Phylogenetic Analysis of Some Species of the Anopheles hyrcanus Group (Diptera: Culicidae) in China Based on Complete Mitochondrial Genomes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Collection and Species Identification
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction, Library Construction, and Next-Generation Sequencing
2.3. Genomic Assembly and Annotation
2.4. Overall Analysis of Mitochondrial Genome Sequences
2.5. Analysis of Variable Sites in PCGs
2.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overall Composition and Structure of the Mitochondrial Genome
3.2. Structural Analysis of PCGs
3.2.1. Composition and Structure of PCGs
3.2.2. Codon Usage in the Protein-Coding Regions
3.3. tRNA Structure Analysis
3.4. Differential Site Analysis
3.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.5.1. Genetic Distance
3.5.2. Phylogenetic Analysis Based on Sequences of 13 PCGs
3.5.3. Phylogenetic Analysis Based on Single or Combined Coding Regions
3.5.4. Phylogenetic Analysis Based on the Complete Mitochondrial Genome Sequence
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Feng, J.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, S. Epidemiological characteristics of malaria and progress on its elimination in China in 2019. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2020, 38, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Feng, J.; Tu, H.; Yin, J.; Xia, Z. Malaria epidemiology in China in 2020. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2021, 39, 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yi, B.; Xia, Z.; Yin, J. Epidemiological characteristics of malaria in China, 2021. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2022, 40, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.; Levens, J.; Zhou, X. Protecting the gains of malaria elimination in China. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2020, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. The malaria situation in the People’s Republic of China. Bull. World Health Organ. 1981, 59, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, L.; Tu, H.; Xia, Z. Vector control in China, from malaria endemic to elimination and challenges ahead. