Comparitive Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Houpoea Plants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chloroplast DNA Extraction
2.2. Annotation and Physical Map Drawing
2.3. SSR and Repeat Sequences Analysis
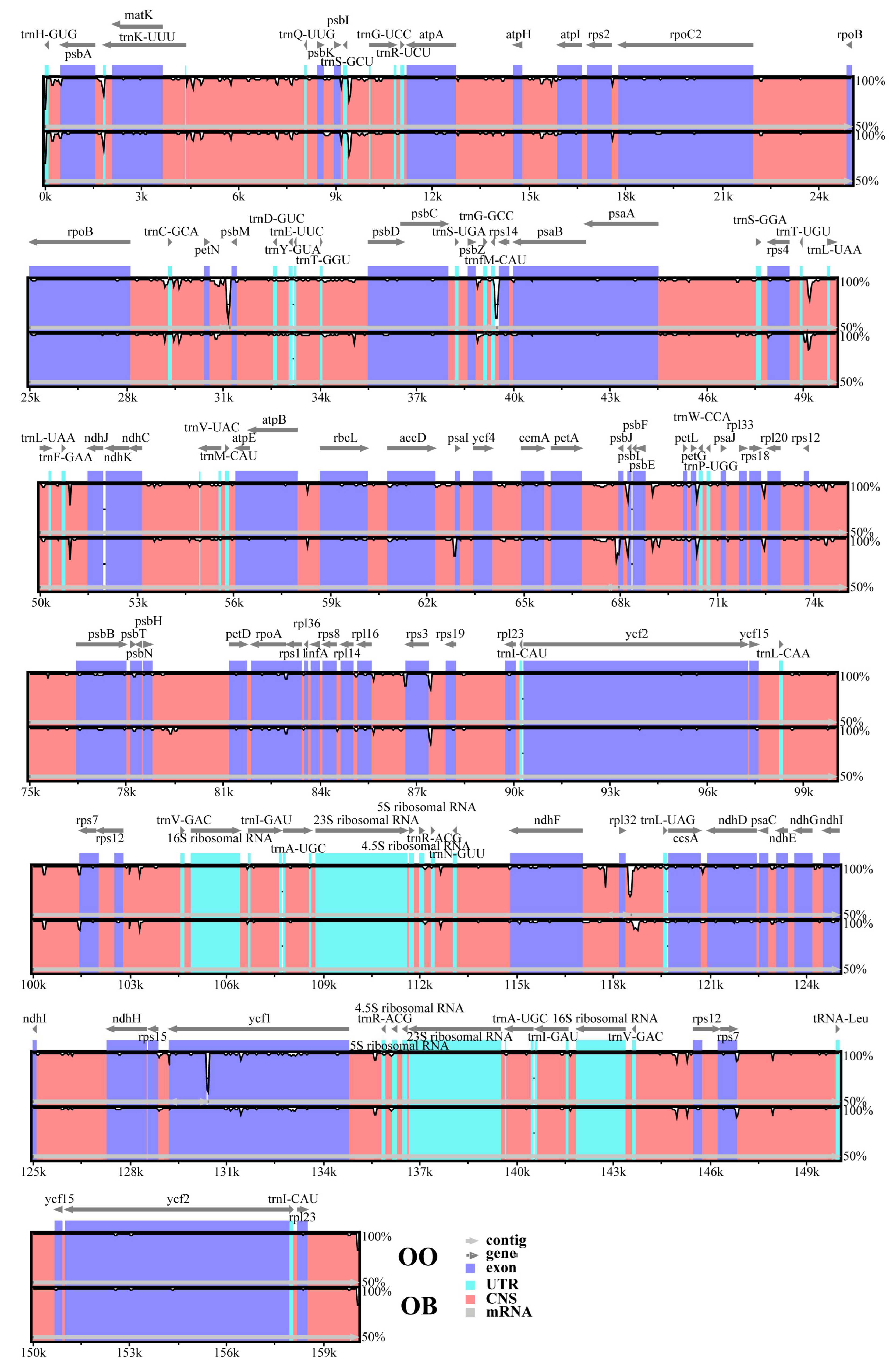
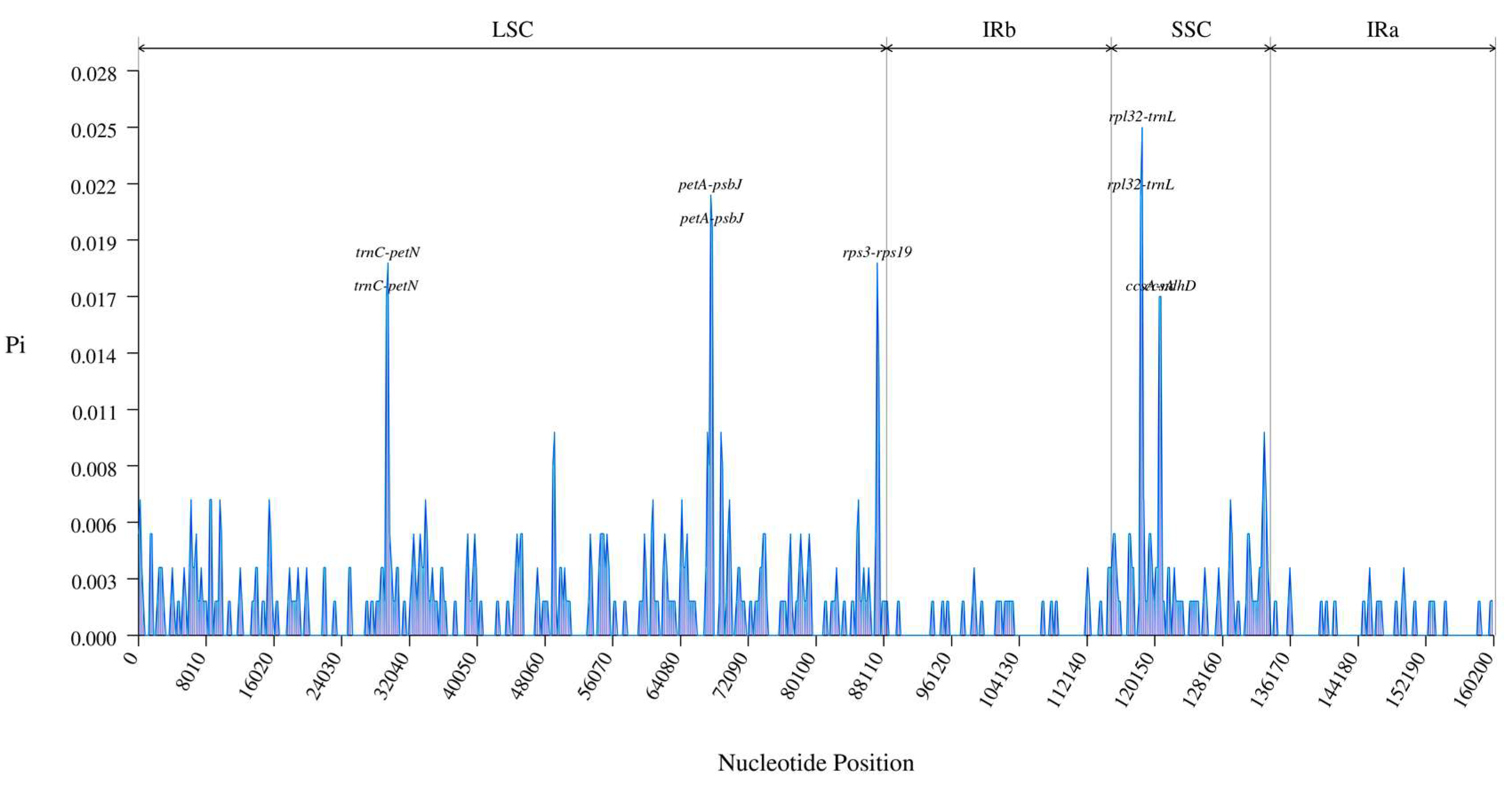
