Cochlear Implant Challenges in Children with Ichthyosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
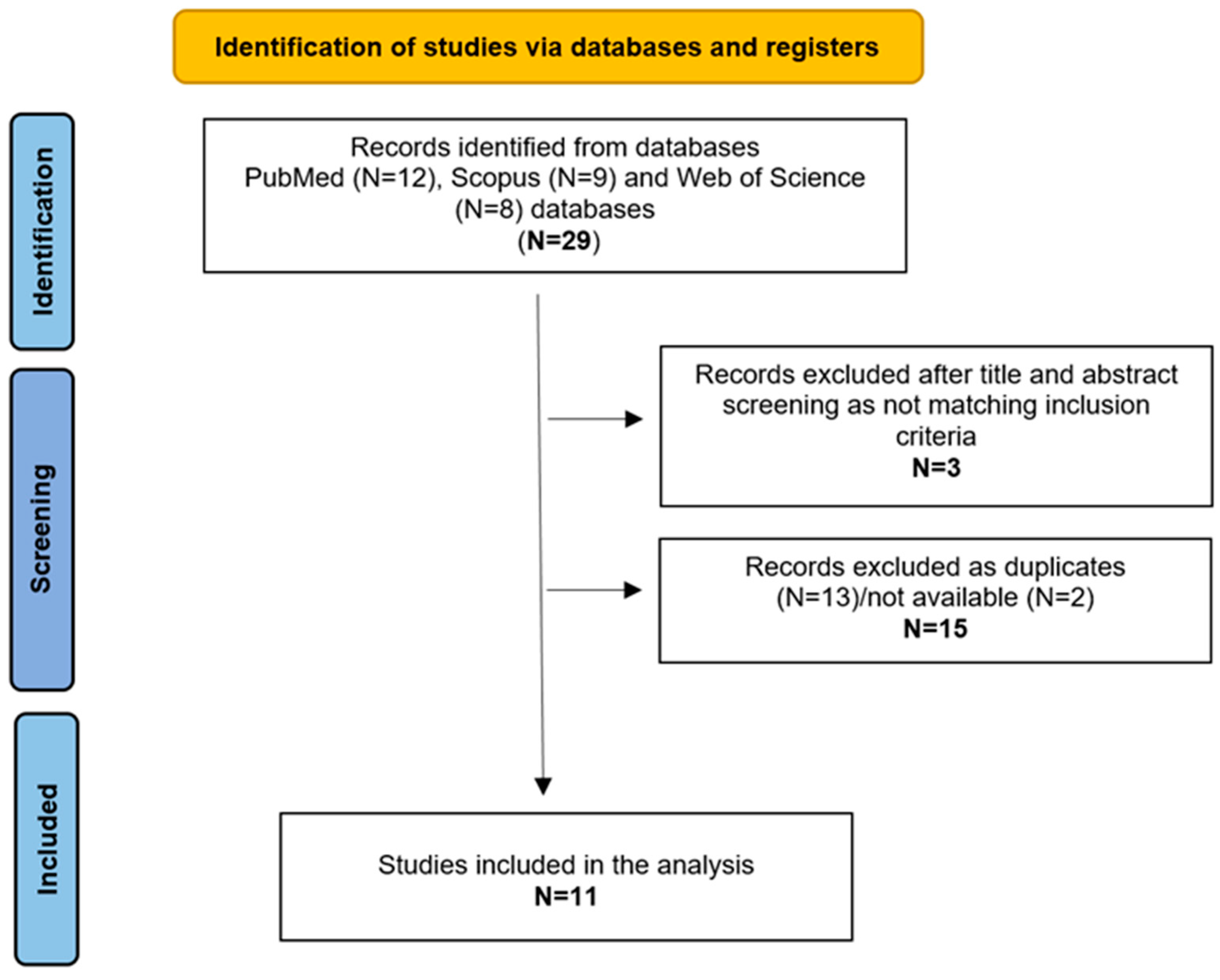
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Population
3.2. Genetic Analysis
3.3. Clinical Features
3.4. Imaging
3.5. Audiological Evaluation
3.6. Therapy, Auditory Rehabilitation, and Outcomes
3.7. Follow-Up and Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Traupe, H.; Fischer, J.; Oji, V. Nonsyndromic types of ichthyoses—An update. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2014, 12, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oji, V.; Tadini, G.; Akiyama, M.; Bardon, C.B.; Bodemer, C.; Bourrat, E.; Coudiere, P.; DiGiovanna, J.J.; Elias, P.; Fischer, J.; et al. Revised nomenclature and classification of inherited ichthyoses: Results of the First Ichthyosis Consensus Conference in Sorèze 2009. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2010, 63, 607–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, S.L.; MacDonald, L.; Propst, E.J.; Sharma, A.; Stockley, T.; Blaser, S.L.; James, A.L.; Papsin, B.C. Successful cochlear implantation in a child with Keratosis, Icthiosis and Deafness (KID) Syndrome and Dandy-Walker malformation. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 72, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamprecht, A.; Goecke, T.; Anton-Lamprecht, I.; Kuster, W. Progressive erythrokeratodermia cochlear hearing impairment: A case report review of the literature. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 1988, 15, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumus, B.; Incesulu, A.; Pinarbasli, M.O. Cochlear Implantation in Patients with Keratitis-Ichthyosis-Deafness Syndrome: A Report of Two Cases. Case Rep. Otolaryngol. 2017, 2017, 3913187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampton, S.M.; Toner, J.G.; Small, J. Cochlear implant extrusion in a child with keratitis, ichthyosis and deafness syndrome. J. Laryngol. Otol. 1997, 111, 465–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, C.M.; Sinnathuray, A.R.; Hughes, A.E.; Toner, J.G. Cochlear implantation in keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome: 10-year follow-up of two patients. Cochlear. Implants Int. 2012, 13, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, S.; McKenna, K. Keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome and carotenaemia. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2003, 28, 394–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.P.; Peng, J.J.; Zheng, H. Cochlear implantation in child with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome: A case report. Asian J. Surg. 2023, 46, 903–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choung, Y.H.; Shin, Y.R.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Ahn, J.H.; Choi, S.J.; Jeong, S.Y.; Park, K. Cochlear implantation and connexin expression in the child with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2008, 72, 911–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, S.; Aschendorff, A.; Schild, C.; Beck, R.; Maier, W.; Laszig, R.; Birkenhäger, R. A novel dominant and a de novo mutation in the GJB2 gene (connexin-26) cause keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness syndrome: Implication for cochlear implantation. Otol. Neurotol. 