Alu Methylation Patterns in Type 1 Diabetes: A Case-Control Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
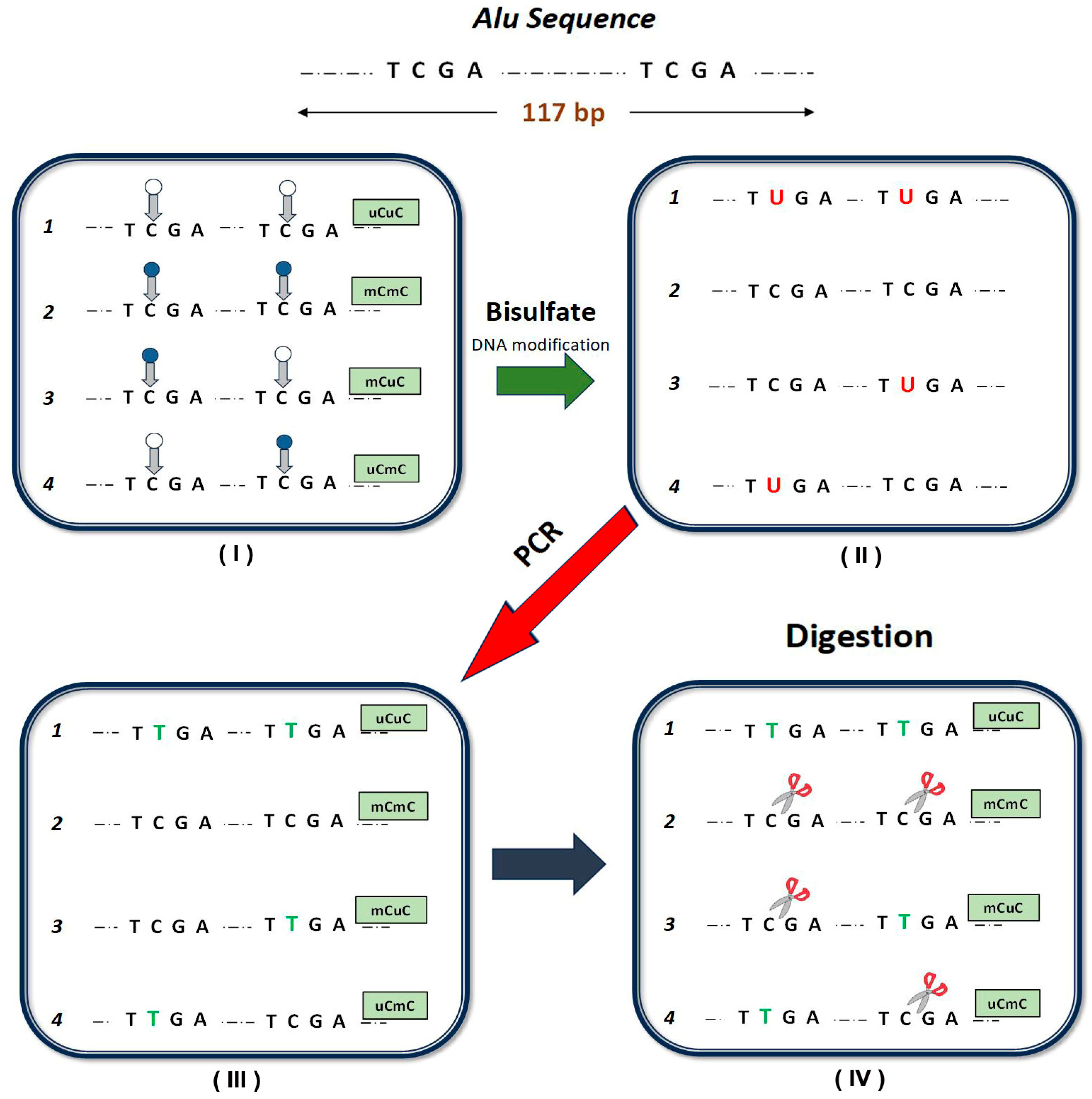
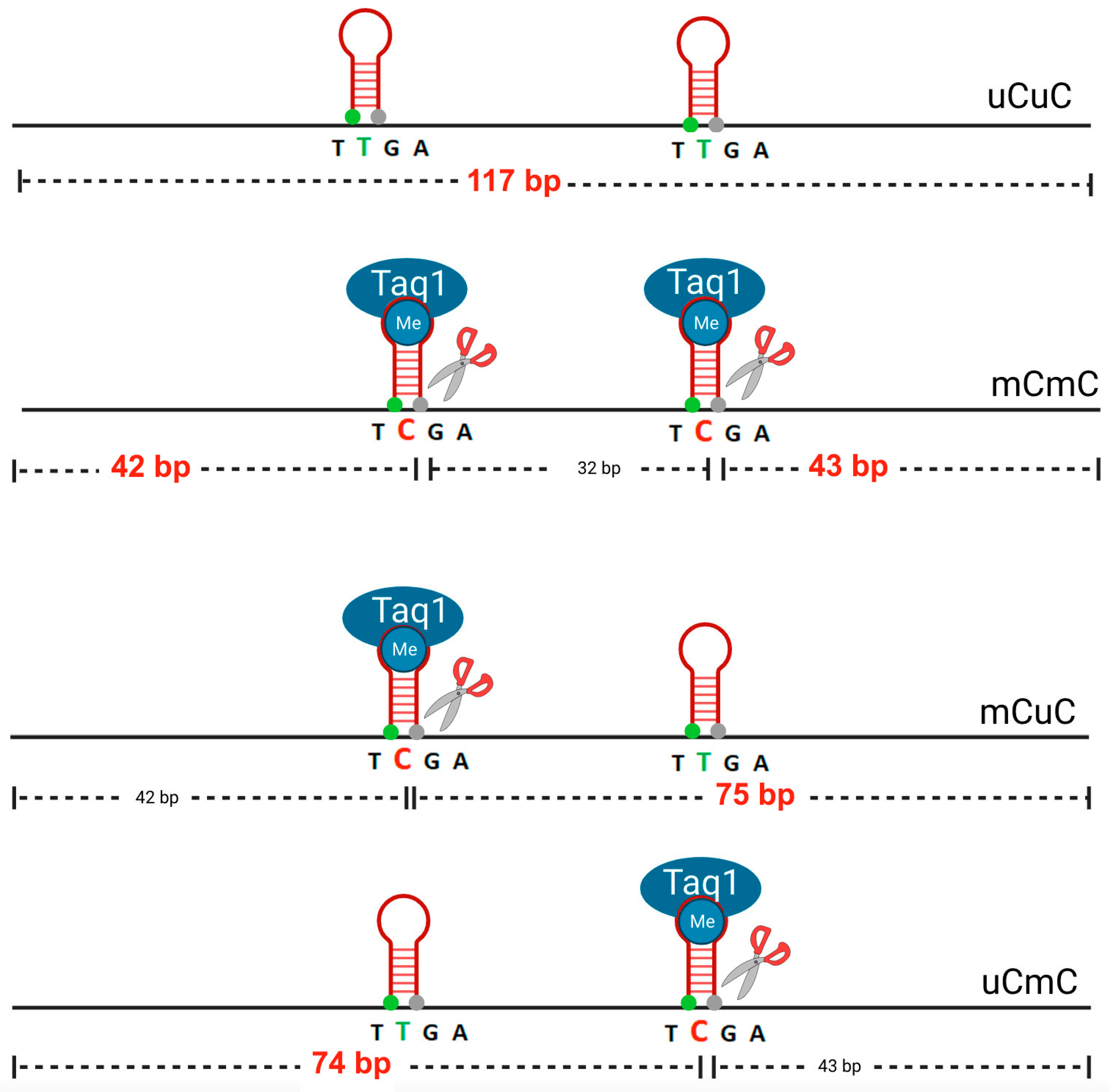
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- Total methylated loci % mC = 100 × (2C + 2B)/(2A + 2B + 2C) = 100 × (2D)/(2A + 2D);
- -
- Methylated pattern % mCmC = 100 × C/(A + B + C);
- -
- Unmethylated pattern % uCuC = 100 × A/(A + B + C);
- -
- And partially methylated patterns (% uCmC + % mCuC) =100 × B/(A + B + C).
