The Role of miRNAs, circRNAs and Their Interactions in Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Insilico Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
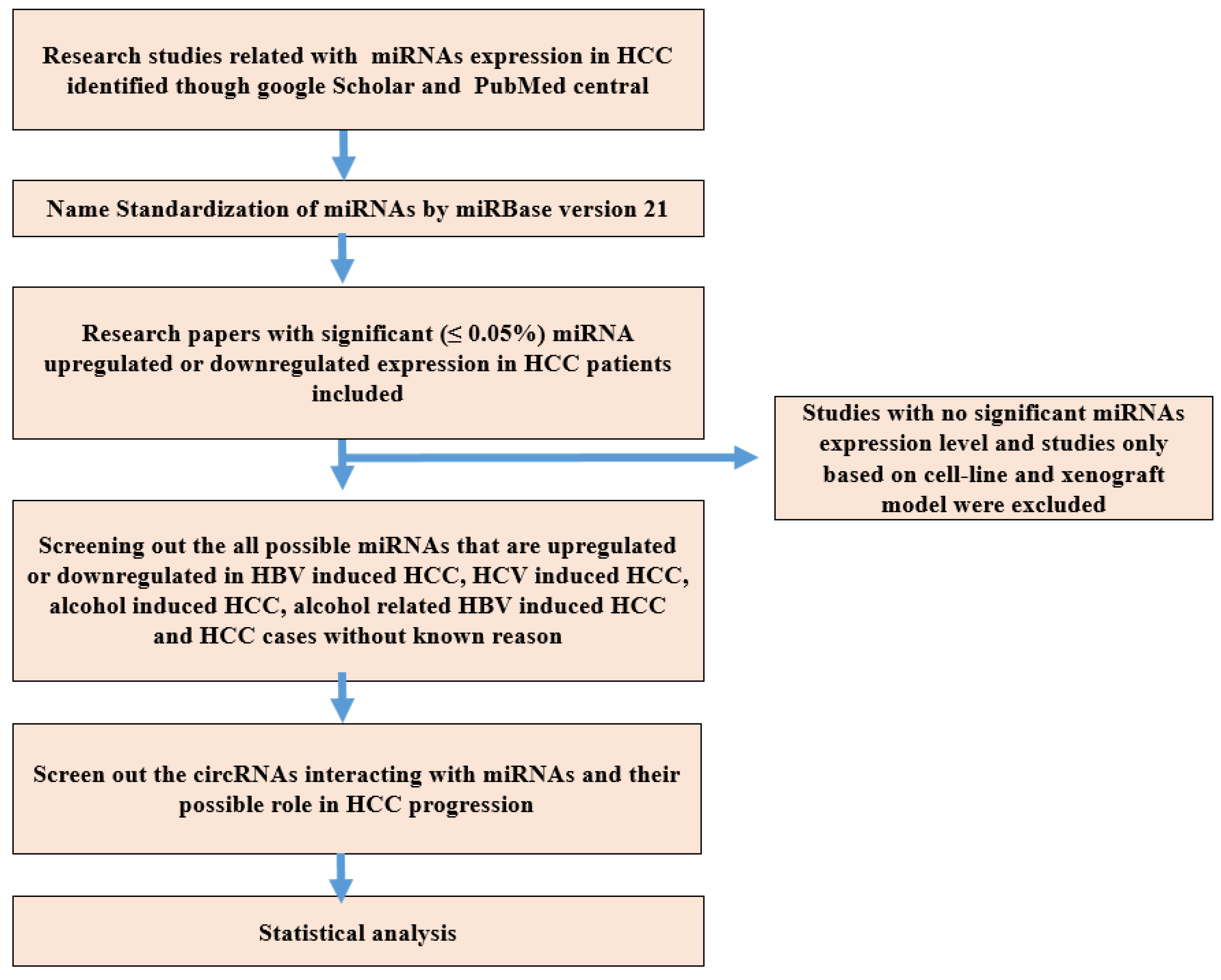
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Strategy
2.2. Name Standardization of miRNA
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria of Research Studies
2.4. CircRNAs and Their Target miRNAs Interaction in HCC
2.5. Data Collection
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Search Data
| Sr. No | miRNAs | Expression in Serum of HCC | Region | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | miR-10b | Upregulated | China | [93] |
| 2 | miR-18a | Upregulated | Korea | [94] |
| 3 | miR-21 | Upregulated | China | [95] |
| 4 | miR-34a | Downregulated | China | [96] |
| 5 | miR-34c | Downregulated | China | [96] |
| 6 | miR-93 | Upregulated | China | [97] |
| 7 | miR-122 | Downregulated | USA | [98] |
| 8 | miR-195 | Downregulated | Korea | [94] |
| 9 | miR-222 | Upregulated | Korea | [94] |
| 10 | miR-223 | Upregulated | UK | [99] |
| 11 | miR-224 | Upregulated | Korea | [94] |
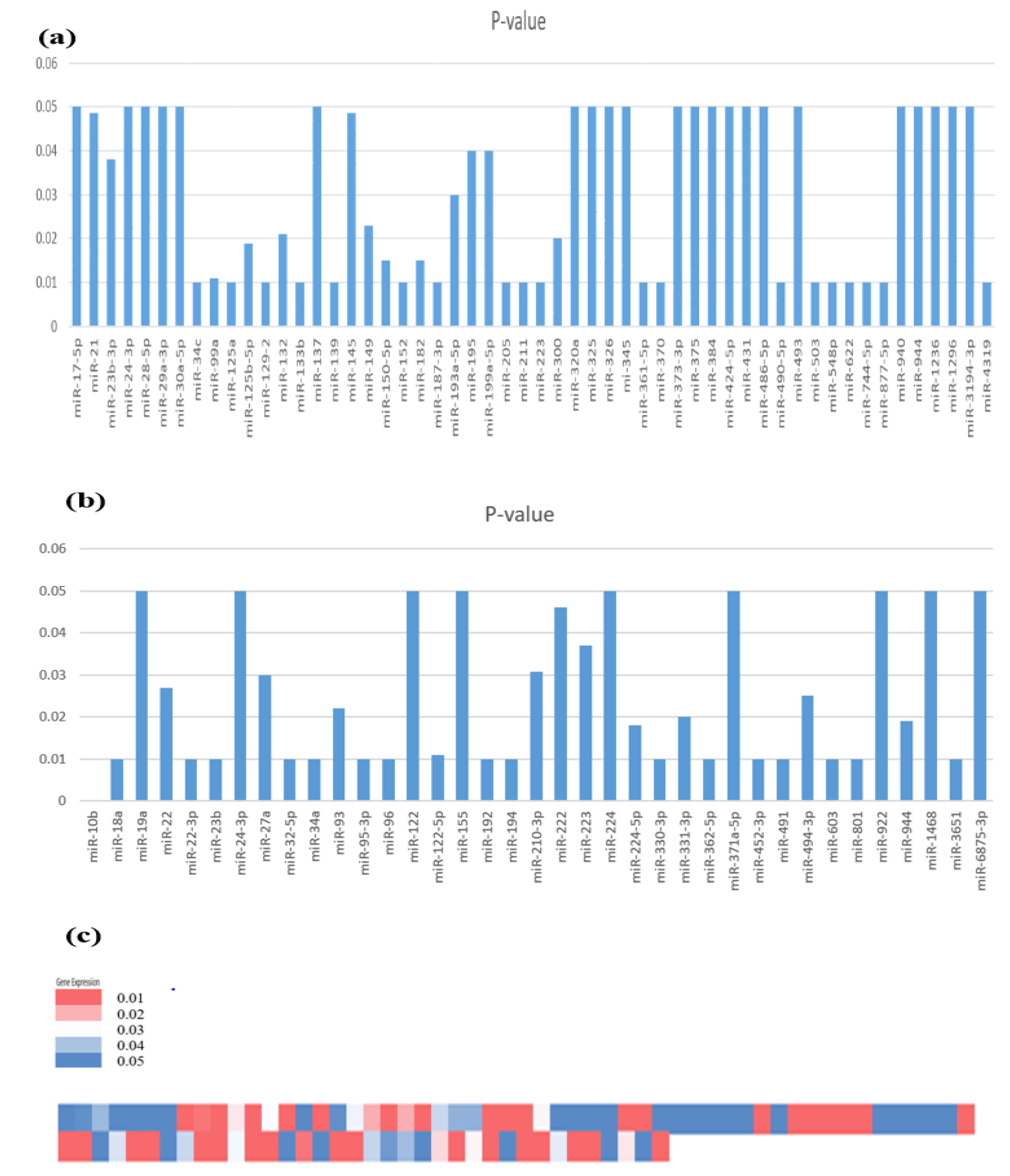
3.2. Expression Profile of Identified miRNAs Involved in HCC Development
3.3. miRNA Expression in HBV-Induced HCC
3.4. miRNA Expression in HCV-Induced HCC
3.5. miRNA Expression in Alcohol-Induced HCC
3.6. miRNA Expression in HCC (Generalized Studies)
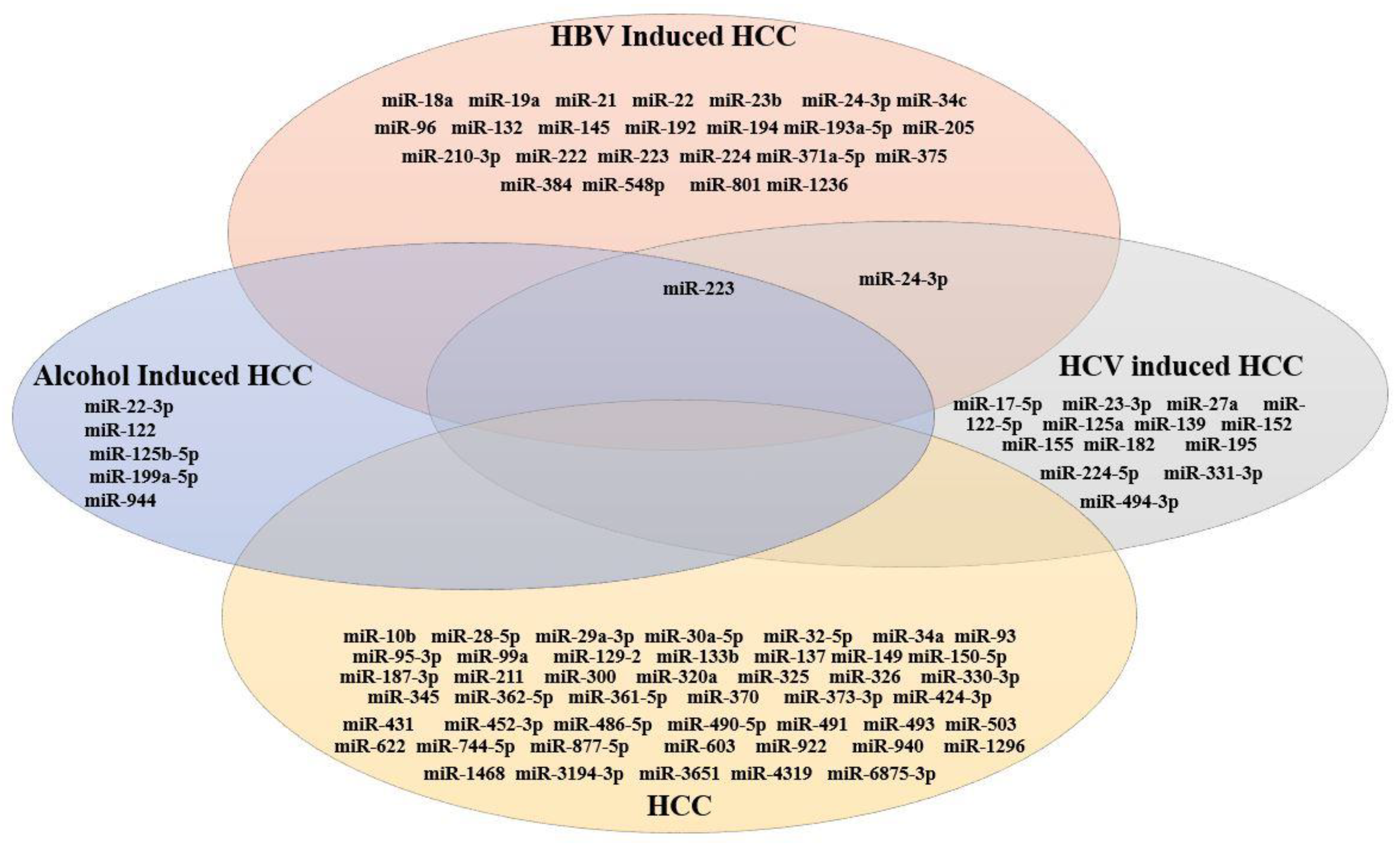
3.7. Comparative Analysis of miRNAs Expressed in HCC
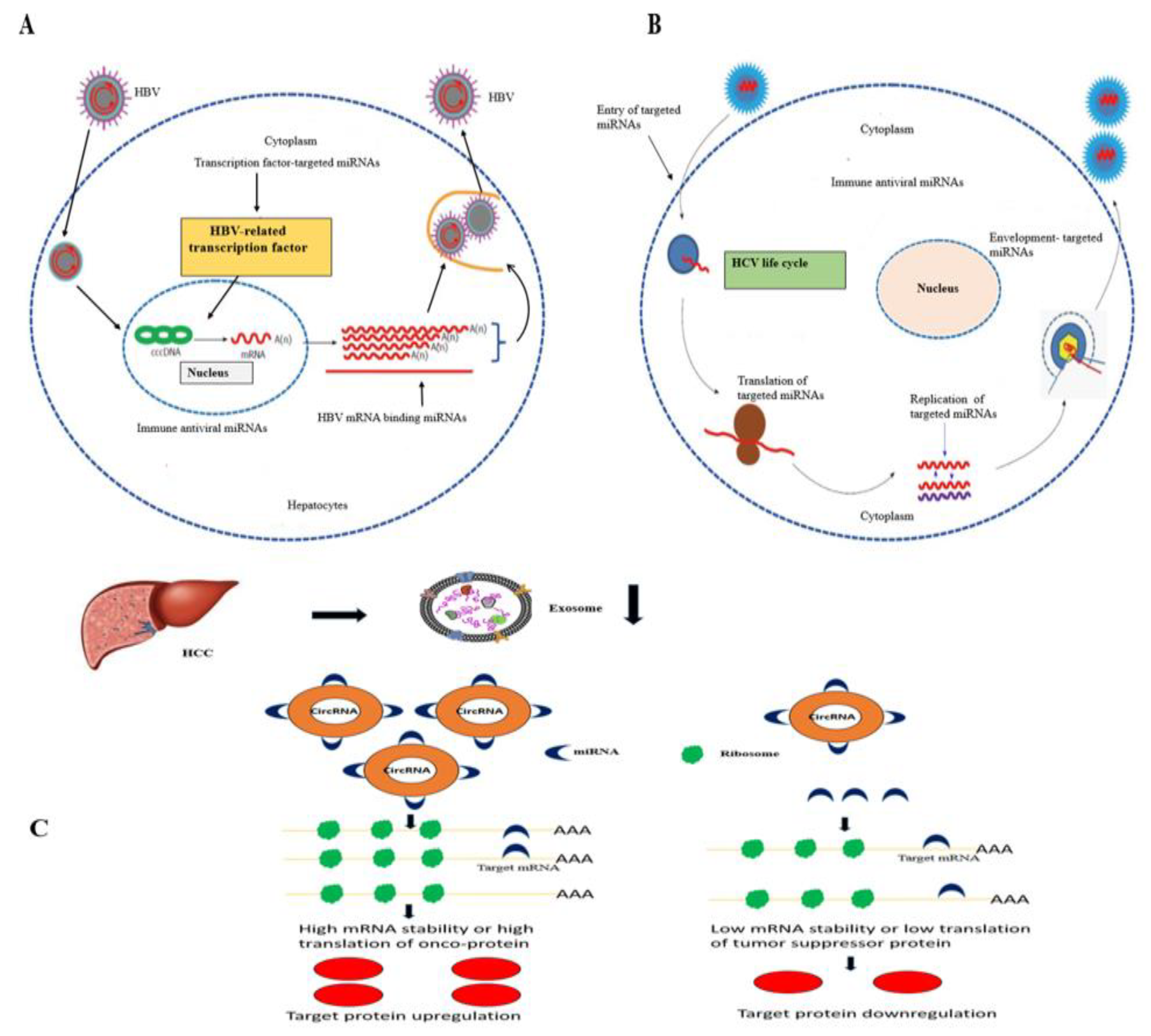
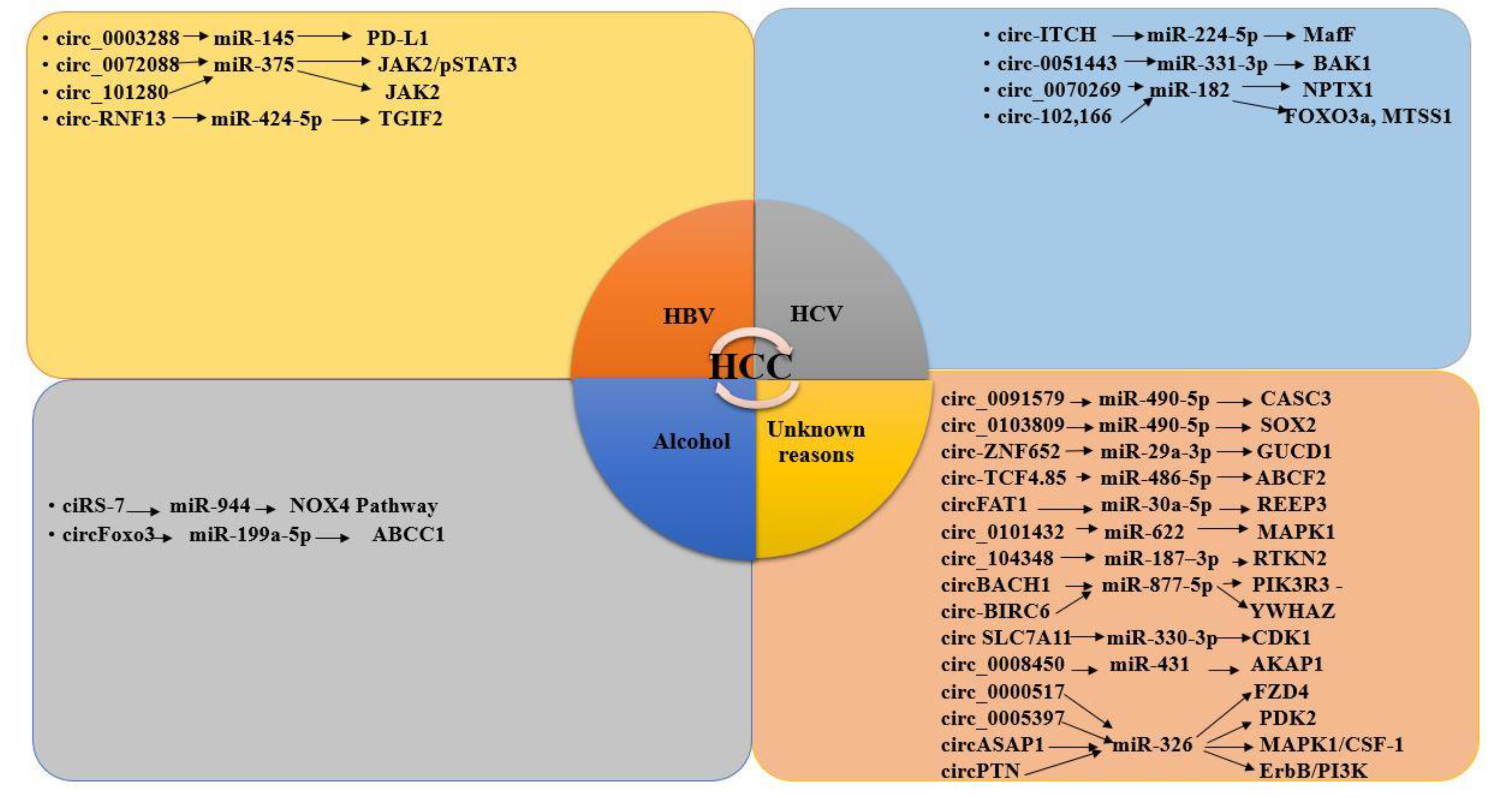
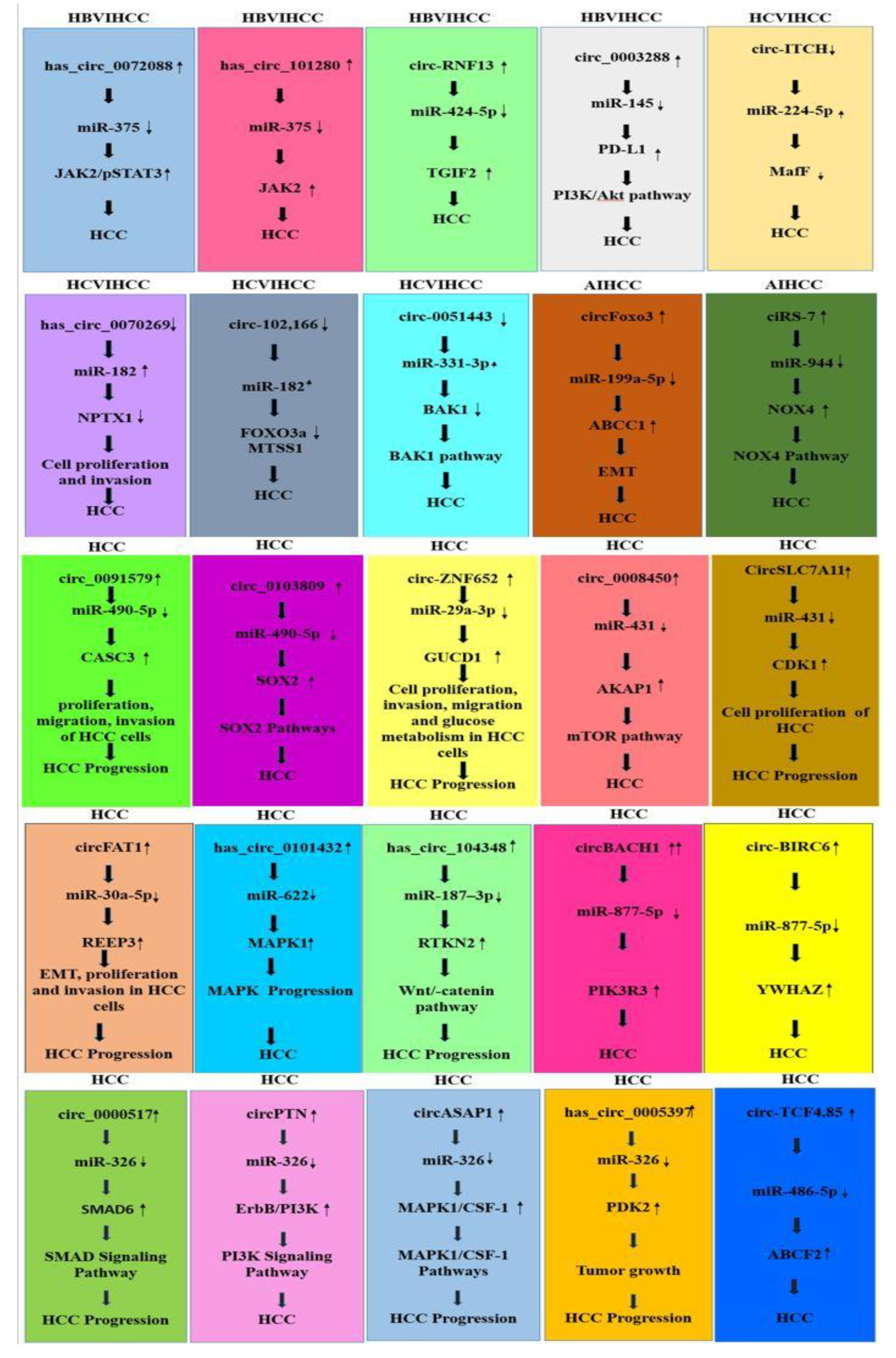
3.8. CircRNAs and miRNAs in HBV/HCV-Induced HCC
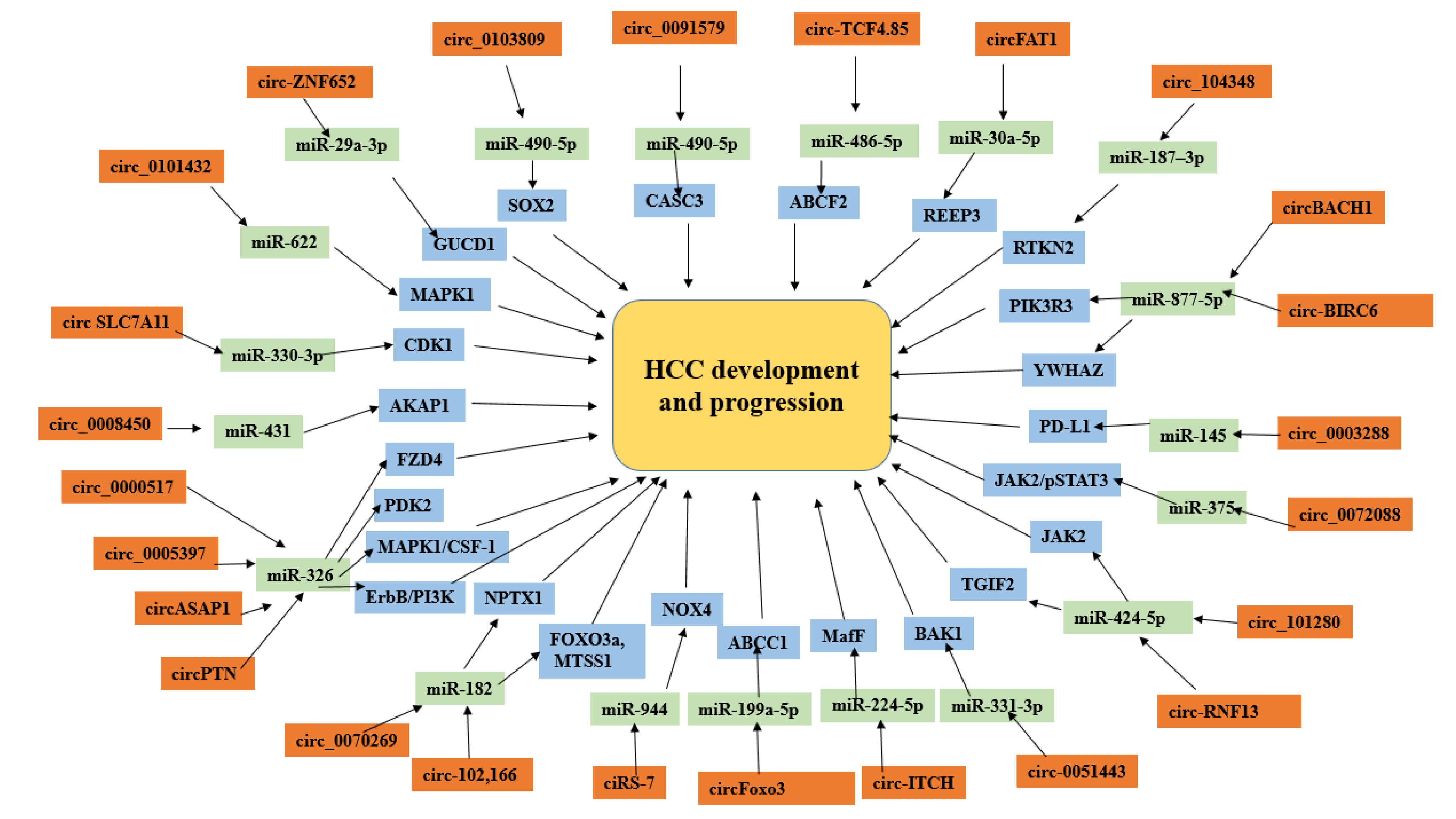
3.9. CircRNA–miRNA Interaction in HCC Development
3.9.1. CircRNA–miRNA Interaction Reported in HBV-Induced HCC Studies
3.9.2. CircRNA –miRNA Interaction in HCV-Induced HCC Studies
3.9.3. CircRNA–miRNA Interaction Reported in Alcohol-Induced HCC Studies
3.9.4. CircRNA–miRNA Interaction in HCC Reported in Generalized Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Q.; Qiu, J.; Yang, H.; Sun, G.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Deng, Z.; Wang, X.; Tang, J.; Jiang, R. Kinesin family member 15 promotes cancer stem cell phenotype and malignancy via reactive oxygen species imbalance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2020, 482, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, T.; Li, L.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, C.; Wang, W.; Dai, L.; Zhang, T.; Wu, H.; Su, B. Peripheral Blood Genetic Biomarkers for the Early Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L.; Kotsiliti, E.; Govaere, O.; Heikenwalder, M. From NASH to HCC: Current concepts and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ura, S.; Honda, M.; Yamashita, T.; Ueda, T.; Takatori, H.; Nishino, R.; Sunakozaka, H.; Sakai, Y.; Horimoto, K.; Kaneko, S. Differential microRNA expression between hepatitis B and hepatitis C leading disease progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1098–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bala, S.; Marcos, M.; Szabo, G. Emerging role of microRNAs in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasuri, F.; Visani, M.; Acquaviva, G.; Brand, T.; Fiorentino, M.; Pession, A.; Tallini, G.; D’Errico, A.; de Biase, D. Role of Micrornas in the Main Molecular Pathways of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, F.; Li, P. Circular RNAs: Characteristics, Function and Clinical Significance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Wu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Shao, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Hui, B.; Liu, R.; Ma, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Construct a circRNA/miRNA/mRNA regulatory network to explore potential pathogenesis and therapy options of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.-D.; Dang, Y.-W.; Lin, P.; Wen, D.-Y.; He, R.-Q.; Luo, D.-Z.; Feng, Z.-B.; Chen, G. A circRNA–miRNA–mRNA network identification for exploring underlying pathogenesis and therapy strategy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Peer, G.; Lefever, S.; Anckaert, J.; Beckers, A.; Rihani, A.; Van Goethem, A.; Volders, P.J.; Zeka, F.; Ongenaert, M.; Mestdagh, P.; et al. Mirbase Tracker: Keeping Track of Microrna Annotation Changes. J. Database 2014, bau080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongliang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhan, C.; Li, X.; Ba, T.; Qiu, Z.; Lv, G.; Zou, C.; Wang, C. Cadm2, as a New Target of Mir-10b, Promotes Tumor Metastasis through Fak/Akt Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Q.; Cheng, S.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Chun-fang, G. Serum Micrornas as Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chinese Patients with Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. PLoS ONE. 2011, 6, e28486. [Google Scholar]
- Zehra, O.; Serin, M.S.; Kaplan, E.; Dogen, A.; Tezcan, S.; Aslan, G.; Emekdas, G.; Sezgin, O.; Altintas, E.; Tiftik, E.N. Serum Micrornas; Mir-30c-5p, Mir-223-3p, Mir-302c-3p and Mir-17-5p Could Be Used as Novel Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Hcv-Positive Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2015, 42, 713–720. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Z.; Zou, A.E.; Saad, M.A.; Wang, X.Q.; Kwok, J.G.; Korrapati, A.; Li, P.; Kisseleva, T.; Wang-Rodriguez, J.; Ongkeko, W.M. Alcohol-Dysregulated Micrornas in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178547. [Google Scholar]
- Lihua, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Mao, Y.; Gao, Q. Serum Mir-18a: A Potential Marker for Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening. J. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2012, 57, 2910–2916. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, Z.; Yu, L.; Gao, X.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, S.; Huang, X. Plasma Microrna Panel to Diagnose Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4781–4788. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Ye, W.; Hou, K.; Liang, M. MiR-19a, miR-122 and miR-223 are differentially regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein and involve in cell proliferation in hepatoma cells. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandopadhyay, M.; Banerjee, A.; Sarkar, N.; Panigrahi, R.; Datta, S.; Pal, A.; Singh, S.P.; Biswas, A.; Chakrabarti, S.; Chakravarty, R. Tumor suppressor micro RNA miR-145 and onco micro RNAs miR-21 and miR-222 expressions are differentially modulated by Hepatitis B virus X protein in malignant hepatocytes. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, Z.; Chen, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, M.; Wang, R. Research on the Serum Level of Microrna-224 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients and Its Clinical Diagnostic Significance. Chin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 576–579. [Google Scholar]
