Genetic Alteration Profiling in North Macedonian Lung Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Demographic Properties of the Patients Included in the Study
2.3. Molecular Testing
2.4. Immunohistochemical (ICH) Analysis
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. EGFR Mutations
4.2. BRAF Mutations
4.3. KRAS Mutations
4.4. PIK3CA Mutations
4.5. ALK and ROS1 Rearrangements
4.6. PD-L1 and HER2/NEU Expression
4.7. Co-Occurring Genetic Alterations
5. Conclusions and Limitations
- (1)
- The absence of clinical follow-up data results in a lack of correlation between detected mutations, survival outcomes and treatment responses. Consequently, this study offers limited insights into the diagnostic and prognostic significance of multigene testing in the context of lung cancer diagnostics and treatment.
- (2)
- It is possible that genetic changes occurring outside the hotspot regions addressed by the specific assays may have been missed.
- (3)
- Tumor biopsy specimens possess an intrinsic limitation in that they fail to capture inter-metastatic tumor heterogeneity. While driver mutations are regarded as truncal events that are present across all disease sites, other co-occurring genetic alterations may have developed subsequently and could exist at locations distinct from the site where the biopsy was conducted. Liquid biopsies (such as circulating tumor DNA analysis) and advanced sequencing technologies may assist in addressing these limitations.
- (4)
- The use of a retrospective database limits the ability to investigate other sources of potential bias.
- (5)
- All participants in the study were Caucasian; therefore, the results obtained may not be relevant to other racial and ethnic groups.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALK | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| FFPE | Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| KRAS | Kirsten rat sarcoma virus |
| LCLC | Large-cell lung carcinoma |
| LCNEC | Large-cell neuroendocrine carcinoma |
| NCCN | National Comprehensive Cancer Network |
| NOS | Lung cancer not otherwise specified |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PCR | Polymerase-chain reaction |
| PD-L1 | Programmed (cell) death-ligand 1 |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
| ROS-1 | Repressor of silencing 1 |
| RR | Response rate |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| SCLC | Small-cell lung cancer |
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| UICC | Union of International Cancer Control |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2020; Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr Canc. Netw. 2022, 20, 497–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraumeni, J.F. Respiratory Carcinogenesis: An Epidemiologic Appraisal. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1975, 55, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janerich, D.T.; Thompson, D.W.; Varela, L.R.; Greenwald, P.; Chorost, S.; Tucci, C.; Zaman, M.; Melamed, M.; Kiely, M.; McKneally, M.F. Lung cancer and exposure to tobacco smoke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, T.; Nelson, D.I.; Steenland, K.; Leigh, J.; Concha-Barrientos, M.; Fingerhut, M.; Prüss-Üstün, A. The global burden of disease due to occupational carcinogens. Am. J. Ind. Med. 2005, 48, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straif, K.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V.; Guha, N.; Freeman, C.; Galichet, L.; et al. A review of human carcinogens—Part C: Metals, arsenic, dusts, and fibres. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 453–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiesweg, M.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Reis, H.; Ting, S.; Savvidou, N.; Skiba, C.; Herold, T.; Christoph, D.C.; Meiler, J.; Worm, K.; et al. High Prevalence of Concomitant Oncogene Mutations in Prospectively Identified Patients with ROS1-Positive Metastatic Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Yatabe, Y.; Austin, J.H.M.; Beasley, M.B.; Chirieac, L.R.; Dacic, S.; Duhig, E.; Flieder, D.B.; et al. The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Lung Tumors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlander, N.; Noone, A.