The Evolving Scenario of ES-SCLC Management: From Biology to New Cancer Therapeutics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Current Treatment Options
2.1. First Line Treatment
2.2. Maintenance Treatment
2.3. Second Line and Beyond
3. Biology of SCLC: Molecular Landscape
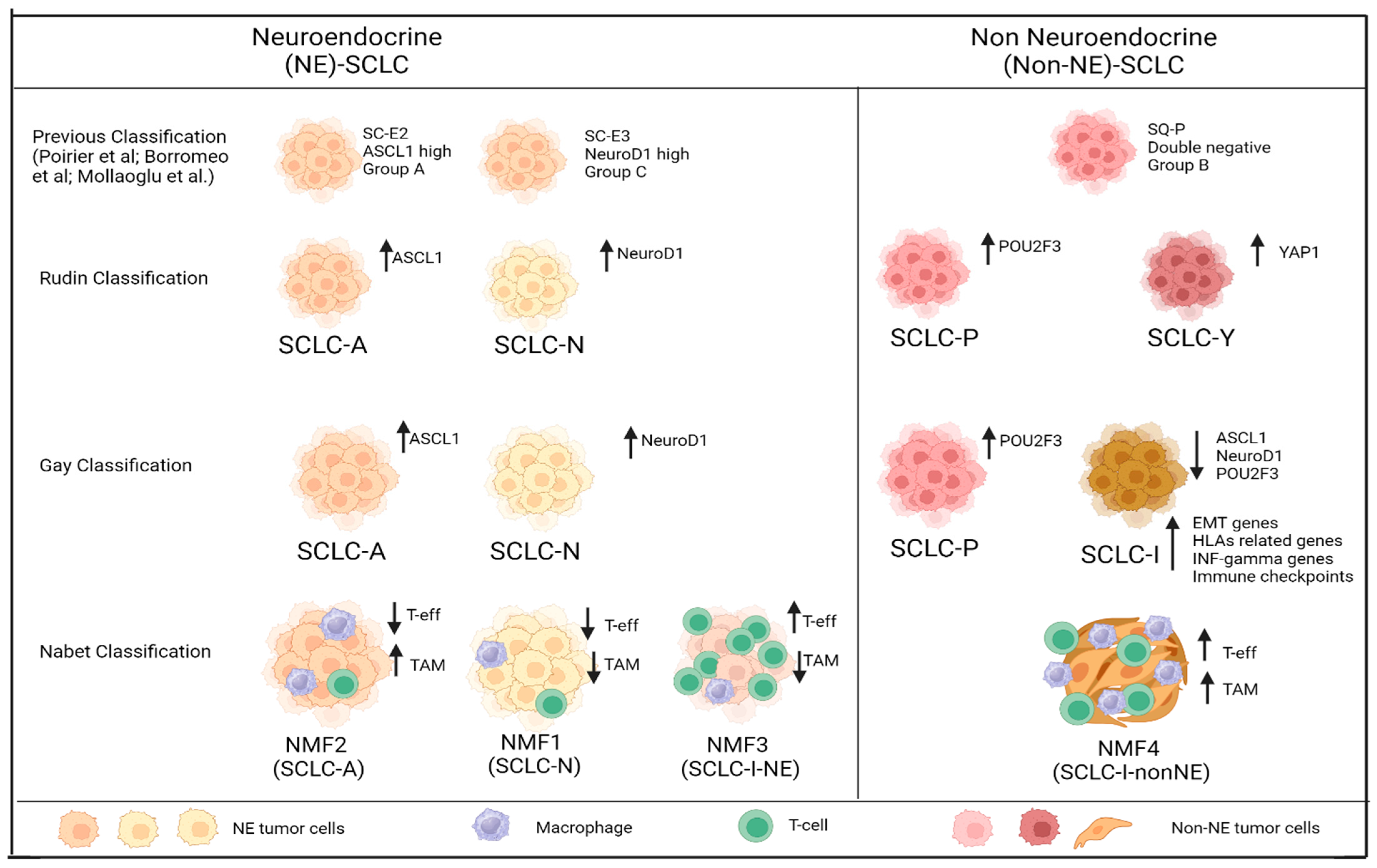
4. Molecular Subtypes
5. New Therapeutics in Development
5.1. Chemotherapeutic Agents
5.2. Immunotherapy
5.3. Antiangiogenics
5.4. PARP Inhibitors
5.5. Targeted Therapy
5.5.1. Inhibition of Cellular Proteins (Membrane, Plasma and Nuclear Proteins)
5.5.2. Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs): Rova-T, S. Govitecan, ABBV-011 and Others
5.5.3. Other Anti-DLL3 Agents: BiTE (Tarlatamab, BI-765432), TCE (HPN328) and Others
6. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Waqar, S.N.; Morgensztern, D. Treatment advances in small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 180, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingemans, A.-M.C.; Früh, M.; Ardizzoni, A.; Besse, B.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Hendriks, L.E.; Lantuejoul, S.; Peters, S.; Reguart, N.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Small-cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 839–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brambilla, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Sage, J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.-M.; Choi, Y.-L.; Ji, J.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, K.-M.; Han, J.; Ahn, M.-J.; Park, K. Small-cell lung cancer detection in never-smokers: Clinical characteristics and multigene mutation profiling using targeted next-generation sequencing. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardona, A.F.; Rojas, L.; Zatarain-Barrón, Z.L.; Ruiz-Patiño, A.; Ricaurte, L.; Corrales, L.; Martín, C.; Freitas, H.; Cordeiro de Lima, V.C.; Rodriguez, J.; et al. Multigene Mutation Profiling and Clinical Characteristics of Small-Cell Lung Cancer in Never-Smokers vs. Heavy Smokers (Geno1.3-CLICaP). Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogino, A.; Choi, J.; Lin, M.; Wilkens, M.K.; Calles, A.; Xu, M.; Adeni, A.E.; Chambers, E.S.; Capelletti, M.; Butaney, M.; et al. Genomic and pathological heterogeneity in clinically diagnosed small cell lung cancer in never/light smokers identifies therapeutically targetable alterations. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, W.K.; Shepherd, F.A.; Feld, R.; Osoba, D.; Dang, P.; Deboer, G. VP-16 and cisplatin as first-line therapy for small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1985, 3, 1471–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Martelli, O.; Di Maio, M. Treatment of patients with small-cell lung cancer: From meta-analyses to clinical practice. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2013, 39, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, L.; Mansfield, A.S.; Szczęsna, A.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Hochmair, M.J.; Huemer, F.; Losonczy, G.; Johnson, M.L.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2220–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab plus platinum–etoposide versus platinum–etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): A randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Guidelines Version 2.2024 Small Cell Lung Cancer. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/sclc.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Stewart, C.A.; Tong, P.; Cardnell, R.J.; Sen, T.; Li, L.; Gay, C.M.; Masrorpour, F.; Fan, Y.; Bara, R.O.; Feng, Y.; et al. Dynamic variations in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), ATM, and SLFN11 govern response to PARP inhibitors and cisplatin in small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28575–28587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttger, F.; Semenova, E.A.; Song, J.-Y.; Ferone, G.; van der Vliet, J.; Cozijnsen, M.; Bhaskaran, R.; Bombardelli, L.; Piersma, S.R.; Pham, T.V.; et al. Tumor Heterogeneity Underlies Differential Cisplatin Sensitivity in Mouse Models of Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3345–3358.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwendenwein, A.; Megyesfalvi, Z.; Barany, N.; Valko, Z.; Bugyik, E.; Lang, C.; Ferencz, B.; Paku, S.; Lantos, A.; Fillinger, J.; et al. Molecular profiles of small cell lung cancer subtypes: Therapeutic implications. Mol. Ther.-Oncolytics 2021, 20, 470–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, C.A.; Gay, C.M.; Xi, Y.; Sivajothi, S.; Sivakamasundari, V.; Fujimoto, J.; Bolisetty, M.; Hartsfield, P.M.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Chalishazar, M.D.; et al. Single-cell analyses reveal increased intratumoral heterogeneity after the onset of therapy resistance in small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundstrøm, S.; Bremnes, R.M.; Kaasa, S.; Aasebø, U.; Hatlevoll, R.; Dahle, R.; Boye, N.; Wang, M.; Vigander, T.; Vilsvik, J.; et al. Cisplatin and Etoposide Regimen Is Superior to Cyclophosphamide, Epirubicin, and Vincristine Regimen in Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From a Randomized Phase III Trial with 5 Years’ Follow-Up. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4665–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascaux, C.; Paesmans, M.; Berghmans, T.; Branle, F.; Lafitte, J.J.; Lemaître, F.; Meert, A.P.; Vermylen, P.; Sculier, J.P. A systematic review of the role of etoposide and cisplatin in the chemotherapy of small cell lung cancer with methodology assessment and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer 2000, 30, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.V.; Reck, M.; Mansfield, A.S.; Mok, T.; Scherpereel, A.; Reinmuth, N.; Garassino, M.C.; De Castro Carpeno, J.; Califano, R.; Nishio, M.; et al. Updated Overall Survival and PD-L1 Subgroup Analysis of Patients With Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer Treated With Atezolizumab, Carboplatin, and Etoposide (IMpower133). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansfield, A.S.; Każarnowicz, A.; Karaseva, N.; Sánchez, A.; De Boer, R.; Andric, Z.; Reck, M.; Atagi, S.; Lee, J.-S.; Garassino, M.; et al. Safety and patient-reported outcomes of atezolizumab, carboplatin, and etoposide in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (IMpower133): A randomized phase I/III trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.V.; Dziadziuszko, R.; Sugawara, S.; Kao, S.; Hochmair, M.; Huemer, F.; Castro, G.; Havel, L.; Caro, R.B.; Losonczy, G.; et al. OA01.04 Five-Year Survival in Patients with ES-SCLC Treated with Atezolizumab in IMpower133: Imbrella a Extension Study Results. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, S44–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; Garassino, M.C.; et al. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: 3-year overall survival update from CASPIAN. ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, J.W.; Dvorkin, M.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Trukhin, D.; Statsenko, G.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab, with or without tremelimumab, plus platinum–etoposide versus platinum–etoposide alone in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): Updated results from a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, T.; Wang, Y.; Dowlati, A.; Lewis, D.A.; Chen, Y.; Mohindra, A.R.; Razaq, M.; Ahuja, H.G.; Liu, J.; King, D.M.; et al. Randomized phase II clinical trial of cisplatin/carboplatin and etoposide (CE) alone or in combination with nivolumab as frontline therapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC): ECOG-ACRIN EA5161. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Awad, M.M.; Navarro, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peters, S.; Csőszi, T.; Cheema, P.K.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Wollner, M.; Yang, J.C.-H.; et al. Pembrolizumab or Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum as First-Line Therapy for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III KEYNOTE-604 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Han, L.; Wu, L.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; Wen, G.; Ji, Y.; Dvorkin, M.; Shi, J.; Pan, Z.; et al. Effect of First-Line Serplulimab vs Placebo Added to Chemotherapy on Survival in Patients With Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. JAMA 2022, 328, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, C.; Yao, W.; Wang, Q.; Min, X.; Chen, G.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Xu, F.; Fang, Y.; et al. Adebrelimab or placebo plus carboplatin and etoposide as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CAPSTONE-1): A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Zhou, C.; Wang, D.; Xia, B.; Bi, M.; Fu, X.; Li, C.; et al. LBA93 EXTENTORCH: A randomized, phase III trial of toripalimab versus placebo, in combination with chemotherapy as a first-line therapy for patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Kang, M.; Yang, N.; Zhong, D.; Wang, Z.; et al. Tislelizumab Plus Platinum and Etoposide Versus Placebo Plus Platinum and Etoposide as First-Line Treatment for Extensive-Stage SCLC (RATIONALE-312): A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Randomized, Phase 3 Clinical Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reck, M.; Luft, A.; Szczesna, A.; Havel, L.; Kim, S.-W.; Akerley, W.; Pietanza, M.C.; Wu, Y.; Zielinski, C.; Thomas, M.; et al. Phase III Randomized Trial of Ipilimumab Plus Etoposide and Platinum Versus Placebo Plus Etoposide and Platinum in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 3740–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, D.C.C.; Polito, L.; Madhavan, S.; Adler, L.; Ogale, S.; Camidge, D.R. Adoption and early clinical outcomes of atezolizumab (atezo) + carboplatin and etoposide (CE) in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) in the real-world (RW) setting. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürbüz, M.; Kutlu, Y.; Akkuş, E.; Köksoy, E.B.; Köse, N.; Öven, B.B.; Uluç, B.O.; Demiray, A.G.; Erdem, D.; Demir, B.; et al. Atezolizumab combined with chemotherapy in the first-line treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A real-life data of the Turkish Oncology Group. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 3547–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bria, E.; Morgillo, F.; Garassino, M.C.; Ciardiello, F.; Ardizzoni, A.; Stefani, A.; Verderame, F.; Morabito, A.; Chella, A.; Tonini, G.; et al. Atezolizumab Plus Carboplatin and Etoposide in Patients with Untreated Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Interim Results of the MAURIS Phase IIIb Trial. Oncologist 2024, 29, e690–e698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Campelo, M.R.; Domine Gomez, M.; De Castro Carpeno, J.; Moreno Vega, A.L.; Ponce Aix, S.; Arriola, E.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Majem Tarruella, M.; Huidobro Vence, G.; Esteban Gonzalez, E.; et al. 1531P Primary results from IMfirst, a phase IIIb open label safety study of atezolizumab (ATZ) + carboplatin (CB)/cisplatin (CP) + etoposide (ET) in an interventional real-world (RW) clinical setting of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) in Spain. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S1246–S1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchero, L.; Guisier, F.; Darrason, M.; Boyer, A.; Dayen, C.; Cousin, S.; Merle, P.; Lamy, R.; Madroszyk, A.; Otto, J.; et al. Long-term effectiveness and treatment sequences in patients with extensive stage small cell lung cancer receiving atezolizumab plus chemotherapy: Results of the IFCT-1905 CLINATEZO real-world study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yao, W.; Yu, Y.; Zang, A.; Cao, L.; Lv, D.; Li, S.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, J.; et al. 519P Final results and subgroup analysis of ORIENTAL: A phase IIIB study of durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of Chinese patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinmuth, N.; Özgüroglu, L.N. LBA2—First-line (1L) durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide for patients with extensive-stage SCLC (ES-SCLC): Primary results from the phase 3b LUMINANCE study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 20 (Suppl. 1), 100535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, M.I.; Arriola, E.; García-Campelo, M.R.; Tain, P.D.; Blanco, C.M.; Piqueras, M.L.B.; Vega, A.M.; Mateos, L.L.; Rodriguez, J.O.; Calderon, V.G.; et al. 1993P—Phase IIIb study of durvalumab plus platinum–etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (CANTABRICO): Safety results. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1062–S1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadgeel, S.M.; Pennell, N.A.; Fidler, M.J.; Halmos, B.; Bonomi, P.; Stevenson, J.; Schneider, B.; Sukari, A.; Ventimiglia, J.; Chen, W.; et al. Phase II Study of Maintenance Pembrolizumab in Patients with Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Park, K.; Govindan, R.; Ready, N.; Reck, M.; Peters, S.; Dakhil, S.R.; Navarro, A.; Rodríguez-Cid, J.; Schenker, M.; et al. Nivolumab and Ipilimumab as Maintenance Therapy in Extensive-Disease Small-Cell Lung Cancer: CheckMate 451. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Behera, M.; Chen, Z.; Bhimani, C.; Curran, W.J.; Khuri, F.R.; Ramalingam, S.S. A Systematic Analysis of Efficacy of Second-Line Chemotherapy in Sensitive and Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardizzoni, A.; Tiseo, M.; Boni, L. Validation of standard definition of sensitive versus refractory relapsed small cell lung cancer: A pooled analysis of topotecan second-line trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2211–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owonikoko, T.K. SCLC Classification by Platinum Sensitivity in the Era of Immunotherapy: Mere Relic or a Valuable Treasure to Keep? J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torasawa, M.; Horinouchi, H.; Nomura, S.; Igawa, S.; Asai, M.; Ishii, H.; Wakui, H.; Ushio, R.; Asao, T.; Namba, Y.; et al. Reconsidering the Cutoff Value for Sensitive and Refractory Relapses in Extensive-Stage SCLC in the Era of Immunotherapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Pawel, J.; Schiller, J.H.; Shepherd, F.A.; Fields, S.Z.; Kleisbauer, J.P.; Chrysson, N.G.; Stewart, D.J.; Clark, P.I.; Palmer, M.C.; Depierre, A.; et al. Topotecan Versus Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, and Vincristine for the Treatment of Recurrent Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1999, 17, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, M.E.R.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Tsekov, H.; Shparyk, Y.; Cuceviá, B.; Juhasz, G.; Thatcher, N.; Ross, G.A.; Dane, G.C.; Crofts, T. Phase III trial comparing supportive care alone with supportive care with oral topotecan in patients with relapsed small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5441–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Pawel, J.; Gatzemeier, U.; Pujol, J.-L.; Moreau, L.; Bildat, S.; Ranson, M.; Richardson, G.; Steppert, C.; Rivière, A.; Camlett, I.; et al. Phase II Comparator Study of Oral Versus Intravenous Topotecan in Patients with Chemosensitive Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 1743–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Pawel, J.; Jotte, R.; Spigel, D.R.; O’Brien, M.E.R.; Socinski, M.A.; Mezger, J.; Steins, M.; Bosquée, L.; Bubis, J.; Nackaerts, K.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Amrubicin Versus Topotecan As Second-Line Treatment for Patients With Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 4012–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaccone, G.; Ferrati, P.; Donadio, M.; Testore, F.; Calciati, A. Reinduction chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Clin. Oncol. 1987, 23, 1697–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genestreti, G.; Tiseo, M.; Kenmotsu, H.; Kazushige, W.; Di Battista, M.; Cavallo, G.; Carloni, F.; Bongiovanni, A.; Burgio, M.A.; Casanova, C.; et al. Outcomes of Platinum-Sensitive Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated With Platinum/Etoposide Rechallenge: A Multi-Institutional Retrospective Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2015, 16, e223–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, Y.; Yamada, K.; Imamura, Y.; Ishii, H.; Matsuo, N.; Tokito, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Azuma, K.; Hoshino, T. Rechallenge treatment with a platinum-based regimen in patients with sensitive relapsed small-cell lung cancer. Med. Oncol. 2018, 35, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baize, N.; Monnet, I.; Greillier, L.; Geier, M.; Lena, H.; Janicot, H.; Vergnenegre, A.; Crequit, J.; Lamy, R.; Auliac, J.-B.; et al. Carboplatin plus etoposide versus topotecan as second-line treatment for patients with sensitive relapsed small-cell lung cancer: An open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, J.F.M.; Martínez-Díez, M.; García-Hernández, V.; Moneo, V.; Domingo, A.; Bueren-Calabuig, J.A.; Negri, A.; Gago, F.; Guillén-Navarro, M.J.; Avilés, P.; et al. PM01183, a new DNA minor groove covalent binder with potent in vitro and in vivo anti-tumour activity. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 161, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santamaría Nuñez, G.; Robles, C.M.G.; Giraudon, C.; Martínez-Leal, J.F.; Compe, E.; Coin, F.; Aviles, P.; Galmarini, C.M.; Egly, J.-M. Lurbinectedin Specifically Triggers the Degradation of Phosphorylated RNA Polymerase II and the Formation of DNA Breaks in Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2399–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trigo, J.; Subbiah, V.; Besse, B.; Moreno, V.; López, R.; Sala, M.A.; Peters, S.; Ponce, S.; Fernández, C.; Alfaro, V.; et al. Lurbinectedin as second-line treatment for patients with small-cell lung cancer: A single-arm, open-label, phase 2 basket trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aix, S.P.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Navarro, A.; Cousin, S.; Bonanno, L.; Smit, E.F.; Chiappori, A.; Olmedo, M.E.; Horvath, I.; Grohé, C.; et al. Combination lurbinectedin and doxorubicin versus physician’s choice of chemotherapy in patients with relapsed small-cell lung cancer (ATLANTIS): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2023, 11, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousin, S.; Paz-Ares, L.G.; Fülöp, A.; Horvath, I.; Trigo Perez, J.M.M.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Bonanno, L.; Lopez-Vilariño, J.A.; Kahatt, C.M.; Fernandez, C.M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of lurbinectedin in elderly patients with relapsed SCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Aix, S.; Coté, G.; Falcón, A.; Jimenez-Aguilar, E.; Lin, J.; Sánchez Simón, I.; Flor, M.J.; Nuñez, R.; Jimenez, A.M.; Jimenez, E.; et al. OA11.04 Lurbinectedin With Irinotecan in Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer. Results From the Expansion Stage of a Phase I-II Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.C.; Mendivil, A.N.; de Spéville, B.D.; Colomé, E.Á.; Luken, M.D.M.; Alvarez, R.M.; Garcia, V.M.; Valles, M.A.; de la Fuente, E.C.; Alcalá, D.; et al. 1989MO—Lurbinectedin (LUR) in combination with pembrolizumab (PBL) in relapsed small cell lung cancer (SCLC): The phase I/II LUPER study. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1062–S1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Reck, M.; Peters, S.; Borghaei, H.; Herbst, R.; Siddiqui, M.; Cuchelkar, V.; Bhatt, K.; Chakrabarti, D.; Wang, L.; et al. EP14.01-015 IMforte: A Phase III Study of Lurbinectedin and Atezolizumab Versus Atezolizumab as Maintenance Therapy in ES-SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S532–S533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, B.; Paz-Ares, L.G.; Peters, S.; Cappuzzo, F.; Reck, M.; Calles, A.; Califano, R.; Lopez-Vilariño, J.A.; Veramendi, S.; Kahatt, C.M.; et al. A phase III study of lurbinectedin alone or in combination with irinotecan vs investigator’s choice (topotecan or irinotecan) in patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer (SCLC.; LAGOON trial). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, TPS8613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, P.A.; Elez, E.; Hiret, S.; Kim, D.