Assessment of Rare Genetic Variants to Identify Candidate Modifier Genes Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Neurofibromatosis 1 Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
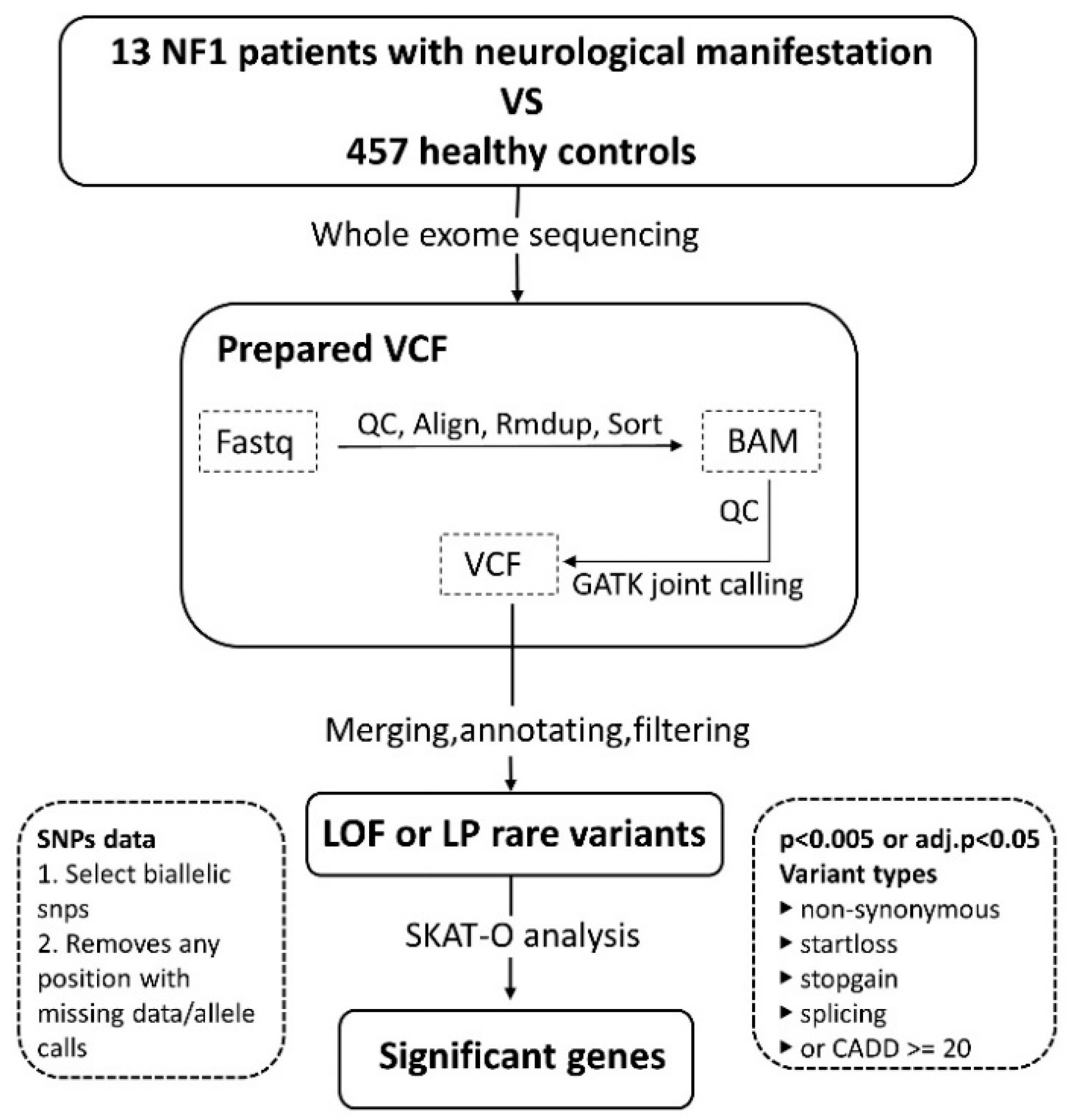
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Enrollment
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Statistics
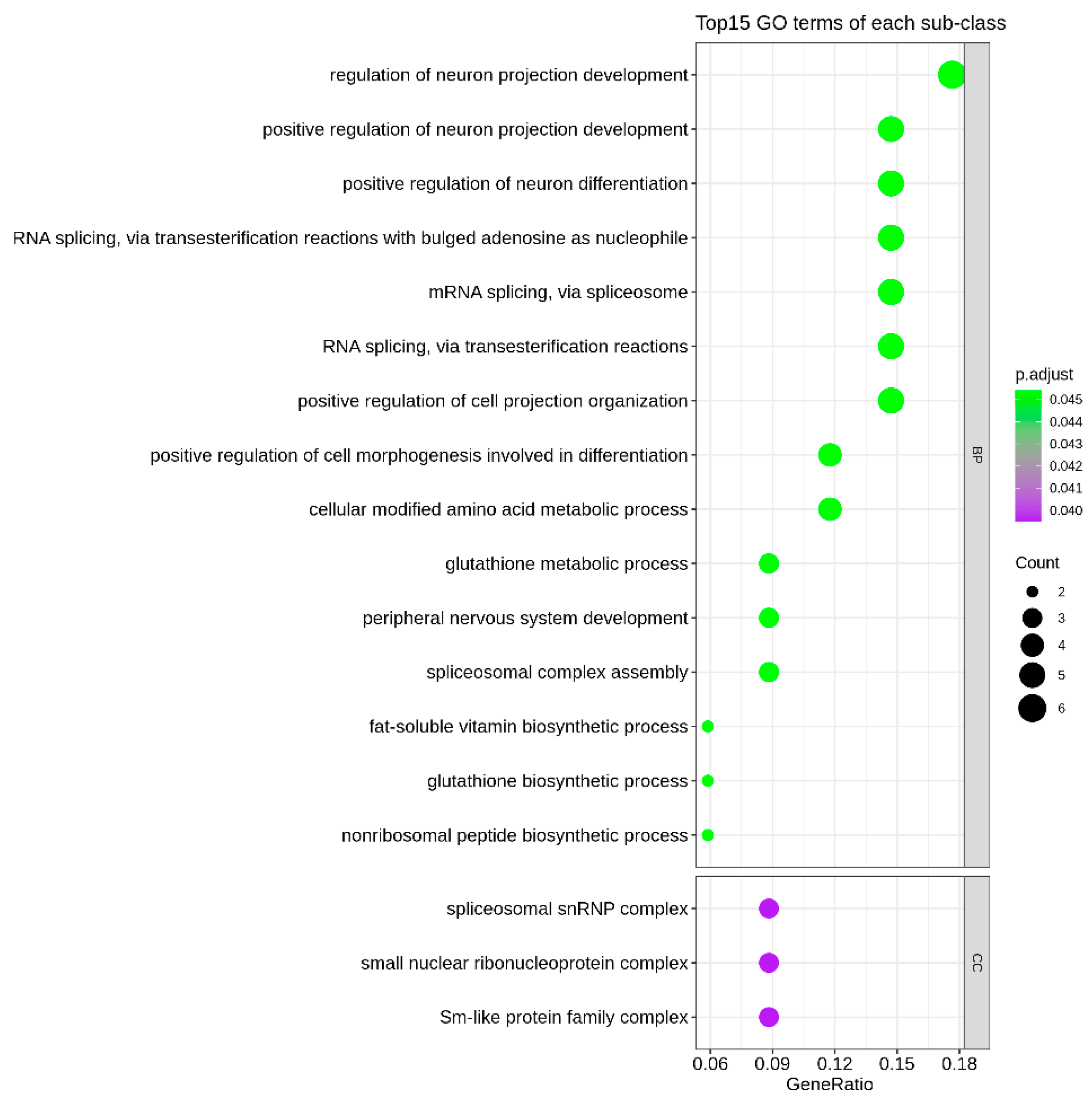
2.4. Pathway Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
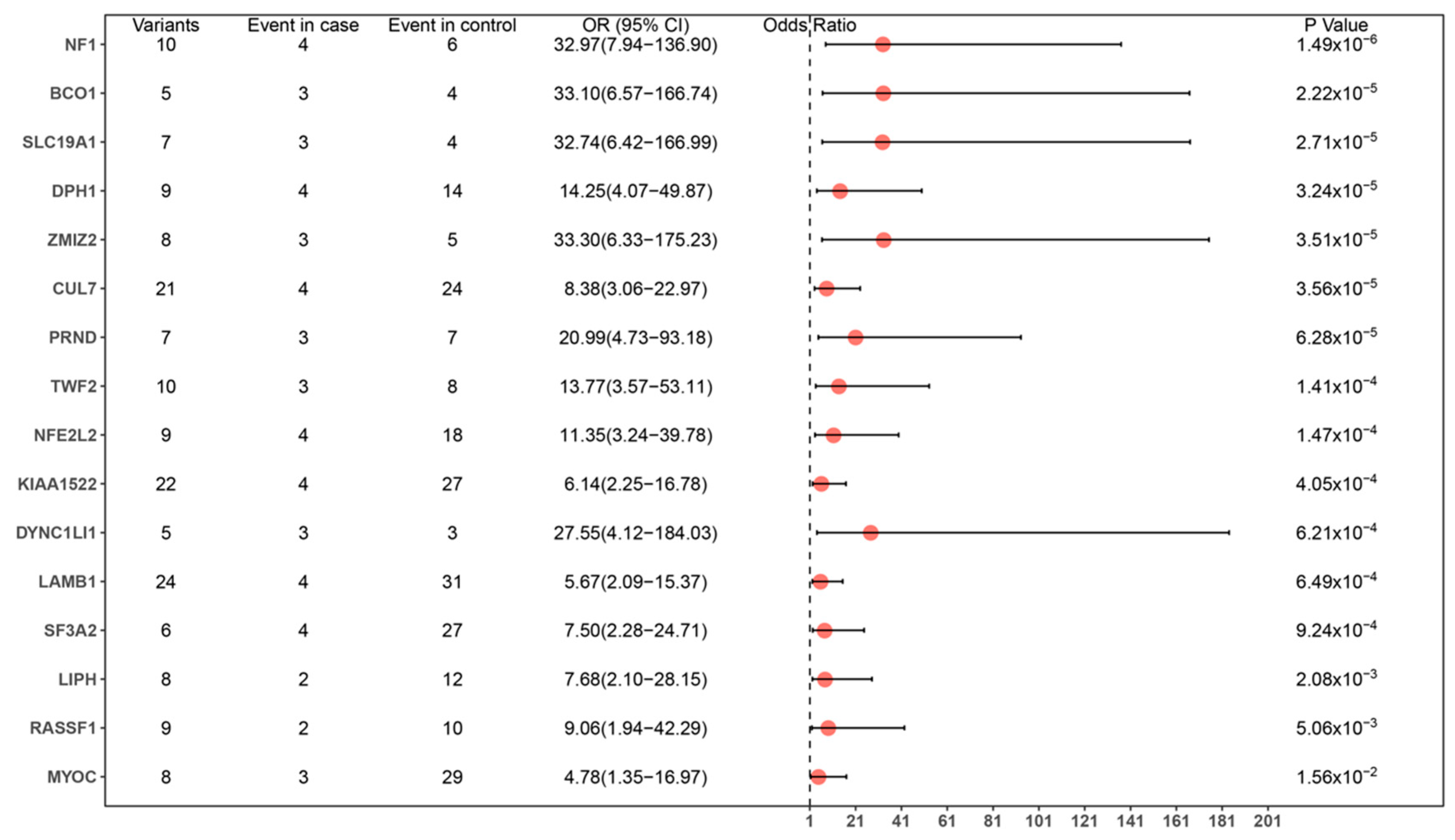
3.2. Variant Calling and Analysis
3.3. Enrichment of Identified Genes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, D.G.; Howard, E.; Giblin, C.; Clancy, T.; Spencer, H.; Huson, S.M.; Lalloo, F. Birth incidence and prevalence of tumor-prone syndromes: Estimates from a UK family genetic register service. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2010, 152, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberly, J.; Jan, M.F. Clinical and genetic aspects of neurofibromatosis 1. Genet. Med. 2010, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg, J.C.; Templer, A.; Gao, F.; Titus, J.B.; Gutmann, D.H. Attention skills in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. J. Child. Neurol. 2013, 28, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.S.B.; López, P.J.; Calvo, E.C.; González, V.I.; Gallart, M.M.; Villagrasa, P.S. Neurological manifestations of neurofibromatosis type 1: Our experience. Neurologia 2022, 37, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koczkowska, M.; Chen, Y.; Callens, T.; Gomes, A.; Sharp, A.; Johnson, S.; Hsiao, M.-C.; Chen, Z.; Balasubramanian, M.; Barnett, C.P.; et al. Genotype-Phenotype Correlation in NF1: Evidence for a More Severe Phenotype Associated with Missense Mutations Affecting NF1 Codons 844-848. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 102, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbagh, A.; Pasmant, E.; Imbard, A.; Luscan, A.; Soares, M.; Blanché, H.; Laurendeau, I.; Ferkal, S.; Vidaud, M.; Pinson, S.; et al. NF1 molecular characterization and neurofibromatosis type I genotype-phenotype correlation: The French experience. Hum. Mutat. 2013, 34, 1510–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyman, S.L.; Shores, A.; North, K.N. The nature and frequency of cognitive deficits in children with neurofibromatosis type 1. Neurology 2005, 65, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margaret, B.R.; David, A.S.; David, H.V.; Tinkle, B.T.; Martin, L.J.; Schorry, E.K. Variable expression of neurofibromatosis 1 in monozygotic twins. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2011, 155, 478–485. [Google Scholar]
