The Draft Genome of the “Golden Tide” Seaweed, Sargassum horneri: Characterization and Comparative Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and DNA Extraction
2.2. Genome Sequencing, Assembly, and Characterization
2.3. Gene Prediction and Functional Annotation
2.4. Comparative Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome Assembly
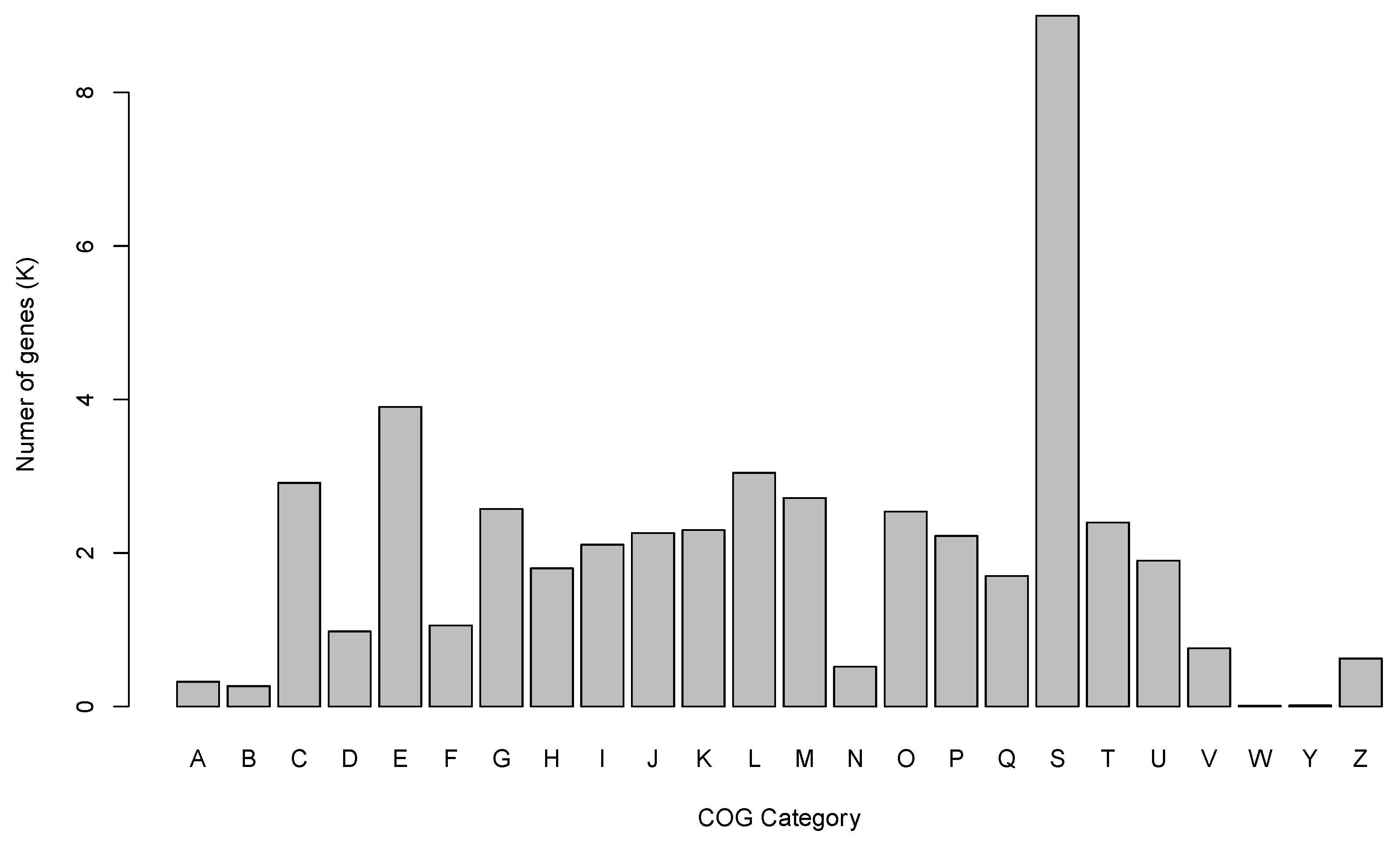
3.2. Gene Prediction and Annotation
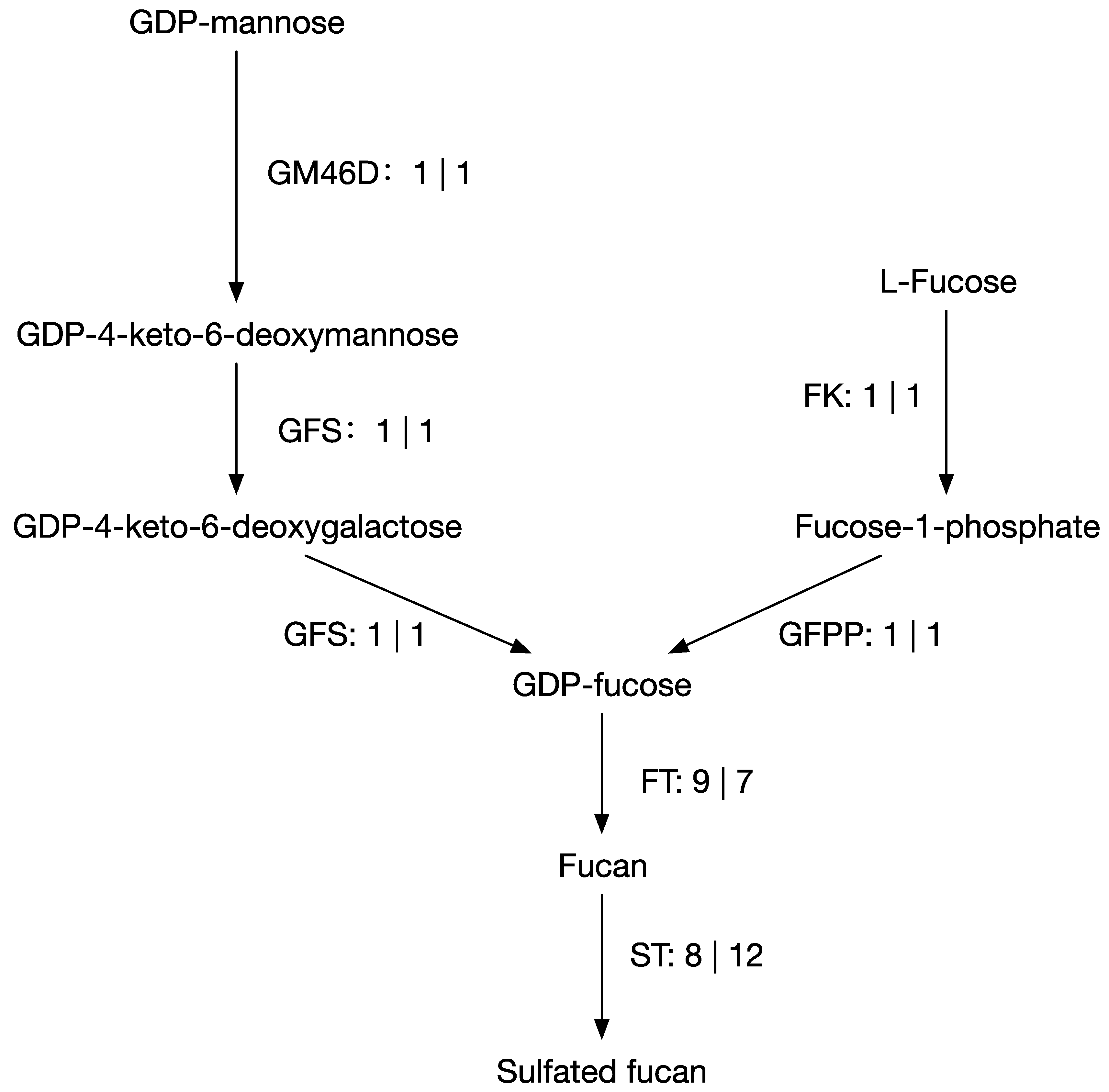
3.3. Putative Genes Associated with Fucoidan Biosynthesis Metabolism
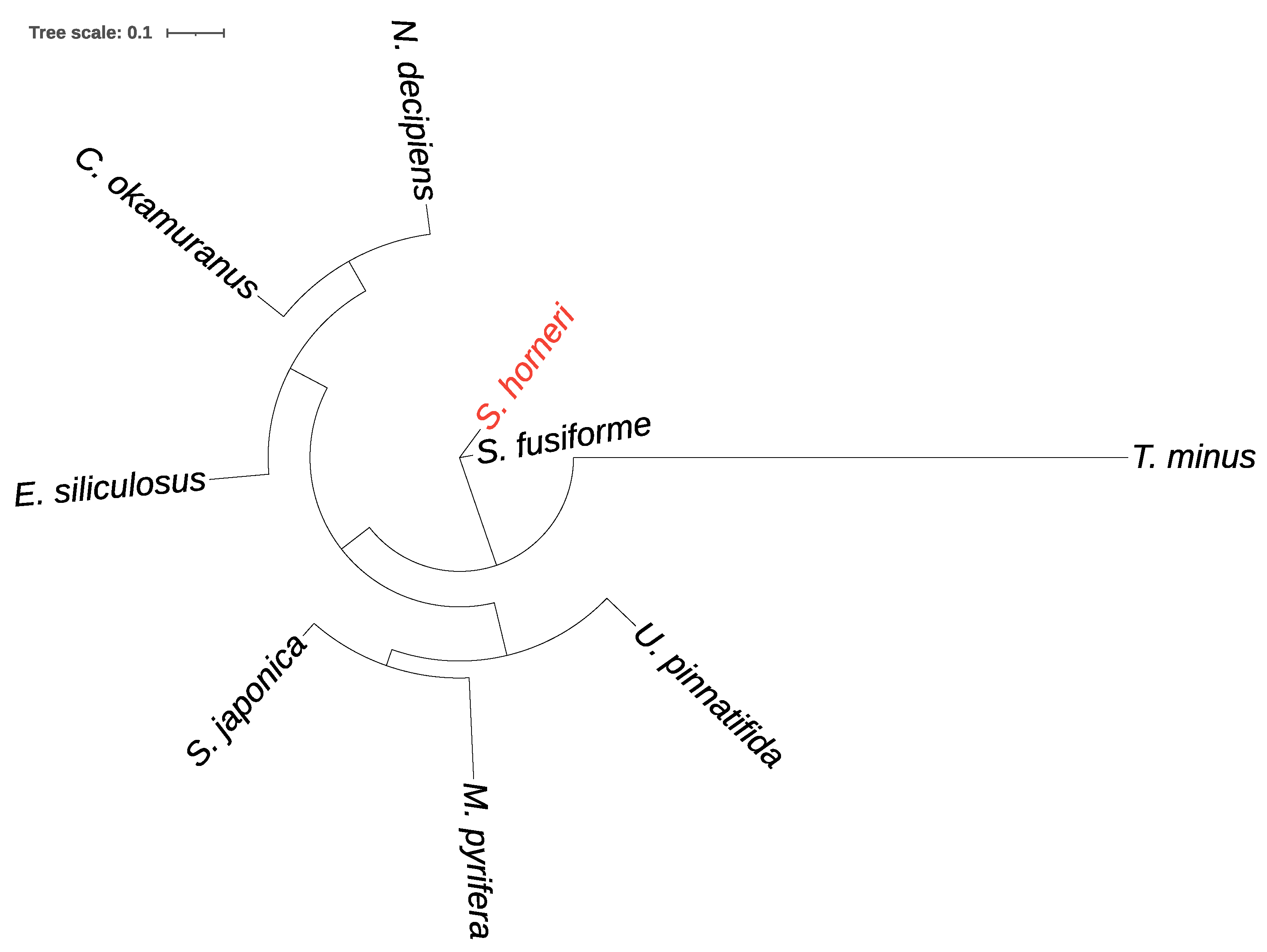
3.4. Comparative Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Fu, M.; Xiao, J. Interannual Variations of Sargassum Blooms in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea during 2017–2021. Harmful Algae 2023, 126, 102451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marks, L.; Salinas-Ruiz, P.; Reed, D.; Holbrook, S.; Culver, C.; Engle, J.; Kushner, D.; Caselle, J.; Freiwald, J.; Williams, J.; et al. Range Expansion of a Non-Native, Invasive Macroalga Sargassum horneri (Turner) C. Agardh, 1820 in the Eastern Pacific. BIR 2015, 4, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Sun, J.; Shen, Y.; Xia, Z.; Hu, M.; Wu, T.; Zhuang, M.; Li, Y.; Tong, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. Removable Carbon and Storage Carbon of Golden Tides. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 191, 114974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Fernando, I.P.S.; Kim, E.-A.; Ahn, G.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.-J. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of a Sulfated Polysaccharide Isolated from an Enzymatic Digest of Brown Seaweed Sargassum horneri in RAW 264.7 Cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2017, 11, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preeprame, S.; Hayashi, K.; Lee, J.B.; Sankawa, U.; Hayashi, T. A Novel Antivirally Active Fucan Sulfate Derived from an Edible Brown Alga, Sargassum horneri. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 484–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.-R.; Li, W.-M.; Li, T.-L.; Chan, Y.-L.; Wu, C.