Epidemiological Study on the Interaction between the PNPLA3 (rs738409) and Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
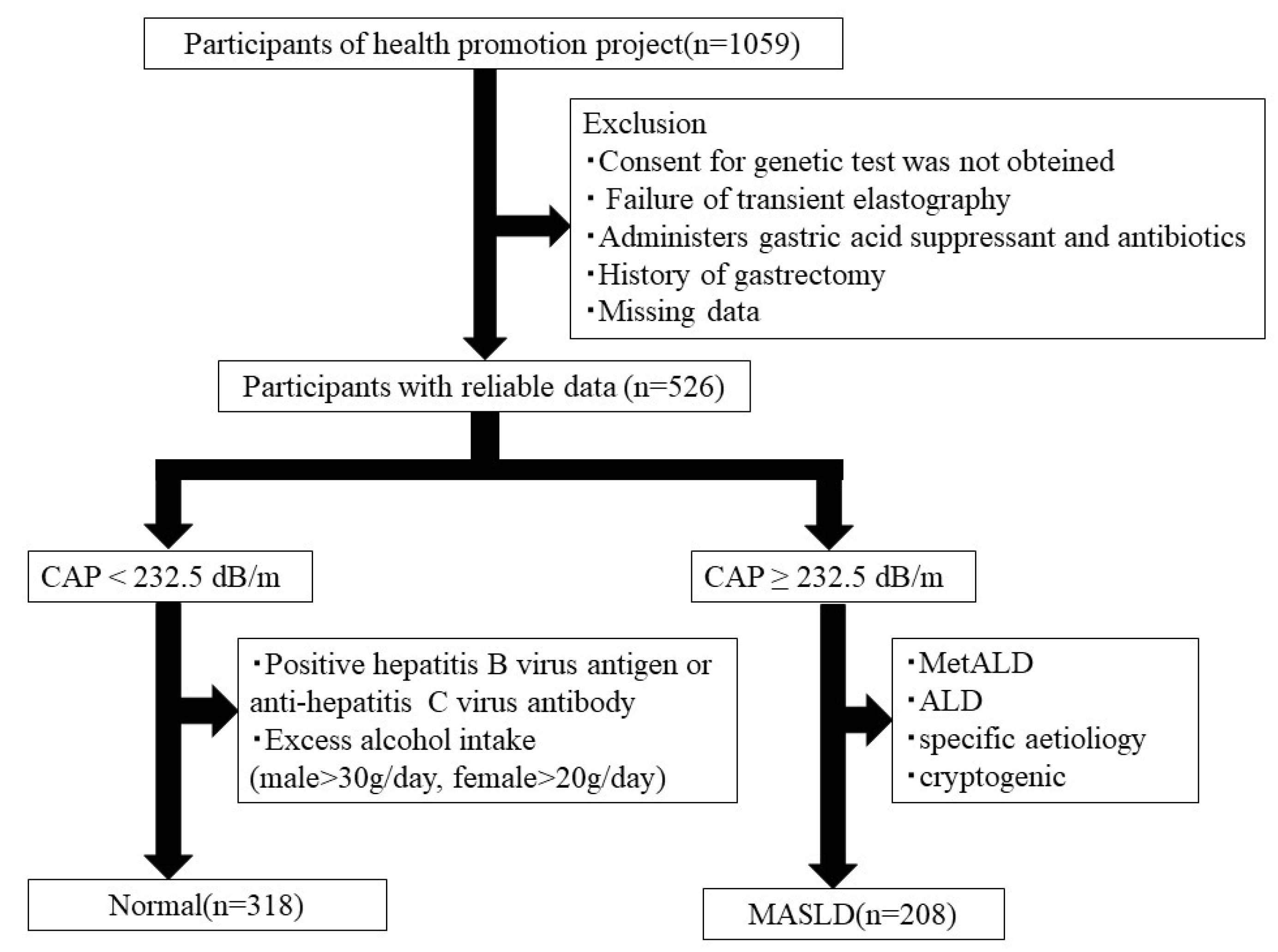
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Transient Elastography
2.3. Clinical Parameters
2.4. MASLD Diagnosis
2.5. DNA Preparation and SNP Genotyping
2.6. Measurements of the Gut Microbiota
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
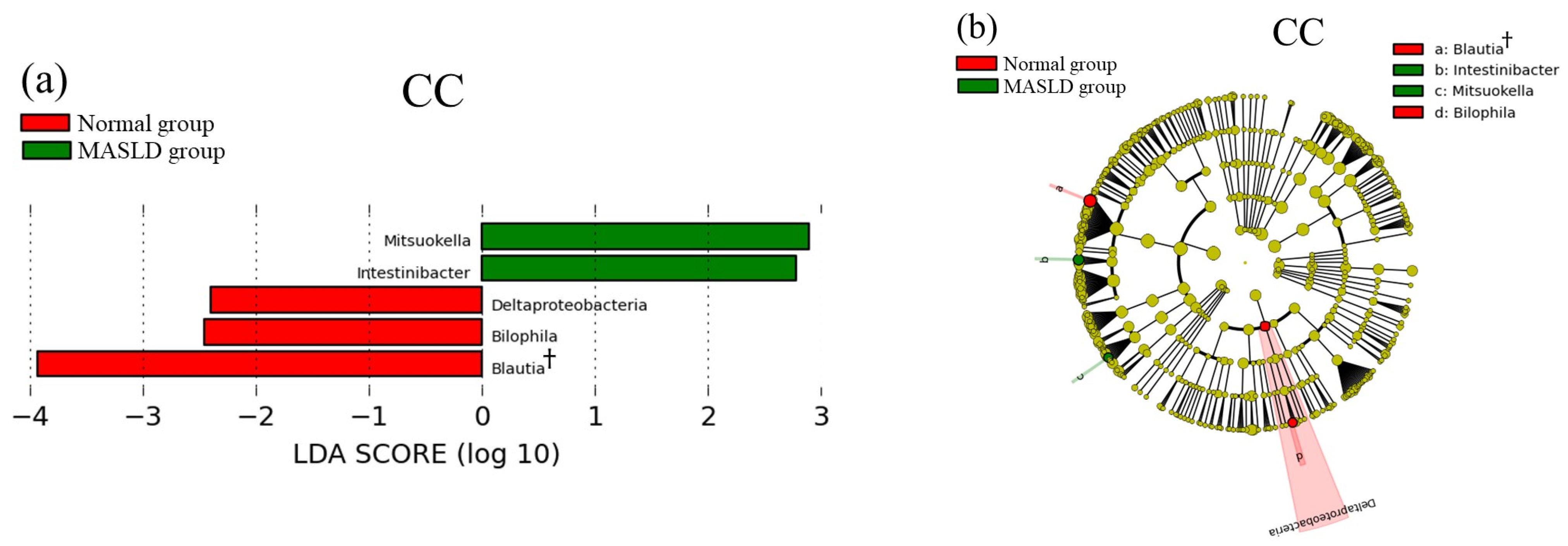
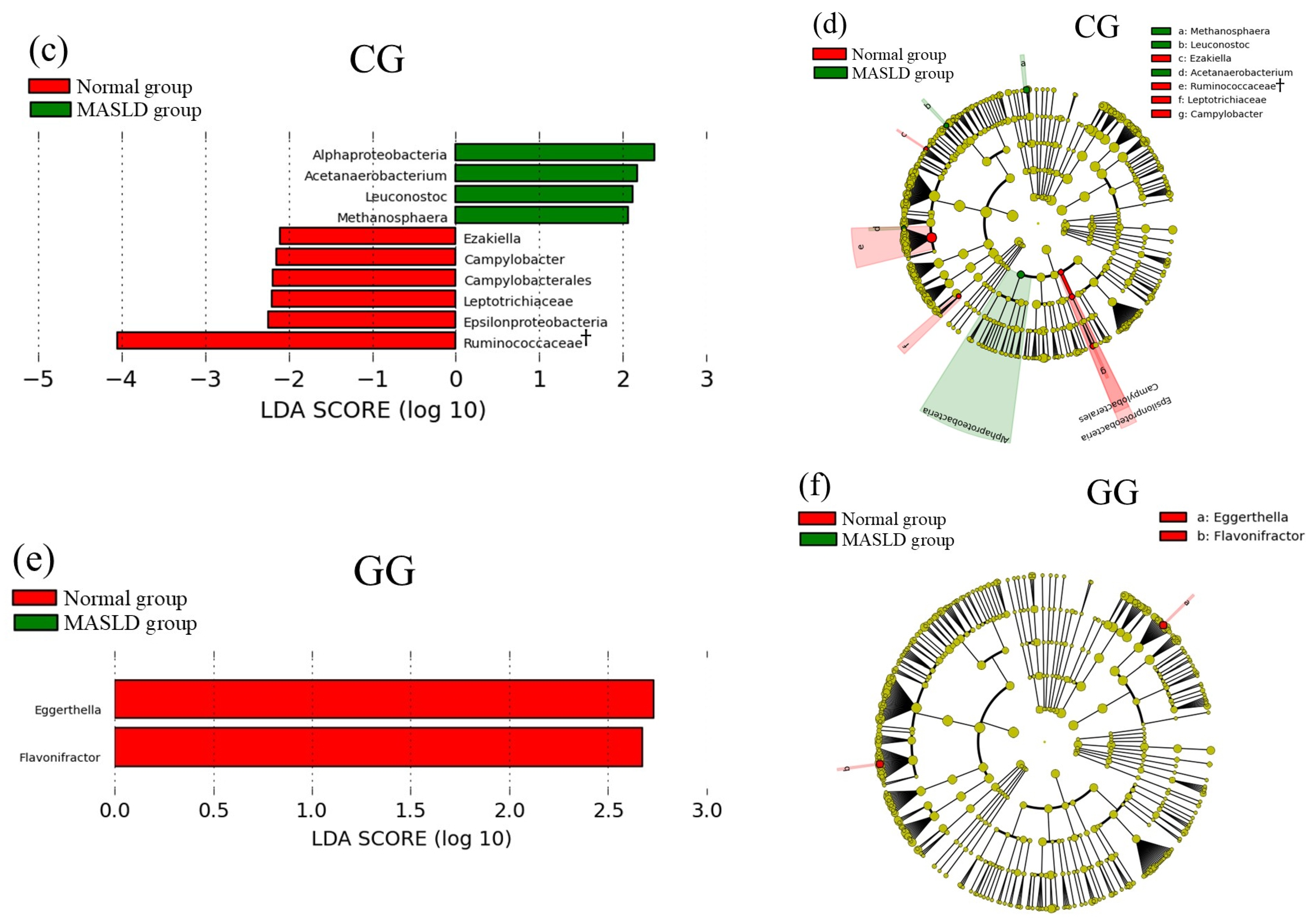
3.2. Comparison of Gut Microbiota between Normal and MASLD Group
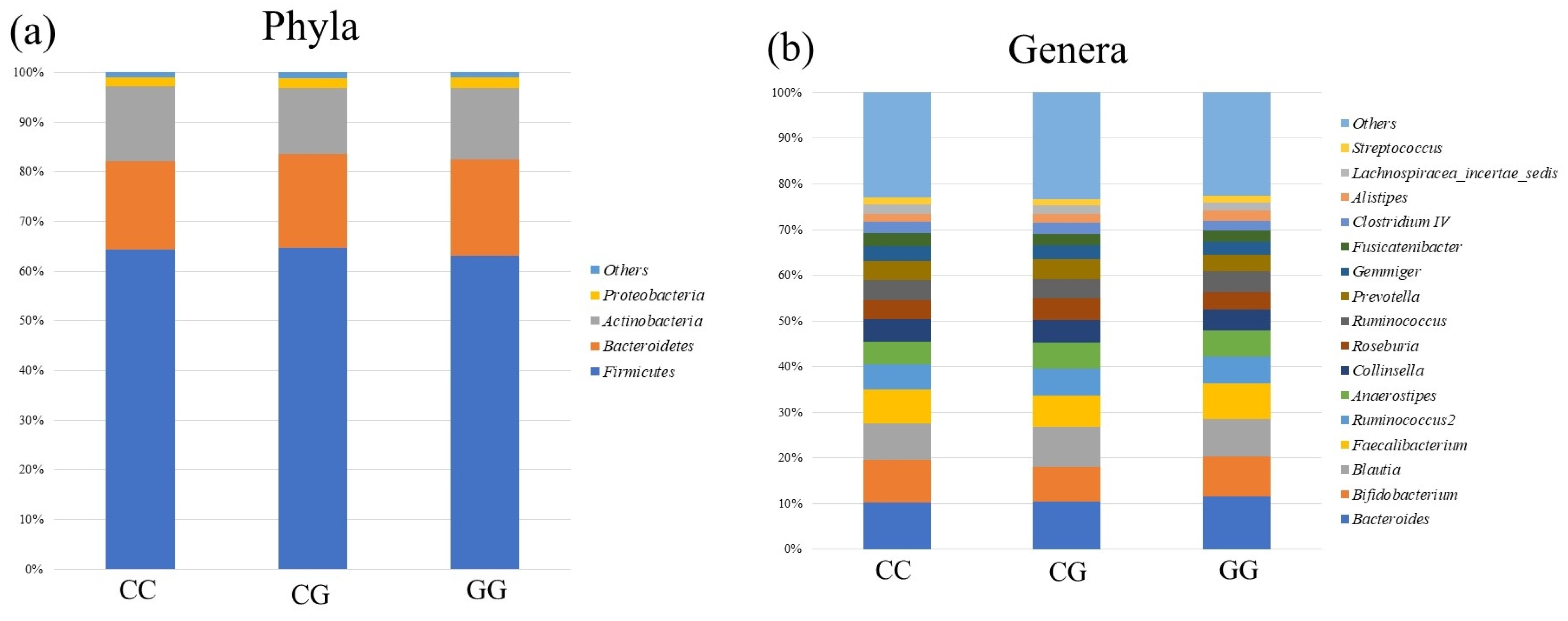
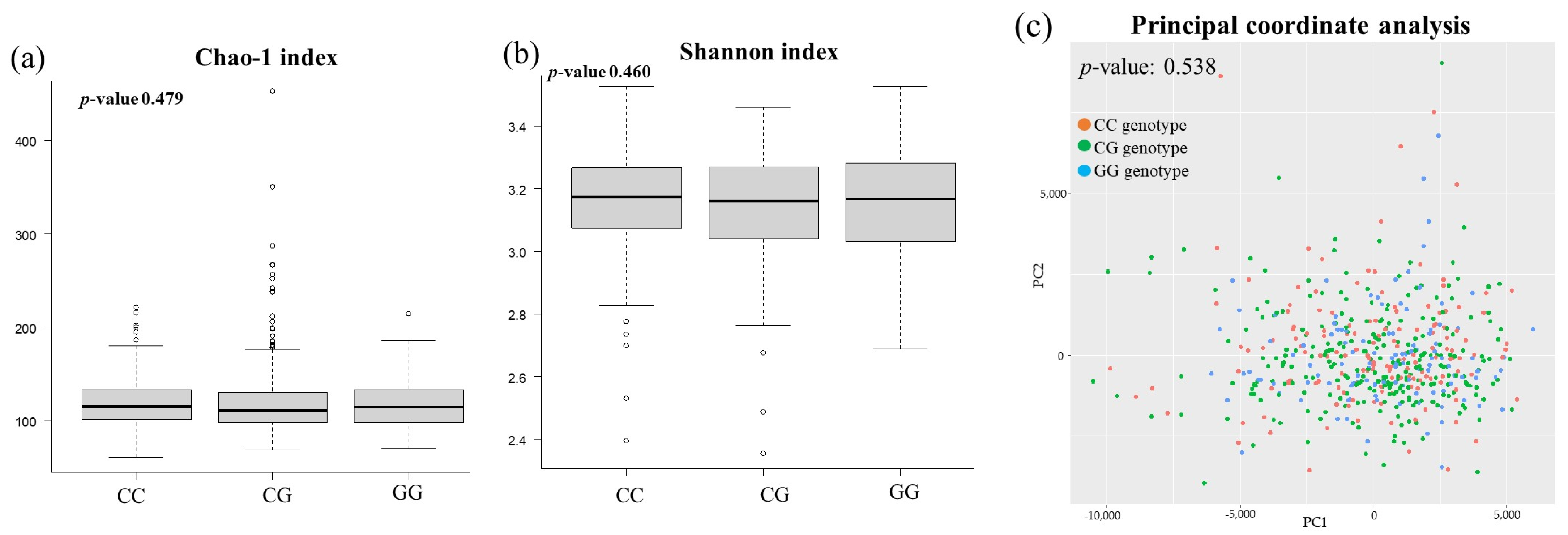
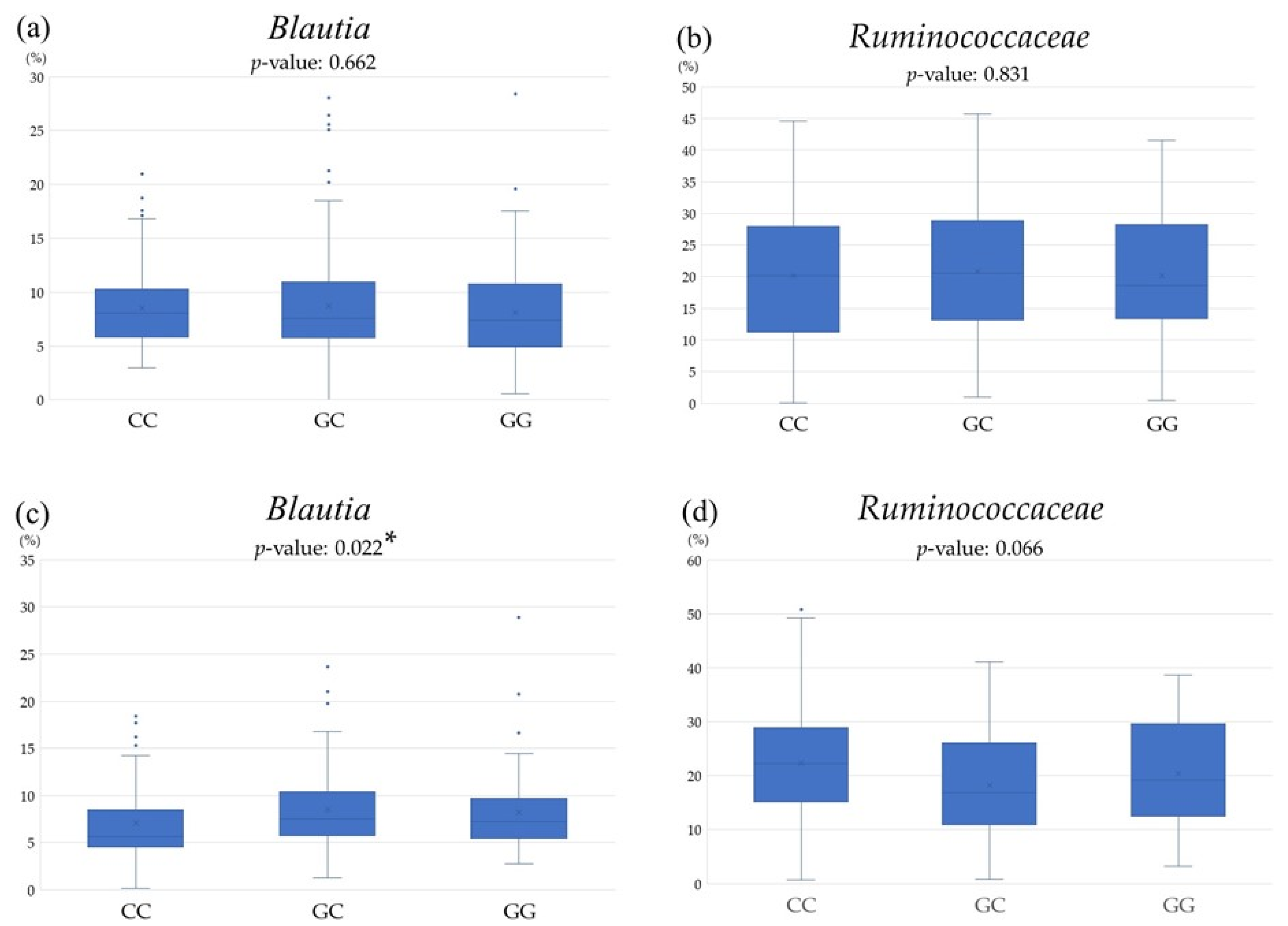
3.3. Comparison of Gut Microbiota among PNPLA3 rs738409 SNP
3.4. Relationship between MASLD-Related Items and Gut Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinella, M.E.; Lazarus, J.V.; Ratziu, V.; Francque, S.M.; Sanyal, A.J.; Kanwal, F.; Romero, D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arab, J.P.; et al. A multisociety Delphi consensus statement on new fatty liver disease nomenclature. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1966–1986. [Google Scholar]
- Hermanson, J.B.; Tolba, S.A.; Chrisler, E.A.; Leone, V.A. Gut microbes, diet, and genetics as drivers of metabolic liver disease: A narrative review outlining implications for precision medicine. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 133, 109704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, T.J.; Jimenez-Ramos, M.; Turner, F.; Ramachandran, P.; Minnier, J.; McColgan, M.D.; Alam, M.; Ellis, H.; Dunbar, D.R.; Kohnen, G.; et al. An integrated gene-to-outcome multimodal database for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2939–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Kounatidis, D.; Psallida, S.; Vythoulkas-Biotis, N.; Adamou, A.; Zachariadou, T.; Kargioti, S.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. NAFLD/MASLD and the Gut-Liver Axis: From Pathogenesis to Treatment Options. Metabolites 2024, 14, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi, Y.; Hyogo, H.; Ono, M.; Mizuta, T.; Ono, N.; Fujimoto, K.; Chayama, K.; Saibara, T. Prevalence and associated metabolic factors of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the general population from 2009 to 2010 in Japan: A multicenter large retrospective study. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albhaisi, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Sanyal, A.J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals. JHEP Rep. 2019, 1, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, W.K.; Yuen, M.F. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia: Emerging perspectives. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Sumida, Y.; Umemura, A.; Matsuo, K.; Takahashi, M.; Takamura, T.; Yasui, K.; Saibara, T.; Hashimoto, E.; Kawanaka, M.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms of the human PNPLA3 gene are strongly associated with severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Japanese. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, K.; Yoneda, M.; Hyogo, H.; Ochi, H.; Mizusawa, S.; Ueno, T.; Chayama, K.; Nakajima, A.; Nakao, K.; Sekine, A. Association of the rs738409 polymorphism in PNPLA3 with liver damage and the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotronen, A.; Johansson, L.E.; Johansson, L.M.; Roos, C.; Westerbacka, J.; Hamsten, A.; Bergholm, R.; Arkkila, P.; Arola, J.; Kiviluoto, T.; et al. A common variant in PNPLA3, which encodes adiponutrin, is associated with liver fat content in humans. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1056–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantartzis, K.; Peter, A.; Machicao, F.; Machann, J.; Wagner, S.; Königsrainer, I.; Königsrainer, A.; Schick, F.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.U.; et al. Dissociation between fatty liver and insulin resistance in humans carrying a variant of the patatin-like phospholipase 3 gene. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2616–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goran, M.I.; Walker, R.; Le, K.A.; Mahurkar, S.; Vikman, S.; Davis, J.N.; Spruijt-Metz, D.; Weigensberg, M.J.; Allayee, H. Effects of PNPLA3 on liver fat and metabolic profile in Hispanic children and adolescents. Diabetes 2010, 59, 3127–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Wu, J.; Hernaez, R.; Kim, L.J.; Palmer, C.D.; Gudnason, V.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Garcia, M.E.; Launer, L.J.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies variants associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that have distinct effects on metabolic traits. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Shima, T.; Mizuno, M.; Mitsumoto, Y.; Umemura, A.; Kanbara, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Sumida, Y.; Yasui, K.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Risk estimation model for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Japanese using multiple genetic markers. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0185490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioji, K.; Mochizuki, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Kamaguchi, M.; Sumida, Y.; Nishimura, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Kadotani, H.; Itoh, Y. The Impact of PNPLA3 rs738409 Genetic Polymorphism and Weight Gain ≥ 10 kg after Age 20 on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Non-Obese Japanese Individuals. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140427. [Google Scholar]
- Blesl, A.; Stadlbauer, V. The Gut-Liver Axis in Cholestatic Liver Diseases. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H. Leaky Gut and Gut-Liver Axis in Liver Cirrhosis: Clinical Studies Update. Gut Liver. 2021, 15, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Vigliotti, C.; Witjes, J.; Le, P.; Holleboom, A.G.; Verheij, J.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Gut microbiota and human NAFLD: Disentangling microbial signatures from metabolic disorders. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasirwan, C.O.M.; Lesmana, C.R.A.; Hasan, I.; Sulaiman, A.S.; Gani, R.A. The role of gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathways of mechanisms. Biosci. Microbiota Food Health 2019, 38, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, S.M.B.; Stefano, J.T.; Oliveira, C.P. Microbiota and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NAFLD/NASH). Ann Hepatol. 