Otofaciocervical Syndrome and Its Overlap with Branchiootorenal Spectrum: An Integrated Literature Analysis of EYA1-Related Disorders, Including a Novel Case with an 8q13.2q13.3 Deletion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical and Molecular Data
2.2. Literature Review and Data Extraction
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Screening and Data Extraction
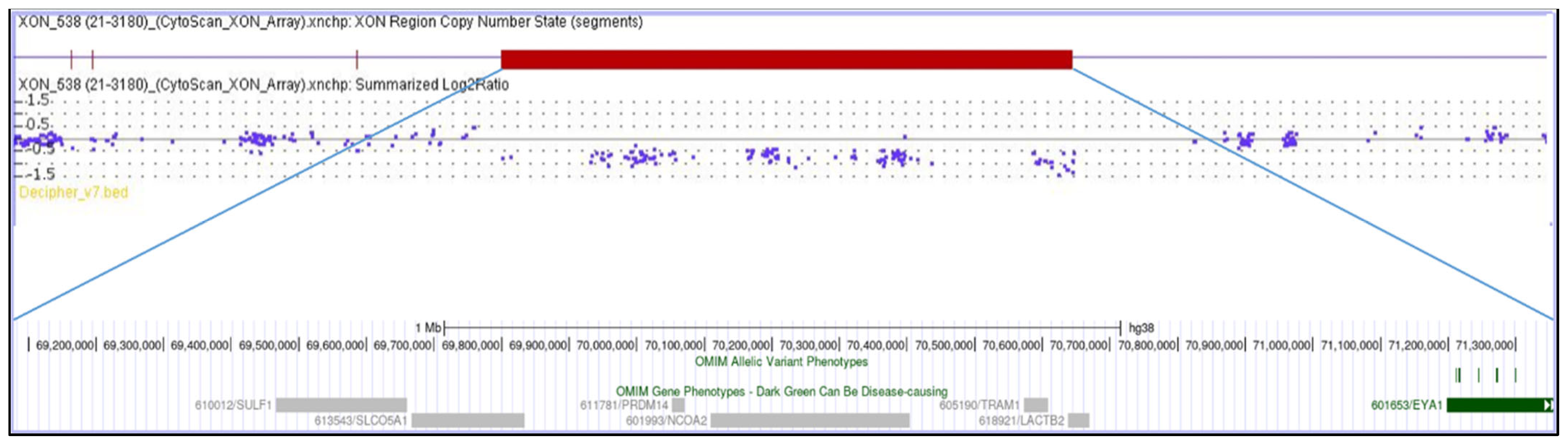
3. Clinical Presentation
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, J.M.; Moonis, G.; Green, G.E.; Carmody, R.; Burbank, H.N. Syndromes of the First and Second Branchial Arches, Part 1: Embryology and Characteristic Defects. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2011, 32, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, A.; Mankad, K.; Offiah, C.; Childs, L. Branchial Cleft Anomalies: A Pictorial Review of Embryological Development and Spectrum of Imaging Findings. Insights Imaging 2016, 7, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fára, M.; Chlupácková, V.; Hrivnákova, J. Familial oto-facio-cervical dysmorphia. Acta Chir. Orthop. Traumatol. Cech. 1967, 34, 511–520. [Google Scholar]
- Gana, S.; Valetto, A.; Toschi, B.; Sardelli, I.; Cappelli, S.; Peroni, D.; Bertini, V. Familial Interstitial 6q23.2 Deletion Including Eya4 Associated With Otofaciocervical Syndrome. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas-Torres, V.M.; Salinas-Torres, R.A. Otofaciocervical Syndrome and Metachondromatosis in a Girl: Presentation of a Novel Association and Remarks on Clinical Variability of Branchial-Arch Disorders. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 85, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castiglione, A.; Melchionda, S.; Carella, M.; Trevisi, P.; Bovo, R.; Manara, R.; Martini, A. EYA1-Related Disorders: Two Clinical Cases and a Literature Review. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 78, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.J. Branchiootorenal Spectrum Disorder. In GeneReviews®; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington, Seattle: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, S.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Choi, W.H.; Lee, S.-Y. Genomic Landscape of Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome through Whole-Genome Sequencing: A Single Rare Disease Center Experience in South Korea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallapiccola, B.; Mingarelli, R. Otofaciocervical Syndrome: A Sporadic Patient Supports Splitting from the Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 1995, 32, 816–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vm, S.-T.; Rivera, H. Branchiootorenal Syndrome with Skeletal Defects: A Novel Association in a Mexican Child. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2015, 24, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krug, P.; Morinière, V.; Marlin, S.; Koubi, V.; Gabriel, H.D.; Colin, E.; Bonneau, D.; Salomon, R.; Antignac, C.; Heidet, L. Mutation Screening of the EYA1, SIX1, and SIX5 Genes in a Large Cohort of Patients Harboring Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome Calls into Question the Pathogenic Role of SIX5 Mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2011, 32, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Qiu, Y.; Xing, Q.; Lu, W. A Novel Mutation in EYA1 in a Chinese Family with Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estefanía, E.; Ramírez-Camacho, R.; Gomar, M.; Trinidad, A.; Arellano, B.; García-Berrocal, J.R.; Verdaguer, J.M.; Vilches, C. Point Mutation of an EYA1-Gene Splice Site in a Patient with Oto-Facio-Cervical Syndrome. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2006, 70, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rickard, S.; Van’T Hoff, W.; Barnicoat, A.; Russell-Eggitt, I.; Winter, R.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M.; Parker, M. Oto-Facio-Cervical (OFC) Syndrome Is a Contiguous Gene Deletion Syndrome Involving EYA1: Molecular Analysis Confirms Allelism with BOR Syndrome and Further Narrows the Duane Syndrome Critical Region to 1 cM. Hum. Genet. 2001, 108, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, C.; Gilbert, R.; Loughlin, S.; Foulds, N. Patient with an EYA1 Mutation with Features of Branchio-Oto-Renal and Oto-Facio-Cervical Syndrome. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2006, 15, 211–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochhar, A.; Orten, D.J.; Sorensen, J.L.; Fischer, S.M.; Cremers, C.W.R.J.; Kimberling, W.J.; Smith, R.J.H. SIX1 Mutation Screening in 247 Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome Families: A Recurrent Missense Mutation Associated with BOR. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskins, B.E.; Cramer, C.H.; Silvius, D.; Zou, D.; Raymond, R.M.; Orten, D.J.; Kimberling, W.J.; Smith, R.J.H.; Weil, D.; Petit, C.; et al. Transcription Factor SIX5 Is Mutated in Patients with Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 80, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.H.; Menezes, M.; Meyer, N.C.; Cucci, R.A.; Vervoort, V.S.; Schwartz, C.E.; Smith, R.J.H. Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome: The Mutation Spectrum in EYA1 and Its Phenotypic Consequences. Hum. Mutat. 