Bisphenol A Alters the Levels of miRNAs That Directly and/or Indirectly Target Neuropeptide Y in Murine Hypothalamic Neurons
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Conditions
2.2. BPA Treatment
2.3. miRNA Mimic Transfection
2.4. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and Quantitative RT-PCR
2.5. In Silico Identification of miRNA Candidates
2.6. Npy 3′ Untranslated Region Construct Synthesis
2.7. Construct and miRNA Mimic Co-Transfection for Dual Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
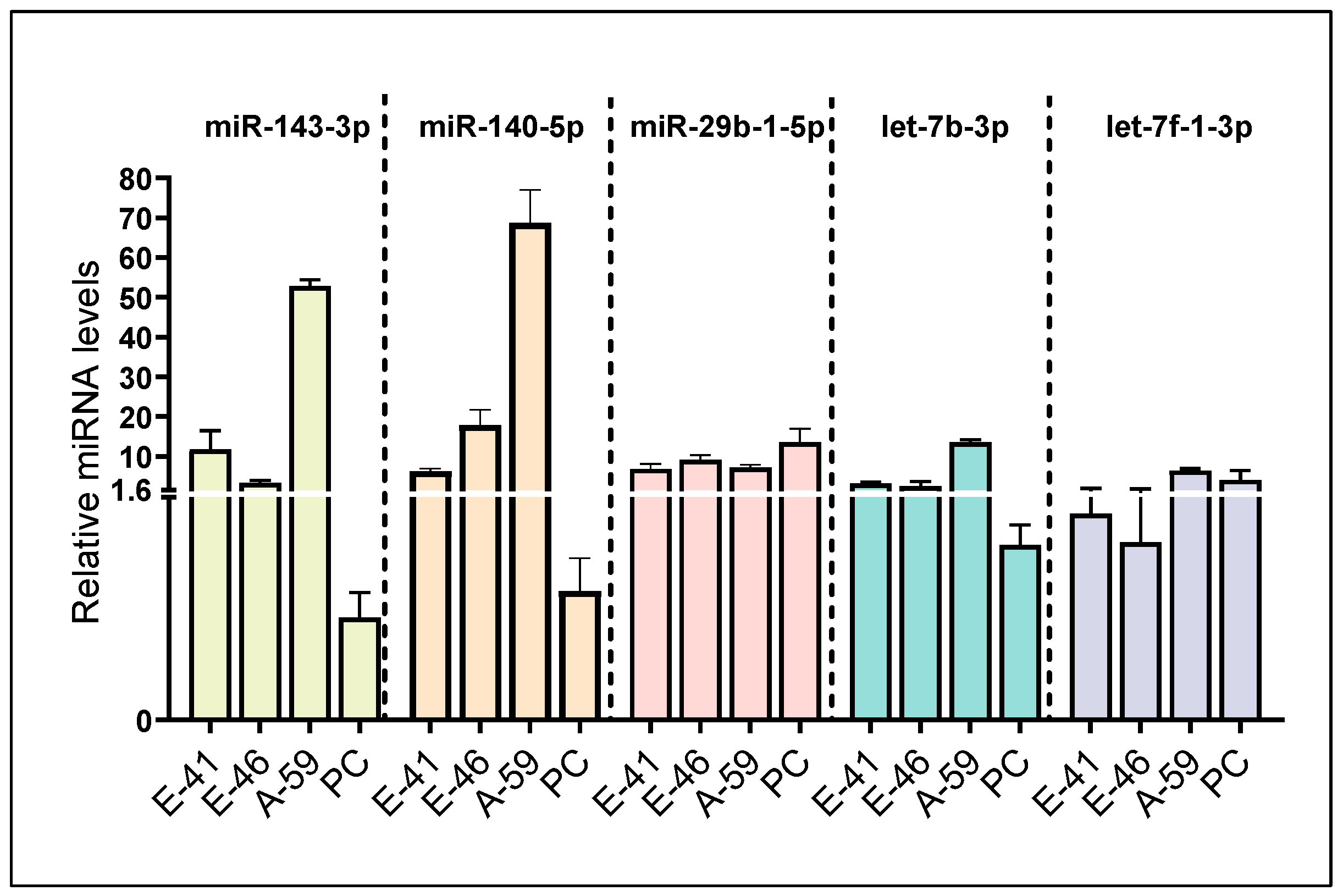
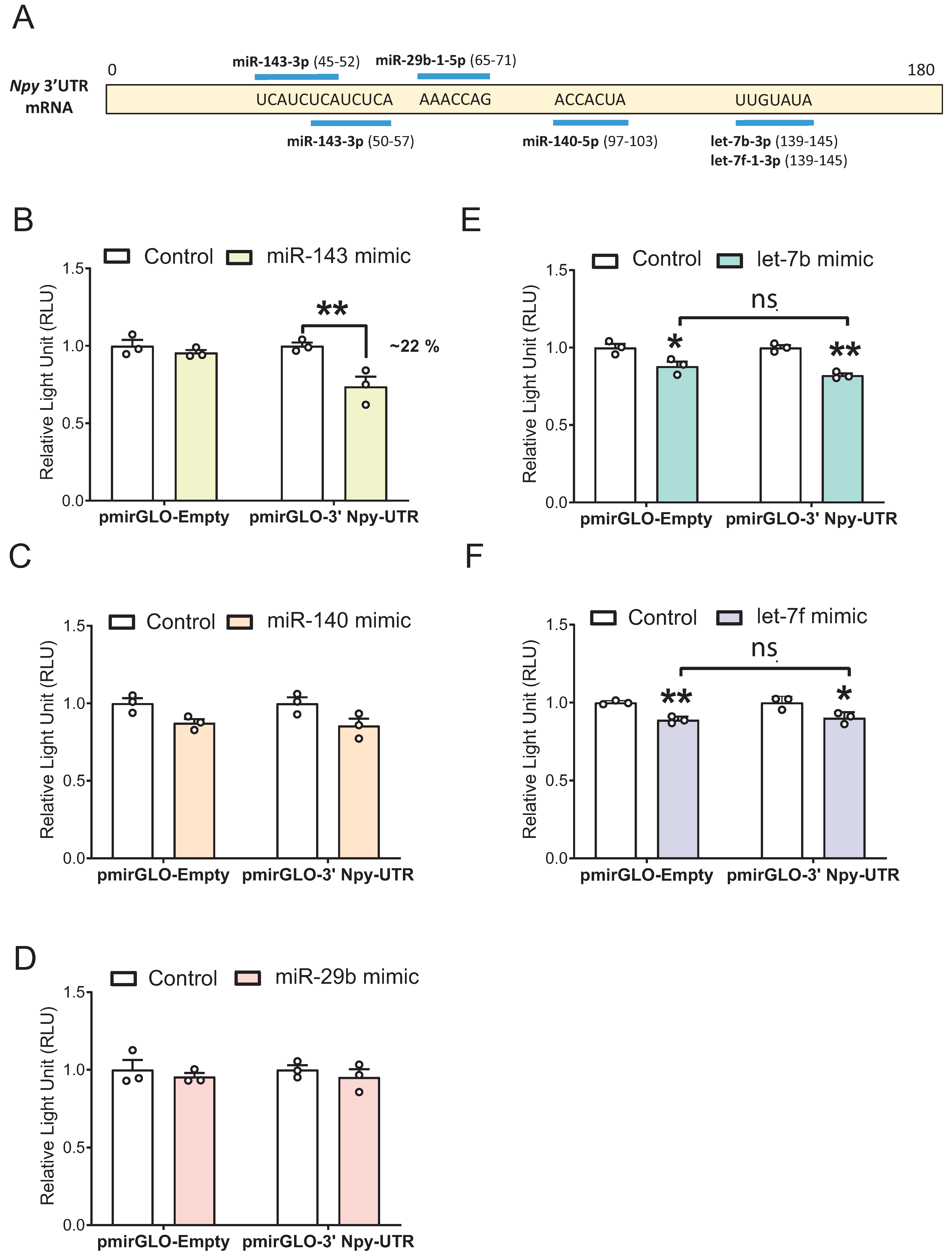
3.1. Identification of Five Putative Npy-Targeting miRNAs through In Silico and In Vitro Analyses
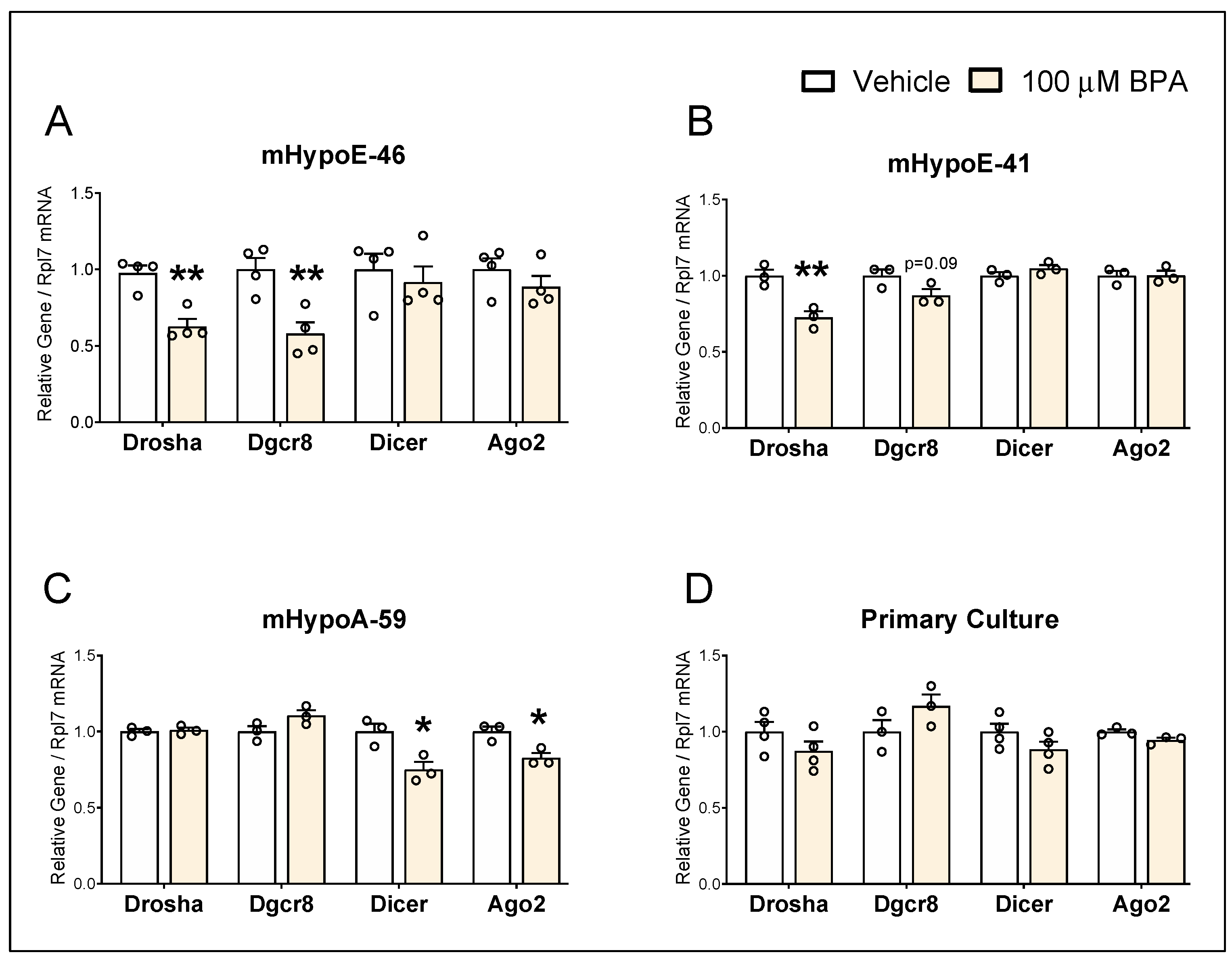
3.2. BPA Alters mRNA Levels of miRNA Biogenesis Components in the Hypothalamic-Derived Neuronal Cell Lines
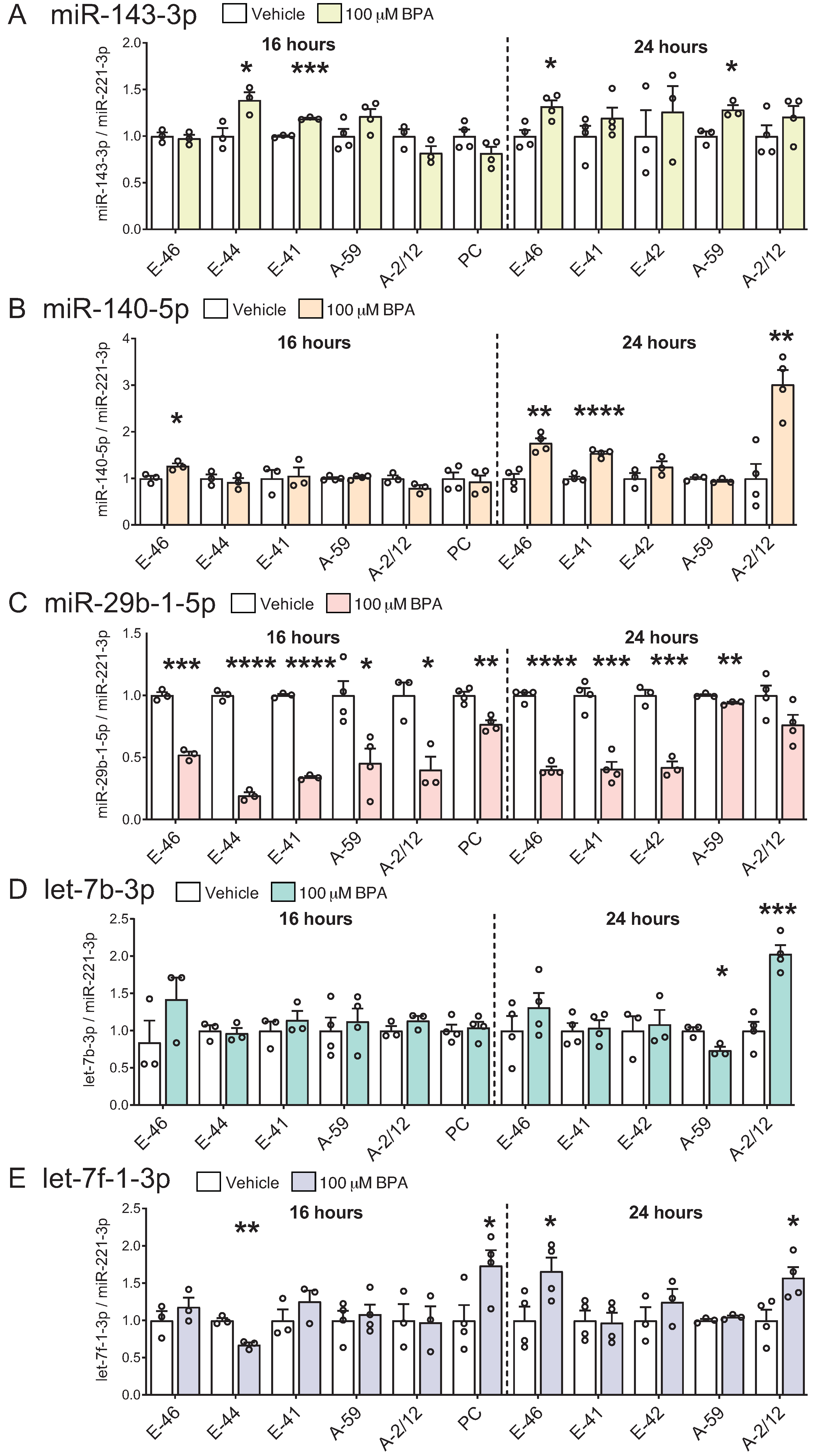
3.3. BPA Induces Differential miRNA Changes in Hypothalamic-Derived Neuronal Cell Lines (mHypoE-41, mHypoE-46, mHypoE-44, mHypoE-42, mHypoA-59, and mHypoA-2/12) and in Neuronal Primary Culture
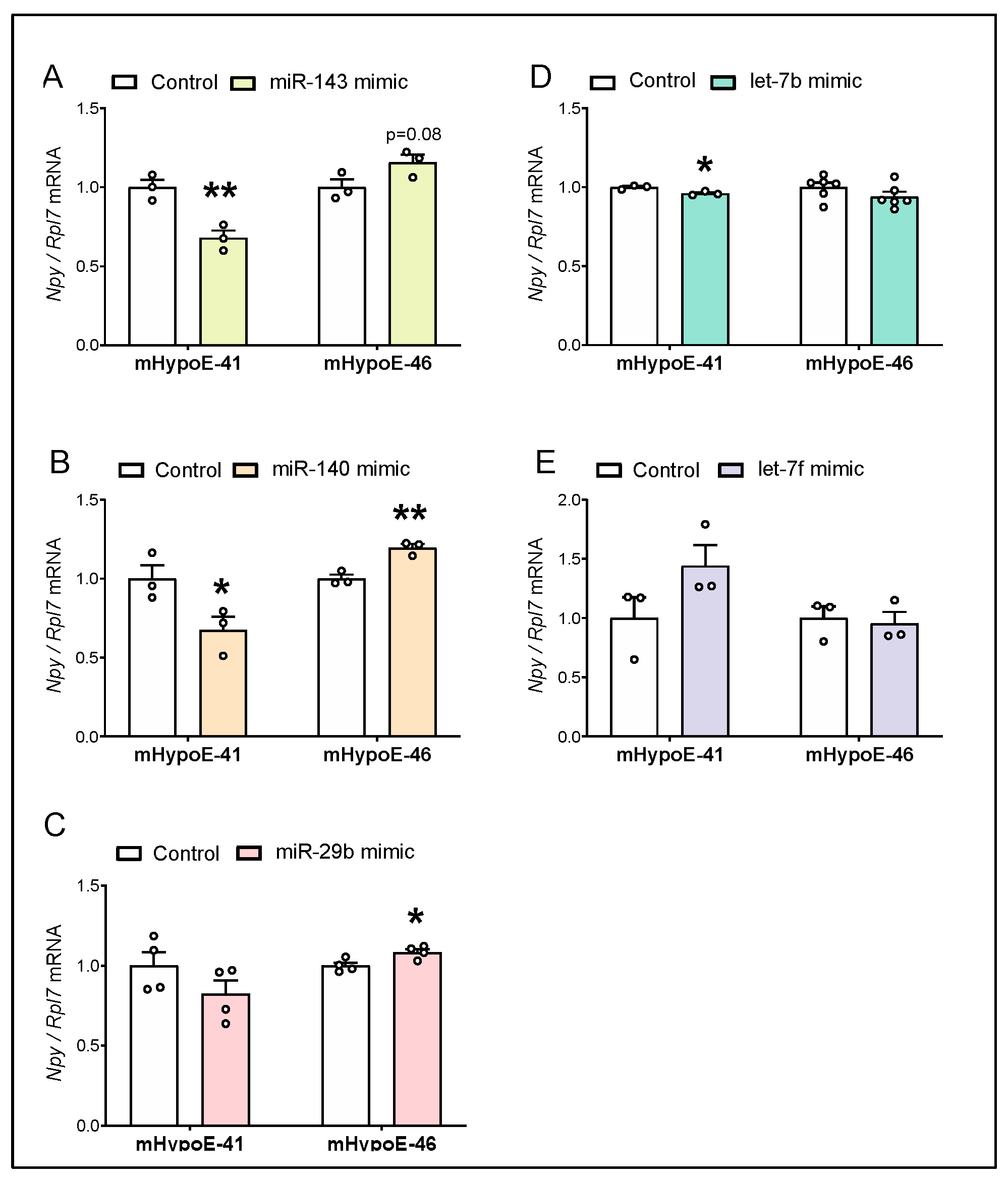
3.4. Overexpression of miR-143-3p, miR-140-5p and let-7b-3p Downregulate Npy mRNA in the Hypothalamic Npy-Expressing mHypoE-41 Cell Model
3.5. miR-143-3p Targets the Npy 3′ UTR in mHypoE-41 Neurons
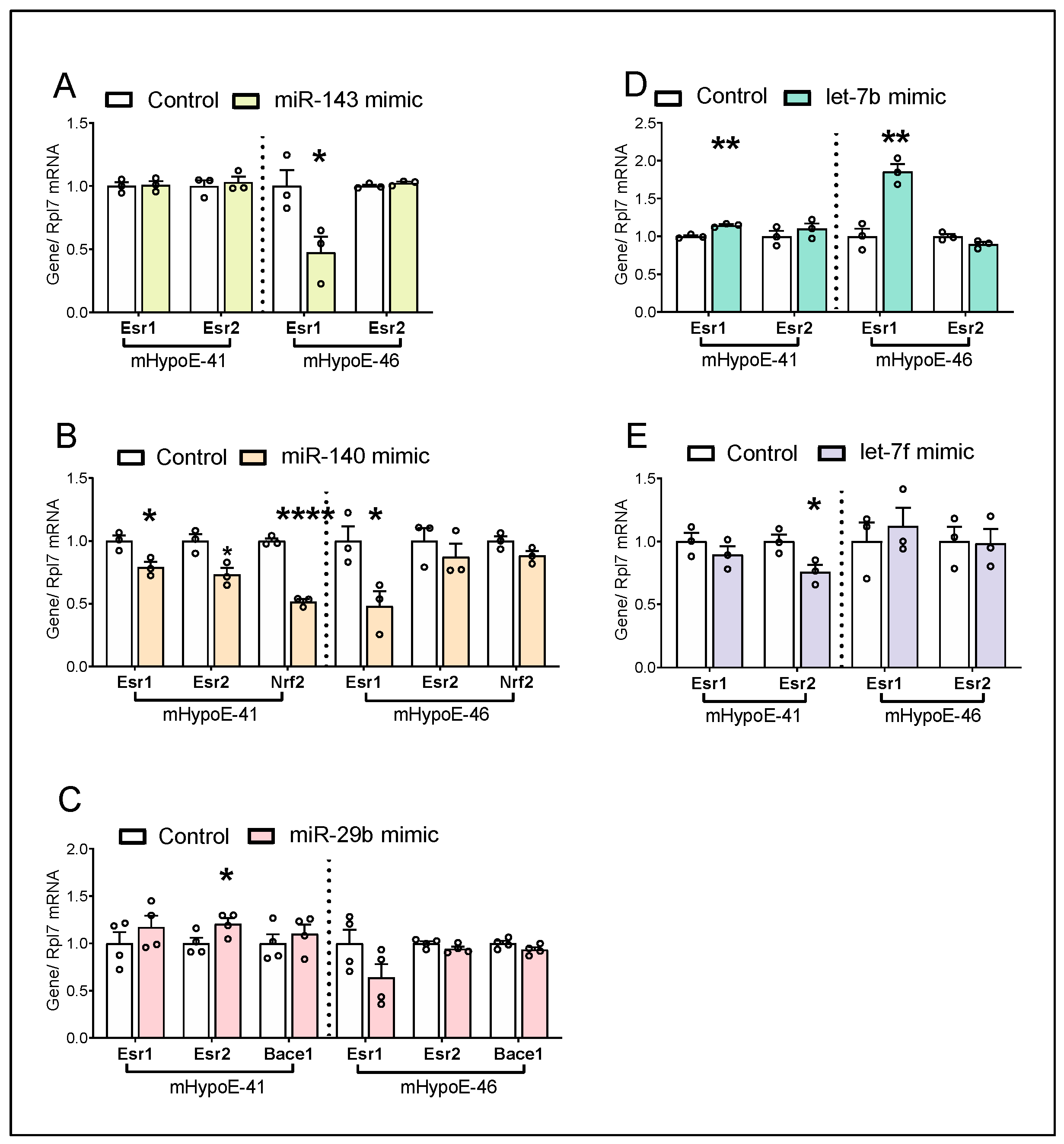
3.6. miRNA Candidates Alter Estrogen Receptor Genes and Metabolism-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guh, D.P.; Zhang, W.; Bansback, N.; Amarsi, Z.; Birmingham, C.L.; Anis, A.H. The incidence of co-morbidities related to obesity and overweight: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health 2009, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluher, M. Obesity: Global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Anubhuti. Role of neuropeptides in appetite regulation and obesity—A review. Neuropeptides 2006, 40, 375–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, K.; Herzog, H.; Shi, Y.C. Regulation of energy homeostasis by the NPY system. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarjevski, N.; Cusin, I.; Vettor, R.; Rohner-Jeanrenaud, F.; Jeanrenaud, B. Chronic intracerebroventricular neuropeptide-Y administration to normal rats mimics hormonal and metabolic changes of obesity. Endocrinology 1993, 133, 1753–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulsey, M.G.; Pless, C.M.; White, B.D.; Martin, R.J. ICV administration of anti-NPY antisense oligonucleotide: Effects on feeding behavior, body weight, peptide content and peptide release. Regul. Pept. 1995, 59, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa-Ferreira, L.; Garrido, M.; Nascimento-Ferreira, I.; Nobrega, C.; Santos-Carvalho, A.; Alvaro, A.R.; Rosmaninho-Salgado, J.; Kaster, M.; Kugler, S.; de Almeida, L.P.; et al. Moderate long-term modulation of neuropeptide Y in hypothalamic arcuate nucleus induces energy balance alterations in adult rats. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, H.; Patterson, Z.R.; Khazall, R.; Patel, S.; Tsirlin, D.; Abizaid, A. Organizational effects of perinatal exposure to bisphenol-A and diethylstilbestrol on arcuate nucleus circuitry controlling food intake and energy expenditure in male and female CD-1 mice. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 1465–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loganathan, N.; McIlwraith, E.K.; Belsham, D.D. BPA Differentially Regulates NPY Expression in Hypothalamic Neurons Through a Mechanism Involving Oxidative Stress. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner-Piquer, I.; Mylonas, C.C.; Calduch-Giner, J.; Maradonna, F.; Gioacchini, G.; Allara, M.; Piscitelli, F.; Di Marzo, V.; Perez-Sanchez, J.; Carnevali, O. Endocrine disruptors in the diet of male Sparus aurata: Modulation of the endocannabinoid system at the hepatic and central level by Di-isononyl phthalate and Bisphenol A. Environ. Int. 2018, 119, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, P.S.; Chalmers, J.A.; Luo, V.; Han, D.Y.; Wellhauser, L.; Liu, Y.; Tran, D.Q.; Castel, J.; Luquet, S.; Wheeler, M.B.; et al. High fat induces acute and chronic inflammation in the hypothalamus: Effect of high-fat diet, palmitate and TNF-alpha on appetite-regulating NPY neurons. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dexheimer, P.J.; Cochella, L. MicroRNAs: From Mechanism to Organism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, F.J.; Mercader, J.M.; Catalan, V.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Pueyo, N.; Sabater, M.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Anglada, R.; Fernandez-Formoso, J.A.; Ricart, W.; et al. Targeting the circulating microRNA signature of obesity. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacomino, G.; Russo, P.; Marena, P.; Lauria, F.; Venezia, A.; Ahrens, W.; De Henauw, S.; De Luca, P.; Foraita, R.; Gunther, K.; et al. Circulating microRNAs are associated with early childhood obesity: Results of the I.Family Study. Genes Nutr. 2019, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandao, B.B.; Lino, M.; Kahn, C.R. Extracellular miRNAs as mediators of obesity-associated disease. J. Physiol. 2022, 600, 1155–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzaro, G.; Filardi, T.; Sabato, C.; Vacca, A.; Migliaccio, S.; Morano, S.; Ferretti, E. Tissue and circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of response to obesity treatment strategies. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2021, 44, 1159–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oses, M.; Margareto Sanchez, J.; Portillo, M.P.; Aguilera, C.M.; Labayen, I. Circulating miRNAs as Biomarkers of Obesity and Obesity-Associated Comorbidities in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeberger, M.; Altirriba, J.; Garcia, A.; Esteban, Y.; Castano, C.; Garcia-Lavandeira, M.; Alvarez, C.V.; Gomis, R.; Claret, M. Deletion of miRNA processing enzyme Dicer in POMC-expressing cells leads to pituitary dysfunction, neurodegeneration and development of obesity. Mol. Metab. 2012, 2, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinnikov, I.A.; Hajdukiewicz, K.; Reymann, J.; Beneke, J.; Czajkowski, R.; Roth, L.C.; Novak, M.; Roller, A.; Dorner, N.; Starkuviene, V.; et al. Hypothalamic miR-103 protects from hyperphagic obesity in mice. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 10659–10674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, M.; Drori, Y.; Ben-Efraim, Y.J.; Chen, A. Hypothalamic miR-219 regulates individual metabolic differences in response to diet-induced weight cycling. Mol. Metab. 2018, 9, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangiao-Alvarellos, S.; Pena-Bello, L.; Manfredi-Lozano, M.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Cordido, F. Perturbation of hypothalamic microRNA expression patterns in male rats after metabolic distress: Impact of obesity and conditions of negative energy balance. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1838–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derghal, A.; Djelloul, M.; Airault, C.; Pierre, C.; Dallaporta, M.; Troadec, J.D.; Tillement, V.; Tardivel, C.; Bariohay, B.; Trouslard, J.; et al. Leptin is required for hypothalamic regulation of miRNAs targeting POMC 3’UTR. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlwraith, E.K.; Belsham, D.D. Palmitate alters miR-2137 and miR-503-5p to induce orexigenic Npy in hypothalamic neuronal cell models: Rescue by oleate and docosahexaenoic acid. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2023, 35, e13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIlwraith, E.K.; Lieu, C.V.; Belsham, D.D. Bisphenol A induces miR-708-5p through an ER stress-mediated mechanism altering neuronatin and neuropeptide Y expression in hypothalamic neuronal models. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2022, 539, 111480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsham, D.D.; Cai, F.; Cui, H.; Smukler, S.R.; Salapatek, A.M.; Shkreta, L. Generation of a phenotypic array of hypothalamic neuronal cell models to study complex neuroendocrine disorders. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belsham, D.D.; Fick, L.J.; Dalvi, P.S.; Centeno, M.L.; Chalmers, J.A.; Lee, P.K.; Wang, Y.; Drucker, D.J.; Koletar, M.M. Ciliary neurotrophic factor recruitment of glucagon-like peptide-1 mediates neurogenesis, allowing immortalization of adult murine hypothalamic neurons. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2009, 23, 4256–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirera, S.; Busk, P.K. Quantification of miRNAs by a simple and specific qPCR method. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1182, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busk, P.K. A tool for design of primers for microRNA-specific quantitative RT-qPCR. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcells, I.; Cirera, S.; Busk, P.K. Specific and sensitive quantitative RT-PCR of miRNAs with DNA primers. BMC Biotechnol. 2011, 11, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Bell, G.W.; Nam, J.W.; Bartel, D.P. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 2015, 4, e05005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGeary, S.E.; Lin, K.S.; Shi, C.Y.; Pham, T.M.; Bisaria, N.; Kelley, G.M.; Bartel, D.P. The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science 2019, 366, eaav1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B.; Carrington, J.C.; Chen, X.; Dreyfuss, G.; Eddy, S.R.