- Runqiu, J.; Deng, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, F.; Xia, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, B. Mir-22 Promotes Hbv-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development in Males. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5593–5603. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, L.; Jin, B.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Song, Y.; Li, N. Serum Microrna Expression Profiling Identifies Serum Biomarkers for Hcv-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer Biomark. 2019, 26, 501–512. [Google Scholar]
- Danlei, C.; Yan, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, D.; He, Y.; Deng, R.; Liu, Y.; Xu, M.; et al. Chronic Alcohol Exposure Promotes Hcc Stemness and Metastasis through Β-Catenin/Mir-22-3p/Tet2 Axis. Aging 2021, 13, 14433–14455. [Google Scholar]
- Rongchang, W.; Yu, Z.; Chen, F.; Xu, H.; Shen, S.; Chen, W.; Chen, L.; Su, Q.; Zhang, L.; Jion, B. Mir-300 Regulates the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting the Fak/Pi3k/Akt Signaling Pathway. J Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 1632–1642. [Google Scholar]
- Guixiang, L.; Wu, M.; Wang, M.; Jiang, X.; Du, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, D.; Ma, N.; Peng, Y.; Wang, L. Mir-320a Regulates High Mobility Group Box 1 Expression and Inhibits Invasion and Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Huifen, L.; Huang, W.; Luo, R. Retracted Article: The Microrna-325 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting High Mobility Group Box 1. J. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Shiping, H.; Ran, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y. Microrna-326 Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Invasion, Activating Apoptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Directly Targeting Lim and Sh3 Protein 1. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1569–1578. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, S.S.; El Fiky, A.; Nabeel, M.M.; Shousha, H.I.; Elbaz, T.; Omran, D.; Marie, M.S.; Elzahry, M.A.; Abul-Fotouh, A.; Hashem, A.; et al. Assessment of circulating levels of microRNA-326, microRNA-424, and microRNA-511 as biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptians. World J. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 1562–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.-L.; Wang, W.; Jia, W.-D. Diagnostic and prognostic significance of serum miR-24-3p in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, N.M.; El-Shal, A.S.; Shalaby, S.M.; Mohamed, S.Y. Serum miRNA-27a and miRNA-18b as potential predictive biomarkers of hepatitis C virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2018, 447, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, G.Q.; Cao, G.M. Abnormal Expression and Mechanism of Mir-330-3p/Btg1 Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 6888–6898. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaomin, S.; Teng, F. Down-Regulated Mir-28-5p in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Correlated with Tumor Proliferation and Migration by Targeting Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 (Igf-1). J Mol. Cell Biochem. 2015, 408, 283–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Xue, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Li, K.; Jia, M.; Jia, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Mir-345 Inhibits Tumor Metastasis and Emt by Targeting Irf1-Mediated Mtor/Stat3/Akt Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhihua, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, H. Xpd Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Migration Via Mir-29a-3p-Mdm2/Pdgf-B Axis in Hcc. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Qiu, L.; He, G.L.; Cai, L.; Peng, B.J.; Cao, Y.L.; Pan, M.X. Microrna-361-5p Suppresses the Tumorigenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Targeting Wt1 and Suppressing Wnt/Beta-Cadherin Pathway. J. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 23, 8823–8832. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.F.; Dai, H. Overexpression of microRNA-30a-5p inhibits liver cancer cell proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting MTDH/PTEN/AKT pathway. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, F.; Zhao, H.; Cui, H.; Wu, Z.; Chen, L.; Hu, Z.; Guo, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. MicroRNA-362-5p promotes tumor growth and metastasis by targeting CYLD in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, M.; Qu, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, T.; Wen, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; et al. Exosomal microRNA-32-5p induces multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yongkang, H.; He, X. Microrna-370 Regulates Cellepithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Migration, Invasion, and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting Gucd1. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Na, L.; Fu, H.; Tie, Y.; Hu, Z.; Kong, W.; Wu, Y.; Zheng, X. Mir-34a Inhibits Migration and Invasion by Down-Regulation of C-Met Expression in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Lett. 2009, 275, 44–53. [Google Scholar]
- Pei-Song, B.; Hou, P.; Kong, Y. Hepatitis B Virus Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis in Male Chinese Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients through the Lef-1/Mir-371a-5p/Srcin1/Pleiotrophin/Slug Pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 370, 174–188. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.; Wang, C.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, X.; Fan, C.; Xu, F.; Zhang, Q.; Li, L.; Li, R.; Sun, W.; et al. Microrna-34c Targets Tgfb-Induced Factor Homeobox 2, Represses Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 3095–3102. [Google Scholar]
- Hongbin, L.; Wang, N.; Xu, Y.; Chang, X.; Ke, J.; Yin, J. Upregulating Microrna-373-3p Promotes Apoptosis and Inhibits Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 1304–1319. [Google Scholar]
- Ohta, K.; Hoshino, H.; Wang, J.; Ono, S.; Iida, Y.; Hata, K.; Huang, S.K.; Colquhoun, S.; Hoon, D.S. Microrna-93 Activates C-Met/Pi3k/Akt Pathway Activity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Directly Inhibiting Pten and Cdkn1a. J. Oncotarget. 2015, 6, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weilu, Z.; Fu, T.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Su, H.; Long, Y.; Ji, Z.; Yan, Y.; Shao, Z. Serum Mir-375 Levels Are Closely Related to Disease Progression from Hbv Infection to Hbv-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5819385. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, Y.; Yao, Y.; Song, Q.; Li, S.; Hu, Z.; Yu, Y.; Hu, C.; Da, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Up-Regulation of Mir-95-3p in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Promotes Tumorigenesis by Targeting P21 Expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Pei-Song, B.; Xia, N.; Sun, H.; Kong, Y. Pleiotrophin, a Target of Mir-384, Promotes Proliferation, Metastasis and Lipogenesis in Hbv-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3023–3043. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Yu, D.; Wang, X. Serum miR-96 is a promising biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 18462–18468. [Google Scholar]