2019, 18, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundogdu, A.; Nalbantoglu, U. Human genome-microbiome interaction: Metagenomics frontiers for the aetiopathology of autoimmune diseases. Microb. Genom. 2017, 3, e000112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, P.; Capparelli, R.; Alifano, M.; Iannelli, A.; Iannelli, D. Gut Microbiota Host-Gene Interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priya, S.; Burns, M.B.; Ward, T.; Mars, R.A.T.; Adamowicz, B.; Lock, E.F.; Kashyap, P.C.; Knights, D.; Blekhman, R. Identification of shared and disease-specific host gene-microbiome associations across human diseases using multi-omic integration. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 780–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Wong, V.W.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Interplay between gut microbiome, host genetic and epigenetic modifications in MASLD and MASLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2024, 29, 332398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, M.B.; Lynch, J.; Starr, T.K.; Knights, D.; Blekhman, R. Virulence genes are a signature of the microbiome in the colorectal tumor microenvironment. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomofuji, Y.; Kishikawa, T.; Sonehara, K.; Maeda, Y.; Ogawa, K.; Kawabata, S.; Oguro-Igashira, E.; Okuno, T.; Nii, T.; Kinoshita, M.; et al. Analysis of gut microbiome, host genetics, and plasma metabolites reveals gut microbiome-host interactions in the Japanese population. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, S.; Kato, K.; Tanaka, M.; Odamaki, T.; Kubo, R.; Mitsuyama, E.; Xiao, J.Z.; Yamaguchi, R.; Uematsu, S.; Imoto, S.; et al. Genome-wide association studies and heritability analysis reveal the involvement of host genetics in the Japanese gut microbiota. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaji, S.; Ihara, K.; Sawada, K.; Parodi, S.; Umeda, T.; Takahashi, I.; Murashita, K.; Kurauchi, S.; Tokuda, I. Social innovation for life expectancy extension utilizing a platform-centered system used in the Iwaki health promotion project: A protocol paper. SAGE Open Med. 2021, 9, 20503121211002606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, K.; Takaki, S.; Hyogo, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Fukuhara, T.; Naeshiro, N.; Honda, Y.; Nakahara, T.; Ohno, A.; Miyaki, D.; et al. Utility of controlled attenuation parameter measurement for assessing liver steatosis in Japanese patients with chronic liver diseases. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 43, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Yu, H.; Fan, G.; Xiang, H.; Long, L.; Xu, H.; Wu, Z.; Chen, M.; Xi, W.; Gao, Z.; et al. Impact of the Gut Microbiome on the Progression of Hepatitis B Virus Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 573923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, S.; El-Mowafy, M.; Elgaml, A.; El-Mesery, M.; El Shabrawi, A.; Elegezy, M.; Hammami, R.; Mottawea, W. Alterations of the Treatment-Naive Gut Microbiome in Newly Diagnosed Hepatitis C Virus Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, P.A.; Green, S.J.; Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A. The