2010, 31, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, E.J.; Briggs, R.J. Cochlear implantation in children with keratitis-ichthyosis-deafness (KID) syndrome: Outcomes in three cases. Cochlear. Implants Int. 2009, 10, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnathuray, A.R.; Toner, J.G.; Geddis, A.; Clarke-Lyttle, J.; Patterson, C.C.; Hughes, A.E. Auditory perception and speech discrimination after cochlear implantation in patients with connexin 26 (GJB2) gene-related deafness. Otol. Neurotol. 2004, 25, 930–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markova, T.G.; Brazhkina, N.B.; Bliznech, E.A.; Bakhshinyan, V.V.; Polyakov, A.V.; Tavartkiladze, G.A. Phenotype in a patient with p.D50N mutation in GJB2 gene resemble both KID and Clouston syndromes. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 81, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogmann, R.J.; Al Khalili, Y. Cochlear Implants. [Updated 2023 Jul 24]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544280/ (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Marschark, M.; Spencer, L.J.; Durkin, A.; Borgna, G.; Convertino, C.; Machmer, E.; Kronenberger, W.G.; Trani, A. Understanding language, hearing status, and visual-spatial skills. J. Deaf Stud. Deaf Educ. 2015, 20, 310–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, N.L.; Hoffman, R.A. Complications of cochlear implant surgery in adults and children. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 1991, 100 Pt 1, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Reference | N and Gender | Genetic Analysis | PTA | Imaging | Comorbidity (except for common otological and skin problems connected to the disease itself) | PA e CI (Age) | Outcome with CI: PTA and/or Language | Complications | Follow-Up |
| Hampton et al., 1997 [7] | 1 F | NR | Profound bilateral SNHL | NR | None | HAs, CI (unspecified whether mono-or bilateral) | Improved PTA Discrimination, speech and imitation improved steadily. | Infection and extensive wound dehiscence | NR |
| Smyth et al., 2012 [8] | 2 (1M, 1F) | D50N: c.148G>A | Profound bilateral HL | CT neative | Shortening of Achilles tendon | HAs, Monolateral CI (for both patients) | Improved PTA and Speech. Poor discrimination, use of sign language | Otitis externa, progressive extensive wound dehiscence, CI explantation, intermittent ottorrhoea, TM perforation | 10 y |
| Ahmadi et al., 2003 [9] | 1 F | NR | SNHL | NR | Prematurity, carotenaemia, encephalomyelitis, shortening of Achilles tendon, | CI (9 m) (unspecified whether mono-or bilateral) | Unsuccessful CI | Poor wound healing | NR |
| Wang et al., 2023 [10] | 1 F | D50N: c.50C>T p.S17F | Profound SNHL | Negative | Elderlylike appearance, photophobia | Monolateral CI | Improved PTA | Mild incision irritating, incision infection | NR |
| Choung et al., 2008 [11] | 1 M | D50N: c.148G>A | Profound SNHL | Negative | Tongue with ulcerative and angular cheilitis, severely decreased visual acuity, neovascularization, corneal scarring, photophobia | HAs (1 y), Monolateral CI | Improved PTA | Difficulties in hearing rehabilitation due to low visual impairment, skin irritation | NR |