-J. Fucoidan from Sargassum hemiphyllum Inhibits Infection and Inflammation of Helicobacter pylori. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byeon, S.Y.; Oh, H.-J.; Kim, S.; Yun, S.H.; Kang, J.H.; Park, S.R.; Lee, H.J. The Origin and Population Genetic Structure of the ‘Golden Tide’ Seaweeds, Sargassum horneri, in Korean Waters. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smetacek, V.; Zingone, A. Green and Golden Seaweed Tides on the Rise. Nature 2013, 504, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Q.; Guo, R.; Wu, L.; An, D.; Cong, M.; Qin, S.; Li, X. High-Resolution Satellite Observations of a New Hazard of Golden Tides Caused by Floating Sargassum in Winter in the Yellow Sea. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Gao, G.; Xu, J.; Wu, H. Physiological Response of a Golden Tide Alga (Sargassum muticum) to the Interaction of Ocean Acidification and Phosphorus Enrichment. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gong, Q. Growth and Resource Accumulation of Drifting Sargassum horneri (Fucales, Phaeophyta) in Response to Temperature and Nitrogen Supply. J. Ocean Univ. China 2019, 18, 1216–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, S.; Mackie, B.; Nothwehr, E. Nitrate and Phosphate Levels Positively Affect the Growth of Algae Species Found in Perry Pond. Tillers 2003, 5, 21–24. [Google Scholar]
- Dawes, C. Chapter 4—Macroalgae Systematics. In Seaweed in Health and Disease Prevention; Fleurence, J., Levine, I., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2016; pp. 107–148. ISBN 978-0-12-802772-1. [Google Scholar]
- Cock, J.M.; Sterck, L.; Rouzé, P.; Scornet, D.; Allen, A.E.; Amoutzias, G.; Anthouard, V.; Artiguenave, F.; Aury, J.-M.; Badger, J.H.; et al. The Ectocarpus Genome and the Independent Evolution of Multicellularity in Brown Algae. Nature 2010, 465, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, N.; Zhang, X.; Miao, M.; Fan, X.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhou, L.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y.; et al. Saccharina Genomes Provide Novel Insight into Kelp Biology. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishitsuji, K.; Arimoto, A.; Higa, Y.; Mekaru, M.; Kawamitsu, M.; Satoh, N.; Shoguchi, E. Draft Genome of the Brown Alga, Nemacystus decipiens, Onna-1 Strain: Fusion of Genes Involved in the Sulfated Fucan Biosynthesis Pathway. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishitsuji, K.; Arimoto, A.; Iwai, K.; Sudo, Y.; Hisata, K.; Fujie, M.; Arakaki, N.; Kushiro, T.; Konishi, T.; Shinzato, C.; et al. A Draft Genome of the Brown Alga, Cladosiphon okamuranus, S-Strain: A Platform for Future Studies of “mozuku” Biology. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahan, K.M.; Polle, J.E.W.; McKie-Krisberg, Z.; Lipzen, A.; Kuo, A.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Lane, T.W.; Davis, A.K. Annotated Genome Sequence of the High-Biomass-Producing Yellow-Green Alga Tribonema minus. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2021, 10, e0032721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Salavarría, E.; García, K.; Reyes-Calderón, A.; Gil-Kodaka, P.; Samolski, I.; Srivastava, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Villena, G.K. Insight into the Genome Data of Commercially Important Giant Kelp Macrocystis pyrifera. Data Brief 2022, 42, 108068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Shi, Y.; Qian, W.; Li, N.; Yan, X.; Zou, H.; Wu, M. First Draft Genome Assembly of the Seaweed Sargassum fusiforme. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 590065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, L.; Shin, Y.; Yang, J.H.; Choi, J.W.; Hwang, I.K.; Nelson, W.; Bhattacharya, D.; Viard, F.; Yoon, H.S. A Genome-Wide Investigation of the Effect of Farming and Human-Mediated Introduction on the Ubiquitous Seaweed Undaria pinnatifida. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, T.; Yuan, J.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Leng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Pang, S. First Genome of the Brown Alga Undaria pinnatifida: Chromosome-Level Assembly Using PacBio and Hi-C Technologies. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An Ultra-Fast All-in-One FASTQ Preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marçais, G.; Kingsford, C. A Fast, Lock-Free Approach for Efficient Parallel Counting of Occurrences of k-Mers. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vurture, G.W.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Nattestad, M.; Underwood, C.J.; Fang, H.; Gurtowski, J.; Schatz, M.C. GenomeScope: Fast Reference-Free Genome Profiling from Short Reads. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2202–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lischer, H.E.L.; Shimizu, K.K. Reference-Guided de novo Assembly Approach Improves Genome Reconstruction for Related Species. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akiyama, R.; Sun, J.; Hatakeyama, M.; Lischer, H.E.L.; Briskine, R.V.; Hay, A.; Gan, X.; Tsiantis, M.; Kudoh, H.; Kanaoka, M.M.; et al. Fine-Scale Empirical Data on Niche Divergence and Homeolog Expression Patterns in an Allopolyploid and Its Diploid Progenitor Species. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 3587–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.M.; Hubley, R.; Goubert, C.; Rosen, J.; Clark, A.G.; Feschotte, C.; Smit, A.F. RepeatModeler2 for Automated Genomic Discovery of Transposable Element Families. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 9451–9457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Eddy, S.R. Automated de Novo Identification of Repeat Sequence Families in Sequenced Genomes. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, A.L.; Jones, N.C.; Pevzner, P.A. De Novo Identification of Repeat Families in Large Genomes. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, i351–i358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem Repeats Finder: A Program to Analyze DNA Sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, K.J.; Lange, S.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M.; Stanke, M. BRAKER1: Unsupervised RNA-Seq-Based Genome Annotation with GeneMark-ET and AUGUSTUS. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate Alignment of Transcriptomes in the Presence of Insertions, Deletions and Gene Fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomsadze, A.; Burns, P.D.; Borodovsky, M. Integration of Mapped RNA-Seq Reads into Automatic Training of Eukaryotic Gene Finding Algorithm. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanke, M.; Waack, S. Gene Prediction with a Hidden Markov Model and a New Intron Submodel. Bioinformatics 2003, 19 (Suppl. S2), ii215–ii225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-Mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capella-Gutiérrez, S.; Silla-Martínez, J.M.; Gabaldón, T. trimAl: A Tool for Automated Alignment Trimming in Large-Scale Phylogenetic Analyses. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1972–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML Version 8: A Tool for Phylogenetic Analysis and Post-Analysis of Large Phylogenies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1312–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An Online Tool for Phylogenetic Tree Display and Annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahm, A.; Bens, M.; Platzer, M.; Szafranski, K. PosiGene: Automated and Easy-to-Use Pipeline for Genome-Wide Detection of Positively Selected Genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdetskiy, A.; Cole, C.; Procter, J.; Barton, G.J. JPred4: A Protein Secondary Structure Prediction Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W389–W394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, N.; Kapraun, D.F.; Gómez Garreta, A.; Ribera Siguan, M.A.; Rull, J.L.; Salvador Soler, N.; Lewis, R.; Kawai, H. Estimates of Nuclear DNA Content in 98 Species of Brown Algae (Phaeophyta). AoB Plants 2011, 2011, plr001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, G.; Tonon, T.; Scornet, D.; Cock, J.M.; Kloareg, B. The Cell Wall Polysaccharide Metabolism of the Brown Alga Ectocarpus siliculosus. Insights into the Evolution of Extracellular Matrix Polysaccharides in Eukaryotes. New Phytol. 2010, 188, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, S.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Shan, G.; Liu, C. Functional Genomics Analysis Reveals the Biosynthesis Pathways of Important Cellular Components (Alginate and Fucoidan) of Saccharina. Curr. Genet. 2018, 64, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.F.; Harholt, J.; Oikawa, A.; Scheller, H.V. Plant Glycosyltransferases Beyond CAZy: A Perspective on DUF Families. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Hong, H. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity and Utilization of Dissolved Organic Phosphorus by Algae in Subtropical Coastal Waters. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1999, 39, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Database | Annotated Number (300 > Protein Length ≥ 100) | Annotated Number (Protein Length ≥ 300) | All Annotated Genes (Total) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nr | 29,413 | 16,859 | 50,634 |
| Swiss-Prot | 16,671 | 12,041 | 30,603 |
| Pfam | 18,453 | 13,294 | 33,720 |
| GO | 4859 | 3692 | 9364 |
| COG | 25,620 | 14,623 | 43,915 |
| Homologous Transcript in E. siliculosus | Transcript in S. horneri | FDR | No. of Species Included | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ec-21_005550.1 | g21358.t1 | 0.022 | 6 | Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, cyclophilin-type |
| Ec-01_007880.1 | g39723.t1 | 0.026 | 6 | Alkaline phosphatase family protein |
| Ec-12_007440.1 | g8237.t1 | 0.026 | 5 | Trinucleotide repeat containing 4, isoform CRA_d |
| Ec-14_004430.1 | g8183.t1 | 0.026 | 7 | Conserved unknown protein |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Wu, M. The Draft Genome of the “Golden Tide” Seaweed, Sargassum horneri: Characterization and Comparative Analysis. Genes 2023, 14, 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101969
Wang S, Wu M. The Draft Genome of the “Golden Tide” Seaweed, Sargassum horneri: Characterization and Comparative Analysis. Genes. 2023; 14(10):1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101969
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shengqin, and Mingjiang Wu. 2023. "The Draft Genome of the “Golden Tide” Seaweed, Sargassum horneri: Characterization and Comparative Analysis" Genes 14, no. 10: 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101969
APA StyleWang, S., & Wu, M. (2023). The Draft Genome of the “Golden Tide” Seaweed, Sargassum horneri: Characterization and Comparative Analysis. Genes, 14(10), 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14101969