- Emily, R.S.; Teresa, A.S.; Lisa, J.M.; Viskochil, D.H.; Stevenson, D.A.; Ullrich, N.J.; Messiaen, L.M.; Schorry, E.K. Analysis of copy number variants in 11 pairs of monozygotic twins with neurofibroma-tosis type 1. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 173, 647–653. [Google Scholar]
- Dana, M.B.; Sarah, F.; Stephan, Z. Genetic modifiers and non-Mendelian aspects of CMT. Brain Res. 2020, 1726, 146459. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, W.P.; Adrian, R.K.; Yimin, H.; Snyder, P.C.; Bridgeman, S.J.; Burghes, A.H. A positive modifier of spinal muscular atrophy in the SMN2 gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 408–413. [Google Scholar]
- DePristo, M.A.; Banks, E.; Poplin, R.; Garimella, K.V.; Maguire, J.R.; Hartl, C.; Philippakis, A.A.; Del Angel, G.; Rivas, M.A.; Hanna, M.; et al. A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talevich, E.; Shain, A.H.; Botton, T.; Bastian, B.C. CNVkit: Genome-Wide Copy Number Detection and Visualization from Targeted DNA Sequencing. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Wu, M.C.; Lin, X. Optimal tests for rare variant effects in sequencing association studies. Biostatistics 2012, 13, 762–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, M.A.; Clark, J.; Ireland, A.; Lomax, J.; Ashburner, M.; Foulger, R.; Eilbeck, K.; Lewis, S.; Marshall, B.; Mungall, C. The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 258–261. [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; Viteri, G.; Gong, C.; Lorente, P.; Fabregat, A.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Cook, J.; Gillespie, M.; Haw, R.; et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, sup-porting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monica, C.; Alexandra, P.S.; Jesus, M.; Del Olmo, B.; Puigmulé, M.; Fernandez-Falgueras, A.; Iglesias, A. Incomplete Penetrance and Variable Expressivity: Hallmarks in Channelopathies Associated with Sudden Cardiac Death. Biology 2017, 7, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Annukka, L.; Emma, H.; Dorothy, T.; Huson, S.M. Behaviour in children with neurofibromatosis type 1: Cognition, executive function, attention, emotion, and social competence. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2013, 55, 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Stephanie, M.M.; Maria, T.A.; Shruti, G.; Payne, J.; Plasschaert, E.; Frazier, T.W.; Gutmann, D.H. Disease Burden and Symptom Structure of Autism in Neurofibromatosis Type 1: A Study of the International NF1-ASD Consortium Team (INFACT). AMA Psychiatry 2016, 73, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar]
