Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biological Functions and Mechanisms of DNA Hydroxymethylation
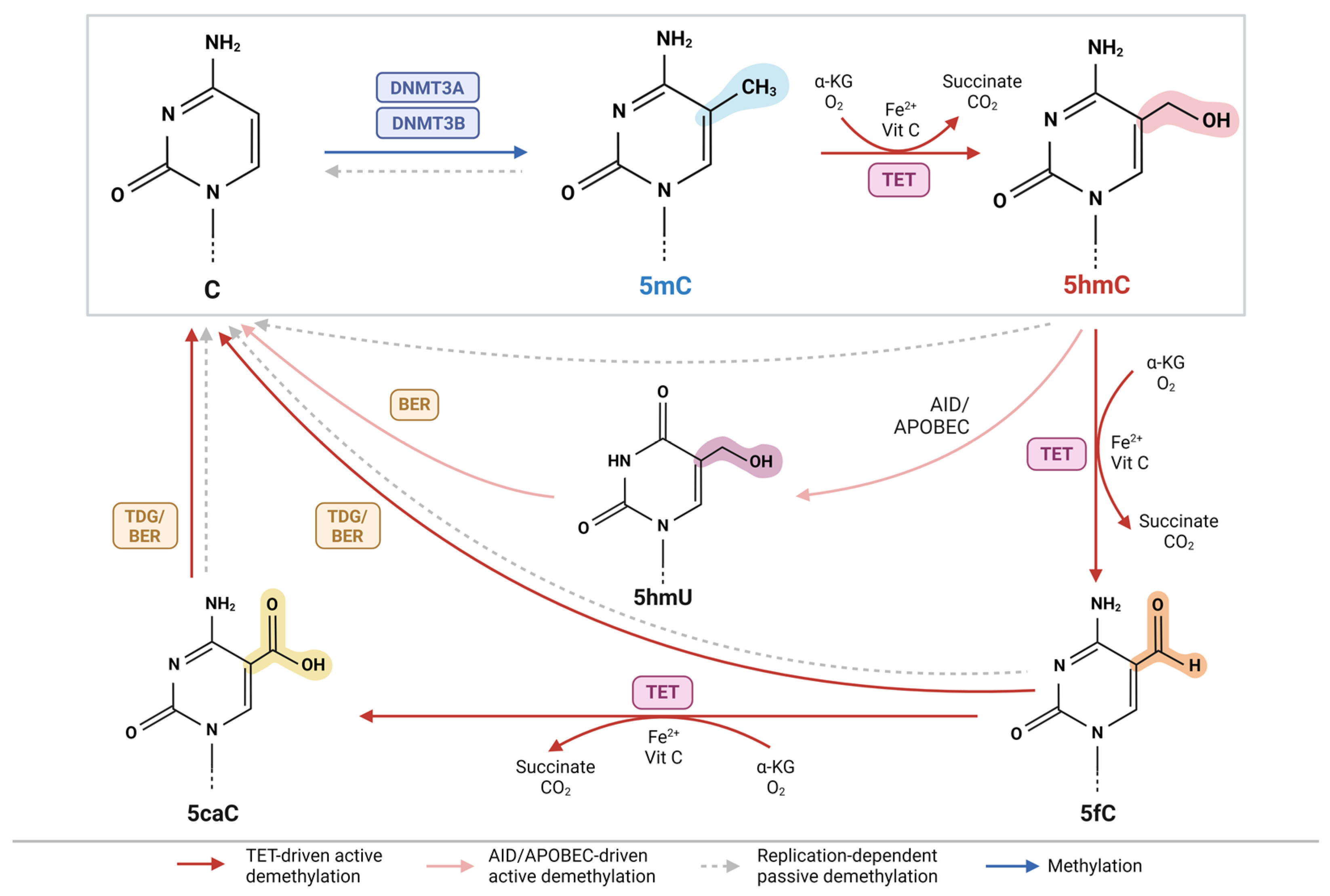
2.1. DNA Hydroxymethylation in the Demethylation Pathway
2.2. Biological Functions and Distribution of DNA Hydroxymethylation
2.3. Cell-Free DNA and the Hydroxymethylome
2.4. DNA Hydroxymethylation Patterns in Cancer
3. Evolution of Hydroxymethylation Detection Methods
3.1. Bisulfite Sequencing Approaches
3.2. Enzymatic and Affinity-Based Approaches
3.2.1. Chemical Capture and Glucosylation-Based Techniques
3.2.2. DNA Deamination Methods
3.2.3. Oxidation-Based Strategies
3.2.4. Antibody-Based Methods
3.3. Emerging Hydroxymethylation Profiling Methods
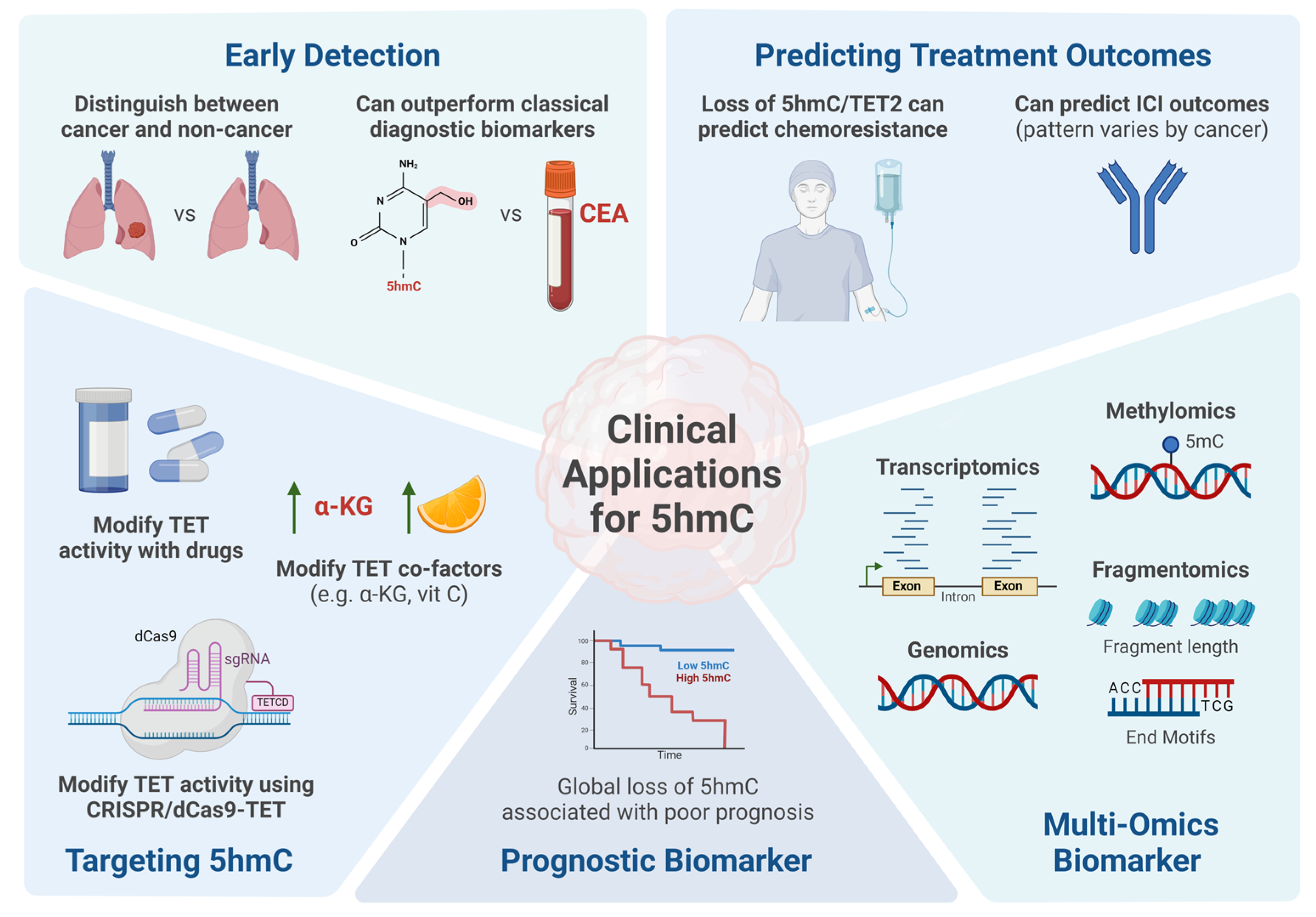
4. DNA Hydroxymethylation and Clinical Applications
4.1. DNA Hydroxymethylation as a Biomarker for Cancer Detection
4.2. Prognostic Value of DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer
4.3. Predicting Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy Response with 5hmC
4.4. Integrating DNA Hydroxymethylation in Multi-Omics Analysis
4.5. Targeting DNA Hydroxymethylation as a Potential Therapeutic for Cancer
5. Challenges and Future Directions
5.1. Choosing the Right 5hmC Detection Method
5.2. Multi-Omics Analyses Using Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomson, J.P.; Meehan, R.R. The Application of Genome-Wide 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Studies in Cancer Research. Epigenomics 2017, 9, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, G.P.; Kadam, S.; Jin, S.-G. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Its Potential Roles in Development and Cancer. Epigenet. Chromatin 2013, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Tateishi, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Asaoka, Y.; Ijichi, H.; Nagae, G.; Yoshida, H.; Aburatani, H.; Koike, K. Loss of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine Is Accompanied with Malignant Cellular Transformation. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pardo, M.; Makarem, M.; Li, J.J.N.; Kelly, D.; Leighl, N.B. Integrating Circulating-Free DNA (cfDNA) Analysis into Clinical Practice: Opportunities and Challenges. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cescon, D.W.; Bratman, S.V.; Chan, S.M.; Siu, L.L. Circulating Tumor DNA and Liquid Biopsy in Oncology. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Gao, H. Hydroxymethylation and Tumors: Can 5-Hydroxymethylation Be Used as a Marker for Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment? Hum. Genom. 2020, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, L.; Bissessur, A.S.; Chen, J.; Mao, M.; Ju, S.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.; et al. Deoxyribonucleic Acid 5-Hydroxymethylation in Cell-Free Deoxyribonucleic Acid, a Novel Cancer Biomarker in the Era of Precision Medicine. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 744990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besaratinia, A.; Caceres, A.; Tommasi, S. DNA Hydroxymethylation in Smoking-Associated Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, Z.D.; Meissner, A. DNA Methylation: Roles in Mammalian Development. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, S.K.T.; O’Donnell, A.H.; Bestor, T.H. Mammalian Cytosine Methylation at a Glance. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 2787–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahiliani, M.; Koh, K.P.; Shen, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Bandukwala, H.; Brudno, Y.; Agarwal, S.; Iyer, L.M.; Liu, D.R.; Aravind, L.; et al. Conversion of 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mammalian DNA by MLL Partner TET1. Science 2009, 324, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Shen, L.; Dai, Q.; Wu, S.C.; Collins, L.B.; Swenberg, J.A.; He, C.; Zhang, Y. Tet Proteins Can Convert 5-Methylcytosine to 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Carboxylcytosine. Science 2011, 333, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. TET-Mediated Active DNA Demethylation: Mechanism, Function and Beyond. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2017, 18, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Globisch, D.; Münzel, M.; Müller, M.; Michalakis, S.; Wagner, M.; Koch, S.; Brückl, T.; Biel, M.; Carell, T. Tissue Distribution of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Search for Active Demethylation Intermediates. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Lu, J.; Cheng, J.; Rao, Q.; Li, Z.; Hou, H.; Lou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, W.; Gong, W.; et al. Structural Insight into Substrate Preference for TET-Mediated Oxidation. Nature 2015, 527, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, H.; Hong, S.; Bhagwat, A.S.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, X. Excision of 5-Hydroxymethyluracil and 5-Carboxylcytosine by the Thymine DNA Glycosylase Domain: Its Structural Basis and Implications for Active DNA Demethylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 10203–10214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabel, C.S.; Jia, H.; Ye, Y.; Shen, L.; Goldschmidt, H.L.; Stivers, J.T.; Zhang, Y.; Kohli, R.M. AID/APOBEC Deaminases Disfavor Modified Cytosines Implicated in DNA Demethylation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, R.M.; Zhang, Y. TET Enzymes, TDG and the Dynamics of DNA Demethylation. Nature 2013, 502, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.-F.; Li, B.-Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ding, J.; Jia, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, L.; et al. Tet-Mediated Formation of 5-Carboxylcytosine and Its Excision by TDG in Mammalian DNA. Science 2011, 333, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, A.; Drohat, A.C. Thymine DNA Glycosylase Can Rapidly Excise 5-Formylcytosine and 5-Carboxylcytosine: Potential Implications for Active Demethylation of CpG Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35334–35338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachman, M.; Uribe-Lewis, S.; Yang, X.; Williams, M.; Murrell, A.; Balasubramanian, S. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is a Predominantly Stable DNA Modification. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Taranova, O.V.; Hong, K.; Sowers, L.C.; Zhang, Y. Role of Tet Proteins in 5mC to 5hmC Conversion, ES-Cell Self-Renewal and Inner Cell Mass Specification. Nature 2010, 466, 1129–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficz, G.; Branco, M.R.; Seisenberger, S.; Santos, F.; Krueger, F.; Hore, T.A.; Marques, C.J.; Andrews, S.; Reik, W. Dynamic Regulation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Mouse ES Cells and during Differentiation. Nature 2011, 473, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guibert, S.; Weber, M. Functions of DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation in Mammalian Development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2013, 104, 47–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawlaty, M.M.; Breiling, A.; Le, T.; Barrasa, M.I.; Raddatz, G.; Gao, Q.; Powell, B.E.; Cheng, A.W.; Faull, K.F.; Lyko, F.; et al. Loss of Tet Enzymes Compromises Proper Differentiation of Embryonic Stem Cells. Dev. Cell 2014, 29, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, S.; Caniçais, C.; Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S.M.; Marques, C.J.; Dória, S. The Role of DNA Hydroxymethylation and TET Enzymes in Placental Development and Pregnancy Outcome. Clin. Epigenet. 