PhenoMetaboDiff: R Package for Analysis and Visualization of Phenotype Microarray Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
- PhenoDiff Module: The main functionality of this module is to identify significant differences in the utilization of metabolites between two comparison groups using the non-parametric Mann–Whitney U-test.
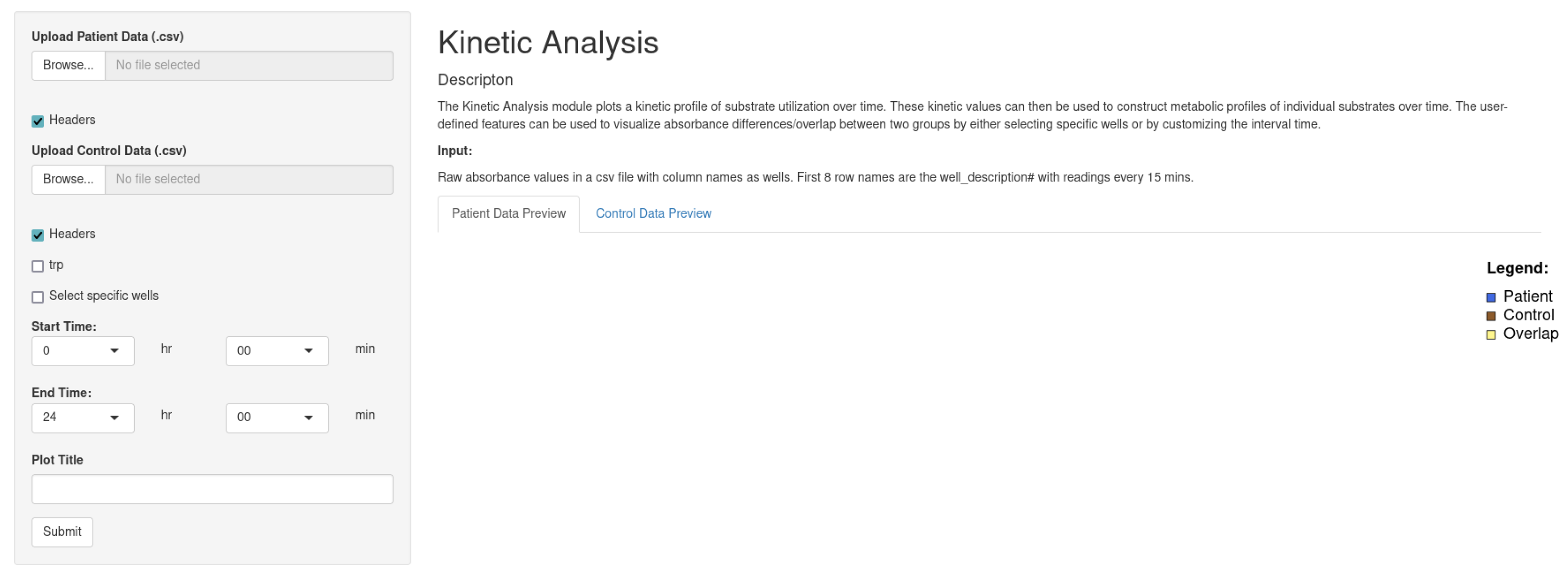
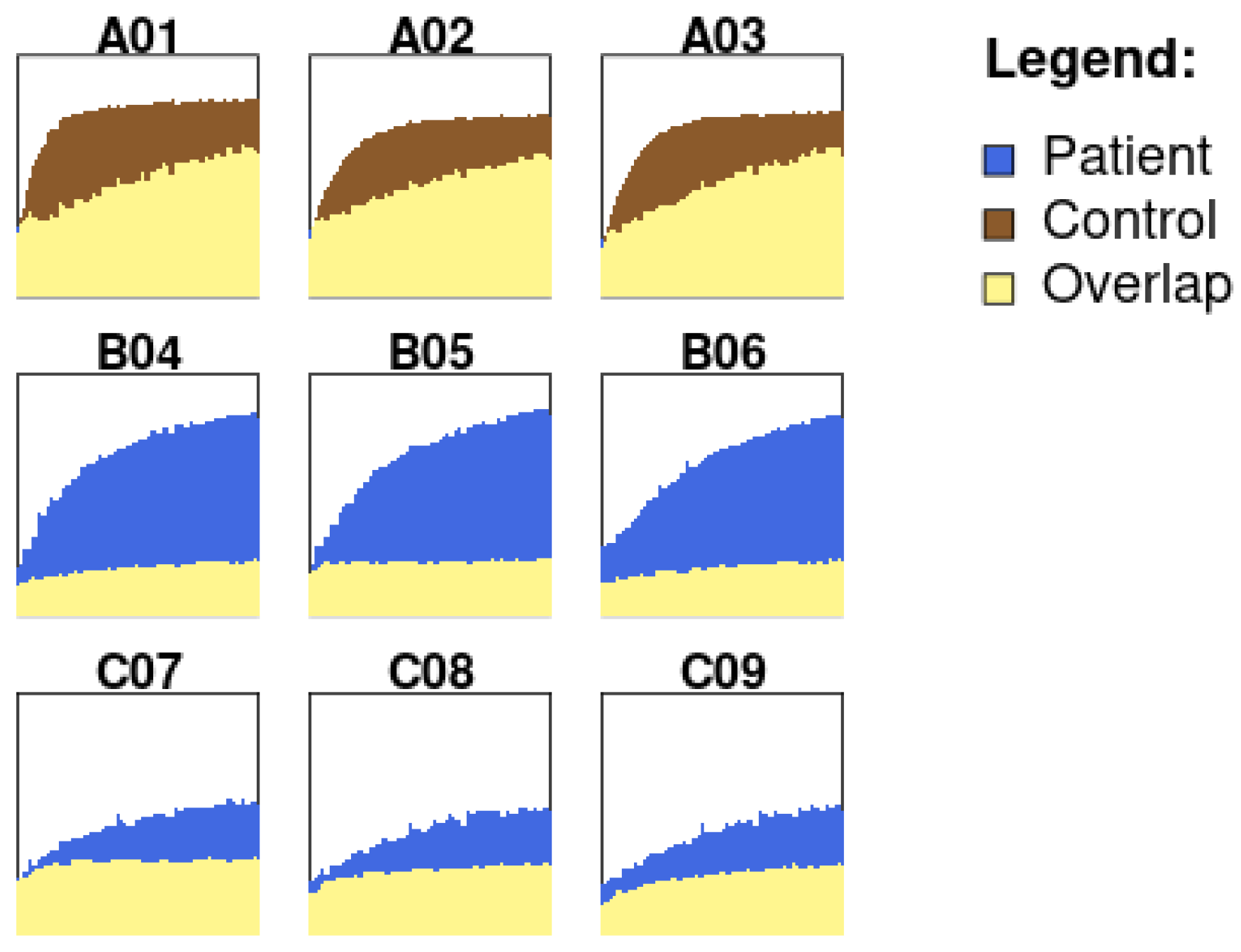
- Kinetic Analysis: The Kinetic Analysis module plots a kinetic profile of the substrate utilization over time. These kinetic values can then be used to construct metabolic profiles of individual substrates over time. The user-defined feature can be used to visualize absorbance differences/overlap between two groups by either selecting specific wells or by customizing the interval time.
