Abstract
Background: Astilbe, consisting of about 18 species, is distributed throughout East Asia and Northeastern America, and most Astilbe species are widely cultivated as ornamental plants. A total of four species of Astilbe have been confirmed to be distributed throughout Korea, two of which are endemic to Korea. Methods: In this study, we sequenced and assembled the complete chloroplast genomes of two endemic Korean plants using Illumina sequencing technology, identified simple sequence repeats (SSRs) and repetitive sequences, and compared them with three previously reported chloroplast genomes. Results: The chloroplast genomes of the two species were 156,968 and 57,142 bp in length and had a four-part circular structure. They consisted of a large single-copy region of 87,223 and 87,272 bp and a small single-copy region of 18,167 and 18,138 bp, separated by a pair of inverted repeats (IRa and IRb, 25,789 and 25,866 bp). The genomes contained 130 genes, 49 SSRs, and 49 long repetitive sequences. Comparative analysis with the chloroplast genomes of five Astilbe species indicated that A. uljinensis was closely related to A. chinensis and A. taquetii to A. koreana. Conclusions: This study provides valuable references for the identification of two endemic Korean Astilbe species and contributes to a deeper understanding of the phylogeny and evolution of the genus Astilbe.
1. Introduction
Saxifragaceae, a member of Saxifragales, comprises dicotyledonous plants including approximately 33 genera and 640 species. These plants are distributed globally, with the primary concentrations in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere. This family encompasses a variety of growth forms, including herbs, shrubs, small trees, and occasionally vines [1]. Astilbe Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don, comprising approximately 18 species, is distributed across East Asia and Northeastern America, with its range extending into Southeast Asia [2,3]. This genus is characterized by three-lobed compound leaves, large panicles, and hairy leaflets along the veins. Most Astilbe species are widely cultivated as ornamental plants [3,4]. The classification of Korean Astilbe taxa was challenging because of repeated changes and the misapplication of scientific names. However, morphological and molecular studies clarified this taxonomy and identified three species of Astilbe in Korea [5,6]. Additionally, the discovery of a new species means that four Astilbe species are now recognized as being distributed throughout the region [7]. Among them, A. taquetii (H. Lév.) Koidz. and A. uljinensis B. U. Oh and H. J. Choi are endemic to Korea, with distributions limited exclusively to Korea [8].
The typical chloroplast (cp) genome of an angiosperm is a circular DNA molecule usually 120–170 kb in length. It typically encodes 101–118 genes, including 66–82 protein-coding genes, 4 rRNA genes, and 29–32 tRNA genes [9]. The cp genome is generally composed of a tetrameric structure, with a large single-copy (LSC) region and a small single-copy (SSC) region connected by pairs of inverted repeat sequences (IRa and IRb). Gene content, sequences, and organization are conserved within the chloroplast genome [10,11]. However, during the evolution of plastid genomes in specific lineages, significant structural changes have been found, including changes in the IR region (expansion or contraction), large-scale inversions, and gene losses. For example, structures lacking a single inverted repeat region have been identified in conifers (Cupressaceae [12], Taxaceae [13]), and Fabaceae [14], whereas Pinaceae species were identified with IR regions reduced to less than 1 kb [15,16]. Additionally, the SSC region has undergone a significant reduction due to IR expansion in Ericaceae [17,18,19,20] and Papaveraceae [21,22]. Pseudogenization of the infA gene is commonly observed in both monocots and dicots [23,24], whereas pseudogenization of the accD gene frequently occurs in Poales [25], Passifloraceae [26], and Primulaceae [27,28]. Furthermore, the study of chloroplast genome rearrangements not only enhances our understanding of genomic evolutionary patterns [22,29,30] but also provides valuable markers for subgenus identification [31]. Comprehensive analysis of complete cp genomes offers critical insights into novel evolutionary patterns.
In this study, we report on the complete chloroplast genomes of two previously unreported endemic Korean Astilbe species. We integrated these data with the three complete cp genomes of Astilbe available from the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) to conduct comparative genomic and phylogenomic analyses. The primary goals of this study were as follows: (1) to characterize and investigate the structure of and variation in the complete chloroplast genomes in Astilbe, (2) to identify variations in long repeats, single sequence repeats (SSRs), and codon usage patterns within these chloroplast genomes, and (3) to elucidate the molecular evolution of Astilbe chloroplast genomes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Collection, DNA Extraction, and Chloroplast Genome Sequencing
Young, fresh leaves of both plants (A. taquetii and A. uljinensis) were collected from Jeju Special Self-governing Province (N: 33°21′41.43″ E: 126°31′3.31″) and Buk-myeon, Uljin-gun, Gyeongsangbuk-do (N: 37°26′37.7″ E: 129°01′49.4″), respectively. Plant DNA was extracted using the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen Inc., Valencia, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. DNA quantification was performed using NanoDrop 2000 (Thermo Fisher Inc., Waltham, MA, USA), and the amount was confirmed using 1% agarose gel. Voucher specimens of the two Astilbe accessions were deposited in the National Arboretum of Korea (Table 1). Illumina paired-end libraries were constructed and sequenced on the MiSeq platform (Macrogen Inc., Seoul, South Korea). Raw data were filtered using Fastp v. 0.23.4 with default parameters [32].