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovic, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, R.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review (CSR) 1975–2018; National Cancer Institute: Betheseda, MD, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tsao, D.-A.; Chang, H.-J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Hsiung, S.-K.; Huang, S.-E.; Ho, S.-Y.; Chang, M.-S.; Chiu, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-F.; Cheng, T.-L.; et al. Gene Expression Profiles for Predicting the Efficacy of the Anticancer Drug 5-Fluorouracil in Breast Cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2010, 29, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mithoowani, H.; Febbraro, M. Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer in 2022: A Review for General Practitioners in Oncology. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 1828–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.M.; Komaki, R.; Johnson, D.H. A Randomized Trial of Postoperative Adjuvant Therapy in Patients with Completely Resected Stage II or IIIa Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.D.; Paulus, R.; Graham, M.V.; Ettinger, D.S.; Johnstone, D.W.; Pilepich, M.V.; Machtay, M.; Komaki, R.; Atkins, J.; Curran, W.J. Phase II Trial of Postoperative Adjuvant Paclitaxel/Carboplatin and Thoracic Radiotherapy in Resected Stage II and IIIA Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Promising Long-Term Results of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group-RTOG 9705. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 3480–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.-M.; Pan, C.; Eisbruch, A.; Haken, R.K.T. Physical Models and Simpler Dosimetric Descriptors of Radiation Late Toxicity. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2007, 17, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonett, J.R.; Suntharalingam, M.; Edelman, M.J.; Patel, A.B.; Gamliel, Z.; Doyle, A.; Hausner, P.; Krasna, M. Pulmonary Resection After Curative Intent Radiotherapy (>59 Gy) and Concurrent Chemotherapy in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 78, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonanno, L.; Favaretto, A.; Rosell, R. Platinum Drugs and DNA Repair Mechanisms in Lung Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leonetti, A.; Wever, B.; Mazzaschi, G.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Rolfo, C.; Quaini, F.; Tiseo, M.; Giovannetti, E. Molecular basis and rationale for combining immune checkpoint inhibitors with chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Drug Resist. Updates 2019, 46, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Aisner, D.L.; Arcila, M.E.; Beasley, M.B.; Bernicker, E.H.; Colasacco, C.; Dacic, S.; Hirsch, F.R.; Kerr, K.; et al. Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment with Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Guideline From the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142, 321–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobin, L.H.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Witterkind, C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 8th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016; Volume 1, ISBN 978-1-119-26357-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sequist, L.V.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yamamoto, N.; O’Byrne, K.; Hirsh, V.; Mok, T.; Geater, S.L.; Orlov, S.; Tsai, C.-M.; Boyer, M.; et al. Phase III Study of Afatinib or Cisplatin Plus Pemetrexed in Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma with EGFR Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3327–3334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Negoro, S.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Tada, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, V.A.; Riely, G.J.; Zakowski, M.F.; Li, A.R.; Patel, J.D.; Heelan, R.T.; Kris, M.G.; Sandler, A.B.; Carbone, D.P.; Tsao, A.; et al. Molecular Characteristics of Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma and Adenocarcinoma, Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Subtype, Predict Response to Erlotinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1472–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sequist, L.V.; Martins, R.G.; Spigel, D.; Grunberg, S.M.; Spira, A.; Jänne, P.A.; Joshi, V.A.; McCollum, D.; Evans, T.L.; Muzikansky, A.; et al. First-Line Gefitinib in Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Somatic EGFR Mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2442–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Bunn, P.A. EGFR testing in lung cancer is ready for prime time. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 432–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, P.K.; Varghese, A.M.; Sima, C.S.; Moreira, A.L.; Ladanyi, M.; Kris, M.G.; Rekhtman, N. Response to Erlotinib in Patients with EGFR Mutant Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancers with a Squamous or Squamous-like Component. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 2535–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, H.; Lin, L.; Takahashi, T.; Nomura, M.; Suzuki, M.; Wistuba, I.I.; Fong, K.M.; Lee, H.; Toyooka, S.; Shimizu, N.; et al. Clinical and Biological Features Associated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Gene Mutations in Lung Cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2005, 97, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eberhard, D.A.; Johnson, B.E.; Amler, L.C.; Goddard, A.D.; Heldens, S.L.; Herbst, R.S.; Ince, W.L.; Jänne, P.A.; Januario, T.; Johnson, D.H.; et al. Mutations in the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and in KRAS Are Predictive and Prognostic Indicators in Patients with Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated with Chemotherapy Alone and in Combination with Erlotinib. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5900–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Wu, Y.-L.; Ding, P.N.; Lord, S.J.; Inoue, A.; Zhou, C.; Mitsudomi, T.; Rosell, R.; Pavlakis, N.; Links, M.; et al. Impact of Specific Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations and Clinical Characteristics on Outcomes After Treatment with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Versus Chemotherapy in EGFR -Mutant Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1958–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Zhou, C.; Liam, C.-K.; Wu, G.; Liu, X.; Zhong, Z.; Lu, S.; Cheng, Y.; Han, B.; Chen, L.; et al. First-line erlotinib versus gemcitabine/cisplatin in patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: Analyses from the phase III, randomized, open-label, ENSURE study. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1883–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuzzo, F.; Ligorio, C.; Toschi, L.; Rossi, E.; Trisolini, R.; Paioli, D.; Magrini, E.; Finocchiaro, G.; Bartolini, S.; Cancellieri, A.; et al. EGFR and HER2 Gene Copy Number and Response to First-Line Chemotherapy in Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2007, 2, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Riely, G.J.; Mekhail, T.; Nguyen, D.; Garcia-Campelo, M.R.; Felip, E.; et al. Treatment Outcomes and Safety of Mobocertinib in Platinum-Pretreated Patients with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion–Positive Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, e214761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Park, E.; Yun, C.-H.; Sng, N.J.; Lucena-Araujo, A.R.; Yeo, W.-L.; Huberman, M.S.; Cohen, D.W.; Nakayama, S.; Ishioka, K.; et al. Structural, biochemical and clinical characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations in lung cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 216ra177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riess, J.W.; Gandara, D.R.; Frampton, G.M.; Madison, R.; Peled, N.; Bufill, J.A.; Dy, G.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Stephens, P.J.; McPherson, J.; et al. Diverse EGFR Exon 20 Insertions and Co-Occurring Molecular Alterations Identified by Comprehensive Genomic Profiling of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riely, G.J.; Neal, J.W.; Camidge, D.R.; Spira, A.I.; Piotrowska, Z.; Costa, D.B.; Tsao, A.S.; Patel, J.D.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Bazhenova, L.; et al. Activity and Safety of Mobocertinib (TAK-788) in Previously Treated Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations From a Phase 1/2 Trial. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Haura, E.B.; Leighl, N.B.; Mitchell, P.; Shu, C.A.; Girard, N.; Viteri, S.; Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, C.K.; et al. Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion–Mutated Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progressing on Platinum Chemotherapy: Initial Results From the CHRYSALIS Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udagawa, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Ohe, Y.; Satouchi, M.; Furuya, N.; Kim, Y.H.; Seto, T.; Soejima, K.; Hayakawa, D.; Kato, T.; et al. OA07.03 Clinical Outcome of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR/HER2 Exon 20 Insertions Identified in the LC-SCRUM-Japan. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.-H.I.; Lin, H.; Hong, J.-L. Real-world response and outcomes in NSCLC patients with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, P.E.N.S.; Gergis, C.; Viray, H.; Varkaris, A.; Fujii, M.; Rangachari, D.; VanderLaan, P.A.; Kobayashi, I.S.; Kobayashi, S.S.; Costa, D.B. EGFR-A763_Y764insFQEA Is a Unique Exon 20 Insertion Mutation That Displays Sensitivity to Approved and In-Development Lung Cancer EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2020, 1, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Costa, D.B. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in non-small-cell lung cancer: Preclinical data and clinical implications. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e23–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelabi, S.; Mignard, X.; Leroy, K.; Monnet, I.; Brosseau, S.; Theou-Anton, N.; Massiani, M.-A.; Friard, S.; Duchemann, B.; Fabre, E.; et al. EGFR Exon 20 Insertion in Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Survival and Clinical Efficacy of EGFR Tyrosine-Kinase Inhibitor and Chemotherapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 5132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, S.; Kim, Y.; Lim, S.W.; Cho, J.H.; Park, S.; Lee, J.; Sun, J.-M.; Choi, Y.-L.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations in Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer in Korea. Cancer Res. Treat. Off. J. Korean Cancer Assoc. 2019, 51, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, F.; Mazzaschi, G.; Minari, R.; Verzè, M.; Azzoni, C.; Bottarelli, L.; Nizzoli, R.; Pluchino, M.; Altimari, A.; Gruppioni, E.; et al. Multicenter Observational Study on Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring BRAF Mutations: Focus on Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Outcome of V600E and Non-V600E Subgroups. Cancers 2022, 14, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slebos, R.J.C.; Hruban, R.H.; Dalesio, O.; Mooi, W.J.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Rodenhuis, S. Relationship Between K-ras Oncogene Activation and Smoking in Adenocarcinoma of the Human Lung. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1991, 83, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Qi, R.; Ren, J.; Lv, D.; Yang, H. Characterization with KRAS Mutant Is a Critical Determinant in Immunotherapy and Other Multiple Therapies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludovini, V. Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase Catalytic Alpha and KRAS Mutations are Important Predictors of Resistance to Therapy with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-G.; Chang, Y.-L.; Yu, C.-J.; Yang, P.-C.; Shih, J.-Y. The Role of PIK3CA Mutations among Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients with Primary and Acquired Resistance to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Che, G. Clinical Significance of PIK3CA Gene in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 3608241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendarme, S.; Bylicki, O.; Chouaid, C.; Guisier, F. ROS-1 Fusions in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Evidence to Date. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 641–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugay, F.; Llamas-Gutierrez, F.; Gournay, M.; Medane, S.; Mazet, F.; Chiforeanu, D.C.; Becker, E.; Lamy, R.; Léna, H.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics of ROS1- and RET-rearranged NSCLC in caucasian patients: Data from a cohort of 713 non-squamous NSCLC lacking KRAS/EGFR/HER2/BRAF/PIK3CA/ALK alterations. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53336–53351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.R.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, H.J.; Hwang, S.K.; Park, J.K.; Shin, E.; Bae, M.K.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Wang, J.; Jewell, S.S.; et al. The frequency and impact of ROS1 rearrangement on clinical outcomes in never smokers with lung adenocarcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 2364–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, A.T.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Bang, Y.-J.; Camidge, D.R.; Solomon, B.J.; Salgia, R.; Riely, G.J.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Shapiro, G.I.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Crizotinib in ROS1 -Rearranged Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 1963–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Ritterhouse, L.L.; Ali, S.M.; Bailey, M.; Schrock, A.B.; Gainor, J.F.; Ferris, L.A.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Miller, V.A.; Iafrate, A.J.; et al. ROS1 Fusions Rarely Overlap with Other Oncogenic Drivers in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambros, L.; Guibourg, B.; Uguen, A. ROS1-rearranged Non–Small Cell Lung Cancers with Concomitant Oncogenic Driver Alterations: About Some Rare Therapeutic Dilemmas. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, e73–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, K.M.; Hirsch, F.R. Programmed Death Ligand-1 Immunohistochemistry: Friend or Foe? Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2016, 140, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xia, Y. Targeting HER2 Alterations in Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuyama, S.; Hotta, K.; Tabata, M.; Segawa, Y.; Fujiwara, Y.; Takigawa, N.; Kiura, K.; Ueoka, H.; Eguchi, K.; Tanimoto, M. Impact of HER2 Gene and Protein Status on the Treatment Outcome of Cisplatin-Based Chemoradiotherapy for Locally Advanced Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, S.L.; Tatum, A.; Herndon, J.E.; Box, J.; Memoli, V.; Green, M.R.; Kern, J.A. Use of neuroendocrine markers, p53, and HER2 to predict response to chemotherapy in patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer: A Cancer and Leukemia Group B study. Lung Cancer 2001, 33, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoulidis, F.; Heymach, J.V. Co-occurring genomic alterations in non-small cell lung cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholl, L.M.; Aisner, D.L.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Berry, L.D.; Dias-Santagata, D.; Wistuba, I.I.; Chen, H.; Fujimoto, J.; Kugler, K.; Franklin, W.A.; et al. Multi-institutional oncogenic driver mutation analysis in lung adenocarcinoma: The Lung Cancer Mutation Consortium experience. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, J.; Woo, K.M.; Sima, C.S.; Plodkowski, A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Chaft, J.; Kris, M.G.; Arcila, M.E.; Ladanyi, M.; Drilon, A. Impact of concurrent PIK3CA mutations on response to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition in EGFR-mutant lung cancers and on prognosis in oncogene-driven lung adenocarcinomas. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1713–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikor, L.A.; Ramnarine, V.R.; Lam, S.; Lam, W.L. Genetic alterations defining NSCLC subtypes and their therapeutic implications. Lung Cancer 2013, 82, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rabe, K.F. Precision Diagnosis and Treatment for Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | n (%) |
|---|---|
| gender | |
| male | 424 (70.32%) |
| female | 179 (29.68%) |
| age mean ± SD | 62.56 ± 9.34 |
| <39 years | 17 (2.82%) |
| 40–49 years | 41 (6.80%) |
| 50–59 years | 111 (18.40%) |
| 60–69 years | 216 (35.82%) |
| 70–79 years | 205 (34.00%) |
| ≥80 years | 13 (2.16%) |
| diagnosis | |
| NSCLC | 598 (99.17%) |
| adenocarcinoma | 560 (92.87%) |
| squamous-cell carcinoma | 27 (4.48%) |
| large-cell carcinoma | 11 (1.82%) |
| SCLC | 5 (0.83%) |
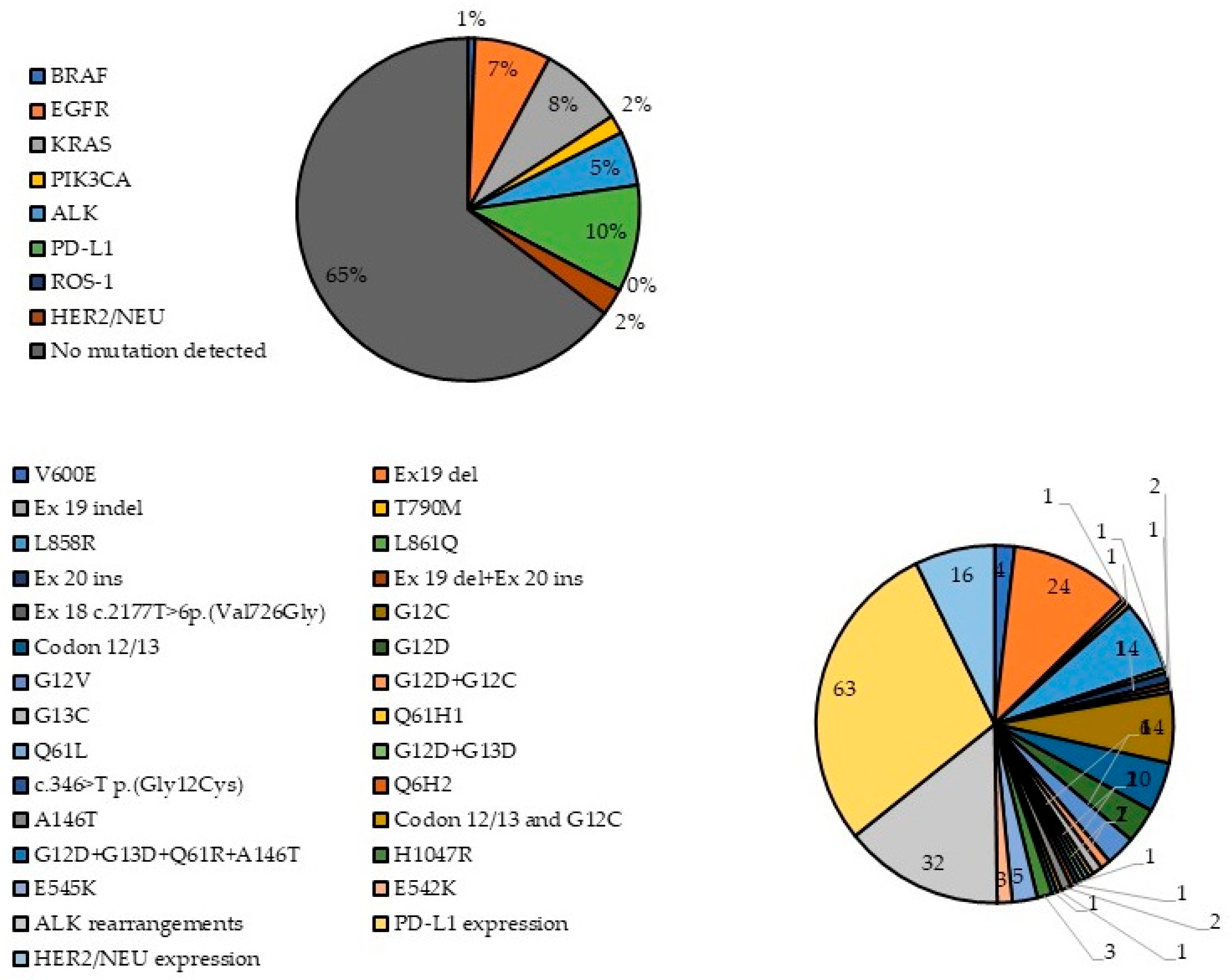