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Marshall, M.; et al. A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 2003, 9, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, B.C.; Axtell, M.J.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P.; Baulcombe, D.; Bowman, J.L.; Cao, X.; Carrington, J.C.; Chen, X.; Green, P.J.; et al. Criteria for annotation of plant MicroRNAs. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 3186–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbach, M.; Schwanhausser, B.; Thierfelder, N.; Fang, Z.; Khanin, R.; Rajewsky, N. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 2008, 455, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, D.; Villen, J.; Shin, C.; Camargo, F.D.; Gygi, S.P.; Bartel, D.P. The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008, 455, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.P.; Lau, N.C.; Garrett-Engele, P.; Grimson, A.; Schelter, J.M.; Castle, J.; Bartel, D.P.; Linsley, P.S.; Johnson, J.M. Microarray analysis shows that some microRNAs downregulate large numbers of target mRNAs. Nature 2005, 433, 769–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nothnick, W.B.; Healy, C.; Hong, X. Steroidal regulation of uterine miRNAs is associated with modulation of the miRNA biogenesis components Exportin-5 and Dicer1. Endocrine 2010, 37, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, T.L.; Bechmann, I.; Naftolin, F.; Kalra, S.P.; Leranth, C. Heterogeneity in the neuropeptide Y-containing neurons of the rat arcuate nucleus: GABAergic and non-GABAergic subpopulations. Brain Res. 1997, 756, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Kalra, P.S.; Crowley, W.R.; Kalra, S.P. Functional heterogeneity in neuropeptide-Y-producing cells in the rat brain as revealed by testosterone action. Endocrinology 1990, 127, 2307–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titolo, D.; Cai, F.; Belsham, D.D. Coordinate regulation of neuropeptide Y and agouti-related peptide gene expression by estrogen depends on the ratio of estrogen receptor (ER) alpha to ERbeta in clonal hypothalamic neurons. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 2080–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Hong, Y.C. MicroRNA expression in response to bisphenol A is associated with high blood pressure. Environ. Int. 2020, 141, 105791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.C.; Long, C.N.; Kinkade, J.A.; Green, M.T.; Martin, R.E.; Marshall, B.L.; Willemse, T.E.; Schenk, A.K.; Mao, J.; Rosenfeld, C.S. Endocrine disruption of gene expression and microRNA profiles in hippocampus and hypothalamus of California mice: Association of gene expression changes with behavioural outcomes. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 32, e12847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kinkade, J.A.; Green, M.T.; Martin, R.E.; Willemse, T.E.; Bivens, N.J.; Schenk, A.K.; Helferich, W.G.; Trainor, B.C.; Fass, J.; et al. Disruption of global hypothalamic microRNA (miR) profiles and associated behavioral changes in California mice (Peromyscus californicus) developmentally exposed to endocrine disrupting chemicals. Horm. Behav. 