Table 1.
Data information for two Astilbe chloroplast genomes.
2.2. Chloroplast Genome Assembly and Annotation
Chloroplast DNA data were drafted using GetOrganelle v.1.7.7.1 [33]. The two chloroplast genomes were assembled and verified using Geneious Prime v.2024.0.7 [34] and annotated using GeSeq v.2.03 [35]. Unannotated or incorrectly annotated sections were manually edited. tRNA sequences were verified using tRNAscan-SE 1.21 [36]. The genome map was drawn using OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW v.1.1.1; Greiner et al. [37]).
2.3. Comparison Between Genomes
We aligned the chloroplast genomes using MAFFT v.1.5.0 [38]. The complete chloroplast genomes of five Astilbe species were compared in mVISTA [39], using A. rivularis Buchanan-Hamilton ex D. Don as a reference. We visualized and compared chloroplast genome junctions using IRplus [40].
2.4. Identification of Divergent Hotspots
To identify highly variable regions among the five Astilbe chloroplast genomes, a DNA polymorphism analysis was performed using DNA Sequence Polymorphism (DnaSP) v6 [41]. Chloroplast genome sequences were aligned using MAFFT implemented in Geneious Prime [34]. The alignment was set to a window length of 800 bp and a step size of 200 bp, respectively.
2.5. Codon Usage Bias and Ka/Ks Analysis
Relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) was computed from the protein-coding gene sequences of the five Astilbe cp genomes. RSCU and codon frequency analyses were performed using DnaSP. A heat map of the RSCU was generated using TBtools-II [42]. To determine the Ka/Ks ratio, nonsynonymous (Ka) and synonymous (Ks) mutations were determined in DnaSP using A. rivulasris as a reference.
2.6. Simple Sequence Repeats (SSRs) and Long-Repeat Sequence Analysis
SSRs in the five Astilbe cp genomes were detected using Krait version 1.5.1 [43] with the following settings: minimum number of mononucleotide repeats: 10; dinucleotide repeats: 6; tri- and tetranucleotide repeats: 5; and penta- and hexanucleotide repeats: 4. REPuter [44] was used to analyze four repeat types (forward, reverse, palindromic, and complementary) within the cp genome with a Hamming distance of 3.
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
Complete chloroplast genome sequences from forty-two Saxifragales and two Cornales (Hydrangeaceae; Deutzia glabrata Kom. and Philadelphus calvescens (Rehder) S. M. Hwang) were downloaded from the NCBI database and used for maximum likelihood (ML) and MrBayes phylogenetic analyses (Supplementary Materials, Table S1). A total of 79 genes from 44 species were aligned using MAFFT (in PhyloSuite v.1.2.2) [45], and ModelFinder (part of IQ-TREE v.1.6.8) was used to determine the optimal alternative model (in PhyloSuite) [46]. Respectively, phylogenetic analyses were performed using IQ trees (ML analysis, [47]) and MrBayes v.3.2.6 (BI analysis) [48].
3. Results
3.1. General Features of the Chloroplast Genomes
In the two endemic Korean Astilbe species, A. taquetii and A. uljinensis, the chloroplast genomes were 156,968 bp and 157,142 bp long, respectively, with typical quadripartite structures. In this structure, the LSC region (87,071 bp and 86,406 bp, respectively) and the SSC region (18,167 bp and 18,145 bp, respectively) were separated into two IRs (25,865 bp and 26,428 bp, respectively; Figure 1 and Table 1). The chloroplasts of A. chinensis were the largest among all the Astilbe plastomes. The cp genomes of the five Astilbe species contained 85 CDSs. The three chloroplast genomes had identical rRNA and tRNA gene contents (8 rRNA and 37 tRNA genes; Table 2). The seventeen genes located in the IR region included six protein-coding (rpl2, rpl23, rps7, rps12, ndhB, and ycf2) and four ribosomal RNA (rrn4.5, rrn5, rrn16, and rrn23) genes. Seven tRNA (trnA-UGC, trnI-CAU, trnI-GAU, trnL-CAA, trnN-GUU, trnR-ACG, and trnV-GAC) and nine protein-coding (atpF, ndhA, ndhB, petB, petD, rpl16, rpoC1, rps12, and rps16) genes each contained one intron, and two protein-coding genes (clpP1 and pafI) contained two introns (Table 2). rps12 was identified as a trans-splice gene consisting of three exons: exon 1 is located in the LSC region, and exons 2 and 3 are located in the IR region.