- Huimin, D.; Xu, Q.; Xiao, S.; Wu, Z.; Gong, J.; Liu, C.; Ren, G.; Wu, H. Microrna-424-5p Acts as a Potential Biomarker and Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting Trim29. Life Sci. 2019, 224, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, L.; Liu, X.; Lin, L.; Hou, J.; Li, N.; Wang, C.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, W. Microrna-99a Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth and Correlates with Prognosis of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 36677–36685. [Google Scholar]
- Kexin, S.; Zeng, T.; Huang, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Qu, Z. Microrna-431 Inhibits Migration and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Targeting the Zeb1-Mediated Epithelial–Mensenchymal Transition. J. FEBS Open Bio. 2015, 5, 900–907. [Google Scholar]
- Ambade, A.; Satishchandran, A.; Szabo, G. Alcoholic hepatitis accelerates early hepatobiliary cancer by increasing stemness and miR-122-mediated HIF-1α activation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Ye, L.; Li, K.; Ding, F.; Feng, X.; Meng, W. Mir-452-3p: A Potential Tumor Promoter That Targets the Cpeb3/Egfr Axis in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 1136–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.P.; Hou, J.; Shen, X.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Xie, Y.A.; Luo, X.L. Micro Rna-486-5p, Which Is Downregulated in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Suppresses Tumor Growth by Targeting Pik3r1. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ahwany, E.; Mourad, L.; Zoheiry, M.; Abu-Taleb, H.; Hassan, M.; Atta, R.; Hassanien, M.; Zada, S. Microrna-122a as a Non-Invasive Biomarker for Hcv Genotype 4-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptian Patients. J. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2019, 15, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, X.; Xu, T.; Liu, H.; Min, Q.; Wang, S.; Song, Q. Mir-490-5p Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting Bub1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Pharmacology 2017, 100, 269–282. [Google Scholar]
- Felgendreff, P.; Raschzok, N.; Kunze, K.; Leder, A.; Lippert, S.; Klunk, S.; Tautenhahn, H.-M.; Hau, H.-M.; Schmuck, R.B.; Reutzel-Selke, A.; et al. Tissue-based miRNA mapping in alcoholic liver cirrhosis: Different profiles in cirrhosis with or without hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomarkers 2020, 25, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Z.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Jiang, R.; Yan, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J. Micro Rna-491 Is Involved in Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inhibitions of Matrix Metalloproteinase and Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. J. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar]
- Zhikui, L.; Dou, C.; Yao, B.; Xu, M.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Tu, K. Methylation-Mediated Repression of Microrna-129-2 Suppresses Cell Aggressiveness by Inhibiting High Mobility Group Box 1 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36909. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Tan, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, F.; Tian, Y.; Li, J.; Pan, X. Microrna-493 Suppresses Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Targeting Zfx in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Cancer Biomark. 2018, 22, 427–434. [Google Scholar]
- Asahiro, M.; Fujita, K.; Iwama, H.; Chiyo, T.; Fujihara, S.; Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Mimura, S.; Nomura, T.; Tani, J. Role of Microrna-210-3p in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G401–G409. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, L.; Xiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, B.; Tang, J. Microrna-133b Inhibits Proliferation, Cellular Migration, and Invasion Via Targeting Lasp1 in Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Oncol. Res. 2017, 25, 1269. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X.; Tian, Q.; He, J.; Huang, M.; Yang, C.; Gong, L. Mir-503 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Growth Via Inhibition of Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Receptor. J. Onco. Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 3535. [Google Scholar]
- Jiachen, W.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Wang, Q.; Shen, X. Upregulation of Mir-137 Expression Suppresses Tumor Growth and Progression Via Interacting with Dnmt3a through Inhibiting the Pten/Akt Signaling in Hcc. J. Onco. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 165. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.M.; Yan, X.H.; Hu, Y.W.; Huang, J.L.; Cao, S.W.; Ren, T.Y.; Tang, Y.T.; Lin, L.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Q. Mirna-548p Suppresses Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Downregulating Oncoprotein Hepatitis B X-Interacting Protein. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.X.; Wu, X.B.; Zheng, C.W.; Zhang, Q.L.; Zhang, G.Q.; Chen, K.; Zhan, Q.; An, F.M. Mechanistic Investigation on the Regulation of Fabp1 by the Il-6/Mir-603 Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8579658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.H.; Feng, X.J.; Gong, S.J.; Chen, J.M.; Wang, S.M.; Xing, D.J.; Zhu, M.H.; Zhang, S.H.; Xu, A.M. Microrna-622 Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1754–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, G.; Chao, Y.-L.; Tang, B.; Li, B.-S.; Xiao, Y.-F.; Xie, R.; Wang, S.-M.; Wu, Y.-Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, X.-D.; et al. miR-149 represses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting actin-regulatory proteins PPM1F. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37808–37823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weifeng, H.; Chen, Q.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, Y.; Wei, X.; Wu, Z. Mir-744-5p Suppresses Tumor Proliferation and Metastasis by Targeting Transforming Growth Factor-Beta 1 (Tgf-Β1) in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (Hcc). J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12, 1811. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, L.; Xie, J.; Shen, C.; Cheng, D.; Shi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhan, Q.; Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Shen, B. Mir-150-5p Inhibits Hepatoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Targeting Mmp14. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115577. [Google Scholar]
