Genome-Wide and Expression Pattern Analysis of the HIT4 Gene Family Uncovers the Involvement of GHHIT4_4 in Response to Verticillium Wilt in Gossypium hirsutum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Discovery of Members of the Cotton HIT4 Gene Family
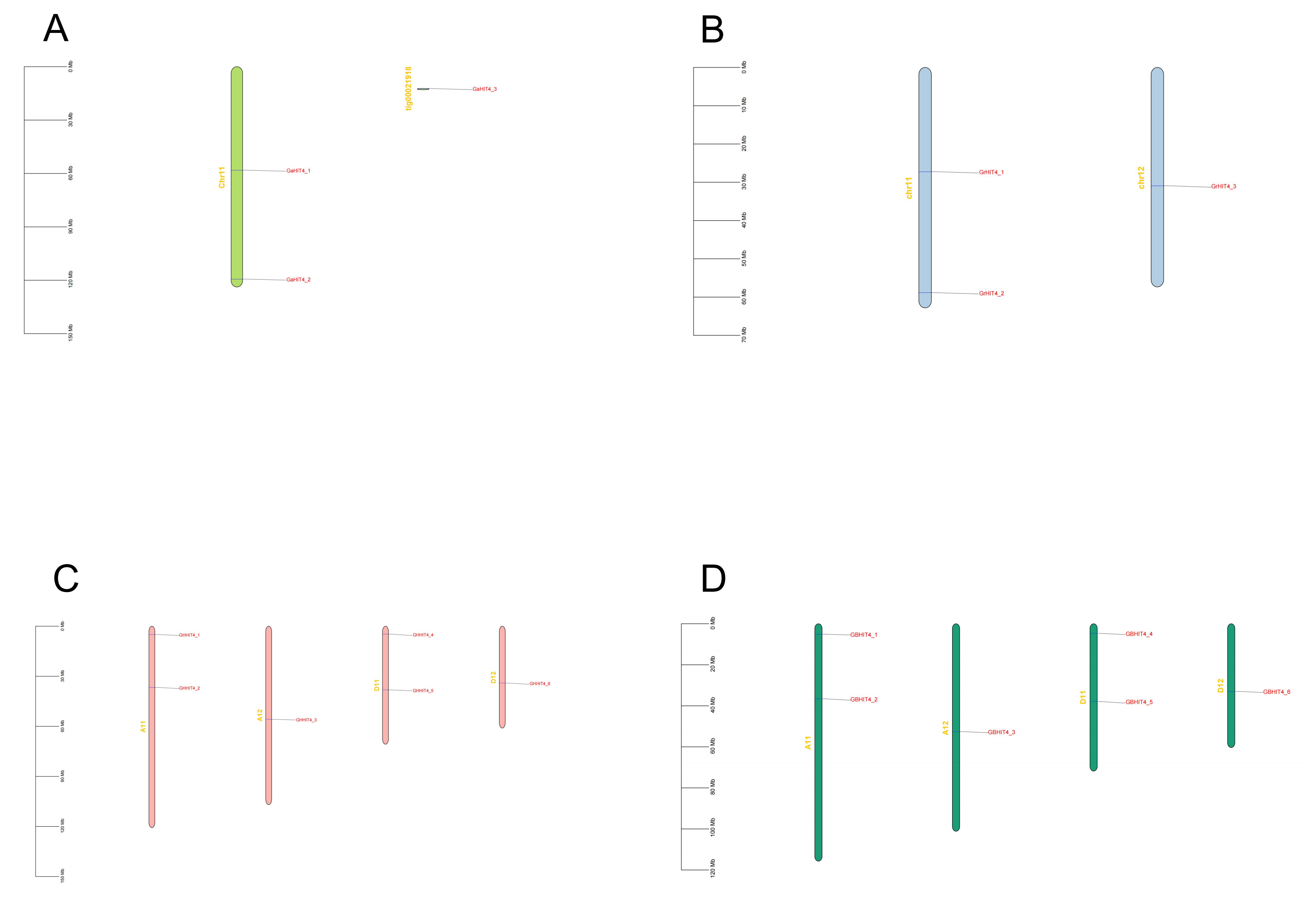
2.2. Determining the Chromosomal Positions and Assessing Gene Duplication Events in the HIT4 Gene Family
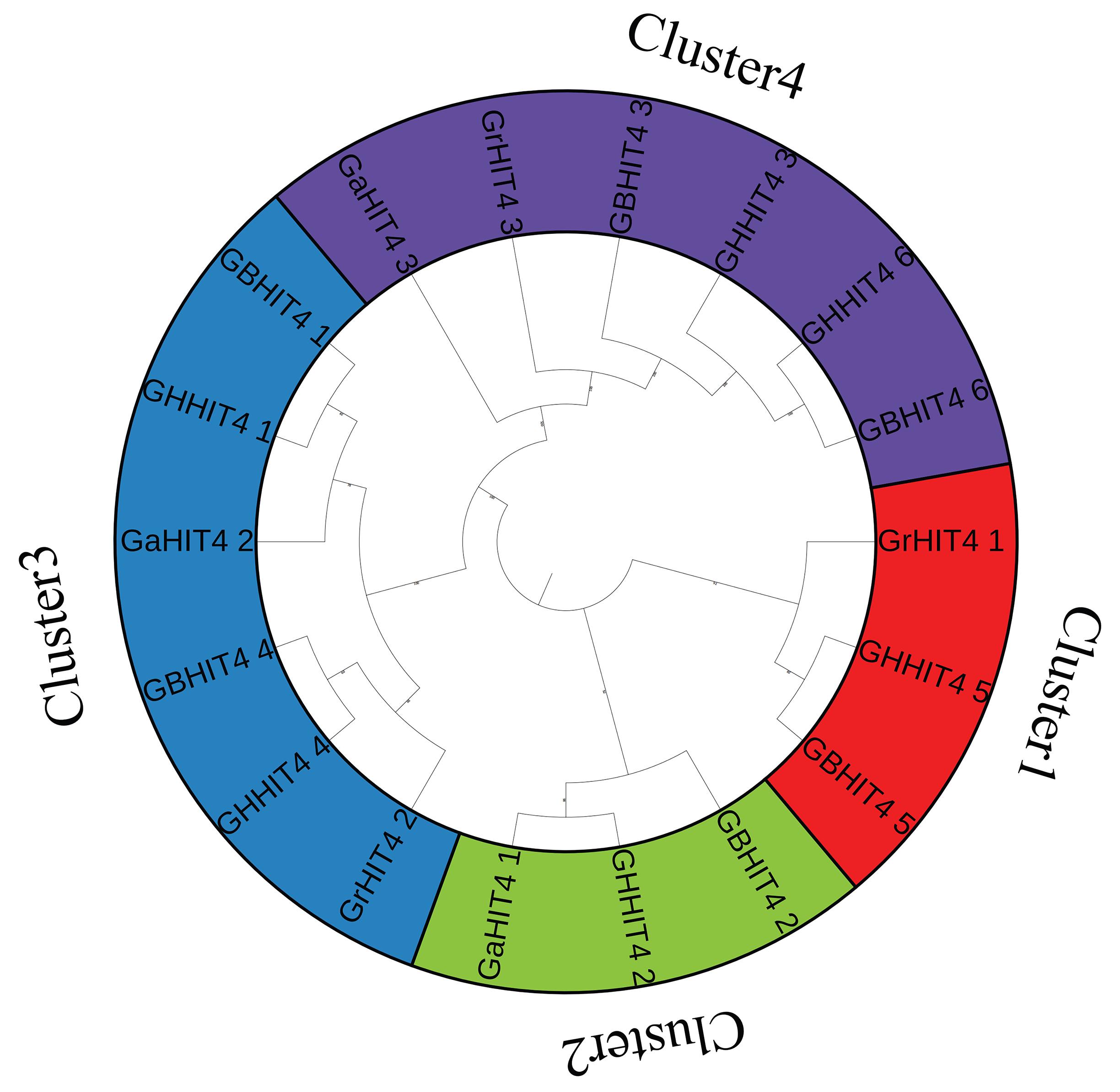
2.3. Development of a Phylogenetic Tree for HIT4 Protein Family Members
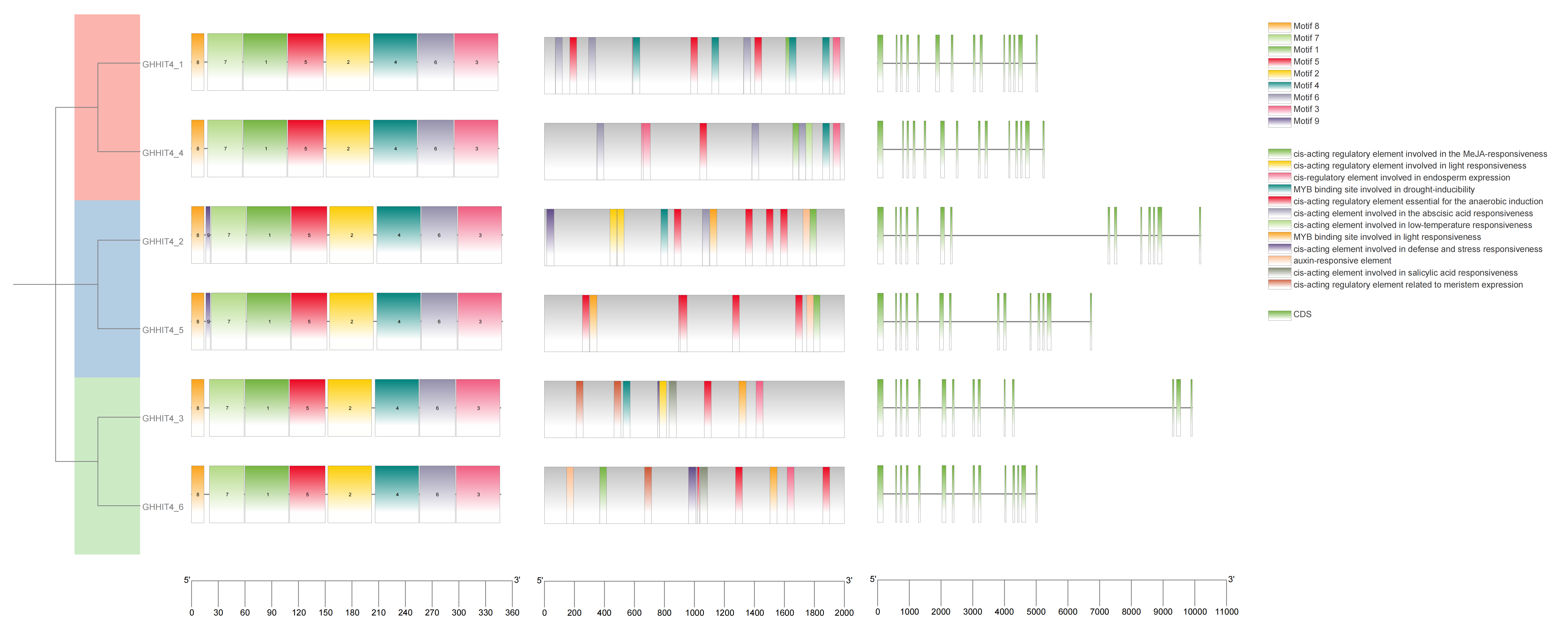
2.4. Exploration of the Gene Architecture and Conserved Protein Motifs within the HIT4 Gene Family
2.5. Investigation of the Expression Patterns and Cis-Elements in HIT4 Family Genes
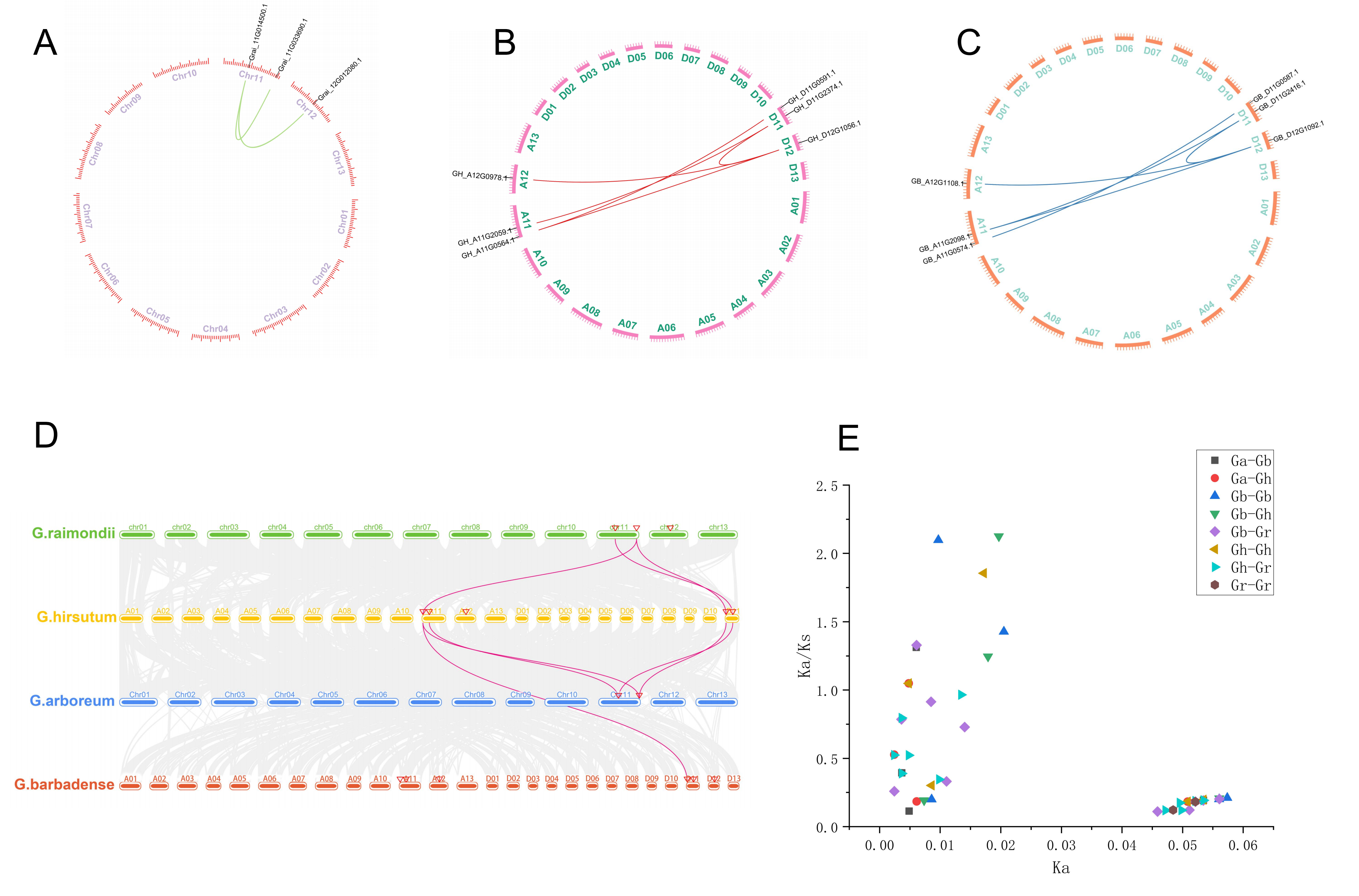
2.6. Collinearity and Selective Pressure Calculation Analysis of HIT4 Family Genes
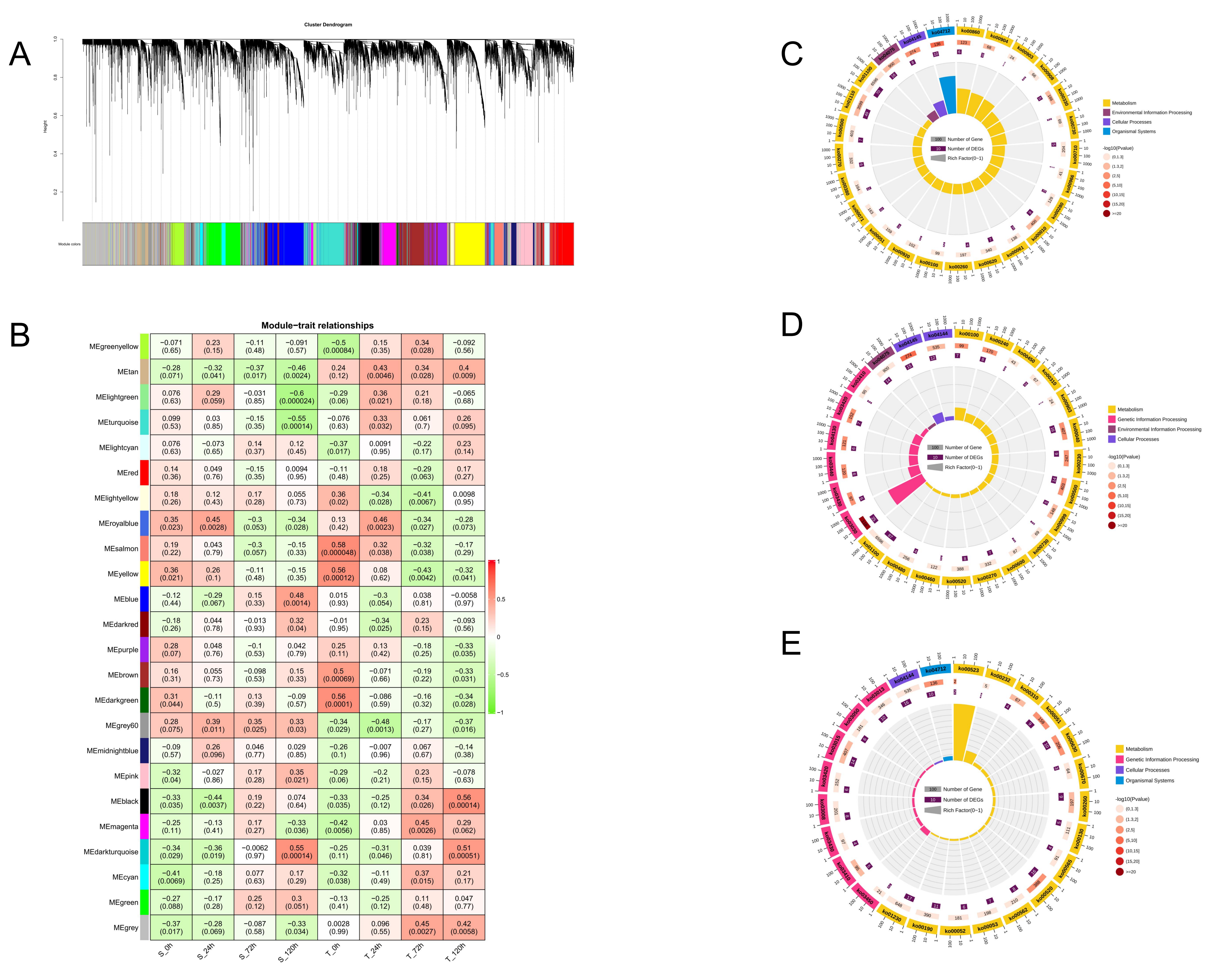
2.7. Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis
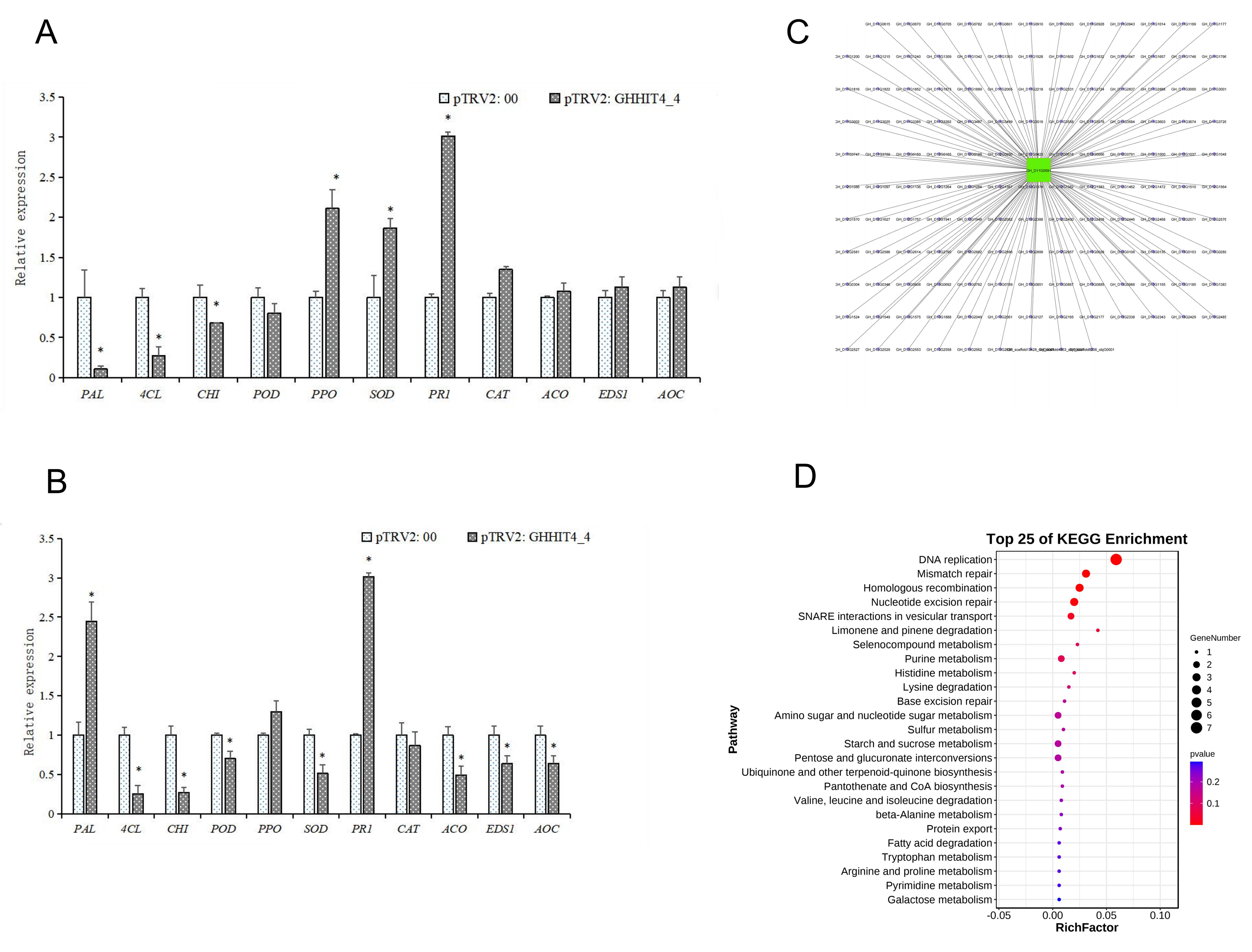
2.8. KEGG Enrichment Analysis and Interaction Network Construction
2.9. Silencing and Heterologous Overexpression of Gene GHHIT4_4
2.10. qRT-PCR Analysis
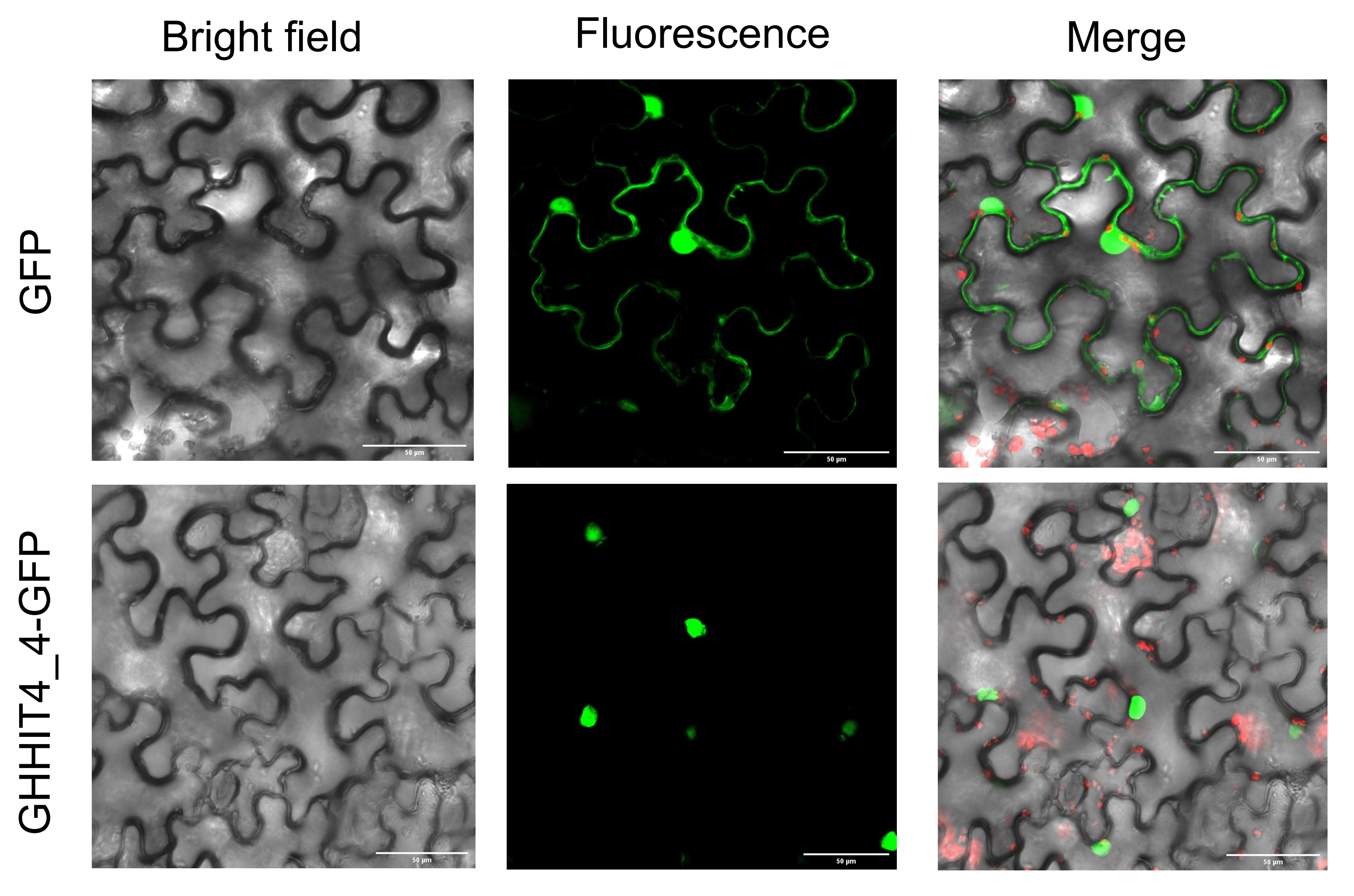
2.11. Subcellular Localization of GHHIT4_4
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Identification of HIT4 Gene
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of HIT4 Genes
3.3. Chromosomal Position of HIT4 in Four Cotton Species
3.4. Examination of Gene Architecture, Protein Motifs, and Cis-Regulatory Elements
3.5. Replication and Collinearity Analysis of the HIT4
3.6. Calculation of Selection Pressure
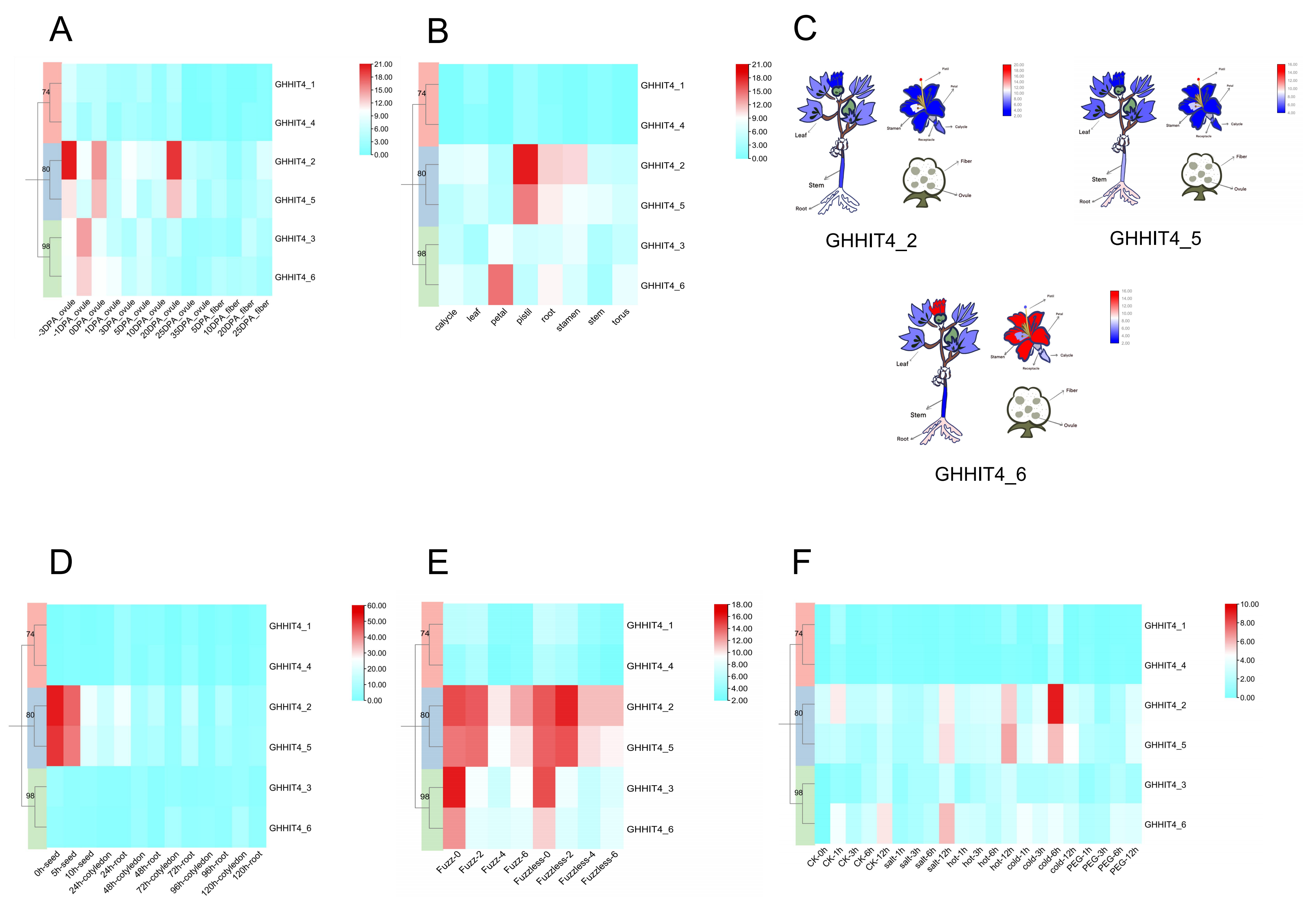
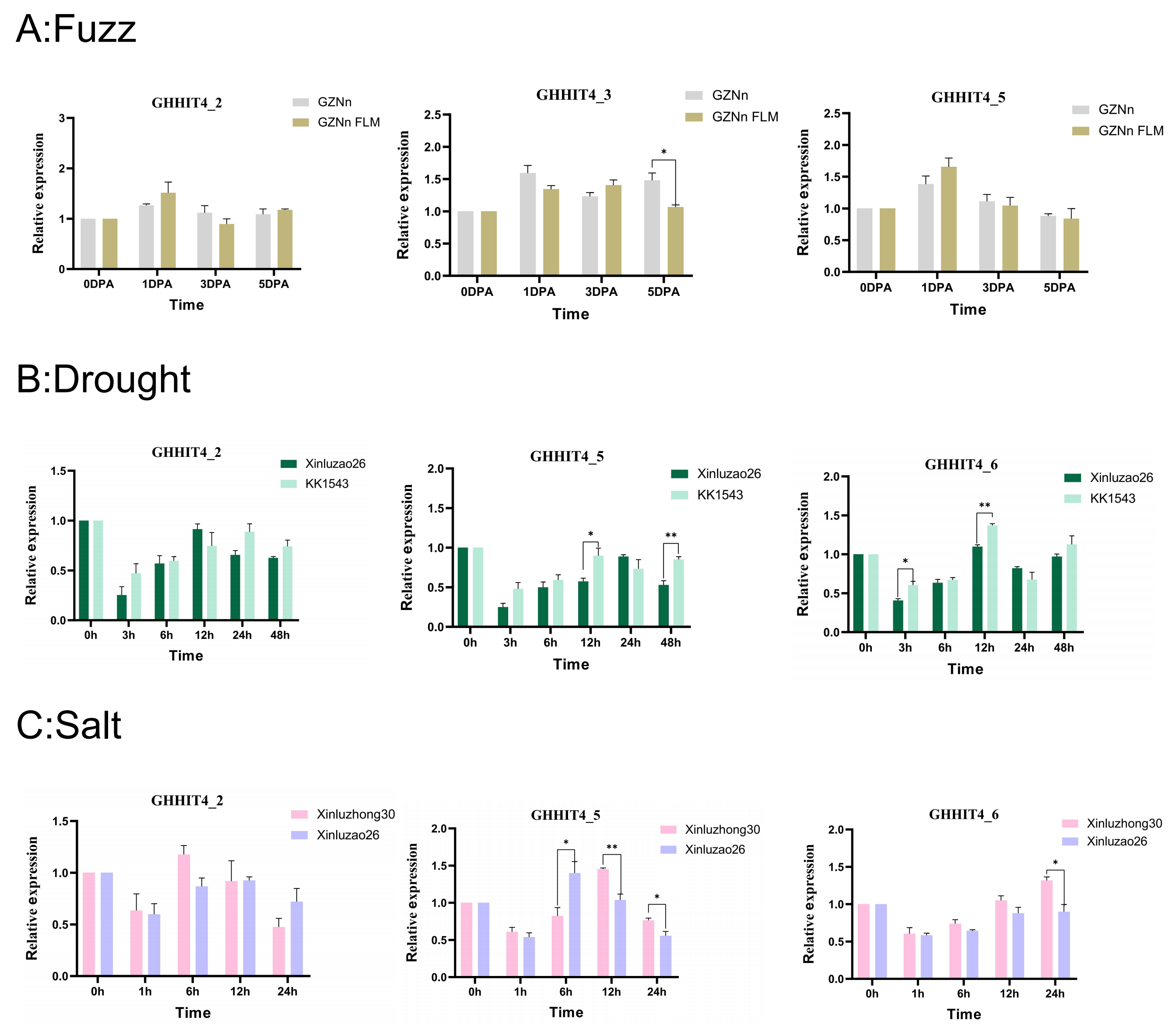
3.7. Expression Patterns of HIT4 Genes in G. hirsutum
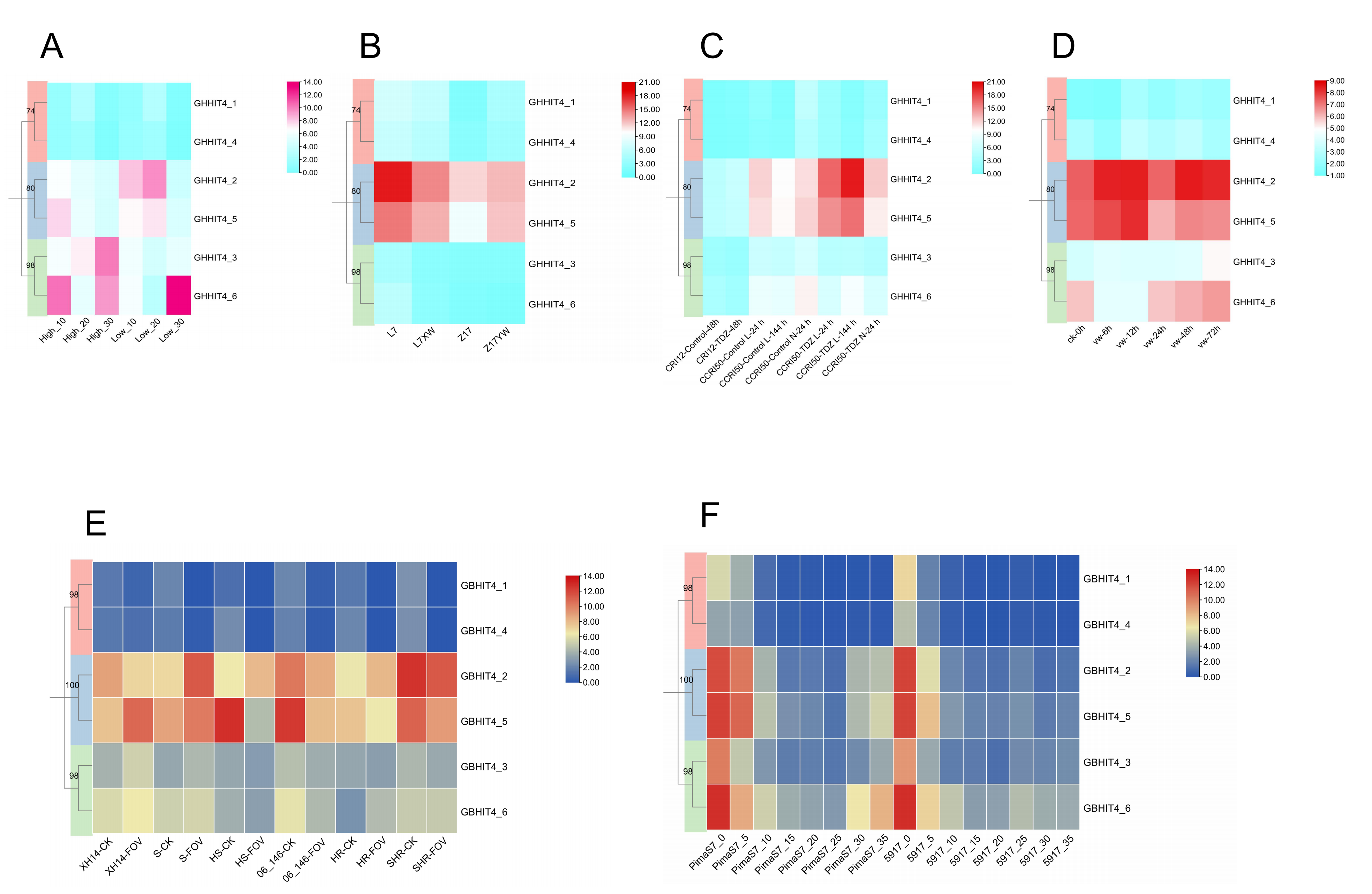
3.8. Expression Patterns of HIT4 Genes in G. barbadense
3.9. Transcription Analysis HIT4 Members in G. hirsutum
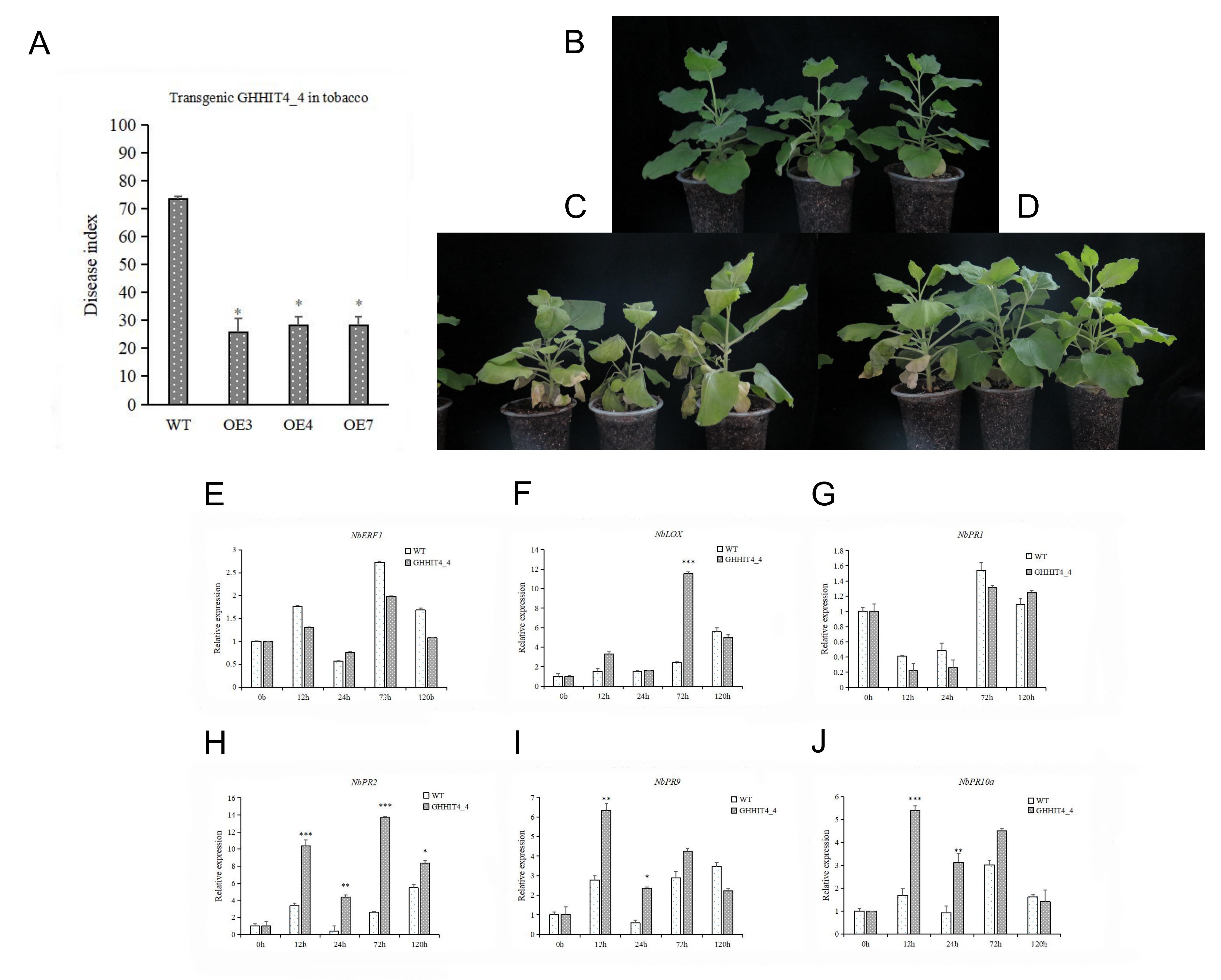
3.10. Overexpression of GHHIT4_4 Enhanced Verticillium Wilt Resistance in Tobacco