-W.; Morosky, A.; Saraf, S.; Piperdi, B.; Mehnert, J.M. Pembrolizumab in Patients With Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the Phase Ib KEYNOTE-028 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.C.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Lopez-Martin, J.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Kao, S.; Miller, W.H.; Delord, J.-P.; Gao, B.; Planchard, D.; Gottfried, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab After Two or More Lines of Previous Therapy in Patients With Recurrent or Metastatic SCLC: Results From the KEYNOTE-028 and KEYNOTE-158 Studies. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; López-Martin, J.A.; Bendell, J.; Ott, P.A.; Taylor, M.; Eder, J.P.; Jäger, D.; Pietanza, M.C.; Le, D.T.; de Braud, F.; et al. Nivolumab alone and nivolumab plus ipilimumab in recurrent small-cell lung cancer (CheckMate 032): A multicentre, open-label, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ready, N.E.; Ott, P.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Hann, C.L.; de Braud, F.; Antonia, S.J.; Ascierto, P.A.; Moreno, V.; Atmaca, A.; et al. Nivolumab Monotherapy and Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Recurrent Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the CheckMate 032 Randomized Cohort. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, J.-L.; Greillier, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Uwer, L.; Hureaux, J.; Guisier, F.; Carmier, D.; Madelaine, J.; Otto, J.; et al. A Randomized Non-Comparative Phase II Study of Anti-Programmed Cell Death-Ligand 1 Atezolizumab or Chemotherapy as Second-Line Therapy in Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the IFCT-1603 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spigel, D.R.; Vicente, D.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Gettinger, S.; Peters, S.; Horn, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Pardo Aranda, N.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Second-line nivolumab in relapsed small-cell lung cancer: CheckMate 331. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://news.bms.com/news/details/2020/Bristol-Myers-Squibb-Statement-on-Opdivo-nivolumab-Small-Cell-Lung-Cancer-US-Indication/default.aspx (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Available online: https://www.merck.com/news/merck-provides-update-on-keytruda-pembrolizumab-indication-in-metastatic-small-cell-lung-cancer-in-the-us/ (accessed on 5 April 2024).
- Rudin, C.M.; Durinck, S.; Stawiski, E.W.; Poirier, J.T.; Modrusan, Z.; Shames, D.S.; Bergbower, E.A.; Guan, Y.; Shin, J.; Guillory, J.; et al. Comprehensive genomic analysis identifies SOX2 as a frequently amplified gene in small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peifer, M.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Sos, M.L.; George, J.; Seidel, D.; Kasper, L.H.; Plenker, D.; Leenders, F.; Sun, R.; Zander, T.; et al. Integrative genome analyses identify key somatic driver mutations of small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretić, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G.; et al. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, S.; Moore, J.A.; Montesion, M.; Sharaf, R.; Lin, D.I.; Colón, C.I.; Fleishmann, Z.; Ebot, E.M.; Newberg, J.Y.; Mills, J.M.; et al. Integrative Analysis of a Large Real-World Cohort of Small Cell Lung Cancer Identifies Distinct Genetic Subtypes and Insights into Histologic Transformation. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 1572–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, B.; Kong, W.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Z. Outcomes in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma With Transformation to Small Cell Lung Cancer After EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Resistance: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 766148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, M.; Salgia, R. Molecular and cellular biology of small cell lung cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2003, 30, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Mahadevan, N.R.; Duplaquet, L.; Hong, D.; Durmaz, Y.T.; Jones, K.L.; Cho, H.; Morrow, M.; Protti, A.; Poitras, M.J.; et al. Aurora A kinase inhibition induces accumulation of SCLC tumor cells in mitosis with restored interferon signaling to increase response to PD-L1. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, K.; Ozasa, H. Aurora kinase B inhibition in small-cell lung cancer: BCL-2 as a potential therapeutic biomarker and combination target. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byers, L.A.; Wang, J.; Nilsson, M.B.; Fujimoto, J.; Saintigny, P.; Yordy, J.; Giri, U.; Peyton, M.; Fan, Y.H.; Diao, L.; et al. Proteomic Profiling Identifies Dysregulated Pathways in Small Cell Lung Cancer and Novel Therapeutic Targets Including PARP1. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 798–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foy, V.; Schenk, M.W.; Baker, K.; Gomes, F.; Lallo, A.; Frese, K.K.; Forster, M.; Dive, C.; Blackhall, F. Targeting DNA damage in SCLC. Lung Cancer 2017, 114, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, T.; Gay, C.M.; Byers, L.A. Targeting DNA damage repair in small cell lung cancer and the biomarker landscape. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 50–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Stewart, C.A.; Wang, Q.; Cardnell, R.J.; Rocha, P.; Fujimoto, J.; Solis Soto, L.M.; Wang, R.; Novegil, V.; Ansell, P.; et al. Dynamic expression of Schlafen 11 (SLFN11) in circulating tumour cells as a liquid biomarker in small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2022, 127, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krushkal, J.; Silvers, T.; Reinhold, W.C.; Sonkin, D.; Vural, S.; Connelly, J.; Varma, S.; Meltzer, P.S.; Kunkel, M.; Rapisarda, A.; et al. Epigenome-wide DNA methylation analysis of small cell lung cancer cell lines suggests potential chemotherapy targets. Clin. Epigenet. 2020, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyokawa, G.; Takada, K.; Tagawa, T.; Kinoshita, F.; Kozuma, Y.; Matsubara, T.; Haratake, N.; Takamori, S.; Akamine, T.; Hirai, F.; et al. Prevalence of Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 in Patients with Resected Small Cell Lung Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3707–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahadevan, N.R.; Knelson, E.H.; Wolff, J.O.; Vajdi, A.; Saigí, M.; Campisi, M.; Hong, D.; Thai, T.C.; Piel, B.; Han, S.; et al. Intrinsic Immunogenicity of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Revealed by Its Cellular Plasticity. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1952–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, P.; Siddiqui, J.A.; Maurya, S.K.; Lakshmanan, I.; Jain, M.; Ganti, A.K.; Salgia, R.; Batra, S.K.; Nasser, M.W. Epigenetic landscape of small cell lung cancer: Small image of a giant recalcitrant disease. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 83, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, E.M.; Taniguchi, H.; Chan, J.M.; Zhan, Y.A.; Chen, X.; Qiu, J.; de Stanchina, E.; Allaj, V.; Shah, N.S.; Uddin, F.; et al. Targeting Lysine-Specific Demethylase 1 Rescues Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Antigen Presentation and Overcomes Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Blockade Resistance in SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 1014–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, B.; Marinov, M.; Arcaro, A. Targeting receptor tyrosine kinase signalling in small cell lung cancer (SCLC): What have we learned so far? Cancer Treat. Rev. 2007, 33, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maulik, G.; Kijima, T.; Ma, P.C.; Ghosh, S.K.; Lin, J.; Shapiro, G.I.; Schaefer, E.; Tibaldi, E.; Johnson, B.E.; Salgia, R. Modulation of the c-Met/hepatocyte growth factor pathway in small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Murray, N.; Salgia, R.; Fossella, F. V Targeted molecules in small cell lung cancer. Semin. Oncol. 2004, 31, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokomizo, A.; Tindall, D.J.; Drabkin, H.; Gemmill, R.; Franklin, W.; Yang, P.; Sugio, K.; Smith, D.I.; Liu, W. PTEN/MMAC1 mutations identified in small cell, but not in non-small cell lung cancers. Oncogene 1998, 17, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Augert, A.; Rongione, M.; Conkrite, K.; Parazzoli, S.; Nikitin, A.Y.; Ingolia, N.; MacPherson, D. PTEN Is a Potent Suppressor of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Kokubu, A.; Tsuta, K.; Hirohashi, S. Oncogenic mutation of PIK3CA in small cell lung carcinoma: A potential therapeutic target pathway for chemotherapy-resistant lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 2009, 283, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krystal, G.W.; Sulanke, G.; Litz, J. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt signaling blocks growth, promotes apoptosis, and enhances sensitivity of small cell lung cancer cells to chemotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2002, 1, 913–922. [Google Scholar]