2021, 128, 104890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, F.; Ru, X.; Wen, T. NRF2, a Transcription Factor for Stress Response and Beyond. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.Q.; Ren, K.; Liu, S.H.; Li, W.M.; Huang, C.J.; Yang, X.H. MicroRNA-140-5p aggravates hypertension and oxidative stress of atherosclerosis via targeting Nrf2 and Sirt2. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meakin, P.J.; Harper, A.J.; Hamilton, D.L.; Gallagher, J.; McNeilly, A.D.; Burgess, L.A.; Vaanholt, L.M.; Bannon, K.A.; Latcham, J.; Hussain, I.; et al. Reduction in BACE1 decreases body weight, protects against diet-induced obesity and enhances insulin sensitivity in mice. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meakin, P.J.; Jalicy, S.M.; Montagut, G.; Allsop, D.J.P.; Cavellini, D.L.; Irvine, S.W.; McGinley, C.; Liddell, M.K.; McNeilly, A.D.; Parmionova, K.; et al. Bace1-dependent amyloid processing regulates hypothalamic leptin sensitivity in obese mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaga, T.; Inui, A.; Okita, M.; Asakawa, A.; Ueno, N.; Kasuga, M.; Fujimiya, M.; Nishimura, N.; Dobashi, R.; Morimoto, Y.; et al. Modest overexpression of neuropeptide Y in the brain leads to obesity after high-sucrose feeding. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1206–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derghal, A.; Astier, J.; Sicard, F.; Couturier, C.; Landrier, J.F.; Mounien, L. Leptin Modulates the Expression of miRNAs-Targeting POMC mRNA by the JAK2-STAT3 and PI3K-Akt Pathways. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangisetty, O.; Chaudhary, S.; Tarale, P.; Cabrera, M.; Sarkar, D.K. miRNA-383 and miRNA-384 suppress proopiomelanocortin gene expression in the hypothalamus: Effects of early life ethanol exposure. Neuroendocrinology 2023, 113, 844–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanidis, S.; Grundler, F.; de Toledo, F.W.; Dimitriou, E.; Tekos, F.; Skaperda, Z.; Kouretas, D.; Doxakis, E. Fasting-mediated metabolic and toxicity reprogramming impacts circulating microRNA levels in humans. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 152, 112187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Zeng, D.; Xiong, J.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.; Xi, Q.; Sun, J.; Ren, X.; et al. The novel importance of miR-143 in obesity regulation. Int. J. Obes. 2023, 47, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frias, F.T.; Rocha, K.C.E.; de Mendonca, M.; Murata, G.M.; Araujo, H.N.; de Sousa, L.G.O.; de Sousa, E.; Hirabara, S.M.; Leite, N.C.; Carneiro, E.M.; et al. Fenofibrate reverses changes induced by high-fat diet on metabolism in mice muscle and visceral adipocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 3515–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromadnikova, I.; Kotlabova, K.; Dvorakova, L.; Krofta, L. Evaluation of Vascular Endothelial Function in Young and Middle-Aged Women with Respect to a History of Pregnancy, Pregnancy-Related Complications, Classical Cardiovascular