Occurrence of High-Risk Clonal Lineages ST58, ST69, ST224, and ST410 among Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Healthy Free-Range Chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) in a Rural Region in Tunisia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites
2.2. Feces Swab Samples and Bacterial Identification
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Resistance Genotypes and Occurrence of Integrons
2.5. Detection of Genes Encoding Virulence Factors
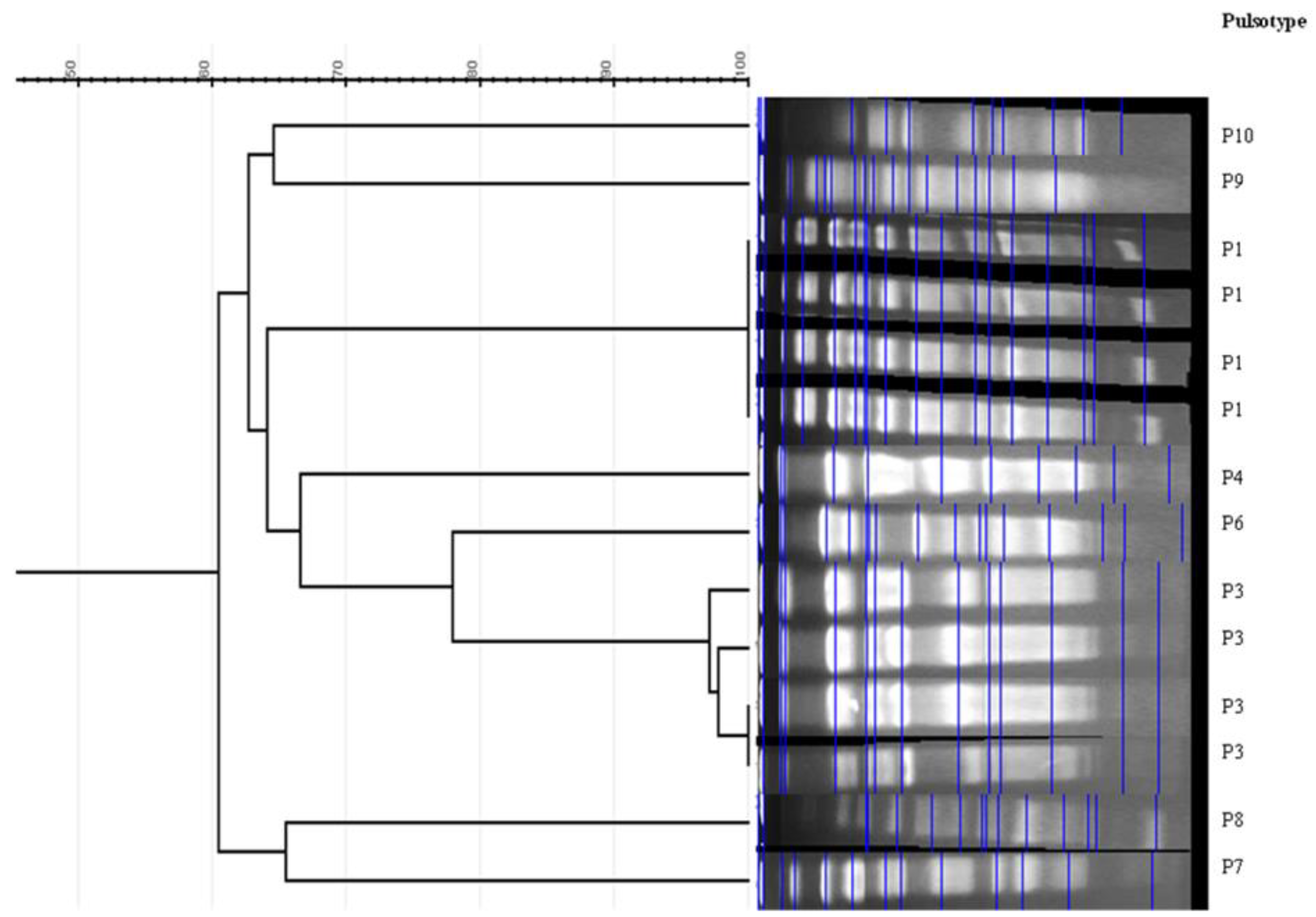
2.6. Phylogrouping of E. coli isolates Genetic Relatedness by Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis (PFGE) and Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST)
3. Results
3.1. Occurrence of ESBL-Producing E. coli and Antibiotic Susceptibilities of Isolates
3.2. Genes Encoding ESBL Enzymes and Non-β-Lactam Antibiotics
3.3. Virulence Genes
3.4. Phylogenetic Groups and Genetic Relatedness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abbassi, M.S.; Badi, S.; Lengliz, S.; Mansouri, R.; Salah, H.; Hynds, P. Hiding in plain sight-wildlife as a neglected reservoir and pathway for the spread of antimicrobial resistance: A narrative review. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2022, 98, fiac045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.; Silva, V.; Dapkevicius, M.D.L.E.; Caniça, M.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Escherichia coli as Commensal and pathogenic bacteria among food-producing animals: Health implications of extended spectrum β-lactamse (ESBL) production. Animals 2020, 10, 2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skandalis, N.; Maeusli, M.; Papafotis, D.; Miller, S.; Lee, B.; Theologidis, I.; Luna, B. Environmental spread of antibiotic resistance. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azargun, R.; Gholizadeh, P.; Sadeghi, V.; Hosainzadegan, H.; Tarhriz, V.; Memar, M.Y.; Pormohammad, A.; Eyvazi, S. Molecular mechanisms associated with quinolone resistance in Enterobacteriaceae: Review and update. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 114, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, G.; Del Giacomo, P.; Posteraro, B.; Sanguinetti, M.; Tumbarello, M. Molecular mechanisms, epidemiology, and clinical importance of β-lactam resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherak, Z.; Loucif, L.; Moussi, A.; Rolain, J.-M. Carbapenemase-producing Gram-negative bacteria in aquatic environments: A review. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 25, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K.; Bradford, P.A. Epidemiology of β-lactamase-producing pathogens. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00047-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolejska, M.; Papagiannitsis, C.C. Plasmid-mediated resistance is going wild. Plasmid 2018, 99, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madec, J.-Y.; Haenni, M. Antimicrobial resistance plasmid reservoir in food and food-producing animals. Plasmid 2018, 99, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Antibiotic/Antimicrobial Resistance-Biggest Threats. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/drugresistance/biggest_threats.html (accessed on 14 November 2017).
- Tacconelli, E.; Magrini, N.; Kahlmeter, G.; Singh, N. Global Priority List of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria to Guide Research, Discovery, and Development of New Antibiotics; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hassen, B.; Abbassi, M.S.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Mama, O.M.; Ibrahim, C.; Benlabidi, S.; Hassen, A.; Torres, C.; Hammami, S. Genetic characterization of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae from a biological industrial wastewater treatment plant in Tunisia with detection of the colistin-resistance mcr-1 gene. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sghaier, S.; Abbassi, M.S.; Pascual, A.; Serrano, L.; De-Alba, P.D.; Ben Said, M.; Hassen, B.; Ibrahim, C.; Hassen, A.; López-Cerero, L. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae from animal origin and wastewater in Tunisia: First detection of O25b-B23-CTX-M-27-ST131 Escherichia coli and CTX-M-15/OXA-204-producing Citrobacter freundii from wastewater. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 17, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Achmon, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, H.; Siame, B.A.; Leung, K.Y. Distribution of antibiotic resistance genes in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Mahanti, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Joardar, S.N.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Sar, T.K.; Mandal, G.P.; Dutta, T.K.; Samanta, I. Pig farm environment as a source of β-lactamase or AmpC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli. Ann. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denamur, E.; Clermont, O.; Bonacorsi, S.; Gordon, D. The population genetics of pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 19, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathayat, D.; Lokesh, D.; Ranjit, S.; Rajashekara, G. Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC): An overview of virulence and pathogenesis factors, zoonotic potential, and control strategies. Pathogens 2021, 10, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenz, J.; Barrington, G.; Garry, F.; Ellis, R.; Magnuson, R. Escherichia coli isolates’ serotypes, genotypes, and virulence genes and clinical coliform mastitis severity. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3408–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szmolka, A.; Nagy, B. Multidrug resistant commensal Escherichia coli in animals and its impact for public health. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.; Kelly, M.; Hynds, P.; Weatherill, J.; Majury, A.; O’Dwyer, J. Groundwater resources as a global reservoir for antimicrobial-resistant bacteria. Water Res. 2019, 170, 115360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA: European Food Safety Authority. Report from the Task Force on Zoonoses Data Collection including guidance for harmonized monitoring and reporting of antimicrobial resistance in commensal Escherichia coli and Enterococcus spp. from food animals. EFSA J. 2008, 141, 141. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, I.; Joardar, S.N.; Das, P.K.; Das, P.; Sar, T.K.; Dutta, T.K.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Batabyal, S.; Isore, D.P. Virulence repertoire, characterization, and antibiotic resistance pattern analysis of Escherichia coli isolated from backyard layers and their environment in India. Avian Dis. 2014, 58, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, I.; Joardar, S.N.; Mahanti, A.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Sar, T.K.; Dutta, T.K. Approaches to characterize extended spectrum β-lactamase/β-lactamase producing Escherichia coli in healthy organized vis-a-vis backyard farmed pigs in India. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 36, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanta, I.; Joardar, S.N.; Das, P.K.; Sar, T.K. Comparative possession of Shiga toxin, intimin, enterohaemolysin and major extended spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL) genes in Escherichia coli isolated from backyard and farmed poultry. Iran J. Vet. Res. 2015, 16, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaouadi, S.; Soufi, L.; Hamza, A.; Fedida, D.; Zied, C.; Awadhi, E.; Mtibaa, M.; Hassen, B.; Cherif, A.; Torres, C.; et al. Co-occurrence of mcr-1 mediated colistin resistance and β-lactamase-encoding genes in multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli from broiler chickens with colibacillosis in Tunisia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2020, 22, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassen, B.; Abbassi, M.S.; Benlabidi, S.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Mama, O.M.; Ibrahim, C.; Hassen, A.; Hammami, S.; Torres, C. Genetic characterization of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from wastewater and river water in Tunisia: Predominance of CTX-M-15 and high genetic diversity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 44368–44377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassen, B.; Abbassi, M.S.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Mama, O.M.; Hassen, A.; Torres, C.; Hammami, S. High prevalence of mcr-1 encoding colistin resistance and first identification of blaCTX-M-55 in ESBL/CMY-2-producing Escherichia coli isolated from chicken faeces and retail meat in Tunisia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 318, 108478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jouini, A.; Vinué, L.; Ben Slama, K.; Sáenz, Y.; Klibi, N.; Hammami, S.; Boudabous, A.; Torres, C. Characterization of CTX-M and SHV extended-spectrum -lactamases and associated resistance genes in Escherichia coli strains of food samples in Tunisia. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 27th ed.; CLSI Supplement, M100; Wayne, P.A., Ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, A.; Sen, M.R.; Prakash, P.; Anupurba, S. Role of beta-lactamase inhibitors in enterobacterial isolates producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 61, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, C.D.; Rasheed, J.K.; Hubert, S.K.; Biddle, J.W.; Raney, P.M.; Anderson, G.J.; Williams, P.P.; Brittain, K.L.; Oliver, A.; McGowan, J.E.; et al. Characterization of clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae from 19 laboratories using the National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards extended-spectrum β-lactamase detection methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2864–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardabassi, L.; Dijkshoorn, L.; Collard, J.-M.; Olsen, J.; Dalsgaard, A. Distribution and in-vitro transfer of tetracycline resistance determinants in clinical and aquatic Acinetobacter strains. J. Med. Microbiol. 2000, 49, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz, Y.; Briñas, L.; Domίnguez, E.; Ruiz, J.; Zarazaga, M.; Vila, J.; Torres, C.; Petraitis, V.; Petraitiene, R.; Kelaher, A.M.; et al. Mechanisms of resistance in multiple-antibiotic-resistant Escherichia coli strains of human, animal, and food origins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3959–3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maynard, C.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Bekal, S.; Sanschagrin, F.; Levesque, R.C.; Brousseau, R.; Masson, L.; Larivière, S.; Harel, J. Antimicrobial resistance genes in Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli O149:K91 isolates obtained over a 23-year period from pigs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3214–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazel, D.; Dychinco, B.; Webb, V.A.; Davies, J. Antibiotic resistance in the ECOR collection: Integrons and identification of a novel aad Gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreten, V.; Boerlin, P. A new sulfonamide resistance gene ( sul3 ) in Escherichia coli is widespread in the pig population of Switzerland. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1169–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay, K.; Robicsek, A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Park, C.H.; Jacoby, G.; Barrett, T.J.; Medalla, F.; Chiller, T.M.; Hooper, D.C. Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance in non-typhi serotypes of Salmonella enterica. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Robicsek, A.; Jacoby, G.A.; Sahm, D.; Hooper, D.C. Prevalence in the United States of aac(6 ′ )-Ib-cr encoding a ciprofloxacin-modifying enzyme. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 3953–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattoir, V.; Poirel, L.; Rotimi, V.; Soussy, C.-J.; Nordmann, P. Multiplex PCR for detection of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance qnr genes in ESBL-producing enterobacterial isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2007, 60, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, K.; Wachino, J.-I.; Suzuki, S.; Arakawa, Y. Plasmid-mediated qepA gene among Escherichia coli clinical isolates from Japan. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 1564–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaco, L.M.; Hasman, H.; Xia, S.; Aarestrup, F.M. qnrD, a novel gene conferring transferable quinolone resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Kentucky and Bovismorbificans strains of human origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, B.B.; Lammens, C.; Ruhal, R.; Kumar-Singh, S.; Butaye, P.; Goossens, H.; Malhotra-Kumar, S. Identification of a novel plasmid-mediated colistin-resistance gene, mcr-2, in Escherichia coli, Belgium, June 2016. Eurosurveillance 2016, 21, 30280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, A.R.; Bortolaia, V.; Kjeldgaard, J.S.; Pedersen, S.K.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Hansen, I.M.; Guerra, B.; Malorny, B.; Borowiak, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; et al. Multiplex PCR for detection of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance determinants, mcr-1, mcr-2, mcr-3, mcr-4 and mcr-5 for surveillance purposes. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17-00672, Erratum in Eurosurveillance 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, T.A.; Wu, X.-Y.; Barchia, I.; Bettelheim, K.A.; Driesen, S.; Trott, D.; Wilson, M.; Chin, J.J.-C. Comparison of virulence gene profiles of Escherichia coli strains isolated from healthy and diarrheic Swine. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 4782–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.-Y.; Chapman, T.; Trott, D.J.; Bettelheim, K.; Do, T.N.; Driesen, S.; Walker, M.J.; Chin, J. Comparative analysis of virulence genes, genetic diversity, and phylogeny of commensal and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolates from weaned pigs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenover, F.C.; Arbeit, R.D.; Goering, R.V.; Mickelsen, P.A.; Murray, B.E.; Persing, D.H.; Swaminathan, B. Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: Criteria for bacterial strain typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 2233–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras, J.; Domínguez, C.; Mata, E.; Pascual, V.; Lozano, C.; Torres, C.; Zarazaga, M. GelJ—A tool for analyzing DNA fingerprint gel images. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.H. Simple method for constructing phylogenetic trees from distance matrices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1981, 78, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartof, S.Y.; Solberg, O.D.; Manges, A.R.; Riley, L.W. Analysis of a uropathogenic Escherichia coli clonal group by Multilocus Sequence Typing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 5860–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamar, E.; Hammami, S.; Alonso, C.A.; Dakhli, N.; Abbassi, M.S.; Ferjani, S.; Hamzaoui, Z.; Saidani, M.; Torres, C.; Boubaker, I.B.-B. High prevalence of extended-spectrum and plasmidic AmpC β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli from poultry in Tunisia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 231, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidani, M.; Messadi, L.; Mefteh, J.; Chaouechi, A.; Soudani, A.; Selmi, R.; Dâaloul-Jedidi, M.; Ben Chehida, F.; Mamlouk, A.; Jemli, M.H.; et al. Various Inc-type plasmids and lineages of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae spreading blaCTX-M-15, blaCTX-M-1 and mcr-1 genes in camels in Tunisia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 19, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolakos, I.; Feudi, C.; Eichhorn, I.; Palmieri, N.; Fasolato, L.; Schwarz, S.; Piccirillo, A. High-resolution characterisation of ESBL/pAmpC-producing Escherichia coli isolated from the broiler production pyramid. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanya, S.H.; Bairy, I.; Nayak, N.; Amberpet, R.; Padukone, S.; Metok, Y.; Bhatta, D.R.; Sathian, B. Detection and characterization of ESBL-producing Enterobacteriaceae from the gut of healthy chickens, Gallus gallus domesticus in rural Nepal: Dominance of CTX-M-15-non-ST131 Escherichia coli clones. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Sajid, A.; Mughal, G.A.; Leghari, R.A.; Malhi, K.K.; Bughio, S.U.D.; Ali, A.; Alam, S.; Khan, S.; et al. Prevalence of extended spectrum beta-lactamase producing Enterobacteriaceae in commercial broilers and backyard chickens. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2016, 4, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Q.; Kamar, A.A.; Velayuthan, R.D.; Chong, C.W.; Teh, C.S.J. Clonal relatedness in the acquisition of intestinal carriage and transmission of multidrug resistant (MDR) Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli and its risk factors among preterm infants admitted to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). Pediatr. Neonatol. 2020, 62, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, M.; Iwasa, T.; Fukuda, A.; Sato, T.; Okubo, T.; Tamura, Y. The Role of flies in spreading the extended-spectrum β-lactamase gene from cattle. Microb. Drug Resist. 2013, 19, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng-Nkrumah, N.; Labi, A.-K.; Blankson, H.; Awuah-Mensah, G.; Oduro-Mensah, D.; Anum, J.; Teye, J.; Kwashie, S.D.; Bako, E.; Ayeh-Kumi, P.F.; et al. Household cockroaches carry CTX-M-15-, OXA-48- and NDM-1-producing enterobacteria, and share β-lactam resistance determinants with humans. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punyadi, P.; Thongngen, P.; Kiddee, A.; Assawatheptawee, K.; Tansawai, U.; Bunchu, N.; Niumsup, P.R. Prevalence of blaCTX-M and emergence of blaCTX-M-5-Carrying Escherichia coli in Chrysomya megacephala (Diptera: Calliphoridae), Northern Thailand. Microb. Drug Resist. 2020, 27, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hölzel, C.S.; Tetens, J.L.; Schwaiger, K. Unraveling the role of vegetables in spreading antimicrobial-resistant bacteria: A need for quantitative risk assessment. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 671–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Oh, S.-S.; Kim, J.; Shin, J. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli isolated from raw vegetables in South Korea. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbassi, M.S.; Torres, C.; Achour, W.; Vinué, L.; Sáenz, Y.; Costa, D.; Bouchami, O.; Ben Hassen, A. Genetic characterisation of CTX-M-15-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli strains isolated from stem cell transplant patients in Tunisia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2008, 32, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferjani, S.; Saidani, M.; Amine, F.S.; Boubaker, I.B.-B. Prevalence and characterization of Plasmid-Mediated Quinolone Resistance genes in extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae in a Tunisian Hospital. Microb. Drug Resist. 2015, 21, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, P.; Sun, Y.; Ji, X.; Du, X.; Guo, X.; Liu, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhou, B.; Zhou, W.; Liu, G.; et al. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance and extended-spectrum β-lactamase genes in Escherichia coli isolated from chickens. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bert, F.; Branger, C.; Lambert-Zechovsky, N. Identification of PSE and OXA β-lactamase genes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa using PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirsalehian, A.; Feizabadi, M.; Nakhjavani, F.A.; Jabalameli, F.; Goli, H.; Kalantari, N. Detection of VEB-1, OXA-10 and PER-1 genotypes in extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from burn patients. Burns 2010, 36, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.-L.; Hou, T.-W.; Xu, S.-B.; Ma, C.-Q.; Yao, Z.-Y.; Li, W.; Wei, L. Detection of drug resistance–associated genes of multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Microb. Drug Resist. 2008, 14, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Baky, R.M.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Mohamed, D.S.; Ahmed, E.F.; Hashem, Z.S. Prevalence of virulence genes and their association with antimicrobial resistance among pathogenic E. coli isolated from Egyptian patients with different clinical infections. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbíčová, T.; Baráková, A.; Florianová, M.; Jamborová, I.; Zelendová, M.; Pospíšilová, L.; Koláčková, I.; Karpíšková, R. Dissemination and comparison of genetic determinants of mcr-mediated colistin resistance in Enterobacteriaceae via retailed raw meat products. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamar, E.; Alonso, C.A.; Hamzaoui, Z.; Dakhli, N.; Abbassi, M.S.; Ferjani, S.; Saidani, M.; Boubaker, I.B.-B.; Torres, C. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin-resistance in CMY-2-producing Escherichia coli of lineage ST2197 in a Tunisian poultry farm. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 269, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, B.; Saloua, B.; Abbassi, M.S.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Mama, O.M.; Hassen, A.; Hammami, S.; Torres, C. mcr-1 encoding colistin resistance in CTX-M-1/CTX-M-15- producing Escherichia coli isolates of bovine and caprine origins in Tunisia. First report of CTX-M-15-ST394/D E. coli from goats. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 67, 101366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeili, M.; Salehzeinali, H.; Mirzaei, S.; Pishnian, Z.; Ahmadi, A. Molecular characterization of quinolone resistance and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Escherichia coli isolated from human and broiler chickens. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2021, 32, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, D.; Aung, M.S.; Carmona, Y.; González, M.K.; Pereda, N.; Hidalgo, M.; Rivero, M.; Zayas, A.; del Campo, R.; Urushibara, N.; et al. High prevalence of CTX-M Type extended-spectrum β-lactamase genes and detection of NDM-1 carbapenemase gene in extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli in Cuba. Pathogens 2020, 9, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, M.; Kumar, S.; Kapoor, R.K.; Virdi, J.S.; Gulati, P. Integrons in Enterobacteriaceae: Diversity, distribution and epidemiology. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 51, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, L.W. Pandemic lineages of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.M.; Sellera, F.P.; Fernandes, M.R.; Moura, Q.; Garino, F.; Azevedo, S.S.; Lincopan, N. Genomic features of a highly virulent, ceftiofur-resistant, CTX-M-8-producing Escherichia coli ST224 causing fatal infection in a domestic cat. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 15, 252–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manges, A.R.; Geum, H.M.; Guo, A.; Edens, T.J.; Fibke, C.D.; Pitout, J.D.D. Global extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) lineages. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00135-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapmaz, M.; Erdem, F.; Abulaila, A.; Yeniaras, E.; Oncul, O.; Aktas, Z. First detection of NDM-1 with CTX-M-9, TEM, SHV and rmtC in Escherichia coli ST471 carrying IncI2, A/C and Y plasmids from clinical isolates in Turkey. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 7, 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, A.M.; Correa, A.; Restrepo, E.; Capataz, C. Escherichia coli ST471 Producing VIM-4 metallo-β-lactamase in Colombia. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivendale, K.A.; Logue, C.M.; Kariyawasam, S.; Jordan, D.; Hussein, A.; Li, G.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Nolan, L.K. Avian-pathogenic Escherichia coli strains are similar to neonatal meningitis E. coli strains and are able to cause meningitis in the rat model of human disease. Infect. Immun. 2010, 78, 3412–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubelová, M.; Koláčková, I.; Gelbíčová, T.; Florianová, M.; Kalová, A.; Karpíšková, R. Virulence properties of mcr-1-positive Escherichia coli isolated from retail poultry meat. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Isolate | Phylogroup | PFGE | ST * | Resistance Profile to Non-β-Lactam Antibiotics | bla Genes | Other Genes Detected/Integrons | Virulence Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| household 1 (29 isolates) | |||||||
| EC20 | A | P1 | ST224 | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII, |
| EC22 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH |
| EC23 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII, |
| EC24 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH |
| EC26 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC27 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC28 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU, CS | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH |
| EC29 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH |
| EC30 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1/int1 + int2 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC31 | A | P1 | - | NAL, CIP, TET | CTX-M-1 | -/- | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC33 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | tetB, sul1/int1 | fimH |
| EC34 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII, iutA |
| EC35 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII, |
| EC36 | A | P1 | ST69 | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-55 | tetB, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC37 | A | P1 | - | TET | CTX-M-1 | tetA/- | fimH, iutA |
| EC38 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC39 | A | P1 | - | TET | CTX-M-1 | -/- | fimH, papGIII, iutA |
| EC40 | A | P1 | - | NAL, CIP, TET, GEN, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1/int1 | fimH |
| EC41 | A | P1 | ST224 | NAL, CIP, TET | CTX-M-15 | tetA/- | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC43 | A | P1 | - | NAL, CIP | CTX-M-15 | -/- | fyuA, fimH iutA |
| EC45 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | tetB, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII, iutA |
| EC46 | A | P1 | - | NAL, CIP, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC47 | A | P1 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC42 | A | P4 | ST410 | TET | CTX-M-15 | tetA/- | fimH, iutA |