3. Results
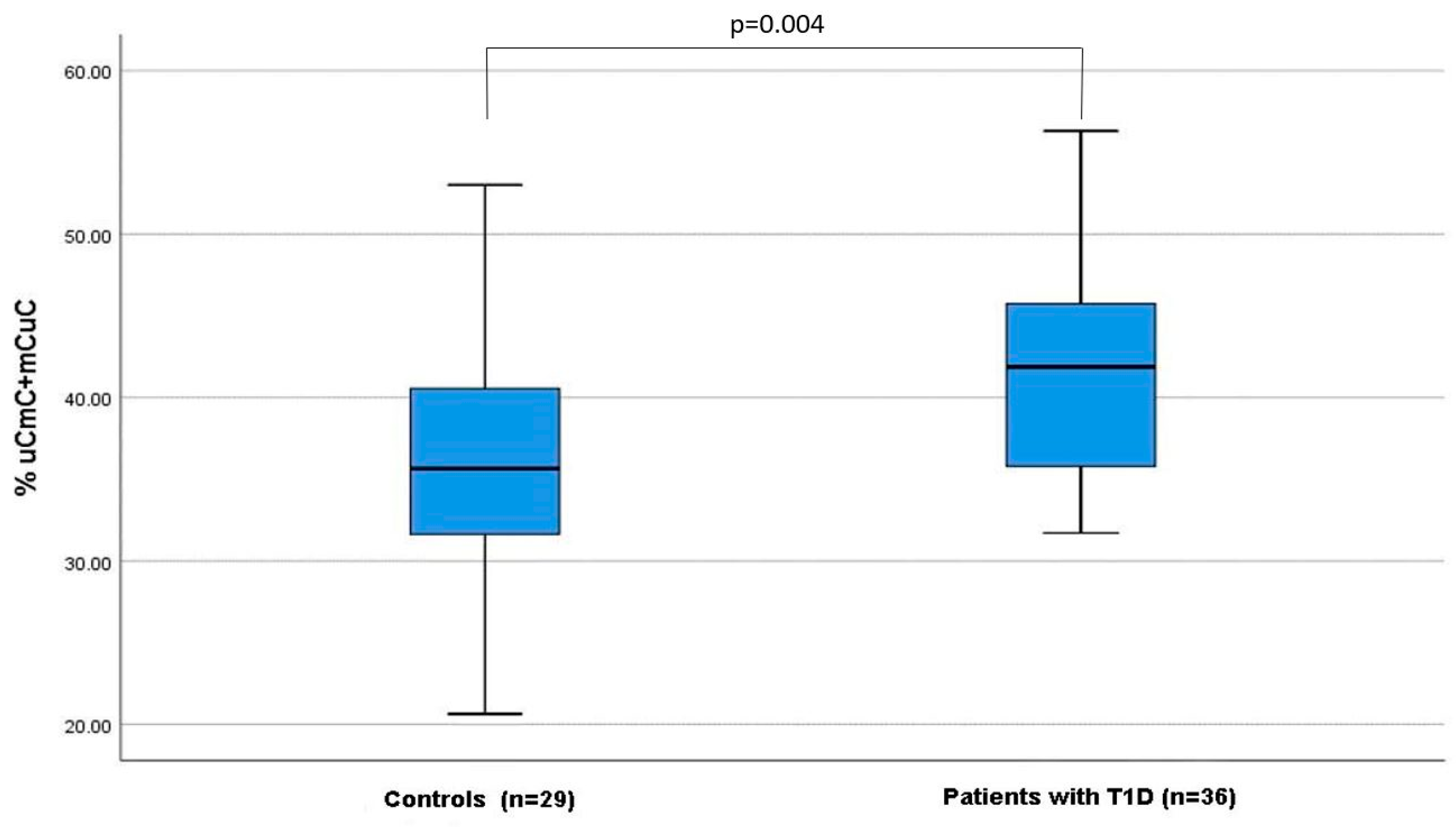
3.1. Investigation of the Total Methylation and the Different Methylation Patterns of Alu Elements in Patients with T1D Compared to Healthy Controls
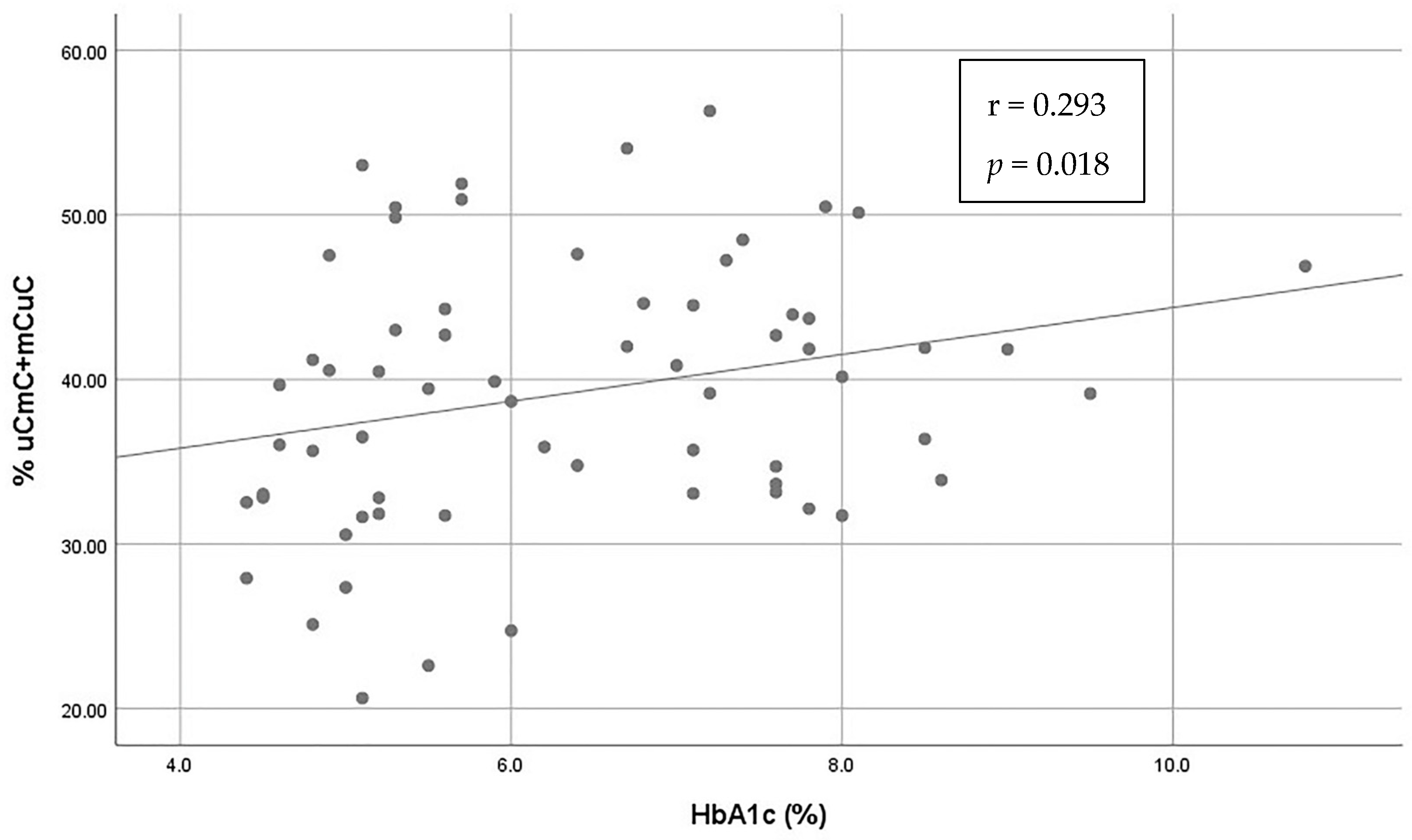
3.2. Investigation of the Association of Alu Methylation and Patterns with Patients’ Characteristics and Glycemic Control (Table 2)
| Variable | mC (%) | mCmC (%) | uCmC + mCuC (%) | uCuC (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | rho = 0.214, p = 0.087 | rho = 0.149, p = 0.235 | rho = 0.09, p = 0.474 | rho = −0.213, p = 0.089 | |
| Sex | Female | 66.9 (62.6–70.1) | 25.57 (19.4–36.3) | 41.2 (33.5–44.5) | 33.0 (30–37.5) |
| Male | 68.0 (64.3–71.9) | 29.3 (20.0–35.6) | 39.4 (33.0–42.7) | 32.0 (28.0–36.0) | |
| MW = 500, p = 0.812 | MW = 480, p = 0.615 | MW = 450, p = 0.368 | MW = 501, p = 0.821 | ||
| Age of diagnosis | rho = 0.250, p = 0.142 | rho = 0.428 **, p = 0.009 | rho = −0.431 **, p = −0.009 | rho = −0.256, p = 0.131 | |
| Duration of disease | rho = 0.134 p = 0.437 | rho = 0.061 p = 0.723 | rho = 0.088 p = 0.611 | rho = −0.128 p = 0.456 | |
| Presence of chronic diabetes complications | No | 66.3 (62.1–69.8) | 25.6 (17.4–34.7) | 40.9 (33.9–46.9) | 33.5 (30.0–38.0) |
| Yes | 68.5 (65.3–71.4) | 24.0 (20.0–27.4) | 42.3 (40.2–44.5) | 31.5 (29.0–35.0) | |
| MW = 117, p = 0.240 | MW = 148, p = 0.860 | MW = 119, p = 0.267 | MW = 116, p = 0.240 | ||
| Fasting glucose | rho = −0.110, p = 0.381 | rho = −0.178, p = 0.156 | rho = 0.187, p = 0.136 | rho = 0.117, p = 0.355 | |
| HBA1c | rho = 0.088, p = 0.486 | rho = −0.135, p = 0.283 | rho = 0.293 *, p = 0.018 | rho = −0.086, p = 0.498 | |
3.3. Differences between Patients with T1D Diagnosed before and after the Age of 15 Years
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lawrence, J.M.; Mayer-Davis, E.J. What do we know about the trends in incidence of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes? Diabetologia 2019, 62, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, A.C. Type 1 diabetes mellitus: Much progress, many opportunities. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e142242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roep, B.O.; Thomaidou, S.; van Tienhoven, R.; Zaldumbide, A. Type 1 diabetes mellitus as a disease of the β-cell (do not blame the immune system?). Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2021, 17, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasham, A.; Tomer, Y. The recent rise in the frequency of type 1 diabetes: Who pulled the trigger? J. Autoimmun. 2011, 37, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, M.; Zhang, W.; Concepcion, E.; Yi, Z.; Tomer, Y. DNA methylation profiles in type 1 diabetes twins point to strong epigenetic effects on etiology. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 50, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerram, S.T.; Dang, M.N.; Leslie, R.D. The Role of Epigenetics in Type 1 Diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2017, 17, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, M.; Lu, Q. An update on epigenetic regulation in autoimmune diseases. J. Transl. Autoimmun. 