- Miquelestorena-Standley, E.; Tallet, A.; Collin, C.; Piver, E.; De Muret, A.; Salamé, E.; Bourlier, P.; Kervarrec, T.; Guyétant, S.; Pagès, J.C. Interest of Variations in Microrna-152 and-122 in a Series of Hepatocellular Carcinomas Related to Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.H.; Chunguang, Q.; Jifan, S.; Li, W.H. Mir-877-5p Suppresses Cell Growth, Migration and Invasion by Targeting Cyclin Dependent Kinase 14 and Predicts Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3038–3046. [Google Scholar]
- Yiliang, Z.; Wei, W.; Cheng, N.; Wang, K.; Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Sun, S. Hepatitis C Virus-Induced up-Regulation of Microrna-155 Promotes Hepatocarcinogenesis by Activating Wnt Signaling. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar]
- Zhikui, L.; Wang, Y.; Dou, C.; Sun, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Xu, Q.; Yang, W.; Liu, Q.; Tu, K. Microrna-1468 Promotes Tumor Progression by Activating Ppar-Γ-Mediated Akt Signaling in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen, N.M.H.; Zayed, N.; Riad, N.M.; Tamim, H.; Shahin, R.M.H.; Labib, D.A.; Elsheikh, S.M.; Moneim, R.A.; Yosry, A.; Khalifa, R.H. Role of circulating miR-182 and miR-150 as biomarkers for cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma post HCV infection in Egyptian patients. Virus Res. 2018, 255, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, R.; Wang, X.; Ji, G.; Huo, L.; Shao, Z.; Li, X. Mir-940 Suppresses Tumor Cell Invasion and Migration Via Regulation of Cxcr2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7618342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, C.; Liu, Z.; Xu, M.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yang, W.; Zheng, X.; Tu, K.; Liu, Q. miR-187-3p inhibits the metastasis and epithelial–mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting S100A4. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhang, C. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Upregulates Alpha-Fetoprotein to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting Mir-1236 and Mir-329. J. Cell Biochem. 2020, 121, 2489–2499. [Google Scholar]
- Amit, G.; Ghosh, A.; Datta, S.; Dasgupta, D.; Das, S.; Ray, S.; Gupta, S.; Datta, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Chatterjee, R. Hepatic Mi R-126 Is a Potential Plasma Biomarker for Detection of Hepatitis B Virus Infected Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 2732–2744. [Google Scholar]
- Junhao, L.; Tang, L.; Xu, Y.; Ge, K.; Huang, J.; Gu, M.; Zhong, J.; Huang, Q. Mir-1287 Suppresses the Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting Pik3r3. J. Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 9229–9238. [Google Scholar]
- Qiuran, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tu, J.; Li, L.; Bao, H.; Yang, L.; Tu, K. Microrna-1296 Inhibits Metastasis and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting Srpk1-Mediated Pi3k/Akt Pathway. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Motawi, T.K.; Shaker, O.G.; El-Maraghy, S.A.; Senousy, M.A. Serum Micrornas as Potential Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Hepatitis C Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptian Patients. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, T.; Niu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Z. Microrna-3194-3p Inhibits Metastasis and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Decreasing Wnt/Β-Catenin Signaling through Targeting Bcl9. J Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3885–3895. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cui, M.; Liu, F.; You, X.; Du, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Lu, Z.; Ye, L. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Inhibits Tumor Suppressor Mir-205 through Inducing Hypermethylation of Mir-205 Promoter to Enhance Carcinogenesis. J. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar]
- Xinyang, Z.; Song, Q.; Miao, G.; Zhu, X. Microrna-3651 Promotes the Growth and Invasion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Targeting Pten. J OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 7045. [Google Scholar]
- Shaoshan, H.; Shi, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, Z.; Song, T.; Liu, Q. Mir-4319 Induced an Inhibition of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Prevented Cancer Stemness of Hcc through Targeting Foxq1. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2936. [Google Scholar]
- Biao, D.; Qu, L.; Li, J.; Fang, J.; Yang, S.; Cao, Z.; Mei, Z.; Sun, X. Mirna-211 Suppresses Cell Proliferation, Migration and Invasion by Targeting Sparc in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23970. [Google Scholar]
- Yingjun, X.; Du, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; Yao, X.; Yang, Y. Mir-6875-3p Promotes the Proliferation, Invasion and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Via Btg2/Fak/Akt Pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Ruivo, C.F.; Adem, B.; Silva, M.; Melo, S.A. The Biology of Cancer Exosomes: Insights and New Perspectivesbiology of Cancer Exosomes. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 6480–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, G.; Zhisu, L. The Utility of Serum Exosomal Micrornas in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar]
- Lucio, B.; Moccetti, T.; Marbán, E.; Vassalli, G. Roles of Exosomes in Cardioprotection. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.H.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, X.X.; Ding, H.; Li, W.; Qin, L.; Pan, Y.L. Role of Exosomes and Exosomal Micrornas in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Potential in Diagnosis and Antitumour Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuangshuang, L.; Yao, J.; Xie, M.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, M. Exosomal Mirnas in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development and Clinical Responses. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Chenbin, L.; Wu, H.; Mao, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, S. Exosomal Micrornas in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 254. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.-H.; Ren, L.-N.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.; Luo, H.; Navarro-Alvarez, N.; Tang, L.-J. Combination of exosomes and circulating microRNAs may serve as a promising tumor marker complementary to alpha-fetoprotein for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis in rats. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.H.; Yang, S.R.; Cho, J.; Cho, H.C.; Shim, S.G.; Paik, Y. Serum Exosomal Micrornas as Novel Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e184. [Google Scholar]
- Wanbo, L.; Chen, S.; Liu, B. Diagnostic and Prognostic Values of Serum Exosomal Microrna-21 in Children with Hepatoblastoma: A Chinese Population-Based Study. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2016, 32, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Chenwei, J.; Jiao, X.; Zhu, A.; Ge, J.; Xu, X. Exosomal Mir-34s Panel as Potential Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Hepatoblastoma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2017, 52, 618–624. [Google Scholar]
