Identification of the Genes Encoding B3 Domain-Containing Proteins Related to Vernalization of Beta vulgaris
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Library Construction and Sequencing
2.3. Transcripts Assembly and LncRNA Identification
2.4. LncRNA Identification
2.5. Different Expression Analysis of mRNAs and lncRNAs
2.6. Target Gene Prediction and Functional Analysis of lncRNAs
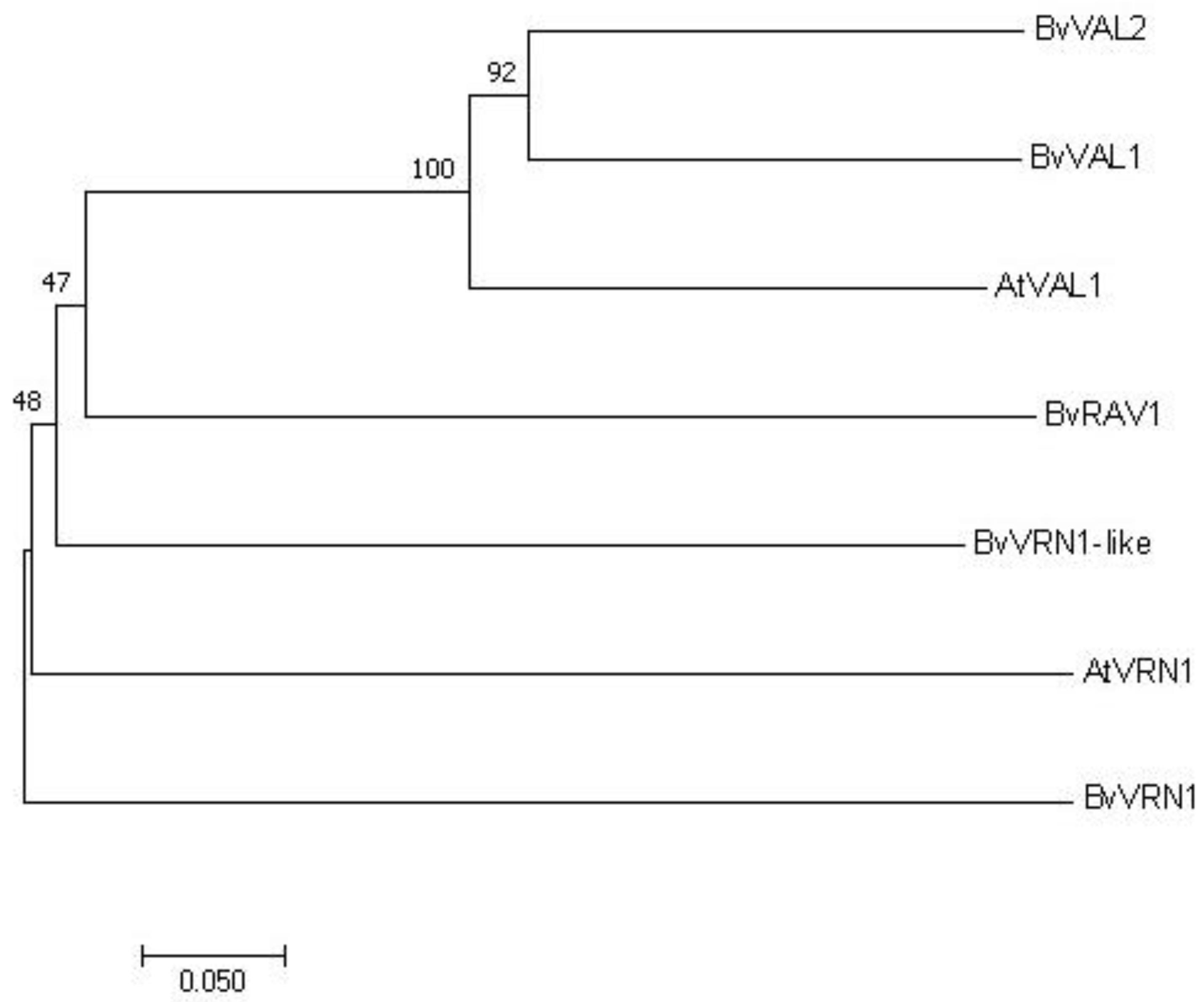
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis of Target Genes in B. vulgaris