| Gumus et al., 2017 [5] | 2 (1M, 1F) | NR | Severe -Profound SNHL | NR | Motor growth retardation | HAs (4 y;10 m), Monolateral CI (7 y; 5 y) | Improved PTA, perception and speech | None | 1 y; 20 m |
| Arndt et al., 2010 [12] | 2 F | D50N: c.89 T>A; GAC9AAC: p.Asp50Asn. | Severe progressive bilateral SNHL | NR | Skin manifestations, bright light sensitivity | - HA (16y), Sequential CI (20 y–25 y); - HAs (3 m), Sequential CI (14m-planned) | Improved open-speech comprehension awarness | Changes in skin morphology under the transmitter coil, skin necrosis, wound dehiscence and partial extrusion of the implant | 7 m |
| Cushing et al., 2008 [3] | 1 (gender unspecified) | D50A: c.149A>C | Profound bilateral SNHL | MRI: hypoplasia of the inferior cerebellar vermis and the fourth ventricle, large posterior fossa midline cyst; CT: hypoplastic cochlea, deficient roof of the SSC on the left and a small modiolus on the right. | Blepharitis, bilateral corneal pannus, mild vascularization, corneal | HAs (5 m), CI (1 y) | Improved PTA, perception and speech. Difficult in open set testing | Incision infection | 4 y |
| Barker et al., 2009 [13] | 3 (gender unspecified) | NR | Severe-Profound bilateral SNHL | NR | Gait problems, Shortening of Achilles tendon, calf and knee muscles, recurrent corneal infections, photophobia | HAs, - Sequential CIs (14 m, 47 m); - Monolateral CI (28 m); - Sequential CI (39 m, 62 m) | Improved speech and language | Abscess of the external ear canal and parotid, recurrent otitis media with otorrhoea, middle ear effusion, skin thickening over the site of the device, mastoiditis | 42 m; 26 m; 12 m |
| Sinnathuray et al., 2004 [14] | 32 (gender unspecified) | D50N: c.35G; D50N: c.35G/169C>T; deletion in GJB6; GJB2-unrelated deafness (20) | Profound SNHL | NR | NR | NR | Improved perception GJB2-related deafness> GJB2-unrelated deafness | NR | NR |
| Markova et al., 2016 [15] | 1F | D50N | Severe bilateral SNHL | NR | None | HAs (30 m), Monolateral CI (42 m) | Improved PTA, perception speech and language | NR | 7 y |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caragli, V.; Luppi, L.; Tegmeyer, N.C.; Genovese, E.; Soloperto, D. Cochlear Implant Challenges in Children with Ichthyosis: A Systematic Review. Genes 2025, 16, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020129
Caragli V, Luppi L, Tegmeyer NC, Genovese E, Soloperto D. Cochlear Implant Challenges in Children with Ichthyosis: A Systematic Review. Genes. 2025; 16(2):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020129
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaragli, Valeria, Laura Luppi, Nicole Carrie Tegmeyer, Elisabetta Genovese, and Davide Soloperto. 2025. "Cochlear Implant Challenges in Children with Ichthyosis: A Systematic Review" Genes 16, no. 2: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020129
APA StyleCaragli, V., Luppi, L., Tegmeyer, N. C., Genovese, E., & Soloperto, D. (2025). Cochlear Implant Challenges in Children with Ichthyosis: A Systematic Review. Genes, 16(2), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16020129






