Comparison of Growth Performance and Plasma Metabolomics between Two Sire-Breeds of Pigs in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval Statement
2.2. Animals and Sample Collection
2.3. Determination of Growth Performance
2.4. Plasma Sample Preparation for LC-MS/MS
2.5. Instruments and Settings
2.6. Data Processing and Metabolite Identification
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
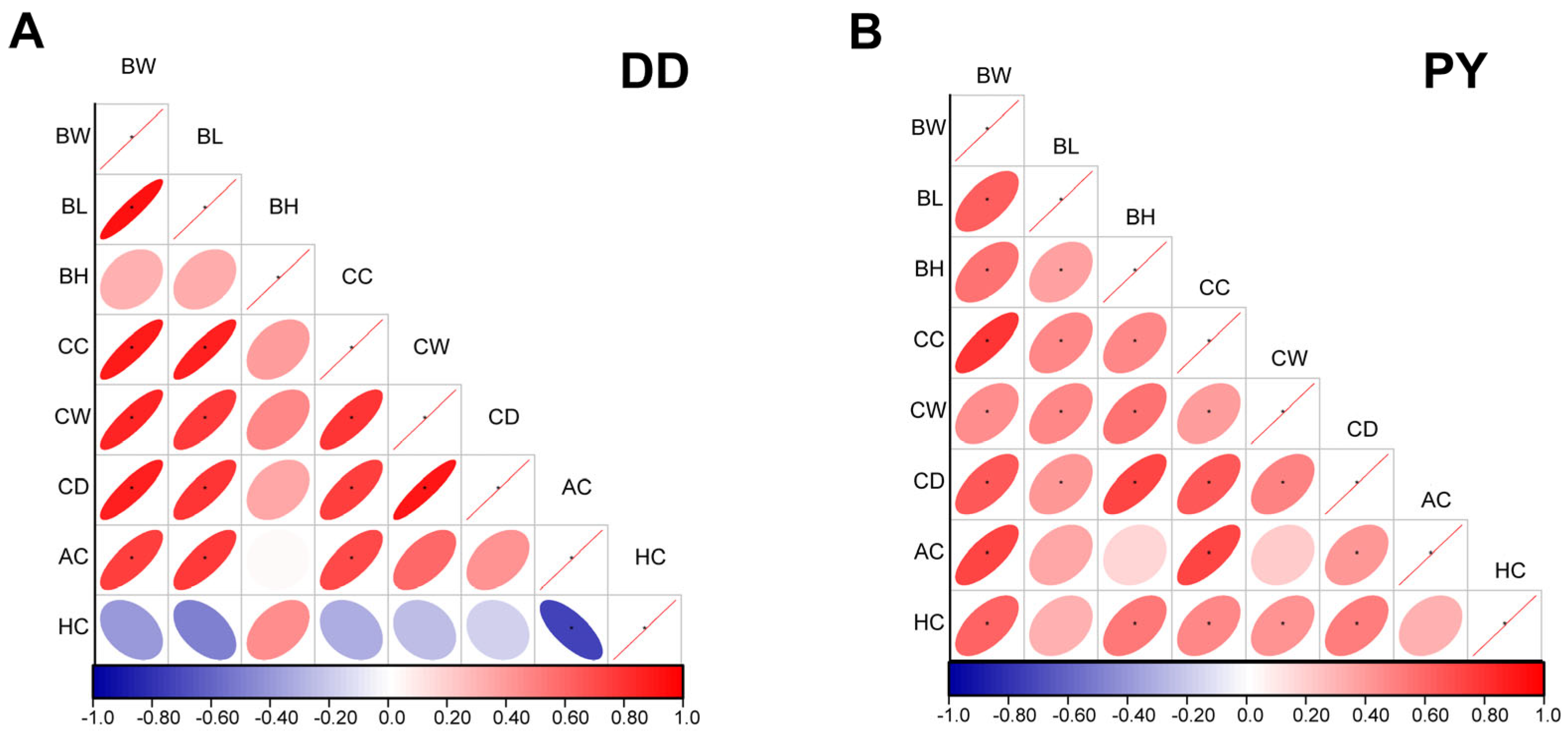
3.1. Determination of Growth Performances of Purebred PY and Purebred Duroc
3.2. Growth Performance of Hybrid Offspring
3.3. Analysis of Plasma Differential Metabolites between Duroc and PY
3.4. Correlation and Functional Enrichment Analysis of Differential Metabolites
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AC | Abdominal circumference |
| BH | Body height |
| BL | Body length |
| BW | Body weight, |
| CC | Chest circumference |
| CD | Chest depth |
| CW | Chest width |
| DLY | Duroc × (Landrace × Yorkshire) |
| FCR | Feed Conversion Ratio |
| HC | Hip circumference |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PY | paternal Yorkshire pigs |
| QC | Quality Control |
| TN | Topigs Norsvin |
| YLY | paternal Yorkshire × (Landrace × Yorkshire) |
References
- Si, R.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H. Unpacking the myth between increased government initiatives and reduced selling of dead live stocks in China: An approach towards exploring hidden danger of zoonotic diseases. One Health 2021, 13, 100344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, N.; Ouyang, G.; Qu, N.; Cui, J.; Qi, Y.; Liao, M.; Jiao, P. A Novel H1N2 Influenza Virus Related to the Classical and Human Influenza Viruses from Pigs in Southern China. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bergamaschi, M.; Tiezzi, F.; Howard, J.; Huang, Y.J.; Gray, K.A.; Schillebeeckx, C.; Mcnulty, N.P.; Maltecca, C. Gut microbiome composition differences among breeds impact feed efficiency in swine. Microbiome 2020, 8, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strathe, A.B.; Danfaer, A.; Sørensen, H.; Kebreab, E. A multilevel nonlinear mixed-effects approach to model growth in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 638–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, L.; Xie, X.; Wu, Z.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, J.; Xiao, S.; Zhou, M.; Ma, J.; et al. Muscle glycogen level and occurrence of acid meat in commercial hybrid pigs are regulated by two low-frequency causal variants with large effects and multiple common variants with small effects. Genet. Sel. Evol. GSE 2019, 51, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Yang, M.; Wang, X.; Quan, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhou, S.; Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Zheng, E.; Cai, G.; et al. Genetic Architecture of Feeding Behavior and Feed Efficiency in a Duroc Pig Population. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, D.N.; Strathe, A.B.; Jensen, J.; Mark, T.; Kadarmideen, H.N. Genetic parameters for different measures of feed efficiency and related traits in boars of three pig breeds. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 91, 4069–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, W.; Li, M.; Li, C. Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Long Intergenic Non-Coding RNAs Contributed to Intramuscular Fat Content Differences between Yorkshire and Wei Pigs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, H.; Yan, H.L.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, B.; Yu, J.; He, J.; Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.H.; Wei, H.; Mao, X.B.; et al. Intestinal microbiota could transfer host Gut characteristics from pigs to mice. Bmc Microbiol. 