2004, 23, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, E.; Aykut, A.; Beleggia, F.; Karaca, E.; Durmaz, B.; Keupp, K.; Arslan, E.; Palamar, M.; Yigit, G.; Özkinay, F.; et al. A Hypofunctional PAX1 Mutation Causes Autosomal Recessively Inherited Otofaciocervical Syndrome. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganini, I.; Sestini, R.; Capone, G.L.; Putignano, A.L.; Contini, E.; Giotti, I.; Gensini, F.; Marozza, A.; Barilaro, A.; Porfirio, B.; et al. A Novel PAX1 Null Homozygous Mutation in Autosomal Recessive Otofaciocervical Syndrome Associated with Severe Combined Immunodeficiency. Clin. Genet. 2017, 92, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherlaw-Sturrock, C.; Austin, T.; Baptista, J.; Gilmour, K.; Naik, S. Dysmorphism and Immunodeficiency-One of the Differential Diagnoses Is PAX1 Related Otofaciocervical Syndrome Type 2. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2022, 65, 104523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbagoury, N.M.; Abdel-Aleem, A.F.; Sharaf-Eldin, W.E.; Ashaat, E.A.; Esswai, M.L. A Novel Truncating Mutation in PAX1 Gene Causes Otofaciocervical Syndrome Without Immunodeficiency. J. Mol. Neurosci. MN 2023, 73, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockley, T.L.; Mendoza-Londono, R.; Propst, E.J.; Sodhi, S.; Dupuis, L.; Papsin, B.C. A Recurrent EYA1 Mutation Causing Alternative RNA Splicing in Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome: Implications for Molecular Diagnostics and Disease Mechanism. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2009, 149A, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unzaki, A.; Morisada, N.; Nozu, K.; Ye, M.J.; Ito, S.; Matsunaga, T.; Ishikura, K.; Ina, S.; Nagatani, K.; Okamoto, T.; et al. Clinically Diverse Phenotypes and Genotypes of Patients with Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 63, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wu, W.K.K.; Liang, Q.; Zhang, N.; He, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Chan, M.T.V.; Ng, S.S.M.; et al. Disruption of NCOA2 by Recurrent Fusion with LACTB2 in Colorectal Cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.; Liang, X.; Sun, X.; Chen, H.; Dong, Y.; Wu, L.; Gu, S.; Han, S. Nuclear Receptor Coactivator 2 Promotes Human Breast Cancer Cell Growth by Positively Regulating the MAPK/ERK Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, N.; Toyota, M.; Suzuki, H.; Honma, T.; Fujikane, T.; Ohmura, T.; Nishidate, T.; Ohe-Toyota, M.; Maruyama, R.; Sonoda, T.; et al. Gene Amplification and Overexpression of PRDM14 in Breast Cancers. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 9649–9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidor, B.; Pichon, O.; Redon, R.; Day-Salvatore, D.; Hamel, A.; Siwicka, K.A.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M.; Heymann, D.; Kjellén, L.; Kraus, C.; et al. Mesomelia-Synostoses Syndrome Results from Deletion of SULF1 and SLCO5A1 Genes at 8q13. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.; Chien, J.; Staub, J.; Avula, R.; Greene, E.L.; Matthews, T.A.; Smith, D.I.; Kaufmann, S.H.; Roberts, L.R.; Shridhar, V. Loss of HSulf-1 up-Regulates Heparin-Binding Growth Factor Signaling in Cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 23107–23117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlich, D.; Hartmann, E.; Prehn, S.; Rapoport, T.A. A Protein of the Endoplasmic Reticulum Involved Early in Polypeptide Translocation. Nature 1992, 357, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orten, D.J.; Fischer, S.M.; Sorensen, J.L.; Radhakrishna, U.; Cremers, C.W.R.J.; Marres, H.A.M.; Van Camp, G.; Welch, K.O.; Smith, R.J.H.; Kimberling, W.J. Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome (BOR): Novel Mutations in the EYA1 Gene, and a Review of the Mutational Genetics of BOR. Hum. Mutat. 2008, 29, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.D.; Kim, S.-C.; Koh, Y.W.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, S.-Y.; Kim, U.-K. A Novel Frameshift Mutation in the EYA1 Gene in a Korean Family with Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2009, 39, 303–306. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.R.; Song, M.H.; Kim, M.-A.; Kim, Y.-R.; Lee, K.-Y.; Sonn, J.K.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, U.-K. Identification of a Novel Nonsynonymous Mutation of EYA1 Disrupting Splice Site in a Korean Patient with BOR Syndrome. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 4321–4327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Lu, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-H.; Su, Y.-N.; Hwu, W.-L.; Yu, I.-S.; Hsu, C.-J. Mutation Screening of the EYA1, SIX1, and SIX5 Genes in an East Asian Cohort with Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. Laryngoscope 2012, 122, 1130–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingbeil, K.D.; Greenland, C.M.; Arslan, S.; Llamos Paneque, A.; Gurkan, H.; Demir Ulusal, S.; Maroofian, R.; Carrera-Gonzalez, A.; Montufar-Armendariz, S.; Paredes, R.; et al. Novel EYA1 Variants Causing Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 98, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ideura, M.; Nishio, S.; Moteki, H.; Takumi, Y.; Miyagawa, M.; Sato, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohyama, K.; Oda, K.; Matsui, T.