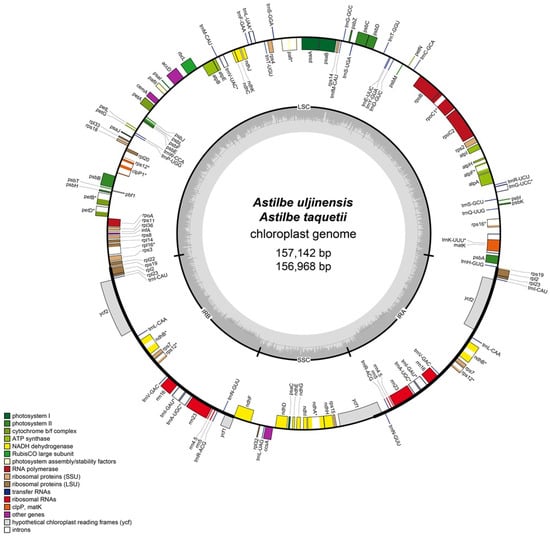
Figure 1.
Chloroplast genome map of A. uljinensis and A. taquetii. The different colors represent genes in each group. Genes that are transcribed counterclockwise are placed on the outside, and genes that are transcribed clockwise are placed on the inside, depending on the direction of gene transcription. * : Indicates genes that contain introns.

Table 2.
Chloroplast genome gene content and functional classification in A. taquetii and A. uljinensis.
3.2. Comparison of Chloroplast Genomes of the Five Astilbe Species
We compared the chloroplast genome structures and gene sequences of the five Astilbe species in mVISTA and found that they were nearly identical (Figure 2). The conservation was higher in the coding regions than in the noncoding regions and in the IR regions than in the LSC and SSC regions. The overall identity of the chloroplast genomes of the five Astilbe species was confirmed at all junctions: LSC/IRb (JLB), IRb/SSC (JSB), SSC/IRa (JSA), and IRa/LSC (JLA). The JLB region was identical in all the species (Figure 3). However, in A. chinensis, ndhF extended by 20 bp from the JSB region to the IR; in A. rivularis, it extended 11 bp away from the JSB region; and in the other three species, it extended 40 bp away from the IR. In the JSA region, A. rivularis extended by 1144 bp to the IR region, which was the shortest among the Astilbe species, while A. chinensis extended by 1172 bp, and in the other three species, it was 1192 bp. In the JLA region, the trnH gene was 12 bp from A. rivularis and 7 bp from the other four species.
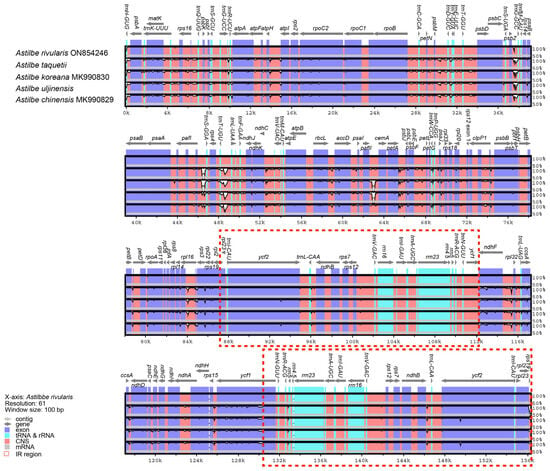
Figure 2.
Aligned sequence plots for the five Astilbe species using the A. rivularis chloroplast genome as reference.
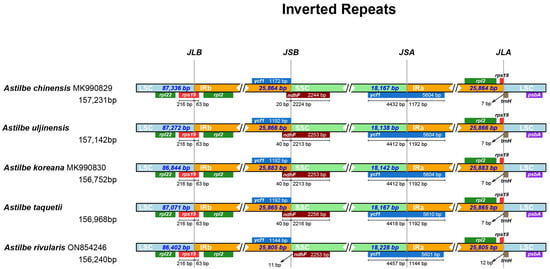
Figure 3.
Comparison of four junctions in the chloroplast genome sequences of the five Astilbe species (large single-copy (LSC) region and inverted repeats (IR) and small single-copy (SSC) region).
3.3. Divergent Hotspots in the Five Astilbe Chloroplast Genomes
The divergence hotspot analysis using DnaSP uncovered highly variable regions in the five Astilbe chloroplast genomes (Figure 4). The average nucleotide diversity (Pi) over the entire cp genome, the average nucleotide diversity (Pi) of the genes, and the average nucleotide diversity (Pi) of noncoding regions were 0.0035, 0.0018, and 0.0058, respectively. We identified five regions with the highest Pi by distinguishing between the gene and noncoding regions. Among these genes, rps19 had the highest Pi value (0.01), followed by trnS-GCU (0.0091), rpl20 (0.0078), psaI (0.0072), and ndhF (0.0067; Figure 4A). The trnY-GUA–trnE-UUC region had the highest Pi value (0.0271), followed by psbZ–trnG-GCC (0.0244), psbC–trnS-UGA (0.0217), rps15–ycf1 (0.0216), and trnH-GUG–psbA (0.0202; Figure 4B).
