Transcriptomic Studies on Intracranial Aneurysms
Abstract
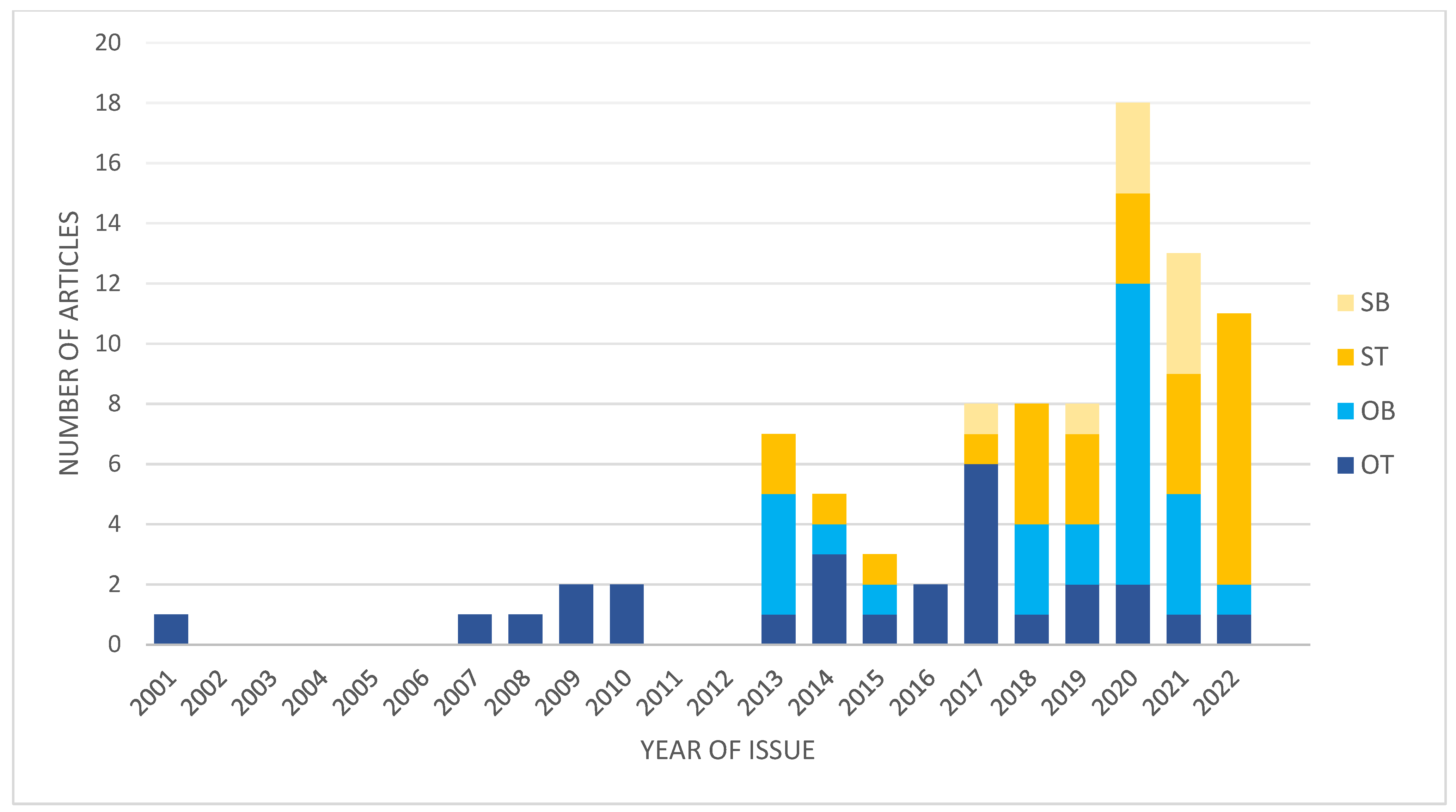
1. Introduction
2. Original Studies
2.1. Transcriptomics in IA Samples
2.2. Transcriptomics in Blood-Derived Samples
3. Studies Based on Existing Datasets
3.1. Transcriptomics in IA Samples
3.2. Transcriptomics in Blood-Derived Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nieuwkamp, D.J.; Setz, L.E.; Algra, A.; Linn, F.H.; de Rooij, N.K.; Rinkel, G.J. Changes in case fatality of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and region: A meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinkel, G.J.; Algra, A. Long-term outcomes of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawton, M.T.; Vates, G.E. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claassen, J.; Park, S. Spontaneous subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet 2022, 400, 846–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, D.G.; Kassam, A.B.; Feingold, E.; Heidrich-O’Hare, E.; Yonas, H.; Ferrell, R.E.; Brufsky, A. Molecular anatomy of an intracranial aneurysm: Coordinated expression of genes involved in wound healing and tissue remodeling. Stroke 2001, 32, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinsheimer, S.; Lenk, G.M.; van der Voet, M.; Land, S.; Ronkainen, A.; Alafuzoff, I.; Kuivaniemi, H.; Tromp, G. Integration of expression profiles and genetic mapping data to identify candidate genes in intracranial aneurysm. Physiol. Genom. 2007, 32, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Tan, H.; Shi, Y.; Huang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Yin, C.; Wang, Q. Global Gene Expression Patterns and Somatic Mutations in Sporadic Intracranial Aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2017, 100, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supriya, M.; Christopher, R.; Devi, B.I.; Bhat, D.I.; Shukla, D.; Kalpana, S.R. Altered MicroRNA Expression in Intracranial Aneurysmal Tissues: Possible Role in TGF-β Signaling Pathway. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 42, 2393–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yang, X.; Jiang, F.; Dusting, G.J.; Wu, Z. Transcriptome-wide characterization of gene expression associated with unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Eur. Neurol. 2009, 62, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Awad, I.A.; Jafari, N.; Lin, S.; Du, P.; Hage, Z.A.; Shenkar, R.; Getch, C.C.; Bredel, M.; Batjer, H.H.; et al. Genomics of human intracranial aneurysm wall. Stroke 2009, 40, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, E.; Vignati, A.; Albanese, A.; Nucci, C.G.; Sabatino, G.; Tirpakova, B.; Lofrese, G.; Zelano, G.; Maira, G. Comparative evaluation of genome-wide gene expression profiles in ruptured and unruptured human intracranial aneurysms. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2010, 24, 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Fan, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. Gene expression profiles in intracranial aneurysms. Neurosci. Bull 2014, 30, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakaoka, H.; Tajima, A.; Yoneyama, T.; Hosomichi, K.; Kasuya, H.; Mizutani, T.; Inoue, I. Gene expression profiling reveals distinct molecular signatures associated with the rupture of intracranial aneurysm. Stroke 2014, 45, 2239–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Han, L.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, F. Genome-wide microRNA changes in human intracranial aneurysms. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekelis, K.; Kerley-Hamilton, J.S.; Teegarden, A.; Tomlinson, C.R.; Kuintzle, R.; Simmons, N.; Singer, R.J.; Roberts, D.W.; Kellis, M.; Hendrix, D.A. MicroRNA and gene expression changes in unruptured human cerebral aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 1390–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Lan, Q.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, J. Identification of a Long Noncoding RNA-Associated Competing Endogenous RNA Network in Intracranial Aneurysm. World Neurosurg. 2017, 97, 684–692.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, H.; Yu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lan, Q.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J. Aberrant expression of lncRNAs and mRNAs in patients with intracranial aneurysm. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 2477–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, H.; Yue, H.; Wang, W.; Yu, L.; Shuo, W.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, J. Comparison between smaller ruptured intracranial aneurysm and larger un-ruptured intracranial aneurysm: Gene expression profile analysis. Neurosurg. Rev. 2017, 40, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J. DNA Methylation Regulates Gene Expression in Intracranial Aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2017, 105, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yue, H.; Hao, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Yu, L.; Zhang, D.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, J. Expression profile of long noncoding RNAs in human cerebral aneurysms: A microarray analysis. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Yu, L.; Zhao, J. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals involvement of TLR-2 signaling in the pathogenesis of intracranial aneurysm. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, Q.Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, S. High-Throughput Data Reveals Novel Circular RNAs via Competitive Endogenous RNA Networks Associated with Human Intracranial Aneurysms. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 4819–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Koseki, H.; Miyata, H.; Itoh, M.; Kawaji, H.; Takizawa, K.; Kawashima, A.; Ujiie, H.; Higa, T.; Minamimura, K.; et al. RNA sequencing analysis revealed the induction of CCL3 expression in human intracranial aneurysms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pera, J.; Korostynski, M.; Krzyszkowski, T.; Czopek, J.; Slowik, A.; Dziedzic, T.; Piechota, M.; Stachura, K.; Moskala, M.; Przewlocki, R.; et al. Gene expression profiles in human ruptured and unruptured intracranial aneurysms: What is the role of inflammation? Stroke 2010, 41, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; He, H.; Chen, J.; Zeng, H.; Li, J.; Duan, R. MicroRNA/mRNA profiling and regulatory network of intracranial aneurysm. BMC Med. Genom. 2013, 6, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, Y.; Li, Q.; Yu, M.; Jiang, Y. Regulation of smooth muscle contractility by competing endogenous mRNAs in intracranial aneurysms. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krischek, B.; Kasuya, H.; Tajima, A.; Akagawa, H.; Sasaki, T.; Yoneyama, T.; Ujiie, H.; Kubo, O.; Bonin, M.; Takakura, K.; et al. Network-based gene expression analysis of intracranial aneurysm tissue reveals role of antigen presenting cells. Neuroscience 2008, 154, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinloog, R.; Verweij, B.H.; van der Vlies, P.; Deelen, P.; Swertz, M.A.; de Muynck, L.; Van Damme, P.; Giuliani, F.; Regli, L.; van der Zwan, A.; et al. RNA Sequencing Analysis of Intracranial Aneurysm Walls Reveals Involvement of Lysosomes and Immunoglobulins in Rupture. Stroke 2016, 47, 1286–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Yang, C.; Jia, C.; Xie, X.; Du, L. miR-566 expression and immune changes in patients with intracranial aneurysm. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 685–691. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Wen, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Yang, L.; Huang, S.; Xu, X.; Cai, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, S. Exploring the association of long noncoding RNA expression profiles with intracranial aneurysms, based on sequencing and related bioinformatics analysis. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Sui, R.; Ge, L.; Xia, D. CircRNA_0079586 and circRNA_RanGAP1 are involved in the pathogenesis of intracranial aneurysms rupture by regulating the expression of MPO. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roder, C.; Kasuya, H.; Harati, A.; Tatagiba, M.; Inoue, I.; Krischek, B. Meta-analysis of microarray gene expression studies on intracranial aneurysms. Neuroscience 2012, 201, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, K.P.; Vinasco-Sandoval, T.; Vialle, R.A.; Paschoal, F.M., Jr.; Bastos, V.A.P.A.; Bor-Seng-Shu, E.; Teixeira, M.J.; Yamada, E.S.; Pinto, P.; Vidal, A.F.; et al. Global miRNA expression profile reveals novel molecular players in aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppenberg, K.E.; Li, L.; Waqas, M.; Paliwal, N.; Jiang, K.; Jarvis, J.N.; Sun, Y.; Snyder, K.V.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H.; et al. Whole blood transcriptome biomarkers of unruptured intracranial aneurysm. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutino, V.M.; Poppenberg, K.E.; Damiano, R.J.; Patel, T.R.; Waqas, M.; Dmytriw, A.A.; Snyder, K.V.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Jarvis, J.N. Characterization of Long Non-coding RNA Signatures of Intracranial Aneurysm in Circulating Whole Blood. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Zhao, J. Differentially Expressed Circular RNA Profile in an Intracranial Aneurysm Group Compared with a Healthy Control Group. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 8889569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutino, V.M.; Lu, Y.; Ishii, D.; Poppenberg, K.E.; Rajabzadeh-Oghaz, H.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Hasan, D.M. Aberrant Whole Blood Gene Expression in the Lumen of Human Intracranial Aneurysms. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, A.; Devaux, Y.; Audibert, G.; Zhang, L.; Bracard, S.; Colnat-Coulbois, S.; Klein, O.; Zannad, F.; Charpentier, C.; Longrois, D.; et al. Gene expression profile of blood cells for the prediction of delayed cerebral ischemia after intracranial aneurysm rupture: A pilot study in humans. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 36, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pera, J.; Korostynski, M.; Golda, S.; Piechota, M.; Dzbek, J.; Krzyszkowski, T.; Dziedzic, T.; Moskala, M.; Przewlocki, R.; Szczudlik, A.; et al. Gene expression profiling of blood in ruptured intracranial aneurysms: In search of biomarkers. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van ‘t Hof, F.N.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; Medic, J.; Sanjabi, B.; van der Vlies, P.; Rinkel, G.J.; Veldink, J.H. Whole Blood Gene Expression Profiles of Patients with a Past Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korostynski, M.; Piechota, M.; Morga, R.; Hoinkis, D.; Golda, S.; Zygmunt, M.; Dziedzic, T.; Moskala, M.; Slowik, A.; Pera, J. Systemic response to rupture of intracranial aneurysms involves expression of specific gene isoforms. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korostynski, M.; Morga, R.; Piechota, M.; Hoinkis, D.; Golda, S.; Dziedzic, T.; Slowik, A.; Moskala, M.; Pera, J. Inflammatory Responses Induced by the Rupture of Intracranial Aneurysms Are Modulated by miRNAs. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morga, R.; Borczyk, M.; Korostynski, M.; Piechota, M.; Hoinkis, D.; Golda, S.; Dziedzic, T.; Slowik, A.; Moskala, M.; Pera, J. Opposite regulation of piRNAs, rRNAs and miRNAs in the blood after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 98, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Stamova, B.; Ander, B.P.; Waldau, B.; Jickling, G.C.; Sharp, F.R.; Ko, N.U. mRNA Expression Profiles from Whole Blood Associated with Vasospasm in Patients with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurocrit. Care 2020, 33, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatino, G.; Rigante, L.; Minella, D.; Novelli, G.; Della Pepa, G.M.; Esposito, G.; Albanese, A.; Maira, G.; Marchese, E. Transcriptional profile characterization for the identification of peripheral blood biomarkers in patients with cerebral aneurysms. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2013, 27, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Chen, J.; Lai, X.; Liu, T.; Qiu, P.; Que, S.; Huang, Y. Circular RNA expression profile in human primary multiple intracranial aneurysm. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutino, V.M.; Zebraski, H.R.; Rajabzadeh-Oghaz, H.; Waqas, M.; Jarvis, J.N.; Bach, K.; Mokin, M.; Snyder, K.V.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Poppenberg, K.E. Identification of Circulating Gene Expression Signatures of Intracranial Aneurysm in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutino, V.M.; Poppenberg, K.E.; Jiang, K.; Jarvis, J.N.; Sun, Y.; Sonig, A.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Snyder, K.V.; Levy, E.I.; Kolega, J.; et al. Circulating neutrophil transcriptome may reveal intracranial aneurysm signature. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutino, V.M.; Poppenberg, K.E.; Li, L.; Shallwani, H.; Jiang, K.; Jarvis, J.N.; Sun, Y.; Snyder, K.V.; Levy, E.I.; Siddiqui, A.H.; et al. Biomarkers from circulating neutrophil transcriptomes have potential to detect unruptured intracranial aneurysms. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppenberg, K.E.; Tutino, V.M.; Li, L.; Waqas, M.; June, A.; Chaves, L.; Jiang, K.; Jarvis, J.N.; Sun, Y.; Snyder, K.V.; et al. Classification models using circulating neutrophil transcripts can detect unruptured intracranial aneurysm. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Li, C.; Ge, H.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y. Circulating microRNA: A novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of intracranial aneurysm rupture a case control study. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, F. Circulating microRNAs serve as novel biological markers for intracranial aneurysms. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, e000972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Song, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Liao, Y.; Lin, J.; et al. Long non-coding RNA TCONS_00000200 as a non-invasive biomarker in patients with intracranial aneurysm. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20182224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supriya, M.; Christopher, R.; Indira Devi, B.; Bhat, D.I.; Shukla, D. Circulating MicroRNAs as Potential Molecular Biomarkers for Intracranial Aneurysmal Rupture. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2020, 24, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, L.; Pu, Y. Altered Expression of Specific MicroRNAs in Plasma of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Patients. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 842888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, X.; Li, Y. Cell-free microRNA-21: Biomarker for intracranial aneurysm rupture. Chin. Neurosurg. J. 2020, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Zhou, M.X.; Zhou, F.K.; Luo, X.M.; Zhong, S.X.; Zhou, Y.F.; Qin, Y.S.; Li, P.P.; Qin, C. Exosome-Derived MiRNAs as Biomarkers of the Development and Progression of Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2020, 27, 545–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wan, J.Q.; Zhou, J.P.; Fan, Y.L.; Jiang, J.Y. Gene expression analysis of ruptured and un-ruptured saccular intracranial aneurysm. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 1374–1381. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Gao, Y.J.; Wei, S.P.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, W.F.; Jiang, J.X.; Sun, Z.Y.; Xu, W. Transcriptome network-based method to identify genes associated with unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Genet. Mol. Res. 2013, 12, 3263–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Fan, Y.; Wan, J. Screening of key genes of unruptured intracranial aneurysms by using DNA microarray data analysis techniques. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Guan, H.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Z. Identification of key genes, transcription factors and microRNAs involved in intracranial aneurysm. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Wei, B.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Gao, Z.; Miao, Z. Bioinformatic analysis of gene expression profiling of intracranial aneurysm. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3473–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Hou, D.; Yu, D. Bioinformatics analysis of gene expression profile data to screen key genes involved in intracranial aneurysms. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4415–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.B.; Lu, J.; Yang, B.; Lenahan, C.; Zhang, J.; Shao, A. Construction of competitive endogenous RNA network reveals regulatory role of long non-coding RNAs in intracranial aneurysm. BMC Neurosci. 2021, 22, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tutino, V.M.; Zebraski, H.R.; Rajabzadeh-Oghaz, H.; Chaves, L.; Dmytriw, A.A.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Kolega, J.; Poppenberg, K.E. RNA Sequencing Data from Human Intracranial Aneurysm Tissue Reveals a Complex Inflammatory Environment Associated with Rupture. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2021, 25, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Zhong, P.; Yue, P.; Sun, Z. Uncovering of Key Pathways and miRNAs for Intracranial Aneurysm Based on Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis. Eur. Neurol. 2022, 85, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xue, C.; Luo, G.; Hu, Y.; Luo, W.; Sun, X. Identification of crucial genes in intracranial aneurysm based on weighted gene coexpression network analysis. Cancer Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Lv, H.; Cui, C.; Leng, J.; Xu, K.; Yu, G.; Chen, J.; Cong, P. Identification of the miRNA-target gene regulatory network in intracranial aneurysm based on microarray expression data. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 3239–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Guan, H.; Jiang, J.; Sun, Z. Integrated analysis of microarray data to identify the genes critical for the rupture of intracranial aneurysm. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4951–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chen, X.; Yi, D.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.H.; Luo, Q. Expression profile analysis of differentially expressed genes in ruptured intracranial aneurysms: In search of biomarkers. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 506, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, A.P.; Balas, M.; Spears, J.; Zador, Z. Microenvironment of ruptured cerebral aneurysms discovered using data driven analysis of gene expression. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, H.; Cao, H.; Chen, F.; Li, H.; Xia, Z.; Feng, S.; Zhang, H.; et al. Genetic Profiles Related to Pathogenesis in Sporadic Intracranial Aneurysm Patients. World Neurosurg. 2019, 131, e23–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Yang, B. The potential biomarkers for the formation and development of intracranial aneurysm. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2020, 81, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, D.; Liu, B.; Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Ye, W.; Liu, C.; Ni, L.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, Y. Identification and validation of key genes mediating intracranial aneurysm rupture by weighted correlation network analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Geng, D.; Zhou, K.; Fan, Y.; Su, R.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, B.; Duysenbi, S. Identification of potential key pathways, genes and circulating markers in the development of intracranial aneurysm based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2020, 48, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, A.; Ding, N.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, G.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Chai, X. Identification of Hub Genes Associated with the Pathogenesis of Intracranial Aneurysm via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 4039–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Q. Comparative analysis of aneurysm subtypes associated genes based on protein-protein interaction network. BMC Bioinform. 2021, 22, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Leng, J.; Lin, Q.; Zhou, F. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition related genes in unruptured aneurysms identified through weighted gene coexpression network analysis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Li, M. Potential Role of the Chemotaxis System in Formation and Progression of Intracranial Aneurysms Through Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 2217–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ma, H.Y.; Wang, Y.; He, J.; Liu, H.J. Identification of Potential Core Genes for the Rupture of Intracranial Aneurysms by a Bioinformatics Analysis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 875007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, X.; Yang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, L. Comprehensive Analysis of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Intracranial Aneurysm. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2022, 16, 865005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, D. Intracranial Aneurysms Induced by RUNX1 Through Regulation of NFKB1 in Patients with Hypertension-An Integrated Analysis Based on Multiple Datasets and Algorithms. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 877801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Liu, Z.; Guo, D.; Ma, C.; Duan, L.; He, Y.; Jia, R.; Guo, C.; Xing, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Transcriptome-Based Dissection of Intracranial Aneurysms Unveils an “Immuno-Thermal” Microenvironment and Defines a Pathological Feature-Derived Gene Signature for Risk Estimation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 878195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Ma, Z.; Shang, J.; Cui, X.; Liu, J.; Shi, R.; Wang, S.; Wu, A. Bioinformatics analysis reveals potential biomarkers associated with the occurrence of intracranial aneurysms. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, F. Novel insight into ferroptosis-related genes, molecular subtypes, and immune characteristics in intracranial aneurysms. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 71, 1347–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.H.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Piao, J.; Chen, X. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis identified six hub genes associated with rupture of intracranial aneurysms. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, B.; Zhang, R.; Rong, Z.; Ni, L.; Di, X.; Liu, C. Construction and Validation of a New Model for the Prediction of Rupture in Patients with Intracranial Aneurysms. World Neurosurg. 2021, 149, e437–e446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Qin, J. A Two-Gene-Based Diagnostic Signature for Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 671655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, L.; Wei, B.; Wang, Z.; Kong, D.; Gao, Z.; Miao, Z. Screening of Critical Genes and MicroRNAs in Blood Samples of Patients with Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms by Bioinformatic Analysis of Gene Expression Data. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 4518–4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Li, S.T.; Zhu, J.; Hua, X.M.; Wan, L. Analysis of Peripheral Blood Cells’ Transcriptome in Patients With Subarachnoid Hemorrhage From Ruptured Aneurysm Reveals Potential Biomarkers. World Neurosurg. 2019, 129, e16–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xu, L.; Qian, H. Bioinformatics analysis of microRNA profiles and identification of microRNA-mRNA network and biological markers in intracranial aneurysm. Medicine 2020, 99, e21186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X. Identification of inflammation-associated circulating long non-coding RNAs and genes in intracranial aneurysm rupture-induced subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4541–4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, W.; Fan, D.; Ren, Z.; Li, Q. Identification of upregulated NF-κB inhibitor alpha and IRAK3 targeting lncRNA following intracranial aneurysm rupture-induced subarachnoid hemorrhage. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wu, Q.; Cai, W.; Xiang, H.; Wen, L.; Zhang, A.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H. Identifying critical genes associated with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage by weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Aging 2021, 13, 22345–22360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laarman, M.D.; Kleinloog, R.; Bakker, M.K.; Rinkel, G.J.E.; Bakkers, J.; Ruigrok, Y.M. Assessment of the Most Optimal Control Tissue for Intracranial Aneurysm Gene Expression Studies. Stroke 2019, 50, 2933–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| PMID/Reference | Cohorts | RNA Type | Detection/Verification Methods | Aim of the Study | Analytical Methods | Major Findings including Differentially Expressed RNAs, Involved Pathways/Functions (Top 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11283408 [5] | 1 RA, 1 STA | mRNA | SAGE-Lite | gene expression profiling in RA | DEGs, putative function | overexpressed: fibronectin, HLA-DR, MAC25, COL1A1, jun-B; putative functions of DEGs: ECM constituent, MMP activation, ECM remodeling, collagen bridging, ECM |
| 17878320 [6] | 8 RA, 4 UA, 12 contralateral artery (postmortem) | mRNA | Affymetrix, Illumina microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in IA | DEGs, WebGestalt for functional annotation (KEGG), Cytoscape for interactions | 810 IA candidate genes; KEGG: adherens junction, MAPK signaling pathway, focal adhesion, regulation of actin cytoskeleton, GnRH signaling pathway |
| 18538937 [28] | 6 RA, 4 UA, 4 AVM feder artery | mRNA | Agilent microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in IA, RA vs. UA | DEGs, IPA network, GO | 521 DEGs; GO: antigen processing; IPA networks: MHC I and MHC II complex-related genes, antigen presentation |
| 19752560 [9] | 3 UA, 3 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in UA | DEGs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | 1160 DEGs: 164 up, 996 down; GO-BP: cellular process, development, growth, regulation of biological process, reproduction; GO-CC: cell, envelope, extracellular region, membrane-enclosed lumen, organelle; GO-MF: binding, catalytic activity, enzyme regulator activity, signal transducer activity, transcription regulator activity; KEGG: focal adhesion, type 1 diabetes mellitus pathway, antigen processing and presentation pathway, complement and coagulation cascades |
| 19228845 [10] | 3 RA, 3UA, 3 STA | mRNA | Illumina microarray | gene expression profiling in IA | DEGs, functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | 326 DEGs: 172 up (KIAA1199, COL11A1, COL1A1, CDH2, POSTN), 154 down (C2orf40, CFD, CASQ2, RBPMS2, MUSTN1); functional groups: collagens, cell communication, angiogenesis, inflammation, apoptosis; GO: organ and system development, cell–cell adhesion, actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis, actin binding, cytoskeletal protein binding; KEGG: focal adhesion, ECM–receptor interaction, cell communication |
| 20044533 [24] | 8 RA, 6 UA, 5 MMA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in IA, RA vs. UA | DEGs, WebGestalt for functional annotation (GO), immunohistochemistry | 159 DEGs: 131 common for RA and UA: 8 up, 123 down, 2 RA-specific (down: CLSTN3, LIG1), 26 UA-specific (up: AIPL1, BLVRA, C18orf30, C2, C20orf59); GO: IA vs. ctrl/RA vs. UA: up: Immune system process, Activation of plasma proteins during acute inflammatory response, Complement activation, Inflammatory response, Activation of immune response; IA vs. ctrl: down: Muscle contraction, Cell adhesion, Cell–matrix adhesion, Cell–substrate adhesion, Organ development |
| 20487632 [11] | 12 RA + 9 ctrl RA (MMA, STA), 10 UA + 12 ctrl UA (MMA, STA), 4 ctrl (STA, MMA) | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in IA and control vessels of IA patients and HC | DEGs, functional annotation | RA vs. UA: 10 up (ELA2, MMP9, MMP14, ADAMTS1, CTSD), 4 down (TIMP3, TIPM4, BCL2L1, BCL2); ctrl RA vs. ctrl UA: 1 up (MMP14), 2 down (TIPM3, TIMP4); RA vs. ctrl: 22 up (ELA2, MMP2, MMP9, MMP12, MM14), 8 down (TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3, TIMP4, BCL2L1); ctrl RA vs. ctrl: 6 up (DAXX, FAS, MMP9, ADAMTS1, CTSD), 6 down (BCL2L1, TIMP3, TIMP4, LOX, COL1A2); pathways: RA vs. UA: proteinases, inhibitors of proteinases, apoptosis, anti-apoptotic genes; ctrl RA vs. ctrl UA: proteinases, inhibitors of proteinases; RA vs. ctrl: proteinases, inhibitors of proteinases, apoptosis, anti-apoptotic genes, extracellular structural matrix proteins; ctrl RA vs. ctrl: proteinases, inhibitors of proteinases, apoptosis, anti-apoptotic genes, extracellular structural matrix proteins |
| 24429729 [12] | 15 IA, 17 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in IA | DEGs | 179 DEGs (up: SPP1, IBSP, APOC1, OLR1, RGS1; down: PDE4C, AIF1L, TRPV1, CYP4B1, CXCL14) |