2023, 15, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, K.; Wu, T.; Huang, B.; Liu, W.; Kou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, H.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Replacement of Oct4 by Tet1 during iPSC Induction Reveals an Important Role of DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation in Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neri, F.; Incarnato, D.; Krepelova, A.; Dettori, D.; Rapelli, S.; Maldotti, M.; Parlato, C.; Anselmi, F.; Galvagni, F.; Oliviero, S. TET1 Is Controlled by Pluripotency-Associated Factors in ESCs and Downmodulated by PRC2 in Differentiated Cells and Tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 6814–6826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, G.; Xie, R. Decoding the Role of TET Family Dioxygenases in Lineage Specification. Epigenet. Chromatin 2018, 11, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senner, C.E.; Chrysanthou, S.; Burge, S.; Lin, H.-Y.; Branco, M.R.; Hemberger, M. TET1 and 5-Hydroxymethylation Preserve the Stem Cell State of Mouse Trophoblast. Stem Cell Rep. 2020, 15, 1301–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Xie, N.; Jin, P.; Wang, T. DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation in Stem Cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2015, 33, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagaratou, A.; Äijö, T.; Lio, C.-W.J.; Yue, X.; Huang, Y.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Lähdesmäki, H.; Rao, A. Dissecting the Dynamic Changes of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in T-Cell Development and Differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3306–E3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiouplis, N.J.; Bailey, D.W.; Chiou, L.F.; Wissink, F.J.; Tsagaratou, A. TET-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation in Immune Cell Development and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 623948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Nobre, A.; Piñeiro, P.; Berciano-Guerrero, M.-Á.; Alba, E.; Cobo, M.; Lauschke, V.M.; Barragán, I. Genetic and Epigenetic Biomarkers of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Response. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, R.C.; Konkel, J.E.; Prendergast, C.T.; Thomson, J.P.; Ottaviano, R.; Leech, M.D.; Kay, O.; Zandee, S.E.J.; Sweenie, C.H.; Wraith, D.C.; et al. Epigenetic Modification of the PD-1 (Pdcd1) Promoter in Effector CD4(+) T Cells Tolerized by Peptide Immunotherapy. eLife 2014, 3, e03416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoodoruth, M.A.S.; Khoodoruth, W.N.C.; Alwani, R.A. Exploring the Epigenetic Landscape: The Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Camb. Prisms Precis. Med. 2024, 2, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.-L.; Nie, J.; Ku, J.; Dougherty, U.; West-Szymanski, D.C.; Collin, F.; Ellison, C.K.; Sieh, L.; Ning, Y.; Deng, Z.; et al. A Human Tissue Map of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines Exhibits Tissue Specificity through Gene and Enhancer Modulation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroud, H.; Feng, S.; Morey Kinney, S.; Pradhan, S.; Jacobsen, S.E. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Associated with Enhancers and Gene Bodies in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulwach, K.E.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Song, C.-X.; Han, J.W.; Kim, S.; Namburi, S.; Hermetz, K.; Kim, J.J.; Rudd, M.K.; et al. Integrating 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine into the Epigenomic Landscape of Human Embryonic Stem Cells. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, W.A.; Pape, U.J.; Huang, Y.; Henderson, H.R.; Lister, R.; Ko, M.; McLoughlin, E.M.; Brudno, Y.; Mahapatra, S.; Kapranov, P.; et al. Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Embryonic Stem Cells. Nature 2011, 473, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzhöfer, D.K.; Gilsbach, R.; Grüning, B.A.; Backofen, R.; Nührenberg, T.G.; Hein, L. 5′-Hydroxymethylcytosine Precedes Loss of CpG Methylation in Enhancers and Genes Undergoing Activation in Cardiomyocyte Maturation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe-Lewis, S.; Stark, R.; Carroll, T.; Dunning, M.J.; Bachman, M.; Ito, Y.; Stojic, L.; Halim, S.; Vowler, S.L.; Lynch, A.G.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Marks Promoters in Colon That Resist DNA Hypermethylation in Cancer. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Kim, H.-P.; Kim, T.-Y.; Bang, D. EBS-Seq: Enrichment-Based Method for Accurate Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single-Base Resolution. Clin. Epigenet. 2023, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Lu, X.; Shih, A.H.; Nie, J.; You, Q.; Xu, M.M.; Melnick, A.M.; Levine, R.L.; He, C. A Highly Sensitive and Robust Method for Genome-Wide 5hmC Profiling of Rare Cell Populations. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, M.R.; Ficz, G.; Reik, W. Uncovering the Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in the Epigenome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 13, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; D’Alessio, A.C.; Ito, S.; Wang, Z.; Cui, K.; Zhao, K.; Sun, Y.E.; Zhang, Y. Genome-Wide Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Distribution Reveals Its Dual Function in Transcriptional Regulation in Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 679–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.K.; Azizgolshani, N.; Zhang, Z.; Perreard, L.; Kolling, F.W.; Nguyen, L.N.; Zanazzi, G.J.; Salas, L.A.; Christensen, B.C. Associations in Cell Type-Specific Hydroxymethylation and Transcriptional Alterations of Pediatric Central Nervous System Tumors. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valinluck, V.; Tsai, H.-H.; Rogstad, D.K.; Burdzy, A.; Bird, A.; Sowers, L.C. Oxidative Damage to Methyl-CpG Sequences Inhibits the Binding of the Methyl-CpG Binding Domain (MBD) of Methyl-CpG Binding Protein 2 (MeCP2). Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 4100–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellén, M.; Ayata, P.; Dewell, S.; Kriaucionis, S.; Heintz, N. MeCP2 Binds to 5hmC Enriched within Active Genes and Accessible Chromatin in the Nervous System. Cell 2012, 151, 1417–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.-Q.; Ali, I.; Tang, J.; Yang, W.-C. New Insights into 5hmC DNA Modification: Generation, Distribution and Function. Front. Genet. 2017, 8, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, J.; Meng, H.; Bai, D.