2.4. Genomic Comparative Analysis
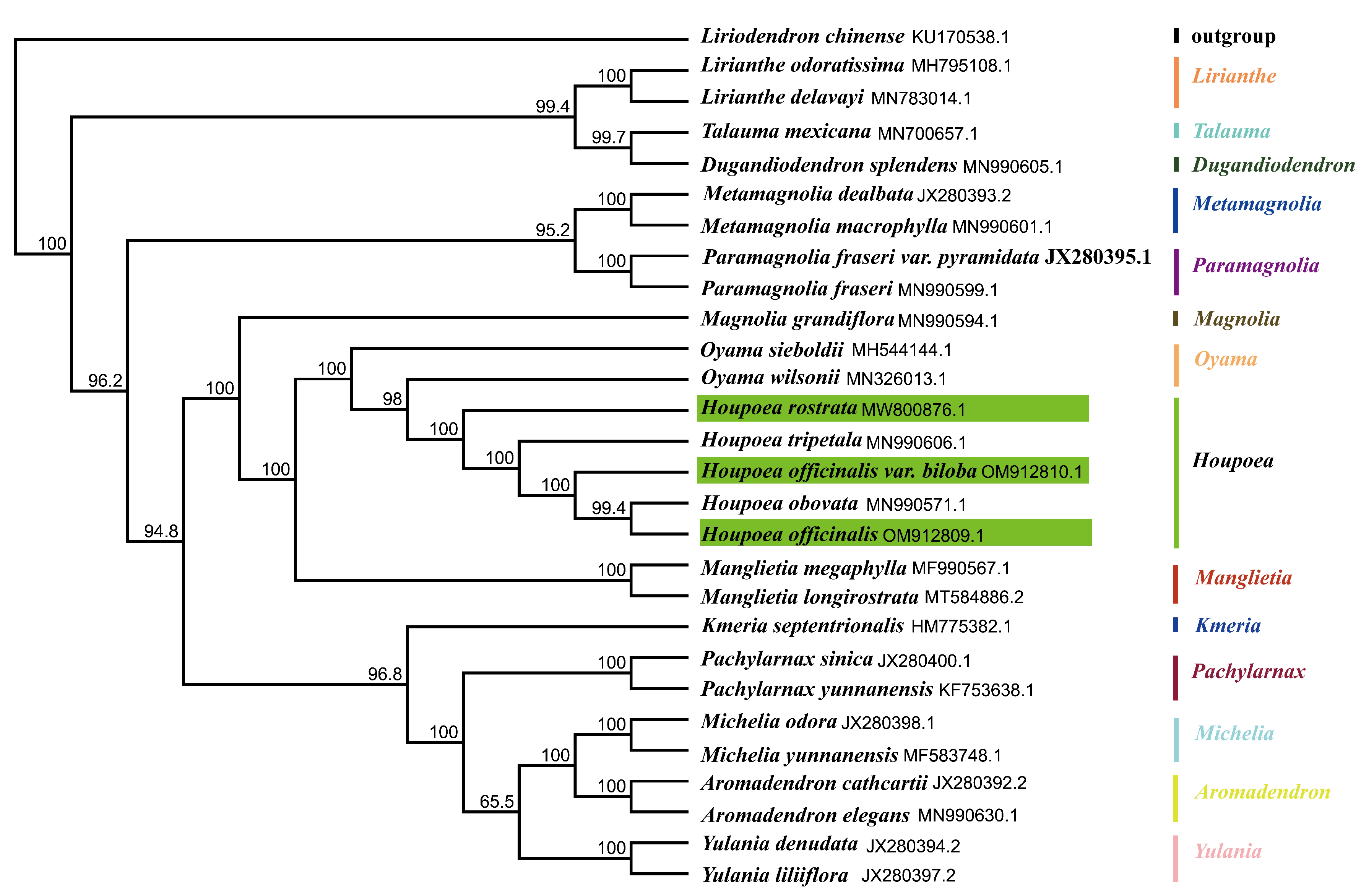
2.5. Phylogenesis Analysis
3. Results
3.1. CPG Organizations
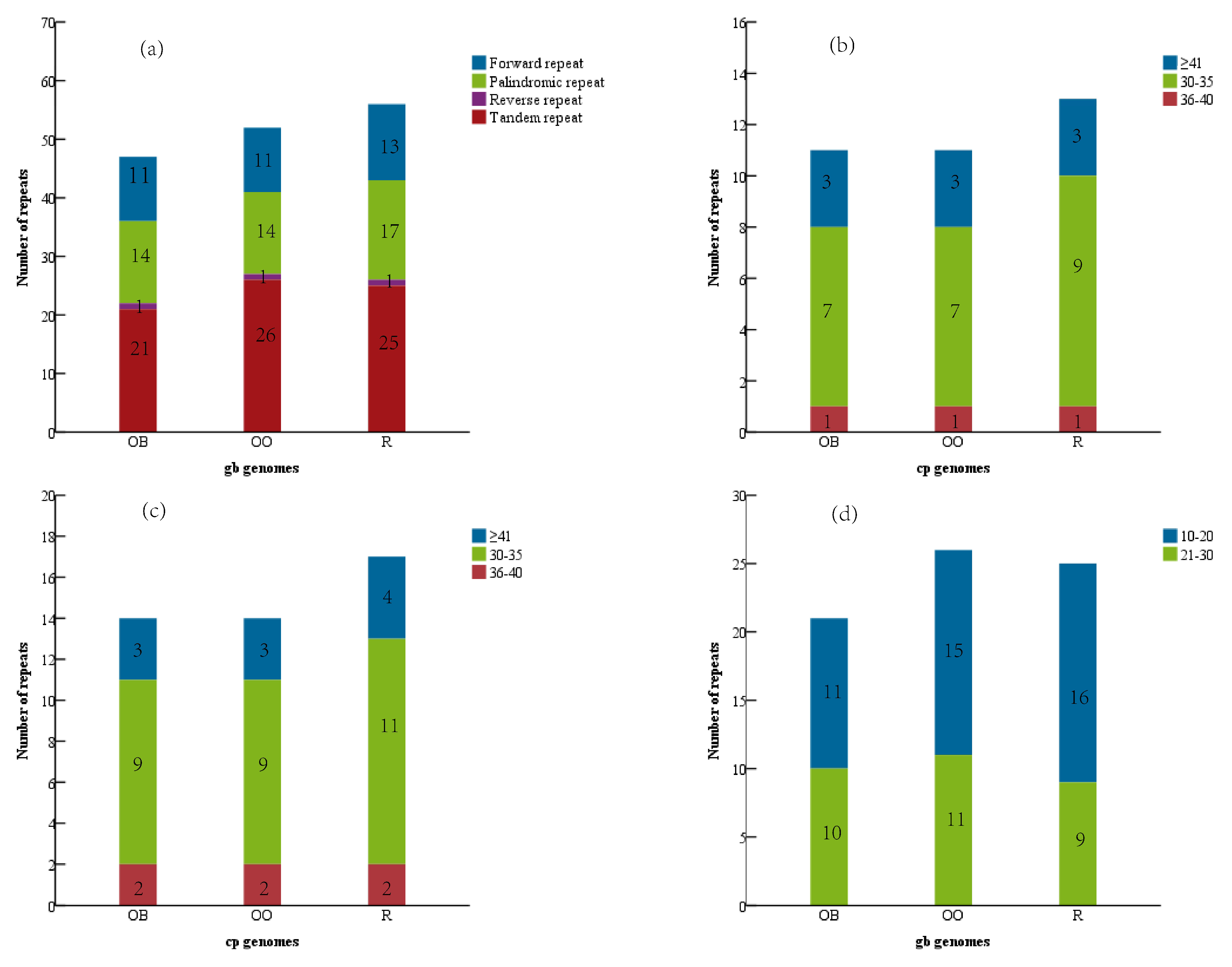
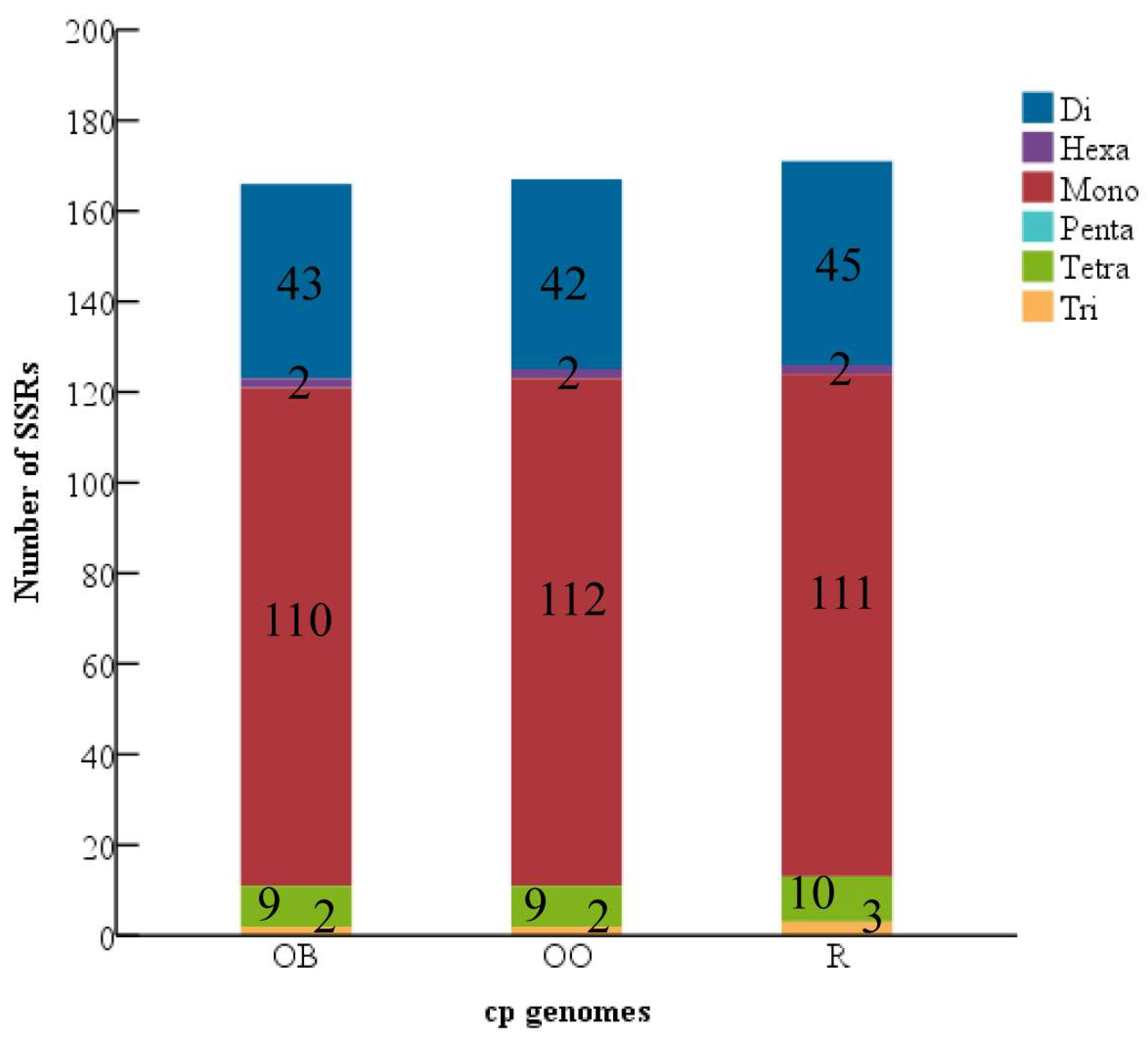
3.2. Analysis of the Repeat and the SSRs
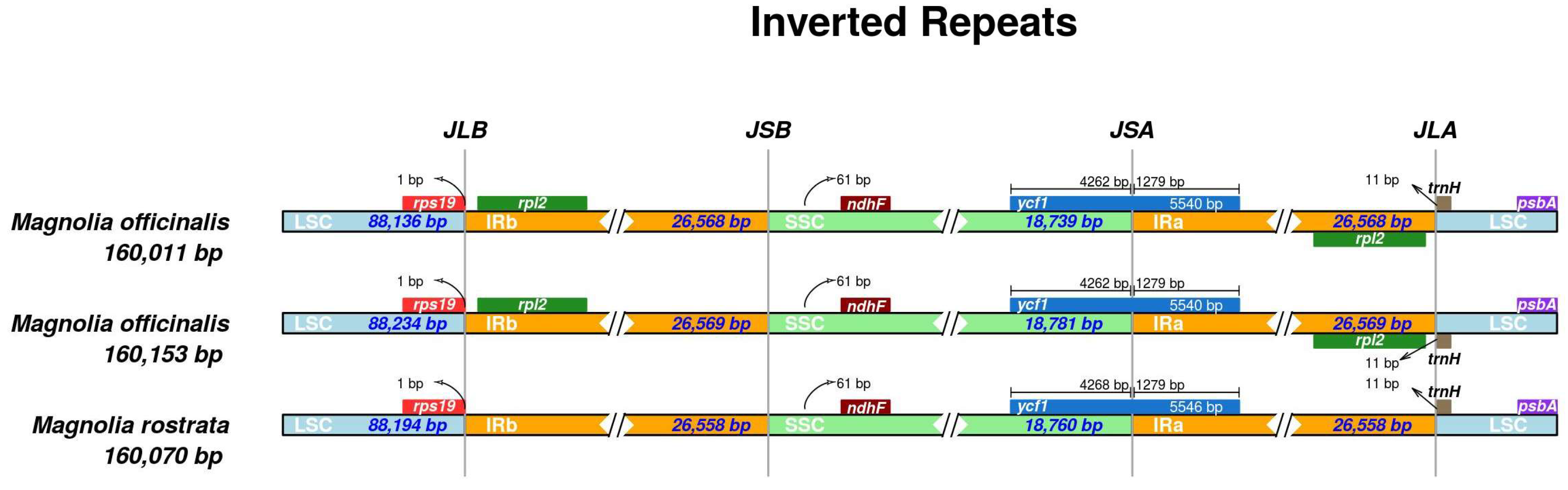
3.3. Comparative Genomics
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3.5. Plant Morphology
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xia, N.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Nooteboom, H.P. Magnoliaceae. Flora China 2008, 7, 48–91. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Liu, J. Determination of magnolol and honokiol in Magnolia officinalis and Lirianthe henryi. Acta Pharm. Sin. 1982, 5, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China (A), 2020th ed.; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; pp. 263–264.