| 24938844 [13] | 8 RA, 5 UA, 10 STA | mRNA | Agilent microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling—signatures of RA | DEGs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | RA vs. UA: 2047 DEGs: 430 up (CSF3R, PFKFB4, FPR1, TFPI2, C19orf59), 617 down (COL10A1, EGR2, C20orf82, NOV, CPXM2); functional analysis: GO up: Nucleosome, Defense response, Inflammatory response, Response to wounding, Immune response; KEGG up: Chemokine signaling pathway, Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Fc γ R-mediated phagocytosis; GO down: Cell adhesion, Calcium ion binding, Extracellular matrix, Extracellular region part, Growth factor binding; KEGG down: N/A |
| 27026628 [29] | 22 RA, 21 UA, 16 cortical artery | mRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | comparison of gene expression profiles between RA, UA, control arteries | DEGs, Bioconductor for functional analysis (GO, KEGG) | IA vs. ctrl: 229 DEGs: 51 up (COL10A1, CILP2, SFRP2, MEX3B, PTHLH), 178 down (FAM134B, SLC13A3, SERPIND1, GREB1, GJB6); GO: inorganic anion transport, skeletal system development, regulation of developmental growth, plasma membrane region, ossification (predominantly: terms related to ECM and transmembrane transporter activity, blood vessel regulation); low-count genes expressed immunoglobulins; RA vs. UA: 1489 DEGs: 958 up (MARCO, TGFBI, HPSE, CD300C, CD300E), 531 down (DOK6, CAMK2A, MYOZ3, IGHG4, TPH1); GO: mitosis, positive regulation of cell development, negative regulation of G-protein-coupled receptor protein signaling pathway, cell–substrate adhesion (predominantly terms related to immune response, lysosomes, cell–cell interaction, in-cell regulation); KEGG: Lysosome, Osteoclast differentiation, Staphylococcus aureus infection, Phagosome, Leishmaniasis; low-count genes expressed: immunoglobulins |
| 28057588 [7] | 1 RA, 2 UA, 3 controls from GSE51878 (coronary artery SMC) | mRNA | RNAseq | gene expression profiling in IA and whole genome sequencing in additional cohort of 6 IA patients | DEGs, GeneCoDis3 for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), Cytoscape for PPI network | DEGs: 1459 up (H19, PIK3R5, CHST15, A2M, SAMSN1), 250 down (HIST1H3J, FTH1P3, IFITM4P, ANXA2P1, ANXA2P3); KEGG: Proteasome, Spliceosome, Huntington disease, Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, Parkinson disease; PPI network: 965 nodes (significant hub proteins: IKBKG, ACTB, MKI67IP) |
| 27841008 [18] | 6 RA, 6 UA, 12 STA | mRNA | Agilent microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in small RA (<10 mm) and larger UA (>10 mm) | DEGs, functional analysis with GO | RA vs. UA: 280 DEGs: 101 up, 179 down; GO: up: fever generation, cellular response to cycloheximide, heat generation, positive regulation of acute inflammatory response, regulation of organ formation; RA vs. ctrl: 2115 DEGs: 1007 up, 1108 down; GO: up: detection of molecule of bacterial origin, positive regulation of monocyte chemotaxis, T cell migration, regulation of monocyte chemotaxis, myeloid cell activation involved in immune response; UA vs. ctrl: 1910 DEGs: 755 up, 1155 down; GO: up: peptide antigen assembly with MHC protein complex, MHC protein complex assembly, T cell chemotaxis, T cell migration, neutrophil activation involved in immune response |
| 28433851 [19] | 7 RA, 20 UA, 20 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in IA plus DNA methylation | DEGs, SAS system for functional annotation (GO, KEGG, BIOCARTA), DNA methylation analysis | 2142 DEGs: 1203 up, 939 down; GO: multicellular organismal development, cell adhesion, regulation of transcription DNA-dependent, inflammatory response, cell differentiation; KEGG: cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, focal adhesion, signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells, TNF signaling pathway, proteoglycans in cancer; 11,022 differentially methylated sites: 6396 hyper, 4626 hypo; 14 genes as potentially associated with IA (CXCL10, HK2, IL12RB1, IL21R, IL7R) |
| 29066233 [21] | 15 IA, 17 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in IA | DEGs, IPA pathways | 179 DEGs; IPA pathways: communication between innate and adaptive immune cells, allograft rejection signaling, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-mediated apoptosis of target cells, graft vs. host disease signaling, antigen presentation pathway; TLR-2 signaling as a key player in IA formation |
| 31316152 [23] | 4 IA, 3 MMA/STA for RNAseq; 18 IA, 18 MMA/STA for qPCR | mRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | gene expression profiling in IA and selected protein expression in IA wall using immunostaining, culture of VSMC | DEGs, functional annotation (GO) | 408 DEGs: 79 up (KRT14, DAPL1, OACYLP, UBL4B, FFAR4), 329 down (HPSE2, ITLN1, CCL21, MYOC, ADIPOQ); GO: up: immune response, cell adhesion, biological adhesion, defense response, inflammatory response; down: muscle contraction, muscle system process, striated muscle contraction, cell adhesion, biological adhesion; CCL3 as important chemoattractant for macrophages in IA |
| 32355516 [30] | 50 IA, 50 ctrl | mRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | gene expression profiling in IA and miR-566 and selected protein expression in IA | DEGs, miR-566 expression, western blot for protein expression | miR-566 up in IA; 256 DEGs: 12 up (ALOX5, VEGF, CCR8, IGKC, PCAR), 4 down (VHL, ReIB, NIK, NGF2) |
| 24079748 [26] | 14 RA, 14 MMA | mRNA, miRNA | Agilent microarray/qPCR | mRNA/miRNA profiling in RA | DEmRNAs, DEmiRNAs, IPA networks and pathways | 30 DEmiRNAs: 1 up, 29 down (hsa-miR-140-3p, hsa-miR-7-1-3p, hsa-miR-29c-3p, hsa-miR-29c-5p, hsa-miR-23b-5p); 681 DEmRNAs as potential DEmiRNAs targets; IPA biological processes for target genes: migration of phagocytes, proliferation of mononuclear leukocytes, cell movement of smooth-muscle cells, differentiation of macrophages, stimulation of T lymphocytes |
| 25868147 [27] | 70 IA, 10 MMA | mRNA, miRNA | Agilent microarray/PCR | mRNA/miRNA expression profiling in IA, regulation of smooth-muscle contractility | DEGs, DEmiRNAs; DAVID and IPA for functional annotation (GO, networks); smooth-muscle cells’ cultures | 1062 DEGs (C1orf115, HLA-DRB1, FFAR4, SDK1, BRCA2); 17 DEmiRNAs (hsa-miR-1274a, hsa-miR-135b-5p, hsa-miR-182-5p, hsa-miR-328, hsa-miR-337-3p); GO: regulation of muscle contraction, regulation of system process, regulation of smooth-muscle contraction, cell adhesion, biological adhesion; IPA networks—10 functional clusters; diseases and functions (Cellular Movement, Cellular Growth and Proliferation, Cardiovascular System Development and Function; Cell Morphology, Cancer, Organismal Injury and Abnormalities; Lipid Metabolism, Small Molecule Biochemistry, Molecular Transport; Cellular Growth and Proliferation, Cellular Movement, Cancer; Cardiovascular System Development and Function, Organ Morphology, Organismal Development) |
| 26918470 [15] | 7 UA, 10 STA | mRNA, miRNA | RNAseq for mRNA, Affymetrix microarray for miRNA | gene and miRNA expression profiling in UA | DEGs, DEmiRNAs, GOFAST for functional annotation (GO) | 1028 DEGs: 623 up (RP11-798K23.5, MMP13, SDS, MIR155HG, APOC1), 405 down (FNA20P, PLA2G2A, SFRP5, PCP4L1, PLIN1); 1338 DEmiRNAs: up (miR-21-5p7, hsa-miR-1246, hsa-miR-6875-3p, hsa-miR-6753-3p, hsa-miR-4685-3p), down (hsa-miR-143-5p, hsa-miR-3195, hsa-miR-6068, hsa-miR-193b-5p, hsa-miR-6848-5p); GO: up: extracellular matrix, extracellular region part, proteinaceous extracellular matrix, extracellular region, cargo receptor activity; down: system process, galactosylceramide sulfotransferase activity, galactose 3-O-sulfotransferase activity, cytoskeletal protein binding, regulation of platelet-derived growth factor production; significant miR-mRNA pairs: miR-21—PAIP2B, miR-143—COL1A1, COL5A1, COL5A2, MARCKS, TANC2, miR-145—ABCA1, ADAMTS2, BCAT1 |
| 25300531 [14] | 6 IA, 6 ctrl STA | miRNA | Agilent microarray/qPCR | miRNA profiling in IA | DEmiRNAs, DAVID and IPA for functional annotation (GO), Cytoscape for interaction networks | 157 DEmiRNAs: 72 up (hsa-miR-298, hsa-miR-422a, hsa-miR-1299, hsa-miR-711, hsa-miR-1208), 85 down (hsa-miR-10b, hsa-miR-199b-5p, hsa-miR-1260, hsa-miR-139-5p, hsa-miR-143); functional analysis—DEmiRNAs-target mRNAs: Programmed cell death, Extracellular matrix organization, Response to oxidative stress, TGF-β signaling pathway, Smooth-muscle cell proliferation |
| 34185228 [8] | 29 RA, 20 controls from dataset GSE161870 (intercostal artery) | miRNA | Exiqon microarray/qPCR for miRNA and mRNA targets | miRNA expression profiling in aSAH patients | DEmiRNAs, DIANA to predict miRNA targets, functional annotation (GO, KEGG), TGFbeta pathway analysis; association with clinical status (aSAH severity, VSP) | 70 DEmiRs: 67 down (hsa-miR-143-3p, hsa-miR-4328, hsa-miR-145-5p, hsa-miR-23c, hsa-miR-143-5p), 3 up (hsa-miR-642b-3p, hsa-miR-103a-2-5p, hsa-miR-4732-5p); KEGG for 10 top miRs: Fatty acid biosynthesis, Wnt signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway; GO-CC: cytoskeleton, intracellular, nucleus, cytoskeleton organization, cytoplasmic membrane-bounded periplasmic space; GO-MF: hydrolase activity, lipid binding, carbohydrate binding, receptor activity, phosphorus phosphatase activity; GO-BP: microtubule organization center, catabolic process, protein transport, cellular homeostasis, mitochondrion organization; decreased in patients with WFNS 3 and 4: miR-125b-5p, miR-143-3p; decreased in patients with VSP: miR-125b-5p, miR-143-3p |
| 27751926 [16] | 6 RA, 6 UA, 12 STA (the same patients) | mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA | Agilent microarray for mRNA and lncRNA, Affymetrix microarray for miRNA | RNAs expression profiling in IA, ceRNA regulatory network in IA | DEGs, DElncRNAs, DEmiRNAs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), MiRanda to predict miRNA targets, ceRNA score and network | 286 DEmiRNAs: 234 up, 52 down; 1518 DElncRNAs: 413 up, 1105 down; 2545 DEGs: 1150 up, 1395 down; GO: cell adhesion, regulation of vascular smooth muscle, positive regulation of protein kinase activity, axon guidance, dorsal aorta morphogenesis; KEGG: axon guidance, cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), oxitocin signaling pathway, cGMP-PKG signaling pathway, vascular smooth-muscle contraction; 1461 miRNA–lncRNA interaction, 9269 miRNA–mRNA interactions; 8401 miRNA–lncRNA–mRNA interactions |
| 27965470 [17] | 12 RA, 15 UA, 27 STA | mRNA, lncRNA | Agilent microarray | mRNA and lncRNA expression profiling in IA | DEGs, DElncRNAs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | 2926 DEGs: 1511 up, 1415 down; 4129 DElncRNAs: 876 up, 3253 down; GO: up: immune response, inflammatory response, regulation of immune response, interferon-γ-mediated signaling pathway, innate immune response; down: muscle contraction, muscle organ development, positive regulation of glucose import, smooth-muscle contraction; KEGG: up: lysosome, phagosome, Staphylococcus aureus infection, tuberculosis, leishmaniasis; down: cGMP-PKG signaling pathway, vascular smooth-muscle contraction, proteoglycans in cancer, focal adhesion, regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes; lncRNA–mRNA networks represented in: immune response, inflammatory response, muscle contraction pathway |
| 28009235 [20] | 12 IA, 12 STA | mRNA, lncRNA | CapitalBio microarray/qPCR | mRNA and lncRNA expression profiling in IA | DEGs, DElncRNAs, GeneSpring, functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | 2545 DEGs: 1150 up, 1395 down; 1518 DElncRNAs: 413 up, 1105 down; GO: up: T cell chemotaxis, T cell migration, lymphocyte chemotaxis, lymphocyte migration, regulation of lymphocyte apoptotic process; down: smooth-muscle contraction, muscle contraction, muscle system process, striated muscle cell differentiation, muscle cell differentiation; KEGG: up: chemokine signaling pathway, cell adhesion molecules, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, lysosome, B-cell receptor signaling pathway; down: vascular smooth-muscle contraction, focal adhesion, dilated cardiomyopathy, adipocytokine signaling pathway, phosphatidylinositol signaling system; CCL5 targeted by 17 lncRNAs as a central player in IA pathogenesis |
| 33023605 [25] | 4 IA, 4 STA; for peripheral blood leukocytes 2 tiers: 130 IA, 130 HC | mRNA, lncRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | mRNA and lncRNA expression profiling in IA and validation of selected lncRNA expression in peripheral blood leukocytes | DEmRNAs, DElncRNAs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), Cytoscape for CNC network | 1193 DElncRNAs: 900 up (LncRNA ENST00000508090, LncRNA ENST00000576153, LncRNA ENST00000569478, LncRNA ENST00000478738, LncRNA ENST00000463972), 293 down (LncRNA ENST00000446406, LncRNA ENST00000469162, LncRNA ENST00000469162, LncRNA ENST00000579688, LncRNA ENST00000474353); 2127 DEGs: 1297 up, 831 down; GO-BP up: defense response to virus, type I interferon signaling pathway, inflammatory response, neutrophil degranulation, innate immune response; GO-CC up: membrane, plasma membrane, Golgi membrane, phagocytic vesicle membrane, cytosol; GO-MF up: protein binding, tumor necrosis factor receptor binding, T cell receptor binding, receptor activity, MHC class I protein binding; GO-BP down: cell adhesion, SRP-dependent cotranslation, translation, translational initiation, nuclear-transcribed mRNA; GO-CC down: extracellular matrix, cytoskeleton, receptor complex, Z-disc, proteinaceous extracellular matrix; GO-MF down: structural constituent of ribosome, actin filament binding, Wnt-activated receptor activity, actin binding, heparin binding; KEGG: up: measles, natural killer cell-mediated signaling, T cell receptor signaling pathway, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, NOD-like receptor signaling; down: ribosome, adherens juction, regulation of lipolysis, dilated cardiomyopathy, axon guidance; 5 DElncRNAs in blood: lncRNA ENST00000471220, lncRNA ENST00000607042, lncRNA ENST00000478738, MALAT1, lncRNA ENST000000576153; good predictive value of lncRNA ENST00000607042 in IA |
| 31254341 [22] | 2 RA, 2 UA, 4 STA; for blood study: 24 RA, 6 UA, 30 HC | mRNA, circRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | mRNA and circRNA expression profiling in IA, ceRNA regulatory network in IA, expression of selected circRNA in peripheral blood | DEGs, DEcircRNA, functional annotation (GO, KEGG), circRNA–miRNA–mRNA network (TargetScan, miRanda, miRTarBase) | DEGs: 1297 up, 831 down; DEcircRNA/host genes: 116 up (chr17: 7480128–7480270: +/SNORD10, chr14: 23371395–23371591: −/RBM23, chr1: 66378927–66384518: +/PDE48, chr17: 80992910–81006661: −/B3GNTL1, chr19: 18285849–18286507: +/IF130), 199 down (chr11: 92085261–92088570: +/FAT3, chr2: 179542851–179542935: −/TTN, chr12: 56094682–56094938: −/ITGA7, chr2: 179515969–179516047: −/TTN, chr5: 38523520–38530768: −/LIFR); GO: up: Inflammatory response, Defense response to virus, Type I interferon, TNF receptor binding, T cell receptor binding; down: Cell adhesion, Extracellular matrix, Cytoskeleton, Ribosomal structure, Actin filament binding; KEGG: up: NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity, T cell receptor, Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, NOD-like receptor, Necroptosis; down: Ribosome, Adherens junction, Regulation of lipolysis in adipocytes, Axon guidance, Parkinson’s disease; hsa_circ_0072309 and hsa_circ_0008433 as potential IA biomarkers |