- Xiaofeng, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, R.; Qin, L. Exosomal Mir-93 Promotes Proliferation and Invasion in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Directly Inhibiting Timp2/Tp53inp1/Cdkn1a. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 502, 515–521. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, B.; Sutandy, F.R.; Syu, G.D.; Middleton, S.; Yi, G.; Lu, K.Y.; Chen, C.S.; Kao, C.C. Heterogeneous Ribonucleoprotein K (Hnrnp K) Binds Mir-122, a Mature Liver-Specific Microrna Required for Hepatitis C Virus Replication. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2015, 14, 2878–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aucher, A.; Rudnicka, D.; Davis, D.M. Micrornas Transfer from Human Macrophages to Hepato-Carcinoma Cells and Inhibit Proliferation. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 6250–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Flemington, E.K. Mirnas in the Pathogenesis of Oncogenic Human Viruses. Cancer Lett. 2011, 305, 186–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.X.; Tang, H. Complex Interactions between Micrornas and Hepatitis B/C Viruses. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2014, 20, 13477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanling, W.; Jiang, L.; Ji, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, X. Hepatitis B Viral Rna Directly Mediates Down-Regulation of the Tumor Suppressor Microrna Mir-15a/Mir-16-1 in Hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18484–18493. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, S.; Steele, R.; Ray, R.; Ray, R.B. Micrornas: Role in Hepatitis C Virus Pathogenesis. Genes Dis. 2015, 2, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isabelle, J.; Shalamova, L.A.; Gerresheim, G.K.; Niepmann, M.; Bindereif, A.; Rossbach, O. Functional Sequestration of Microrna-122 from Hepatitis C Virus by Circular Rna Sponges. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Lianghai, W.; Zhou, L.; Hou, J.; Meng, J.; Lin, K.; Wu, X.; Chen, X. Three Novel Circrnas Upregulated in Tissue and Plasma from Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients and Their Regulatory Network. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, P.; Liang, H.; Xu, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, W.; Li, M.; Huang, J.; Ni, C.; Zhang, X.; et al. Circular Rna Hsa_Circ_0003288 Induces Emt and Invasion by Regulating Hsa_Circ_0003288/Mir-145/Pd-L1 Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Settleman, J. EMT, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Li, S.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wu, X. Circ-Rnf13, as an Oncogene, Regulates Malignant Progression of Hbv-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells and Hbv Infection through Cerna Pathway of Circ-Rnf13/Mir-424-5p/Tgif2. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2021, 21, 555. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, A.E.; Taniguchi, K.; Hao, Y.; Melhuish, T.A.; Shah, A.; Turner, S.D.; Sutherland, A.E.; Wotton, D. Tgif1 and Tgif2 Repress Expression of the RabGAP Evi5l. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 37, e00527-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, C.; Wang, G.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, L. Hsa_Circ_101280 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regulating Mir-375/Jak2. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 218–228. [Google Scholar]
- Sonohara, F.; Nomoto, S.; Inokawa, Y.; Hishida, M.; Takano, N.; Kanda, M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Fujii, T.; Koike, M.; Sugimoto, H.; et al. High expression of Janus kinase 2 in background normal liver tissue of resected hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with worse prognosis. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 767–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiao, C.; He, K.; Xiang, G. Circ_0072088 Promotes Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Activating Jak2/Stat3 Signaling Pathway Via Mir-375. IUBMB Life 2021, 73, 1153–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Quan, Y.; Fan, S.; Wang, H.; Liang, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; He, P.; Ye, Y. Exosome-Transmitted Circular Rna Hsa_Circ_0051443 Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Cancer Lett. 2020, 475, 119–128. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.-D.; Cai, N.; Wu, X.-L.; Cao, H.-Z.; Xie, L.-L.; Zheng, P.-S. OCT4 promotes tumorigenesis and inhibits apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by miR-125b/BAK1 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaotong, S.; Su, J.; He, H.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, H. Hsa_Circ_0070269 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through Modulating Mir-182/Nptx1 Axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 120, 109497. [Google Scholar]
- Boles, N.C.; Hirsch, S.E.; Le, S.; Corneo, B.; Najm, F.; Minotti, A.P.; Wang, Q.; Lotz, S.; Tesar, P.J.; Fasano, C.A. NPTX1 Regulates Neural Lineage Specification from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 724–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.-Q.; You, A.-B.; Zhu, X.-D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, S.-Z.; Zhang, K.-W.; Cai, H.; Shi, W.-K.; Li, X.-L.; et al. miR-182-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing FOXO3a. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Huang, Z.-L.; Bin Xu, B.; Chen, Z.; Re, T.J.; Zheng, Q.; Tang, Z.-Y.; Huang, X.-Y. Elevated MTSS1 expression associated with metastasis and poor prognosis of residual hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Deng, Y.; Liang, J.; Hu, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Fu, B.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q. Circular Rna Circ-102,166 Acts as a Sponge of Mir-182 and Mir-184 to Suppress Hepatocellular Carcinoma Proliferation and Invasion. J. Cell Oncol. 2021, 44, 279–295. [Google Scholar]
- Minhua, W.; Deng, X.; Zhong, Y.; Hu, L.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Ye, X. Maff Is Regulated Via the Circ-Itch/Mir-224-5p Axis and Acts as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Oncol. Res. 2020, 28, 299. [Google Scholar]