Gastrointestinal Microbiome: Alcohol Effects on the Composition of Intestinal Microbiota. Alcohol. Res. 2015, 37, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Newsome, P.N.; Sasso, M.; Deeks, J.J.; Paredes, A.; Boursier, J.; Chan, W.K.; Yilmaz, Y.; Czernichow, S.; Zheng, M.H.; Wong, V.W.; et al. FibroScan-AST (FAST) score for the non-invasive identification of patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis with significant activity and fibrosis: A prospective derivation and global validation study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, Y.; Mimori, T.; Kojima, K.; Nariai, N.; Danjoh, I.; Saito, R.; Yasuda, J.; Yamamoto, M.; Nagasaki, M. Japonica array: Improved genotype imputation by designing a population-specific SNP array with 1070 Japanese individuals. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaki, M.; Yasuda, J.; Katsuoka, F.; Nariai, N.; Kojima, K.; Kawai, Y.; Yamaguchi-Kabata, Y.; Yokozawa, J.; Danjoh, I.; Saito, S.; et al. Rare variant discovery by deep whole-genome sequencing of 1,070 Japanese individuals. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Tomita, J.; Nishioka, K.; Hisada, T.; Nishijima, M. Development of a prokaryotic universal primer for simultaneous analysis of Bacteria and Archaea using next-generation sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105592. [Google Scholar]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlas, T.; Petroff, D.; Sasso, M.; Fan, J.G.; Mi, Y.Q.; de Lédinghen, V.; Kumar, M.; Lupsor-Platon, M.; Han, K.H.; Cardoso, A.C.; et al. Individual patient data meta-analysis of controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) technology for assessing steatosis. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Revelo, X.; Malhi, H. Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Overview. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, K.A.; Palmer, N.D.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Langefeld, C.D.; Norris, J.M.; Wang, N.; Xiang, A.H.; Guo, X.; Williams, A.H.; Chen, Y.I.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Loci for Liver Enzyme Concentrations in Mexican Americans: The GUARDIAN Consortium. Obesity 2019, 27, 1331–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Xiao, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Deng, G.; Sun, X.; Zhong, L.; et al. Association of patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Han Chinese population. Medicine 2016, 95, e4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, M.A.; Samie, R.M.A.; Ezzat, A.; Ramadan, N.; Rashed, L.A.; ElSayed, A.M. PNPLA3 and TNF-α G238A genetic polymorphisms in Egyptian patients with different grades of severity of NAFLD. Open J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 6, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bayley, J.P.; Ottenhoff, T.H.; Verweij, C.L. Is there a future for TNF promoter polymorphisms? Genes Immun. 2004, 5, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Metabolic syndrome: From the genetics to the pathophysiology. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2011, 13, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, T.; Lu, X.; Xie, H.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Overexpression of variant PNPLA3 gene at I148M position causes malignant transformation of hepatocytes via IL-6-JAK2/STAT3 pathway in low dose free fatty acid exposure: A laboratory investigation in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 1319. [Google Scholar]