| 34611229 [31] | 18 RA, 16 UA | circRNA | Affymetrix microarray/qPCR | profiling of circRNA expression in EC from RA vs. UA and shear stress effect on circRNA and miRNA expression in EC culture | DEcircRNAs, in vitro analyses | RA vs. UA: 9 up (circRNA_0004543, circRNA_0079586, circRNA_0000231, circRNA_0003204, circRNA_0454542); 6 down (circRNA_0003492, circRNA_0011032, circRNA_0004264, circRNA_0002331, circRNA_0004528); MPO as a potential biomarker for IA rupture |
| PMID/Reference | Cohorts | Source | RNA Type | Detection/Verification Methods | Aim of the Study | Analytical Methods | Major Findings including Differentially Expressed RNAs, Involved Pathways/Functions (Top 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24135536 [38] | 32 RA: 16 DCI+, 16 DCI− | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | RNG/MRC microarray/qPCR | Gene expression profiling in in aSAH w/wo DCI | DEGs | 17 DEGs: 10 up in DCI+ (NAMPT, NRG1, HGMCL, HTRA1, AF034187_186, PPP2R5C), 7 up in DCI− (EIF3K, HCST, PSMC3IP, TRPC4AP, SUSD3) |
| 23512133 [39] | 43 RA, 18 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | Illumina microarray/qPCR | Gene expression profiling in RA | DEGs, WebGestalt for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), cell type-specific gene expression (GSE28491) | 135 DEGs: 78 up (ACSL1, ALPL, ANKRD22, ANXA3, ARG1), 57 down (ABLIM1, ATP8B2, BCL11B, C2orf89, CCND2); GO: all DEGs: immune system process, immune response, lymphocyte differentiation, leukocyte differentiation, T cell differentiation; up DEGs: defense response, innate immune response, negative regulation of cytokine production during immune response, immune response, pentose biosynthetic process; down DEGs: immune system process, immune response, lymphocyte differentiation, leukocyte activation, lymphocyte activation; KEGG: all DEGs: Hematopoietic cell lineage, Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Primary immunodeficiency, T cell receptor signaling pathway, Systemic lupus erythematosus; up DEGs: Systemic lupus erythematosus, Metabolic pathways, Insulin signaling pathway, Fructose and mannose metabolism, Starch and sucrose metabolism; down DEGs: Hematopoietic cell lineage, Primary immunodeficiency, T cell receptor signaling pathway, Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs); up: transcripts related to monocytes, neutrophils, down: transcripts related to T cell |
| 24152840 [45] | 15 RA, 15 UA, 15 ctrl | PBMC | mRNA | Agilent microarray | gene expression profiling in peripheral blood cells in IA | DEGs | DEGs: RA vs. UA: 1 up (JUN), 6 down (SNCA, MMP1, IFI27, FN1, MMP9); UA vs. ctrl: 14 up (HNRNPA1, GBP1, ITGB2, STAT1, TP53), 48 down (E2F1, WIPF1, TUBA4A, CXCR4, LMNA); RA vs. ctrl: 16 up (ZFAT, ITGB2, SUMO1, C22orf9, SMA4), 37 down (PTGS2, ACTN1, GPR84, RAB32, PTX3); functional gene groups: extracellular matrix structural proteins, heat shock proteins, cytoskeleton proteins, intracellular and extracellular signal cascade proteins, pro-apoptotic genes |
| 26439625 [40] | 119 RA, 118 ctrl (2/3 discovery, 1/3 replication) | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | Illumina microarray | Gene expression profiling in past aSAH (>2 years) | DEGs, WGCNA for co-expression network (co-differential co-expression, CDC; differential co-expression, CD), DAVID for functional annotation (GO) | No DEGs including previously identified in GWAS studies IA-associated genes; WGCNA modules: CDC; 0 significant genes modules; CD: yellow module with 129 hub genes (CLCN6); GO: pathways involved in processes in the vacuole and lysosome |
| 29342213 [48] | 11 IA, 11 ctrl | blood neutrophils | mRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | gene expression profiling in peripheral blood neutrophils in IA | DEGs, TermFinder for functional annotation (GO), IPA networks | 82 DEGs (up: MAOA, C21orf15, CYP1B1, ARMC12, CD177; down: PRSS21, ETV7, SEPT4, EGR2, GBP1P1); GO: up: defense response, leukocyte activation, stem cell maintenance, maintenance of cell, stem cell development; down: immune response, immune system process; 4 IPA networks with 7 hub genes (ERK1/2, AP1, CXCL8, AKT, VEGF) |
| 30593281 [49] | 15 UA, 15 ctrl; testing: 5 UA, 5 ctrl | blood neutrophils | mRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | gene expression profiling in peripheral blood neutrophils in UA, prediction of UA presence | DEGs, GORILLA for functional annotation (GO); classification algorithms | 95 DEGs; GO: up: Regulation of defense response, Regulation of inflammatory response, cGMP-mediated signaling, Regulation of response to external stimulus, Negative regulation of defense response; down: Glutathione binding, Tetrapyrrole binding; classification model with 26 transcripts as a potential biomarker for UA |
| 31046777 [41] | 19 acute RA, 20 chronic RA, 20 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | gene expression profiling in RA: acute and chronic | DEGs, Enrichr for functional annotation (GO, WikiPathways, cell-type enrichment), TFBSs (ChIP Enrichment Analysis), mononuclear leukocytes subtypes (flow cytometry) | 491 DEmRNAs, acute RA vs. ctrl: 403 DEmRNAs: 177 up, 226 down; chronic RA vs. ctrl: 0 DEmRNAs; acute RA vs. chronic RA: 268 DEmRNAs: 178 up, 290 down: WikiPathways: up: IL-1 Signaling Pathway, Structural Pathway of Interleukin 1 (IL-1), Regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway, IL-4 Signaling Pathway, IL-1 signaling pathway, down: G-protein signaling pathways, purine metabolism, inflammatory response pathway, inflammatory response pathway, MAPK signaling pathway; GO-BP: up: MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway, toll-like receptor signaling pathway, pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway, innate immune response-activating signal transduction, activation of innate immune response, down: regulation of lymphocyte activation, regulation of leukocyte activation, T cell differentiation, positive regulation of leukocyte activation, positive regulation of lymphocyte activation; cell type-specific: up: CD33+_Myeloid, CD14+_Monocytes, down: CD4+_Tcells, CD8+_Tcells, CD56+_NKCells, FetalThyroid 721_B_lymphoblasts; TFBSs: up: SMRT, Nerf2, LXR, FOXM1, AHR, down: STAT6, RUNX, MYB, GATA3, MAF; alternative expression—148 specific gene isoforms (HEATR1, ACBD6, CCND2, PLEKHA1, ELF2) |
| 31595394 [44] | 29 RA VSP+, 21 RA VSP− | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray | gene expression profiling in peripheral blood cells in RA with/without VSP | DEGs, differential exon expression, alternative splicing, IPA pathways/function | 259 DEGs (ZMAT4, OR2D3, MGC39372, RGS18, ALDH3B2); 1210 differential exons from 1093 genes (LMO1, GLDN, HOXB6, ESPL1, DNAH10); 4 transcripts with alternative splicing (IL23A, RSU1, PAQR6, TRIP6); IPA pathways: Cardiac β-adrenergic signaling, α-Adrenergic signaling, Synaptic long-term depression, Synaptic long-term potentiation, GNRH signaling |
| 33059716 [50] | training: 39 UA, 55 ctrl; testing: 16 UA, 24 ctrl | peripheral blood neutrophils | mRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | gene expression profiling in peripheral blood neutrophils in UA, prediction of UA presence | DEGs, IPA networks, GORILLA for functional annotation (GO); classification algorithms | 65 DEGs: 42 up, 23 down; GO: up: forebrain anterior/posterior pattern specification, telencephalon cell migration, forebrain cell migration, T cell migration, disruption of cells of other organism; down: regulation of presynaptic membrane potential, motor learning, membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential, regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure by aortic arch baroreceptor feedback; IPA networks: cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, nervous system development and function, cell morphology; dermatological diseases and conditions, organismal injury and abnormalities, connective tissue development and function; cell death and survival, connective tissue disorders, inflammatory disease; 37 IA-specific genes (AC011380.1, C1QL1, CCDC42B, CEP295NL, CERS4) |
| 33156839 [34] | training: 24 UA, 23 ctrl; testing: 10 UA, 10 ctrl | whole blood | mRNA | RNAseq | gene expression profiling in whole blood in UA, prediction models | DEGs, CIBERSORT for cell composition analysis, GORILLA for functional annotation (GO), IPA networks and pathways; prediction model | 18 genes with the greatest predictive value (ATF3, CBWD6, CCDC85B, CCR8, CHMP4B); 2 IPA networks: cardiovascular system development and function and tissue development; cancer endocrine system disorders and gastrointestinal disease; CIBERSORT: no statistically significant difference in proportions of cell types; GO for predictive genes: negative regulation of secretion, negative regulation of protein secretion, negative regulation of peptide secretion, cytokine-mediated signaling pathway |
| 34203780 [47] | 24 IA, 28 ctrl; validation: 25% of discovery | PBMC | mRNA | RNAseq | expression profiling in PBMC in IA | DEGs, CIBERSORT for cell composition analysis, GOSt for functional annotation (GO), IPA networks, IA risk correlation | 54 DEGs: 40 up (ANKRD24, HLA-DQB2, OR2AK2, PHOSPHO1, ANKRD2), 14 down (PHGDH, PDZK1IP1, BOK, RETN, DEFA4); GO-BP up: biological process, cellular process, biological regulation, regulation of biological process, multicellular organismal process, regulation of cellular process; GO-CC up: cellular component, cellular anatomical entity, cell periphery, plasma membrane, intrinsic component of membrane; GO-MF up: molecular function, binding, protein binding, protein domain specific binding, molecular transducer activity; GO-BP down: multicellular organismal process, cellular process, biological process, response to stimulus; GO-CC down: cellular anatomical entity, cellular component, extracellular region, vesicle, organelle; GO-MF down: binding, molecular function, protein binding, signaling receptor binding; IPA networks: behavior, cell death and survival, connective tissue disorders; amino acid metabolism, cell cycle, cellular development; cardiovascular system development and function, cellular assembly and organization, cellular development; CIBERTSORT: no statistically significant differences in proportions of cell types; risk analysis: MKRN3 most significantly positively correlated with IA size; PHGDH and TIMD4 most significantly negatively correlated with 5-year rupture risk % |
| 34441376 [37] | 31 IA: 37 IA lumen, 31 IA proximal vessels | whole blood | mRNA | qPCR—genes selected based on PMID: 33156839 | gene expression in IA lumen vs. proximal parent vessel | DEGs, correlation with IA characteristics | 18 DEGs: 6 up (CBWD6, MT2A, MZT2B, PIM3, SLC37A3), 3 down (ST6GALNAC1, TCN2, UFSP1) |
| 24279374 [51] | 6 IA bleb+, 6 IA bleb−, 6 RA, 6 ctrl | plasma | circulating miRNA | Agilent microarray | miRNA expression profiling circulating in plasma in RA, UA w/wo daughter aneurysm | DEmiRNAs, TargetScan for gene prediction, WebGestalt for functional annotation of predicted targets (GO) | IA bleb+ vs. ctrl: 68 DEmiRNAs up, 0 down; IA bleb− vs. ctrl: 13 DEmiRNAs: 4 up, 9 down; RA vs. ctrl: 15 DEmiRNAs: 2 up, 13 down; common: UA bleb+ and bleb−) vs. ctrl: 3 up (miRNA-21, miRNA-22, miRNA-3665); IA bleb+ and RA vs. ctrl: 1 up (miRNA-3679-5p); IA bleb− and RA vs. ctrl: 5 down (hsa-miR-1471, hsa-miR-3945, hsa-miR-4253, hsa-miR-4314, hsa-miR-574-5p); GO: negative regulation of smooth-muscle cell proliferation, negative regulation of transcription factor activity, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway, actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis, negative regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter |
| 25249297 [52] | 20 RA, 20 UA, 20 HC; validation: 93 IA, 50 HC | plasma | circulating miRNA | Agilent miRNA/qPCR | miRNA expression profiling circulating in plasma in IA | DEmiRNAs | 99 DEmiRNAs: 69 up (has-let-7d-3p, has-let-7d-5p, hsa-let-7f-5p, hsa-miR-1181, hsa-miR-1227-5p), 30 down (hsa-miR-4644, hsa-miR-4649-3p, hsa-miR-4665-3p, hsa-miR-5100, hsa-miR-6069) |
| 29884860 [33] | 14 RA VSP+, 13 RA VSP−, 6 ctrl | peripheral blood | miRNA | RNAseq | miRNA expression profiling in peripheral blood in aSAH with/without VSP | DEmiRNAs, miRTarBase, DIANA, miRTargetLink for target prediction, mirDeep2 for novel miRNA; functional annotation for targets (KEGG) | RA vs. ctrl: 8 DEmiRNAs: 3 up (hsa-miR-146a-5p, hsa-miR-589-5p, and hsa-miR-941), 5 down (let-7f-5p, hsa-miR-486-5p, hsa-miR-126-5p, hsa-miR-17-5p, hsa-miR-451a); RA VSP+ vs. VSP−: 0 DEmiRNAs; KEGG: Pathways in cancer, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, HTLV-I infection, Focal adhesion, Proteoglycans in cancer; 33 potential novel miRNAs |
| 31654316 [42] | 19 acute RA, 20 chronic RA, 20 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | miRNA | RNAseq | miRNAand target genes expression profiling in RA: acute and chronic | DEmRNAs, DEmiRNAs, miAAE for functional annotation (miRWalk, GO, HMDD2), DEmRNAs, miRBase for target prediction | DEmiRNAs: acute RA vs. chronic RA vs. ctrl: 106 mature miRNAs, 90 miRNA precursors; acute RA: up 42 miRNAs, down 39 miRNAs, chronic RA: down 11 miRNAs; miRWalk: Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Translation Factors, Adipogenesis, Parkinson disease, Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis; HMDD2: Carcinoma Hepatocellular, Carcinoma Non-Small-Cell Lung, Hepatoblastoma, Muscular Disorders Atrophic, Polycythemia Vera; GO: receptor binding, extracellular space, perinuclear region of cytoplasm, protein homodimerization activity, regulation of transcription DNA dependent; 23 predicted targets related to cytokine activity and cytokine–cytokine receptor interactions (CXCL5, CSF1, FASLG, HMGB1, INHBB) |
| 31597886 [57] | discovery: 8 RA, 4 UA, 4 HC; validation: 39 RA, 30 UA, 30 HC | plasma | exosomal miRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | expression profiling of exosomal miRNA in IA development and progression | DEmiRNAs | 181 DEmiRNAs: UA vs. ctrl: 9 up (hsa-miR1296-5p, hsa-miR215-5p, hsa-miR129-5p, hsa-miR200b-3p, hsa-miR3074-5p), 20 down (hsa-miR96-5p, hsa-miR598-3p, hsa-miR202-3p, hsa-miR660-5p, hsa-miR92a-1-5p); RA vs. ctrl: 21 up (hsa-let-7a2-3p, hsa-miR1245a, hsa-miR208b-3p, hsa-miR4454, hsamiR-1976), 10 down (hsa-miR874-5p, hsa-miR6874-3p, hsa-miR3146, hsa-miR3529-5p, hsa-miR369-5p); RA vs. UA: 92 up (hsa-miR145-5p, hsa-miR202-5p, hsa-miR598-3p, hsa-miR451a, hsa-miR96-5p), 29 down (hsa-miR215-5p, hsamiR-5683, hsa-miR3679-3p, hsa-miR483-5p, hsa-miR6874-3p) |