| EC25 | F | P5 | ST471 | TET, SXT, SU | SHV-2 | -/- | fimH, iutA |
| EC21 | A | P10 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH |
| EC19 | A | NT | - | NAL, TET, SXT, CS | CTX-M-55 | tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC32 | C | NT | - | NAL, CIP | CTX-M-15 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH |
| EC44 | A | NT | ST617 | NAL, TET, SXT, SU, CS | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| household 2 (18 isolates) | |||||||
| EC1 | A | P2 | ST410 | NAL, TE, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 + OXA10 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH, papGIII |
| EC3 | A | P2 | - | NAL, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 + OXA10 | qnrS, tetA, sul2/- | fimH |
| EC5 | A | P3 | ST1642 | NAL, CIP, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | tetA, tetB, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC6 | A | P3 | - | NAL, CIP, TET, SXT, SU, CS | CTX-M-1 | tetA, sul1, sul2/int1 | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC7 | A | P3 | ST46 | NAL, CIP, TET, SXT, SU, CS | CTX-M-55 | tetA, sul1, sul2/int1 | fimH, iutA |
| EC8 | A | P3 | - | NAL, CIP, TET, SXT, SU, CS | CTX-M-1 | tetA, sul1, sul2, mcr-2/int1 + int2 | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC10 | A | P3 | - | NAL, CIP, TET | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr qnrS, tetA/- | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC2 | A | P4 | ST410 | NAL, CIP, TET, CS | CTX-M-1 + OXA10 | tetA, tetB, mcr-2/- | fyuA fimH, iutA |
| EC12 | A | P4 | - | TET | CTX-M-55 | tetA/- | fimH, iutA |
| EC16 | A | P4 | - | TET, CS | CTX-M-1 | tetA/- | fimH, iutA |
| EC18 | D | P4 | ST410 | NAL, CIP, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-1 | aac(6′)-Ib-cr, qnrB, tetA, tetB, sul2/int2 | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC14 | A | P5 | ST471 | TET, GEN, CS | CTX-M-1 | tetA/- | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC13 | A | P6 | ST2460 | NAL, CIP, TET, CS | CTX-M-1 | tetA/- | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC17 | A | P6 | - | NAL, CIP, TET, CS | CTX-M-1 | tetA/- | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC4 | C | P7 | - | NAL, CIP, TET, GEN | CTX-M-1 | tetA, sul1/int1 | fimH |
| EC9 | F | P8 | - | TET, SXT, SU, CS | SHV-12 | tetB, sul2/int2 | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC15 | F | P9 | - | NAL, CIP, TET, SXT, SU | CTX-M-15 | tetB/int2 | fyuA, fimH, iutA |
| EC11 | A | NT | ST58 | TET, SXT, SU, CS | CTX-M-55 | sul1, sul2/int1 | fimH, iutA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benlabidi, S.; Raddaoui, A.; Lengliz, S.; Cheriet, S.; Hynds, P.; Achour, W.; Ghrairi, T.; Abbassi, M.S. Occurrence of High-Risk Clonal Lineages ST58, ST69, ST224, and ST410 among Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Healthy Free-Range Chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) in a Rural Region in Tunisia. Genes 2023, 14, 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040875
Benlabidi S, Raddaoui A, Lengliz S, Cheriet S, Hynds P, Achour W, Ghrairi T, Abbassi MS. Occurrence of High-Risk Clonal Lineages ST58, ST69, ST224, and ST410 among Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Healthy Free-Range Chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) in a Rural Region in Tunisia. Genes. 2023; 14(4):875. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040875
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenlabidi, Saloua, Anis Raddaoui, Sana Lengliz, Sarah Cheriet, Paul Hynds, Wafa Achour, Taoufik Ghrairi, and Mohamed Salah Abbassi. 2023. "Occurrence of High-Risk Clonal Lineages ST58, ST69, ST224, and ST410 among Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Healthy Free-Range Chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) in a Rural Region in Tunisia" Genes 14, no. 4: 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040875
APA StyleBenlabidi, S., Raddaoui, A., Lengliz, S., Cheriet, S., Hynds, P., Achour, W., Ghrairi, T., & Abbassi, M. S. (2023). Occurrence of High-Risk Clonal Lineages ST58, ST69, ST224, and ST410 among Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Isolated from Healthy Free-Range Chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) in a Rural Region in Tunisia. Genes, 14(4), 875. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14040875