- Sofia, G.; Reinhard, E.F.; Anna, K.L.; Augustin, M.; Mautner, V.F. Influence of learning disabilities on the tumour predisposition syndrome NF1--survey from adult patients’ perspective. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 3675–3681. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, M.; Kooy, R.F.; Simon, T.J.; Reyniers, E.; Girirajan, S.; Tassone, F. A higher rare CNV burden in the genetic background potentially contributes to intel-lectual disability phenotypes in 22q11.2 deletion syndrome. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2018, 61, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elysa, J.M.; Anne, B.A.; Vishnu, P.N.; da Gente, G.; Gerdes, M.R.; Bologlu, L.; Thomas, S.; Sherr, E.H. Burden of de novo mutations and inherited rare single nucleotide variants in children with sensory processing dysfunction. BMC Med. Genom. 2018, 11, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.J.; Frankland, P.W.; Marowitz, Z.; Friedman, E.; Lazlo, G.; Cioffi, D.; Jacks, T.; Bourtchuladze, R. A mouse model for the learning and memory deficits associated with neurofibromatosis type I. Nat. Genet. 1997, 15, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assunto, A.; Ferrara, U.; De Luca, A.; Pivonello, C.; Lombardo, L.; Piscitelli, A.; Tortora, C.; Pinna, V.; Daniele, P.; Pivonello, R.; et al. Isoform-specific NF1 mRNA levels correlate with disease severity in Neurofibromatosis type 1. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litterman, N.; Ikeuchi, Y.; Gallardo, G.; Connell, B.C.; Sowa, M.E.; Gygi, S.P.; Harper, J.W.; Bonni, A. An OBSL1-Cul7Fbxw8 ubiquitin ligase signaling mechanism regulates Golgi morphology and dendrite patterning. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.H.; Ma, Y.T.; Fang, Y.C.; Huang, J.-J.; Gan, Y.-L.; Chang, P.-T.; Jow, G.-M.; Tang, C.-Y.; Jeng, C.-J. Cullin 7 mediates proteasomal and lysosomal degradations of rat Eag1 potassium channels. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazami, A.M.; Patel, N.; Shamseldin, H.E.; Anazi, S.; Al-Dosari, M.S.; Alzahrani, F.; Hijazi, H.; Alshammari, M.; Aldahmesh, M.A.; Salih, M.; et al. Accelerating novel candidate gene discovery in neurogenetic disorders via whole-exome sequencing of prescreened multiplex consanguineous families. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.S.W.; Luk, H.M.; Lo, I.F.M. An adult Chinese patient with developmental delay with short stature, dysmorphic features, and sparse hair (Loucks-Innes syndrome). Am. J. Med. Genet. 