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Tissue-Specific 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Landscape of the Human Genome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestor, C.E.; Ottaviano, R.; Reddington, J.; Sproul, D.; Reinhardt, D.; Dunican, D.; Katz, E.; Dixon, J.M.; Harrison, D.J.; Meehan, R.R. Tissue Type Is a Major Modifier of the 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Content of Human Genes. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, M. Distribution of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Different Human Tissues. J. Nucleic Acids 2011, 2011, 870726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-X.; Szulwach, K.E.; Fu, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yi, C.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.-H.; Zhang, W.; Jian, X.; et al. Selective Chemical Labeling Reveals the Genome-Wide Distribution of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haffner, M.C.; Chaux, A.; Meeker, A.K.; Esopi, D.M.; Gerber, J.; Pellakuru, L.G.; Toubaji, A.; Argani, P.; Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.; Nelson, W.G.; et al. Global 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Content Is Significantly Reduced in Tissue Stem/Progenitor Cell Compartments and in Human Cancers. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munari, E.; Chaux, A.; Vaghasia, A.M.; Taheri, D.; Karram, S.; Bezerra, S.M.; Gonzalez Roibon, N.; Nelson, W.G.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Netto, G.J.; et al. Global 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Levels Are Profoundly Reduced in Multiple Genitourinary Malignancies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambichler, T.; Sand, M.; Skrygan, M. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Ten-Eleven Translocation 2 Protein Expression in Malignant Melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2013, 23, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-X.; Yin, S.; Ma, L.; Wheeler, A.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, W.; Hu, J.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Cell-Free DNA Provide Information about Tumor Types and Stages. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; You, L.; Song, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Nie, J.; Zheng, W.; Xu, D.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Diagnostic Biomarkers for Human Cancers. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Gao, C.; Xing, Y.; Qi, Z.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.-G.; Li, X.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylome in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as A Potential Biomarker for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Liu, W.; Shi, G.; Ge, Y.; Gao, P.; Yang, Y.; et al. Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as a Non-Invasive Approach for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut 2019, 68, 2195–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guler, G.D.; Ning, Y.; Ku, C.-J.; Phillips, T.; McCarthy, E.; Ellison, C.K.; Bergamaschi, A.; Collin, F.; Lloyd, P.; Scott, A.; et al. Detection of Early Stage Pancreatic Cancer Using 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures in Circulating Cell Free DNA. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, B.C.-H.; Zhang, Z.; You, Q.; Zeng, C.; Stepniak, E.; Bracci, P.M.; Yu, K.; Venkataraman, G.; Smith, S.M.; He, C.; et al. Prognostic Implications of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines from Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2790–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Xia, L.; Dong, X.; Chen, G.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhong, S.; Wang, Y.; et al. Liquid Biopsy by Combining 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures of Plasma Cell-Free DNA and Protein Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Shah, S.; Ganguly, S.; Zu, Y.; He, C.; Li, Z. Classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Genes 2023, 14, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Xu, Y.; Olsen, R.J.; Kasparian, S.; Sun, K.; Mathur, S.; Zhang, J.; He, C.; Chen, S.-H.; Bernicker, E.H.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Cell-Free DNA Predicts Immunotherapy Response in Lung Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Lin, S.; Cai, M.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y.; Sui, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Lu, X.; Zhong, Y.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiling from Genomic and Cell-Free DNA for Colorectal Cancers Patients. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3530–3537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; Ge, G.; Gong, Y.; Zhan, Y.; He, S.; Guan, B.; Li, Y.; Xu, Z.; Hao, H.; He, Z.; et al. Vitamin C Increases 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Level and Inhibits the Growth of Bladder Cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applebaum, M.A.; Barr, E.K.; Karpus, J.; Nie, J.; Zhang, Z.; Armstrong, A.E.; Uppal, S.; Sukhanova, M.; Zhang, W.; Chlenski, A.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiles Are Prognostic of Outcome in Neuroblastoma and Reveal Transcriptional Networks That Correlate with Tumor Phenotype. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, D.; Rao, A.K.D.M.; Balaiah, M.; Vittal Rangan, A.; Sundersingh, S.; Veluswami, S.; Thangarajan, R.; Mani, S. Locus-Specific Enrichment Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Reveals Novel Genes Associated with Breast Carcinogenesis. Cells 2022, 11, 2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, X.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Luo, M.; He, J. Decreased 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Levels Correlate with Cancer Progression and Poor Survival: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 1944–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.-R.; Zhang, C.; Cai, J.-B.; Zhang, P.-F.; Shi, G.-M.; Gao, D.-M.; Sun, H.-C.; Qiu, S.-J.; Zhou, J.; Ke, A.-W.; et al. Role of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Level in Diagnosis and Prognosis Prediction of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 2763–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Gu, J.; Wu, Y.; Long, X.; Ge, D.I.; Xu, J.; Ding, J. Low Level of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Predicts Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 3753–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Shao, Y.; Sui, F.; Yang, Q.; Shi, B.; Hou, P.; Ji, M. Decreased 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) Predicts Poor Prognosis in Early-Stage Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Liu, F.; Yi, S.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Xiao, C.; Lian, C.G.; Tu, P.; Wang, Y. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is an Epigenetic Biomarker in Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, Z.; She, Y.; He, Y.