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Syndromic Hearing Loss Patients in Japan. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, M.; Lu, S.; Xu, H.; Tang, W.; Zheng, G. Novel Likely Pathogenic Variant in the EYA1 Gene Causing Branchio Oto Renal Syndrome and the Exploration of Pathogenic Mechanisms. BMC Med. Genomics 2024, 17, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedhammer, K.M.; Ćomić, J.; Tasic, V.; Putnik, J.; Abazi-Emini, N.; Paripovic, A.; Stajic, N.; Meitinger, T.; Nushi-Stavileci, V.; Berutti, R.; et al. Exome Sequencing in Individuals with Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract (CAKUT): A Single-Center Experience. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2023, 31, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Yang, J.; Zhu, J. Prenatal Diagnosis and Genetic Analysis of a Fetus with Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome: A Case Report. Medicine 2022, 101, e31172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Deffenbacher, K.; Cremers, C.W.; Van Camp, G.; Kimberling, W.J. Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome: Identification of Novel Mutations, Molecular Characterization, Mutation Distribution, and Prospects for Genetic Testing. Genet. Test. 1997, 1, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.H.; Sun, J.W.; Wan, G.L.; Chen, H.; Li, W.J.; Zhao, W.; Pan, C.C. A new pathogenic variation of EYA1 gene in a family with BOR syndrome and the diagnostic exploration. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2020, 55, 1069–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickard, S.; Boxer, M.; Trompeter, R.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M. Importance of Clinical Evaluation and Molecular Testing in the Branchio-Oto-Renal (BOR) Syndrome and Overlapping Phenotypes. J. Med. Genet. 2000, 37, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sanggaard, K.M.; Rendtorff, N.D.; Kjaer, K.W.; Eiberg, H.; Johnsen, T.; Gimsing, S.; Dyrmose, J.; Nielsen, K.O.; Lage, K.; Tranebjaerg, L. Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome: Detection of EYA1 and SIX1 Mutations in Five out of Six Danish Families by Combining Linkage, MLPA and Sequencing Analyses. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 15, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhak, S.; Kalatzis, V.; Heilig, R.; Compain, S.; Samson, D.; Vincent, C.; Weil, D.; Cruaud, C.; Sahly, I.; Leibovici, M.; et al. A Human Homologue of the Drosophila Eyes Absent Gene Underlies Branchio-Oto-Renal (BOR) Syndrome and Identifies a Novel Gene Family. Nat. Genet. 1997, 15, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.H.; Kwon, T.-J.; Kim, H.R.; Jeon, J.H.; Baek, J.-I.; Lee, W.-S.; Kim, U.-K.; Choi, J.Y. Mutational Analysis of EYA1, SIX1 and SIX5 Genes and Strategies for Management of Hearing Loss in Patients with BOR/BO Syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kwon, M.-J.; Boo, S.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Cho, Y.-S.; Chung, W.-H.; Hong, S.H. A Novel Splice Site Mutation in the EYA1 Gene in a Korean Family with Branchio-Oto (BO) Syndrome. Acta Otolaryngol. 2009, 129, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, M.; Kanno, A.; Nara, K.; Mutai, H.; Morisada, N.; Iijima, K.; Morimoto, N.; Nakano, A.; Sugiuchi, T.; Okamoto, Y.; et al. Phenotype-Genotype Correlation in Patients with Typical and Atypical Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Ling, J.; Peng, X.; Liu, X.; Mao, S.; Chen, Y.; Qin, M.; Zhang, S.; Bai, Y.; Song, J.; et al. A Novel EYA1 Mutation Causing Alternative RNA Splicing in a Chinese Family with Branchio-Oto Syndrome: Implications for Molecular Diagnosis and Clinical Application. Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. 2023, 16, 342–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, M.; Fujimaru, R.; Morimoto, N.; Satomura, K.; Kaku, Y.; Tsuzuki, K.; Nozu, K.; Okuyama, T.; Iijima, K. EYA1 and SIX1 Gene Mutations in Japanese Patients with Branchio-Oto-Renal (BOR) Syndrome and Related Conditions. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2006, 21, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.-K.; Wang, S.-Y.; Xia, X.; Ding, W.-J.; Duan, L.; Cui, X.; Xu, B.-C.; Zhu, Y.-M.; Liu, X.-W. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing Identifies a Novel Frameshift EYA1 Variant Causing Branchio-Otic Syndrome in a Chinese Family. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2020, 138, 110202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruijt, L.; Hoefsloot, L.H.; van Schaijk, G.H.W.H.; van Waardenburg, D.; Kremer, B.; Brackel, H.J.L.; de Die-Smulders, C.E.M. Identification of a Novel EYA1 Mutation Presenting in a Newborn with Laryngomalacia, Glossoptosis, Retrognathia, and Pectus Excavatum. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 140, 1343–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, J.; Pei, Y.; Mo, Y.; Jiang, X.; Chen, L. Misdiagnosed Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome Presenting as Proteinuria and Renal Insufficiency with Insidious Signs since Early Childhood: A Report of Three Cases. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retterer, K.; Juusola, J.; Cho, M.T.; Vitazka, P.; Millan, F.; Gibellini, F.; Vertino-Bell, A.; Smaoui, N.; Neidich, J.; Monaghan, K.G.; et al. Clinical Application of Whole-Exome Sequencing across Clinical Indications. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Huang, R.; Ma, X.L.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.S.; Ruan, B. Identification and genetic analysis of new mutations in EYA1 gene of BOS syndrome. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2021, 56, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalcouyé, A.; Traoré, O.; Diarra, S.; Schrauwen, I.; Esoh, K.; Kadlubowska, M.K.; Bharadwaj, T.; Adadey, S.M.; Kéita, M.; Guinto, C.O.; et al. A Monoallelic Variant in EYA1 Is Associated with Branchio-Otic Syndrome in a Malian Family. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2022, 10, e1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namba, A.; Abe, S.; Shinkawa, H.; Kimberling, W.J.; Usami, S.I. Genetic Features of Hearing Loss Associated with Ear Anomalies: PDS and EYA1 Mutation Analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 46, 518–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bałdyga, N.; Oziębło, D.; Gan, N.; Furmanek, M.; Leja, M.L.; Skarżyński, H.; Ołdak, M. The Genetic Background of Hearing Loss in Patients with EVA and Cochlear Malformation. Genes 2023, 14, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Shen, Q.; Sun, L.; Liu, H.; An, Y.; Xu, H. A de Novo and Novel Mutation in the EYA1 Gene in a Chinese Child with Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2018, 7, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardi, E.; Palermo, A.; Cusimano, P.; Mulè, G.; Cerasola, G. Young Woman with Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome and a Novel Mutation in the EYA-1 Gene. Clin. Nephrol. 2011, 76, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, M.; d’Altilia, M.; Montemurno, E.; Diella, S.; Bruno, F.; Netti, G.S.; Ranieri, E.; Stallone, G.; Infante, B.; Grandaliano, G.; et al. Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome (BOR) Associated with Focal Glomerulosclerosis in a Patient with a Novel EYA1 Splice Site Mutation. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, P.; Liu, H.; Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhu, W.; Wu, H.; Yang, T. EYA1 Mutations Leads to Branchio-Oto Syndrome in Two Chinese Han Deaf Families. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 123, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wang, H.; Che, J.; Cui, F.; Guo, J.; Tian, W.; Peng, J.; Yang, B.; Li, H.; et al. Prenatal Phenotypic Analysis of Branchio-Oto-Renal Spectrum Disorder Attributable to EYA1 Gene Pathogenic Variants and Systematic Literature Review. Prenat. Diagn. 2024, 44, 1509–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spahiu, L.; Merovci, B.; Ismaili Jaha, V.; Batalli Këpuska, A.; Jashari, H. Case Report of a Novel Mutation of the EYA1 Gene in a Patient with Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome. Balk. J. Med. Genet. 2016, 19, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Mahmoudi, A.; Gu, Y.; Fu, J.; Yuan, Q.; Liu, W. Case Report: A Novel Mutation in the EYA1 Gene in a Child with Branchiootic Syndrome with Secretory Otitis Media and Bilateral Vestibular Hypofunction. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1292085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.F.; Xu, G.E.; Chen, B.; Sun, S.P.; Zeng, B.P.; Tang, W.X.; Lu, W. Branchio-oto-renal syndrome or branchio-oto syndrome: The clinical and genetic analysis in five Chinese families. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 2022, 57, 1433–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Lin, K.; Gao, Y.; Ming, C.; Ma, J. Clinical phenotypic and genetic analysis of syndrome families with EYA1 gene variants. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi = J. Clin. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 38, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Okada, M.; Usami, S.-I.; Okuyama, T. Phenotypic Consequences in a Japanese Family Having Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome with a Novel Frameshift Mutation in the Gene EYA1. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007, 127, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, C.; Kalatzis, V.; Compain, S.; Levilliers, J.; Slim, R.; Graia, F.; Pereira, M.L.; Nivelon, A.; Croquette, M.F.; Lacombe, D. A Proposed New Contiguous Gene Syndrome on 8q Consists of Branchio-Oto-Renal (BOR) Syndrome, Duane Syndrome, a Dominant Form of Hydrocephalus and Trapeze Aplasia; Implications for the Mapping of the BOR Gene. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1994, 3, 1859–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Watanabe, Y.; Ohto, H.; Kawakami, K. Molecular Interaction and Synergistic Activation of a Promoter by Six, Eya, and Dach Proteins Mediated through CREB Binding Protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 6759–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Yan, Y.; Mei, Q.; Wu, K. Retinal Determination Gene Networks: From Biological Functions to Therapeutic Strategies. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmik, Z.; Holland, N.D.; Kreslova, J.; Oliveri, D.; Schubert, M.; Jonasova, K.; Holland, L.Z.; Pestarino, M.; Benes, V.; Candiani, S. Pax–Six–Eya–Dach Network during Amphioxus Development: Conservation in Vitro but Context Specificity in Vivo. Dev. Biol. 2007, 306, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, P.B.; Chernos, J.E.; Thomas, M.A. Review of the Recurrent 8q13.2q13.3 Branchio-oto-renal Related Microdeletion, and Report of an Additional Case with Associated Distal Arthrogryposis. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2016, 170, 2984–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisada, N.; Nozu, K.; Iijima, K. Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome: Comprehensive Review Based on Nationwide Surveillance in Japan. Pediatr. Int. Off. J. Jpn. Pediatr. Soc. 2014, 56, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.; Bierhals, T.; Kortüm, F.; Bartels, I.; Liehr, T.; Burfeind, P.; Shoukier, M.; Frank, V.; Bergmann, C.; Kutsche, K. Branchio-Otic Syndrome Caused by a Genomic Rearrangement: Clinical Findings and Molecular Cytogenetic Studies in a Patient with a Pericentric Inversion of Chromosome 8. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 142, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, L.; Hasegawa, A.; Kamura, H.; Hasegawa, F.; Yamamura, M.; Taniguchi, K.; Ito, Y.; Hata, K.; Samura, O.; Okamoto, A. Missense BICD2 Variants in Fetuses with Congenital Arthrogryposis and Pterygia. Hum. Genome Var. 2024, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewerin, S.; Aurnhammer, C.; Skubic, C.; Blagotinšek Cokan, K.; Jeruc, J.; Rozman, D.; Pfister, F.; Dittrich, K.; Mayer, B.; Schönauer, R.; et al. Mechanisms of Pathogenicity and the Quest for Genetic Modifiers of Kidney Disease in Branchiootorenal Syndrome. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, sfad260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, J.; Akdemir, Z.C.; Zhao, Y.; Du, R.; Ye, Y.; et al. TBX6 Missense Variants Expand the Mutational Spectrum in a Non-Mendelian Inheritance Disease. Hum. Mutat. 2020, 41, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barat-Houari, M.; Dumont, B.; Fabre, A.; Them, F.T.; Alembik, Y.; Alessandri, J.-L.; Amiel, J.; Audebert, S.; Baumann-Morel, C.; Blanchet, P.; et al. The Expanding Spectrum of COL2A1 Gene Variants IN 136 Patients with a Skeletal Dysplasia Phenotype. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 24, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Markova, T.; Kenis, V.; Melchenko, E.; Osipova, D.; Nagornova, T.; Orlova, A.; Zakharova, E.; Dadali, E.; Kutsev, S. Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of COL2A1-Associated Skeletal Dysplasias in 60 Russian Patients: Part I. Genes 2022, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olavarrieta, L.; Morales-Angulo, C.; del Castillo, I.; Moreno, F.; Moreno-Pelayo, M.A. Stickler and Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndromes in a Patient with Mutations in EYA1 and COL2A1 Genes. Clin. Genet. 2008, 73, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brophy, P.D.; Alasti, F.; Darbro, B.W.; Clarke, J.; Nishimura, C.; Cobb, B.; Smith, R.J.; Manak, J.R. Genome-Wide Copy Number Variation Analysis of a Branchio-Oto-Renal Syndrome Cohort Identifies a Recombination Hotspot and Implicates New Candidate Genes. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 1339–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Disorder | Genotype | Phenotype | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | OMIM | Inher. | Branchial | Ear | Renal | Eye | Musculoskeletal | Neurologic | Immunologic | ||
| BORS | |||||||||||
| Type 1 | EYA1 | 113650 | AD | + | + | + | ± | − | − | − | |
| Type 2 | SIX5 | 610896 | AD | + | + | + | − | − | − | − | |
| BOS | |||||||||||
| Type 1 | EYA1 | 120502 | AD | + | + | − | ± | − | − | − | |
| Type 2 | - | 602588 | AD | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | |
| Type 3 | SIX1 | 608389 | AD | + | + | − | − | − | − | − | |
| OTFCS | |||||||||||
| Type 1 | EYA1 | 166780 | AD | + | + | + | − | + | + | ± | |
| Type 2 | PAX1 | 615560 | AR | + | + | − | ± | + | + | + |
| Gene | MIM Number | pHaplo | Phenotypes | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EYA1 | 601653 | 0.90 | BORS, OTFCS. | - |
| LACTB2 | 618921 | 0.31 | - | May have a role in mitochondrial function and cell viability (Yu et al., 2016) [25] |
| NCOA2 | 601993 | 0.99 | - | Encodes a nuclear receptor coactivator, which aids in the function of nuclear hormone receptors (Cai et al., 2019) [26] |
| PRDM14 | 611781 | 0.59 | - | Gene amplification has frequently been observed in human tumors (Nishikawa et al., 2007) [27] |
| SLCO5A1 | 613543 | 0.35 | - | Highly expressed in fetal and adult brain and heart (Isidor et al., 2010) [28] |
| SULF1 | 610012 | 0.66 | - | Involved in cell signaling by heparin-binding growth factors (Lai et al., 2003) [29] |
| TRAM1 | 605190 | 0.88 | - | Functional analysis indicated that it influences glycosylation and is stimulatory or required for the translocation of secretory proteins (Gorlich et al., 1992) [30] |
| Genotype | Phenotype | Reference | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CDS (c.) | Protein (p.) | Exon(s) | Variant type | Author | |
| 164C>T | Thr55Met | 4 | ms | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 283C>T | Pro62Ser | 6 | ms | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 321del | Ala108HisfsTer133 | 6 | fs | BOR | Lee et al., Ann. Clin. Lab Sci. (2009) [32] |