2021, 185, 1925–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.R.; You, L.R.; Yan, Y.T.; Chen, C.M. Role of OVCA1/DPH1 in craniofacial abnormalities of Miller-Dieker syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 5579–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Gong, X.; Rubin, L.P.; Choi, S.W.; Kim, Y. β-Carotene 15,15’-oxygenase inhibits cancer cell stemness and metastasis by regulating differentiation-related miRNAs in human neuroblastoma. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 69, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Song, J.; Tan, M.; Albers, K.M.; Jia, J. Mitochondrial fission proteins in peripheral blood lymphocytes are potential biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2012, 19, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnjec, A.; D’Costa, K.J.; Laws, S.M.; Hedley, R.; Balakrishnan, K.; Taddei, K.; Martins, G.; Paton, A.; Verdile, G.; Gandy, S.E.; et al. Association of alleles carried at TNFA -850 and BAT1 -22 with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Yin, Z.; Liu, A.; Wang, H.; Zeng, S.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, H.; Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, M. Identifying Rare Genetic Variants of Immune Mediators as Risk Factors for Autism Spectrum Disorder. Genes 2022, 13, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vilder, E.Y.G.; Martin, L.; Lefthériotis, G.; Coucke, P.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Vanakker, O.M. Rare Modifier Variants Alter the Severity of Cardiovascular Disease in Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: Identification of Novel Candidate Modifier Genes and Disease Pathways Through Mixture of Effects Analysis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 612581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, C.E.; Rounds, J.C.; Charen, K.; Shubeck, L.; Hipp, H.S.; Spencer, J.B.; Johnston, H.R.; Cutler, D.J.; Zwick, M.E.; Epstein, M.P.; et al. Identifying susceptibility genes for primary ovarian insufficiency on the high-risk genetic background of a fragile X premutation. Fertil. Steril. 2021, 116, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Patient ID | Gender | Age | Age at Diagnosis | NF1 Variants | Inheritance | NF1-Related Neurological Involvement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14646 | Male | 10 y | 8 y 6 m | c.2125T > C p.Cys709Arg | dn | ADHD, sleep disturbance |