- Chuangjie, M.; Wen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Ge, Q. Cirs-7 Enhances the Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Mir-944/Nox4 Pathway. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2022, 32, 31–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, S.J.; Tatsunami, R.; Yamamura, H.; Fukai, T.; Ushio-Fukai, M. Ros-Induced Ros Release Orchestrated by Nox4, Nox2, and Mitochondria in Vegf Signaling and Angiogenesis. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C749–C764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fay, N.; Feng, R. Mechanisms of Photoreceptor Death in Retinitis Pigmentosa. J. Genes Megaw. 2020, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Huang, F.; Feng, C. Circfoxo3 Promotes Adriamycin Resistance through Regulation of Mir-199a-5p/Atp Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 1 Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5113. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, J.; Yao, X.; Tian, T.; Fu, X.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Shi, T.; Suo, A.; Ruan, Z.; Guo, H.; et al. ABCB5-ZEB1 Axis Promotes Invasion and Metastasis in Breast Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2017, 25, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianbo, G.; Duan, H.E.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.; Yuan, L.U. A Novel Circular Rna Circ-Znf652 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis through Inducing Snail-Mediated Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Sponging Mir-203/Mir-502-5p. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 812–819. [Google Scholar]
- Yuhui, L.; Zang, H.; Zhang, X.; Huang, G. Exosomal Circ-Znf652 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Glycolysis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Via Mir-29a-3p/Gucd1 Axis. J Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 7739. [Google Scholar]
- Bellet, M.M.; Piobbico, D.; Bartoli, D.; Castelli, M.; Pieroni, S.; Brunacci, C.; Chiacchiaretta, M.; DEL Sordo, R.; Fallarino, F.; Sidoni, A.; et al. NEDD4 controls the expression of GUCD1, a protein upregulated in proliferating liver cells. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1902–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.; Qu, Z.; Guo, P.; Liu, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, N. The function and regulation network mechanism of circRNA in liver diseases. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailiang, W.; Yan, S.; Hui, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Chang, Z. Circfat1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression Via Mir-30a-5p/Reep3 Pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 14561–14570. [Google Scholar]
- Ambros, V.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B.; Carrington, J.C.; Chen, X.; Dreyfuss, G.; Eddy, S.R.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Marshall, M.; et al. A uniform system for microRNA annotation. RNA 2003, 9, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Liang, M.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Li, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, X. CircRNA hsa_circRNA_104348 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through modulating miR-187-3p/RTKN2 axis and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katagiri, T.; Dat, L.T.; Matsuo, T.; Yoshimaru, T.; Kakiuchi, S.; Goto, H.; Hanibuchi, M.; Kuramoto, T.; Nishioka, Y.; Sone, S. Identification of genes potentially involved in bone metastasis by genome-wide gene expression profile analysis of non-small cell lung cancer in mice. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 40, 1455–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuwei, H.; Guo, Z.; Kang, Q.; Wang, X.; Han, X. Circular Rna Hsa_Circ_0000517 Modulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Advancement Via the Mir-326/Smad6 Axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 360. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, X.; Derynck, R. Does Smad6 Methylation Control Bmp Signaling in Cancer? Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, T. Up-Regulation of hsa_circ_0000517 Predicts Adverse Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianzhuang, G.; Du, C.; Sun, N.; Xiao, X.; Wu, H. Circular Rna Hsa_Circ_0005397 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Regulating the Mir-326/Pdk2 Axis. J. Gene Med. 2021, 23, e3332. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.Q.; Zhou, S.L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.J.; Wang, P.C.; Xin, H.Y.; Mao, L.; Luo, C.B.; Yu, S.Y.; Huang, X.W.; et al. Circular Rna Sequencing Identifies Circasap1 as a Key Regulator in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metastasis. Hepatology 2020, 72, 906–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jin, H.; Gao, D.; Lieftink, C.; Evers, B.; Jin, G.; Xue, Z.; Wang, L.; Beijersbergen, R.L.; Qin, W.; et al. Phospho-ERK is a biomarker of response to a synthetic lethal drug combination of sorafenib and MEK inhibition in liver cancer. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangsheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, B.; Lu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xiu, P.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. Circ-Birc6, a Circular Rna, Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting the Mir-3918/Bcl2 Axis. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 976–989. [Google Scholar]
- Benli, J.; Yin, X.; Wang, Y.; Qian, J.; He, Y.; Yang, C.; Yu, G.; Guo, B.; Meng, X. Circrna-Ptn Sponges Mir-326 to Promote Proliferation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 4893. [Google Scholar]
- Carmen, B.; Castillo, J.; Prieto, J.; Avila, M.A. New Molecular Targets for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Erbb1 Signaling System. Liver Int. 2007, 27, 174–185. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhu, Z.; Johnson, C.; Stoops, J.; Eaker, A.E.; Bowen, W.; DeFrances, M.C. PIK3IP1, a Negative Regulator of PI3K, Suppresses the Development of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5591–5598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ge, W.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J.; Kong, Y.; Cui, B.; Gao, B.; Qian, X.; Wang, W. The Circular Rna Circslc7a11 Functions as a Mir-330-3p Sponge to Accelerate Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Regulating Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 Expression. J. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Asghar, U.; Witkiewicz, A.K.; Turner, N.C.; Knudsen, E.S. The history and future of targeting cyclin-dependent kinases in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juan, Z.; Chang, Y.; Xu, L.; Qin, L. Elevated Expression of Circular Rna Circ_0008450 Predicts Dismal Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Regulates Cell Proliferation, Apoptosis, and Invasion Via Sponging Mir-548p. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 120, 9487–9494. [Google Scholar]