| 348del | Gly117GlufsTer124 | 6 | fs | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 402C>A | Gly107Ser | 6 | ms | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 418G>A | Gly140Ser | 6 | ms | BOR/BO | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011), Kim et al., Mol. Biol. Rep. (2014) [11,33] |
| 418+1G>C | Invariant ‘gt’ | IVS6 | sp | BOR | Unzaki et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2018) [24] |
| 450_451del | Gly151IlefsTer36 | 7 | fs | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 466C>T | Gln156Ter | 7 | ns | BOR | Wang et al., Laryngoscope (2012) [34] |
| 525del | Gly176AspfsTer65 | 7 | fs | BOR | Klingbeil et al., Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. (2017) [35] |
| 529C>T | Gln177Ter | 7 | ns | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 553C>T | Gln185Ter | 7 | ns | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 588T>G | Tyr196Ter | 8 | ns | BO | Ideura et al., Sci. Rep. (2019) [36] |
| 592G>T | Gly198Ter | 8 | ns | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 602C>G | Ser201Ter | 8 | ns | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 634C>T | Gln212Ter | 8 | ns | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 638A>T | Gln213Leu | 8 | ms | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 639G>C | Gln213His | 8 | ms | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 639+1G>A | Invariant ‘gt’ | IVS8 | sp | OTFC | Estefanía et al., Ann. Hum. Genet. (2006) [13] |
| 639+1G>C | Invariant ‘gt’ | IVS8 | sp | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 639+2del | Invariant ‘gt’ | IVS8 | sp | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 639+3A>C | exon skipping | IVS8 | sp | BOR | Zhang et al., BMC Med. Genomics (2024) [37] |
| 640-15G>A | New splice acceptor | IVS8 | sp | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 769del | Gln257SerfsTer109 | 9 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 678C>A | Tyr226Ter | 9 | ns | BOR | Riedhammer et al., Eur. J. Hum. Genet. (2023) [38] |
| 685_695dup | Ser233IlefsTer12 | 9 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 698C>A | Ser233Ter | 9 | ns | BOR | Unzaki et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2018) [24] |
| 715dup | Tyr239LeufsTer50 | 9 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 735_743delCAGCCCAACinsTG | Ser246GlyfsTer118 | 9 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 768C>A | Tyr256Ter | 9 | ns | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 777dup | Glu260ArgfsTer29 | 9 | fs | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 802C>T | Gln268Ter | 9 | ns | BOR | Cho et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci. (2024) [8] |
| 821del | Thr274LysfsTer92 | 9 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 827-1G>C | Invariant ‘at’ | IVS9 | sp | BOR | Tang et al., Medicine (Baltimore) (2022) [39] |
| 845_852del | Ser282AsnfsTer4 | 10 | fs | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 851C>G | Ser284Ter | 10 | ns | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 863_866del | Lys288IlefsTer77 | 10 | fs | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 866del | Asp289ValfsTer77 | 10 | fs | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 875dup | Asp293Ter | 10 | ns | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 880C>T | Arg294Ter | 10 | ns | BOR | Kumar et al., Genet. Test. (1997) [40] |
| 882del | Leu295CysfsTer71 | 10 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 889C>T | Arg297Ter | 10 | fs | BOR/BO | Rickard et al., J. Med. Gen. (2000); Wang et al., Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi (2020) [41,42] |
| 920del | Arg307fsTer365 | 10 | fs | BOR | Sanggaard et al., Eur. J. Hum. Genet. (2007) [43] |
| 922C>T | Arg308Ter | 10 | ns | BOR/BO | Abdelhak et al., Nat. Gen. (1997); Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31,44] |
| 965A>G | Glu322Gly | 10 | ms | BOR/BO | Song et al., PloS ONE (2013) [45] |
| 966+5G>A | ? | IVS10 | sp | BOR/BO | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011); Stockley et al., Am. J. Med. Genet. A (2009) [11,23] |
| 966_966+14del | splice junction loss | IVS10 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 967-1G>A | Invariant ‘ag’ | IVS10 | sp | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 967-2A>G | Invariant ‘ag’ | IVS10 | sp | BOR | Kwon et al., Acta Otolaryngol. (2009) [46] |
| 967A>T | Arg323 | 11 | ns | BOR | Wang et al., BMC Med. Genet. (2018) [12] |
| 977T>A | Ile326Asn | 11 | ms | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 979T>C | Trp327Arg | 11 | ms | BO | Klingbeil et al., Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. (2017) [35] |
| 979T>G | Trp327Gly | 11 | ms | BOR | Masuda et al., Sci. Rep. (2022) [47] |
| 989A>T | Glu330Val | 11 | ms | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1029del | Tyr344ThrfsTer22 | 11 | fs | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1050+1G>T | Invariant ‘gt’ | IVS11 | sp | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1050+2T>C | Invariant ‘gt’ | IVS11 | sp | BOR | Unzaki et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2018) [24] |
| 1050+3G>T | ? | IVS11 | sp | BOR | Masuda et al., Sci. Rep. (2022) [47] |