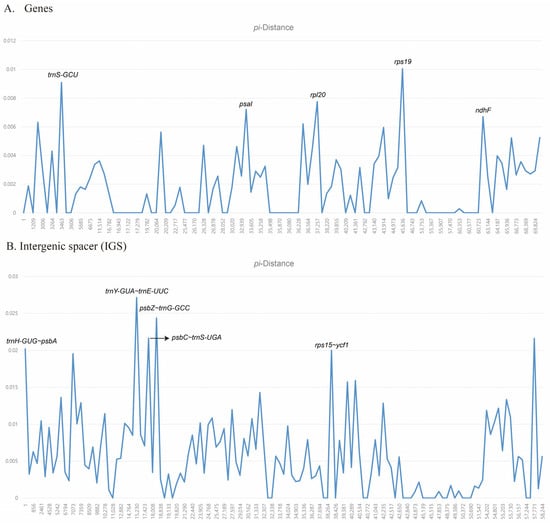
Figure 4.
Nucleotide polymorphism analysis of the chloroplast genomes of 5 Astilbe species.
3.4. Codon Usage Analysis
A total of 79 CDSs from the five Astilbe chloroplast genomes were used to estimate the relative frequency of synonymous codon usage, excluding three stop codons. The number of codons was confirmed to be 22,599 (A. rivularis) to 22,716 (A. koreana). Leucine (Leu; 2393–2391) was the most abundant amino acid, whereas cysteine (Cys; 258–259) was the least abundant amino acid in the plastomes of these taxa (Table S1). In addition, we generated a heat map (Figure 5) based on the RSCU results for the five Astilbe species. The evolutionary tree was divided into two major branches based on the RSCU values of the 61 codons. The first branch consisted of 29 codons with RSCU values greater than 1.12, and the second branch included the remaining codons. These five Astilbe species exhibited high similarities in codon usage. Codons ending in A or T exhibited higher coding rates. Except for leucine (CUA) and isoleucine (AUA), codons ending in A or T had RSCU > 1, whereas codons ending in C or G had RSCU < 1. Although there are some differences, amino acids usually have at least two synonymous codons, with arginine (Arg), Leu, and serine (Ser) having the most, with six codons. Methionine (AUG) and tryptophan (UGG) both had RUSC values of 1. Based on the RSCU values, A. rivularis branched first; A. koreana and A. taquetii formed sister groups; and A. chinensis and A. uljinensis formed sister groups.
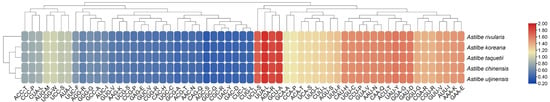
Figure 5.
Heat map for RSCU analysis of the five Astilbe species. The RSCU values of 61 codons were used for tree clustering. Each column represents a different codon. Each row represents a different Astilbe species. The darker the blue, the lower the RSCU value. The darker the red, the higher the RSCU value.
The Ka/Ks ratio was calculated for the seventy-nine shared protein-coding genes between the Astilbe species cp genomes (Figure 6). Among the protein-coding genes of Astilbe, psbD, psaB, psaA, pafII, psbJ, infA, rpl14, psaC, atpA, atpF, atpH, petB, and psbA showed no nonsynonymous substitution rates, and six genes (pbf1, psbT, rps8, rpl22, rpl32, and rpl33) showed no synonymous substitution rates. The genes with the smallest and highest mean Ka/Ks ratio were petA (0.063) and rbcL (1.527), respectively. The genes inferred to be undergoing positive selection were rbcL and rpl20 (mean Ka/K ratio > 1).
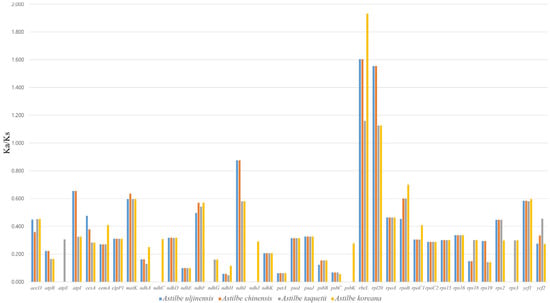
Figure 6.
The Ka/Ks ratio of 79 CDSs of 4 Astilbe chloroplast genomes in comparison with A. rivularis. Ka/Ks ratio > 1 indicates strong positive selection.
3.5. SSRs and Long-Repeat Analysis
The distribution of SSRs was analyzed in the five Astilbe chloroplast genomes using Krait. The lowest number of repeats (44) was identified in A. rivularis, while the highest number of repeats (65) was identified in A. chinensis. Among these five species, mononucleotide repeats were the most abundant. The second most abundant repeat sequence comprised dinucleotide repeats. Tetro- and pentanucleotide repeats were identified only in A. chinensis. Most SSRs contained the A/T motif (Table 3, Figure 7, Supplementary Materials, Table S2).