- Rafaqat, S.; Gluscevic, S.; Mercantepe, F.; Rafaqat, S.; Klisic, A. Interleukins: Pathogenesis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Metabolites 2024, 14, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Liu, H.; Yuan, D.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, X.; Xu, F.; Liang, H. PNPLA3 I148M mediates the regulatory effect of NF-kB on inflammation in PA-treated HepG2 cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Castaño, G.O.; Burgueño, A.L.; Gianotti, T.F.; Rosselli, M.S.; Pirola, C.J. A nonsynonymous gene variant in the adiponutrin gene is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease severity. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 2111–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishijima, S.; Suda, W.; Oshima, K.; Kim, S.W.; Hirose, Y.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M. The gut microbiome of healthy Japanese and its microbial and functional uniqueness. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, M.; Ozato, N.; Tsuda, H.; Mori, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Katashima, M.; Katsuragi, Y.; Nakaji, S.; Maeda, H. Mouse Model of Anti-Obesity Effects of Blautia hansenii on Diet-Induced Obesity. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 7147–7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozato, N.; Saito, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Katashima, M.; Tokuda, I.; Sawada, K.; Katsuragi, Y.; Kakuta, M.; Imoto, S.; Ihara, K.; et al. Blautia genus associated with visceral fat accumulation in adults 20–76 years of age. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, R.; Onuki, M.; Hattori, K.; Ito, M.; Yamada, T.; Kamikado, K.; Kim, Y.G.; Nakamoto, N.; Kimura, I.; Clarke, J.M.; et al. Commensal microbe-derived acetate suppresses NAFLD/NASH development via hepatic FFAR2 signalling in mice. Microbiome 2021, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrncir, T.; Hrncirova, L.; Kverka, M.; Hromadka, R.; Machova, V.; Trckova, E.; Kostovcikova, K.; Kralickova, P.; Krejsek, J.; Tlaskalova-Hogenova, H. Gut Microbiota and NAFLD: Pathogenetic Mechanisms, Microbiota Signatures, and Therapeutic Interventions. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Baker, S.S.; Gill, C.; Liu, W.; Alkhouri, R.; Baker, R.D.; Gill, S.R. Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients: A connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH. Hepatology 2013, 57, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateda, T.; Iino, C.; Sasada, T.; Sato, S.; Igarashi, G.; Kawaguchi, S.; Mikami, K.; Endo, T.; Sawada, K.; Mikami, T.; et al. Evaluation of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease using FibroScan, diet, and microbiota: A large cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0277930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosomi, K.; Saito, M.; Park, J.; Murakami, H.; Shibata, N.; Ando, M.; Nagatake, T.; Konishi, K.; Ohno, H.; Tanisawa, K.; et