- Marinov, M.; Ziogas, A.; Pardo, O.E.; Tan, L.T.; Dhillon, T.; Mauri, F.A.; Lane, H.A.; Lemoine, N.R.; Zangemeister-Wittke, U.; Seckl, M.J.; et al. AKT/mTOR Pathway Activation and BCL-2 Family Proteins Modulate the Sensitivity of Human Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to RAD001. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebe, N.; Miele, L.; Harris, P.J.; Jeong, W.; Bando, H.; Kahn, M.; Yang, S.X.; Ivy, S.P. Targeting Notch, Hedgehog, and Wnt pathways in cancer stem cells: Clinical update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 12, 445–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, G.; Sparrow, D.B.; Kremmer, E.; Dunwoodie, S.L. Notch inhibition by the ligand Delta-Like 3 defines the mechanism of abnormal vertebral segmentation in spondylocostal dysostosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 905–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, L.R.; Bankovich, A.J.; Anderson, W.C.; Aujay, M.A.; Bheddah, S.; Black, K.; Desai, R.; Escarpe, P.A.; Hampl, J.; Laysang, A.; et al. A DLL3-targeted antibody-drug conjugate eradicates high-grade pulmonary neuroendocrine tumor-initiating cells in vivo. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, aac9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, K.W.; Reed, J.C. Bcl-2 family proteins and cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 6398–6406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeriswyl, V.; Christofori, G. The angiogenic switch in carcinogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2009, 19, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratigos, M.; Matikas, A.; Voutsina, A.; Mavroudis, D.; Georgoulias, V. Targeting angiogenesis in small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Batenchuk, C.; Badzio, A.; Boyle, T.A.; Czapiewski, P.; Chan, D.C.; Lu, X.; Gao, D.; Ellison, K.; Kowalewski, A.A.; et al. PD-L1 Expression by Two Complementary Diagnostic Assays and mRNA In Situ Hybridization in Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carney, D.N.; Gazdar, A.F.; Bepler, G.; Guccion, J.G.; Marangos, P.J.; Moody, T.W.; Zweig, M.H.; Minna, J.D. Establishment and identification of small cell lung cancer cell lines having classic and variant features. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 2913–2923. [Google Scholar]
- Gazdar, A.F.; Carney, D.N.; Nau, M.M.; Minna, J.D. Characterization of variant subclasses of cell lines derived from small cell lung cancer having distinctive biochemical, morphological, and growth properties. Cancer Res. 1985, 45, 2924–2930. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poirier, J.T.; Gardner, E.E.; Connis, N.; Moreira, A.L.; de Stanchina, E.; Hann, C.L.; Rudin, C.M. DNA methylation in small cell lung cancer defines distinct disease subtypes and correlates with high expression of EZH2. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5869–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borromeo, M.D.; Savage, T.K.; Kollipara, R.K.; He, M.; Augustyn, A.; Osborne, J.K.; Girard, L.; Minna, J.D.; Gazdar, A.F.; Cobb, M.H.; et al. ASCL1 and NEUROD1 Reveal Heterogeneity in Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Tumors and Regulate Distinct Genetic Programs. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollaoglu, G.; Guthrie, M.R.; Böhm, S.; Brägelmann, J.; Can, I.; Ballieu, P.M.; Marx, A.; George, J.; Heinen, C.; Chalishazar, M.D.; et al. MYC Drives Progression of Small Cell Lung Cancer to a Variant Neuroendocrine Subtype with Vulnerability to Aurora Kinase Inhibition. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, J.T.; Dobromilskaya, I.; Moriarty, W.F.; Peacock, C.D.; Hann, C.L.; Rudin, C.M. Selective Tropism of Seneca Valley Virus for Variant Subtype Small Cell Lung Cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-H.; Klingbeil, O.; He, X.-Y.; Wu, X.S.; Arun, G.; Lu, B.; Somerville, T.D.D.; Milazzo, J.P.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Demerdash, O.E.; et al. POU2F3 is a master regulator of a tuft cell-like variant of small cell lung cancer. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.S.; Ibaseta, A.; Fischer, M.M.; Cancilla, B.; O’Young, G.; Cristea, S.; Luca, V.C.; Yang, D.; Jahchan, N.S.; Hamard, C.; et al. Intratumoural heterogeneity generated by Notch signalling promotes small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2017, 545, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Girard, L.; Zhang, Y.A.; Haruki, T.; Papari-Zareei, M.; Stastny, V.; Ghayee, H.K.; Pacak, K.; Oliver, T.G.; Minna, J.D.; et al. Small cell lung cancer tumors and preclinical models display heterogeneity of neuroendocrine phenotypes. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Poirier, J.T.; Byers, L.A.; Dive, C.; Dowlati, A.; George, J.; Heymach, J.V.; Johnson, J.E.; Lehman, J.M.; MacPherson, D.; et al. Molecular subtypes of small cell lung cancer: A synthesis of human and mouse model data. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, C.M.; Stewart, C.A.; Park, E.M.; Diao, L.; Groves, S.M.; Heeke, S.; Nabet, B.Y.; Fujimoto, J.; Solis, L.M.; Lu, W.; et al. Patterns of transcription factor programs and immune pathway activation define four major subtypes of SCLC with distinct therapeutic vulnerabilities. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 346–360.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baine, M.K.; Hsieh, M.-S.; Lai, W.V.; Egger, J.V.; Jungbluth, A.A.; Daneshbod, Y.; Beras, A.; Spencer, R.; Lopardo, J.; Bodd, F.; et al. SCLC Subtypes Defined by ASCL1, NEUROD1, POU2F3, and YAP1: A Comprehensive Immunohistochemical and Histopathologic Characterization. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, S.; Fetsch, P.; Thomas, A.; Pommier, Y.; Schrump, D.S.; Miettinen, M.M.; Chen, H. Molecular Subtypes of Primary SCLC Tumors and Their Associations With Neuroendocrine and Therapeutic Markers. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Dwivedi, B.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Barwick, B.; Ernani, V.; Zhang, G.; Gilbert-Ross, M.; Carlisle, J.; Khuri, F.R.; et al. YAP1 Expression in SCLC Defines a Distinct Subtype With T-cell–Inflamed Phenotype. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caeser, R.; Egger, J.V.; Chavan, S.; Socci, N.D.; Jones, C.B.; Kombak, F.E.; Asher, M.; Roehrl, M.H.; Shah, N.S.; Allaj, V.; et al. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of a library of small cell lung cancer patient-derived xenografts. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Guo, C.; Hu, L.; Xu, Y.; Ma, X.; Gao, J.; Xie, M.; et al. Integrative analysis of multi-omics data reveals the heterogeneity and signatures of immune therapy for small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Huang, J.; Higgs, B.W.; Hu, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Yao, X.; Conley, S.; Zhong, H.; Liu, Z.; Brohawn, P.; et al. Genomic Landscape Survey Identifies SRSF1 as a Key Oncodriver in Small Cell Lung Cancer. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Kudoh, S.; Fujino, K.; Sanada, M.; Tenjin, Y.; Saito, H.; Nakaishi-Fukuchi, Y.; Kameyama, H.; Ichimura, T.; Udaka, N.; et al. Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cells and Small Cell Lung Carcinoma: Immunohistochemical Study Focusing on Mechanisms of Neuroendocrine Differentiation. ACTA Histochem. Cytochem. 2022, 55, 22–00031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabet, B.Y.; Hamidi, H.; Lee, M.C.; Banchereau, R.; Morris, S.; Adler, L.; Gayevskiy, V.; Elhossiny, A.M.; Srivastava, M.K.; Patil, N.S.; et al. Immune heterogeneity in small-cell lung cancer and vulnerability to immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 429–443.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, K.; Ohe, Y.; Shibata, T.; Seto, T.; Takahashi, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Tanaka, H.; Takeda, K.; Nishio, M.; Mori, K.; et al. Combined chemotherapy with cisplatin, etoposide, and irinotecan versus topotecan alone as second-line treatment for patients with sensitive relapsed small-cell lung cancer (JCOG0605): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, R.; Watanabe, S.; Shoji, S.; Ichikawa, K.; Abe, T.; Baba, J.; Tanaka, J.; Tsukada, H.; Terada, M.; Sato, K.; et al. A Phase II Study of Irinotecan for Patients with Previously Treated Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncology 2018, 94, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgeer, M.; Neil Watkins, D.; Banakh, I.; Kumar, B.; Gough, D.J.; Markman, B.; Ganju, V. A phase IIa study of HA-irinotecan, formulation of hyaluronic acid and irinotecan targeting CD44 in extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.M.; Chansky, K.; Baggstrom, M.Q.; Thompson, M.A.; Sanborn, R.E.; Villano, J.L.; Waqar, S.N.; Hamm, J.; Leggas, M.; Willis, M.; et al. Phase II Trial of Carfilzomib Plus Irinotecan in Patients With Small-cell Lung Cancer Who Have Progressed on Prior Platinum-based Chemotherapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 357–364.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Guo, L.; Pu, H.; Bai, S.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y. 1805P Apatinib combined with irinotecan in the treatment of small cell lung cancer: A phase II, single-arm, prospective study. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Paz-Ares, L.G.; Chen, Y.; Jove, M.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Rich, P.; Hayes, T.; Calderón, V.G.; Caro, R.B.; Navarro, A.; et al. MO01.39 Liposomal Irinotecan in Adults with Small Cell Lung Cancer who Progressed on Platinum-Based Therapy: Subgroup Analyses by Platinum Sensitivity. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelman, M.; Dvorkin, M.; Laktionov, K.K.; Navarro, A.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Kozlov, V.; Golden, G.; Jordan, O.; Deng, C. The anti-disialoganglioside (GD2) antibody dinutuximab (D) for second-line treatment (2LT) of patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory small cell lung cancer (RR SCLC): Results from part II of the open-label, randomized, phase II/III distinct study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Fujita, Y.; Nakamura, A.; Kikuchi, E.; Kawai, Y.; Harada, T.; Watanabe, N.; Yokouchi, H.; Usui, K.; et al. Randomized phase 2 study comparing irinotecan versus amrubicin as maintenance therapy after first-line induction therapy for extensive disease small cell lung cancer (HOT1401/NJLCG1401). Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, D.-W.; Kim, S.-W.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, J.-H.; An, H.J.; Kim, J.-S.; Jang, J.-S.; et al. A randomised phase 2b study comparing the efficacy and safety of belotecan vs. topotecan as monotherapy for sensitive-relapsed small-cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, I.; Kawada, K.; Morise, M.; Hase, T.; Hayashi, H.; Sokai, A.; Fukatsu, A.; Kondo, M.; Nomura, F.; Hasegawa, Y. A phase II trial of Ifosfamide combination with recommended supportive therapy for recurrent SCLC in second-line and heavily treated setting. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2018, 81, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietanza, M.C.; Waqar, S.N.; Krug, L.M.; Dowlati, A.; Hann, C.L.; Chiappori, A.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Woo, K.M.; Cardnell, R.J.; Fujimoto, J.; et al. Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase II Study of Temozolomide in Combination With Either Veliparib or Placebo in Patients with Relapsed-Sensitive or Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2386–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.; Cummings, A.; Mendenhall, M.; Velez, M.A.; Babu, S.; Johnson, T.; Alcantar, J.; Dakhil, S.; Kanamori, D.; Lawler, W.; et al. Phase 2 Study Analysis of Talazoparib (TALA) Plus Temozolomide (TMZ) for Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (ES-SCLC). In Proceedings of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer 2022 World Conference Lung Cancer, Vienna, Austria, 6–9 August 2022. Abstr. OA12.03. [Google Scholar]