- Qiajun, D.; Han, J.; Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Pan, Y. Hypoxia-Induced Circular Rna Hsa_Circ_0008450 Accelerates Hepatocellular Cancer Progression Via the Mir-431/Akap1 Axis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 388. [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldi, L.; Sepe, M.; Donne, R.D.; Conte, K.; Arcella, A.; Borzacchiello, D.; Amente, S.; De Vita, F.; Porpora, M.; Garbi, C.; et al. Mitochondrial AKAP1 supports mTOR pathway and tumor growth. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, G.; Dai, C.; Yu, X.; Yin, X.; Zhou, F. Circ-Tcf4. 85 Silencing Inhibits Cancer Progression through Microrna-486-5p-Targeted Inhibition of Abcf2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 447–461. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, S.; Tian, L.; Guo, E.; Luan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, S. Genome-wide identification and characterization of ATP-binding cassette transporters in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degot, S.; Régnier, C.H.; Wendling, C.; Chenard, M.-P.; Rio, M.-C.; Tomasetto, C. Metastatic Lymph Node 51, a novel nucleo-cytoplasmic protein overexpressed in breast cancer. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4422–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wei, L.; Yin, C.; Liu, Y. Circular Rna Circ_0091579 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Glycolysis through Mir-490-5p/Casc3 Axis. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2021, 36, 863–878. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Hu, B.; Ji, L.; Ruan, X.; Zheng, Z. Hsa_circ_0103809 promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-490-5p/SOX2 signaling pathway. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2018, 10, 1690–1702. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, G.; Yang, L.; Xie, X.; Peng, L.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-490-5p is a novel tumor suppressor targeting c-FOS in human bladder cancer. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Cheng, X.; Sun, S.; Zhou, J. Transcriptional activation of PD-L1 by Sox2 contributes to the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3061–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Xu, X.; Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, L.; Yao, Y.; Xiang, G.; Huang, X.; Wang, G. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Hsa_circ_0101432 promotes the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by adsorbing miR-1258 and miR-622. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 2398–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Peng, L. MAPK1 up-regulates the expression of MALAT1 to promote the proliferation of cardiomyocytes through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 15947–15953. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xu, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. CircBACH1 (hsa_circ_0061395) promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth by regulating p27 repression via HuR. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 6929–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Bian, L.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, X. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0061395 accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via regulation of the miR-877-5p/PIK3R3 axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Han, W.; Xu, H.; Wen, L.; Deng, Y.; Liu, K. RETRACTED: Long non-coding RNA LINC00160 functions as a decoy of microRNA-132 to mediate autophagy and drug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma via inhibition of PIK3R3. Cancer Lett. 2020, 478, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, L.; Guo, J.; Shen, K.; Wang, R.; Chen, C.; Liao, Z.; Zhou, J. Paclitaxel Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Tumorigenesis through Regulating Circ-Birc6/Mir-877-5p/Ywhaz Axis. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 9377. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.-Y.; Hu, M.; Zhao, L.; Guo, W.-S. MiR-451a suppresses cell proliferation, metastasis and EMT via targeting YWHAZ in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5158–5167. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Ge, X.; Xu, Z.; Chen, D. Identification of circular RNA–microRNA–messenger RNA regulatory network in hepatocellular carcinoma by integrated analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 35, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Tao, Q.; Kao, X.; Zhu, X. Hsa-circRNA-103809 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development via MicroRNA-1270/PLAG1 Like Zinc Finger 2 Axis. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 2021, 66, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.-M.; Tsang, F.H.-C.; Ng, I.O.-L. Non-coding RNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma: Molecular functions and pathological implications. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, F.G.; Sun, X.G.; Chen, L.; Xiu, H.; Liu, X.S. Long Noncoding Rna Casc2c Inhibited Cell Proliferation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Inactivated Erk1/2 and Wnt/Β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 22, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, E.; Abdul-Baki, E.A.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Hagras, M.M.; Zidan, A.; Abdel-Naby, A.Y.; Watny, M.; Elkabash, I.A.; Salem, M.L.; Elshanshoury, M. Microrna Signature in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients: Identification of Potential Markers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4945–4953. [Google Scholar]
- El-Maraghy, S.A.; Adel, O.; Zayed, N.; Yosry, A.; El-Nahaas, S.M.; Gibriel, A.A. Circulatory miRNA-484, 524, 615 and 628 expression profiling in HCV mediated HCC among Egyptian patients; implications for diagnosis and staging of hepatic cirrhosis and fibrosis. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 22, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, J.; Cui, J.; Zhong, L.; Zeng, L.; Ge, S. circRNA_100290 plays a role in oral cancer by functioning as a sponge of the miR-29 family. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4551–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jing, B.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. Circular RNA circTMEM45A Acts as the Sponge of MicroRNA-665 to Promote Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.U.; Agarwal, V.; Guo, H.; Bartel, D.P. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingqiu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, P.; Le, Y.; Zhou, C.; Wang, S.; Xu, D.; Lin, H.; Gong, Z. Circular Rnas in Cancer: Novel Insights into Origins, Properties, Functions and Implications. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 472. [Google Scholar]
| Sr. No | miRNAs | Region | References | Sr. No | miRNAs | Region | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | miR-10b | China | [11] | 46 | miR-222 | China | [12] |
| 2 | miR-17-5p | Turkey | [13] | 47 | miR-223 | USA | [14] |
| 3 | miR-18a | China | [15] | miR-223 | China | [16] | |
| 4 | miR-19a | China | [17] | miR-223 | China | [17] | |
| 5 | miR-21 | India | [18] | 48 | miR-224 | China | [19] |
| 6 | miR-22 | China | [20] | 49 | miR-224-5p | China | [21] |
| 7 | miR-22-3p | China | [22] | 50 | miR-300 | China | [23] |
| 8 | miR-23b | China | [16] | 51 | miR-320a | China | [24] |
| 9 | miR-23b-3p | China | [21] | 52 | miR-325 | China | [25] |
| 10 | miR-24-3p | Turkey | [13] | 5354 | miR-326 | Egypt | [26] |
| miR-24-3p | China | [27] | miR-331-3p | China | [21] | ||
| 11 | miR-27a | Egypt | [28] | 55 | miR-330-3p | China | [29] |
| 12 | miR-28-5p | China | [30] | 56 | mi-345 | China | [31] |
| 13 | miR-29a-3p | China | [32] | 58 | miR-361-5p | China | [33] |