Table 3.
Types and numbers of SSRs in the chloroplast genomes of the five Asatilbe species.
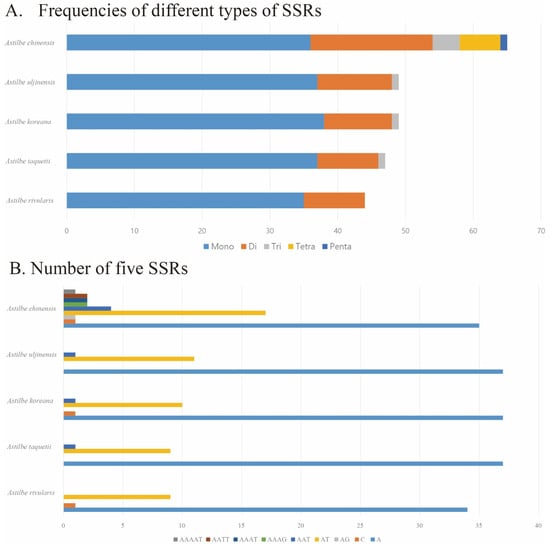
Figure 7.
Analysis of SSRs in the five Astilbe cp genomes. (A) Frequencies of different types of SSRs. (B) Number of five SSRs.
Long-repeat analysis revealed that more forward and palindromic repeats were identified than reverse and complementary repeats in the five astilbe species. A total of 49 long repeats were identified in all five species. Forward repeats (F) were found in 13–16 species, reverse repeats (R) in 11–14 species, palindromic repeats (P) in 19–21 species, and complementary repeats (C) in 2 out of all 5 species. Repeated analyses of these species may lead to the development of potential molecular markers for species identification in Astilbe. Repeat sizes of 20 or less were identified as 16 to 22, repeat sizes of 21 to 30 were identified as 20 to 25, repeat sizes of 51 to 60 were identified in A. chinensis and A. koreana, and repeat sizes of 61 or more were identified in A. chinensis and A. taquetii (Table 4, Figure 8, Supplementary Materials, Table S3).

Table 4.
Types and numbers of repeats in the chloroplast genomes of the five Astilbe species using REPuter.
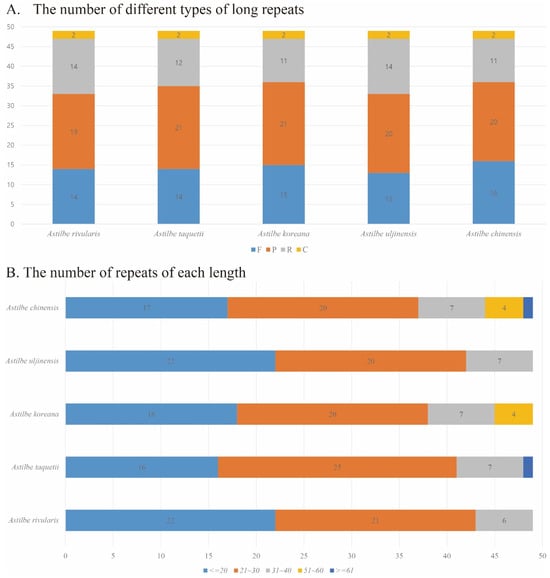
Figure 8.
Analysis of long repeats in the chloroplast genomes of the five Astilbe species. (A) The number of different types of long repeats. (B) The number of repeats of each length.
3.6. Phylogenetic Analysis of Astilbe and Related Taxa
Using ModelFinder, GTR + R3 + F was confirmed as the best model for ML, and GTR + F + I + G4 was confirmed as the best model for MrBayes. Phylogenetic analysis was conducted using two methods (ML method and MrBayes method) and 79 genes from 42 Saxifragales and 2 Cornales chloroplast genomes (Figure 9 and Table S2). The resulting phylogeny analysis showed that the monophyly of the Saxifragales was highly supported by bootstrap values (BS = 100, PP = 1.00). In this order, the Hammamelidaceae and Daphniphyllaceae–Cercidiphyllaceae groups branched first to form the basal group (BS = 100, PP = 1.00). Grossulariaceae formed a sister group with Saxifragaceae (BS = 100, PP = 1.00). There are five groups within the Saxifragaceae family. One of them is the Astilbe group. Within this group, A. rivularis was first distinguished, and A. taquetii was grouped with A. koreana (BS = 100, PP = 1.00) A. uljinensis was grouped with A. chinensis (BS = 100, PP = 1.00).