| 32323261 [54] | discovery: 20 RA, 20 ctrl; validation: 68 RA, 90 ctrl, 20 SAH IA- | plasma | miRNA | Exiqon platform/qPCR | plasma miRNA expression profiling in aSAH | DEmiRNAs, miRWalk for target prediction, DIANA-miRPath for pathways of predicted targets (KEGG), Bingo for functional annotation (GO) | 76 DEmiRNAs: 35 up (hsa-miR-122-5p, hsa-miR-192-5p, hsa-miR-215-5p, hsa-miR-99a-5p, hsa-miR-885-5p), 41 down (hsa-miR-328-3p, hsa-miR-28-3p, hsa-miR-18b-5p, hsa-miR-376c-3p, hsa-miR-142-5p); KEGG for 8 candidate miRNAs: Fatty acid biosynthesis, TGF-β signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer, p53 signaling pathway, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway; GO-BP: microtubule organizing center, catabolic process, protein transport, cellular homeostasis, mitochondrion organization; GO-MF: hydrolase activity, lipid binding, carbohydrate binding, receptor activity, phosphoprotein phosphatase activity; GO-CC: cytoskeleton, intracellular, nucleus, cytoskeleton organization, cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle |
| 32922944 [56] | 4 RA, 4 UA high risk, 4 UA low risk, 4 ctrl; validation: 10 RA, 10 UA high risk, 10 UA low risk, 10 ctrl | serum | miRNA | Agilent microarray/qPCR | serum miRNA expression profiling in IA, role of miRNA-21 | DEmiRNAs, GO for predicted targets of miR-21 | 77 DEmiRNAs: RA vs. ctrl: up: hsa-miR-425, hsa-miR-148b, hsa-miR-27a, hsa-miR-101, hsa-miR-151-5p; down: hsa-miR-3198, hsa-miR-4314, hsa-miR-140-3p, hsa-miR-550a, hsa-miR-148a; miR-21 as potential biomarker of IA formation and rupture |
| 35242102 [55] | 65 RA, 55 HC | plasma | miRNA | Agilent microarray/qPCR | miRNA expression profiling in aSAH plasma | DEmiRNAs, TargetScan, PITA, microRNAorg for target prediction, functional annotation (GO, KEGG) of predicted genes | 14 DEmiRNAs: microarray: 6 up, 8 down on microarray; validated: 5 down (hsa-miR-23-3p, miR-590-5p, miR-20-5p, miR-142-3p, miR-29b-3p); GO: connective tissue development, angiogenesis, DNA-templated transcription initiation, collagen-activated signaling pathway, muscle tissue development; KEGG: TGF-β-signaling pathway, Hippo signaling pathway, p53 signaling pathway, cellular senescence, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway |
| 31710082 [53] | lncRNAs: 5 IA, 5 HC; validation + mRNA: 30 IA, 30 HC | plasma | lncRNA, mRNA | Arraystar microarray/qPCR | lncRNA expression profiling in plasma in IA, mRNA for CNC networks and functional analyses | DElncRNAs, DEGs, CNC network, functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | 797 DElncRNAs: 519 up (TCONS_00000200, ENST00000511927), 278 down (ENST00000421997, ENST00000538202); GO: Negative regulation of striated muscle tissue development, TRNA metabolic process, Transcytosis, Keratinocyte proliferation, Negative regulation of muscle organ development; KEGG: Mineral absorption, Folate biosynthesis, AGE-RAGE signaling pathway in diabetic complications, Platinum drug resistance, Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs); TCONS_00000200 as potential IA biomarker |
| 33023605 [25] | 4 IA, 4 STA; for peripheral blood leukocytes 2 tiers: 130 IA, 130 HC | tissue; peripheral blood leukocytes | mRNA, lncRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | mRNA and lncRNA expression profiling in IA plus validation of selected lncRNA expression in peripheral blood leukocytes | DEmRNAs, DElncRNAs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), Cytoscape for CNC network | 5 DElncRNAs in peripheral blood leukocytes: lncRNA ENST00000471220, lncRNA ENST00000607042, lncRNA ENST00000478738, MALAT1, lncRNA ENST000000576153; details on tissue analyses presented in Table 1 |
| 32939739 [35] | 34 IA, 33 ctrl | whole blood | lncRNA | RNAseq | lncRNA expression profiling in whole blood in IA, co-expression analysis | DElncRNAs, IPA networks and pathways, lncRNA ontology database, co-expression networks | 263 DElncRNAs; GO-BP: macromolecule metabolism, cellular macromolecule metabolism, RNA processing, regulation of primary metabolism, ncRNA metabolism; GO-CC: DNA package complex, nuclear inner membrane, proteasome complex, spliceosomal complex, small ribosomal subunit; GO-MF: damaged DNA binding, RNA binding, tRNA binding, mRNA binding, nucleoside phosphatase binding; 8 signature lncRNAs for IA (CTC-360G5.6, RP11-72304.9, CTD-2095E4.5, CTA-331P3.1, LINC01226) |
| 33574968 [36] | 5 RA, 5 UA, 5 HC | peripheral blood | circRNA | Arraystar microarray/qPCR | circular RNA expression profiling in blood in IA | DEcircRNAs, homemade software for miRNA target prediction, functional annotation (GO, KEGG), Cytoscape for circRNA–miRNA networks, pathways | IA vs. ctrl: DEcircRNAs: 150 up, 85 down; GO-BP: positive regulation of cellular process, homophilic cell adhesion via plasma membrane adhesion molecules, cell–cell signaling, cell–cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules, positive regulation of cellular metabolic process; KEGG: human papillomavirus infection, proteoglycans in cancer, pathways in cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, autophagy—animal |
| 33603847 [46] | 3 multiple IA, 3 HC | PBMC | circRNA | RNAseq/qPCR | circRNA expression profiling in PBMC in multiple IA | DEcircRNAs, functional annotation (GO, KEGG), TargetScan, circBank, miRanda, miRTarBase for circRNA–miRNA–mRNA network construction, ceRNA network | 60 DEcircRNAs: 20 up (hsa_circ_0135895, hsa_circ_0008911, hsa_circ_0008122, hsa_circ_0074837, hsa_circ_0078380), 40 down (hsa_circ_0009076, hsa_circ_0000982, hsa_circ_0001492, hsa_circ_0000698, hsa_circ_0141172); GO-BP up: negative regulation of execution phase of apoptosis, extracellular negative regulation of signal transduction, negative regulation of signaling receptor activity, drug metabolic process, hydrogen peroxide catabolic process; GO-CC up: BLOC-1 complex, intracellular, mitochondrial matrix, mitochondrion, cytoplasm; GO-MF up: receptor antagonist activity, receptor inhibitor activity, thiaoredaoxin peroxidase activity, peroxiredoxin activity, oxidoreductase activity; KEGG up: thiamine metabolism, antigen processing and presentation, protein digestion and absorption, Fanconi anemia pathway, amoebiasis; GO-BP down: metabolic process, cellular metabolic process, cellular nitrogen compound metabolic process, macromolecule metabolic process, primary metabolic process; GO-CC down: intracellular, intracellular organelle, intracellular membrane-bounded organelle, membrane-bounded organelle, cytoplasm; GO-MF down: protein binding, peptide binding, amide binding, enzyme binding, RNA binding; KEGG down: leukocyte transendothelial migration, viral carcinogenesis, protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity; ceRNA networks: 3 circRNAs (predicted miRNAs): hsa_circ_0135895 (hsa-miR-619-3p, hsa-miR-4324, hsa-miR-5687, hsa-miR-3529-5p, hsa-miR-379-5p), hsa_circ_0000682 (hsa-miR-448, hsa-miR-1248, hsa-miR-302a-5p, hsa-miR-627-3p, hsa-miR-1248), hsa_circ_0000690 (hsa-miR-4726-3p, hsa-miR-4520-3p, hsa-miR-4514, hsa-miR-4692, hsa-miR-6842-3p) and regulated genes: PTK2, PRKCB, ITGAL |
| 32424559 [43] | 19 acute RA, 20 chronic RA, 20 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | sRNA | RNAseq | small RNA expression profiling in RA acute and chronic | DEsRNAs (piRNA, tRNA, scRNA, snoRNA, rRNA, miRNA), conservation analysis (phastCons), TFBSs (seqinspector) | 542 DEsRNAs (108 piRNAs, 99 rRNAs, 90 miRNAs, 43 scRNAs, 36 tRNAs, 32 snoRNAs), 105 DEsRNAs in RA acute, 77 DEsRNAs in RA chronic, 286 DEsRNAs in RA vs. ctrl; RA: up: miRNAs, down: piRNAs, rRNAs; TFBSs: GR, RXRA, ERALPHA |
| PMID/Reference | Datasets ID | Cohorts | RNA Type | Detection/Verification Methods | Aim of the Study | Analytical Methods | Major Findings including Differentially Expressed RNAs, Involved Pathways/Functions (Top 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 23740452 [58] | GSE13353 | 11 RA, 8 UA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray | gene expression profiling in RA and UA | DEGs, DAVID, GSEA for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING for PPI network, TfactS for TF prediction, Sylamer for associated miRNAs prediction | 2119 DEGs: 1062 up in RA, 1057 down in RA; GO: inflammatory response, response to wounding, defense response; PPI: GRB2, PPP2R2B; TFs: NFKB1, HIF1A, SP1, JUN; predicted miRNAs: miR-33a-5p, miR-659-3p, miR-524-5p, miR-661, miR-1207-5p |
| 24065667 [59] | GSE26969 | 3 UA, 3 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray | gene expression profiling in UA | DEGs, functional annotation with PATHWAY (KEGG), BiNGO (GO), TRANSFAC, TRED for regulation network (TFs) | 3661 DEGs; GO: antigen processing and presentation of peptide or polysaccharide antigen via MHC II class, response to organic substance, antigen processing and presentation, multicellular organismal homeostasis, negative regulation of RNA metabolic processes, negative regulation of macromolecule metabolic process; KEGG: adherens junction, phosphatydylinositol signaling system, ribosome, cicardian rhythm, Parkinson’s disease; 7 TFs (STAT1, FLT1, ETS2, SMAD2, ADD1) with 15 DEGs—16 regulatory relationships |
| 24615040 [60] | GSE26969 | 3 UA, 3 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray | gene expression profiling in UA | DEGs, STRING for PPI network, FuncAssociate for functional annotation (GO) | 169 DEGs: 4 up, 165 down; GO: Muscle contraction, Muscle system process, Regulation of muscle contraction, Regulation of muscle system process, Actomyosin structure organization; PPI network with MYH11 as a main hub gene |
| 25721208 [67] | GSE54083 GSE15629 | 16 RA, 11 UA, 15 ctrl (STA, MMA) | mRNA | Affymetrix, Agilent microarray | gene expression profiling, interaction networks in IA | DEGs, functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING for PPI network, WGCNA for functional modules | RA vs. ctrl: 452 DEGs: 299 up, 153 down; GO up: Cartilage condensation, Response to transforming growth factor-β, Cellular response to transforming growth factor-β stimulus, Response to calcium ion, Response to mineralocorticoid, GO down: Cellular response to temperature stimulus, Response to prostaglandin D, Cellular response to prostaglandin D stimulus, Intestine smooth-muscle contraction, Gastrointestinal system smooth-muscle contraction; KEGG up: Osteoclast differentiation, Arginine and proline metabolism, RNA transport, Chagas disease (American trypanosomiasis); PPI networks with 238 nodes (hub genes: FOS, GCG, NTS, CASR); WGCNA: grey module (GO: response to wounding, extracellular structure organization, immune response, cell adhesion, biological adhesion; KEGG: ECM–receptor interaction, arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC)); UA vs. ctrl: 570 DEGs: 312 up, 258 down; GO up: Regulation of vasculature development, Carbohydrate-mediated signaling, Osteoclast differentiation, Organ formation, Immune system process; GO down: Negative regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transporter activity, Apolipoprotein A-I-mediated signaling pathway, Regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum, Regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity, Regulation of cardiac muscle cell membrane potential; KEGG up: Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Arginine and proline metabolism, Rheumatoid arthritis, Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis-keratan sulfate, ECM–receptor interaction KEGG down: Spliceosome, Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, Mucin-type O-glycan biosynthesis; PPI networks with 161 nodes (hub genes: FOS, NTS, CD68, GCG, ALPP); WGCNA: yellow module (GO: male sex determination, response to vitamin D, sex determination, response to temperature stimulus, membrane invagination; KEGG: cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction) |
| 29115560 [61] | GSE54083 | 8 RA, 10 STA | mRNA | Agilent microarray | gene expression profiling in IA, regulation with miRNA, TFs | DEGs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING, CytoNCA for PPI network, miRNA target genes prediction (MiRwalk2, MiRDB, RNA22, miRanda, RNAhybrid, TargetScan), TF prediction (ITFP, TRANSFAC), TF-target-miRNA network (Cytoscape) | 777 DEGs: 402 up, 275 down; GO up: cellular respiration, regulation of programmed cell death, respiratory electron transport chain, energy derivation by oxidation of organic compounds, immune system development; GO down: neuron projection morphogenesis, cellular component morphogenesis, neuron projection development, cell morphogenesis involved in differentiation, cell morphogenesis; KEGG up: primary immunodeficiency, asthma, Huntington disease, Alzheimer disease, cellular response; KEGG down: pathways in cancer, melanogenesis, natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity; PPI network (nodes: CD40, CD40LG, DRD2, TGFB1); DEGs as TFs: ARHGAP25, CCNE1, CIAO1, CIRBP, STF; 12 IA associated miRNAs (hsa-miR-125a, hsa-miR-125b, hsa-miR-145, hsa-miR-146a, hsa-miR-21) |
| 29328431 [62] | GSE26969 | 3 UA, 3 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray | gene expression profiling in UA | DEGs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), BIND, ClusterOne for PPI network, TFs regulatory network | 1124 DEGs: 989 up (MMP16, SOX4, NUFIP2, TWIST1, COL5A2), 135 down (PLN, ADH1C, MYL9, SORBS1); GO: RNA binding, organelle lumen, membrane-enclosed lumen, nuclear lumen, RNA splicing, mRNA metabolic process; KEGG: splicesosome; PPI network (HFN4A, ORC2L, MAFK, JUN); 6 TFs (HNF6, HNF4A, E2F4, YY1, H4) and 24 DEGs in TFS regulatory network; regulatory pathway HFN6-HFN4-E2F4 |
| 29552131 [69] | GSE13353 GSE15629 | 19 RA, 14 UA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray | gene expression profiling in RA and UA, genes critical for rupture | DEGs, functional annotation (KEGG), PPI network (Biological General Repository for Interaction Datasets, Human Protein Reference Database, Database of Interacting Proteins) | 1,029 DEGs: 527 up, 502 down; KEGG: MAPK signaling pathway, Pathways in cancer, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, ErbB signaling pathway, Cysteine and methionine metabolism; PPI network with 510 nodes (FN1, A4, APP, NXF1, STAT3) |