3.11. VIGS Validation of GHHIT4_4 in Cotton
3.12. Subcellular Localization Analysis
3.13. qRT-PCR Analysis of HIT4 Gene in Different Upland Cotton Materials
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Members of the HIT4 Family
4.2. Investigation of Expression Profiles of Members of the HIT4 Gene Family
4.3. Functional Verification of GHHIT4_4 Gene in Upland Cotton
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luger, K.; Mäder, A.; Richmond, R.; Sargent, D.; Richmond, T. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8 A resolution. Nature 1997, 389, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Workman, J.; Kingston, R. Alteration of nucleosome structure as a mechanism of transcriptional regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 545–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapier, C.; Cairns, B. The biology of chromatin remodeling complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 273–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narlikar, G.; Sundaramoorthy, R.; Owen-Hughes, T. Mechanisms and functions of ATP-dependent chromatin-remodeling enzymes. Cell 2013, 154, 490–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentner, G.; Henikoff, S. Regulation of nucleosome dynamics by histone modifications. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, D.; Crabtree, G. ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling: Genetics, genomics and mechanisms. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 396–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knizewski, L.; Ginalski, K.; Jerzmanowski, A. Snf2 proteins in plants: Gene silencing and beyond. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, S.; Yang, P.; Yang, J.; Yang, S.; Wu, K. Identification and Expression Analysis of Snf2 Family Proteins in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2019, 2019, 5080935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Mishina, K.; Zhu, H.; Kikuchi, S.; Sassa, H.; Oono, Y.; Komatsuda, T. Genome-Wide Analysis of Snf2 Gene Family Reveals Potential Role in Regulation of Spike Development in Barley. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, N.; Wang, X.; Yi, Q.; Zhu, D.; Lai, Y.; Zhao, Y. Analysis of rice Snf2 family proteins and their potential roles in epigenetic regulation. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 70, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, J.; Han, J. Chromatin remodeling factors regulate environmental stress responses in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 438–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; He, X. Chromatin-remodeling complexes: Conserved and plant-specific subunits in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Wu, M.; Cui, S.; Wagner, D. Roles and activities of chromatin remodeling ATPases in plants. Plant J. 2015, 83, 62–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, C.; Wagner, D. Unwinding chromatin for development and growth: A few genes at a time. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Hsu, Y.; Wu, S. Arabidopsis HIT4, a regulator involved in heat-triggered reorganization of chromatin and release of transcriptional gene silencing, relocates from chromocenters to the nucleolus in response to heat stress. New Phytol. 2015, 205, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Chang, W.; Yeh, C.; Ke, Y.; Lu, C.; Wu, S. Arabidopsis HIT4 encodes a novel chromocentre-localized protein involved in the heat reactivation of transcriptionally silent loci and is essential for heat tolerance in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 1689–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Fang, L.; Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Saski, C.; Scheffler, B.; Stelly, D.; et al. Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Ye, W.; Wang, J.; Song, G.; Yue, Z.; Cong, L.; Shang, H.; Zhu, S.; et al. The draft genome of a diploid cotton Gossypium raimondii. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Huang, G.; He, S.; Yang, Z.; Sun, G.; Ma, X.; Li, N.