- Li, L. Win-win green reconstruction. Chengdu Daily, 13 April 2011; 003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, R.Y.; Liang, K.H. A preliminary study on phytocoenological characteristics of Parakmeria omeiensis community. Guihaia 1993, 13, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Fan, J.C.; Lu, C.T.; Zhao, B. Biological characteristics and conservation measures of an threatened species Magnolia omeiensis. Sci. Tech. Sichuan Agric. 2015, 4, 22–25. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.P.; Wen, X.Y.; Li, C.H. The reintroduction of Parakmeria omeiensis Cheng, a Critically Endangered endemic plant. In Conservation and Reintroduction of Rare and Endangered Plants in China; Ren, H., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Juck, Z.; Wu, J.; Huang, Z.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y. Studies on the chemical constituents of the leaves of Houpoea officinalis var. biloba. Fujian J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 49, 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, B. Pharmacological research progress of Magnolia officinalis. J. Chongqing Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2005, 28, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L. Chemical constituents of volatile oil from Magnolia officinalis. Chin. Herb. Med. 2001, 08, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, N.-H. A new classification system of the family Magnoliaceae. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on the Family Magnoliaceae, Guangzhou, China, 5–8 May 2009; Xia, N.-H., Zeng, Q.-W., Xu, F.-X., Wu, Q.G., Eds.; Huazhong University Science Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 2012; pp. 12–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sima, Y.K.; Lu, S.G. A new system for the family Magnoliaceae. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on the Family Magnoliaceae, Guangzhou, China, 5–8 May 2009; Xia, N.H., Zeng, Q.W., Xu, F.X., Wu, Q.G., Eds.; Huazhong University Science Technology Press: Wuhan, China, 2012; pp. 55–71. [Google Scholar]
- Figlar Richard, B.; Nooteboom Hans, P. Notes on Magnoliaceae IV. Blumea J. Plant. Taxon. Plant. Geogr. 2004, 49, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-B.; Liu, B.-B.; Nie, Z.-L.; Chen, H.-F.; Chen, F.-J.; Figlar, R.B.; Wen, J. Major clades and a revised classification of Magnolia and Magnoliaceae based on whole plastid genome sequences via genome skimming. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 58, 673–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Henry, R.J.; Rossetto, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Plant DNA barcoding: From gene to genome. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2015, 90, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Wu, Z.Q.; Zhao, K.K.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhang, N.N.; Guo, J.Y.; Tembrock, L.R.; Xu, D. Comparative analyses of five complete chloroplast genomes from the genus Pterocarpus (Fabacaeae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Shi, T.; Luo, W.; Ni, X.; Iqbal, S.; Ni, Z.; Huang, X.; Yao, D.; Shen, Z.; Gao, Z. Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genome among Prunus mume, P. armeniaca, and P. salicina. Hortic. Res. 2019, 6, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.-S.; Li, P.; Qiu, Y.-X. The Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Three Cardiocrinum (Liliaceae) Species: Comparative Genomic and Phylogenetic Analyses. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 7, 2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Duan, D.; Yang, J.; Feng, L.; Zhao, G. Comparative Analysis of the Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Five Quercus Species. Front. Plant. Sci. 2016, 7, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.-B.; Lim, C.E.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.H.; Yu, H.-J.; Mun, J.-H. Comparative chloroplast genome analysis of Artemisia (Asteraceae) in East Asia: Insights into evolutionary divergence and phylogenomic implications. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Hu, Y.X.; Lv, W.Q.; Wang, Q.H.; Liu, G.X.; Hu, Z.Y. Chloroplast genomes of five Oedogonium species: Genome structure, phylogenetic analysis and adaptive evolution. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Zhi, L.Q.; Jia, Y.; Zhong, Q.Y.; Liu, Z.L.; Yue, M.; Li, Z.H. Nucleotide diversity and demographic history of Pinus bungeana, an endangered conifer species endemic in China. J. Syst. Evol. 2020, 58, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.J.; Wang, T.; Shu, X.C.; Wang, N.; Zhuang, W.B.; Wang, Z. Complete chloroplast genomes and comparative analyses of L. chinensis, L. anhuiensis, and L. aurea (Amaryllidaceae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.T.; Yi, T.S.; Gao, L.M.; Ma, P.F.