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2022, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbach, R. The classification of genus Anopheles (Diptera: Culicidae): A working hypothesis of phylogenetic relationships. Bull. Èntomol. Res. 2004, 94, 537–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bortel, W.; Trung, H.D.; Roelants, P.; Harbach, R.E.; Backeljau, T.; Coosemans, M. Molecular identification of Anopheles minimus s.l. beyond distinguishing the members of the species complex. Insect Mol. Biol. 2000, 9, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohuet, A.; Toto, J.C.; Simard, F.; Kengne, P.; Fontenille, D.; Coetzee, M. Species identification within the Anopheles funestus group of malaria vectors in Cameroon and evidence for a new species. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 69, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennessen, J.A.; Ingham, V.A.; Toé, K.H.; Guelbéogo, W.M.; Sagnon, N.; Kuzma, R.; Ranson, H.; Neafsey, D.E. A population genomic unveiling of a new cryptic mosquito taxon within the malaria-transmitting Anopheles gambiae complex. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, J. Progress of taxonomic study on the Anopheline mosquitoes in China. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2015, 26, 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, J. The Hyrcanus group of Anopheles (Anopheles) in China (Diptera: Culicidae): Species discrimination and phylogenetic relationships inferred by ribosomal DNA internal transcribed spacer 2 sequences. J. Med. Entomol. 2005, 42, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, U.W. Revisited ITS2 phylogeny of Anopheles (Anopheles) Hyrcanus group mosquitoes: Reexamination of unidentified and misidentified ITS2 sequences. Parasitol. Res. 2007, 101, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rueda, L.M. Two new species of Anopheles (Anopheles) Hyrcanus Group (Diptera: Culicidae) from the Republic of South Korea. Zootaxa 2005, 941, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Cao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xi, Y.; Chen, H. Interspecific relationship between Anopheles kunmingensis and Anopheles liangshanensis. Sichuan J. Zool. 1992, 11, 30–31. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Lei, X. Comparison of rDNA-ITS2 sequences and morphological characters of Anopheles kunmingensis and Anopheles langshanensis in China, with discussion on taxonomic status. Chin. J. Parasitol. Parasit. Dis. 2000, 18, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Ponçon, N.; Toty, C.; Kengne, P.; Alten, B.; Fontenille, D. Molecular evidence for similarity between Anopheles hyrcanus (Diptera: Culicidae) and Anopheles pseudopictus (Diptera: Culicidae), sympatric potential vectors of malaria in France. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 576–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djadid, N.D.; Jazayeri, H.; Gholizadeh, S.; Rad, S.P.; Zakeri, S. First record of a new member of Anopheles Hyrcanus Group from Iran: Molecular identification, diagnosis, phylogeny, status of kdr resistance and Plasmodium infection. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taai, K.; Baimai, V.; Saeung, A.; Thongsahuan, S.; Min, G.-S.; Otsuka, Y.; Park, M.-H.; Fukuda, M.; Somboon, P.; Choochote, W. Genetic compatibility between Anopheles lesteri from Korea and Anopheles paraliae from Thailand. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2013, 108, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beebe, N.W. DNA barcoding mosquitoes: Advice for potential prospectors. Parasitology 2018, 145, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.M.; Lee, Y.; Kitchen, A.; Collier, T.; Pringle, J.C.; Muleba, M.; Irish, S.; Stevenson, J.C.; Coetzee, M.; Cornel, A.J.; et al. Complete Anopheles funestus mitogenomes reveal an ancient history of mitochondrial lineages and their distribution in southern and central Africa. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.F.; Machado, L.C.; de Paula, M.B.; Vieira, C.J.D.S.P.; Bronzoni, R.V.D.M.; Santos, M.A.V.D.M.; Wallau, G.L. Culicidae evolutionary history focusing on the Culicinae subfamily based on mitochondrial phylogenomics. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.-J.; He, Z.; Li, W.; Si, F.; Tang, Y.; He, Q.; Qiao, L.; Yan, Z.; Fu, W.; et al. De novo transcriptome sequencing and sequence analysis of the malaria vector Anopheles sinensis (Diptera: Culicidae). Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Yan, Z.; Fu, W.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Chen, B. Complete mitogenomes of Anopheles peditaeniatus and Anopheles nitidus and phylogenetic relationships within the genus Anopheles inferred from mitogenomes. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-P.; Zhang, P.-Y.; Xu, S.; Tang, J.-X.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Li, J.-L.; Wang, D.-J.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Fang, Q.; Xia, H.; et al. The complete mitochondrial genome of major malaria vector Anopheles anthropophagus (Diptera: Culicidae) in China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 2022, 7, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, W.J.; Kim, H.C.; Ryu, J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Chong, S.T.; Klein, T.A.; Choi, K.S. Multiplex PCR assay for the identification of eight Anopheles species belonging to the Hyrcanus, Barbirostris and Lindesayi groups. Malar. J. 2021, 20, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierckxsens, N.; Mardulyn, P.; Smits, G. NOVOPlasty: De novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 45, e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, S. MitoZ: A toolkit for animal mitochondrial genome assembly, annotation and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. jModelTest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Zou, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xu, W.; Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Fu, W.; Li, T.; Chen, B. Complete mitochondrial genomes of Anopheles stephensi and An. dirus and comparative evolutionary mitochondriomics of 50 mosquitoes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Villegas, L.; Assis-Geraldo, J.; Koerich, L.; Collier, T.C.; Lee, Y.; Main, B.; Rodrigues, N.B.; Orfano, A.S.; Pires, A.C.A.M.; Campolina, T.B.; et al. Characterization of the complete mitogenome of Anopheles aquasalis, and phylogenetic divergences among Anopheles from diverse geographic zones. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, B.L.S.; da Silva, F.S.; Nunes-Neto, J.P.; de Almeida Medeiros, D.B.; Cruz, A.C.R.; da Silva, S.P.; da Silva ESilva, L.H.; de Oliveira Monteiro, H.A.; Dias, D.D.; Vieira, D.B.R.; et al. First Description of the Mitogenome and Phylogeny of Culicinae Species from the Amazon Region. Genes 2021, 12, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.M.P.; Foster, P.G.; Bergo, E.S.; Nagaki, S.S.; Sanabani, S.S.; Marinotti, O.; Marinotti, P.N.; Sallum, M.A.M. Mitochondrial Genomes of Anopheles (Kerteszia) (Diptera: Culicidae) From the Atlantic Forest Brazil. J. Med. Entomol. 