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Liu, M.; et al. Resequencing of 243 diploid cotton accessions based on an updated A genome identifies the genetic basis of key agronomic traits. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Tu, L.; Yuan, D.; Zhu, D.; Shen, C.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Pei, L.; Wang, P.; Zhao, G.; et al. Reference genome sequences of two cultivated allotetraploid cottons, Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Yang, X.; Qiu, D. Verticillium dahliae PevD1, an Alt a 1-like protein, targets cotton PR5-like protein and promotes fungal infection. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Z.; Cui, Y.; Ke, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, G.; et al. A large-scale genomic association analysis identifies a fragment in Dt11 chromosome conferring cotton Verticillium wilt resistance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2126–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, P.; Qu, Y.; Sun, G.; Chen, Q. Integrative transcriptomic and gene co-expression network analysis of host responses upon Verticillium dahliae infection in Gossypium hirsutum. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, T.; Liang, C.; Meng, Z.; Sun, G.; Meng, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhang, R. CottonFGD: An integrated functional genomics database for cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, M.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.; Williams, K.; Appel, R.; Hochstrasser, D. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Page, J. Optimized cDNA libraries for virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) using tobacco rattle virus. Plant Methods 2008, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradin, E.; Zhang, Z.; Juarez, A.; Castroverde, C.; Nazar, R.; Robb, J.; Thomma, B. Genetic dissection of Verticillium wilt resistance mediated by tomato Ve1. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 150, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 1985, 227, 1229–1231. [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparkes, I.; Runions, J.; Kearns, A.; Hawes, C. Rapid, transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2019–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Chen, J.; Fang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, W.; Niu, Y.; Ju, L.; Deng, J.; Zhao, T.; Lian, J.; et al. Gossypium barbadense and Gossypium hirsutum genomes provide insights into the origin and evolution of allotetraploid cotton. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendel, J.F.; Cronn, R. Polyploidy and the evolutionary history of cotton. Biol. Adv. Agron. 2003, 78, 139. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Stiller, W.; Moncuquet, P.; Gordon, S.; Yuan, Y.; Barnes, S.; Wilson, L. Genetic mapping and transcriptomic characterization of a new fuzzless-tufted cottonseed mutant. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2021, 11, jkaa042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Le, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, X.; Lin, Z. A global survey of the gene network and key genes for oil accumulation in cultivated tetraploid cottons. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1170–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Liu, S.; Zuo, D.; Wang, Q.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Yu, J.; Song, G. Identification of MYB gene family and functional analysis of GhMYB4 in cotton (Gossypium spp.). Mol. Genet. Genom. 2023, 298, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Gui, H.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Q.; Sikder, R.; Yang, G.; Song, M. Chemical Defoliant Promotes Leaf Abscission by Altering ROS Metabolism and Photosynthetic Efficiency in Gossypium hirsutum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Chen, D.; Zhan, L.; Zeng, K.; Gu, A.