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.B.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Fritsch, P.W.; Cai, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Origin of angiosperms and the puzzle of the Jurassic gap. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parris, J.K.; Ranney, T.G.; Knap, H.T.; Baird, W.V. Ploidy levels, relative genome sizes, and base pair composition in Magnolia. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 135, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.X.; Hu, G.X.; Hu, G.W. Comparative genomics and phylogenetic relationships of two endemic and endangered species (Handeliodendron bodinieri and Eurycorymbus cavaleriei) of two monotypic genera within Sapindales. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; He, R.; Yang, Y.B.; Lu, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, J. Study on the difference of pharmacological effects of Houpoea officinalis var. biloba and Houpoea officinalis on experimental gastrointestinal motility disorder. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2010, 35, 2624–2627. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, L.; Ren, B.; Wang, L.; Shi, X.; Hou, F.; Peng, C.; Gao, J. Comparative study on chloroplast genomes of three species of Houpoea. Guihaia 2022, 42, 1394–1401. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y. The Research of Chloroplast Genome of Ginkgo biloba Abstract; Nanjing Forestry University: Nanjing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.-J.; Yu, W.-B.; Yang, J.-B.; Song, Y.; Depamphilis, C.W.; Yi, T.-S.; Li, D.-Z. GetOrganelle: A fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; Guan, X. CpGAVAS, an integrated web server for the annotation, visualization, analysis, and GenBank submission of completely sequenced chloroplast genome sequences. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 715–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torsten, S. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar]
- Cock, P.J.; Chilton, J.M.; Grüning, B.; Johnson, J.E.; Soranzo, N. NCBI BLAST+ integrated into Galaxy. GigaScience 2015, 4, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, J. KaaS: Key as a Service over Quantum Key Distribution Integrated Optical Networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2019, 57, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthew, K.; Richard, M.; Amy, W.; Steven, S.-H.; Matthew, C.; Shane, S.; Simon, B.; Alex, C.; Sidney, M.; Chris, D.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz, S.; Choudhuri, J.V.; Ohlebusch, E.; Schleiermacher, C.; Stoye, J.; Giegerich, R. REPuter: The manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4633–4642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, T.; Michalek, W.; Varshney, R.; Graner, A. Exploiting EST databases for the development and characterization of genederived SSR-markers in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. mVISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32 (Suppl. 2), W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Ma, P.-F.; Li, D.-Z. High-Throughput Sequencing of Six Bamboo Chloroplast Genomes: Phylogenetic Implications for Temperate Woody Bamboos (Poaceae: Bambusoideae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT: Iterative refinement and additional methods. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1079, 131–146. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, C.; Wang, L.; Lei, J.; Duan, B.; Ma, W.; Xiao, S.; Qi, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Shen, X.; et al. A Comparative Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Four Salvia Medicinal Plants. Engineering 2019, 5, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaradua, S.S.; Alzahrani, D.A.; Albokhary, E.J.; Abba, A.; Bello, A. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Justicia flava: Genome comparative analysis and phylogenetic relationships among Acanthaceae. Biomed. Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitzendanner, M.A.; Soltis, P.S.; Yi, T.S.; Li, D.Z.; Soltis, D.E. Plastome phylogenetics: 30 years of inferences into plant evolution. Adv. Bot. Res. 2018, 85, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicke, S.; Schneeweiss, G.M.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Muller, K.F.; Quandt, D. The evolution of the plastid chromosome in land plants: Gene content, gene order, gene function. Plant. Mol. Biol. 2011, 76, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Hu, N.; Huang, H.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Gao, L.