2016, 53, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, F.S.; Cruz, A.C.R.; Medeiros, D.B.D.A.; da Silva, S.P.; Nunes, M.R.T.; Martins, L.C.; Chiang, J.O.; Lemos, P.D.S.; Cunha, G.M.; de Araujo, R.F.; et al. Mitochondrial genome sequencing and phylogeny of Haemagogus albomaculatus, Haemagogus leucocelaenus, Haemagogus spegazzinii, and Haemagogus tropicalis (Diptera: Culicidae). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.-Y.; Peng, H.; Ma, Y.-J. Sequencing and analysis of the complete mitochondrial genome in Anopheles sinensis (Diptera: Culicidae). Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.; Li, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, H.; Luo, P.; Wu, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhao, T. The phylogenetic relationships of known mosquito (Diptera: Culicidae) mitogenomes. Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2018, 29, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva E Silva, L.H.; Da Silva, F.S.; Medeiros, D.B.D.A.; Cruz, A.C.R.; da Silva, S.P.; Aragão, A.D.O.; Dias, D.D.; Sena Do Nascimento, B.L.; Júnior, J.W.R.; Vieira, D.B.R.; et al. Description of the mitogenome and phylogeny of Aedes spp. (Diptera: Culicidae) from the Amazon region. Acta Trop. 2022, 232, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes-Esquivel, C.; Harbach, R.E.; Townson, H. Molecular taxonomy of members of the Anopheles hyrcanus group from Thailand and Indonesia. Med. Vet. Èntomol. 2011, 25, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.; Chiang, L.; Hapuarachchi, H.C.; Tan, C.; Pang, S.; Lee, R.; Lee, K.; Ng, L.; Lam-Phua, S. DNA barcoding: Complementing morphological identification of mosquito species in Singapore. Parasites Vectors 2014, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lin, L.; Wang, Y. Phylogenetic relationship among some species of genus Anopheles subgenus Anopheles (Diptera: Culicidae) in China: Based on rDNA-ITS2 sequences. Chin. J. Vector Biol. Control 2013, 24, 382–388. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Luo, S.; Gao, M.; Tao, F.; Gao, J.; Chen, H.; Li, X.; Peng, H.; Ma, Y. Phylogeny of certain members of Hyrcanus group (Diptera: Culicidae) in China based on mitochondrial genome fragments. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2019, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Shi, W.-Q.; Zhang, Y. Molecular phylogeny of Anopheles hyrcanus group (Diptera: Culicidae) based on mtDNA COI. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2017, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, R.; Wu, L.; Luo, C.; Guo, X.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y. Molecular phylogeny of the Anopheles hyrcanus group (Diptera: Culicidae) based on rDNA–ITS2 and mtDNA–COII. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, P.G.; de Oliveira, T.M.P.; Bergo, E.S.; Conn, J.E.; Sant’ana, D.C.; Nagaki, S.S.; Nihei, S.; Lamas, C.E.; González, C.; Moreira, C.C.; et al. Phylogeny of Anophelinae using mitochondrial protein coding genes. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morón-López, J.; Vergara, K.; Sato, M.; Gajardo, G.; Ueki, S. Intraspecies variation of the mitochondrial genome: An evaluation for phylogenetic approaches based on the conventional choices of genes and segments on mitogenome. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
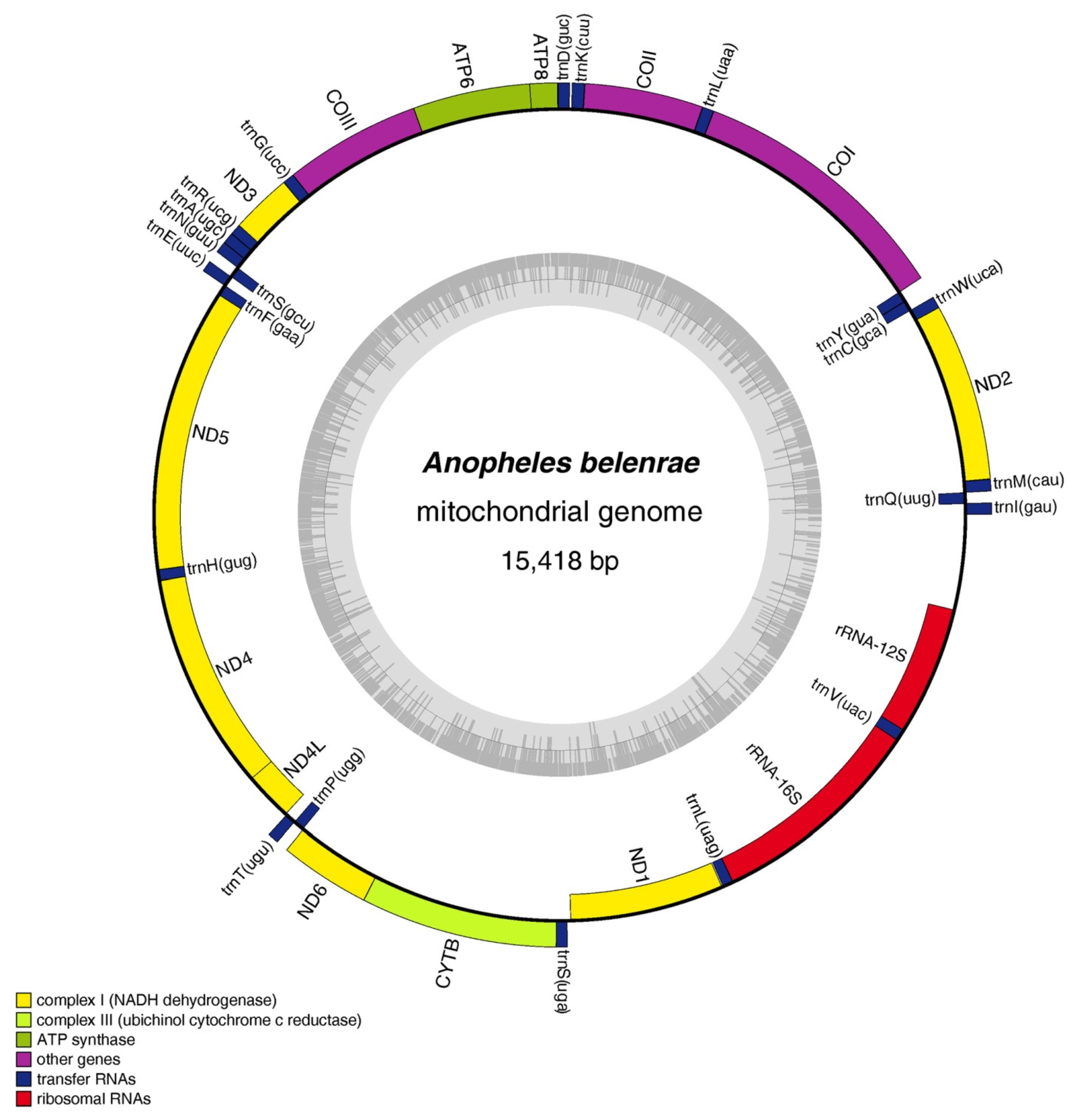
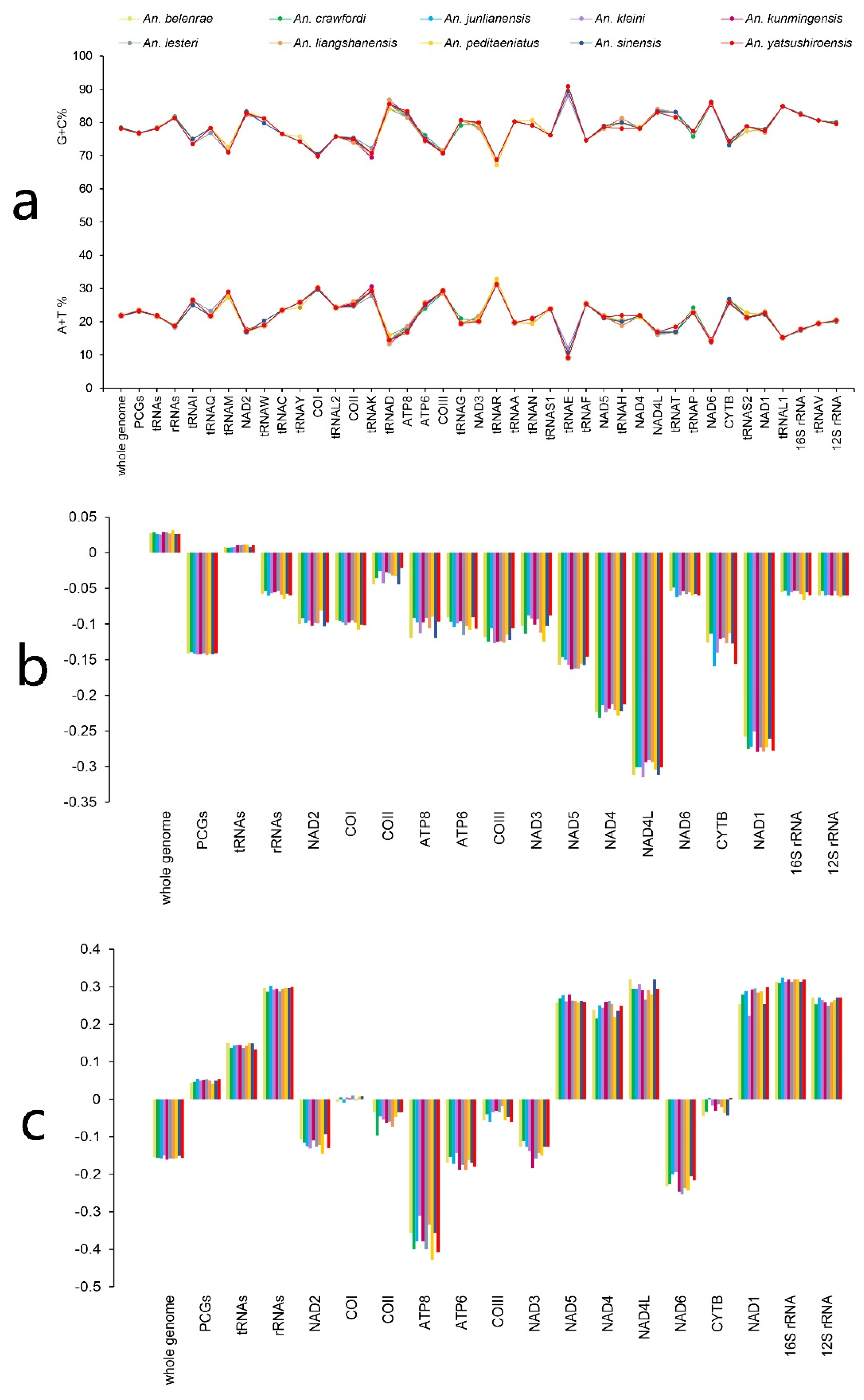
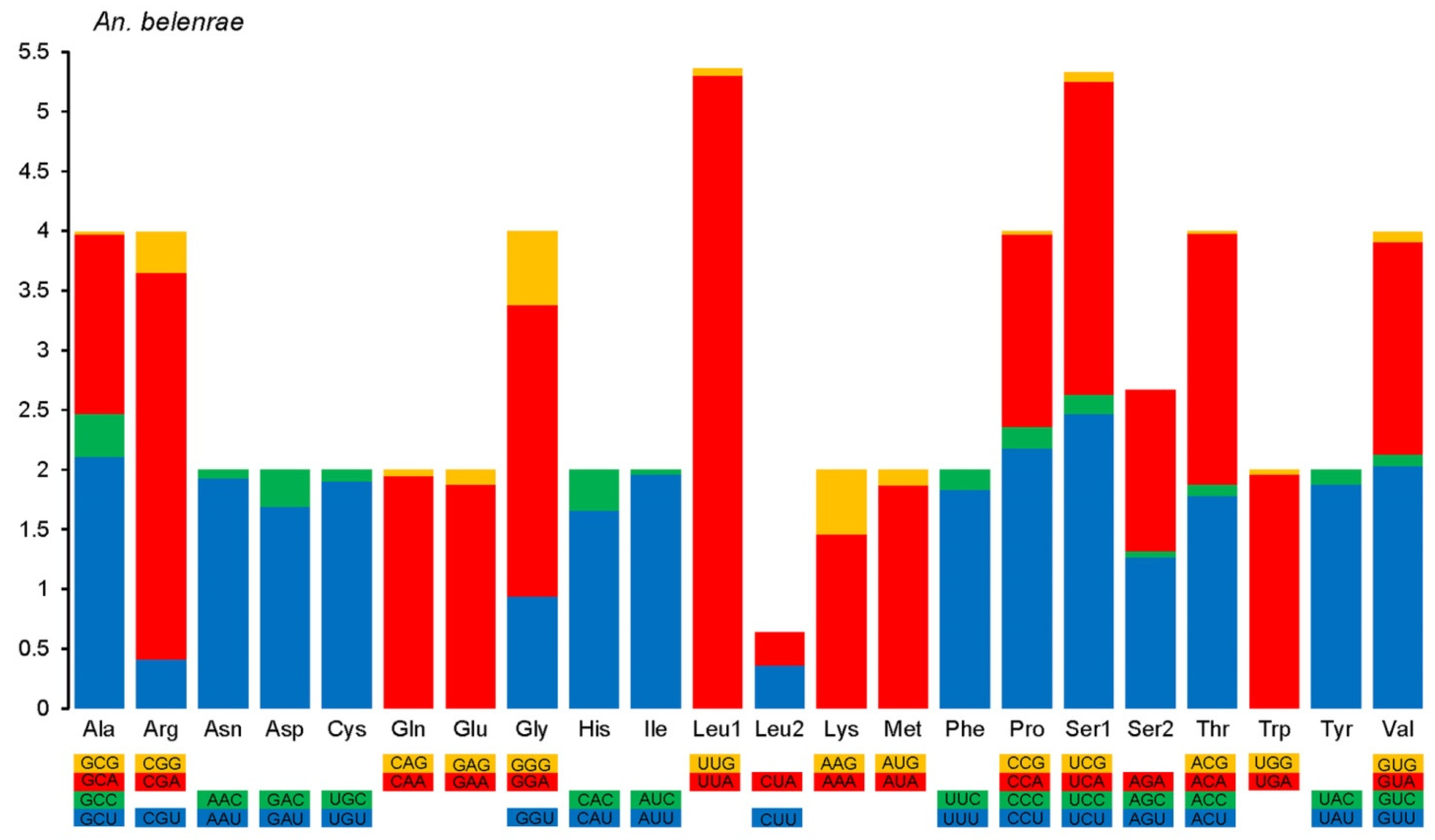

| Species | Collection Site | Year | Coordinate | Raw Data Reads | Clean Data Reads | Mapped Reads | Mean Depth |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| An. belenrae * | Jining City, Shandong Province, China | 1999 | 116.50° E, 35.32° N | 147,214,292 | 143,104,848 | 162,947 | 5755 |
| An. crawfordi * | Puer City, Yunnan Province, China | 2005 | 101.08° E, 22.77° N | 90,487,882 | 85,354,442 | 826,314 | 7538 |
| An. junlianensis * | Junlian City, Sichuan Province, China | 1997 | 104.50° E, 28.15° N | 119,378,626 | 114,520,300 | 9971 | 83 |
| An. kleini * | Suifenhe City, Heilongjiang Province, China | 2018 | 131.15° E, 44.41° N | 87,311,928 | 87,130,712 | 163,512 | 1438 |
| An. kunmingensis * | Kunming City, Yunnan Province, China | 1997 | 102.61° E, 24.80° N | 88,922,520 | 86,777,074 | 475,510 | 4387 |
| An. lesteri | Pujiang City, Sichuan Province, China | 2006 | 103.51° E, 30.20° N | 57,068,184 | 56,937,040 | 266,795 | 2553 |
| An. liangshanensis * | Zhaojue City, Sichuan Province, China | 1997 | 102.80° E, 28.01° N | 80,987,418 | 80,314,882 | 714,708 | 6716 |