Risk Factors, and Epigenetics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degano, I.R.; Camps-Vilaro, A.; Subirana, I.; Garcia-Mateo, N.; Cidad, P.; Munoz-Aguayo, D.; Puigdecanet, E.; Nonell, L.; Vila, J.; Crepaldi, F.M.; et al. Association of Circulating microRNAs with Coronary Artery Disease and Usefulness for Reclassification of Healthy Individuals: The REGICOR Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawaf, H.A. Circulating microRNAs and adipokines as markers of metabolic syndrome in adolescents with obesity. Clin Nutr 2019, 38, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xihua, L.; Shengjie, T.; Weiwei, G.; Matro, E.; Tingting, T.; Lin, L.; Fang, W.; Jiaqiang, Z.; Fenping, Z.; Hong, L. Circulating miR-143-3p inhibition protects against insulin resistance in Metabolic Syndrome via targeting of the insulin-like growth factor 2 receptor. Transl. Res. 2019, 205, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auer, E.D.; de Carvalho Santos, D.; de Lima, I.J.V.; Boldt, A.B.W. Non-coding RNA network associated with obesity and rheumatoid arthritis. Immunobiology 2022, 227, 152281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takanabe, R.; Ono, K.; Abe, Y.; Takaya, T.; Horie, T.; Wada, H.; Kita, T.; Satoh, N.; Shimatsu, A.; Hasegawa, K. Up-regulated expression of microRNA-143 in association with obesity in adipose tissue of mice fed high-fat diet. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 376, 728–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Zeng, D.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Chen, X.; Luo, J.; Chen, T.; Xi, Q.; et al. miR-143-null Is against Diet-Induced Obesity by Promoting BAT Thermogenesis and Inhibiting WAT Adipogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benoit, C.; Doubi-Kadmiri, S.; Benigni, X.; Crepin, D.; Riffault, L.; Poizat, G.; Vacher, C.M.; Taouis, M.; Baroin-Tourancheau, A.; Amar, L. miRNA Long-Term Response to Early Metabolic Environmental Challenge in Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Murgia, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Sirakawin, C.; Konovalov, R.; Kovzel, N.; Xu, Y.; Kang, X.; Tiwari, A.; et al. Neuronal miR-29a protects from obesity in adult mice. Mol. Metab. 2022, 61, 101507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Gao, L.; Ning, M.; Wu, F.; Dong, F.; Ni, X.; Wu, Y.; Jing, Q.; Gao, Y. Correlation between decreased plasma miR-29a and vascular endothelial injury induced by hyperlipidemia. Herz 2023, 48, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, E.C.; da Silva, I.B.; Lima, V.M.; Miranda, J.B.; Albuquerque, R.P.; Ferreira, J.C.B.; Barreto-Chaves, M.L.M.; Diniz, G.P. High fat diet reduces the expression of miRNA-29b in heart and increases susceptibility of myocardium to ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9399–9407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.M.; Jeong, H.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, W. Induction of miR-29a by saturated fatty acids impairs insulin signaling and glucose uptake through translational repression of IRS-1 in myocytes. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 2170–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Lee, E.; Zhang, M.; Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Pancreatic β cells control glucose homeostasis via the secretion of exosomal miR-29 family. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavera, J.J.; Dube, M.G.; Kalra, P.S.; Kalra, S.P. Anorectic effects of estrogen may be mediated by decreased neuropeptide-Y release in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Endocrinology 1994, 134, 2367–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S.S.; Belsham, D.D. Leptin differentially regulates NPY secretion in hypothalamic cell lines through distinct intracellular signal transduction pathways. Regul. Pept. 2011, 167, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, C.M.; Belsham, D.D. Insulin directly regulates NPY and AgRP gene expression via the MAPK MEK/ERK signal transduction pathway in mHypoE-46 hypothalamic neurons. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 307, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Hill, J.W.; Levine, J.E. Attenuation of luteinizing hormone surges in neuropeptide Y knockout mice. Neuroendocrinology 2000, 72, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer-Dantoin, A.C.; McDonald, J.K.; Levine, J.E. Neuropeptide Y potentiates luteinizing hormone (LH)-releasing hormone-induced LH secretion only under conditions leading to preovulatory LH surges. Endocrinology 1992, 131, 2946–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besecke, L.M.; Wolfe, A.M.; Pierce, M.E.; Takahashi, J.S.; Levine, J.E. Neuropeptide Y stimulates luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone release from superfused hypothalamic GT1-7 cells. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steuernagel, L.; Lam, B.Y.H.; Klemm, P.; Dowsett, G.K.C.; Bauder, C.A.; Tadross, J.A.; Hitschfeld, T.S.; Del Rio Martin, A.; Chen, W.; de Solis, A.J.; et al. HypoMap-a unified single-cell gene expression atlas of the murine hypothalamus. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 1402–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIlwraith, E.K.; Loganathan, N.; Belsham, D.D. Phoenixin Expression Is Regulated by the Fatty Acids Palmitate, Docosahexaenoic Acid and Oleate, and the Endocrine Disrupting Chemical Bisphenol A in Immortalized Hypothalamic Neurons. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene or miRNA | Forward Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Rpl7 | TCGCAGAGTTGAAGGTGAAG | GCCTGTACTCCTTGTGATAGTG |
| Npy | CAGAAAACGCCCCCAGAA | AAAAGTCGGGAGAACAAGTTTCATT |
| Dicer | TCGAGCCTCCATTGTTGGTC | TGGTCTCCTCCTCGTCATGT |
| Drosha | CCCGGAGAAGAGGCAATCAA | GGTCAGAGGAGCATGTGCAA |
| Dgcr8 | TGCAAAGATGAATCAGTTGATCTGG | TTCCGCTTCATCTCACGGTT |
| Ago2 | TTCCCACTACCACGTGCTTT | GCTTCCTTCAGCGCTGTCAT |
| Esr1 | GAGTGCCAGGCTTTGGGGACTT | CCATGGAGCGCCAGACGAGA |
| Esr2 | ATCTGTCCAGCCACGAATCAGTGT | TCTCCTGGATCCACACTTGACCAT |
| Nrf2 | GGACATGGAGCAAGTTTGGC | CCAGCGAGGAGATCGATGAG |
| Bmal1 | GGGAGGCCCACAGTCAGATT | GTACCAAAGAAGCCAATTCATCAA |
| Mmu-miR-221-3p | GCAGAGCTACATTGTCTGCT | CAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGAAACCCA |
| Mmu-miR-143-3p | CAGTGAGATGAAGCACTGTAG | GGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGAG |
| Mmu-miR-140-5p | CAGCAGTGGTTTTACCCTATG | GGTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTCTAC |
| Mmu-let-7f-1-3p | GCAGCTATACAATCTATTGCCT | GTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGGGA |
| Mmu-let-7b-3p | CAGCTATACAACCTACTGCCT | GTCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTGGGA |
| Mmu-miR-29b-1-5p | GCAGGCTGGTTTCATATGG | TCCAGTTTTTTTTTTTTTTTAAACCAC |
| miRNA | Binding Position in the Npy 3′ UTR | Expression Confidence | Annotation Confidence |
|---|---|---|---|
| mmu-miR-147-5p | 35–41 | Low | High |
| mmu-miR-143-3p | 45–52, 50–57 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-29b-2-5p | 64–70 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-29b-1-5p | 65–71 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-698-5p | 76–87 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-92a-2-5p | 81–87 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-33-5p | 86–92 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-140-5p | 97–103 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-25-5p | 111–117 | High | High |
| mmu-let-7a-1-3p | 139–145 | Low | High |
| mmu-let-7c-2-3p | 139–145 | Low | High |
| mmu-let-7b-3p | 139–145 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-98-3p | 139–145 | Low | High |
| mmu-let-7f-1-3p | 139–145 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-381-3p | 139–145 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-539-3p | 139–145 | Low | High |
| mmu-miR-669b-3p | 140–147 | Low | High |
| mmu-miR-669f-3p | 140–147 | High | High |
| mmu-miR-669c-3p | 148–154 | High | High |
| mHypoE-41 | mHypoE-46 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA Mimic | Npy Expression | Esr2/Esr1 | Npy Expression | Esr2/Esr1 |
| miR-143-3p | ↓ | 1.02 | ~ | 2.16 |
| miR-140-5p | ↓ | 0.92 | ↑ | 1.70 |
| miR-29b-1-5p | ~ | 0.99 | ↑ | 1.68 |
| let-7b-3p | ↓ | 0.96 | ~ | 0.49 |
| let-7f-1-3p | ~ | 0.85 | ~ | 0.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mak, K.W.Y.; He, W.; Loganathan, N.; Belsham, D.D. Bisphenol A Alters the Levels of miRNAs That Directly and/or Indirectly Target Neuropeptide Y in Murine Hypothalamic Neurons. Genes 2023, 14, 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091773
Mak KWY, He W, Loganathan N, Belsham DD. Bisphenol A Alters the Levels of miRNAs That Directly and/or Indirectly Target Neuropeptide Y in Murine Hypothalamic Neurons. Genes. 2023; 14(9):1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091773
Chicago/Turabian StyleMak, Kimberly W. Y., Wenyuan He, Neruja Loganathan, and Denise D. Belsham. 2023. "Bisphenol A Alters the Levels of miRNAs That Directly and/or Indirectly Target Neuropeptide Y in Murine Hypothalamic Neurons" Genes 14, no. 9: 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091773
APA StyleMak, K. W. Y., He, W., Loganathan, N., & Belsham, D. D. (2023). Bisphenol A Alters the Levels of miRNAs That Directly and/or Indirectly Target Neuropeptide Y in Murine Hypothalamic Neurons. Genes, 14(9), 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091773