| 1050+4A>C | exon skipping | IVS11 | sp | BO | Chen et al., Clin. Exp. Otorhinolaryngol. (2023) [48] |
| 1051-12T>G | New splice acceptor | IVS11 | sp | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1051-1G>C | Invariant ‘ag’ | IVS11 | sp | BOR | Okada et al., Pediatr. Nephrol. (2006) [49] |
| 1054_1055insG | Pro352ArgfsTer26 | 12 | fs | BOR | Masuda et al., Sci. Rep. (2022) [47] |
| 1075_1077delinsAT | Gly359IlefsTer | 12 | fs | BO | Xing et al., Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. (2020) [50] |
| 1081C>T | Arg361Ter | 12 | ns | BOR/BO | Kumar et al., Genet. Test. (1997); Spruijt et al., Am. J. Med. Gen. A (2006) [40,51] |
| 1088A>T | Glu363Val | 12 | ms | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1138G>T | Glu380Ter | 12 | ns | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1140+1G>A | ? | IVS12 | sp | BOR/BO | Song et al., PloS ONE (2013) [45] |
| 1171del | Ser391fsTer9 | 12 | fs | BOR | Lin et al., BMC Nephrol. (2023) [52] |
| 1161_1164del | Ile387MetfsTer12 | 12 | fs | BO | Unzaki et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2018) [24] |
| 1118del | His373LeufsTer4 | 12 | fs | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1122del | Leu374PhefsTer6 | 12 | fs | BOR | Unzaki et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2018) [24] |
| 1138_1140+1del | Invariant ‘gt’ | 12; IVS12 | sp | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1140+1G>A | Invariant ‘gt’ | IVS12 | sp | BOR/BO | Song et al., PloS ONE (2013) [45] |
| 1141-1G>A | Invariant ‘ag’ | 13 | fs | BOR | Sanggaard et al., Eur. J. Hum. Genet. (2007) [43] |
| 1156del | His386IlefsTer2 | 13 | fs | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1189C>T | Gln397Ter | 13 | ns | BO | Ideura et al., Sci. Rep. (2019) [36] |
| 1199+1G>C | Invariant ‘gt’ | IVS13 | sp | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1200-1G>A | Invariant ‘ag’ | IVS13 | sp | BO | Retterer et al., Genet. Med. (2016) [53] |
| 1220G>A | Arg407Gln | 14 | ms | BO | Cho et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci. (2024) [8] |
| 1254_1255del | Cys419PhefsTer32 | 14 | fs | BO | Ideura et al., Sci. Rep. (2019) [36] |
| 1255del | Cys419ValfsTer13 | 14 | fs | BO | Ma et al., Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi (2021) [54] |
| 1268del | Gly423ValfsTer9 | 14 | fs | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1276G>A | Gly426Ser | 14 | ms | BOR | Cho et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci. (2024) [8] |
| 1286A>G | Asp429Gly | 14 | ms | BO | Namba et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2001); Yalcouyé et al., Mol. Genet. Genomic Med. (2022) [55,56] |
| 1289G>A | Trp430Ter | 14 | ns | BOR | Unzaki et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2018) [24] |
| 1315_1318dup | Arg440GlnfsTer13 | 14 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1319G>A | Arg440Gln | 14 | ms | BOR | Unzaki et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2018) [24] |
| 1329_1330 | Glu443AspfsTer8 | 14 | fs | BOR | Bałdyga et al., Genes (2023) [57] |
| 1330_1331dup | Tyr445SerfsTer24 | 14 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1350delinsCC | Asn451GlnfsTer10 | 14 | fs | BO | Abdelhak et al., Nat. Genet. (1997) [44] |
| 1360+4A>G | ? | IVS14 | sp | BOR | Sanggaard et al., Eur. J. Hum. Genet. (2007) [43] |
| 1361-1G>A | Invariant ‘ag’ | IVS14 | sp | BOR | Riedhammer et al., Eur. J. Hum. Genet. (2023) [38] |
| 1377_1378 delinsAT | Lys460Ter | 15 | ns | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1381del | Arg461GlyfsTer7 | 15 | fs | BOR | Li et al., Intractable Rare Dis. Res. (2018) [58] |
| 1405del | Ala469ProfsTer6 | 15 | fs | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1420_1421del | Leu474AspfsTer57 | 15 | fs | BOR | Nardi et al., Clin. Nephrol. (2011) [59] |
| 1471_1474dup | Arg492LeufsTer41 | 15 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1475G>C | Arg492Pro | 15 | ms | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1475+1G>C | Invariant ‘gt’ | 15 | sp | BOR | Gigante et al. BMC Nephrol.(2013) [60] |
| 1476-2A>G | Invariant ‘ag’ | IVS15 | sp | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1487del | Val496GlyfsTer4 | 16 | fs | BOR | Masuda et al., Sci. Rep. (2022) [47] |
| 1493_1494insAT | Ile498PhefsTer3 | 16 | fs | BOR | Chen et al., Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. (2019) [61] |
| 1496del | Leu499Ter | 16 | ns | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1510C>T | Gln504Ter | 16 | ns | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1524del | Leu509TrpfsTer9 | 16 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1533dup | Val512SerfsTer20 | 16 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1534G>T | Val512Phe | 16 | ms | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1538T>C | Leu513Pro | 16 | ms | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1541T>C | Leu514Pro | 16 | ms | BO/OTFC | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011); Mercer et al., Clin. Dysm. (2006) [11,15] |
| 1570G>T | Glu524Ter | 16 | ns | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1579T>A | Tyr527Asn | 16 | ms | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1580A>G | yr527Cys | 16 | ms | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1591A>T | Lys531Ter | 16 | ns | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1597G>A | Gly533Arg | 16 | ms | BO | Castiglione et al., Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. (2014) [6] |