al. Oral administration of Blautia wexlerae ameliorates obesity and type 2 diabetes via metabolic remodeling of the gut microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Bayer, E.A.; Rincon, M.T.; Lamed, R.; White, B.A. Polysaccharide utilization by gut bacteria: Potential for new insights from genomic analysis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, T.; Huang, G.; Cai, D.; Liang, X.; Su, H.; Zhu, Z.; Li, D.; Yang, Y.; Shen, P.; et al. Gut Microbiota Community and Its Assembly Associated with Age and Diet in Chinese Centenarians. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willing, B.P.; Dicksved, J.; Halfvarson, J.; Andersson, A.F.; Lucio, M.; Zheng, Z.; Järnerot, G.; Tysk, C.; Jansson, J.K.; Engstrand, L. A pyrosequencing study in twins shows that gastrointestinal microbial profiles vary with inflammatory bowel disease phenotypes. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1844–1854.e1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, X.C.; Tickle, T.L.; Sokol, H.; Gevers, D.; Devaney, K.L.; Ward, D.V.; Reyes, J.A.; Shah, S.A.; LeLeiko, N.; Snapper, S.B.; et al. Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Zheng, R.-D.; Sun, X.-Q.; Ding, W.-J.; Wang, X.-Y.; Fan, J.-G. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2017, 16, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warmbrunn, M.V.; Boulund, U.; Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; de Goffau, M.C.; Abeka, R.E.; Davids, M.; Bresser, L.R.F.; Levin, E.; Clement, K.; Galenkamp, H.; et al. Networks of gut bacteria relate to cardiovascular disease in a multi-ethnic population: The HELIUS study. Cardiovasc. Res. 2024, 120, 372–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benítez-Páez, A.; Gómez Del Pugar, E.M.; López-Almela, I.; Moya-Pérez, Á.; Codoñer-Franch, P.; Sanz, Y. Depletion of Blautia Species in the Microbiota of Obese Children Relates to Intestinal Inflammation and Metabolic Phenotype Worsening. mSystems 2020, 5, e00857-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Qian, G.; Fang, D.; Shi, D.; Guo, L.; Li, L. Gut dysbiosis in acute-on-chronic liver failure and its predictive value for mortality. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H. Role of Gut Dysbiosis in Liver Diseases: What Have We Learned So Far? Diseases 2019, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CC | CG | GG | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n =150 | n = 260 | n = 116 | ||
| MASLD | 55 (36.7%) | 105 (40.4%) | 48 (41.4%) | 0.684 |
| Sex, male | 43 (28.7%) | 95 (36.5%) | 40 (34.5%) | 0.264 |
| Age (year) | 55.5 (43.8–66.0) | 52.0 (39.0–65.8) | 54.0 (39.0–66.0) | 0.379 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.1 (20.2–24.5) | 22.8 (20.2–25.1) | 22.0 (19.8–24.7) | 0.326 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 74.5 (67.5–81.0) | 76.3 (69.3–84.6) | 74.3 (69.0–83.3) | 0.146 |
| Fasting blood sugar (mmHg) | 92.0 (86.0–98.3) | 91.5 (86.0–99.0) | 90.0 (84.3–97.0) | 0.162 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.7 (5.6–5.9) | 5.7 (5.5–5.9) | 5.6 (5.4–5.9) | 0.269 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 122.0 (111.8–134.0) | 122.5 (110.3–133.0) | 122.5 (112.3–133.8) | 0.750 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 76.0 (69.0–82.3) | 76.5 (69.0–84.0) | 77.0 (69.0–85.0) | 0.854 |