| 30366668 [70] | GSE15629 GSE54083 GSE13353 GSE6551 GSE26969 GSE36791 | vessel wall: 31 RA, 23 UA; blood: 43 RA, 18 UA | mRNA | Affymetrix, Agilent, Illumina microarray | gene expression profiling in RA | DEGs, clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING for PPI network, MCODE for subnetworks; common DEGs for tissue and blood samples | 158 DEGs; GO: Antigen processing and presentation of peptide or polysaccharide antigen via MHC class II, Cellular response to interferon-γ, Interferon-γ-mediated signaling pathway, Antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II, MHC class II protein complex assembly 3; KEGG: Th17 cell differentiation, Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation, systemic lupus erythematosus, Staphylococcus aureus infection, rheumatoid arthritis; PPI network with 155 nodes; 9 common key genes for tissue and blood (BASP1,CD74, CEBPB, ECHDC2, GZMK) |
| 31329646 [71] | GSE13353 GSE15629 | 19 RA, 14 UA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray | gene expression profiling in RA, drug candidates for rupture prevention | co-expression networks with WGCNA modules, DAVID for functional annotation (GO), computational drug repurposing (L1000), PSEA (population specific expression analysis), GoSemSim | 12 WGCNA modules (4 mapped to immune function); 164 module-based drug/compound candidates (prostratin, tereic-acid, phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate, ingenol, MLN-4924); GO for cell types (PSEA): UA: macrophage (immune response, inflammatory response, innate immune response, cellular response to lipopolysaccharide, leukocyte migration), T cell (T cell activation, cell surface receptor signaling pathway, T cell differentiation, regulation of immune response, adaptive immune response), smooth-muscle (platelet aggregation, muscle organ development, muscle contraction); RA: macrophage (immune response, peptide/polysaccharide presentation via MHC II, exogenous peptide presentation via MHC II, inflammatory response, antigen processing and presentation), T cell (T cell activation, regulation of immune response, cell surface receptor signaling pathway, immune response, T cell receptor signaling pathway) |
| 31238169 [72] | GSE75436 GSE6551 GSE26969 GSE13353 | 42 IA, 18 ctrl | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray | gene expression profiling in IA, IA formation | DEGs, clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), GSEA, STRING for PPI network, MCODE for subnetworks | 114 DEGs: 43 up, 71 down; GO-BP: muscle system process, muscle contraction, muscle cell differentiation, regulation of muscle contraction, regulation of muscle system process; GO-CC: proteinaceous extracellular matrix, contractile fiber part, contractile fiber, sarcomere, myofibril; GO-MF: cytokine activity, G-protein-coupled receptor binding, structural constituent of muscle, structural constituent of cytoskeleton, insulin-like growth factor binding; KEGG: calcium signaling pathway, neuractive ligand-receptor interaction, complement and coagulation cascades, vascular smooth-muscle contraction, apelin signaling pathway; GSEA: vascular smooth-muscle cell proliferation, smooth-muscle contraction, complement activation, complement receptor-mediated signaling pathway, vascular smooth-muscle contraction; PPI network with 50 nodes (MYH11, CNN1, MYOCD, ACTA1, LMOD1) |
| 31545495 [63] | GSE75436 | 15 IA, 14 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray | gene expression profiling in IA | DEGs, DAVID, GSEA for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING for PPI network | 782 DEGs: 392 up, 390 down; GO-BP up: inflammatory response, immune response, cell adhesion, extracellular matrix organization, neutrophil chemotaxis; GO-BP down: muscle contraction, nervous system development, cell adhesion, smooth-muscle contraction, neurotransmitter catabolic process; GO-CC up: plasma membrane, extracellular region, extracellular space, integral component of plasma membrane, collagen trimer; GO-CC down: Z disc, proteinaceous extracellular matrix, actin cytoskeleton, sarcolemma, sarcoplasmic reticulum membrane; GO-MF up: extracellular matrix structural constituent, IgG binding, chemokine activity, coreceptor activity, carbohydrate binding; GO-MF down: actin binding, structural constituent of muscle, ion channel binding, cytoskeletal protein binding, primary amine oxidase activity; KEGG: staphylococcus aureus infection, amoebiasis, phagosome, leishmaniasis, ECM–receptor interaction; PPI network with 33 nodes (TNF, IL8, TLR4, PLCB4, AGTR1) |
| 33222929 [73] | GSE75436 GSE54083 | 28 IA, 20 ctrl STA | mRNA | Affymetrix, Agilent microarray | gene expression profiling in IA | DEGs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING, CytoNCA for PPI networks and module, MCODE for subnetworks, Enrichr tool for miRNAs-DEGs, TRANSFAC, ITFP for TFs prediction, TF-miRNA-target regulatory network construction | 1332 DEGs: 720 up, 612 down; GO up: chemotaxis, inflammatory response, response to wounding, defense response, immune response; GO down: regulation of blood pressure, regulation of ehart rate, cell adhesion, muscle filament sliding, muscle contraction; KEGG up: allograft rejection, cytokine–cytokine interaction, ECM–receptor interaction, intestinal immune network for IgA production, cell adhesion molecules (CAMs); KEGG down: calcium signaling pathway, adrenergic signaling in cardiomyocytes, focal adhesion, cGMP-PKG signaling pathway, vascular smooth-muscle contraction; PPI networks: up: 539 nodes (TNF, PTPRC, IL8, IL10, TYROBP); down: 385 nodes (CALM1, ACTA1, ACTN2, ACTA2, ACTC1); miRNA: 7 for up DEGs, 14 for down DEGs; 17 TFs for up DEGs; 22 TFs for down DEGs; VCAM1, TNF, CTSS, IL10, IL1B, IL6, miR-19A/B/C as potential IA biomarkers |
| 33313152 [74] | GSE13353 GSE15629 GSE54083 GSE122897 | 24 RA, 18 UA | mRNA | Affymetrix, Agilent, Illumina microarray | gene expression profiling in RA | DEGs, co-expression networks with WGCNA modules, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), MCODE for key gene cluster, GSEA for key genes | 49 DEGs: 28 up (PPBP, PF4, S100A8, FPR1, C15orf48); 21 down (NR1D2, ATP1A2, FMO2, SLC6A1, CYP4X1); RA: GO-BP: Signal transduction, Inflammatory response, Immune response, Innate immune response, Defense response to bacterium; KEGG: Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Chemokine signaling pathway; WGCNA modules (hub gene): 8 gene modules for RA: Blue (SLC7A7), Cyan (GFPT2), Green (ARF4), Green yellow (MAL), Lightcyan (KLHL34), Midnightblue (PLCB4), Purple (PRKG1), Salmon (VNN2); 6 gene modules for UA: Brown (BCHE), Lightcyan (LNPEP), Lightgreen (MT1G), Purple (MYADM), Salmon (CD53); KEGG: RA: Blue Brown: Lysosome, Tuberculosis, Phagosome, Osteoclast differentiation, Chemokine signaling pathway; Cyan: Pathways in cancer, HTLV-I infection, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Proteoglycans in cancer, Focal adhesion; Green: Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Focal adhesion, ECM–receptor interaction, Proteoglycans in cancer; Green-yellow: Arginine and proline metabolism, Gastric acid secretion, Histidine metabolism, Prion diseases, Mineral absorption; Midnightblue: Pathways in cancer, Amoebiasis, Calcium signaling pathway, Inositol phosphate metabolism, ECM–receptor interaction; Purple: Pathways in cancer, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Regulation of actin cytoskeleton, Focal adhesion, cGMP-PKG signaling pathway; Salmon: Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Chemokine signaling pathway; UA: Brown: PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), Focal adhesion, Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling, Glutamatergic synapse; Lightcyan: Pathways in cancer, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Proteoglycans in cancer, Regulation of actin cytoskeleton, Focal adhesion; Lightgreen: Mineral absorption, Glycolysis/Gluconeogenesis, Biosynthesis of antibiotics, Biosynthesis of amino acids, Carbon metabolism; Purple: Focal adhesion, ECM–receptor interaction, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Leukocyte transendothelial migration, Regulation of actin cytoskeleton; Salmon: Focal adhesion, ECM–receptor interaction, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, Leukocyte transendothelial migration, Regulation of actin cytoskeleton; Key genes for RA: C15orf48, AQP9, SLA, MPP1, PDZRN3 |
| 32589050 [75] | GSE6551 GSE13353 GSE26969 GSE75436 GSE106520 GSE36791 | vessel wall: 33 IA, 27 ctrl; serum: 16 UA, 16 ctrl; blood: 43 RA, 18 UA | mRNA | Affymetrix, Agilent, Ilumina microarray | gene expression profiling in IA—vessel wall and blood | DEGs, co-expression networks with WGCNA modules, clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | UA vs. ctrl: DEGs: 783 up, 1097 down; WGCNA modules: purple, green-yellow, yellow; GO: purple: signal release, regulation of neuron projection development, regulation of hormone secrection, regulation of amino acid transport, positive regulation of secretion by cells, green-yellow: protein retention in ER lumen, nucleobase-containing small molecule biosynthese process, maintenance of protein localization in organelle, yellow: regulation of plasma lipoprotein particle levels, receptor catabolic process, plasma lipoprotein particle clearence, neutrophil-mediated immunity, neutrophil degranulation; KEGG: purple: steroid hormone biosynthesis, Ras signaling pathway, mannose type O-glycan biosynthesis, glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism, glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis—heparan sulfate, green-yellow: nucleotide excision repair, mismatch repair, glutathione metabolism, fructose and mannose metabolism, DNA replication, yellow: riboflavin metabolism, platinum drug resistance, pentose and glucuronate interconversion, other glycan degradation, N-glycan biosynthesis; RA vs. ctrl: DEGs: 711 up, 1020 down; WGCNA modules: blue, turquoise; GO: blue: translational inhibition, SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, protein targeting to membrane, protein targeting to ER, protein targeting, turquoise: regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity, regulation of innate immune response, reactive oxygen species metabolic process, positive regulation of hemopoiesis, positive regulation of cell activation; KEGG: blue: starch and sucrose metabolism, spliceosome, ribosome, proteosome, proponoate metabolism, turquoise: Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, platelet activation, phagosome, osteoclast differentiation, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway; 24 hub genes expression in blood consistent with tissue; potential circulating markers for RA: CD163, FCEREG, FPRT1, ITGAM, NLRC4 |
| 34354366 [76] | GSE15629, GSE75436 GSE26969 GSE6551 GSE122897 | 34 IA, 26 ctrl; validation: 44 IA, 16 ctrl | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray RNA, RNAseq | gene expression profiling in IA, potential hub genes and pathways in IA | DEGs, RRA (Robust Rank Aggregation), clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING for PPI network, cytoHubba (hub genes) | RRA: 136 DEGs: 45 up (DSP, KRT14, FAP, COL5A2, ARL4C), 91 down (RERGL, NPY1R, PDZRN4, AOC3, RBPMS2); GO: extracellular matrix structural constituent, extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength, glycosaminoglycan binding, carbohydrate binding, structural constituent of muscle; KEGG: ECM–receptor interaction, protein digestion and absorption, phenylalanine metabolism, cAMP signaling pathway, amphetamine addiction; PPI: 8 hub genes associated with IA development: VCAN, COL1A1, COL11A1, COL5A2, POSTN, THBS2, CDH2 |
| 34403136 [65] | GSE122897 | 21 RA, 21 UA, 16 cortical artery | mRNA | RNAseq | gene expression profiling in RA and UA | DEGs, g:GOSt tool in the g:Profiler, REVIGO for functional annotation (GO), IPA networks; validation with available data: PRJNA553307, PRJNA665639, PMID: 29729990, PMID: 32525733, PMID: 25528428 | total 1768 DEGs, 318 DEGs in multiple comparisons; UA vs. ctrl: 377 DEGs: 123 up (COL10A1, IGHM, PMEL, SELP, PLVAP), 254 down (B3GAT1, SLC6A13, SLC13A4, GPR37L1, PTGDS); GO-BP up: extracellular matrix organization, extracellular structure organization, cell motility, localization of cell, skeletal system development; GO-MF up: extracellular matrix structural constituent, structural molecule activity, glycosaminoglycan binding; GO-CC up: extracellular matrix, extracellular region, endoplasmic reticulum lumen, collagen type IV trimer; GO-BP down: chemical synaptic transmission, regulation of neurotransmitter levels, neurotransmitter transport, cell–cell signaling, nervous system development; GO-MF down: metal ion transmembrane transporter activity, transmembrane transporter activity, inorganic solute uptake transmembrane transporter activity, transporter activity, active ion transmembrane transporter activity; GO-CC down: synapse, cell junction, presynapse, cell periphery, cell projection; IPA networks: Amino acid metabolism, molecular transport, small molecule biochemistry; behavior, cellular function and maintenance, small molecule biochemistry; endocrine system disorders, organ morphology, organismal injury and abnormalities; cell morphology, lipid metabolism, small molecule biochemistry; carbohydrate metabolism, connective tissue development and function, skeletal and muscular system development and function; cell morphology, connective tissue development and function, skeletal and muscular system development and function; RA vs. ctrl: 925 DEGs: 349 up (CXCL5, ACAN, LAMC2, PLAC8, CD300E), 576 down (KIF1A, PSD2, RUNDC3A, BCAN, CAMK2A); GO-BP up: immune system process, response to cytokine, extracellular matrix organization, extracellular structure organization, immune response; GO-MF up: oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, 2-oxoglutarate as one donor, and incorporation of one atom each of oxygen into both donors, dioxygenase activity, extracellular matrix structural constituent; GO-CC up: endomembrane system, endoplasmic reticulum lumen, extracellular matrix, cytoplasmic vesicle, specific granule; GO-BP down: nervous system development, chemical synaptic transmission, cell–cell signaling, regulation of neurotransmitter levels, neurotransmitter transport; GO-MF down: metal ion transmembrane transporter activity, inorganic solute uptake transmembrane transporter activity, transmembrane transporter activity, transporter activity, cytoskeletal protein binding; GO-CC down: synapse, cell junction, neuron projection, cell projection, postsynapse; IPA networks: Cellular development, embryonic development, organismal development; cancer, hematological disease, organismal injury and abnormalities; cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, molecular transport, nervous system development and function; cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, cellular assembly and organization, cellular development; cardiovascular disease, organismal injury and abnormalities, tissue morphology; RA vs. UA: 466 DEGs: 383 up (MTRNR2L1, CD300E, MARCO, ANPEP, CLEC5A), 83 down (CRLF1, KIF1A, KRT17, HMCN2, THBS4); GO-BP up: immune response, immune system process, cell activation, leukocyte degranulation, secretion by cell; GO-MF up: cargo receptor activity, Toll-like receptor binding, identical protein binding, Rac GTPase binding, cytokine binding; GO-CC up: plasma membrane, cell periphery, secretory granule, vesicle, membrane; GO-BP down: multicellular organismal process, system development; IPA networks: Cellular development, cellular function and maintenance, cellular growth and proliferation; carbohydrate metabolism, cellular movement, hematological disease; cell-to-cell signaling and interaction, hematological system development and function, hypersensitivity response; carbohydrate metabolism, cell morphology, inflammatory response; cellular development, cellular growth and proliferation, hematological system development and function; in validation—common genes/protein: ALDH1A1, HMOX1, PPIF, TYMP |