-Z. An Improved Chloroplast DNA Extraction Procedure for Whole Plastid Genome Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Diaz, S.; Nunez, F.A.A.; Veltjen, E.; Asselman, P.; Larridon, I.; Samain, M.S. Comparison of Magnoliaceae plastomes: Adding neotropical Magnolia to the discussion. Plants 2022, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaf, S.; Khan, A.L.; Khan, A.; Al-Harrasi, A. Unraveling the chloroplast genomes of two Prosopis species to identify its genomic information, comparative analyses and phylogenetic relationship. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Cao, L.; Xiang, F. Morphological and histological identification of Magnolia rostrata. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 1994, 1, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Penaflor, C.; Kuehl, J.V.; Leebens-Mack, J.; E Carlson, J.; de Pamphilis, C.W.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. Complete plastid genome sequences of Drimys, Liriodendron, and Piper: Implications for the phylogenetic relationships of magnoliids. BMC Evol. Biol. 2006, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, P.; Flegel, W.A. Codon usage in vertebrates is associated with a low risk of acquiring nonsense mutations. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalier-Smith, T. Chloroplast evolution: Secondary symbiogenesis and multiple losses. Curr. Biol. 2002, 12, R62–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Dang, Y.Y.; Li, Q.; Lu, J.J.; Li, X.W.; Wang, Y.T. Complete chloroplast genome sequence of poisonous and medicinal plant Datura stramo-nium: Organizations and implications for genetic engineering. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110656. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.W.; Luo, Y.Y.; He, Y.; Qin, X.S.; Li, C.G.; Deng, X.M. Complete chloroplast genome of Michelia shiluensis and a comparative analysis with four Mag-noliaceae species. Forests 2020, 11, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marechal, A.; Brisson, N. Recombination and the maintenance of plant organelle genome stability. New Phytol. 2010, 186, 299–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad-Panah, N.; Shabanian, N.; Khadivi, A.; Rahmani, M.-S.; Emami, A. Genetic structure of gall oak (Quercus infectoria) characterized by nuclear and chloroplast SSR markers. Tree Genet. Genomes 2017, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhang, M.F.; Xue, J.; Dong, R.; Du, Y.P.; Zhang, X.H. Chloroplast genomic resources for phylogeny and DNA barcoding: A case study on Fritillaria. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.K.; Liu, T.J.; Yuan, X.; Xu, Y.; Yan, H.F.; Hao, G. Chloroplast genomes and comparative analyses among thirteen taxa within Myrsinaceae s.str. clade (Myrsinoideae, Primulaceae). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Kohn, C.; Conrad, K.; Kramer, M.; Pooler, M. Genetic diversity of Magnolia ashei characterized by SSR markers. Conserv. Genet. 2018, 19, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.M.; Chen, K.; Gu, C.H.; Zheng, S.Y.; Ma, L. Comparative and phylogenetic analyses of 26 Magnoliaceae species based on complete chloroplast genome sequences. Can. J. For. Res. 2018, 48, 1456–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.W.; Lin, C.X.; Lee, S.Y.; Mao, L.F.; Meng, K.K. Comparative analysis of complete Ilex (Aquifoliaceae) chloroplast genomes: Insights into evolutionary dynamics and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Genomics. 2022, 23, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Jin, H.; Zhong, Y.; He, X.; Huang, Y.; Tan, F.; Boufford, D.E. Phylogenetic relationships of the Magnoliaceae inferred from cpDNA matK sequences. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 101, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-T.; Luo, Y.; Gan, L.; Ma, P.-F.; Gao, L.-M.; Yang, J.-B.; Cai, J.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Fritsch, P.W.; Zhang, T.; et al. Plastid phylogenomic insights into relationships of all flowering plant families. BMC Biol. 2021, 19, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
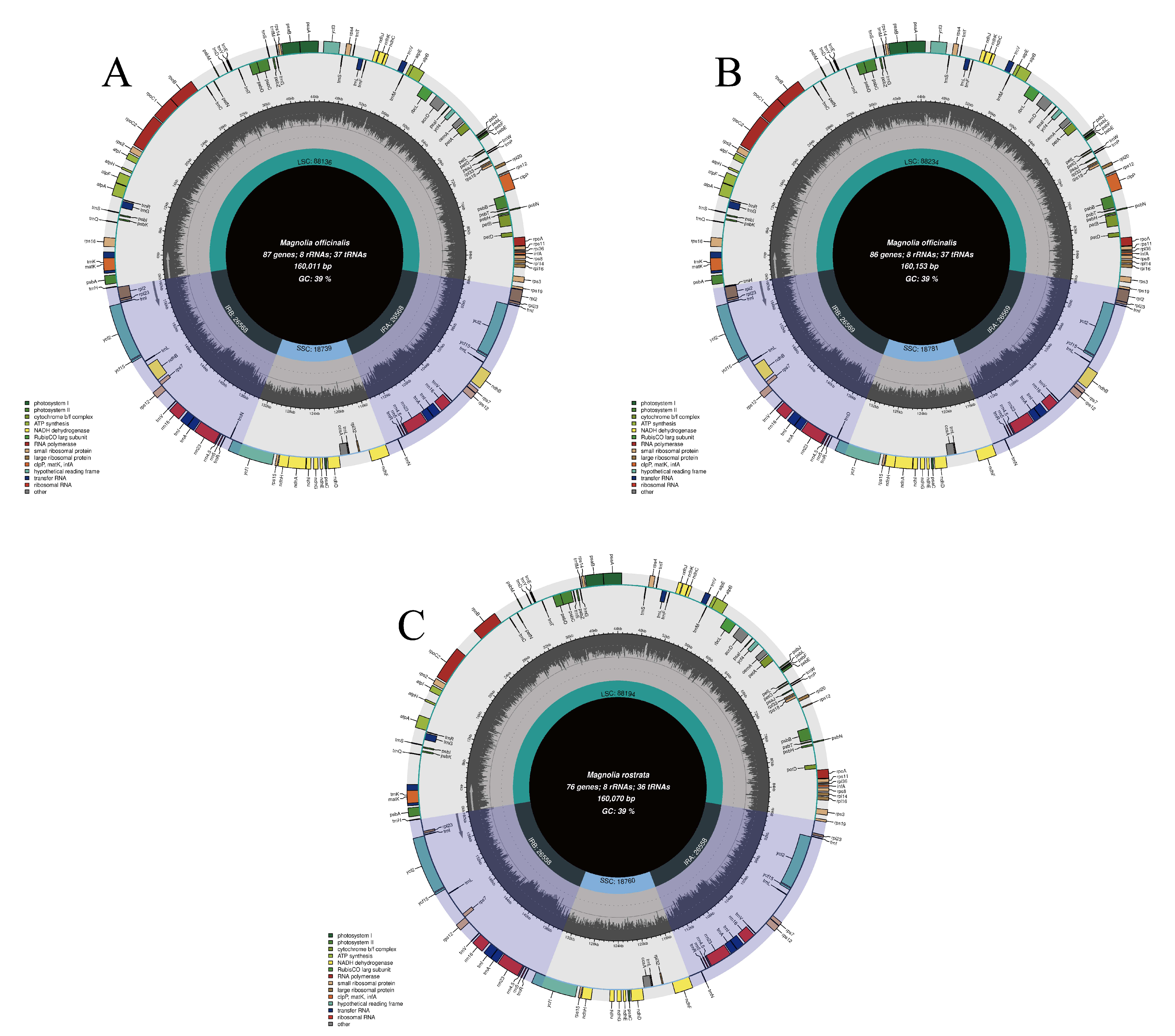
| Lable | Species | Genome Size (bp) | LSC Region (bp) | IR Region (bp) | SSC Region (bp) | Number of Genes | PCGs | tRNAs | rRNAs | GC Content (%) | Number of Accession in Genbank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OB | H. officinalis var. biloba | 160,011 | 88,136 | 26,568 | 18,739 | 132 | 87 | 37 | 8 | 39.22 | OM912810 |
| R | H. rostrata | 160,070 | 88,194 | 26,558 | 18,760 | 120 | 76 | 36 | 8 | 39.26 | MW800876 |
| OO | H. officinalis | 160,153 | 88,234 | 26,569 | 18,781 | 131 | 86 | 37 | 8 | 39.26 | OM912809 |
| Category | Gene Group | Gene Name |
|---|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | Photosystem I | psaA, psaB, psaC, psaI, psaJ |
| Photosystem II | psbA, psbB, psbC, psbD, psbE, psbF, psbH, psbI, psbJ, psbK, psbL, psbM, psbN, psbT, psbZ | |