2022, 5, 100176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Chang, C.; Huang, G.; Zhou, Z. The Role of Epigenetics in Type 1 Diabetes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1253, 223–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Pinney, S.E. DNA methylation and its role in the pathogenesis of diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2017, 18, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suomi, T.; Kalim, U.U.; Rasool, O.; Laiho, A.; Kallionpää, H.; Vähä-Mäkilä, M.; Nurmio, M.; Mykkänen, J.; Härkönen, T.; Hyöty, H.; et al. Type 1 Diabetes in Children with Genetic Risk May Be Predicted Very Early with a Blood miRNA. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, e77–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štangar, A.; Kovač, J.; Šket, R.; Tesovnik, T.; Zajec, A.; Čugalj Kern, B.; Jenko Bizjan, B.; Battelino, T.; Dovč, K. Contribution of Retrotransposons to the Pathogenesis of Type 1 Diabetes and Challenges in Analysis Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hancks, D.C.; Kazazian, H.H. Roles for retrotransposon insertions in human disease. Mob. DNA 2016, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.R.; Doucet, A.J.; Kopera, H.C.; Moldovan, J.B.; Garcia-Perez, J.L.; Moran, J.V. The Influence of LINE-1 and SINE Retrotransposons on Mammalian Genomes. Microbiol. Spectr. 2015, 3, MDNA3-0061-2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, D.J.; Boeke, J.D.; Fink, G.R. Ty element transposition: Reverse transcriptase and virus-like particles. Cell. 1985, 42, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirivanichsuntorn, P.; Keelawat, S.; Danuthai, K.; Mutirangura, A.; Subbalekha, K.; Kitkumthorn, N. LINE-1 and Alu hypomethylation in mucoepidermoid carcinoma. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2013, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazazian, H.H.; Moran, J.V. Mobile DNA in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, A.; Carnevali, D.; Bollati, V.; Fustinoni, S.; Pellegrini, M.; Dieci, G. Identification of RNA polymerase III-transcribed Alu loci by computational screening of RNA-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 817–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yooyongsatit, S.; Ruchusatsawat, K.; Noppakun, N.; Hirankarn, N.; Mutirangura, A.; Wongpiyabovorn, J. Patterns and functional roles of LINE-1 and Alu methylation in the keratinocyte from patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.E.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Poscablo, C.; Real, F.X.; Kogevinas, M.; Silverman, D.; García-Closas, R.; Chanock, S.; Tardón, A.; Silverman, D.; et al. Genomic DNA hypomethylation as a biomarker for bladder cancer susceptibility in the Spanish Bladder Cancer Study: A case-control study. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 9, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalitchagorn, K.; Shuangshoti, S.; Hourpai, N.; Kongruttanachok, N.; Tangkijvanich, P.; Thong-ngam, D.; Voravud, N.; Sriuranpong, V.; Mutirangura, A. Distinctive pattern of LINE-1 methylation level in normal tissues and the association with carcinogenesis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8841–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tollefsbol, T.O. DNA methylation methods: Global DNA methylation and methylomic analyses. Methods 2021, 187, 28–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremenskoy, M.; Kremenska, Y.; Ohgane, J.; Hattori, N.; Tanaka, S.; Hashizume, K.; Shiota, K. Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation status of CpG islands in embryoid bodies, teratomas, and fetuses. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 311, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jintaridth, P.; Mutirangura, A. Distinctive patterns of age-dependent hypomethylation in interspersed repetitive sequences. Physiol Genom. 2010, 41, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wang, F.; Guan, J.; Le, J.; Wu, L.; Zou, J.; Zhao, H.; Pei, L.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, T. Relation between hypomethylation of long interspersed nucleotide elements and risk of neural tube defects. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajuddin, S.M.; Amaral, A.F.S.; Fernández, A.F.; Rodríguez-Rodero, S.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Moore, L.E.; Tardón, A.; Carrato, A.; García-Closas, M.; Silverman, D.T.; et al. Genetic and non-genetic predictors of LINE-1 methylation in leukocyte DNA. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangsri, S.; Subbalekha, K.; Kitkumthorn, N.; Mutirangura, A. Patterns and Possible Roles of LINE-1 Methylation Changes in Smoke-Exposed Epithelia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunaud, L.; Alberto, J.-M.; Ayav, A.; Gérard, P.; Namour, F.; Antunes, L.; Braun, M.; Bronowicki, J.-P.; Bresler, L.; Guéant, J.-L. Effects of vitamin B12 and folate deficiencies on DNA methylation and carcinogenesis in rat liver. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2003, 41, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukapan, P.; Promnarate, P.; Avihingsanon, Y.; Mutirangura, A.; Hirankarn, N. Types of DNA methylation status of the interspersed repetitive sequences for LINE-1, Alu, HERV-E and HERV-K in the neutrophils from systemic lupus erythematosus patients and healthy controls. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 59, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrman, M.A.; Schneider, W.J.; Südhof, T.C.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L.; Russell, D.W. Mutation in LDL Receptor: Alu-Alu Recombination Deletes Exons Encoding Transmembrane and Cytoplasmic Domains. Science 1985, 227, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konkel, M.K.; Batzer, M.A. A mobile threat to genome stability: The impact of non-LTR retrotransposons upon the human genome. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2010, 20, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jintaridth, P.; Tungtrongchitr, R.; Preutthipan, S.; Mutirangura, A. Hypomethylation of Alu elements in post-menopausal women with osteoporosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongsroy, J.; Patchsung, M.; Mutirangura, A. The association between Alu hypomethylation and severity of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Epigenetics 2017, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Pfeifer, G.P. Aging and DNA methylation. BMC Biol. 2015, 13, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The Hallmarks of Aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Pociot, F. Alu Elements as Novel Regulators of Gene Expression in Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility Genes? Genes 2015, 6, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malipatil, N.; Lunt, M.; Narayanan, R.P.; Siddals, K.; Cortés Moreno, G.Y.; Gibson, M.J.; Gu, H.F.; Heald, A.H.; Donn, R.P. Assessment of global long interspersed nucleotide element-1 (LINE-1) DNA methylation in a longitudinal cohort of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) individuals. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2018, 73, e13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rönn, T.; Ling, C. DNA methylation as a diagnostic and therapeutic target in the battle against Type 2 diabetes. Epigenomics 2015, 7, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, C.C.; Harjutsalo, V.; Rosenbauer, J.; Neu, A.; Cinek, O.; Skrivarhaug, T.; Rami-Merhar, B.; Soltesz, G.; Svensson, J.; Parslow, R.C.; et al. Trends and cyclic variation in the incidence of childhood type 1 diabetes in 26 European centres in the 25-year period 1989–2013: A multicentre prospective registration study. Diabetologia 2018, 62, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttmer, R.; Spijkerman, A.M.; Kok, R.M.; Jakobs, C.; Blom, H.J.; Serne, E.H.; Dekker, J.M.; Smulders, Y.M. Metabolic syndrome components are associated with DNA hypomethylation. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2013, 7, e106–e115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.L.; Bressan, J.; Peluzio, M.D.C.G.; Hermsdorff, H.H.M. LINE-1 in Obesity and Cardiometabolic Diseases: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitkumthorn, N.; Keelawat, S.; Rattanatanyong, P.; Mutirangura, A. LINE-1 and Alu Methylation Patterns in Lymph Node Metastases of Head and Neck Cancers. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2012, 13, 4469–4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, C.C.; Dahlquist, G.G.; Gyürüs, E.; Green, A.; Soltész, G.; EURODIAB Study Group. Incidence trends for childhood type 1 diabetes in Europe during 1989–2003 and predicted new cases 2005–20: A multicentre prospective registration study. Lancet 2009, 373, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongsroy, J.; Mutirangura, A. Decreased Alu methylation in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients increases HbA1c levels. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2023, 37, e24966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redondo, M.J.; Concannon, P. Genetics of Type 1 Diabetes Comes of Age. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Stefan-Lifshitz, M.; Tomer, Y. Genetic and environmental factors regulate the type 1 diabetes gene CTSH via differential DNA methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fradin, D.; Le Fur, S.; Mille, C.; Naoui, N.; Groves, C.; Zelenika, D.; McCarthy, M.; Lathrop, M.; Bougnères, P. Association of the CpG methylation pattern of the proximal insulin gene promoter with type 1 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, M.; Nizam, R.; Hebbar, P.; Jacob, S.; John, S.E.; Channanath, A.; Al-Kandari, H.; Thanaraj, T.A.; Al-Mulla, F. Differentially methylated and expressed genes in familial type 1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laajala, E.; Kalim, U.U.; Grönroos, T.; Rasool, O.; Halla-Aho, V.; Konki, M.; Kattelus, R.; Mykkänen, J.; Nurmio, M.; Vähä-Mäkilä, M.; et al. Umbilical cord blood DNA methylation in children who later develop type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1534–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Azadzoi, K.M.; Dai, P.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J.-B.; Zhang, W.-T.; Shu, Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Yan, Z. Alu RNA accumulation in hyperglycemia augments oxidative stress and impairs eNOS and SOD2 expression in endothelial cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 426, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.G.; Mychaleckyj, J.C.; Onengut-Gumuscu, S.; Orchard, T.J.; Costacou, T. TXNIP DNA methylation is associated with glycemic control over 28 years in type 1 diabetes: Findings from the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications (EDC) study. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2023, 11, e003068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Miao, F.; Braffett, B.H.; Lachin, J.M.; Zhang, L.; Wu, X.; Roshandel, D.; Carless, M.; Li, X.A.; Tompkins, J.D.; et al. DNA methylation mediates development of HbA1c-associated complications in type 1 diabetes. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 744–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, A.S.; Sarras, M.P.; Leontovich, A.; Intine, R.V. Heritable transmission of diabetic metabolic memory in zebrafish correlates with DNA hypomethylation and aberrant gene expression. Diabetes 2012, 61, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.T.; Dayeh, T.A.; Volkov, P.A.; Kirkpatrick, C.L.; Malmgren, S.; Jing, X.; Renström, E.; Wollheim, C.B.; Nitert, M.D.; Ling, C. Increased DNA methylation and decreased expression of PDX-1 in pancreatic islets from patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.K.; Vanderlinden, L.A.; Dong, F.; Carry, P.M.; Seifert, J.; Waugh, K.; Shorrosh, H.; Fingerlin, T.; Frohnert, B.I.; Yang, I.V.; et al. Longitudinal DNA methylation differences precede type 1 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starskaia, I.; Laajala, E.; Grönroos, T.; Härkönen, T.; Junttila, S.; Kattelus, R.; Kallionpää, H.; Laiho, A.; Suni, V.; Tillmann, V.; et al. Early DNA methylation changes in children developing β cell autoimmunity at a young age. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 844–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saul, D.; Kosinsky, R.L. Epigenetics of Aging and Aging-Associated Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongsroy, J.; Mutirangura, A. The association between Alu hypomethylation and the severity of hypertension. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buj, R.; Mallona, I.; Díez-Villanueva, A.; Barrera, V.; Mauricio, D.; Puig-Domingo, M.; Reverter, J.L.; Matias-Guiu, X.; Azuara, D.; Ramírez, J.L.; et al. Quantification of unmethylated Alu (QUAlu): A tool to assess global hypomethylation in routine clinical samples. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10536–10546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, R.D. Predicting adult-onset autoimmune diabetes: Clarity from complexity. Diabetes 2010, 59, 330–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Variable | Patients with T1D | Controls | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 36) | (n = 29) | ||
| Subject Characteristics | |||
| Age (years, median, IQR) | 27.5 (19.0–38.0) | 29.0 (22.0–33.0) | 0.905 |
| Males/Females (%) | 55.60/44.4 | 58.60/41.4 | 0.804 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg, median, IQR) | 120.0 (110.0–130.0) | 115.0 (100.0–125.0) | 0.325 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg, median, IQR) | 75.0 (70.0–80.0) | 75.0 (70.0–80.0) | 0.761 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.0 (21.0–23.0) | 22.2 (21.0–23.0) | 0.599 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dl, median, IQR) | 116.5 (95.5–170.5) | 82.0 (76.0–90.0) | <0.001 * |
| HbA1c (%,median, IQR) | 7.5 (6.8–8.0) | 5.1 (4.8–5.3) | <0.001 * |
| Methylation Patterns | |||
| mC (%, median, IQR) | 67.3 (64.4–70.9) | 68.0 (62.0–71.1) | 0.874 |
| mCmC (%, median, IQR) | 24.8 (18.1–34.0) | 32.9 (23.3–37.9) | 0.073 |
| uCmC + mCuC (%, median, IQR) | 41.9 (35.8–45.8) | 36.0 (31.7–40.55) | 0.004 * |
| uCuC (%, median, IQR) | 33.5 (29.5–36.0) | 32.0 (29.0–38.0) | 0.916 |
| Methylation | Age at Diagnosis | n | Median (25th–75th) | U | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mC | <15 | 21 | 66.64 (63.04–68.72) | 86 | 0.040 * |
| ≥15 | 14 | 70.10 (65.30–72.08) | |||
| mCmC | <15 | 21 | 20.08 (17.33–27.38) | 87 | 0.044 * |
| ≥15 | 14 | 29.58 (21.37–36.71) | |||
| uCmC + mCuC | <15 | 21 | 42.70 (39.16–47.62) | 97 | 0.096 |
| ≥15 | 14 | 40.01 (34.71–43.93) | |||
| uCuC | <15 | 21 | 33.00 (31.00–37.00) | 86 | 0.040 * |
| ≥15 | 14 | 30.00 (28.00–35.00) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Katsanou, A.; Kostoulas, C.A.; Liberopoulos, E.; Tsatsoulis, A.; Georgiou, I.; Tigas, S. Alu Methylation Patterns in Type 1 Diabetes: A Case-Control Study. Genes 2023, 14, 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122149
Katsanou A, Kostoulas CA, Liberopoulos E, Tsatsoulis A, Georgiou I, Tigas S. Alu Methylation Patterns in Type 1 Diabetes: A Case-Control Study. Genes. 2023; 14(12):2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122149
Chicago/Turabian StyleKatsanou, Andromachi, Charilaos A. Kostoulas, Evangelos Liberopoulos, Agathocles Tsatsoulis, Ioannis Georgiou, and Stelios Tigas. 2023. "Alu Methylation Patterns in Type 1 Diabetes: A Case-Control Study" Genes 14, no. 12: 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122149
APA StyleKatsanou, A., Kostoulas, C. A., Liberopoulos, E., Tsatsoulis, A., Georgiou, I., & Tigas, S. (2023). Alu Methylation Patterns in Type 1 Diabetes: A Case-Control Study. Genes, 14(12), 2149. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14122149