| 14811 | Male | 12 y 6 m | 7 y 9 m | c.3739_3742del p.Phe1247IlefsTer18 | dn | Severe learning disabilities, irritability |
| 15098 | Female | 6 y | 4 y 3 m | c.6709C > T p.Arg2237Ter | dn | Autism, severe sleep disturbance |
| 15966 | Male | 8 y | 6 y 9 m | c.5013_5041dup p.Gly1681ValfsTer6 | dn | AHDH, autism, psychological problems |
| 16169 | Male | 14 y | 9 y | c.2971_2972del p.Met991AspfsTer29 | dn | Migraine headaches, sleep disturbance, mild intellectual disability |
| 17296 | Female | 9 y | 7 y | c.2851-6_2851-3het_del | dn | ADHD, learning problem, |
| 19654 | Female | 7 y 7 m | 4 y 6 m | c.3472G > C p.Asp1158His | Paternal | Language developmental delay, learning disabilities, |
| 19917 | Female | 7 y | 4 y | c.2409 + 1G > C | N/A | autism, ADHD |
| 19928 | Male | 5 y 3 m | 3 y 6 m | c.2180C > A p.Ser727Ter | dn | Epilepsy, language-development delay |
| 20586 | Female | 4 y 6 m | 3 y | c.499_502het_del p.Cys167GlnfsTer10 | Maternal | Autism, language-development delay |
| 21178 | Male | 9 m | 6 m | c.1019_1020del p.Ser340CysfsTer12 | dn | Epilepsy, cerebral hypoplasia, gross developmental delay |
| 21265 | Male | 8 y | 4 y | c.1019_1020del p.Ser340CysfsTer12 | dn | Abnormal brain MRI, intellectual disability |
| 21432 | Female | 15 m | 6 m | c.6974_6977del p.Asp2325ValfsTer49 | dn | Epilepsy, gross developmental delay |
| Symbol | Name | Associated Monogenic Phenotype (#OMIM) | Expression in Normal Human Nervous Tissue | Association with Neurological System | Pubmed ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CUL7 | Cullin 7 | 3-M syndrome 1 | Y | Core component of a Cul7-RING ubiquitin–protein ligase, which mediates ubiquitination and consequent degradation of important proteins of nervous system | 21572988 |
| DUSP26 | Dual specificity phosphatase 26 | None | Y | A member of the tyrosine phosphatase family of proteins, which regulates neuronal proliferation | 28701747 |
| OR1L8 | Olfactory receptor family 1 subfamily L member 8 | None | Y | Olfactory receptors interact with odorant molecules in the nose, to initiate a neuronal response that triggers the perception of a smell | 14983052 |
| HIGD1C | HIG1 hypoxia-inducible domain family member 1C | None | Y | None | |
| SLC19A1 | Solute carrier family 19 member 1 | ?Megaloblastic anemia, folate-responsive | Y | A transporter of folate, which may play a role in the pathogenesis of pediatric brain tumors | 18406541 |
| DPH1 | Diphthamide biosynthesis 1 | Developmental delay with short stature, dysmorphic facial features, and sparse hair | Y | An enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of diphthamide, which is involved in intellectual development | 25558065, 26220823 |
