ProGeo-Neo v2.0: A One-Stop Software for Neoantigen Prediction and Filtering Based on the Proteogenomics Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data
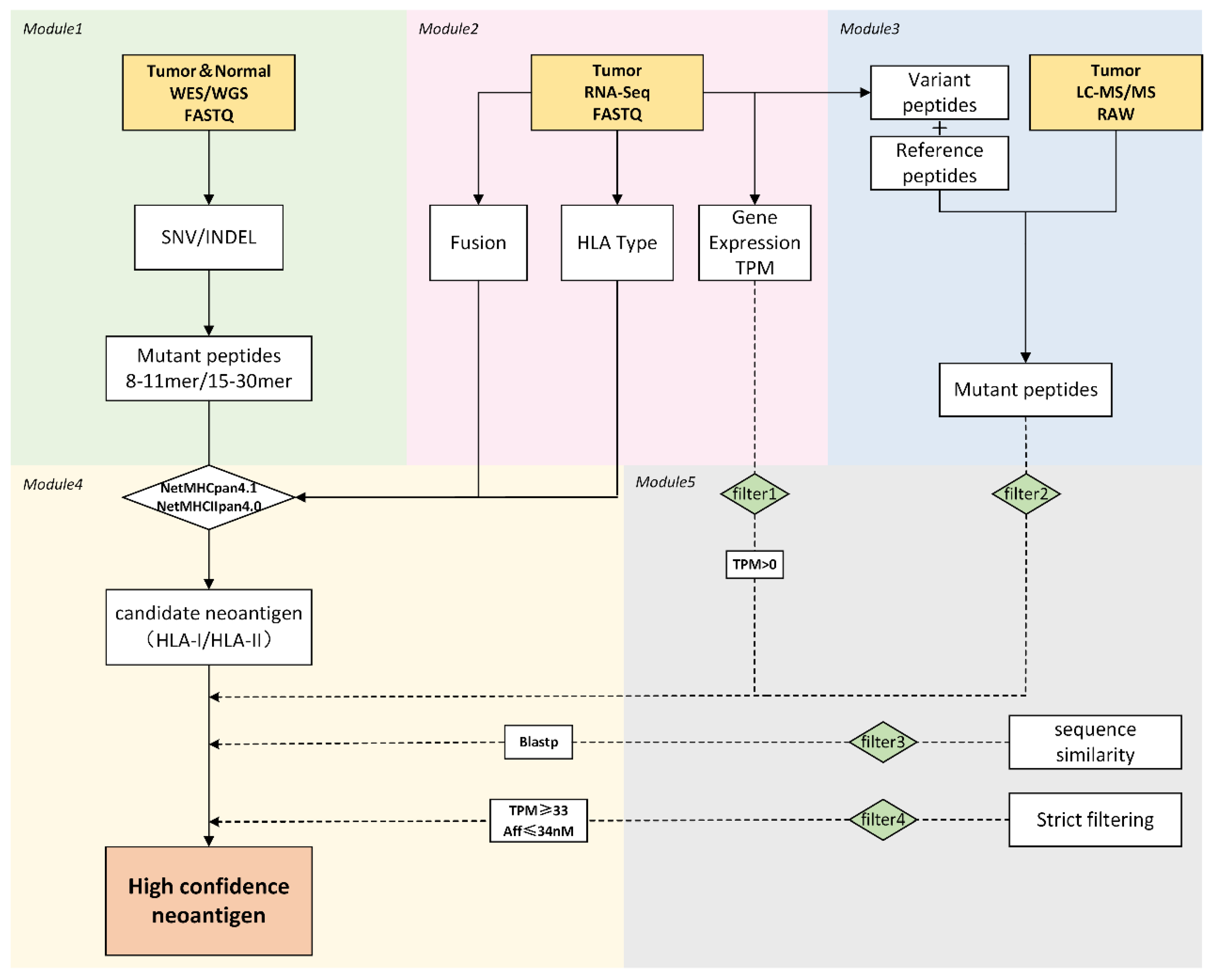
2.2. Description of the ProGeo-Neo v2.0
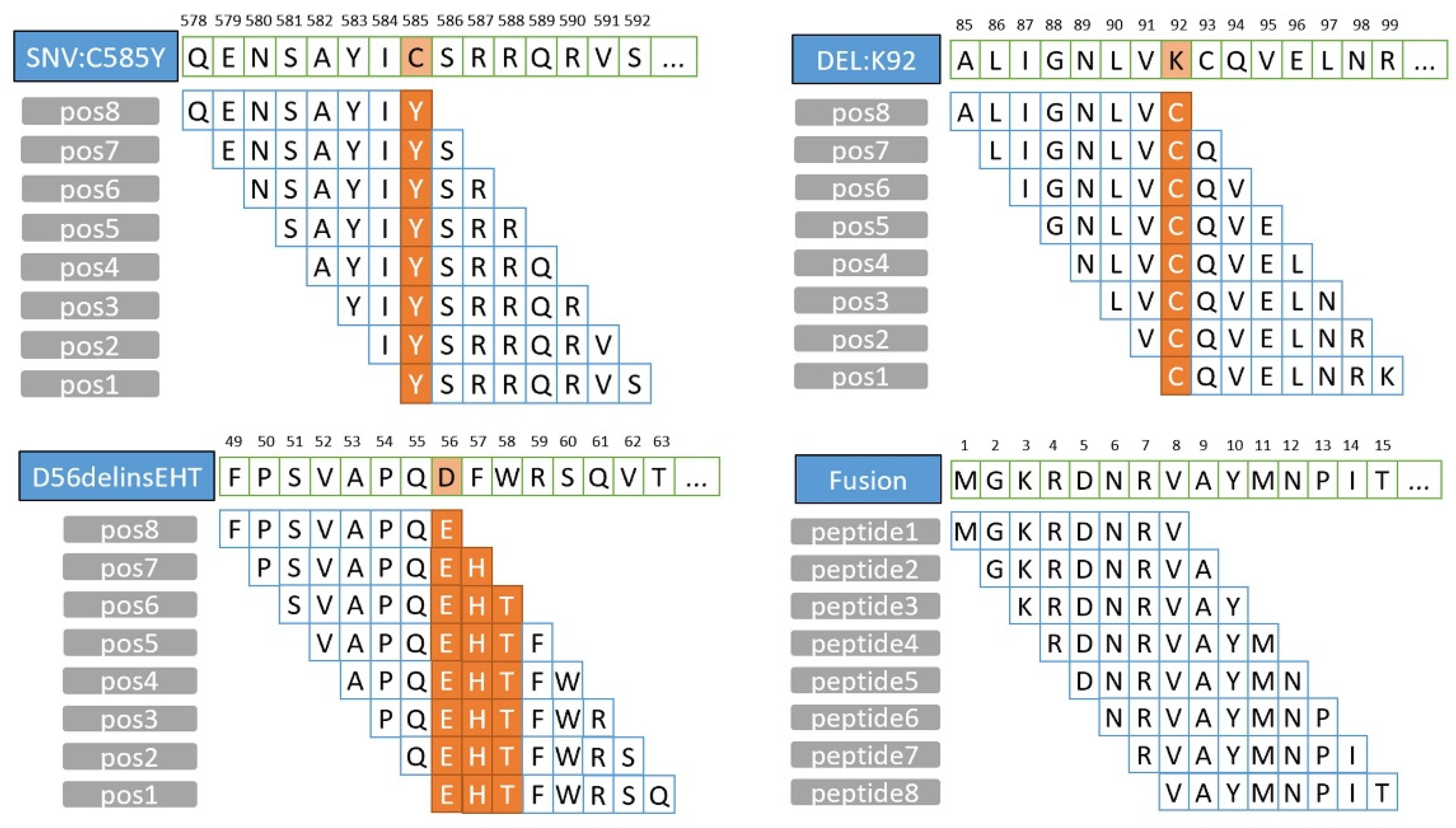
2.3. Module 1: Identification of SNV/INDEL Based on WGS/WES Data
2.4. Module 2: RNA-Seq Data Processing
2.5. Module 3: Building Protein Database and MS Searching
2.6. Module 4: Neoantigen Prediction
2.7. Module 5: Neoantigen Filtration
3. Results
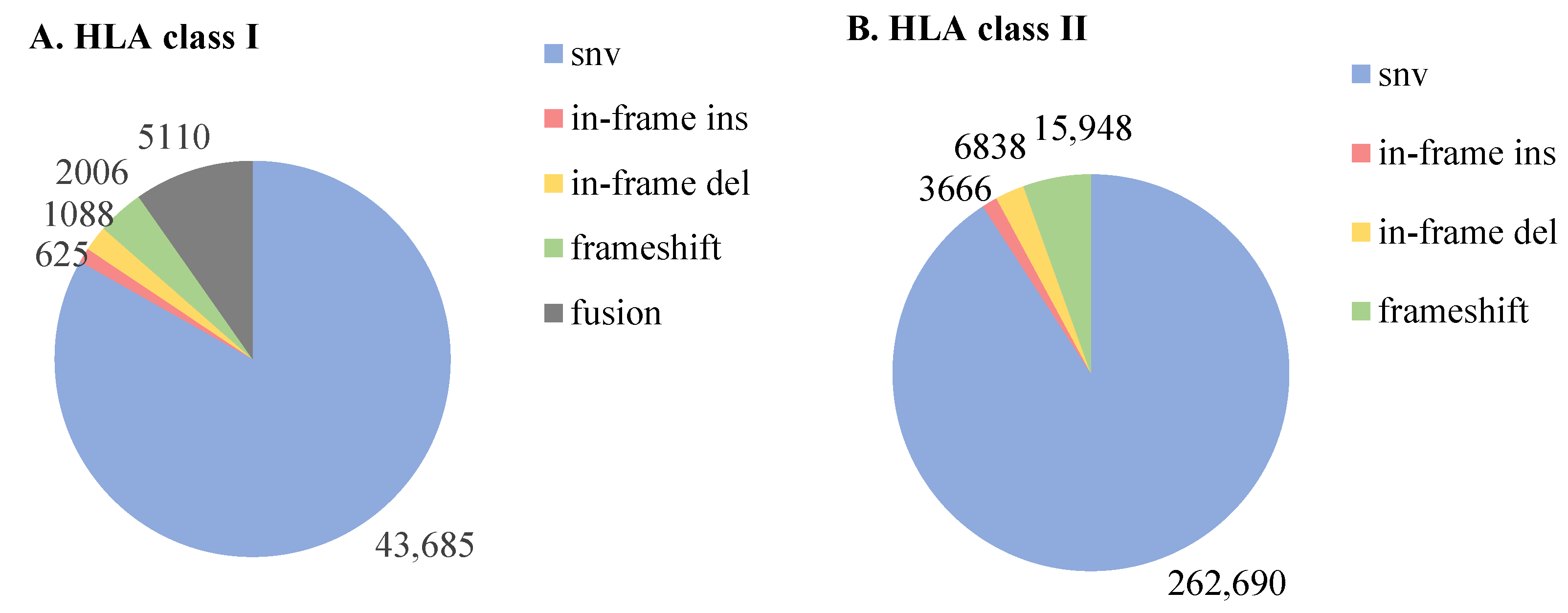
3.1. Features Updated from ProGeo-Neo v1.0
3.2. The Performance of ProGeo-Neo v2.0 on Jurkat Cell Line Data
3.3. Performance Enhancements from ProGeo-Neo v1.0
3.4. Screening Validity of ProGeo-Neo v2.0
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blass, E.; Ott, P.A. Advances in the development of personalized neoantigen-based therapeutic cancer vaccines. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Akbari, M.; Ghanaatian, M.; Roozbahani Moghaddam, P.; Adelian, S.; Borjian Boroujeni, M.; Yazdani, E.; Ahmadi, A.; Hamblin, M.R. Development of neoantigens: From identification in cancer cells to application in cancer vaccines. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supabphol, S.; Li, L.; Goedegebuure, S.P.; Gillanders, W.E. Neoantigen vaccine platforms in clinical development: Understanding the future of personalized immunotherapy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2021, 30, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremova, M.; Finotello, F.; Rieder, D.; Trajanoski, Z. Neoantigens