| 14 | miR-30a-5p | China | [34] | 57 | miR-362-5p | China | [35] |
| 15 | miR-32-5p | China | [36] | 58 | miR-370 | China | [37] |
| 16 | miR-34a | USA | [38] | 59 | miR-371a-5p | China | [39] |
| 17 | miR-34c | China | [40] | 60 | miR-373-3p | China | [41] |
| 18 | miR-93 | USA | [42] | 61 | miR-375 | China | [43] |
| 19 | miR-95-3p | China | [44] | 62 | miR-384 | China | [45] |
| 20 | miR-96 | China | [46] | 63 | miR-424-5p | China | [47] |
| 21 | miR-99a | China | [48] | 64 | miR-431 | China | [49] |
| 22 | miR-122 | USA | [50] | 65 | miR-452-3p | China | [51] |
| 23 | miR-122-5p | China | [21] | 66 | miR-486-5p | China | [52] |
| 24 | miR-125a | Egypt | [53] | 67 | miR-490-5p | China | [54] |
| 25 | miR-125b-5p | Germany | [55] | 68 | miR-491 | China | [56] |
| 26 | miR-129-2 | China | [57] | 69 | miR-493 | China | [58] |
| 27 | miR-132 | China | [59] | 70 | miR-494-3p | China | [21] |
| 28 | miR-133b | China | [60] | 71 | miR-503 | China | [61] |
| 29 | miR-137 | China | [62] | 72 | miR-548p | China | [63] |
| 30 | miR-139 | Egypt | [53] | 73 | miR-603 | China | [64] |
| 31 | miR-145 | India | [18] | 74 | miR-622 | China | [65] |
| 32 | miR-149 | China | [66] | 75 | miR-744-5p | China | [67] |
| 33 | miR-150-5p | China | [68] | 76 | miR-801 | China | [16] |
| 34 | miR-152 | France | [69] | 77 | miR-877-5p | China | [70] |
| 35 | miR-155 | China | [71] | 78 | miR-922 | China | [72] |
| 36 | miR-182 | Egypt | [73] | 79 | miR-940 | China | [74] |
| 37 | miR-187-3p | China | [75] | 80 | miR-944 | USA | [14] |
| 38 | miR-192 | China | [16] | 81 | miR-1236 | China | [76] |
| 39 | miR-193-5p | India | [77] | 82 | miR-1287 | China | [78] |
| 40 | miR-194 | China | [16] | 83 | miR-1296 | China | [79] |
| 41 | miR-195 | Egypt | [80] | 84 | miR-1468 | China | [72] |
| 42 | miR-199a-5p | Germany | [81] | 85 | miR-3194-3p | China | [56] |
| 43 | miR-205 | China | [82] | 86 | miR-3651 | China | [83] |
| 44 | miR-210-3p | Japan | [59] | 87 | miR-4319 | China | [84] |
| 45 | miR-211 | China | [85] | 88 | miR-6875-3p | China | [86] |
| Scheme | Symbol | Expression | p-Value | References | Sr. No | Symbol | Expression | p-Value | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | miR-18a | High | <0.01 | [15] | 13 | miR-194 | High | <0.01 | [16] |
| 2 | miR-19a | High | ˂0.05 | [17] | 14 | miR-205 | Low | <0.01 | [82] |
| 3 | miR-21 | Low | 0.0487 | [18] | 15 | miR-210-3p | High | <0.0308 | [59] |
| 4 | miR-22 | High | 0.027 | [20] | 16 | miR-222 | High | 0.046 | [12] |
| 5 | miR-23b | High | <0.01 | [16] | 17 | miR-223 | Low | <0.01 | [16] |
| 6 | miR-24-3p | High | ˂0.05 | [27] | 18 | miR-224 | High | ˂0.05 | [19] |
| 7 | miR-34c | Low | <0.01 | [40] | 19 | miR-371a-5p | High | <0.05 | [39] |
| 8 | miR-96 | High | ˂0.01 | [46] | 20 | miR-375 | Low | ˂0.05 | [43] |
| 9 | miR-132 | Low | 0.021 | [59] | 21 | miR-384 | Low | <0.05 | [45] |
| 10 | miR-145 | Low | 0.0486 | [18] | 22 | miR-548p | Low | <0.01 | [63] |
| 11 | miR-192 | High | <0.01 | [16] | 23 | miR-801 | High | <0.01 | [16] |
| 12 | miR-193a-5p | Low | <0.03 | [77] | 24 | miR-1236 | Low | <0.05 | [76] |
| Sr. No | Symbol | Expression | p-Value | References | Sr. No | Symbol | Expression | p-Value | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | miR-17-5p | Low | ˂0.05 | [13] | 9 | miR-155 | High | ˂0.05 | [71] |
| 2 | miR-23b-3p | Low | 0.038 | [21] | 10 | miR-182 | Low | 0.015 | [73] |
| 3 | miR-24-3p | Low | ˂0.05 | [13] | 11 | miR-195 | Low | 0.04 | [80] |
| 4 | miR-27a | High | 0.03 | [28] | 12 | miR-223 | Low | ˂0.05 | [17] |
| 5 | miR-122-5p | High | 0.011 | [21] | 13 | miR-224-5p | High | 0.018 | [21] |
| 6 | miR-125a | Low | <0.01 | [53] | 14 | miR-331-3p | High | 0.020 | [21] |
| 7 | miR-139 | Low | <0.01 | [53] | 15 | miR-494-3p | High | 0.025 | [21] |
| 8 | miR-152 | Low | <0.01 | [69] |
| Sr. No | Symbol | Expression in HCC | p-Value | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | miR-22-3p | High | ˂ 0.01 | [22] |
| 2 | miR-122 | High | ˂ 0.05 | [50] |
| 3 | miR-125b-5p | Low | 0.019 | [81] |
| 4 | 199a-5p | Low | 0.04 | [81] |
| 5 | miR-223 | High | 0.037 | [14] |
| 6 | miR-944 | High | 0.019 | [14] |
| Sr. No | Symbol | Expression | p-Value | References | Sr. No | Symbol | Expression | p-Value | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | miR-10b | High | < 0.01 | [11] | 25 | miR-362-5p | High | < 0.01 | [35] |
| 2 | miR-28-5p | Low | <0.05 | [30] | 26 | miR-370 | Low | <0.01 | [37] |
| 3 | miR-29a-3p | Low | <0.05 | [32] | 27 | miR-373-3p | Low | <0.05 | [41] |
| 4 | miR-30a-5p | Low | <0.05 | [34] | 28 | miR-424-5p | Low | <0.05 | [47] |
| 5 | miR-32-5p | High | <0.01 | [36] | 29 | miR-431 | Low | <0.05 | [49] |
| 6 | miR-34a | High | <0.01 | [38] | 30 | miR-452-3p | High | <0.01 | [51] |
| 7 | miR-93 | High | 0.022 | [42] | 31 | miR-486-5p | Low | <0.05 | [52] |
| 8 | miR-95-3p | High | <0.01 | [44] | 32 | miR-490-5p | Low | <0.01 | [54] |
| 9 | miR-99a | Low | <0.01 | [48] | 33 | miR-491 | High | <0.01 | [56] |
| 10 | miR-129-2 | Low | <0.01 | [57] | 34 | miR-493 | Low | <0.05 | [58] |
| 12 | miR-133b | Low | <0.01 | [60] | 35 | miR-503 | Low | <0.01 | [61] |
| 13 | miR-137 | Low | <0.05 | [62] | 36 | miR-603 | High | <0.01 | [64] |
| 14 | miR-149 | Low | 0.023 | [66] | 37 | miR-622 | Low | <0.01 | [65] |
| 15 | miR-150-5p | Low | 0.015 | [68] | 38 | miR-744-5p | Low | <0.01 | [67] |
| 16 | miR-187-3p | Low | <0.01 | [75] | 39 | miR-877-5p | Low | <0.01 | [70] |
| 17 | miR-211 | Low | <0.01 | [85] | 40 | miR-922 | High | <0.05 | [72] |
| 18 | miR-300 | Low | 0.02 | [23] | 41 | miR-940 | Low | <0.05 | [74] |
| 19 | miR-320a | Low | <0.05 | [24] | 42 | miR-1296 | Low | <0.05 | [79] |
| 20 | miR-325 | Low | <0.05 | [25] | 43 | miR-1468 | High | <0.05 | [72] |
| 21 | miR-326 | Low | <0.05 | [100] | 44 | miR-3194-3p | Low | <0.05 | [56] |
| 22 | miR-330-3p | High | <0.01 | [29] | 45 | miR-3651 | High | <0.01 | [83] |
| 23 | mi-345 | Low | <0.05 | [31] | 46 | miR-4319 | Low | <0.01 | [84] |
| 24 | miR-361-5p | Low | <0.01 | [33] | 47 | miR-6875-3p | High | <0.05 | [86] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ishaq, Y.; Ikram, A.; Alzahrani, B.; Khurshid, S. The Role of miRNAs, circRNAs and Their Interactions in Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Insilico Approach. Genes 2023, 14, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010013
Ishaq Y, Ikram A, Alzahrani B, Khurshid S. The Role of miRNAs, circRNAs and Their Interactions in Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Insilico Approach. Genes. 2023; 14(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleIshaq, Yasmeen, Aqsa Ikram, Badr Alzahrani, and Sana Khurshid. 2023. "The Role of miRNAs, circRNAs and Their Interactions in Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Insilico Approach" Genes 14, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010013
APA StyleIshaq, Y., Ikram, A., Alzahrani, B., & Khurshid, S. (2023). The Role of miRNAs, circRNAs and Their Interactions in Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Insilico Approach. Genes, 14(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010013