| BCO1 | β-carotene oxygenase 1 | ?Hypercarotenemia and vitamin A deficiency, autosomal dominant | Y | Plays a role in regulating miRNAs associated with neuronal differentiation, cell–cell adhesion, and the Wnt signaling pathway | 31048207 |
| ZMIZ2 | Zinc finger MIZ-type containing 2 | None | Y | None | |
| GSTM3 | Glutathione S-transferase Mu 3 | None | Y | Gene variations in GSTM3 are a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease | 18423940, 17904251 |
| PRND | Prion-like protein doppel | None | Y | Polymorphisms within the PRND are associated with the Alzheimer’s disease and Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease | 11702213, 14745079, 19422537 |
| TWF2 | Twinfilin actin-binding protein 2 | None | Y | None | |
| RASSF1 | Ras association domain family member 1 | None | Y | The inactivation of RASSF1A may be an important step in the tumorigenesis of the central nervous system | 14586413, 19165202, 17899687 |
| ASCC1 | Activating signal cointegrator 1 complex subunit 1 | Barrett esophagus/esophageal adenocarcinoma Spinal muscular atrophy with congenital bone fractures 2 | Y | May play a role in the development of neuromuscular junction | 28218388, 34204919 |
| NFE2L2 | NFE2-like BZIP transcription factor 2 | Immunodeficiency, developmental delay, and hypohomocysteinemia | Y | NFE2L2 promotes neuronal cell differentiation and controls neuroinflammation. NFE2L2 deregulation has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases | 19573594, 32545924, 29969760, 26541884 |
| PARP6 | Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 6 | None | Y | A regulator of dendrite morphogenesis in hippocampal neurons | 34067418, 26725726 |
| LIPH | Lipase H | Hypotrichosis 7 Woolly hair, autosomal recessive 2 with or without hypotrichosis | Y | None | |
| SF3A2 | Splicing factor 3a subunit 2 | None | Y | None | |
| KIAA1522 | KIAA1522 | None | Y | None | |
| LAMB1 | Laminin subunit β 1 | Lissencephaly 5 | Y | Involved in the organization of the laminar architecture of cerebral cortex | 23472759, 21370991 |
| DYNC1LI1 | Dynein cytoplasmic 1 light intermediate chain 1 | None | Y | DYNC1I1 deficiency causes neuronal atrophy in primary hippocampal neurons | 27510948 |
| MYOC | Myocilin | Glaucoma 1A, primary open angle | Y | Mediates myelination in the peripheral nervous system and plays a role in neurite outgrowth | 23897819, 12799138 |
| U2SURP | U2 SnRNP-associated SURP domain-containing | None | Y | None | |