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, W.; et al. The susceptibility of sea-island cotton recombinant inbred lines to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vasinfectum infection is characterized by altered expression of long noncoding RNAs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2894. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, K.; Cai, Y.; Long, Y.; Zhao, J.; Guo, Y.; Sun, F.; Qu, Y. Analysis of transcriptome data and quantitative trait loci enables the identification of candidate genes responsible for fiber strength in Gossypium barbadense. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2022, 12, jkac167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, C.; Wang, L.; Su, X.; Huang, J.; Cheng, H.; Guo, H. Repression of GhTUBB1 Reduces Plant Height in Gossypium hirsutum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Pu, Y.; Qu, Y.; Sun, G. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis Unveil the Involvement of the Cold Shock Protein (CSP) Gene Family in Cotton Hypothermia Stress. Plants 2024, 13, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, C.; Pan, Z.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Hou, X.; Liu, J.; Nie, X.; Wu, Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Analysis of the WNK Kinase Gene Family in Upland Cotton. Plants 2023, 12, 4036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Shi, Y.; Xiao, X.; Song, J.; Li, P.; Gong, J.; Zhang, H.; Gong, W.; Liu, A.; Peng, R.; et al. Genome-wide characterization of trichome birefringence-like genes provides insights into fiber yield improvement. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1127760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Sun, F.; Wang, P.; Yusuyin, M.; Kuerban, W.; Lai, C.; Li, C.; Ma, J.; Xiao, F. Genome-Wide Identification and Preliminary Functional Analysis of BAM (β-Amylase) Gene Family in Upland Cotton. Genes 2023, 14, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Li, L.; Han, S.; Jia, M.; Jiang, J. Activation of Gossypium hirsutum ACS6 Facilitates Fiber Development by Improving Sucrose Metabolism and Transport. Plants 2023, 12, 3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, Y.; Li, P.; Lu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Hu, N.; Wan, S.; Zhang, B.