- Slope and AUC Calculator: The “Slope and AUC” module calculates the descriptive curve parameters, including lag phase, steepness of the slope, maximum curve height, and area under the curve, AUC.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Description of the Biolog Metabolic Arrays and Customized Plates
2.3. Components of PhenoMetaboDiff
2.3.1. Implementation
2.3.2. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
2.3.3. PhenoDiff
2.3.4. Kinetic Analysis
2.3.5. Slope and AUC Calculator
2.4. Demonstration Example: Kinetic Analysis of NADH
3. Results
3.1. Resources and Innovation
3.2. Translational Impact
3.3. Functional Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chong, J.; Wishart, D.; Xia, J. Using MetaboAnalyst 4.0 for comprehensive and integrative metabolomics data analysis. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2019, 68, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccuto, L.; Chen, C.; Pittman, A.; Skinner, C.; Mccartney, H.; Jones, K.; Bochner, B.; Stevenson, R.; Schwartz, C. Decreased tryptophan metabolism in patients with autism spectrum disorders. Mol. Autism 2013, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Brazill, J.; Liu, S.; Bello, C.; Zhu, Y.; Morimoto, M.; Cascio, L.; Pauly, R.; Diaz-perez, Z.; Malicdan, M. Spermine synthase deficiency causes lysosomal dysfunction and oxidative stress in models of Snyder-Robinson syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarate, Y.; Boccuto, L.; Srikanth, S.; Pauly, R.; Ocal, E.; Balmakund, T.; Hinkle, K.; Stefans, V.; Schaefer, G.; Collins, R. Constitutive activation of the PI3K-AKT pathway and cardiovascular abnormalities in an individual with Kosaki overgrowth syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2019, 179, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaas, L.; Sikorski, J.; Hofner, B.; Fiebig, A.; Buddruhs, N.; Klenk, H.; Göker, M. opm: An R package for analysing OmniLog® phenotype microarray data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1823–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooleycoleman, J.; Gass, J.; Srikanth, S.; Pauly, R.; Ziats, C.; Everman, D.; Skinner, S.; Bell, S.; Louie, R.; Cascio, L. Clinical and functional characterization of germline PIK3CA variants in patients with PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum disorders. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2023, 32, 1457–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascio, L.; Chen, C.; Pauly, R.; Srikanth, S.; Jones, K.; Skinner, C.; Stevenson, R.; Schwartz, C.; Boccuto, L. Abnormalities in the genes that encode Large Amino Acid Transporters increase the risk of Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, L.; Oberman, L.; Beamer, L.; Cascio, L.; May, M.; Srikanth, S.; Skinner, C.; Jones, K.; Allen, B.; Rogers, C. Genetic and metabolic profiling of individuals with Phelan-McDermid syndrome presenting with seizures. Clin. Genet. 2022, 101, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, B.; Oberman, L.; Beamer, L.; Srikanth, S.; Jain, L.; Cascio, L.; Jones, K.; Pauly, R.; May, M.; Skinner, C. Sleep disturbances in Phelan-McDermid syndrome: Clinical and metabolic profiling of 56 individuals. Clin. Genet. 2023, 104, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffitt, B.; Sarasua, S.; Ivankovic, D.; Ward, L.; Valentine, K.; Bennettjr, W.; Rogers, C.; Phelan, K.; Boccuto, L. Stratification of a Phelan–McDermid syndrome population based on their response to human growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor. Genes 2023, 14, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, Z.; Moffitt, B.; Treaster, M.; Larkins, A.; Khulordava, N.; Benjock, J.; Spencer, J.; Henrie, K.; Wurst, M.; Broom, A.; et al. Effects of Origanum majorana on Breast Cancer Cells: An Alternative to Chemotherapy? Metabolites 2023, 13, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochner, B.; Gadzinski, P.; Panomitros, E. Phenotype microarrays for high-throughput phenotypic testing and assay of gene function. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 1246–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erheiden, M.; Cantley, L.; Thompson, C. Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009, 324, 1029–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Pourtavakoli, A.; Hussen, B.; Taheri, M.; Ayatollahi, S. A Review on the Role of Genetic Mutations in the Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 5256–5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Yin, Z.; Hou, M.; Guo, P.; Wang, H.; Liu, N.; Cai, C.; Wang, M. Comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of the association between common genetic variants and autism spectrum disorder. Gene 2023, 887, 147723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kereszturi, É. Diversity and Classification of Genetic Variations in Autism Spectrum Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, G.; Mourad, M.; Iqbal, S.; Moses-fynn, E.; Ita, A.; Siddhartha, S.; Sood, R.; Srinivasan, K.; Subbaiah, R.; Tiwari, A. Conceptualizing Epigenetics and the Environmental Landscape of Autism Spectrum Disorders. Genes 2023, 14, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenella, M.; Matuleviciute, R.; Tamouza, R.; Leboyer, M.; Mcalonan, G.; Bralten, J.; Murphy, D. Immunogenetics of autism spectrum disorder: A systematic literature review. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 114, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siracusano, M.; Arturi, L.; Riccioni, A.; Noto, A.; Mussap, M.; Mazzone, L. Metabolomics: Perspectives on clinical employment in autism spectrum disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takenouchi, T.; Okuno, H.; Kosaki, K. Kosaki overgrowth syndrome: A newly identified entity caused by pathogenic variants in platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta. In American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C: Seminars in Medical Genetics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; Volume 181, pp. 650–657. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, A.; Chalot, B.; Antoniadi, T.; Schaefer, E.; Keelagher, R.; Ryan, G.; Thomas, Q.; Philippe, C.; Bruel, A.; Sorlin, A. Kosaki overgrowth syndrome: A novel pathogenic variant in PDGFRB and expansion of the phenotype including cerebrovascular complications. Clin. Genet. 2020, 98, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawliński, P.; Pelc, M.; Ciara, E.; Jhangiani, S.; Jurkiewicz, E.; Gambin, T.; Różdżyńska-świątkowska, A.; Dawidziuk, M.; Coban-akdemir, Z.; Guilbride, D. Phenotype expansion and development in Kosaki overgrowth syndrome. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, C.; Peron, A.; Kutler, M. Snyder-Robinson Syndrome; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Norris, J.; Schwartz, C.; Alexov, E. Revealing the effects of missense mutations causing Snyder-Robinson syndrome on the stability and dimerization of spermine synthase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, C.; Wang, X.; Stevenson, R.; Pegg, A. Spermine synthase deficiency resulting in X-linked intellectual disability (Snyder–Robinson syndrome). In Polyamines: Methods and Protocols; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 437–445. [Google Scholar]
- Murray-stewart, T.; Dunworth, M.; Foley, J.; Schwartz, C.; Caserojr, R. Polyamine homeostasis in Snyder-Robinson syndrome. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vehkala, M.; Shubin, M.; Connor, T.; Thomson, N.; Er, J. Novel R pipeline for analyzing biolog phenotypic microarray data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pauly, R.; Iqbal, M.; Lee, N.; Moffitt, B.A.; Sarasua, S.M.; Li, L.; Hubig, N.C.; Boccuto, L. PhenoMetaboDiff: R Package for Analysis and Visualization of Phenotype Microarray Data. Genes 2024, 15, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111362
Pauly R, Iqbal M, Lee N, Moffitt BA, Sarasua SM, Li L, Hubig NC, Boccuto L. PhenoMetaboDiff: R Package for Analysis and Visualization of Phenotype Microarray Data. Genes. 2024; 15(11):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111362
Chicago/Turabian StylePauly, Rini, Mehtab Iqbal, Narae Lee, Bridgette Allen Moffitt, Sara Moir Sarasua, Luyi Li, Nina Christine Hubig, and Luigi Boccuto. 2024. "PhenoMetaboDiff: R Package for Analysis and Visualization of Phenotype Microarray Data" Genes 15, no. 11: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111362
APA StylePauly, R., Iqbal, M., Lee, N., Moffitt, B. A., Sarasua, S. M., Li, L., Hubig, N. C., & Boccuto, L. (2024). PhenoMetaboDiff: R Package for Analysis and Visualization of Phenotype Microarray Data. Genes, 15(11), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15111362