| DDX39B | DExD-box helicase 39B | None | Y | Association of DDX39B polymorphisms with Alzheimer’s disease | 18715507 |
| ZMAT2 | Zinc finger matrin-type 2 | None | Y | None | |
| GFI1 | Growth factor independent 1 transcriptional repressor | None | Y | Important for neuroendocrine differentiation and regulation of neurite outgrowth | 15466176, 19026687 |
| SNAPC5 | Small nuclear RNA-activating complex polypeptide 5 | None | Y | None | |
| RBPMS | RNA-binding protein, MRNA-processing factor | None | Y | A selective marker of ganglion cells in the mammalian retina | 24318667 |
| DBF4 | DBF4 zinc finger | None | Y | None | |
| DMAC2L | Distal membrane arm assembly component 2 like | None | Y | None | |
| HIST1H3E | H3 clustered histone 6 | None | Y | None | |
| FIS1 | Fission, mitochondrial 1 | None | Y | Potential biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease | 22340708 |
| RIT1 | Ras-like without CAAX 1 | Noonan syndrome 8 | Y | RIT1 cooperates with nerve growth factor to promote neuronal development and regeneration | 15632082 12668729 |
| TRAPPC5 | Trafficking protein particle complex subunit 5 | None | Y | None | |
| CELF3 | CUGBP Elav-like family member 3 | None | Y | None | |
| LRRC3C | Leucine-rich repeat-containing 3C | None | Y | None | |
| GCLM | Glutamate–cysteine ligase-modifier subunit | (Myocardial infarction, susceptibility to) | Y | None |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Li, N.; Li, G.; Wang, J.; Yu, T.; Yao, R. Assessment of Rare Genetic Variants to Identify Candidate Modifier Genes Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Neurofibromatosis 1 Patients. Genes 2022, 13, 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122218
Tang J, Li N, Li G, Wang J, Yu T, Yao R. Assessment of Rare Genetic Variants to Identify Candidate Modifier Genes Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Neurofibromatosis 1 Patients. Genes. 2022; 13(12):2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122218
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Jie, Niu Li, Guoqiang Li, Jian Wang, Tingting Yu, and Ruen Yao. 2022. "Assessment of Rare Genetic Variants to Identify Candidate Modifier Genes Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Neurofibromatosis 1 Patients" Genes 13, no. 12: 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122218
APA StyleTang, J., Li, N., Li, G., Wang, J., Yu, T., & Yao, R. (2022). Assessment of Rare Genetic Variants to Identify Candidate Modifier Genes Underlying Neurological Manifestations in Neurofibromatosis 1 Patients. Genes, 13(12), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122218