- Kurata, T.; Okamoto, I.; Tamura, K.; Fukuoka, M. Amrubicin for non-small-cell lung cancer and small-cell lung cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2007, 25, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Zhou, N.; Ma, L.; Jin, W. Amrubicin therapy improves patients with refractory small-cell lung cancer: A single-arm confirmatory Chinese clinical study. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, H.; Kogure, Y.; Ando, M.; Kitagawa, C.; Iwasaku, M.; Niwa, T.; Saka, H. Phase II Study of Weekly Amrubicin for Refractory or Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer. In Vivo 2018, 32, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wu, L.; Ma, Z.; Liu, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Lei, G.; Zhou, N.; Bai, Y.; et al. P48.08 Phase IV Clinical Study on the Safety and Efficacy of Lobaplatin-Based Regimen With Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S502–S503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelsomino, F.; Tiseo, M.; Barbieri, F.; Riccardi, F.; Cavanna, L.; Frassoldati, A.; Delmonte, A.; Longo, L.; Dazzi, C.; Cinieri, S.; et al. Phase 2 study of NAB-paclitaxel in SensiTivE and refractory relapsed small cell lung cancer (SCLC) (NABSTER TRIAL). Br. J. Cancer 2020, 123, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moharana, L.; Lokanatha, D.; Jacob, L.A.; Sureshbabu, M.; Lokesh, K.; Rudresha, A.; Rajeev, L.; Smitha, S. 524P—A study in recurrent small cell lung cancer patients, comparing weekly paclitaxel, irinotecan and temozolomide in second-line: A prospective study from a south Indian tertiary cancer hospital. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, ix157–ix181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scagliotti, G.; Nishio, M.; Satouchi, M.; Valmadre, G.; Niho, S.; Galetta, D.; Cortinovis, D.; Benedetti, F.; Yoshihara, E.; Makris, L.; et al. A phase 2 randomized study of TAS-102 versus topotecan or amrubicin in patients requiring second-line chemotherapy for small cell lung cancer refractory or sensitive to frontline platinum-based chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2016, 100, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akamatsu, H.; Teraoka, S.; Hayashi, H.; Fujimoto, D.; Hayata, A.; Haratani, K.; Ozawa, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Iwasa, T.; Shimokawa, T.; et al. Pembrolizumab Plus Amrubicin in Patients With Relapsed SCLC: Multi-Institutional, Single-Arm Phase 2 Study. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-J.; Keam, B.; Ock, C.-Y.; Song, S.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, D.-W.; et al. A phase II study of pembrolizumab and paclitaxel in patients with relapsed or refractory small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 136, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lycan, T.; Dothard, A.; Ruiz, J.; Levine, B.; Grant, S.; Petty, W. P48.01 Gemcitabine and Nivolumab for Subsequent Treatment of Metastatic Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, M.; Murakami, S.; Kawakami, H.; Okishio, K.; Tamiya, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Fujimoto, D.; Sugawara, S.; Kozuki, T.; Oya, Y.; et al. Phase II Study of the Liposomal Formulation of Eribulin (E7389-LF) in Combination with Nivolumab: Results from the Small Cell Lung Cancer Cohort. Cancer Res. Commun. 2024, 4, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Huang, D.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Fang, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhou, C.; Hu, Y.; et al. Camrelizumab Plus Apatinib in Extensive-Stage SCLC (PASSION): A Multicenter, Two-Stage, Phase 2 Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, S.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, L.; Jia, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, J.; et al. Penpulimab plus anlotinib as second-line treatment for the small cell lung cancer after failure of platinum-based systemic chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 8568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Garassino, M.C.; Chen, Y.; Reinmuth, N.; Hotta, K.; Poltoratskiy, A.; Trukhin, D.; Hochmair, M.J.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Ji, J.H.; et al. Durvalumab ± Tremelimumab + Platinum-Etoposide in Extensive-Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer (CASPIAN): Outcomes by PD-L1 Expression and Tissue Tumor Mutational Burden. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.N.; George, J.; Scheel, A.H.; Schloesser, H.A.; Vehreschild, M.; Brossart, P.; Engel-Riedel, W.; Griesinger, F.; Grohé, C.; Kambartel, K.-O.; et al. BIOLUMA: A phase II trial of nivolumab in combination with ipilimumab to evaluate efficacy and safety in lung cancer and to evaluate biomarkers predictive for response—Preliminary results from the SCLC cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakkala, S.; Higgins, K.; Chen, Z.; Sica, G.; Steuer, C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, G.; Wang, S.; Hossain, M.S.; Nazha, B.; et al. Durvalumab and tremelimumab with or without stereotactic body radiation therapy in relapsed small cell lung cancer: A randomized phase II study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, R.; Min, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Fang, L.; et al. Safety and efficacy of QL1706 plus carboplatin/etoposide (EC) as first-line (1L) treatment for extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC): The results from a phase II single-arm study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Liu, S.V.; Soo, R.A.; Lu, S.; Hong, M.H.; Lee, J.-S.; Bryl, M.; Dumoulin, D.W.; Rittmeyer, A.; Chiu, C.-H.; et al. SKYSCRAPER-02: Tiragolumab in Combination With Atezolizumab Plus Chemotherapy in Untreated Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 42, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uboha, N.V.; Milhem, M.M.; Kovacs, C.; Amin, A.; Magley, A.; Purkayastha, D.D.; Piha-Paul, S.A. Phase II study of spartalizumab (PDR001) and LAG525 in advanced solid tumors and hematologic malignancies. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Mao, C.; Qian, J.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, C.; Xiong, A.; Li, W.; He, Y.; et al. IBI110 (anti-LAG-3 mAb) as a single agent or in combination with sintilimab (anti-PD-1 mAb) in patients with advanced solid tumors: Updated results from the phase Ia/Ib dose-escalation study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, N.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Bordoni, R.; Ellis, P.M.; Hochmair, M.; Müller, V.; Levchenko, E.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, B.; Lara-Guerra, H.; et al. 114TiP KEYNOTE-B99: Phase II study of pembrolizumab plus investigational agents combined with chemotherapy as first-line therapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spigel, D.R.; Townley, P.M.; Waterhouse, D.M.; Fang, L.; Adiguzel, I.; Huang, J.E.; Karlin, D.A.; Faoro, L.; Scappaticci, F.A.; Socinski, M.A. Randomized Phase II Study of Bevacizumab in Combination With Chemotherapy in Previously Untreated Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the SALUTE Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pujol, J.-L.; Lavole, A.; Quoix, E.; Molinier, O.; Souquet, P.-J.; Barlesi, F.; Le Caer, H.; Moro-Sibilot, D.; Fournel, P.; Oster, J.P.; et al. Randomized phase II–III study of bevacizumab in combination with chemotherapy in previously untreated extensive small-cell lung cancer: Results from the IFCT-0802 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, M.; Boni, L.; Ambrosio, F.; Camerini, A.; Vitale, M.G.; Baldini, E.; Cinieri, S.; Zanelli, F.; Defraia, E.; Passalacqua, R.; et al. Italian Multicenter Phase III Randomized Study of Cisplatin–Etoposide With or Without Bevacizumab as First-Line Treatment in Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer: Treatment Rationale and Protocol Design of the GOIRC-AIFA FARM6PMFJM Trial. Clin. Lung Cancer 2015, 16, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrini, E.; Lamberti, G.; Mazzoni, F.; Riccardi, F.; Bonetti, A.; Follador, A.; Giardina, D.; Genova, C.; Guaitoli, G.; Frassoldati, A.; et al. EP14.01-006 CeLEBrATE: Phase II trial of CarbopLatin, Etoposide, Bevacizumab and Atezolizumab in Patients with exTEnsive-Stage SCLC-GOIRC-01-2019. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S528–S529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meder, L.; Schuldt, P.; Thelen, M.; Schmitt, A.; Dietlein, F.; Klein, S.; Borchmann, S.; Wennhold, K.; Vlasic, I.; Oberbeck, S.; et al. Combined VEGF and PD-L1 Blockade Displays Synergistic Treatment Effects in an Autochthonous Mouse Model of Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4270–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lu, H.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Gong, L.; Chen, K.; et al. Apatinib in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer after second-line or third-line chemotherapy: A phase II, single-arm, multicentre, prospective study. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, X.; Jun, J.; Yang, L.; Zhou, S.; Liu, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Hao, X.; Shi, Y. Efficacy and safety of apatinib in extensive stage small cell lung cancer patients failed from two or more lines of chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 8553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, D.