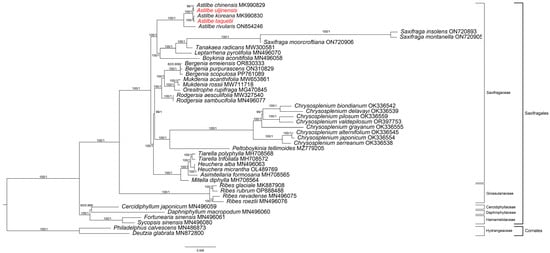
Figure 9.
Maximum likelihood (ML) and Bayesian phylogenetic tree based on 79 protein-coding genes from 42 Saxifragales and 2 Cornales species. The ML posterior probability and BI posterior probability are mentioned above the lines. In red are species reported in this study.
4. Discussion
Astilbe plants are mainly used for ornamental purposes due to large inflorescences, and some species, especially A. rivularis, are used in traditional medicine [49,50]. With the development of NGS technology, phylogenetic studies and species identification based on cp genomes have attracted increasing attention. To date, there have been only three studies on the Astilbe chloroplast genome, and not only has there been no comparative study on the Astilbe chloroplast genome, but this is the first study on the endemic Astilbe plant in Korea. Here, we report on the cp genomes of A. taquetii and A. uljinensis using NGS. Complete circular cp genomes, 156,968 and 157,142 bp in length, were obtained. Similar to the chloroplast genomes of other Saxifragales, they display a typical four-part structure and maintain a similar level of conservation in the overall genome structure, including gene content and gene organization [51,52,53]. The two Astilbe species were consistent with other Saxifragales species in regard to their structural organization and gene number, indicating the overall conservation of plant chloroplast genomes.
Comparison of the IR boundaries with the five Astilbe chloroplast genome sequences revealed a high level of conservation in both the single-copy region and the IR region. There were more variable regions identified in both analyses (mVISTA and nucleotide diversity) than in standard DNA barcodes for plant taxonomic and phylogenetic analyses, and thus, these could be utilized for future molecular marker development [54].
Among these genes, the most variable gene was rps19 (Pi = 0.01), which was located in the junction region between the LSC and IR regions. Contrarily, in IGS, trnY-GUA–trnE-UUC (Pi = 0.0271) was located in the LSC region. The IGS region was confirmed to be more variable than that of the other genes. Although a comprehensive collection of species in this genus and further studies are needed, the 10 variable regions identified in this study suggest that they can be useful tools for phylogenetic inference or evolutionary history studies.
The codon usage bias of the cp genome is mainly caused by mutation pressure and natural selection, and the important role is mainly in the third base of the synonymous codons. Similar to other plant chloroplast genomes, the chloroplast genomes of both Astilbe species contained 29 codons with high codon usage (RSCU > 1), all of which were identified as A/U. In contrast, there were 30 codons with low codon usage (RSCU < 1), most of which were identified as C/G.
Ka/Ks analysis is an important tool used in molecular evolution studies for assessing selective pressure on gene sequences in chloroplast genomes. Compared to those of the nonsynonymous (Ka) substitutions, synonymous (Ks) nucleotide substitutions are more frequent in most organism genes; therefore, Ka/Ks values are typically less than 1. Ka/Ks ratios greater than 1 indicated positive selection, whereas Ka/Ks ratios less than 1 indicated purifying selection. In this study, most protein-coding genes had Ka/Ks ratios of <1, indicating purifying selection. Additionally, the results indicated that two genes (rbcL and rpl20) were under strong positive selection. The rbcL gene encodes the large subunit (LSU) of RuBisCO and was widely used in phylogenetic studies. The rpl20 gene is one of the proteins in the large ribosomal subunit.
Additionally, SSRs are highly polymorphic and codominant, and they were used as molecular markers in population genetics and phylogenetic studies [55]. Most of the detected SSRs had high A/T content, and in particular, A/T motifs were the most common mononucleotide repeats. Additionally, the Astilbe cp genome contains repetitive sequences, including forward repeats, palindromes, inverted repeats, and complementary repeats. The various repetitive sequences identified in this study can be used as molecular markers for future research on Astilbe species.
We constructed a phylogenetic tree of Saxifragales by thoroughly analyzing the chloroplast genomes of 44 species using maximum likelihood (ML) and MrBayes. The phylogenetic placement of the Saxifragales was consistent with that reported in earlier studies [56]. Astilbe comprised a strong monophyletic group; A. uljinensis was the sister group to A. chinensis, and A. taquetii was the sister group to A. koreana. A comprehensive analysis of whole chloroplast genomes is important when studying Saxifragales phylogeny because it provides higher accuracy than a fragment analysis. Therefore, the results of this study greatly contribute to our understanding of the evolutionary history of Saxifragales and Astilbe.