| Triglycerides (mmHg) | 76.5 (52.8–118.0) | 76.5 (56.3–110.0) | 80.5 (55.5–105.0) | 0.960 |
| HDL cholesterol (mmHg) | 66.5 (53.0–76.0) | 62.0 (51.3–77.0) | 63.0 (54.3–75.8) | 0.415 |
| LDL cholesterol (mmHg) | 121.5 (105.0–139.3) | 117.0 (99.0–138.0) | 114.0 (95.0–132.8) | 0.105 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase (IU/L) | 21.0 (17.0–25.3) | 20.0 (17.0–23.0) | 22.0 (19.0–27.0) | <0.001 ** |
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) | 17.0 (13.0–24.0) | 17.0 (13.0–23.0) | 20.0 (13.3–30.3) | 0.031 * |
| γ-Glutamyl TransPeptidase (IU/L) | 21.0 (15.0–28.5) | 21.0 (15.0–33.5) | 19.0 (15.0–30.8) | 0.703 |
| CAP (dB/m) | 216.5 (179.0–260.0) | 222.5 (190.3–260.8) | 224.0 (178.0–267.8) | 0.595 |
| LSM (kPa) | 4.3 (3.5–5.4) | 4.2 (3.5–5.2) | 4.4 (3.7–5.6) | 0.787 |
| Smoking habit | 19 (12.7%) | 40 (15.4%) | 10 (8.6%) | 0.196 |
| Exercise habit | 31 (20.7%) | 36 (13.8%) | 27 (23.3%) | 0.050 |
| Medication of hypertension | 31 (20.7%) | 50 (19.2%) | 27 (23.3%) | 0.668 |
| Medication of diabetes mellitus | 7 (4.7%) | 12 (4.6%) | 3 (2.6%) | 0.623 |
| Taking dyslipidemia | 20 (13.3%) | 22 (8.5%) | 16 (13.8%) | 0.177 |
| Fatty liver index | 13.4 (4.8–29.0) | 14.1 (6.27–33.6) | 9.8 (5.0–30.1) | 0.344 |
| APRI | 0.19 (0.15–0.25) | 0.19 (0.15–0.25) | 0.23 (0.17–0.28) | 0.005 ** |
| FIB-4 index | 0.95 (0.67–1.41) | 0.91 (0.59–1.43) | 1.00 (0.75–1.47) | 0.276 |
| FAST score | 0.05 (0.03–0.10) | 0.05 (0.03–0.09) | 0.06 (0.04–0.14) | 0.006 ** |
| NFS | −2.05 (−2.97–1.11) | −2.0 (−3.14–0.90) | −2.09 (−3.15–1.04) | 0.920 |
| Blautia | ||||||
| CC | CG | GG | ||||
| r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | |
| CAP | −0.181 | 0.026 * | −0.091 | 0.144 | 0.035 | 0.710 |
| BMI | −0.179 | 0.028 * | −0.106 | 0.088 | <0.001 | 0.998 |
| Waist circumference | −0.146 | 0.076 | −0.130 | 0.037 * | −0.048 | 0.606 |
| Systolic blood pressure | −0.001 | 0.953 | −0.018 | 0.770 | −0.002 | 0.980 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 0.047 | 0.570 | 0.013 | 0.840 | −0.039 | 0.677 |
| Blood glucose | −0.026 | 0.751 | −0.176 | 0.005 ** | 0.129 | 0.169 |
| HbA1c | −0.024 | 0.772 | −0.106 | 0.090 | −0.049 | 0.601 |
| Triglycerides | −0.044 | 0.597 | −0.064 | 0.307 | −0.083 | 0.374 |
| HDL cholesterol | 0.128 | 0.118 | −0.003 | 0.958 | 0.132 | 0.159 |
| Ruminococcaceae | ||||||
| CC | CG | GG | ||||
| r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | |
| CAP | 0.069 | 0.401 | −0.149 | 0.016 * | 0.034 | 0.718 |
| BMI | −0.029 | 0.728 | −0.098 | 0.115 | −0.084 | 0.372 |
| Waist circumference | −0.057 | 0.490 | −0.138 | 0.026 * | −0.026 | 0.783 |
| Systolic blood pressure | −0.020 | 0.805 | 0.001 | 0.996 | 0.051 | 0.584 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | −0.139 | 0.091 | −0.092 | 0.140 | −0.028 | 0.764 |
| Blood glucose | −0.052 | 0.527 | 0.073 | 0.241 | 0.077 | 0.415 |
| HbA1c | 0.017 | 0.842 | 0.091 | 0.142 | 0.108 | 0.249 |
| Triglycerides | −0.211 | 0.009 ** | −0.217 | <0.001 ** | −0.162 | 0.082 |
| HDL cholesterol | 0.098 | 0.232 | 0.099 | 0.112 | 0.034 | 0.720 |
| Blautia | |||||||||
| CC | CG | GG | |||||||
| β | p-Value | R2 | β | p-Value | R2 | β | p-Value | R2 | |