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M.; Deng, L.; Wu, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, L.; Tan, J.; et al. OA03.01 A Non-Randomized, Open-Label, Prospective, Multicenter Study of Apatinib as Second-Line and Later-Line Therapy in Patients with ES-SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, S210–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y.; et al. Apatinib with etoposide capsules as a third- or further-line therapy for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: An open-label, multicenter, single-arm phase II trial. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, C.; Guo, Y.; Qiu, S. FP10.05 A Prospective Phase II Study of Apatinib Plus Chemotherapy for Pretreated Patients With Advanced Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S216–S217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Li, K.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, L.; Han, B.; Chen, G.; He, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Anlotinib vs placebo as third- or further-line treatment for patients with small cell lung cancer: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase 2 study. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lv, D.; Wu, X.; Ye, J.; Zhou, C.; Wang, J.; Ling, L.; Yang, H. 1649P Anlotinib plus oral fluoropyrimidine S1 in treating patients with refractory or relapsed small cell lung cancer (SALTER TRIAL): An open-label, multicenter, single-arm, phase II trial. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, S1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, J.; Ye, J.; Ma, S.; Xia, B. Anlotinib plus irinotecan or docetaxel in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) relapsed within six months: Updated results from a single-arm, phase Ⅱ study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, e20629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Xie, C.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, N.; Huang, C.; Wei, S.; Sun, H.; et al. OA01.03 Benmelstobart with Anlotinib plus Chemotherapy as First-line Therapy for ES-SCLC: A Randomized, Double-blind, Phase III Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2023, 18, S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.-M.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, B.-S.; Kim, H.-G.; Min, Y.J.; Yi, S.Y.; Yun, H.J.; Jung, S.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; et al. Pazopanib maintenance after first-line etoposide and platinum chemotherapy in patients with extensive disease small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled Phase II study (KCSG-LU12-07). Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koinis, F.; Agelaki, S.; Karavassilis, V.; Kentepozidis, N.; Samantas, E.; Peroukidis, S.; Katsaounis, P.; Hartabilas, E.; Varthalitis, I.I.; Messaritakis, I.; et al. Second-line pazopanib in patients with relapsed and refractory small-cell lung cancer: A multicentre phase II study of the Hellenic Oncology Research Group. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Fang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, Z.; Sun, T. Abstract CT157: An exploratory phase 2 study of chiauranib monotherapy for small cell lung cancer after two or more lines of previous therapy. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, CT157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, R.; Chen, J. Benmelstobart with anlotinib plus chemotherapy as first-line therapy for ES-SCLC: A randomized, double-blind, phase III trial. In Proceedings of the 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer, Singapore, 9–12 September 2023. Abstract OA01.03. [Google Scholar]
- Cardnell, R.J.; Feng, Y.; Diao, L.; Fan, Y.-H.; Masrorpour, F.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Mills, G.B.; Minna, J.D.; Heymach, J.V.; et al. Proteomic Markers of DNA Repair and PI3K Pathway Activation Predict Response to the PARP Inhibitor BMN 673 in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6322–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Sica, G.L.; Wagner, L.I.; Wade, J.L.; Srkalovic, G.; Lash, B.W.; Leach, J.W.; Leal, T.B.; Aggarwal, C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Trial of Cisplatin and Etoposide in Combination With Veliparib or Placebo for Extensive-Stage Small-Cell Lung Cancer: ECOG-ACRIN 2511 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Hafez, N.; Soliman, H.H.; Fu, S.; Kato, S.; Lara, P.; Vaishampayan, U.N.; Abdul Razak, A.R.; Cardin, D.B.; Munster, P.N.; et al. Preliminary efficacy data of platinum-pretreated small cell lung cancer (SCLC) cohort of NCI 9881 study: A phase II study of cediranib in combination with olaparib in advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Mortimer, P.G.; Smith, S.; Kim, H.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.-M.; Ahn, J.S.; Ahn, M.-J.; Park, W.-Y.; Lee, S.-H.; et al. The clinical efficacy of olaparib monotherapy or combination with ceralasertib (AZD6738) in relapsed small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 8562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Vilimas, R.; Trindade, C.; Erwin-Cohen, R.; Roper, N.; Xi, L.; Krishnasamy, V.; Levy, E.; Mammen, A.; Nichols, S.; et al. Durvalumab in Combination with Olaparib in Patients with Relapsed SCLC: Results from a Phase II Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1447–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Huang, Z.; Fang, J.; Liu, A.; Xu, Y.; Ma, X.; Shen, Y. P11.03 SHR-1316 in Combination With Fluzoparib in Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Open-Label, Multicenter, Two-Stage, Phase Ⅰb Trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, S1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jia, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, L. Phase II study of durvalumab plus olaparib as maintenance therapy in extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (TRIDENT): Preliminary efficacy and safety results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Karim, N.F.; Miao, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Gay, C.M.; Byers, L.A.; Zhao, Y.; Redman, M.W.; Carrizosa, D.R.; Wang, W.-L.; Petty, W.J.; et al. SWOG S1929: Phase II randomized study of maintenance atezolizumab (A) versus atezolizumab + talazoparib (AT) in patients with SLFN11 positive extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 8504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Lou, J.; Srivastava, M.; Zhao, B.; Feng, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Huang, J. SLFN11 inhibits checkpoint maintenance and homologous recombination repair. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owonikoko, T.K.; Niu, H.; Nackaerts, K.; Csoszi, T.; Ostoros, G.; Mark, Z.; Baik, C.; Joy, A.A.; Chouaid, C.; Jaime, J.C.; et al. Randomized Phase II Study of Paclitaxel plus Alisertib versus Paclitaxel plus Placebo as Second-Line Therapy for SCLC: Primary and Correlative Biomarker Analyses. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorc, V.; Cavina, R.; Novello, S.; Grossi, F.; Lazzari, C.; Capelletto, E.; Genova, C.; Salini, G.; Lambiase, A.; Santoro, A. NGR-hTNF and Doxorubicin as Second-Line Treatment of Patients with Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2018, 23, 1133-e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Chu, Q.S.-C.; Gandhi, L.; Stephenson, J.J.; Govindan, R.; Bradford, D.S.; Bonomi, P.D.; Ellison, D.M.; Eaton, K.D.; Fritsch, H.; et al. An open-label, phase II study of the polo-like kinase-1 (Plk-1) inhibitor, BI 2536, in patients with relapsed small cell lung cancer (SCLC). Lung Cancer 2017, 104, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappori, A.A.; Otterson, G.A.; Dowlati, A.; Traynor, A.M.; Horn, L.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Ross, H.J.; Hann, C.L.; Abu Hejleh, T.; Nieva, J.; et al. A Randomized Phase II Study of Linsitinib (OSI-906) Versus Topotecan in Patients with Relapsed Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Oncologist 2016, 21, 1163–1164e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro, B.A.; Perets, R.; Dowlati, A.; LoRusso, P.; Yonemori, K.; He, L.; Munasinghe, W.; Noorani, B.; Johnson, E.F.; Zugazagoitia, J. Mirzotamab clezutoclax as monotherapy and in combination with taxane therapy in relapsed/refractory solid tumors: Dose expansion results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udagawa, H.; Ikeda, T.; Umemura, S.; Daga, H.; Toyozawa, R.; Harada, D.; Sakakibara-Konishi, J.; Morise, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Phase II study of gedatolisib for small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients (pts) with genetic alterations in PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway based on a large-scale nationwide genomic screening network in Japan (EAGLE-PAT/LC-SCRUM-Japan). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 9064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Shim, J.; Mortimer, P.G.S.; Smith, S.A.; Godin, R.E.; Hollingsworth, S.J.; Kim, H.; Jung, H.A.; Sun, J.; Park, W.-Y.; et al. Biomarker-driven phase 2 umbrella trial study for patients with recurrent small cell lung cancer failing platinum-based chemotherapy. Cancer 2020, 126, 4002–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgensztern, D.; Rose, M.; Waqar, S.N.; Morris, J.; Ma, P.C.; Reid, T.; Brzezniak, C.E.; Zeman, K.G.; Padmanabhan, A.; Hirth, J.; et al. RRx-001 followed by platinum plus etoposide in patients with previously treated small-cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappori, A.; Fidler, M.J.; Salamat, M.A.; Reid, T.R.; Guo, X.; Wang, X.; Abrouk, N.D.; Caroen, S.; Burbano, E.; Quinn, M.F.; et al. An explorary analysis of a COVID-truncated REPLATINUM phase 3 trial in SCLC. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, e20594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Pietanza, M.C.; Bauer, T.M.; Ready, N.; Morgensztern, D.; Glisson, B.S.; Byers, L.A.; Johnson, M.L.; Burris, H.A.; Robert, F.; et al. Rovalpituzumab tesirine, a DLL3-targeted antibody-drug conjugate, in recurrent small-cell lung cancer: A first-in-human, first-in-class, open-label, phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgensztern, D.; Besse, B.; Greillier, L.; Santana-Davila, R.; Ready, N.; Hann, C.L.; Glisson, B.S.; Farago, A.F.; Dowlati, A.; Rudin, C.M.