5. Conclusions
To our knowledge, this study reports on the first complete chloroplast genome sequences of two endemic Korean species, A. taquetii and A. uljinensis. The chloroplast genome structure of Astilbe is similar to that of reported angiosperms and has a typical four-branched structure with conserved genome arrangement and gene signatures. Several key features, including A/U stop codon preference and the presence of repeats, were identified, and 10 regions were identified as mutation hotspots. Two genes (rbcL and rpl20) showed signs of positive selection, suggesting that these genes may have a potential role in adaptive evolution. Phylogenetically, Astilbe is strongly monophyletic in Saxifragaceae, and the two endemic Korean species form different sister and branching groups. The genomic data presented in this study provide a baseline for comparative analyses of Astilbe and an essential genetic resource for enriching our understanding of the evolutionary patterns of Saxifragales.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/genes15111410/s1: Table S1: NCBI Data information used in ML Analysis; Table S2: SSR information for five Astilbe species, Table S3: Long-repeat information for five Astilbe species.
Author Contributions
The collection of experimental materials was completed by S.-C.K. and B.K.P. Data analysis was carried out by S.-C.K.; preparations for drafting the manuscript and diagrams were completed by S.-C.K. and H.-J.K. The revision and manuscript editing were completed by S.-C.K. and B.K.P. Proofreading of the English manuscript was completed by S.-C.K. and H.-J.K. Resources were provided by all authors. The funds were provided by H.-J.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the Scientific Research (KNA1-1-13, 14–1) of the Korea National Arboretum.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in GenBank; see Table 1 for accession numbers.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dong Ha Kim for helping with sampling throughout this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Xu, Z.; Deng, M.; Xu, Z.; Deng, M. Saxifragaceae. Identif. Control. Common Weeds 2017, 2, 487–490. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.T.; Gu, C.Z.; Huang, S.M.; Wei, Z.F.; Jin, S.Y.; Lu, L.D.; Akiyama, S.; Alexander, C.; Bartholomew, B.; Cullen, J.; et al. Saxifragaceae. Flora China 2001, 8, 269–452. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.D.; Nie, Z.L.; Wen, J.; Sun, H. Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of Astilbe (Saxifragaceae) in Asia and eastern North America. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2013, 171, 377–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trader, B.W. Molecular and Morphological Investigation of Astilbe. Doctoral Dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Shin, H.C.; Kim, Y.D. Molecular phylogeny of Astilbe: Implications for phylogeography and morphological evolution. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2009, 39, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.H.; Oh, B.U. A morphological study of Korean Astilbe (Saxifragaceae). J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2019, 12, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, A.; Han, S.H.; Oh, B.U. Astilbe uljinensis (Saxifragaceae), a new species from South Korea. PhytoKeys 2020, 161, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, G.Y.; Jang, H.D.; Chang, K.S.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Son, D.C. A checklist of endemic plants on the Korean Peninsula II. Korean J. Plant Taxon. 2023, 53, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.K.; Ruhlman, T.A. Plastid genomes of seed plants. In Genomics of Chloroplasts and Mitochondria; Bock, R., Knoop, V., Eds.; Springer: Dutch, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.K.; Raubeson, L.A.; Boore, J.L.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Chumley, T.W.; Haberle, R.C.; Wyman, S.K.; Alverson, A.J.; Peery, R.; Herman, S.J.; et al. Methods for obtaining and analyzing whole chloroplast genome sequences. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 395, 348–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, J.D. Comparative organization of chloroplast genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1985, 19, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Lee, J.W. The complete chloroplast genome of Chamaecyparis obtusa (Cupressaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020, 5, 3278–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.; Kim, S.C.; Hong, K.N.; Kang, H.; Lee, J.W. The complete chloroplast genome of Torreya nucifera (Taxaceae) and phylogenetic analysis. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019, 4, 2537–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H.; Ding, Y.; Hu, Y.; Xu, Z. The complete chloroplast genome of an inverted-repeat-lacking species, Vicia sepium, and its phylogeny. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2018, 3, 137–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.I.; Lee, H.O.; Lee, I.H.; Kim, I.S.; Lee, S.W.; Yang, T.J.; Shim, D. Complete chloroplast genome of Pinus densiflora Siebold & Zucc. and comparative analysis with five pine trees. Forests 2019, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, M.W.; Baek, S.H.; Hong, K.N. The complete chloroplast genome sequences of Larix kaempferi and Larix olgensis var. koreana (Pinaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resourc. 2018, 3, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Hyun, H.J. Complete chloroplast genome of Vaccinium oldhamii and phylogenetic analysis. Mitochondrial DNA B 2019, 4, 902–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Gong, J.; Yi, Y. The complete chloroplast genome of Rhododendron delavayi (Ericaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resourc 2020, 5, 37–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Feng, H.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Cao, H.L. The complete chloroplast genome of Rhododendron datiandingense (Ericaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021, 6, 1749–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Chang, L.W.; Cao, H.L. The complete chloroplast genome of Rhododendron kawakamii (Ericaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021, 6, 2538–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, D. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Corydalis inopinata Prain ex Fedde (Papaveraceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020, 5, 3284–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Ha, Y.H.; Park, B.K.; Jang, J.E.; Kang, E.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kimspe, T.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.J. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of Papaveraceae to identify rearrangements within the Corydalis chloroplast genome. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0289625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Park, K.T.; Park, S. The chloroplast genome of Symplocarpus renifolius: A comparison of chloroplast genome structure in Araceae. Genes 2017, 8, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. The chloroplast genome sequence of bittersweet (Solanum dulcamara): Plastid genome structure evolution in Solanaceae. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0196069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, M.E.; Meyer, G.; Vandergon, T.; Vandergon, V.O. Loss of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase (accD) gene in Poales. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 31, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cauz-Santos, L.A.; Munhoz, C.F.; Rodde, N.; Cauet, S.; Santos, A.A.; Penha, H.A.; Dornelas, M.C.; Varani, A.M.; Oliveira, G.C.X.; Bergès, H.; et al. The chloroplast genome of Passiflora edulis (Passifloraceae) assembled from long sequence reads: Structural organization and phylogenomic studies in Malpighiales. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Yan, H.F.; Zhang, L.; Ge, X.J.; Hao, G. Complete plastid genome sequence of Primula sinensis (Primulaceae): Structure comparison, sequence variation and evidence for accD transfer to nucleus. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kim, S.C.; Ha, Y.H.; Kim, D.K.; Son, D.C.; Kim, H.J.; Choi, K. Comparative analysis and phylogenetic study of the chloroplast genome sequences of two Korean endemic Primula varieties. Diversity 2022, 14, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.S.; Choi, B.H. The distinct plastid genome structure of Maackia fauriei (Fabaceae: Papilionoideae) and its systematic implications for genistoids and tribe Sophoreae. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.S.; Ha, Y.H.; Gil, H.Y.; Choi, K.; Kim, D.K.; Oh, S.H. Two Korean endemic Clematis chloroplast genomes: Inversion, reposition, expansion of the inverted repeat region, phylogenetic analysis, and nucleotide substitution rates. Plants 2021, 10, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.C.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.H. Insight into infrageneric circumscription through complete chloroplast genome sequences of two Trillium species. AoB Plants 2016, 8, plw015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.J.; Yu, W.B.; Yang, J.B.; Song, Y.; DePamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillich, M.; Lehwark, P.; Pellizzer, T.; Ulbricht-Jones, E.S.; Fischer, A.; Bock, R.; Greiner, S. GeSeq—Versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W6–W11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.P.; Lin, B.Y.; Mak, A.J.; Lowe, T.M. TRNAscan-SE 2.0: Improved detection and functional classification of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 9077–9096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, S.; Lehwark, P.; Bock, R. OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3. 1: Expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W59–W64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Kuma, K.I.; Toh, H.; Miyata, T. MAFFT version 5: Improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor, C.; Brudno, M.; Schwartz, J.R.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.S.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Visualizing global DNA sequence alignments of arbitrary length. Bioinformatics 2000, 16, 1046–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez Menéndez, C.; Poczai, P.; Williams, B.; Myllys, L.; Amiryousefi, A. IRplus: An augmented tool to detect inverted repeats in plastid genomes. Genome Biol. Evol. 2023, 15, evad177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yue, B.; Hancock, J. Krait: An ultrafast tool for genome-wide survey of microsatellites and primer design. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 681–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, A.R.; Badola, H.K.; Dhyani, P.P.; Rana, S.K. Integrating ethnobiological knowledge into biodiversity conservation in the Eastern Himalayas. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2017, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, K.; Wada, M.; Yahara, S.; Watanabe, T.; Devkota, H.P. Antioxidant phenolic compounds from the rhizomes of Astilbe rivularis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Xin, C. Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome sequence of Deutzia glabrata (Saxifragaceae). Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020, 5, 764–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.A.; Sewnath, N.; Xiang, C.L.; Sinn, B.T.; Guralnick, R.P. Degradation of key photosynthetic genes in the critically endangered semi-aquatic flowering plant Saniculiphyllum guangxiense (Saxifragaceae). BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, L.; Li, N.; Fardous Mohammad Safiul, A.; Li, S.; Zhao, T.; Wang, J.; Zou, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, S. Characteristics of the complete chloroplast genome of Saxifragaceae species Bergenia purpurascens (Hook. f. et Thoms.) Engl. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2023, 8, 1454–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Z.; Li, M.; Liu, Z.; Peng, D. Complete chloroplast genomes and comparative analyses of three Paraphalaenopsis (Aeridinae, Orchidaceae) species. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, F.; Labra, M.; Scienza, A.; Imazio, S. Chloroplast SSR markers to assess DNA diversity in wild and cultivated grapevines. Vitis 2002, 41, 157–158. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wei, P.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Liu, X. Comparative analysis of chloroplast genomes within Saxifraga (Saxifragaceae) takes insights into their genomic evolution and adaption to the high-elevation environment. Genes 2022, 13, 1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).