| 1597+1G>A | Invariant ‘gt’ | IVS16 | sp | BOR | Tian et al., Prenat. Diagn. (2024) [62] |
| 1598-2A>C | Invariant ‘at’ | IVS16 | sp | BOR/BO | Song et al., PloS ONE (2013) [45] |
| 1603_1607del | Glu535LeufsTer3 | 17 | fs | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1623_1626dup | Gln543AsnfsTer90 | 17 | fs | BOR | Cho et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci. (2024) [8] |
| 1627C>T | Gln543Ter | 17 | ns | BOR | Spahiu et al., Balkan J. Med. Genet. (2016) [63] |
| 1644del | Val549TrpfsTer6 | 17 | fs | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1641_1645del | Arg547SerfsTer83 | 17 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1643_1644dup | Val549LysfsTer7 | 17 | fs | BOR | Unzaki et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2018) [24] |
| 1649T>A | Val550Glu | 17 | ms | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1653T>G | Tyr551Ter | 17 | ns | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1657_1659del | Val553del | 17 | indel | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1697dup | His567AlafsTer65 | 17 | fs | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1697_1698delAGinsT | Lys566IlefsTer73 | 17 | fs | BO | He et al., Front. Genet. (2024) [64] |
| 1698+1G>T | Invariant ‘gt’ | 17 | sp | BOR | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1706T>C | Met569Thr | 18 | ms | BO | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1715G>T | Trp572Leu | 18 | ms | BO | Feng et al., Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi (2022) [65] |
| 1715G>A | Trp572Ter | 18 | ns | BOR | Cho et al., Int. J. Mol. Sci. (2024) [8] |
| 1716G>A | Trp572Ter | 18 | ns | BO | Orten et al., Hum. Mutat. (2008) [31] |
| 1730_1745del | His577ProfsTer57 | 18 | fs | BO | Unzaki et al., J. Hum. Genet. (2018) [24] |
| 1735del | Asp579ThrfsTer60 | 18 | fs | BOR | Wang et al., Laryngoscope (2012) [34] |
| 1744del | Ala582ProfsTer57 | 18 | fs | BO | Shao et al., Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi (2024) [66] |
| 1754dup | His585GlnfsTer47 | 18 | fs | BOR | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1766dup | Glu590GlyfsTer42 | 18 | fs | BOR | Masuda et al., Sci. Rep. (2022) [47] |
| 1768del | Glu590SerfsTer49 | 18 | fs | BO | Klingbeil et al., Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. (2017) [35] |
| 1773C>G | Tyr591Ter | 18 | ns | BO | Sanggaard et al., Eur. J. Hum. Genet. (2007) [43] |
| 1777T>A | Ter593LysextTer6 | 18 | sl | BO | Krug et al., Hum. Mutat. (2011) [11] |
| 1777_1778delTAinsGT | Ter593Val | 18 | sl | BO | Matsunaga et al., Acta Otolaryngol. (2007) [67] |
| Reference | Patients (n.) | HL | BA | EA | RA | MSK | NDD | ST | Other | Genotype | Variant Type | Inheritance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vincent et al., 1994 [68] | 1 | + | + | NT | + | + | + | − | Hydrocephalus | 8q12.2–q21.2del | CNV | de novo |
| Rickard et al., 2001 [14] | 1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | del(ex7,9,13) | CNV | de novo |
| 2 | + | + | + | + | − | + | − | − | del(ex7,9,13) | CNV | de novo | |
| Estefanía et al., 2006 [13] | 1 | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | IgA deficiency | c.639+1G>A | SNV | de novo |
| Mercer et al., 2006 [15] | 1 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | c.1442T>C | SNV | NT |
| This study | 1 | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | − | 8q13.2q13.3del | CNV | de novo |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graziani, L.; Carriero, M.L.; Melchionda, S.; Augello, B.; Palumbo, O.; Bengala, M.; Castori, M.; Novelli, G. Otofaciocervical Syndrome and Its Overlap with Branchiootorenal Spectrum: An Integrated Literature Analysis of EYA1-Related Disorders, Including a Novel Case with an 8q13.2q13.3 Deletion. Genes 2025, 16, 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111267
Graziani L, Carriero ML, Melchionda S, Augello B, Palumbo O, Bengala M, Castori M, Novelli G. Otofaciocervical Syndrome and Its Overlap with Branchiootorenal Spectrum: An Integrated Literature Analysis of EYA1-Related Disorders, Including a Novel Case with an 8q13.2q13.3 Deletion. Genes. 2025; 16(11):1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111267
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraziani, Ludovico, Miriam Lucia Carriero, Salvatore Melchionda, Bartolomeo Augello, Orazio Palumbo, Mario Bengala, Marco Castori, and Giuseppe Novelli. 2025. "Otofaciocervical Syndrome and Its Overlap with Branchiootorenal Spectrum: An Integrated Literature Analysis of EYA1-Related Disorders, Including a Novel Case with an 8q13.2q13.3 Deletion" Genes 16, no. 11: 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111267
APA StyleGraziani, L., Carriero, M. L., Melchionda, S., Augello, B., Palumbo, O., Bengala, M., Castori, M., & Novelli, G. (2025). Otofaciocervical Syndrome and Its Overlap with Branchiootorenal Spectrum: An Integrated Literature Analysis of EYA1-Related Disorders, Including a Novel Case with an 8q13.2q13.3 Deletion. Genes, 16(11), 1267. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16111267