| An. peditaeniatus | Meilan District, Hainan Province, China | 2013 | 110.51° E, 19.99° N | 101,979,708 | 91,150,574 | 48,331 | 396 |
| An. sinensis | Jiuzhaigou City, Sichuan Province, China | 2015 | 104.28° E, 33.24° N | 121,676,660 | 120,939,142 | 1,180,177 | 7656 |
| An. yatsushiroensis * | Donggang City, Liaoning Province, China | 2000 | 124.15° E, 39.86° N | 117,486,358 | 114,193,620 | 162,947 | 1511 |
| ATP6 | ATP8 | COI | COII | COIII | CYTB | ND1 | ND2 | ND3 | ND4 | ND4L | ND5 | ND6 | PCGs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of sites | 681 | 162 | 1537 | 685 | 787 | 1137 | 945 | 1026 | 354 | 1342 | 300 | 1743 | 525 | 11,224 | |
| Single base substitution (transitions: transversions) | SIN and BEL | N | N | 7:2 | N | 2:0 | 5:0 | 2:1 | 7:0 | N | 5:0 | N | 3:0 | 2:0 | 33:3 |
| SIN and KLE | 10:2 | 0:1 | 23:5 | 4:3 | 9:0 | 20:4 | 21:5 | 14:2 | 1:1 | 31:2 | 0:1 | 21:7 | 3:0 | 157:33 | |
| KLE and BEL | 10:2 | 0:1 | 25:5 | 4:3 | 9:0 | 19:4 | 22:4 | 17:2 | 1:1 | 30:2 | 0:1 | 20:7 | 3:0 | 160:32 | |
| JUN and YAT | 2:1 | 2:0 | 20:0 | 2:2 | 4:0 | 8:3 | 3:0 | 7:0 | N | 9:1 | N | 13:1 | 3:0 | 73:8 | |
| KUN and LIA | 6:2 | 1:0 | 10:3 | 3:2 | 7:3 | 7:1 | 15:0 | 12:2 | 3:0 | 15:5 | N | 22:3 | 1:0 | 102:21 | |
| PED and CRA | 21:20 | 5:4 | 35:24 | 21:11 | 19:13 | 40:28 | 24:20 | 29:8 | 6:5 | 42:28 | 7:3 | 52:31 | 11:5 | 312:201 | |
| Total amino acid number | 227 | 54 | 512 | 228 | 262 | 379 | 315 | 342 | 118 | 447 | 100 | 581 | 175 | 3741 | |
| Amino acid mutation (synonymous: non-synonymous) | SIN and BEL | N | N | 8:1 | N | 2:0 | 5:0 | 3:0 | 5:2 | N | 5:0 | N | 3:0 | 2:0 | 33:3 |
| SIN and KLE | 11:1 | 0:1 | 28:0 | 7:0 | 8:1 | 24:0 | 24:1 | 14:2 | 2:0 | 30:1 | 1:0 | 28:0 | 3:0 | 180:7 | |
| KLE and BEL | 11:1 | 0:1 | 29:1 | 7:0 | 8:1 | 23:0 | 24:1 | 19:0 | 2:0 | 29:1 | 1:0 | 27:0 | 3:0 | 183:6 | |
| JUN and YAT | 3:0 | 2:0 | 20:0 | 4:0 | 4:0 | 11:0 | 3:0 | 6:1 | N | 10:0 | N | 14:0 | 3:0 | 80:1 | |
| KUN and LIA | 8:0 | 0:1 | 13:0 | 5:0 | 10:0 | 8:0 | 15:0 | 14:0 | 3:0 | 18:2 | N | 24:1 | 1:0 | 119:4 | |
| PED and CRA | 39:1 | 9:0 | 59:0 | 32:0 | 30:2 | 67:0 | 42:2 | 37:0 | 10:1 | 70:0 | 9:1 | 79:4 | 14:2 | 497:13 |
| BEL | CRA | JUN | KLE | KUN | LES | LIA | PED | SIN | YAT | BAR | LIN | DIR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRA | 0.048 | ||||||||||||
| JUN | 0.040 | 0.049 | |||||||||||