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rovalpituzumab Tesirine in Third-Line and Beyond Patients with DLL3-Expressing, Relapsed/Refractory Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Results From the Phase II TRINITY Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6958–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackhall, F.; Jao, K.; Greillier, L.; Cho, B.C.; Penkov, K.; Reguart, N.; Majem, M.; Nackaerts, K.; Syrigos, K.; Hansen, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rovalpituzumab Tesirine Compared With Topotecan as Second-Line Therapy in DLL3-High SCLC: Results From the Phase 3 TAHOE Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://news.abbvie.com/news/press-releases/abbviediscontinues-rovalpituzumab-tesirine-rova-t-researchand-development-program.htm (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Available online: https://news.abbvie.com/news/phase-3-trialrova-t-as-second-line-therapy-for-advanced-small-celllung-cancer-tahoe-study-halted.htm (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Shvartsur, A.; Bonavida, B. Trop2 and its overexpression in cancers: Regulation and clinical/therapeutic implications. Genes Cancer 2014, 6, 84–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamura, K.; Yokouchi, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Ninomiya, H.; Sakakibara, R.; Subat, S.; Nagano, H.; Nomura, K.; Okumura, S.; Shibutani, T.; et al. Association of tumor TROP2 expression with prognosis varies among lung cancer subtypes. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 28725–28735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.E.; Heist, R.S.; Starodub, A.N.; Camidge, D.R.; Kio, E.A.; Masters, G.A.; Purcell, W.T.; Guarino, M.J.; Misleh, J.; Schneider, C.J.; et al. Therapy of Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) with a Topoisomerase-I–inhibiting Antibody–Drug Conjugate (ADC) Targeting Trop-2, Sacituzumab Govitecan. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5711–5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Messersmith, W.A.; Kio, E.A.; Berlin, J.D.; Vahdat, L.; Masters, G.A.; Moroose, R.; Santin, A.D.; Kalinsky, K.; Picozzi, V.; et al. Sacituzumab govitecan, a Trop-2-directed antibody-drug conjugate, for patients with epithelial cancer: Final safety and efficacy results from the phase I/II IMMU-132-01 basket trial. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowlati, A.; Cervantes, A.; Babu, S.; Hamilton, E.P.; Wong, S.F.; Tazbirkova, A.; Sullivan, I.G.; de Lummen, C.V.M.; Italiano, A.; Patel, J.; et al. 1990MO—Sacituzumab govitecan (SG) as second-line (2L) treatment for extensive stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC): Preliminary results from the phase II TROPiCS-03 basket trial. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S1062–S1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgensztern, D.; Ready, N.E.; Johnson, M.L.; Dowlati, A.; Choudhury, N.J.; Carbone, D.P.; Schaefer, E.S.; Arnold, S.M.; Puri, S.; Piotrowska, Z.; et al. First-in-human study of ABBV-011, a seizure-related homolog protein 6 (SEZ6)–targeting antibody-drug conjugate, in patients with small cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Awad, M.; Koyama, T.; Gutierrez, M.; Falchook, G.S.; Piha-Paul, S.A.; Doi, T.; Satoh, T.; Okamoto, N.; Singh, J.; et al. Ifinatamab deruxtecan (I-DXd; DS-7300) in patients with refractory SCLC: A subgroup analysis of a phase 1/2 study. In Proceedings of the 2023 World Conference on Lung Cancer, Singapore, 9–12 September 2023. Abstr. OA05.05. [Google Scholar]
- Gunnersen, J.M.; Kim, M.H.; Fuller, S.J.; De Silva, M.; Britto, J.M.; Hammond, V.E.; Davies, P.J.; Petrou, S.; Faber, E.S.L.; Sah, P.; et al. Sez-6 Proteins Affect Dendritic Arborization Patterns and Excitability of Cortical Pyramidal Neurons. Neuron 2007, 56, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedemeyer, W.R.; Gavrilyuk, J.; Schammel, A.; Zhao, X.; Sarvaiya, H.; Pysz, M.; Gu, C.; You, M.; Isse, K.; Sullivan, T.; et al. ABBV-011, A Novel, Calicheamicin-Based Antibody–Drug Conjugate, Targets SEZ6 to Eradicate Small Cell Lung Cancer Tumors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2022, 21, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Champiat, S.; Lai, W.V.; Izumi, H.; Govindan, R.; Boyer, M.; Hummel, H.-D.; Borghaei, H.; Johnson, M.L.; Steeghs, N.; et al. Tarlatamab, a First-in-Class DLL3-Targeted Bispecific T-Cell Engager, in Recurrent Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Open-Label, Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2893–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champiat, S.; Boyer, M.J.; Govindan, R.; Paz-Ares, L.G.; Owonikoko, T.K.; Borghaei, H.; Izumi, H.; Steeghs, N.; Blackhall, F.H.; Terbuch, A.; et al. Tarlatamab in small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Safety and efficacy analyzed by baseline brain metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.-J.; Cho, B.C.; Felip, E.; Korantzis, I.; Ohashi, K.; Majem, M.; Juan-Vidal, O.; Handzhiev, S.; Izumi, H.; Lee, J.-S.; et al. Tarlatamab for Patients with Previously Treated Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2063–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermke, M.; Felip, E.; Kuboki, Y.; Morgensztern, D.; Sayehli, C.; Sanmamed, M.F.; Arriola, E.; Oum’Hamed, Z.; Song, E.; Studeny, M.; et al. First-in-human dose-escalation trial of BI 764532, a delta-like ligand 3 (DLL3)/CD3 IgG-like T-cell engager in patients (pts) with DLL3-positive (DLL3+) small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) and neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, N.; Jain, P.; Dowlati, A.; Thompson, J.; Johnson, M.L.; Mamdani, H.; Sanborn, R.E.; Schenk, E.L.; Aggarwal, R.; Sankar, K.; et al. 698P Interim results from a phase I/II study of HPN328, a tri-specific, half-life (T1/2) extended DLL3-targeting T cell engager in patients (pts) with small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and other neuroendocrine neoplasms (NEN). Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, S486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT06223711?recrs=ab&cond=SCLC%2CExtensive+Stage&draw=2&rank=31 (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Barnard, W.G. The nature of the “oat-celled sarcoma” of the mediastinum. J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 1926, 29, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzopardi, J.G. Oat-cell carcinoma of the bronchus. J. Pathol. Bacteriol. 1959, 78, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnofsky, D.A.; Abelmann, W.H.; Craver, L.F.; Burchenal, J.H. The use of the nitrogen mustards in the palliative treatment of carcinoma.With particular reference to bronchogenic carcinoma. Cancer 1948, 1, 634–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, W.L.; Berg, J.W. Oat cell lung cancer. Cancer 1962, 15, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberto, P.; Brunner, K.W.; Martz, G.; Obrecht, J.-P.; Sonntag, R.W. Treatment of bronchogenic carcinoma with simultaneous or sequential combination chemotherapy, including methotrexate, cyclophosphamide, procarbazine and vincristine. Cancer 1976, 38, 2208–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowenbraun, S.; Bartolucci, A.; Smalley, R.V.; Stephen Krauss, M.L.B.; Durant, J.R. The superiority of combination chemotherapy over single agent chemotherapy in small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 1979, 44, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, W.K.; Feld, R.; Osoba, D.; Shepherd, F.A.; Dill, J.; Deboer, G. VP-16 alone and in combination with cisplatin in previously treated patients with small cell lung cancer. Cancer 1984, 53, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, W.K.; Feld, R.; Murray, N.; Willan, A.; Coy, P.; Osoba, D.; Shepherd, F.A.; Clark, D.A.; Levitt, M.; MacDonald, A. Superiority of alternating non-cross-resistant chemotherapy in extensive small cell lung cancer. A multicenter, randomized clinical trial by the National Cancer Institute of Canada. Ann. Intern. Med. 1987, 107, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihde, D.C.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kramer, B.S.; Steinberg, S.M.; Linnoila, R.I.; Gazdar, A.F.; Edison, M.; Phelps, R.M.; Lesar, M.; Phares, J.C. Prospective randomized comparison of high-dose and standard-dose etoposide and cisplatin chemotherapy in patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 1994, 12, 2022–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Nathanson, T.; Rizvi, H.; Creelan, B.C.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Ahuja, A.; Ni, A.; Novik, J.B.; Mangarin, L.M.B.; Abu-Akeel, M.; et al. Genomic Features of Response to Combination Immunotherapy in Patients with Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 843–852.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.C.; Lopez-Martin, J.A.; Kao, S.C.-H.; Miller, W.H.; Ros, W.; Gao, B.; Marabelle, A.; Gottfried, M.; Zer, A.; Delord, J.-P.; et al. Phase 2 study of pembrolizumab in advanced small-cell lung cancer (SCLC): KEYNOTE-158. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiatt, J.B.; Sandborg, H.; Garrison, S.M.; Arnold, H.U.; Liao, S.-Y.; Norton, J.P.; Friesen, T.J.; Wu, F.; Sutherland, K.D.; Rienhoff, H.Y.; et al. Inhibition of LSD1 with Bomedemstat Sensitizes Small Cell Lung Cancer to Immune Checkpoint Blockade and T-Cell Killing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4551–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, B.H.; Gardner, E.E.; Schneeberger, V.E.; Ni, A.; Desmeules, P.; Rekhtman, N.; de Stanchina, E.; Teicher, B.A.; Riaz, N.; Powell, S.N.; et al. PARP Inhibitor Activity Correlates with SLFN11 Expression and Demonstrates Synergy with Temozolomide in Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 523–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubczak, M.; Michlewska, S.; Bryszewska, M.; Aigner, A.; Ionov, M. Nanoparticles for local delivery of siRNA in lung therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 114038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huang, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhi, C.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; He, J.; Lian, H.; Zhou, J.; et al. CAR NK-92 cells targeting DLL3 kill effectively small cell lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 112, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, A.S.; Micinski, A.M.; Kastner, D.W.; Guo, B.; Wait, S.J.; Spainhower, K.B.; Conley, C.C.; Chen, O.S.; Guthrie, M.R.; Soltero, D.; et al. MYC Drives Temporal Evolution of Small Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes by Reprogramming Neuroendocrine Fate. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 60–78.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| IMPOWER-133 | CASPIAN £ | ΚΕΥΝOΤΕ-604 | ECOG-ACRIN EA516 | ASTRUM-005 | CAPSTONE-1 | EXTENTORCH | RATIONALE-312 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase | III | III | III | II | III | III | III | III |