| Gene | Number of Patients Examined (% of All Patients) | Gender | Average Age of Patients with Gene Mutations | Average Age of wt Patients | Diagnosis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients with Gene Mutation (% of Tested) | M | F | Adenocarcinoma | Squamous-Cell Cancer | LCLC | SCLC | |||
| BRAF | 432 (71.64%) 4 (0.93%) | 3 | 1 | 57.75 | 62.87 | 3 | 1 | - | - |
| EGFR | 527 (87.40%) 45 (8.54%) | 23 | 22 | 61.36 | 62.82 | 45 (+2 planocellular cancer) | - | - | - |
| KRAS | 193 (32.00%) 50 (25.91%) | 34 | 16 | 61.25 | 64.25 | 44 | 2 (+1 patient with adenosquamous cancer) | 1 | - |
| PIK3CA | 142 (23.55%) 11 (7.75%) | 6 | 5 | 66.91 | 61.86 | 9 (+1 patient with planocellular cancer) | 1 | - | - |
| ALK | 411 (68.04%) 32 (7.79%) | 22 | 10 | 60.94 | 62.81 | 26 (+2 planocellular cancer) | 3 | 1 | - |
| PD-L1 | 264 (43.71%) 63 (23.86%) | 47 | 15 | 63.12 | 62.35 | 50 (+6 planocellular cancer) | 4 (+1 patient with adenosquamous cancer) | 1 | 1 |
| ROS-1 | 117 (19.37%) 0 (0%) | 0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| HER2/NEU | 144 (23.84%) 16 (11.11%) | 12 | 4 | 63.81 | 62.22 | 9 (+1 planocellular cancer) | 4 | 1 | - |
| Patient | Diagnosis | Gender | Age | Gene 2 | Gene 2 | Gene 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 71 | KRAS codon 12/13 | ALK | PD-L1 |
| P2 | Carcinoma bronchii | M | 65 | - | ALK | PD-L1 |
| P3 | Carcinoma planocellulare | M | 64 | - | ALK | PD-L1 |
| P4 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 67 | G12D, G12C KRAS | H1047R PIK3CA | - |
| P5 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 61 | G12C KRAS | ALK | - |
| P6 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 66 | KRAS codon 12/13 | BRAF V600E | - |
| P7 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 49 | - | ALK | PD-L1 |
| P8 | Carcinoma bronhii | M | 68 | G12C KRAS | BRAF V600E | - |
| P9 | Adenocarcinoma | F | 60 | V600E BRAF | - | PD-L1 |
| P10 | Adenocarcinoma | F | 60 | G12C KRAS | E542K PIK3CA | - |
| P11 | Adenocarcinoma | F | 56 | G12C KRAS | HER2 | - |
| P12 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 59 | KRAS c. s346G>T | ALK | - |
| P13 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 74 | - | HER2 | PD-L1 |
| P14 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 37 | - | EGFR | PD-L1 |
| P15 | Adenocarcinoma | F | 72 | G12V KRAS | - | PD-L1 |
| P16 | Adenocarcinoma | F | 61 | L858R EGFR | H1047R PIK3CA | - |
| P17 | Adenocarcinoma | F | 67 | E545K PIK3CA | ALK | - |
| P18 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 64 | - | HER2 | PD-L1 |
| P19 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 66 | G12C KRAS | HER2 | - |
| P20 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 67 | G12D, G12C KRAS | E545K PIK3CA | - |
| P21 | Adenocarcinoma | F | 59 | KRAS codon 12/13 | - | PD-L1 |
| P22 | Adenocarcinoma | M | 74 | KRAS codon 12/13 | ALK | PD-L1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eftimov, A.; Jovanovic, R.; Kostadinova Kunovska, S.; Bogdanovska Todorovska, M.; Ilievski, B.; Zdravkovski, P.; Komina, S.; Krstevska, B.; Crvenkova, S.; Simonovska, M.; et al. Genetic Alteration Profiling in North Macedonian Lung Cancer Patients. Genes 2025, 16, 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101177
Eftimov A, Jovanovic R, Kostadinova Kunovska S, Bogdanovska Todorovska M, Ilievski B, Zdravkovski P, Komina S, Krstevska B, Crvenkova S, Simonovska M, et al. Genetic Alteration Profiling in North Macedonian Lung Cancer Patients. Genes. 2025; 16(10):1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101177
Chicago/Turabian StyleEftimov, Aleksandar, Rubens Jovanovic, Slavica Kostadinova Kunovska, Magdalena Bogdanovska Todorovska, Boro Ilievski, Panche Zdravkovski, Selim Komina, Blagica Krstevska, Simonida Crvenkova, Marija Simonovska, and et al. 2025. "Genetic Alteration Profiling in North Macedonian Lung Cancer Patients" Genes 16, no. 10: 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101177
APA StyleEftimov, A., Jovanovic, R., Kostadinova Kunovska, S., Bogdanovska Todorovska, M., Ilievski, B., Zdravkovski, P., Komina, S., Krstevska, B., Crvenkova, S., Simonovska, M., & Petrushevska, G. (2025). Genetic Alteration Profiling in North Macedonian Lung Cancer Patients. Genes, 16(10), 1177. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes16101177





