Ullah, A.; Zhu, L. Genome-wide identification of lipoxygenase gene family in cotton and functional characterization in response to abiotic stresses. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, H.; Rocha-Sosa, M. Plant lipoxygenases. Physiological and molecular features. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanath, K.K.; Varakumar, P.; Reddy, R.; Basha, S.J.; Ampasala, A. Plant Lipoxygenases and Their Role in Plant Physiology. J. Plant Biol. 2020, 63, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, Z.; Sun, M. Hydrogen peroxide acts as a signaling molecule for the methyl jasmonate-induced antioxidant defense in wheat callus to promote enhanced drought tolerance. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 7, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Sun, N.; Liu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Han, Y. Functional diversity of jasmonates in rice. Rice 2015, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarde, S.J.; Kumar, A.; Remme, R.N.; Dicke, M. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression of lipoxygenase gene family in pepper. Plant Mol. Biol. 2018, 98, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Shen, L.; Fan, B.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, Y.; Sheng, J. The effect of MeJA on ethylene biosynthesis and induced disease resistance to Botrytis cinerea in tomato. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2009, 54, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lang, D.; Zhang, X. The roles of methyl jasmonate to stress in plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 2019, 46, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, T.; Wang, W.; Hu, H.; Wei, Q.; Wei, X.; Bao, C. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Lipoxygenase Gene Family in Radish (Raphanus sativus) and Functional Characterization in Response to Abiotic and Biotic Stresses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.A.; Vicente, J.; Kulasekaran, S.; Vellosillo, T.; Martínez, M.; Irigoyen, M.L.; Cascón, T.; Bannenberg, G.; Hamberg, M.; Castresana, C. Antagonistic role of 9-lipoxygenase-derived oxylipins and ethylene in the control of oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and plant defence. Plant J. 2011, 67, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).