| Place | Global | Global | Global | Global | China + 5 countries * | China | China | China |
| N (pts) | 403 | 537 | 453 | 160 | 585 | 462 | 442 | 457 |
| Drug (ICI) | Atezolizumab | Durvalumab | Pembrolizumab | Nivolumab | Serplulimab | Adebrelimab | Toripalimab | Tislelizumab |
| Class | Anti-PD-L1 | Anti-PD-L1 | anti-PD-1 | Anti-PD-1 | Anti-PD-1 | Anti-PD-L1 | Anti-PD-1 | Anti-PD-1 |
| Princ. Endp. | OS, PFS | OS | OS, PFS | PFS | OS | OS | PFS, OS | OS |
| CT/ICI Cycles (N) § | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4–6 | 4–6 | 4 |
| CT arm Cycles (N) §,% | 4 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4–6 | 4–6 | 4 |
| Platins | Carboplatin | Carboplatin/Cisplatin | Carboplatin/Cisplatin | Carboplatin/Cisplatin | Carboplatin | Carboplatin | Carboplatin/Cisplatin | Carboplatin/Cisplatin |
| M phase | Atezolizuma/Placebo | Durvalumab/control | Pembrolizuma/Placebo | Nivolumab/observation | Serplulimab/Placebo | Adebrelimab/Placebo | Toripalimab/Placebo | Tislelizumab/Placebo |
| PS | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 |
| PCI | Both arms | CT Arm | Both arms | Both arms | No | Both arms | No | No |
| mPFS | ||||||||
| CT/ICI | 5.2 mos | 5.1 mos | 4.5 mos | 5.5 mos | 5.7 mos | 5.9 mos | 5.8 mos | 4.7 mos |
| CT | 4.3 mos | 5.4 mos | 4.3 mos | 4.6 mos | 4.3 mos | 5.7 mos | 5.6 mos | 4.3 mos |
| HR [95% CI] | 0.77 [0.62–0.96] | 0.78 [0.65–0.94] | 0.75 [0.61–0.91] | 0.65 [0.46–0.91] | 0.48 [0.38–0.9] | 0.70 [0.57–0.86] | 0.66 [0.53–0.82] | 0.64 [0.52–0.78] |
| mOS | ||||||||
| CT/ICI | 12.3 mos | 13.0 mos | 10.8 mos | 11.3 mos | 15.4 mos | 15.3 mos | 14.6 mos | 15.5 mos |
| CT | 10.3 mos | 10.3 mos | 9.7 mos | 8.5 mos | 10.9 mos | 12.8 mos | 13.3 mos | 13.5 mos |
| HR [95% CI] | 0.70 [0.54–0.91] | 0.73 [0.59–0.91] | 0.80 [0.64–0.98] | 0.67 [0.46–0.98] | 0.63 [0.49–0.82] | 0.72 [0.58–0.90] | 0.79 [0.64–0.98] | 0.75 [0.61–0.92] |
| FDA | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No | BD | No |
| EMA | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| Other | China | China | China |
| Subtype | Phenotype | George Set (n = 81) | IMpower133 Set (n = 276) | TF Expression | Other Molecular Characteristics | Sensitiviness to Platinum and PARPi | Other Drug Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCLC-A | NE | 36% | 51% | High expression of ASCL1 and a low expression of NEUROD1 | High expression of MYCL, SOX2, TTF-1, BCL2, CHGA, SYP, DLL3 and CEACAM5 | Sensitive or refractory on the basis of SLFN11 expression (sensitive only with high expression of SLFN11) | Sensitive to BCL2 inhibitors and DLL3 agents |
| SCLC-N | NE | 31% | 23% | High expression of NEUROD1 and a low expression of ASCL1 | Lacks of TTF1, high levels of INSM1,HES6, CHGA, SYP, DLL3 and SSTR2 | Refractory to cisplatin and PARPi | Sensitive to AKI |
| SCLC-P | non-NE | 16% | 7% | High expression of POU2F3 and low expression of ASCL1 and NEUROD1 | High expression of REST and c-MYC amplification. High expression of MICA (MCH I) *. Unexpressed DLL3 | Sensitive but in this subgroup it is not linked with the expression of SLFN11, which is modest | Sensitive to PARPi, antimetabolites (anti-folates), and AKI |
| SCLC-I | non-NE | 17% | 18% | Low expression of ASCL1, NEUROD1 and POU2F3 | High levels of mesenchymal markers (VIM and AXL). High expression of genes related to HLAs, interferon-γ activation, and immune checkpoints. High expression of BTK. Unexpressed DLL3 | Refractory to cisplatin and PARPi | Sensitive to BTKi (e.g., ibrutinib), HDACi (e.g., mocetinistat) and ICIs |
| Subsets | Phenotype | TF Expression | Gay’s SCLC Subtype | Immune Composition | Benefit to IO (mOS with A-CP/ET vs. mOS with P-CP/ET) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MNF1 | NE | Uniquely high NEUROD1 expression; high expression of ASLC1. | SCLC-N | T-eff-low/TAM-low | 11.14 mos vs. 9.65 mos (HR 0.58; 95% CI: 0.36–0.95) |
| NMF2 | NE | Highest expression of ASLC1. | SCLC-A | T-eff-low/TAM-high | 10.84 mos vs. 10.02 mos (HR 0.79; 95% CI: 0.47–1.30) |
| NMF3 | NE | High expression of ASLC1, YAP1 was elevated similar to NMF4, NOTCH3 mutations was enriched. | SCLC-I (NE) and SCLC-A | T-eff-high/TAM-low | 16.37 mos vs. 8.63 mos (HR 0.45; 95% CI: 0.22–0.89) |
| NMF4 | non-NE | POU2F3 uniquely expressed, low expression of ASCL1, YAP1 was elevated similar to NMF3, other non-NE drives such as REST and MYC were elevated compared to other NMF subsets. | SCLC-I (non-NE) and SCLC-P | T-eff-high/TAM-high | 9.19 mos vs. 10.11 mos (HR 1.02; 95% CI: 0.55–1.91) |
| Reference | Ph | Setting | Drug | Target | Payload | N. SCLC | ORR | mPFS | mOS | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRINITY Morgensztern et al. [190] | II | ≥3L | Rova-T | DLL3 | PBD | 339 [287 +] * [238 high] % | 12.4% 13.2% 14.3% | 3.5 mos 3.8 mos 3.8 mos | 5.6 mos 5.6 mos 5.7 mos | most common AEs any grade (G≥3 65%): fatigue 38%, photosensitivity reaction 36%, edema 31%. anorexia 30% |
| TAHOE Blackhall et al. [191] | III | 2L | Rova-T vs. topotecan | DLL3 | PBD | 296 148 | 15% 21% | 3 mos 4.3 mos | 6.3 mos 8.3 mos | Rova-T was also more toxic than topotecan |
| MERU Johnson et al. [192] | III | M | Rova-T vs. placebo | DLL3 | PBD | 372 376 | 10% $ 5% $ | 4.7 mos 1.4 mos | 8.5 mos 9.8 mos | AEs G>3 (59%): thrombocytopenia 9%, pleural effusion 4%, photosensitivity 4% |
| NCT01631552 IMMU-132-01 Gray et al. [196] | I | ≥2L | Sacituzumab govitecan | TROP2 | SN-38 | 50 | 14% | 3.7 mos | 7.5 mos | Benefit observed both in CT-sensitive and CT-refractory SCLC |
| IMMU-132-01 Bardia et al. [197] | I | ≥2L | Sacituzumab govitecan | TROP2 | SN-38 | 62 | 17.7% | 3.7 mos | 7.1 mos | Basket trial in all solid tumors |
| TROPiCS03 NCT03964727 Dowlati et al. [198] | II | 2L | Sacituzumab govitecan | TROP2 | SN-38 | 30 | 37% & | NA | NA | Any AEs (G≥3 60%): diarrhea 67% (G3 7%), neutropenia 47% (G3 14%), constipation 43% (G3 0%), fatigue 43% (G3 3%), nausea 43% (G3 0%) |
| NCT03639194 Morgensztern et al. [199] | I | ≥2L | ABBV-011 | SEZ6 | Calicheamicin | 40 # | 25% | 3.5 mos | NA | Any AEs (G≥3 65%): fatigue 48% (G3 10%), nausea 45% (G3 3%), anorexia 38% (G3 0%), platelet count decreased 38% (G3 10%), vomiting 35% (G3 3%) |
| IDeate-Lung01 NCT05280470 Johnson et al. [200] | II | ≥2L | Ifinatamab Deruxtecan | B7-H3 | Dxd | 21 | 52.4% | 5.8 mos | 12.2 mos | Most common AEs (G≥3 36.4%): nausea and diarrhea |
| Trial | Ph | Setting | Drug | Class | Pt N | ORR | mPFS | mOS | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeLLphi301 | RII | ≥3L | Tarlatamab 10 mg vs. 100 mg | BiTE | 134 88 | 40% 32% | 4.9 mos 3.9 mos | 14.3 mos NR | CRS 51; ICANs 8% CRS 61%; ICANs 28% |
| NCT05361395 | Ib | 1L | Tarlatamab + anti-PD-L1 + CT | BiTE | 340 | - | - | - | Principal endpoint: safety Recruiting |
| DeLLphi-305 NCT06211036 | III | M | Durvalumab ± Tarlatamab | BiTE | 550 | - | - | - | Principal endopoint: OS Recruiting |
| DeLLphi-304 NCT05740566 | III | 2L | Tarlatamab vs. lurbinectedin or topotecan or amrubicin | BiTE | 700 | - | - | - | Principal endpoint: OS Recruiting |
| NCT0442908 | I | ≥2L | BI764532 | BiTE | 107 57 SCLC | 25% 39% | NR | NR | Any AEs, G ≥3 27% CRS (59%, G ≥3 (2%), LCD (20% G ≥3 (16%) dysgeusia (20% G ≥3 (0) asthenia (19 G ≥3 (1%) pyrexia (18% G ≥3 (0) |
| DAREONTM-5 NCT05882058 | II | ≥3L | BI764532 | BiTE | 120 * | - | - | - | Primary endpoint: ORR Recruiting |
| DAREONTM-8 NCT06077500 | Ib | 1L | BI764532 + anti-PD-L1 + CT | BiTE | 60 | - | - | - | Principal endpoint: DLTs Recruiting |
| NCT04471727 | I/II | ≥2L | HPN328 | TCE | 44 29 SCLC | - | - | - | Principal endpoint: safety and DLTs Recruiting |
| NCT05507593 | I | ≥2L | DLL3-CAR-NK cells | CAR | 18 | - | - | - | Principal endpoint: DLTs/MTD Recruiting |
| NCT05680922 | I | ≥2L | DLL3 autologous CAR-T-cells | CAR-T | 41 | - | - | - | Principal endpoint: RP2D Recruiting |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trillo Aliaga, P.; Del Signore, E.; Fuorivia, V.; Spitaleri, G.; Asnaghi, R.; Attili, I.; Corvaja, C.; Carnevale Schianca, A.; Passaro, A.; de Marinis, F. The Evolving Scenario of ES-SCLC Management: From Biology to New Cancer Therapeutics. Genes 2024, 15, 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060701
Trillo Aliaga P, Del Signore E, Fuorivia V, Spitaleri G, Asnaghi R, Attili I, Corvaja C, Carnevale Schianca A, Passaro A, de Marinis F. The Evolving Scenario of ES-SCLC Management: From Biology to New Cancer Therapeutics. Genes. 2024; 15(6):701. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060701
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrillo Aliaga, Pamela, Ester Del Signore, Valeria Fuorivia, Gianluca Spitaleri, Riccardo Asnaghi, Ilaria Attili, Carla Corvaja, Ambra Carnevale Schianca, Antonio Passaro, and Filippo de Marinis. 2024. "The Evolving Scenario of ES-SCLC Management: From Biology to New Cancer Therapeutics" Genes 15, no. 6: 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060701
APA StyleTrillo Aliaga, P., Del Signore, E., Fuorivia, V., Spitaleri, G., Asnaghi, R., Attili, I., Corvaja, C., Carnevale Schianca, A., Passaro, A., & de Marinis, F. (2024). The Evolving Scenario of ES-SCLC Management: From Biology to New Cancer Therapeutics. Genes, 15(6), 701. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15060701