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of RF2 Gene Family and the Critical Role of GhRF2-32 in Response to Drought Stress in Cotton. Plants 2023, 12, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Wu, H.; Qanmber, G.; Ali, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yu, D.; Wang, Q.; Xu, A.; Yang, Z. Genome-Wide Study of the GATL Gene Family in Gossypium hirsutum L. Reveals that GhGATL Genes Act on Pectin Synthesis to Regulate Plant Growth and Fiber Elongation. Genes 2020, 11, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Li, M.; Ju, J.; Hai, H.; Wei, W.; Ling, P.; Li, D.; Su, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Genome-Wide Identification of the GhANN Gene Family and Functional Validation of GhANN11 and GhANN4 under Abiotic Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, X.; Ma, D.; Liu, C. Identification and Evolutionary Analysis of Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) WOX Family Genes and Their Potential Function in Somatic Embryogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchy, N.; Lehti-Shiu, M.; Shiu, S. Evolution of Gene Duplication in Plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 171, 2294–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Ju, J.; Zhang, X.; Ling, P.; Luo, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, W.; Su, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. GhBRX.1, GhBRX.2, and GhBRX4.3 improve resistance to salt and cold stress in upland cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1353365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, A.; Lahoucine, A.; Parvathi, K.; Liu, C.; Srinivasa, R.; Wang, L. The phenylpropanoid pathway and plant defence-a genomics perspective. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2002, 3, 371–390. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yeh, C.; Sayler, R.; Lee, Y. Arabidopsis HIT1, a putative homolog of yeast tethering protein Vps53p, is required for pollen tube elongation. Bot. Stud. 2008, 49, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, C.; Gu, T.; Ma, R.; Yao, W.; Huang, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhao, G. Biochemical characterization of a GH19 chitinase from Streptomyces alfalfae and its applications in crystalline chitin conversion and biocontrol. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 167, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, N.; Tewari, R.; Hoondal, G. Biotechnological aspects of chitinolytic enzymes: A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Jiao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Lv, N.; Sun, G. Genome-Wide and Expression Pattern Analysis of the HIT4 Gene Family Uncovers the Involvement of GHHIT4_4 in Response to Verticillium Wilt in Gossypium hirsutum. Genes 2024, 15, 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030348
Zhang G, Jiao Y, Zhao Z, Chen Q, Wang Z, Zhu J, Lv N, Sun G. Genome-Wide and Expression Pattern Analysis of the HIT4 Gene Family Uncovers the Involvement of GHHIT4_4 in Response to Verticillium Wilt in Gossypium hirsutum. Genes. 2024; 15(3):348. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030348
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guoli, Yang Jiao, Zengqiang Zhao, Quanjia Chen, Zhijun Wang, Jincheng Zhu, Ning Lv, and Guoqing Sun. 2024. "Genome-Wide and Expression Pattern Analysis of the HIT4 Gene Family Uncovers the Involvement of GHHIT4_4 in Response to Verticillium Wilt in Gossypium hirsutum" Genes 15, no. 3: 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030348
APA StyleZhang, G., Jiao, Y., Zhao, Z., Chen, Q., Wang, Z., Zhu, J., Lv, N., & Sun, G. (2024). Genome-Wide and Expression Pattern Analysis of the HIT4 Gene Family Uncovers the Involvement of GHHIT4_4 in Response to Verticillium Wilt in Gossypium hirsutum. Genes, 15(3), 348. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15030348