| KLE | 0.017 | 0.049 | 0.042 | ||||||||||
| KUN | 0.042 | 0.051 | 0.035 | 0.041 | |||||||||
| LES | 0.041 | 0.048 | 0.037 | 0.042 | 0.037 | ||||||||
| LIA | 0.044 | 0.053 | 0.036 | 0.042 | 0.011 | 0.036 | |||||||
| PED | 0.049 | 0.046 | 0.049 | 0.049 | 0.050 | 0.050 | 0.052 | ||||||
| SIN | 0.003 | 0.048 | 0.039 | 0.017 | 0.041 | 0.041 | 0.043 | 0.048 | |||||
| YAT | 0.040 | 0.050 | 0.007 | 0.042 | 0.036 | 0.036 | 0.038 | 0.049 | 0.040 | ||||
| BAR | 0.077 | 0.075 | 0.076 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.078 | 0.081 | 0.075 | 0.077 | 0.076 | |||
| LIN | 0.088 | 0.086 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.090 | 0.091 | 0.089 | 0.088 | 0.091 | 0.090 | ||
| DIR | 0.096 | 0.095 | 0.097 | 0.099 | 0.100 | 0.100 | 0.101 | 0.099 | 0.096 | 0.097 | 0.097 | 0.101 | |
| MIN | 0.095 | 0.093 | 0.096 | 0.098 | 0.097 | 0.096 | 0.098 | 0.096 | 0.095 | 0.096 | 0.090 | 0.098 | 0.098 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, H.; Yuan, H.; Yang, X.; Shan, W.; Zhou, Q.; Tao, F.; Zhao, C.; Bai, J.; Li, X.; Ma, Y.; et al. Phylogenetic Analysis of Some Species of the Anopheles hyrcanus Group (Diptera: Culicidae) in China Based on Complete Mitochondrial Genomes. Genes 2023, 14, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14071453
Dong H, Yuan H, Yang X, Shan W, Zhou Q, Tao F, Zhao C, Bai J, Li X, Ma Y, et al. Phylogenetic Analysis of Some Species of the Anopheles hyrcanus Group (Diptera: Culicidae) in China Based on Complete Mitochondrial Genomes. Genes. 2023; 14(7):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14071453
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Haowei, Hao Yuan, Xusong Yang, Wenqi Shan, Qiuming Zhou, Feng Tao, Chunyan Zhao, Jie Bai, Xiangyu Li, Yajun Ma, and et al. 2023. "Phylogenetic Analysis of Some Species of the Anopheles hyrcanus Group (Diptera: Culicidae) in China Based on Complete Mitochondrial Genomes" Genes 14, no. 7: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14071453
APA StyleDong, H., Yuan, H., Yang, X., Shan, W., Zhou, Q., Tao, F., Zhao, C., Bai, J., Li, X., Ma, Y., & Peng, H. (2023). Phylogenetic Analysis of Some Species of the Anopheles hyrcanus Group (Diptera: Culicidae) in China Based on Complete Mitochondrial Genomes. Genes, 14(7), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14071453