| CAP | −0.195 | 0.031 * | 0.050 | −0.058 | 0.378 | 0.042 | 0.017 | 0.858 | 0.103 |
| BMI | −0.198 | 0.028 * | 0.051 | −0.083 | 0.206 | 0.045 | −0.001 | 0.992 | 0.103 |
| Waist circumference | −0.188 | 0.058 | 0.043 | −0.109 | 0.140 | 0.047 | −0.076 | 0.505 | 0.106 |
| Systolic blood pressure | 0.015 | 0.865 | 0.018 | 0.052 | 0.455 | 0.041 | −0.004 | 0.973 | 0.103 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | 0.055 | 0.526 | 0.021 | 0.056 | 0.391 | 0.041 | −0.052 | 0.587 | 0.105 |
| Blood glucose | −0.012 | 0.900 | 0.018 | −0.149 | 0.061 | 0.052 | 0.139 | 0.184 | 0.051 |
| HbA1c | −0.000 | 0.999 | 0.018 | −0.074 | 0.360 | 0.042 | −0.071 | 0.514 | 0.106 |
| Triglycerides | −0.047 | 0.620 | 0.020 | −0.039 | 0.571 | 0.040 | −0.117 | 0.255 | 0.113 |
| HDL cholesterol | 0.151 | 0.105 | 0.036 | −0.013 | 0.854 | 0.0.39 | 0.103 | 0.329 | 0.111 |
| Ruminococcaceae | |||||||||
| CC | CG | GG | |||||||
| β | p-Value | R2 | β | p-Value | R2 | β | p-Value | R2 | |
| CAP | 0.107 | 0.214 | 0.137 | −0.170 | 0.008 ** | 0.109 | 0.017 | 0.857 | 0.124 |
| BMI | 0.010 | 0.905 | 0.128 | −0.080 | 0.211 | 0.089 | −0.000 | 0.999 | 0.124 |
| Waist circumference | 0.045 | 0.632 | 0.129 | −0.107 | 0.138 | 0.091 | 0.111 | 0.322 | 0.132 |
| Systolic blood pressure | −0.052 | 0.545 | 0.130 | −0.079 | 0.242 | 0.088 | 0.143 | 0.169 | 0.139 |
| Diastolic blood pressure | −0.139 | 0.090 | 0.145 | −0.114 | 0.073 | 0.095 | −0.012 | 0.902 | 0.124 |
| Blood glucose | −0.047 | 0.602 | 0.129 | 0.030 | 0.700 | 0.084 | 0.110 | 0.287 | 0.133 |
| HbA1c | −0.002 | 0.979 | 0.128 | 0.045 | 0.569 | 0.084 | 0.078 | 0.471 | 0.128 |
| Triglycerides | −0.196 | 0.027 * | 0.157 | −0.217 | <0.001 ** | 0.122 | −0.180 | 0.074 | 0.150 |
| HDL cholesterol | −0.040 | 0.646 | 0.129 | −0.004 | 0.953 | 0.083 | −0.051 | 0.626 | 0.126 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sato, S.; Iino, C.; Sasada, T.; Soma, G.; Furusawa, K.; Yoshida, K.; Sawada, K.; Mikami, T.; Nakaji, S.; Sakuraba, H.; et al. Epidemiological Study on the Interaction between the PNPLA3 (rs738409) and Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Genes 2024, 15, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091172
Sato S, Iino C, Sasada T, Soma G, Furusawa K, Yoshida K, Sawada K, Mikami T, Nakaji S, Sakuraba H, et al. Epidemiological Study on the Interaction between the PNPLA3 (rs738409) and Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Genes. 2024; 15(9):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091172
Chicago/Turabian StyleSato, Satoshi, Chikara Iino, Takafumi Sasada, Go Soma, Keisuke Furusawa, Kenta Yoshida, Kaori Sawada, Tatsuya Mikami, Shigeyuki Nakaji, Hirotake Sakuraba, and et al. 2024. "Epidemiological Study on the Interaction between the PNPLA3 (rs738409) and Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease" Genes 15, no. 9: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091172
APA StyleSato, S., Iino, C., Sasada, T., Soma, G., Furusawa, K., Yoshida, K., Sawada, K., Mikami, T., Nakaji, S., Sakuraba, H., & Fukuda, S. (2024). Epidemiological Study on the Interaction between the PNPLA3 (rs738409) and Gut Microbiota in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Genes, 15(9), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091172