| NADH dehydrogenase | ndhC, ndhD, ndhE, ndhF, ndhG, ndhH, ndhI, ndhJ, ndhK, ndhA*, ndhB(2), ndhA*, ndhB(2) | |
| Cytochrome b/f complex | petA, petD, petG, petL, petN, petB*, petB* | |
| ATP synthase | atpA, atpB, atpE, atpH, atpI, atpF*, atpF* | |
| Large subunit of rubisco | rbcL | |
| Self-replication | Proteins ribosomal (LSU) | rpl14, rpl16, rpl20, rpl23(2), rpl32, rpl33, rpl36, rpl2*(2), rpl2*(2), rpl32 |
| Proteins ribosomal (SSU) | rps11, rps12**(2), rps14, rps15, rps18, rps19, rps2, rps3, rps4, rps7(2), rps8, rps16*, rps16* | |
| RNA polymerase | rpoA, rpoB, rpoC2, rpoC1*, rpoC1* | |
| Ribosomal RNAs | rrn16(2), rrn23(2), rrn4.5(2), rrn5(2) | |
| Transfer RNAs | tRNA-Leu, trnA-UGC*(2), trnC-GCA, trnD-GUC, trnE-UUC, trnF-GAA, trnG-GCC, trnG-UCC*, trnH-GUG, trnI-CAU(2), trnI-GAU*(2), trnK-UUU*, trnL-CAA, trnL-UAA*, trnL-UAG, trnM-CAU, trnN-GUU, trnP-UGG, trnQ-UUG, trnR-ACG(2), trnR-UCU, trnS-GCU, trnS-GGA, trnS-UGA, trnT-GGU, trnT-UGU, trnV-GAC(2), trnV-UAC*, trnW-CCA, trnY-GUA, trnfM-CAU, trnA*, trnI, trnI*, trnI-CAU, trnI-GAU*, trnL, trnL*trnM, trnV, trnV-GAC, trnA-UGC*, trnD, trnA-UGC*(2), trnI-CAU(2), trnI-GAU*(2), trnL, trnL-UAA*, trnN-GUU(2), trnV-GAC(2), trnfM-CAU | |
| Other genes | Maturase | matK |
| Protease | clpP** clpP** | |
| Envelope membrane | cemA | |
| Acetyl-CoA carboxylase | accD | |
| c-type cytochrome synthesis gene | ccsA | |
| Translation initiation factor | infA | |
| Conserved hypothetical chloroplast ORF | ycf1, ycf15(2), ycf2(2), ycf4, ycf3**, ycf3** |
| Gene | OO | OB | R | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EpI | InI | EpII | InII | EpIII | EpI | InI | EpII | InII | EpIII | EpI | InI | EpII | InII | EpIII | |
| rps12 a | 114 | 536 | 232 | 26 | 114 | 536 | 232 | 26 | 114 | 536 | 232 | 26 | |||
| trnK-UUU | 37 | 2491 | 35 | 37 | 2491 | 35 | 37 | 2491 | 35 | ||||||
| rps16 | 42 | 824 | 219 | 42 | 824 | 219 | |||||||||
| trnG-UCC | 24 | 770 | 48 | 24 | 768 | 748 | 24 | 766 | 48 | ||||||
| atpF | 144 | 711 | 411 | 144 | 709 | 411 | |||||||||
| rpoC1 | 434 | 722 | 1624 | 434 | 722 | 1624 | |||||||||
| ycf3 | 126 | 734 | 228 | 728 | 153 | 126 | 734 | 228 | 728 | 153 | |||||
| trnL | 35 | 491 | 50 | ||||||||||||
| trnL-UAA | 35 | 491 | 50 | 35 | 491 | 50 | |||||||||
| trnV-UAC | 39 | 584 | 37 | 39 | 584 | 37 | 39 | 584 | 37 | ||||||
| rps12 b | 114 | 536 | 232 | 26 | 114 | 536 | 232 | 26 | 114 | 536 | 232 | 26 | |||
| clpP | 69 | 785 | 291 | 628 | 246 | 69 | 782 | 291 | 629 | 246 | |||||
| petB | 6 | 784 | 642 | 6 | 779 | 642 | |||||||||
| rpl2 a | 393 | 658 | 432 | 393 | 658 | 432 | |||||||||
| ndhB a | 777 | 700 | 756 | 777 | 700 | 756 | |||||||||
| trnI-GAU a | 42 | 936 | 35 | 42 | 936 | 35 | 42 | 936 | 35 | ||||||
| trnA-UGC a | 38 | 799 | 35 | 38 | 799 | 35 | 38 | 799 | 35 | ||||||
| ndhA | 552 | 1080 | 540 | 552 | 1078 | 540 | |||||||||
| trnA | 38 | 799 | 35 | ||||||||||||
| trnI | 42 | 936 | 35 | ||||||||||||
| trnA-UGC b | 38 | 799 | 35 | 38 | 799 | 35 | |||||||||
| trnI-GAU b | 42 | 936 | 35 | 42 | 936 | 35 | |||||||||
| ndhB b | 777 | 700 | 756 | 777 | 700 | 756 | |||||||||
| rpl2 b | 393 | 658 | 432 | 393 | 658 | 432 | |||||||||
| Botanical Traits | OO | OB | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leaf | White, long hair, concave leaf apex, shallow lobes in two obtuse circles. | White, long hair, short, acute or obtuse at the apex of leaves, without notch. | White, reddish-brown hair, apex broadly rounded, with a short, acute point. |
| Fruit | Aggregate fruit; oblong ovoid | Aggregate fruit; oblong ovoid. | Aggregate fruit is cylindrical and upright. |
| Flower | White, fragrant, 12 cm in diameter. | White, fragrant, 13 cm in diameter. | White, fragrant, 9 cm in diameter. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Li, Z.; Wu, N.; Yang, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhao, T.; Sima, Y.; Xu, T. Comparitive Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Houpoea Plants. Genes 2023, 14, 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061262
Xu Q, Li Z, Wu N, Yang J, Yuan L, Zhao T, Sima Y, Xu T. Comparitive Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Houpoea Plants. Genes. 2023; 14(6):1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061262
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qinbin, Zhuoran Li, Nannan Wu, Jing Yang, Lang Yuan, Tongxing Zhao, Yongkang Sima, and Tao Xu. 2023. "Comparitive Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Houpoea Plants" Genes 14, no. 6: 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061262
APA StyleXu, Q., Li, Z., Wu, N., Yang, J., Yuan, L., Zhao, T., Sima, Y., & Xu, T. (2023). Comparitive Analysis of the Chloroplast Genomes of Three Houpoea Plants. Genes, 14(6), 1262. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14061262