2016, 16, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalik, E.L.; Willig, L.K.; Rice, B.J.; van Velkinburgh, J.C.; Mohney, R.P.; Mcdunn, J.E.; Dinwiddie, D.L.; Miller, N.A.; Mayer, E.S.; Glickman, S.W.; et al. Renal systems biology of patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; Liu, C.; Feng, C.; Fan, Z.; Dai, Z.; Lai, C.; Li, Z.; Wu, G.; Wang, J. Metabolomic analysis reveals differences in umbilical vein plasma metabolites between normal and growth-restricted fetal pigs during late gestation. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 990–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xia, P.; Lu, Z.; Su, Y.; Zhu, W. Metabolome-Microbiome Responses of Growing Pigs Induced by Time-Restricted Feeding. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 681202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; Luo, J.; Gao, Y.Q.; Yang, X.L.; Guo, T.F.; Li, W.H.; Du, T.Q. Transcriptome-metabolome analysis of fatty acid of Bamei pork and Gansu Black pork in China. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Weng, X. Metabolomic Analysis and Identification of Sperm Freezability-Related Metabolites in Boar Seminal Plasma. Animals 2021, 11, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Yalan, Y.; Ying, L.; Jie, C.; Bing, Y.; Tang, Z. High serum reproductive hormone levels at mid-pregnancy support Meishan pig prolificacy. J. Integr. Agric. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Ajuwon, K.M. Metabolomics of heat stress response in pig adipose tissue reveals alteration of phospholipid and fatty acid composition during heat stress. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 3184–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, C.; Ribeiro, D.; Almeida, A.M.; Larzul, C.; Liaubet, L.; Murani, E. Omics Application in Animal Science-A Special Emphasis on Stress Response and Damaging Behaviour in Pigs. Genes 2020, 11, 920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Otero, Y.; Fernández-López, P.; Delgado-Bermúdez, A.; Nolis, P.; Roca, J.; Miró, J.; Barranco, I.; Yeste, M. Metabolomic fingerprinting of pig seminal plasma identifies in vivo fertility biomarkers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 12, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Ren, Y.; Gao, C.; Jiao, T.; Cai, Y.; Zhao, S. Transcriptome and Metabolome Integration Provides New Insights Into the Regulatory Networks of Tibetan Pig Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells in Response to Hypoxia. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 812411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovo, S.; Mazzoni, G.; Galimberti, G.; Calò, D.G.; Fanelli, F.; Mezzullo, M.; Schiavo, G.; Manisi, A.; Trevisi, P.; Bosi, P.; et al. Metabolomics evidences plasma and serum biomarkers differentiating two heavy pig breeds. Animal 2016, 10, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohart, F.; Paris, A.; Laurent, B.; Canlet, C.; Molina, J.; Mercat, M.J.; Tribout, T.; Muller, N.; Iannuccelli, N.; Villa-Vialaneix, N.; et al. Phenotypic prediction based on metabolomic data for growing pigs from three main European breeds. J. Anim. Sci. 2012, 90, 4729–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropka-Molik, K.; Pawlina-Tyszko, K.; żukowski, K.; Piórkowska, K.; żak, G.; Gurgul, A.; Derebecka, N.; Wesoły, J. Examining the Genetic Background of Porcine Muscle Growth and Development Based on Transcriptome and miRNAome Data. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Yang, X.; Ma, X.; Xiong, Y.; Tian, Z.; Fan, Q.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z. CIDE gene expression in adipose tissue, liver, and skeletal muscle from obese and lean pigs. Journal of Zhejiang University. Sci. B 2017, 18, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyeurt, H.; Gillon, A.; Vanderick, S.; Mayeres, P.; Bertozzi, C.; Gengler, N. Estimation of heritability and genetic correlations for the major fatty acids in bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 4435–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreyesus, G.; Lund, M.S.; Janss, L.; Poulsen, N.A.; Larsen, L.B.; Bovenhuis, H.; Buitenhuis, A.J. Short communication: Multi-trait estimation of genetic parameters for milk protein composition in the Danish Holstein. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 2863–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntawubizi, M.; Colman, E.; Janssens, S.; Raes, K.; Buys, N.; De Smet, S. Genetic parameters for intramuscular fatty acid composition and metabolism in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88, 1286–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ibáñez-Escriche, N.; Magallón, E.; Gonzalez, E.; Tejeda, J.F.; Noguera, J.L. Genetic parameters and crossbreeding effects of fat deposition and fatty acid profiles in Iberian pig lines. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peukert, M.; Zimmermann, S.; Egert, B.; Weinert, C.H.; Schwarzmann, T.; Brüggemann, D.A. Sexual Dimorphism of Metabolite Profiles in Pigs Depends on the Genetic Background. Metabolites 2021, 11, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroeve, J.H.; Saccenti, E.; Bouwman, J.; Dane, A.; Strassburg, K.; Vervoort, J.; Hankemeier, T.; Astrup, A.; Smilde, A.K.; van Ommen, B.; et al. Weight loss predictability by plasma metabolic signatures in adults with obesity and morbid obesity of the DiOGenes study. Obesity 2016, 24, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaz, J.A.; García, S.; González, L.A. The metabolomics profile of growth rate in grazing beef cattle. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, I.; Moorby, J.M.; Fraser, M.D.; Erban, A.; Kopka, J. Relationship between grazing lamb growth rate and blood plasma analytes as profiled by gas chromatography with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC-TOF/MS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rempel, L.A.; Vallet, J.L.; Nonneman, D.J. Characterization of plasma metabolites at late gestation and lactation in early parity sows on production and post-weaning reproductive performance. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotte, J.P. Biological functions of sphingomyelins. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 424–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.L.; Chen, S.S.; Zhong, L.X.; He, K.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Chen, W.W.; Zeng, Q.T.; Tang, S.H. Vitamin D intake as well as circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and risk for the incidence and recurrence of colorectal cancer precursors: A meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 877275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoukalas, D.; Fragoulakis, V.; Papakonstantinou, E.; Antonaki, M.; Vozikis, A.; Tsatsakis, A.; Buga, A.M.; Mitroi, M.; Calina, D. Prediction of Autoimmune Diseases by Targeted Metabolomic Assay of Urinary Organic Acids. Metabolites 2020, 10, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.; Kim, Y. Vitamin D Insufficiency Exacerbates Adipose Tissue Macrophage Infiltration and Decreases AMPK/SIRT1 Activity in Obese Rats. Nutrients 2017, 9, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommelaere, S.; Millet, V.; Gensollen, T.; Bourges, C.; Eeckhoute, J.; Hennuyer, N.; Baugé, E.; Chasson, L.; Cacciatore, I.; Staels, B.; et al. PPARalpha regulates the production of serum Vanin-1 by liver. Febs Lett. 2013, 587, 3742–3748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Liu, S.; Hou, L.; Li, K.; Wang, L.; Gao, K.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Z. Supplemental Choline Modulates Growth Performance and Gut Inflammation by Altering the Gut Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism in Weaned Piglets. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, Z.; Wen, C.; Huang, L. Kunxian Capsule for Rheumatoid Arthritis: Inhibition of Inflammatory Network and Reducing Adverse Reactions Through Drug Matching. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochacka-ćwikła, A.; Mączyński, M.; Czyżnikowska, Ż.; Wiatrak, B.; Jęśkowiak, I.; Czerski, A.; Regiec, A. New Oxazolo[5,4-d]pyrimidines as Potential Anticancer Agents: Their Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro Biological Activity Research. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgard, J.; Valli, M.; Graf, A.B.; Gasser, B.; Mattanovich, D. Biomarkers allow detection of nutrient limitations and respective supplementation for elimination in Pichia pastoris fed-batch cultures. Microb. Cell. Fact. 2017, 16, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; He, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, K.; Lin, H.; Qu, C.; Miao, J. Regulatory Effects of Functional Soluble Dietary Fiber from Saccharina japonica Byproduct on the Liver of Obese Mice with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Heis, S.; Crozier, S.R.; Robinson, S.M.; Harvey, N.C.; Cooper, C.; Inskip, H.M.; Godfrey, K.M. Higher maternal serum concentrations of nicotinamide and related metabolites in late pregnancy are associated with a lower risk of offspring atopic eczema at age 12 months. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romani, M.; Hofer, D.C.; Katsyuba, E.; Auwerx, J. Niacin: An old lipid drug in a new NAD(+) dress. J. Lipid Res. 2019, 60, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, K.; Jiang, F.; Wang, H.; Tang, D.; Liu, D.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; He, X.; et al. The chicken gut metagenome and the modulatory effects of plant-derived benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. Microbiome 2018, 6, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.L.; Nakamura, M.T.; Ma, D. Differentiating the biological effects of linoleic acid from arachidonic acid in health and disease. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 135, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sex | Breed | Age of Days to 100 kg, Days | Average backfat thickness, mm | Eye-muscle area, cm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | PY (n = 15) | 145.07 ± 2.58 ** | 7.69 ± 1.48 | 67.77 ± 3.82 ** |
| Duroc (n = 12) | 162.91 ± 6.73 | 7.6 ± 2.15 | 55.93 ± 7.14 | |
| Female | PY (n = 15) | 145.91 ± 1.51 ** | 7.54 ± 1.33 | 64.75 ± 4.78 ** |
| Duroc (n = 12) | 167.57 ± 7.96 | 8.58 ± 1.73 | 55.07 ± 5.44 |
| Group | Numbers | Days | Weight, kg | Average Daily Feed Intake, g | Feed Conversion Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ‘YLY’ 1 | 1660 | 168.97 | 129.62 | 1942.43 | 2.64 |
| ‘YLY’ 2 | 1141 | 176.67 | 136.31 | 1867.80 | 2.53 |
| ‘YLY’ 3 | 1018 | 174.05 | 144.86 | 1994.52 | 2.49 |
| ‘DLY’ 1 | 1057 | 183.84 | 139.35 | 1831.23 | 2.53 |
| ‘DLY’ 2 | 995 | 179.82 | 136.38 | 1996.62 | 2.76 |
| ‘DLY’ 3 | 1380 | 186.96 | 134.93 | 1707.96 | 2.47 |
| ‘YLY’ # | 3819 | 173.23 ± 3.91 ** | 136.93 ± 7.64 | 1934.92 ± 63.69 | 2.55 ± 0.08 |
| ‘DLY’ # | 3432 | 183.54 ± 3.58 | 136.89 ± 2.25 | 1845.27 ± 144.84 | 2.58 ± 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, Z.; Gan, M.; Du, J.; Du, G.; Luo, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhu, K.; Cheng, W.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Comparison of Growth Performance and Plasma Metabolomics between Two Sire-Breeds of Pigs in China. Genes 2023, 14, 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091706
Xie Z, Gan M, Du J, Du G, Luo Y, Liu B, Zhu K, Cheng W, Chen L, Zhao Y, et al. Comparison of Growth Performance and Plasma Metabolomics between Two Sire-Breeds of Pigs in China. Genes. 2023; 14(9):1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091706
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Zhongwei, Mailin Gan, Junhua Du, Gao Du, Yi Luo, Bin Liu, Kangping Zhu, Wenqiang Cheng, Lei Chen, Ye Zhao, and et al. 2023. "Comparison of Growth Performance and Plasma Metabolomics between Two Sire-Breeds of Pigs in China" Genes 14, no. 9: 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091706
APA StyleXie, Z., Gan, M., Du, J., Du, G., Luo, Y., Liu, B., Zhu, K., Cheng, W., Chen, L., Zhao, Y., Niu, L., Wang, Y., Wang, J., Zhu, L., & Shen, L. (2023). Comparison of Growth Performance and Plasma Metabolomics between Two Sire-Breeds of Pigs in China. Genes, 14(9), 1706. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14091706