| 34895131 [77] | Aneurysm Gene Database www.cuilab.cn/agd (accessed on 31 December 2022) | different types of aneurysms: IA, AAA, TAA, TAAD, AA, AD, RA | mRNA | microarray RNA | gene expression profiling and protein–protein interaction networks in different types of aneurysms | PPI networks, DEGs, clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | IA: GO-MF: ubiquitin protein ligase binding, ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding, phosphatase binding, RNA polymerase II transcription factor binding; GO-BP: regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity, regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway, regulation of binding, positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity, peptidyl-serine phosphorylation; KEGG: hepatitis B, viral carcinogenesis, Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection, Ebstein-Barr virus infection, proteoglycans in cancer; RA: GO-MF: ubiquitin ligase binding, ubiquitin-like protein ligase binding, disordered domain specific binding, phosphatase binding, protein phosphatase binding; GO-BP: regulation of binding, regulation of protein binding, response to heat, positive regulation of proteolysis, response to reactive oxygen species; KEGG: fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis, prostate cancer, proteoglycans in cancer, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, viral carcinogenesis; candidate driver genes: IA: CUL3, JUN, CAV1, WWOX, EGFR; RA: TXN, HP, MMP9, YWHAQ, GRB2 |
| 34997174 [78] | GSE13353 GSE54083 GSE75436 | total: 11 RA, 23 UA, 15 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix, Agilent microarray | epithelial–mesenchymal transition genes expression in UA | DEGs focused on EMT-related genes (900); co-expression network with WGCNA modules, clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING for PPI, GSEA for hub genes | RA vs. ctrl: DEGs: 61 up (SDC1, HK2, TIMP1, HAVCR2, CCR5), 15 down (SERPINI1, ADIPOQ, AGTR1, AFAPIL2, WNT11); GO-BP: response to lipopolysaccharide, response to molecule of bacterial origin, cellular response to lipopolysaccharide, cellular response to molecule of bacterial origin, cellular response to biotic stimulus; GO-CC: collagen-containing extracellular matrix, secretory granule lumen, cytoplasmic vesicle lumen, vesicle lumen, external side of plasma membrane; GO-MF: receptor-ligand activity, signaling receptor activator activity, cytokine activity, G-protein-coupled receptor binding, cytokine receptor binding; KEGG: chemokine signaling pathway, proteoglycans in cancer, lipid and atherosclerosis, shigellosis, viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor; RA vs. UA: DEGs: 35 up (CD36, WNT11, HAS2, PDGFD, MYC), 8 down (NUAK1, CDH11, DLX2, FZD7, VCAN); GO-BP: regulation of vasculature development, epithelial cell proliferation, ameboidal-type cell migration, regulation of angiogenesis, urogenital system development; GO-CC: collagen-containing extracellular matrix, endoplasmic reticulum lumen, transcription regulator complex, focal adhesion, cell-substrate junction; GO-MF: receptor ligand activity, signaling receptor activator activity, cytokine activity, cytokine receptor binding, G-protein-coupled receptor binding; KEGG: proteoglycans in cancer, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, human cytomegalus virus infection, viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; UA vs. ctrl: DEGs: 40 up (CEMIP, CDKN2A, CDH2, CDH11, SALL1), 30 down (ADIPOQ, WNT11, GPC3, CCL21, HAS2); GO-BP: ossification, urogenital system development, renal system development, cell chemotaxis, epithelial tube morphogenesis; GO-CC: collagen-containing extracellular matrix, endoplasmic reticulum lumen, membrane raft, membrane microdomain, membrane region; GO-MF: receptor ligand activity, signaling receptor activator activity, cytokine activity, G-protein-coupled receptor binding, cytokine receptor binding; KEGG: cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, proteoglycans in cancer, Salmonella infection, viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor, malaria; 3 common gene for all: ADIPOQ, WNT1, CCL21; WGCNA modules: green positively correlated with ctrl and negatively with UA; red negatively correlated with ctrl and positively with UA; GSEA hub genes: green module: WNT11, GLI1, PCDH9, GPC3, L1CAM; red module: KRT18, CTHRC1, POSTN, CDH11, FHL2; PPI hub genes: CDH11, SPARC, FSTL1, FN1, PCDH9 |
| 35250300 [79] | GSE13353 GSE54083 GSE75436 | 47 IA, 25 STA | mRNA | Affymetrix, Agilent microarray | gene expression profiling in IA | DEGs, WebGestalt for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), co-expression network with WGCNA modules, STRING for PPI networks, CytoHubba for hub genes, CIBERSORT for infiltrating cell composition analysis | 266 DEGs: 162 up (COL11A1, EME2, ADAMTS10, HTR4, DAPLI), 104 down (CASQ2, ITLN1, RBPMS2, MYOT, ACTAI); GO-BP: inflammatory response, defense response, immune response, muscle system process, muscle contraction; KEGG: chemokine signaling pathway, rheumatoid arthritis, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway; WGCNA modules (pathways): blue (immune response, inflammatory response, leukocyte activation, chemokine signaling pathway, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway), pink (inflammatory response, defense response, myeloid leukocyte cytokine production, cytokine production involved in immune response, regulation of mast cell cytokine production, regulation of inflammatory response, positive regulation of immune system process, leukocyte-mediated immunity, mast cell cytokine production, regulation of intreleukin-10 production, complement and coagulation cascades); Hub genes: blue module: CCR5, CCL20, pink module: FPR3, CCL4; CIBERSORT: macrophages, neutrophils proportions higher in ctrl, M0, M2 macrophages, activated mast cells proportions higher in IA |
| 35432454 [80] | GSE13353 GSE15629 GSE54083 | 27 RA, 19 UA | mRNA | Affymetrix, Agilent microarray | gene expression profiling in RA | DEGs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING for PPI network, CytoHubba for hub genes, MCODE for subnetworks | 249 common DEGs: 96 up, 153 down; GO-BP up: Positive regulation of cell proliferation, Apoptotic process, Response to lipopolysaccharide, Inflammatory response, Negative regulation of cell proliferation; GO-CC up: Nucleoplasm, Membrane, Endoplasmic reticulum, Endoplasmic reticulum membrane, Cell surface; GO-MF up: Protein binding, Receptor activity, SH3 domain binding, KDEL sequence binding, ER retention sequence binding; KEGG up: Proteoglycans in cancer, Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Mineral absorption, Hepatitis B, Malaria; GO-BP down: Positive regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, Protein phosphorylation, Positive regulation of gene expression, Positive regulation of apoptotic process, Axonogenesis; GO-CC down: Extracellular exosome, Receptor complex, Myelin sheath, Endosome membrane, Mitochondrial membrane; GO-MF down: Metal ion binding, ATP binding, Kinase activity, NADP binding, Steroid hormone binding; KEGG down: Focal adhesion, Pancreatic secretion, Thyroid hormone signaling pathway, Staphylococcus aureus infection, ErbB signaling pathway; PPI network: 241 nodes (STAT3, APP, JUN, ITGB2, GSK3B); potential biomarker for RA—hub genes: APP, JUN, GSK3B, ErbB2, PPBP, THBS1 |
| 35465608 [81] | GSE75436 GSE54083 GSE26969 GSE13353 GSE15629 GSE158558 GSE122897 GSE66240 | 108 IA, 73 ctrl; training: microarray; validation: RNAseq | mRNA | Affymetrix, Agilent, Illumina microarray, RNAseq | expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-related genes in IA | DEGs, GSEA for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), ERS (endoplasmic reticulum stress)-related DEGs, and pathways, immunocyte infiltration, VSMC phenotype, co-expression analysis with WGCNA modules, ERS-TF-miRNA networks | DEGSs: training: 1628 up, 2013 down; validation: 590 up, 685 down; ERS-related DEGs: 6 up (FKBP14, TOR1A, EDEM1, BAX, CALR, SEC61B), 2 down (STUB1, ADD1); GO: endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment, response to topologically incorrect protein, response to unfolded protein, lysosomal membrane, rough endoplasmic reticulum; KEGG: protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum, lysosome, oxidative phosphorylation, pyruvate metabolism, phagosome; GSEA: up in IA: biological regulation, cellular anatomical entity, cytoplasm, endomembrane system, response to stimulus; up in ctrl: cellular macromolecule metabolic process, cellular metabolic process, gene expression, nuclear lumen, regulation of macromolecule metabolic process; VSMC phenotype in IA: VSCMC-synthesis-phenotype-feature genes |
| 35655614 [82] | GSE75360 GSE122897 GSE13353 GSE166676 | PBMC HA: 11 HA, 10 ctrl; tissue: 44 IA, 16 ctrl; 11 RA, 8 UA; AAA tissue sc: 4 AAA, 2 ctrl | mRNA | RNAseq, single-cell RNAseq, microarray | gene expression profiling in IA with HA, identification of potential therapeutic targets | DEGs, monocyte/macrophage-related DEGs from scRNAseq (AAA), TRRUST for TF-gene network, Molecular Complex Detection for subnetworks, GSEA for functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | 95 DEGs common for IA and HA including 5 monocyty/macrophage-related DEGs (IFI30, SERPINE1, HMOX1, IL24, RUNX1); functional pathways: up: viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor, HIF-1 signaling pathway, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, receptor ligand activity, phosphatidylinositol-3,4-biphosphate binding; down: exocytic vesicle membrane, synaptic vesicle membrane, neuron to neuron synapse, synaptic membrane, neuronal cell body; TF-gene network: RUNX1 as hub gene for IA |
| 35918429 [84] | GSE122897 GSE157628 GSE161044 | 48 IA, 19 ctrl | mRNA | Agilent microarray RNA, RNAseq | gene expression profiling in IA | DEGs, co-expression network with WGCNA modules, clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), GSVA for pathways, GSEA of the key gene, predicted TFs (Enrichr, hTFtarget), miRNA targets (GeneCards), ferroptosis markers (FerrDb), validation in animal model | DEGs of GSE122897: CFTR, MTMR7, TSPOAP1, YBX2, ABCC8; DEGs of GSE157628: PDE7B, XLOC_011278, LOC100131176, PLEKHA6, GNA14, C12orf40; WGCNA modules: green (115 hub genes: ATP1A4, LCNL1, TUB, PPP1R1B, GJB6); pink (130 hub genes: KDELR2, SEC24D, FBN1, CALU, COL5A2); GO-BP: organic acid transport, carboxylic acid transport, organic anion transport, monocarboxylic acid transport, multicellular organismal signaling; KEGG: butanoate metabolism, valine leucine and izoleucine degradation, propanoate metabolism, β alanine metabolism, limonene and pinene degradation; SLC2A12 as key gene related to the ferroptosis phenotype and ferroptosis marker; TFs: AR, NANOG; miRs: mir-223-5p, miR-502-3p |
| 36057911 [85] | GSE122897 GSE75436 GSE15629 GSE75434 | 72 IA, 36 ctrl | mRNA | Affymetrix microarray RNA, RNAseq | Ferroptosis-related genes’ expression profiling in IA | DEGs, ferroptosis-related genes (FRG), STRING for PPI network, clusterProfiler, MSigDB, GSVA for functional annotation (GO, KEGG, HALLMARKS), GSEA, xCell algorithm for immune cell infiltration, co-expression network for FRG with WGCNA, RegNetwork for predicted miRNAx and TFs, DGIdb for drugs prediction | 28 DEFRGs: 22 up, 6 down; PPI network: 17 markers, 7 drivers, 4 suppressors; GO-BP: heme NADPH as acceptor, amino transmembrane acid transporter, single donors molecular incorporation, cyclin-dependent proteine serine-threonine kinase, cytokine receptor factor activator; KEGG: ferroptosis, bladder cancer, HIF-1 signaling pathway, rheumatoid arthritis, IL-17 signaling pathway; HALLMARKS: epithelial–mesenchymal transition, P53 pathway interferone response, apoptosis, oxidative phosphorylation, pancreas β cells; immune response activity in IA: antigen processing and presentation, cytokines, interleukins; immunocyte-FRGs correlation: positive ALOX5-macropahe, negative ATP6V1G2-effector memory CD8 T cell; hub FRGs: ABCC1, CDKN1A, MT3, ZFP69B; 2 ferroptosis subtypes; suggested drug targets: FCGR3A, FCGR2A (etanercept, rituximab, trastuzumab, cetuximab, infliximab, adalimumab) |
| 28587396 [68] | GSE54083 GSE46337 GSE26969 GSE15629 GSE6551 GSE50867 GSE46336 | mRNA: 37 IA, 25 ctrl; miRNA: 11 IA, 7 ctrl | mRNA, miRNA | Agilent, Affymetrix microarray | mRNA and miRNA expression profiling in IA, regulatory networks construction | DEGs, DEmiRNAs, miRNA target prediction (DIANAmT, miRanda, miRDB, miRWalk, PICTAR, TargetScan), GENECODIS for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), miRNA-target gene network construction | 15 DEmiRNAs: 10 up (hsa-miR-188-5p, hsa-miR-1183, hsa-miR-18a, hsa-miR-7, hsa-miR-590-5p), 5 down (hsa-miR-425a, hsa-miR-182, hsa-miR-1825, hsa-miR-139-5p, hsa-miR-193b); 1,447 DEGs: 682 up, 765 down; GO-BP: Peptide transport, Amide transport, Positive regulation of phosphorylation, Single-organism catabolic process, Positive regulation of phosphorus metabolic process; GO-CC: Collagen trimer, Endoplasmic reticulum lumen; GO-MF: ATP binding, Adenyl ribonucleotide binding, Adenyl nucleotide binding, ATPase activity coupled to movement of substances, Primary active transmembrane transporter activity; KEGG: Focal adhesion, Pathways in cancer, Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Amoebiasis, Chemokine signaling pathway; key in networks: hsa-miR-7, hsa-miR182, hsa-miR-324-3p, hsa-miR-139-5p, hsa-miR-130b, RPS6KA3, TSC1, AIM1, GAS7, GFOD1 |