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; He, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Chen, C. A Highly Sensitive and Specific Non-Invasive Test through Genome-Wide 5-Hydroxymethylation Mapping for Early Detection of Lung Cancer. Small Methods 2023, 8, e2300747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Pradhan, K.; Campbell, N.; Mazdo, J.; Vasantkumar, A.; Maqbool, S.; Bhagat, T.D.; Gupta, S.; Suzuki, M.; Yu, Y.; et al. Altered Hydroxymethylation Is Seen at Regulatory Regions in Pancreatic Cancer and Regulates Oncogenic Pathways. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 1830–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Bernicker, E.H.; He, C.; Li, Z. Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine as a Marker for Common Cancer Detection. Clin. Transl. Discov. 2022, 2, e136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjöström, M.; Zhao, S.G.; Levy, S.; Zhang, M.; Ning, Y.; Shrestha, R.; Lundberg, A.; Herberts, C.; Foye, A.; Aggarwal, R.; et al. The 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Landscape of Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 3888–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Wu, Y.; Cao, D.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, D.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, X. Genome-Wide 5-Hydroxymethylcytosines in Circulating Cell-Free DNA as Noninvasive Diagnostic Markers for Gastric Cancer. Gastric Cancer Off. J. Int. Gastric Cancer Assoc. Jpn. Gastric Cancer Assoc. 2024, 27, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Steinbacher, J.; Kraus, T.F.J.; Michalakis, S.; Hackner, B.; Pfaffeneder, T.; Perera, A.; Müller, M.; Giese, A.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; et al. Age-Dependent Levels of 5-Methyl-, 5-Hydroxymethyl-, and 5-Formylcytosine in Human and Mouse Brain Tissues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 12511–12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriaucionis, S.; Heintz, N. The Nuclear DNA Base 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Present in Purkinje Neurons and the Brain. Science 2009, 324, 929–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeze, L.I.; Aslanyan, M.G.; van Rooij, A.; Koorenhof-Scheele, T.N.; Massop, M.; Carell, T.; Boezeman, J.B.; Marie, J.-P.; Halkes, C.J.M.; de Witte, T.; et al. Characterization of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Based on Levels of Global Hydroxymethylation. Blood 2014, 124, 1110–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahal, T.; Green, O.; Hananel, U.; Michaeli, Y.; Shabat, D.; Ebenstein, Y. Simple and Cost-Effective Fluorescent Labeling of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2016, 4, 044003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berney, M.; McGouran, J.F. Methods for Detection of Cytosine and Thymine Modifications in DNA. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2018, 2, 332–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Stroup, E.K.; Zhang, Z.; Chiu, B.C.-H.; Zhang, W. Towards Precision Medicine: Advances in 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Cancer Biomarker Discovery in Liquid Biopsy. Cancer Commun. 2019, 39, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Loo, C.E.; Kohli, R.M. Enzymatic Approaches for Profiling Cytosine Methylation and Hydroxymethylation. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Yao, H.; Yi, C. Advances in the Joint Profiling Technologies of 5mC and 5hmC. RSC Chem. Biol. 2024, 5, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommer, M.; McDonald, L.E.; Millar, D.S.; Collis, C.M.; Watt, F.; Grigg, G.W.; Molloy, P.L.; Paul, C.L. A Genomic Sequencing Protocol That Yields a Positive Display of 5-Methylcytosine Residues in Individual DNA Strands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.J.; Branco, M.R.; Ficz, G.; Oxley, D.; Krueger, F.; Reik, W.; Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative Sequencing of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single-Base Resolution. Science 2012, 336, 934–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, S.K.; Morris, T.J.; Guilhamon, P.; Bulstrode, H.; Bachman, M.; Balasubramanian, S.; Beck, S. oxBS-450K: A Method for Analysing Hydroxymethylation Using 450K BeadChips. Methods 2015, 72, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, T.; Moriyama, Y.; Nagae, G.; Aburatani, H.; Okamoto, A. DNA-Friendly Cu(Ii)/TEMPO-Catalyzed 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine-Specific Oxidation. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 5756–5759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuzawa, S.; Takahashi, S.; Tachibana, K.; Tajima, S.; Suetake, I. Simple and Accurate Single Base Resolution Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by Catalytic Oxidative Bisulfite Sequencing Using Micelle Incarcerated Oxidants. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4254–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skvortsova, K.; Zotenko, E.; Luu, P.-L.; Gould, C.M.; Nair, S.S.; Clark, S.J.; Stirzaker, C. Comprehensive Evaluation of Genome-Wide 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiling Approaches in Human DNA. Epigenet. Chromatin 2017, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Hon, G.C.; Szulwach, K.E.; Song, C.-X.; Zhang, L.; Kim, A.; Li, X.; Dai, Q.; Shen, Y.; Park, B.; et al. Base-Resolution Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in the Mammalian Genome. Cell 2012, 149, 1368–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, S.; Arribas, C.; Esteller, M. Validation of a DNA Methylation Microarray for 850,000 CpG Sites of the Human Genome Enriched in Enhancer Sequences. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, M.A.; Li, A.X.; Wu, X.; Pfeifer, G.P. Single Base Resolution Analysis of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by RRBS and TAB-RRBS. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1238, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, W.A.; Huang, Y.; Henderson, H.R.; Agarwal, S.; Rao, A. The GLIB Technique for Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1909–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.B.; Dahl, J.A.; Ougland, R.; Klungland, A. Pull-down of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine DNA Using JBP1-Coated Magnetic Beads. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Chung, T.H.; Tan, D.; Sun, X.; Jia, X.-Y. JBP1-Seq: A Fast and Efficient Method for Genome-Wide Profiling of 5hmC. Genomics 2014, 104, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestor, C.E.; Meehan, R.R. Hydroxymethylated DNA Immunoprecipitation (hmeDIP). Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1094, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Zepeda-Martínez, J.A.; Rao, A. The Anti-CMS Technique for Genome-Wide Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1897–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutsky, E.K.; DeNizio, J.E.; Hu, P.; Liu, M.Y.; Nabel, C.S.; Fabyanic, E.B.; Hwang, Y.; Bushman, F.D.; Wu, H.; Kohli, R.M. Nondestructive, Base-Resolution Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Using a DNA Deaminase. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsova, K.; Bogdanovic, O. TAB-Seq and ACE-Seq Data Processing for Genome-Wide DNA Hydroxymethylation Profiling. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2272, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisvila, R.; Ponnaluri, V.K.C.; Sun, Z.; Langhorst, B.W.; Saleh, L.; Guan, S.; Dai, N.; Campbell, M.A.; Sexton, B.S.; Marks, K.; et al. Enzymatic Methyl Sequencing Detects DNA Methylation at Single-Base Resolution from Picograms of DNA. Genome Res. 2021, 31, 1280–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.; He, B.; Xia, B.; Bai, D.; Lu, X.; Cai, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, A.; Zhu, C.; Meng, H.; et al. Bisulfite-Free, Nanoscale Analysis of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Single Base Resolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 13190–13194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Siejka-Zielińska, P.; Velikova, G.; Bi, Y.; Yuan, F.; Tomkova, M.; Bai, C.; Chen, L.; Schuster-Böckler, B.; Song, C.-X. Bisulfite-Free Direct Detection of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Base Resolution. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, L.; Cui, X.; Gao, Y.; Dai, Q.; Lu, X.; Kou, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Jump-Seq: Genome-Wide Capture and Amplification of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8694–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibas, P.; Narmontė, M.; Staševskij, Z.; Gordevičius, J.; Klimašauskas, S.; Kriukienė, E. Precise Genomic Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine via Covalent Tether-Directed Sequencing. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shi, X.; Gong, Y.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Peng, C.; Xu, Y. Selective Chemical Labeling and Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in DNA at Single-Base Resolution. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 749211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.-B.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Ji, T.-T.; Guo, X.; Gang, F.-Y.; Wang, Y.-F.; Feng, Y.-Q.; Liang, Y.; Ci, W.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine at Base Resolution by Bisulfite-Free Single-Step Deamination with Engineered Cytosine Deaminase. ACS Cent. Sci. 2023, 9, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flusberg, B.A.; Webster, D.R.; Lee, J.H.; Travers, K.J.; Olivares, E.C.; Clark, T.A.; Korlach, J.; Turner, S.W. Direct Detection of DNA Methylation during Single-Molecule, Real-Time Sequencing. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.-X.; Clark, T.A.; Lu, X.-Y.; Kislyuk, A.; Dai, Q.; Turner, S.W.; He, C.; Korlach, J. Sensitive and Specific Single-Molecule Sequencing of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Methods 2011, 9, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füllgrabe, J.; Gosal, W.S.; Creed, P.; Liu, S.; Lumby, C.K.; Morley, D.J.; Ost, T.W.B.; Vilella, A.J.; Yu, S.; Bignell, H.; et al. Simultaneous Sequencing of Genetic and Epigenetic Bases in DNA. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, R.; Cheruba, E.; Wong, P.-M.; Yi, Y.; Ngang, S.; Chong, D.Q.; Loh, Y.-H.; Tan, I.B.; Cheow, L.F. DARESOME Enables Concurrent Profiling of Multiple DNA Modifications with Restriction Enzymes in Single Cells and Cell-Free DNA. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadi0197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, D.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, H.; Guo, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yi, C. Simultaneous Single-Cell Analysis of 5mC and 5hmC with SIMPLE-Seq. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabyanic, E.B.; Hu, P.; Qiu, Q.; Berríos, K.N.; Connolly, D.R.; Wang, T.; Flournoy, J.; Zhou, Z.; Kohli, R.M.; Wu, H. Joint Single-Cell Profiling Resolves 5mC and 5hmC and Reveals Their Distinct Gene Regulatory Effects. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 960–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chialastri, A.; Sarkar, S.; Schauer, E.E.; Lamba, S.; Dey, S.S. Combinatorial Quantification of 5mC and 5hmC at Individual CpG Dyads and the Transcriptome in Single Cells Reveals Modulators of DNA Methylation Maintenance Fidelity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2024, 31, 1296–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Pastor, W.A.; Shen, Y.; Tahiliani, M.; Liu, D.R.; Rao, A. The Behaviour of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Bisulfite Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Salz, T.; Hansen, K.D.; Feinberg, A. Whole-Genome Analysis of the Methylome and Hydroxymethylome in Normal and Malignant Lung and Liver. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1730–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, M.J.; Ost, T.W.B.; Beraldi, D.; Bell, N.M.; Branco, M.R.; Reik, W.; Balasubramanian, S. Oxidative Bisulfite Sequencing of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janku, F.; Huang, H.J.; Pereira, D.Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Chiu, C.H.; Call, S.G.; Woodbury, K.T.; Chao, F.; Marshak, D.R.; Chiu, R.Y.T. A Novel Method for Liquid-Phase Extraction of Cell-Free DNA for Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Okamoto, A. Degradation of DNA by Bisulfite Treatment. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 1912–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szwagierczak, A.; Bultmann, S.; Schmidt, C.S.; Spada, F.; Leonhardt, H. Sensitive Enzymatic Quantification of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahal, T.; Koren, O.; Shefer, G.; Stern, N.; Ebenstein, Y. Hypersensitive Quantification of Global 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by Chemoenzymatic Tagging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1038, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Luo, K.; Shi, H.; Yan, X.; Huang, R.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.; Xie, D.; Zhang, W. Integrated 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine and Fragmentation Signatures as Enhanced Biomarkers in Lung Cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2022, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.P.; Hunter, J.M.; Nestor, C.E.; Dunican, D.S.; Terranova, R.; Moggs, J.G.; Meehan, R.R. Comparative Analysis of Affinity-Based 5-Hydroxymethylation Enrichment Techniques. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordevičius, J.; Narmontė, M.; Gibas, P.; Kvederavičiūtė, K.; Tomkutė, V.; Paluoja, P.; Krjutškov, K.; Salumets, A.; Kriukienė, E. Identification of Fetal Unmodified and 5-Hydroxymethylated CG Sites in Maternal Cell-Free DNA for Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing. Clin. Epigenet. 2020, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriwardena, S.; Chen, K.; Bhagwat, A.S. The Functions and Malfunctions of AID/APOBEC Family Deaminases: The Known Knowns and the Known Unknowns. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12688–12710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siejka-Zielińska, P.; Cheng, J.; Jackson, F.; Liu, Y.; Soonawalla, Z.; Reddy, S.; Silva, M.; Puta, L.; McCain, M.V.; Culver, E.L.; et al. Cell-Free DNA TAPS Provides Multimodal Information for Early Cancer Detection. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabh0534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Q.; Chen, D.-J.; Li, Y.; Yuan, W.-B.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, F.; Jiang, X.; Chen, J.-P.; Wang, D.-D.; et al. Epigenetic Silencing of TET1 Mediated Hydroxymethylation of Base Excision Repair Pathway during Lung Carcinogenesis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieli, T.; Sharim, H.; Nifker, G.; Jeffet, J.; Shahal, T.; Arielly, R.; Levi-Sakin, M.; Hoch, L.; Arbib, N.; Michaeli, Y.; et al. Epigenetic Optical Mapping of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Nanochannel Arrays. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 7148–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, A.H.; Derrington, I.M.; Brinkerhoff, H.; Langford, K.W.; Nova, I.C.; Samson, J.M.; Bartlett, J.J.; Pavlenok, M.; Gundlach, J.H. Detection and Mapping of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine with Nanopore MspA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18904–18909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Diao, J. Single-Molecule Quantification of 5-Methylcytosine and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Cancer Genome. View 2020, 1, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, C.; Veneruso, I.; De Simone, R.R.; Di Bonito, G.; Secondino, A.; D’Argenio, V. The Third-Generation Sequencing Challenge: Novel Insights for the Omic Sciences. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yuan, T.; Song, L.; Fan, Y.; Ren, L.; Song, W.; Peng, J.; An, R.; Gu, Q.; et al. Single-Cell Bisulfite-Free 5mC and 5hmC Sequencing with High Sensitivity and Scalability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2310367120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, B.; Ding, K.-F.; Pan, Z.; Su, G.; Zhang, W.; Liu, T.; Zhong, Y.; He, G.; et al. A 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine-Based Non-Invasive Model for Early Detection of Colorectal Carcinomas and Advanced Adenomas: The METHOD-2 Study. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 3337–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-L.; Wu, Y.-H.; Cao, D.-H.; Jia, Z.-F.; Shen, A.; Jiang, J.; Cao, X.-Y. Increased 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is a Favorable Prognostic Factor of Helicobacter Pylori-Negative Gastric Cancer Patients. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 14, 1295–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B. Association of Tet Methylcytosine Dioxygenase 2 and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma and Its Clinical Significance. BMC Women’s Health 2024, 24, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Olsen, R.J.; Kasparian, S.; He, C.; Bernicker, E.H.; Li, Z. Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Signatures for Lung Cancer Prognosis. Cells 2024, 13, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-J.; Huang, X.-Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, J.-C.; Wei, C.-Y.; Gao, C.; Pei, Y.-Z.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Q.-M.; Cai, J.-B.; et al. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Induces Chemotherapy Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the 5-hmC/PCAF/AKT Axis. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Zhang, W.-L.; Zhang, L.; Yang, P.; Li, F.; Yang, Z.-R.; Wang, J.; Pang, M.; Hong, Y.; Yan, C.; et al. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Profiles of cfDNA Are Highly Predictive of R-CHOP Treatment Response in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Patients. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guler, G.D.; Ning, Y.; Coruh, C.; Mognol, G.P.; Phillips, T.; Nabiyouni, M.; Hazen, K.; Scott, A.; Volkmuth, W.; Levy, S. Plasma Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation Profiling Reveals Anti-PD-1 Treatment Response and Resistance Biology in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Pi, X.; Gao, C.; Zhang, J.; Xia, L.; Yan, X.; Hu, X.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wei, A.; et al. Integrated Fragmentomic Profile and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine of Capture-Based Low-Pass Sequencing Data Enables Pan-Cancer Detection via cfDNA. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 34, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.-D.; Han, X.-X.; Song, Z.-J.; Dong, Y.; Pang, K.; Wang, X.-L.; Liu, X.-Y.; Lu, H.; Xu, G.-Z.; Hao, L.; et al. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Depicts the Methylome and Hydroxymethylome in Recurrent Bladder Cancers and Identifies Biomarkers for Predicting PD-L1 Expression. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilgour, E.; Rothwell, D.G.; Brady, G.; Dive, C. Liquid Biopsy-Based Biomarkers of Treatment Response and Resistance. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Yin, S.; Yuan, Y.; Xia, L.; Cao, F.; Yan, X.; Yan, Z.; Mao, Q.; et al. Noninvasive Detection of Brain Gliomas Using Plasma Cell-Free DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Sequencing. Int. J. Cancer 2023, 152, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storebjerg, T.M.; Strand, S.H.; Høyer, S.; Lynnerup, A.-S.; Borre, M.; Ørntoft, T.F.; Sørensen, K.D. Dysregulation and Prognostic Potential of 5-Methylcytosine (5mC), 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-Formylcytosine (5fC), and 5-Carboxylcytosine (5caC) Levels in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2018, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizgolshani, N.; Petersen, C.L.; Chen, Y.; Levy, J.J.; Salas, L.A.; Perreard, L.; Nguyen, L.N.; Christensen, B.C. DNA 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Pediatric Central Nervous System Tumors May Impact Tumor Classification and Is a Positive Prognostic Marker. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Ou, J.; Wang, B.; Cen, X. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine as a Poor Prognostic Factor for Primary Testicular Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.E.; Olivas, A.; Parilla, M.; Yassan, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.S.; Weber, C.; Keutgen, X.M.; Hart, J.; Krausz, T.; et al. Epigenetic Dysregulation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine in Well-Differentiated Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. AIMM 2022, 30, e11–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-X.; Chen, Y.-X.; Wang, Z.-X.; Zhao, Q.; He, M.-M.; Wang, Y.-N.; Wang, F.; Xu, R.-H. Alteration in TET1 as Potential Biomarker for Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Multiple Cancers. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, D.; He, A.; He, S.; Ge, G.; Wang, S.; Ci, W.; Li, X.; Xia, D.; Zhou, L. Ascorbic Acid Induced TET2 Enzyme Activation Enhances Cancer Immunotherapy Efficacy in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhang, J.; Yan, M.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Tao, Q.; Yan, B.; Chen, X.; Peng, C. Supplementation with α-Ketoglutarate Improved the Efficacy of Anti-PD1 Melanoma Treatment through Epigenetic Modulation of PD-L1. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doroshow, D.B.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Hastings, K.; Politi, K.; Rimm, D.L.; Chen, L.; Melero, I.; Schalper, K.A.; Herbst, R.S. Immunotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Facts and Hopes. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4592–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, S.; Sharma, G.; Karmakar, S.; Banerjee, S. Multi-OMICS Approaches in Cancer Biology: New Era in Cancer Therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penny, L.; Main, S.C.; De Michino, S.D.; Bratman, S.V. Chromatin- and Nucleosome-Associated Features in Liquid Biopsy: Implications for Cancer Biomarker Discovery. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2024, 102, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudecova, I.; Smith, C.G.; Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Chilamakuri, C.S.; Morris, J.A.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Heider, K.; Chandrananda, D.; Cooper, W.N.; Gale, D.; et al. Characteristics, Origin, and Potential for Cancer Diagnostics of Ultrashort Plasma Cell-Free DNA. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Zheng, B.; Liu, J.-F.; Bai, J.; Du, L.-T.; Qian, Y.-S.; Fan, R.; Liu, X.-L.; Wu, L.; et al. Genome-Scale Profiling of Circulating Cell-Free DNA Signatures for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Cirrhotic Patients. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 589–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, N.J.; Rashid, M.; Yu, S.; Bignell, H.; Lumby, C.K.; Livi, C.M.; Howell, K.; Morley, D.J.; Morganella, S.; Barrell, D.; et al. Hydroxymethylation Profile of Cell-Free DNA Is a Biomarker for Early Colorectal Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdar, S.N.; Ho, L.T.; Kron, K.J.; Isserlin, R.; van der Kwast, T.; Zlotta, A.R.; Fleshner, N.E.; Bader, G.; Bapat, B. Dynamic Interplay between Locus-Specific DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Regulates Distinct Biological Pathways in Prostate Carcinogenesis. Clin. Epigenet. 2016, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, Y.; Xu, R.; Pan, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.; Xu, Y.; Ji, G. Dynamic Changes in DNA Methylation and Hydroxymethylation Revealed the Transformation of Advanced Adenoma into Colorectal Carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhommeau, F.; Dupont, S.; Della Valle, V.; James, C.; Trannoy, S.; Massé, A.; Kosmider, O.; Le Couedic, J.-P.; Robert, F.; Alberdi, A.; et al. Mutation in TET2 in Myeloid Cancers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2289–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Wahab, O.; Mullally, A.; Hedvat, C.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Patel, J.; Wadleigh, M.; Malinge, S.; Yao, J.; Kilpivaara, O.; Bhat, R.; et al. Genetic Characterization of TET1, TET2, and TET3 Alterations in Myeloid Malignancies. Blood 2009, 114, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, M.; Huang, Y.; Jankowska, A.M.; Pape, U.J.; Tahiliani, M.; Bandukwala, H.S.; An, J.; Lamperti, E.D.; Koh, K.P.; Ganetzky, R.; et al. Impaired Hydroxylation of 5-Methylcytosine in Myeloid Cancers with Mutant TET2. Nature 2010, 468, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, C.G.; Xu, Y.; Ceol, C.; Wu, F.; Larson, A.; Dresser, K.; Xu, W.; Tan, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhan, Q.; et al. Loss of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is an Epigenetic Hallmark of Melanoma. Cell 2012, 150, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudra, R.; Woappi, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, S.; Wells, M.; Schmults, C.D.; Lian, C.G.; Ramsey, M.R. Regulation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine by TET2 Contributes to Squamous Cell Carcinoma Tumorigenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 1270–1279.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrehaili, A.A.; Gharib, A.F.; Alghamdi, S.A.; Alhazmi, A.; Al-Shehri, S.S.; Hagag, H.M.; Alsaeedi, F.A.; Alhuthali, H.M.; Raafat, N.; Etewa, R.L.; et al. Evaluation of TET Family Gene Expression and 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine as Potential Epigenetic Markers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. In Vivo 2023, 37, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wu, J.; Ji, M.; Hu, W.; Wu, C.; Jiang, J. TET2 Inhibits the Proliferation and Metastasis of Lung Adenocarcinoma Cells via Activation of the cGAS-STING Signalling Pathway. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, V.; Ciric, M.; Petkovic, M.; Golubovic, M. Vitamin C and Epigenetics: A Short Physiological Overview. Open Med. 2023, 18, 20230688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Hu, C.; Ferchen, K.; Nie, J.; Cui, X.; Chen, C.-H.; Cheng, L.; Zuo, Z.; Seibel, W.; He, C.; et al. Targeted Inhibition of STAT/TET1 Axis as a Therapeutic Strategy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, S.R.; Cui, Y.; Lubecka, K.; Stefanska, B.; Irudayaraj, J. CRISPR-dCas9 Mediated TET1 Targeting for Selective DNA Demethylation at BRCA1 Promoter. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46545–46556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, S.; Noguchi, H.; Horii, T.; Nakabayashi, K.; Kimura, M.; Okamura, K.; Sakai, A.; Nakashima, H.; Hata, K.; Nakashima, K.; et al. Targeted DNA Demethylation in Vivo Using dCas9-Peptide Repeat and scFv-TET1 Catalytic Domain Fusions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tan, X.; Tampe, B.; Wilhelmi, T.; Hulshoff, M.S.; Saito, S.; Moser, T.; Kalluri, R.; Hasenfuss, G.; Zeisberg, E.M.; et al. High-Fidelity CRISPR/Cas9- Based Gene-Specific Hydroxymethylation Rescues Gene Expression and Attenuates Renal Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Lister, R. Genomic Targeting of TET Activity for Targeted Demethylation Using CRISPR/Cas9. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2272, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayliak, M.M.; Lushchak, V.I. Pleiotropic Effects of α-Ketoglutarate as a Potential Anti-Ageing Agent. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 66, 101237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Kim, S.-H.; Ito, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Xiao, M.-T.; et al. Oncometabolite 2-Hydroxyglutarate Is a Competitive Inhibitor of α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Liu, Y.; Cai, S.J.; Qian, M.; Ding, J.; Larion, M.; Gilbert, M.R.; Yang, C. IDH Mutation in Glioma: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Targets. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.-G.; Jiang, Y.; Qiu, R.; Rauch, T.A.; Wang, Y.; Schackert, G.; Krex, D.; Lu, Q.; Pfeifer, G.P. 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Is Strongly Depleted in Human Cancers but Its Levels Do Not Correlate with IDH1 Mutations. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7360–7365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minor, E.A.; Court, B.L.; Young, J.I.; Wang, G. Ascorbate Induces Ten-Eleven Translocation (Tet) Methylcytosine Dioxygenase-Mediated Generation of 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 13669–13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.; Mao, S.