Generated by Individual Mutations and Their Role in Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Algarra, I.; Garrido, F.; Garcia-Lora, A.M. MHC heterogeneity and response of metastases to immunotherapy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.M.; Bhattacharya, R.; Huang, J.; Sivakumar, I.; Karchin, R. High-Throughput Prediction of MHC Class I and II Neoantigens with MHCnuggets. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yarchoan, M.; Johnson, B.A., 3rd; Lutz, E.R.; Laheru, D.A.; Jaffee, E.M. Targeting neoantigens to augment antitumour immunity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, U.; Derhovanessian, E.; Miller, M.; Kloke, B.P.; Simon, P.; Löwer, M.; Bukur, V.; Tadmor, A.D.; Luxemburger, U.; Schrörs, B.; et al. Personalized RNA mutanome vaccines mobilize poly-specific therapeutic immunity against cancer. Nature 2017, 547, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hundal, J.; Carreno, B.M.; Petti, A.A.; Linette, G.P.; Griffith, O.L.; Mardis, E.R.; Griffith, M. pVAC-Seq: A genome-guided in silico approach to identifying tumor neoantigens. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, E.; Lee, M.G.; Shin, E.C.; Paik, S.; Kim, S. Neopepsee: Accurate genome-level prediction of neoantigens by harnessing sequence and amino acid immunogenicity information. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Lyu, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Wu, S.; Zhou, J.; Gu, X.; Su, Z.; Chen, S. TSNAD: An integrated software for cancer somatic mutation and tumour-specific neoantigen detection. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 170050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verma, A.; Halder, A.; Marathe, S.; Purwar, R.; Srivastava, S. A proteogenomic approach to target neoantigens in solid tumors. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2020, 17, 797–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Tan, X.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, M.; Song, X.; Liu, Q.; Leng, Q.; Chen, L.; Xie, L. ProGeo-neo: A customized proteogenomic workflow for neoantigen prediction and selection. BMC Med. Genom. 2020, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gioia, L.; Siddique, A.; Head, S.R.; Salomon, D.R.; Su, A.I. A genome-wide survey of mutations in the Jurkat cell line. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrett, T.; Troup, D.B.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Rudnev, D.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Soboleva, A.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for high-throughput functional genomic data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D885–D890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheynkman, G.M.; Shortreed, M.R.; Frey, B.L.; Smith, L.M. Discovery and mass spectrometric analysis of novel splice-junction peptides using RNA-Seq. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2013, 12, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D204–D212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 6 April 2022).