| 35034029 [66] | GSE122897 | 8 IA, 10 ctrl | mRNA, miRNA | Illumina microarray | miRNA expression profiling and pathways in IA | DEmRNAs, DEmiRNAs, co-expression network with WGCNA, functional annotation (KEGG), miRNA–mRNA regulatory network | 955 DEmRNAs: 480 up, 475 down; 46 DEmiRNAs: 36 up, 10 down; KEGG for DEmRNA: ECM–receptor interaction, focal adhesion, cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), complement and coagulation cascades, hematopoietic cell lineage; WGCNA: yellow module, 16 hub miRNAs; KEGG for predicted target DEmRNAs: vascular smooth-muscle contraction, focal adhesion, regulation of actin cytoskeleton, PPAR signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway |
| 33750300 [64] | GSE66240 | 6 IA, 12 STA | mRNA, lncRNA, miRNA | RNAseq, miRNA microarray | ceRNA networks in IA | DElncRNAs, DEmiRNAs, DEmRNAs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), miRcode for lncRNA–miRNA interactions, miRDB, miRTArBase, TargetScan for miRNA targets, Cytoscape for ceRNA networks | 2914 DEmRNAs: 1807 up, 1107 down; 234 DEmiRNAs: 10 up, 224 down; 341 DElncRNAs: 201 up, 141 down; GO-BP: skeletal system development, positive regulation of cell migration, muscle contraction, inflammatory response, extracellular matrix organization; KEGG: viral myocarditis, vascular smooth-muscle contraction, proteoglycans in cancer, protein digestion and absorption, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway; ceRNA networks with 90 nodes (60 mRNAs, 9 miRNAs, 22 lncRNAs); highest degree: hsa-miR-17, PVT1, NEAT1, KCNQ1OT1 |
| 35711443 [83] | GSE122897 GSE54083 GSE75436 GSE13353 GSE66239 GSE36791 GSE159610 | vessel wall: 39 RA, 29 UA, 28 IA, 51 ctrl; blood: 43 RA, 25 UA, 40 ctrl | mRNA, lncRNA, miRNA | RNAseq, microarray | transcriptomic profiling in IA focused on immune microenvironment | DEGs, DElncRNAs, immune-related DEGs, estimation of immune cell infiltration (single-sample GSEA, ssGSEA), GSEA for functional annotation (GO. KEGG), STRING for PPI network, immunohistochemistry, DEmiRNAs, miRNA targets (miRWalk, lncBase), ceRNA regulatory networks, drug-gene interactions (GDIdb), co-expression network with WGCNA | IA: 746 DEmrNAs, 552 DElncRNAs; 1775 immune-related DEGs: 146 up; 99 down; KEGG: JAK-STAT signaling pathway, lysosome, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, T cell receptor signaling pathway, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway; immune-related DEGs: KEGG up: cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, viral protein interaction with cyokine and cytokine receptor, Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection, JAK-STAT signaling pathway, chemokine signaling pathway; KEGG down: neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, axon guidance, Ras signaling pathway, cAMP signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway; GO up: positive regulation of T cell activation, lymphocyte proliferation, regulation of T cell activation, leukocyte cell–cell adhesion, positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation; GO down: axonogenesis, regulation of neurogenesis, stem cell development, negative regulation of nervous system development, regulation of cell development; infiltrating cells (expression results): IA: effector immune cells (macrophage, activated, dendritic cell (DC), natural killer (NK) cell, NK T cell, CD56+ NK cell, myeloid-derived suppressor cell (MDSC), activated CD4 T cell, activated CD8 T cell, γ delta (gd) T cell, regulatory T (Treg) cell, and Type 1 T helper (Th1) cell, RA vs. UA: mast cell, neutrophil; PPI network hub genes: IL6, IL10, STAT1, CXCL10, VEGFA; WGCNA modules: yellow positively correlated with RA (γ delta T cell, macrophage; enriched in: extracellular matrix organization, external encapsulating structure organization, collagen metabolic process, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, ECM–receptor interaction), brown negatively correlated with RA (CD56+ NK cell, macrophage; enriched in SMC-contraction-related genes: muscle contraction, regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration, calcium ion transmembrane import into the cytosol, cAMP signaling pathway, calcium signaling pathway); potential therapeutics: IL6 inhibitors (Olokizumab, Siltuximab), VEGFA inhibitors (Aflibercept, Bevacizumab, Pegaptanib sodium) |
| PMID/Reference | Datasets ID | Cohorts | Source | RNA Type | Detection/Verification Methods | Aim of the Study | Analytical Methods | Major Findings including Differentially Expressed RNAs, Involved Pathways/Functions (Top 5) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28930970 [89] | GSE36791 | 43 RA, 18 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | Illumina microarray | gene expression profiling in RA and regulatory miRNA prediction | DEGs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), co-expression network with WGCNA modules, cGRNB for predicted miRNA–gene interactions | 304 DEGs: 167 up, 137 down; GO down: translational elongation, structural constituent of ribosome, cytosolic ribosome, ribosomal subunit, ribosome; KEGG down: Ribosome; WGCNA modules: up (GO, KEGG): blue (cell fraction, IgG binding), brown (nucleosome assembly, chromatin assembly), turquoise (innate immune response, inflammatory response), yellow (interleukin-1 receptor activity, interleukin-1 binding); down: blue (cytolysis, cellular defense response), turquoise (translational elongation, Ribosome); 16 predicted regulatory miRNAs (hsa-miR-1304, hsa-miR-373 hsa-miR-514, hsa-miR-33b, hsa-miR-568) |
| 31026661 [90] | GSE36791 | 43 RA, 18 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | Illumina microarray | gene expression profiling in RA | DEGs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING for PPI network, GSEA for pathways of key genes | 528 DEGs: 311 up (C19ORF59, CA1, IL1R2, ARG1, ANXA3), 217 down (MAL, CD7, ABLIM1, CD6, IL2RB); GO: translation, T cell activation, innate immune response, immunoglobulin-mediated immune response, protein phosphorylation; KEGG: Ribosome, Hematopoietic cell lineage, Transcriptional misregulation in cancer, T cell receptor signaling pathway, Systemic lupus erythematosus; PPI network with hub genes (ARG1, MAPK14, RPS2, SPI1, FYN); GSEA (potential aSAH biomarkers): up: MAPK14, CEBPB, FLOT1, down: CD4 |
| 32084215 [86] | GSE36791 GSE73378 | 146 RA, 125 ctrl; validation in: 10 UA, 10 RA, 10 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | Illumina microarray; validation: qPCR | gene expression profiling and hub genes in RA | DEGs, co-expression network with WGCNA modules and hub genes, clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | 396 DEGs (BASP1, CD74, CEBPB, ECHDC2, GZMK); WGCNA modules: turquoise (190 hub genes), blue (38 hub genes), brown (10 hub genes); GO-BP: rRNA processing, Ribonucleoprotein complex biogenesis, rRNA metabolic process, Ribosome biogenesis, ncRNA processing; GO-CC: Cytosolic ribosome, Ribosomal subunit, Ribosome, Focal adhesion, Cell–substrate adherens junction; GO-MF: Structural constituent of ribosome; KEGG: Ribosome; 6 potential biomarkers of the progression and IA rupture: BASP1, CEBPB, ECHDC2, GZMK, KLHL3, SLC2A3 |
| 33174039 [92] | GSE36791 | 43 RA, 18 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | Illumina microarray | gene expression profiling in RA, identification of aSAH-related lncRNA | DEGs, DElncRNA, co-expression network with WGCNA modules, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), lncRNA–mRNA regulatory network construction (Cytoscape), Comparative Toxigenomics Database (DTB) for aSAH-related pathways | 25 DElncRNAs: 12 up, 13 down; 1979 DEGs: 781 up, 1198 down; WGCNA modules (DEGs and/or DElncRNAs): purple (50), turquoise (201), green (140), pink (76); ceRNAs networks with 382 nodes, 7 up lncRNA (HCG27, ZFAS1 antisense RNA, LINC002665, MRV1-AS1, CYP1B1-AS1); GO-BP in WGCNA modules: green: leukocyte activation, inflammatory response, response to wounding, cell activation, positive regulation of apoptosis; pink: intracellular signaling cascade, phosphate metabolic process, phosphorus metabolic process, phosphorylation, protein amino acid phosphorylation; purple: regulation of apoptosis, regulation of programmed cell death, regulation of cell death, apoptosis, programmed cell death; turquoise: carbohydrate catabolic process, cellular carbohydrate catabolic process, defense response, hexose catabolic process; KEGG: Chemokine signaling pathway, Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, MAPK signaling pathway, Leukocyte transendothelial migration, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway |
| 33567366 [87] | GSE36791 GSE54083 GSE13353 GSE26969 GSE122897 | internal validation: 62 RA, 16 UA, 31 ctrl; external validation: 22 RA, 21 UA, 16 ctrl | peripheral blood | mRNA | microarray | gene expression profiling in iA, predictive models for aSAH | DEGs, co-expression network with WGCNA modules, clusterProfiler, GSEA for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), STRING for PPI network and hub genes (CytoHubba), prediction model construction (LASSO) | 433 DEGs (up: CEBPD, MMP9, IL18RAP, IL1R2, S100A12; down: CEACAM8, EME2, ADAMTS10, XK, ARG1); WGCN modules: black with strongest association with RA; GO-BP: inflammatory response, defense response to bacterium, innate immunity response, positive regulation of mast cell degranulation, MyD88-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway; GO-CC: extracellular exosome, extracellular space, specific granule, plasma membrane, IPAF inflammasome complex; GO-MF: catalytic activity, glucose binding, cysteine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity, protein homodimerization activity, transcription corepressor activity; KEGG: inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), amoebiasis, legionellosis, fatty acid biosynthesis, salmonella infection; PPI network with 30 hub genes; 4 rupture-related genes: TNFAIP6, NCF2, OSM, IRAK3 |
| 34485395 [88] | GSE36791 GSE6551 | 51 RA, 6 UA, 18 ctr | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | Illumina microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in RA | DEGs, clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), CIBERSORT for cell composition analysis, STRING for PPI network, MCODE for subnetworks | RA vs. ctrl: 58 DEGs:50 up, 8 down; GO-BP: neutrophil activation, neutrophil degranulation, neutrophil activation involved in immune response, neutrophil-mediated immunity, killing of cells of other organism; KEGG: Staphylococcus aureus infection, Transcriptional misregulation in cancer, Viral protein interaction with cytokine and cytokine receptor, Cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); CIBERSORT: B_cells_memory, T_cells_CD8, T_cells_CD4_memory_resting, T_cells_CD4_naive, Macrophages_M0, Macrophages_M2, NK_cells_resting, monocytes, neutrophils; PPI network with 24 hub genes: IL2RB and CCR7—down in RA |
| 34542421 [94] | GSE36791 | 43 RA, 18 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | mRNA | Illumina microarray/qPCR | gene expression profiling in RA | co-expression network with WGCNA modules and hub genes, METASCAPE for functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | WGCNA modules (hub genes): red (ARRB2, CSF3R, DENND3, DYSF, GMIP); blue (ABCF1, ABHD14A, ACSL1, ADA, AIP); brown (ABHD14A, ACAD9, ACTR5, AFG3L2, ALKBH3); cyan (ACTR1A, AKAP11, API5, BRIX1, BUB3); GO-BP: peptide biosynthetic process, rRNA processing, ncRNA processing, cotranslational protein targeting to membrane, SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane; KEGG: HTLV-1 infection, Toxoplasmosis, RNA transport, Th17 cell differentiation, spliceosome; 7 genes as potential aSAH biomarkers: CD27, ANXA3, ACSL1, PGLYRP1, ALPL, ARG1, TPST1; 3 genes changed with aSAH progression: ANXA3, ALPL, ARG1 |
| 32756097 [91] | GSE50867 | 40 IA, 20 ctrl | plasma | circulating miRNA | Agilent microarray | circulating miRNA expression profiling in IA | co-expression network with WGCNA modules and hub genes, GSVA (hub miRNAs—disease state), predicted targets (diana_microt, elmmo, microcosm, Miranda, mirdb, pictar, pita, TargetScan), STRING for PPI network, Cytoscape for miRNA–mRNA network; clusterProfiler for functional annotation (GO, KEGG) | WGCNA brown module: GO-BP: gland development, cell cycle G1/S phase transition, positive regulation of cell cycle, cell–cell adhesion via plasma-membrane adhesion molecules, G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle; GO-MF: DNA-binding transcription activator activity RNA polymerase II-specific, proximal promoter sequence-specific DNA binding, RNA polymerase II proximal promoter sequence-specific DNA binding, SMAD binding; WGCNA modules (hub miRNAs): brown (hsa-miR-363-3p, hsa-miR-192-5p, hsa-miR-425-5p, hsa-miR-25-3p, hsa-miR-423-5p), green (hsa-miR-1281, hsa-miR-1825, hsa-miR-498-5p, hsa-miR-1280, hsa-miR-1234-3p); miRNA–mRNA network: 243 nodes (PTEN, VEGFA, CCND1, MDM2, CREB1) and hub miRNA (hsa-miR-93-5p); key pathway: PI3K/Akt signaling pathway |
| 33990177 [93] | GSE36791 | 43 RA, 18 ctrl | peripheral blood cells | mRNA, lncRNA | Illiumina microarray | mRNA and lncRNA expression profiling in RA | DEGs, DElncRNAs, DAVID for functional annotation (GO, KEGG), co-expression network with WGCNA modules, lncRNA–mRNA regulatory network construction (Cytoscape), GSEA in regulatory network | 25 DElncRNAs: 10 up (MRVI1-AS1, ZFAS1, FAM157C, CYP1B1-AS1, LINC02035); 15 down (INTS6-AS1, SNHG5, SNHG14, PRKCQ-AS1, DANCR), 536DEmRNAs: 307 up (S100A12, HP, IL18R1, CST7, MMP9); 229 down (FCER1A, CLC, CD27, IL2RB, CCR7); GO-BP: regulation of lymphocyte activation, positive regulation of cell activation, regulation of cell activation, positive regulation of immune response, positive regulation of response to stimulus; KEGG: adipocytokine signaling pathway, T cell receptor signaling pathway, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, cytokine–cytokine receptor interaction, ribosome; WGCNA modules (hub genes): yellow (CASP4, TNFSF13B, FNDC3B, N4BP2L2, OSM), blue (HIST2H2AB, ATP6V1C1, NFE2, USB1, NTN3), red (CEACAM4, SMAP2, CSGALNACT2, TLR2, TMIGD3), brown (IDI1, GNAI3, E2F3, WSB1, NRBF2), black (PFKFB4, SLC9A8, LIN7A, MGAM2, LILRB3), pink (ENTPD1, USP32, LTB4R, FGR, SBNO2); regulatory network: LINC00265 (NFKBIA, IRAK3), LINC00937 (NFKBIA) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morga, R.; Pera, J. Transcriptomic Studies on Intracranial Aneurysms. Genes 2023, 14, 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030613
Morga R, Pera J. Transcriptomic Studies on Intracranial Aneurysms. Genes. 2023; 14(3):613. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030613
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorga, Rafal, and Joanna Pera. 2023. "Transcriptomic Studies on Intracranial Aneurysms" Genes 14, no. 3: 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030613
APA StyleMorga, R., & Pera, J. (2023). Transcriptomic Studies on Intracranial Aneurysms. Genes, 14(3), 613. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14030613