-Q.; Zhao, B.; Chong, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, D.; Huang, H.; Gao, J.; Li, Z.; et al. Ascorbic Acid Enhances Tet-Mediated 5-Methylcytosine Oxidation and Promotes DNA Demethylation in Mammals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 10396–10403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathocleous, M.; Meacham, C.E.; Burgess, R.J.; Piskounova, E.; Zhao, Z.; Crane, G.M.; Cowin, B.L.; Bruner, E.; Murphy, M.M.; Chen, W.; et al. Ascorbate Regulates Haematopoietic Stem Cell Function and Leukaemogenesis. Nature 2017, 549, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafson, C.B.; Yang, C.; Dickson, K.M.; Shao, H.; Van Booven, D.; Harbour, J.W.; Liu, Z.-J.; Wang, G. Epigenetic Reprogramming of Melanoma Cells by Vitamin C Treatment. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, K.U. Clinical Circulating Tumor DNA Testing for Precision Oncology. Cancer Res. Treat. Off. J. Korean Cancer Assoc. 2023, 55, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiala, C.; Diamandis, E.P. Utility of Circulating Tumor DNA in Cancer Diagnostics with Emphasis on Early Detection. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kustanovich, A.; Schwartz, R.; Peretz, T.; Grinshpun, A. Life and Death of Circulating Cell-Free DNA. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2019, 20, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Pol, Y.; Mouliere, F. Toward the Early Detection of Cancer by Decoding the Epigenetic and Environmental Fingerprints of Cell-Free DNA. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 350–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.; Dang, H.X.; Chauhan, P.S.; Feng, W.; Shiang, A.; Harris, P.K.; Pachynski, R.K.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Maher, C.A. PACT: A Pipeline for Analysis of Circulating Tumor DNA. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ul Haq, S.; Schmid, S.; Aparnathi, M.K.; Hueniken, K.; Zhan, L.J.; Sacdalan, D.; Li, J.J.N.; Meti, N.; Patel, D.; Cheng, D.; et al. Cell-Free DNA Methylation-Defined Prognostic Subgroups in Small Cell Lung Cancer Identified by Leukocyte Methylation Subtraction. iScience 2022, 25, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Method | Year | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enzymatic/bisulfite (BS) sequencing methods | ||||
| BS-seq [89] (Bisulfite sequencing) | 1992 |
|
|
|
| OxBS-seq [90] (Oxidative BS-seq) | 2012 |
|
|
|
| TAB-seq [95] (TET-assisted BS-seq) | 2012 |
|
|
|
| Enzymatic or affinity-based methods | ||||
| GLIB [40,98] (Glucosylation, periodate oxidation, biotinylation) | 2011 |
|
|
|
| HMe-SEAL [54,58] (5hmC-selective chemical labeling assay) | 2011 |
|
|
|
| JBP1-seq [99,100] (J-binding protein 1 sequencing) | 2012 |
|
|
|
| hMeDIP-seq [101] (5hmC DNA immunoprecipitation) | 2014 |
|
|
|
| ACE-seq [103,104] (APOBEC-coupled epigenetic sequencing) | 2018 |
|
|
|
| hmC-CATCH [106] (Chemical-assisted C-to-T conversion of 5hmC sequencing) | 2018 |
|
|
|
| TAPS-seq [107] (TET-assisted pyridine borane sequencing) | 2019 |
|
|
|
| Jump-seq [108] | 2019 |
|
|
|
| hmTOP-seq [109] (5hmC-specific tethered oligonucleotide-primed sequencing) | 2020 |
|
|
|
| DIP-CAB-Seq [110] (DNA immunoprecipitation-coupled chemical modification-assisted bisulfite sequencing) | 2021 |
|
|
|
| SSD-seq [111] (Single-step deamination sequencing) | 2023 |
|
|
|
| EBS-seq [43] (Enrichment-based sequencing) | 2023 |
|
|
|
| Simultaneous epigenetic and genetic sequencing | ||||
| SMRT [112,113] (Single molecule, real-time sequencing) | 2010 |
|
|
|
| 6-letter seq [114] | 2023 |
|
|
|
| DARESOME [115] (DNA analysis by restriction enzyme for simultaneous detection of multiple epigenomic states) | 2023 |
|
|
|
| SIMPLE-seq [116] (Single-cell intracellular metabolite profiling and labeling experiment sequencing) | 2024 |
|
|
|
| Joint-snhmC-seq [117] | 2024 |
|
|
|
| Dyad-seq [118] | 2024 |
|
|
|
| Study | Cancer (n) | Profiling Method | Sample Type | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic biomarker | ||||
| Shao et al., 2022 [78] | Pan cancer (Bladder [n = 41], breast [n = 62], colorectal [n = 45], kidney [n = 54], lung [n = 57], prostate [n = 125)) | Nano-hmC-Seal | cfDNA |
|
| Chang et al., 2024 [137] | Colorectal cancer (n = 2576) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Prognostic biomarker | ||||
| Dong et al., 2015 [72] | Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (n = 16) | IHC, dot blot, tissue microarray | Tissue |
|
| Fu et al., 2022 [138] | Gastric cancer (n = 144) | ELISA | Tissue |
|
| Kuang et al., 2024 [139] | Endometrial cancer (n = 264) | IHC | Tissue |
|
| Chiu et al., 2019 [63] | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (n = 48) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Cai et al., 2021 [64] | Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC, n = 135) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Shao et al., 2023 [65] | Acute myeloid leukemia (AML, n = 54) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Shao et al., 2024 [140] | Lung cancer (n = 97) | Nano-hmC-Seal | cfDNA |
|
| Predictive biomarker | ||||
| Guo et al., 2023 [141] | Hepatocellular carcinoma (n = 101) | IHC, tissue microarray | Tissue |
|
| Chen et al., 2021 [142] | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL, n = 86) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Shao et al., 2024 [66] | Lung cancer (n = 83) | Nano-hmC-Seal | cfDNA |
|
| Guler et al., 2024 [143] | Lung cancer (n = 31 with plasma, n = 18 with tissue) | Chemical capture with biotin and streptavidin beads | cfDNA |
|
| Multi-omics biomarker | ||||
| Hu et al., 2022 [126] | Lung cancer (n = 157) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Zhang et al., 2023 [144] | Pan cancer (Liver [n = 132], pancreas [n = 74], lung [n = 33], glioblastoma [n = 33]) | HMe-SEAL | cfDNA |
|
| Shi et al., 2023 [145] | Bladder cancer (n = 44) | RRBS, oxRRBS | cfDNA |
|
| Lee et al., 2024 [47] | Pediatric central nervous system tumours (n = 32) | Infinium Human-Methylation EPIC BeadChips OxBS-seq | cfDNA |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.J.N.; Liu, G.; Lok, B.H. Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications. Genes 2024, 15, 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091160
Li JJN, Liu G, Lok BH. Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications. Genes. 2024; 15(9):1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091160
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Janice J. N., Geoffrey Liu, and Benjamin H. Lok. 2024. "Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications" Genes 15, no. 9: 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091160
APA StyleLi, J. J. N., Liu, G., & Lok, B. H. (2024). Cell-Free DNA Hydroxymethylation in Cancer: Current and Emerging Detection Methods and Clinical Applications. Genes, 15(9), 1160. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15091160