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M.; et al. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haas, B.; Dobin, A.; Stransky, N.; Bo, L.; Xiao, Y.; Tickle, T.; Bankapur, A.; Ganote, C.; Doak, T.; Pochet, N. STAR-Fusion: Fast and Accurate Fusion Transcript Detection from RNA-Seq. BioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szolek, A.; Schubert, B.; Mohr, C.; Sturm, M.; Feldhahn, M.; Kohlbacher, O. OptiType: Precision HLA typing from next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3310–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Warren, R.L.; Choe, G.; Freeman, D.J.; Castellarin, M.; Munro, S.; Moore, R.; Holt, R.A. Derivation of HLA types from shotgun sequence datasets. Genome Med. 2012, 4, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyanova, S.; Temu, T.; Cox, J. The MaxQuant computational platform for mass spectrometry-based shotgun proteomics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 2301–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurtz, V.; Paul, S.; Andreatta, M.; Marcatili, P.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M. NetMHCpan-4.0: Improved Peptide-MHC Class I Interaction Predictions Integrating Eluted Ligand and Peptide Binding Affinity Data. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 3360–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karosiene, E.; Rasmussen, M.; Blicher, T.; Lund, O.; Buus, S.; Nielsen, M. NetMHCIIpan-3.0, a common pan-specific MHC class II prediction method including all three human MHC class II isotypes, HLA-DR, HLA-DP and HLA-DQ. Immunogenetics 2013, 65, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynisson, B.; Alvarez, B.; Paul, S.; Peters, B.; Nielsen, M. NetMHCpan-4.1 and NetMHCIIpan-4.0: Improved predictions of MHC antigen presentation by concurrent motif deconvolution and integration of MS MHC eluted ligand data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W449–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Li, D.; Huang, P.; Jian, X.; Wan, H.; Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, J.; Lin, Y.; Xie, L. dbPepNeo: A manually curated database for human tumor neoantigen peptides. Database J. Biol. Databases Curation 2020, 2020, baaa004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. BLAST: At the core of a powerful and diverse set of sequence analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W20–W25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, D.K.; van Buuren, M.M.; Dang, K.K.; Hubbard-Lucey, V.M.; Sheehan, K.C.F.; Campbell, K.M.; Lamb, A.; Ward, J.P.; Sidney, J.; Blazquez, A.B.; et al. Key Parameters of Tumor Epitope Immunogenicity Revealed Through a Consortium Approach Improve Neoantigen Prediction. Cell 2020, 183, 818–834.e813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.; Chen, M.Y.; Goedegebuure, S.P.; Gillanders, W.E. Challenges targeting cancer neoantigens in 2021: A systematic literature review. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2021, 20, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

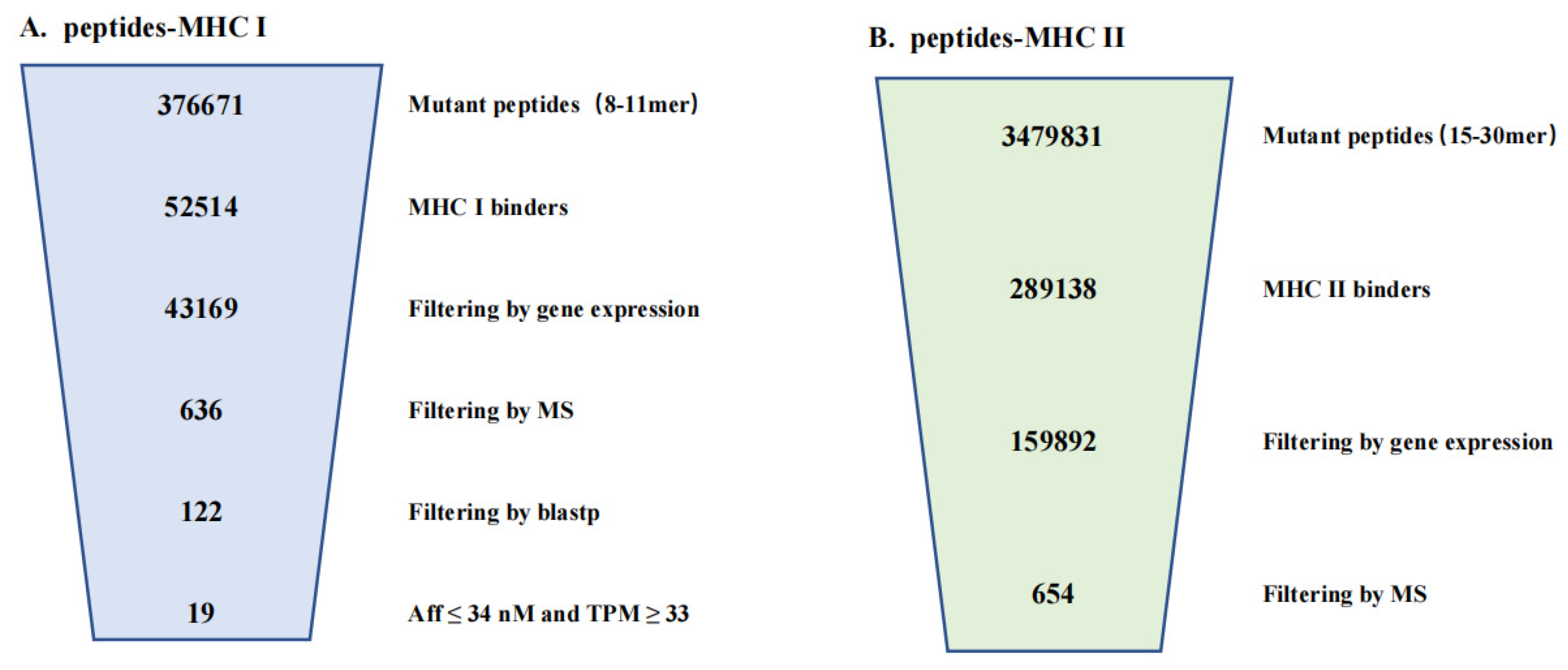
| Mutant Peptides | MHC I Binders | Filtering by Gene Expression | Filtering by MS | Aff ≤ 34 nM TPM ≥ 33 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ProGeo-neo v2.0 | 376,671 | 52,514 | 43,169 | 636 | 19 |
| Matching ratio | 14.31% | 19.18% | 21.05% | ||
| ProGeo-neo v1.0 | 373,046 | 36,835 | 30,142 | 655 | |
| Matching ratio | 11.45% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Jian, X.; Tan, X.; Lu, M.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, L.; et al. ProGeo-Neo v2.0: A One-Stop Software for Neoantigen Prediction and Filtering Based on the Proteogenomics Strategy. Genes 2022, 13, 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050783
Liu C, Zhang Y, Jian X, Tan X, Lu M, Ouyang J, Liu Z, Li Y, Xu L, Chen L, et al. ProGeo-Neo v2.0: A One-Stop Software for Neoantigen Prediction and Filtering Based on the Proteogenomics Strategy. Genes. 2022; 13(5):783. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050783
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chunyu, Yu Zhang, Xingxing Jian, Xiaoxiu Tan, Manman Lu, Jian Ouyang, Zhenhao Liu, Yuyu Li, Linfeng Xu, Lanming Chen, and et al. 2022. "ProGeo-Neo v2.0: A One-Stop Software for Neoantigen Prediction and Filtering Based on the Proteogenomics Strategy" Genes 13, no. 5: 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050783
APA StyleLiu, C., Zhang, Y., Jian, X., Tan, X., Lu, M., Ouyang, J., Liu, Z., Li, Y., Xu, L., Chen, L., Lin, Y., & Xie, L. (2022). ProGeo-Neo v2.0: A One-Stop Software for Neoantigen Prediction and Filtering Based on the Proteogenomics Strategy. Genes, 13(5), 783. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13050783