2.8. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and qRT-PCR
3. Results
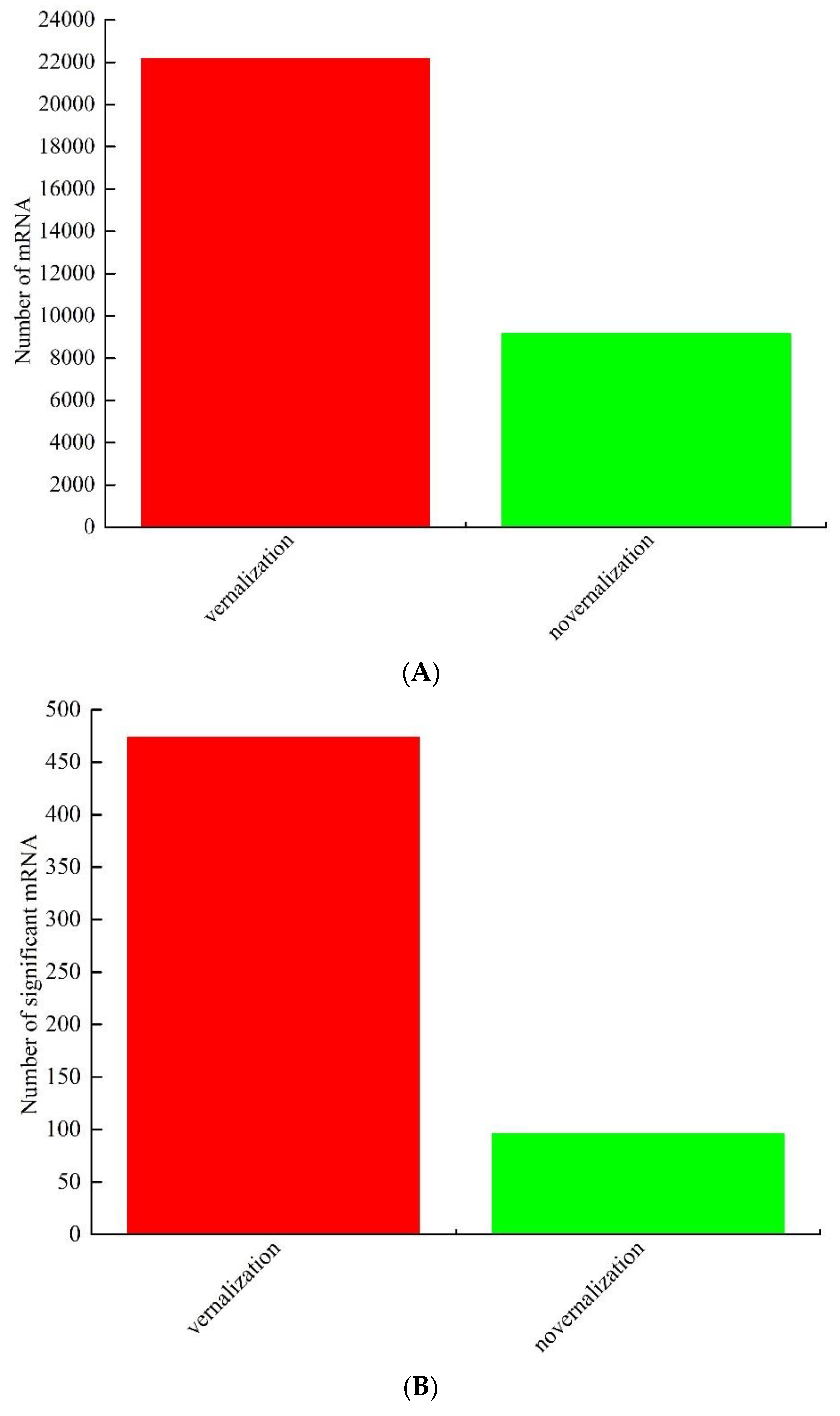
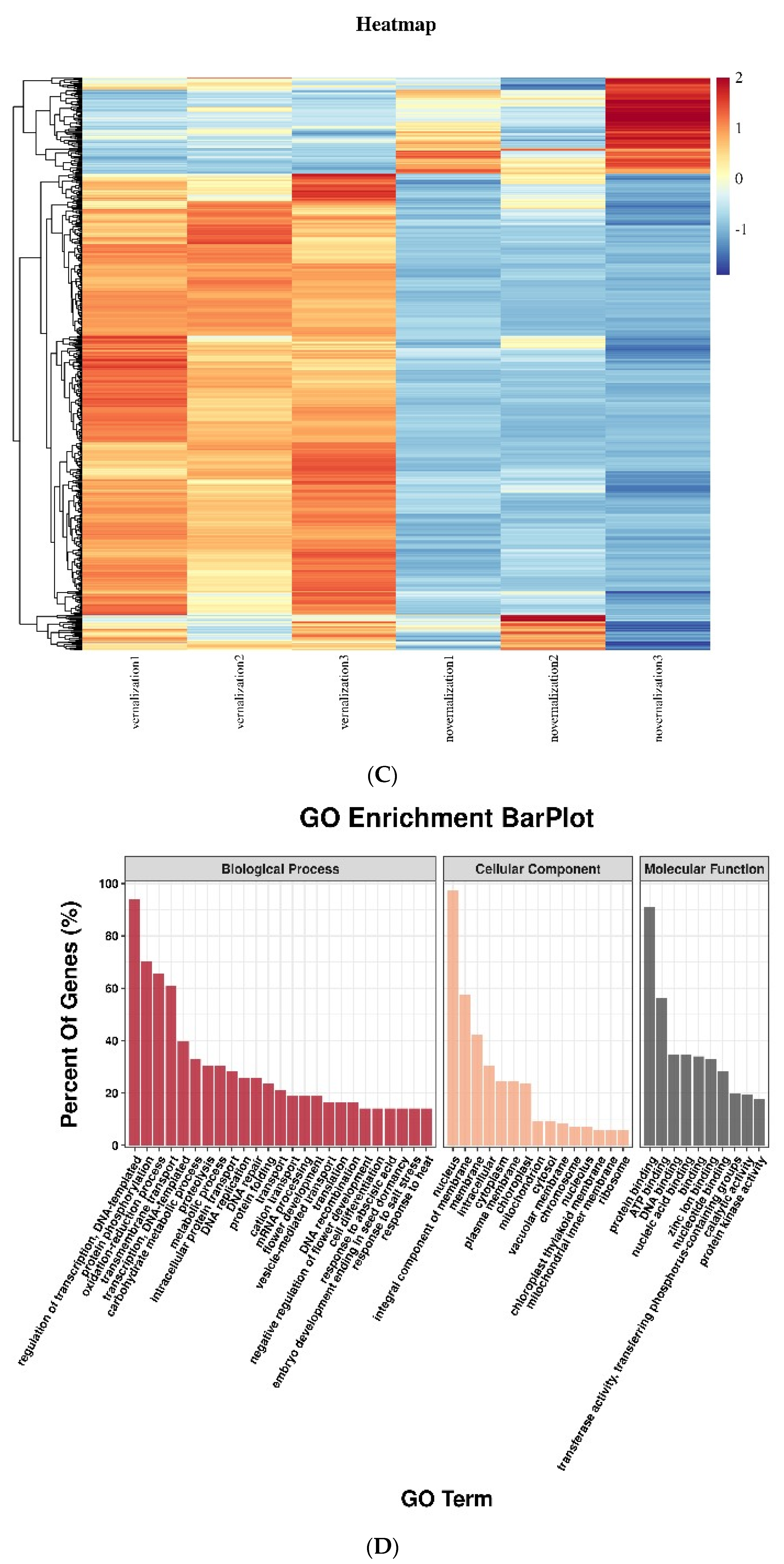
3.1. Identification and Analysis of Differentially Expressed mRNAs between Vernalized and Nonvernalized Samples
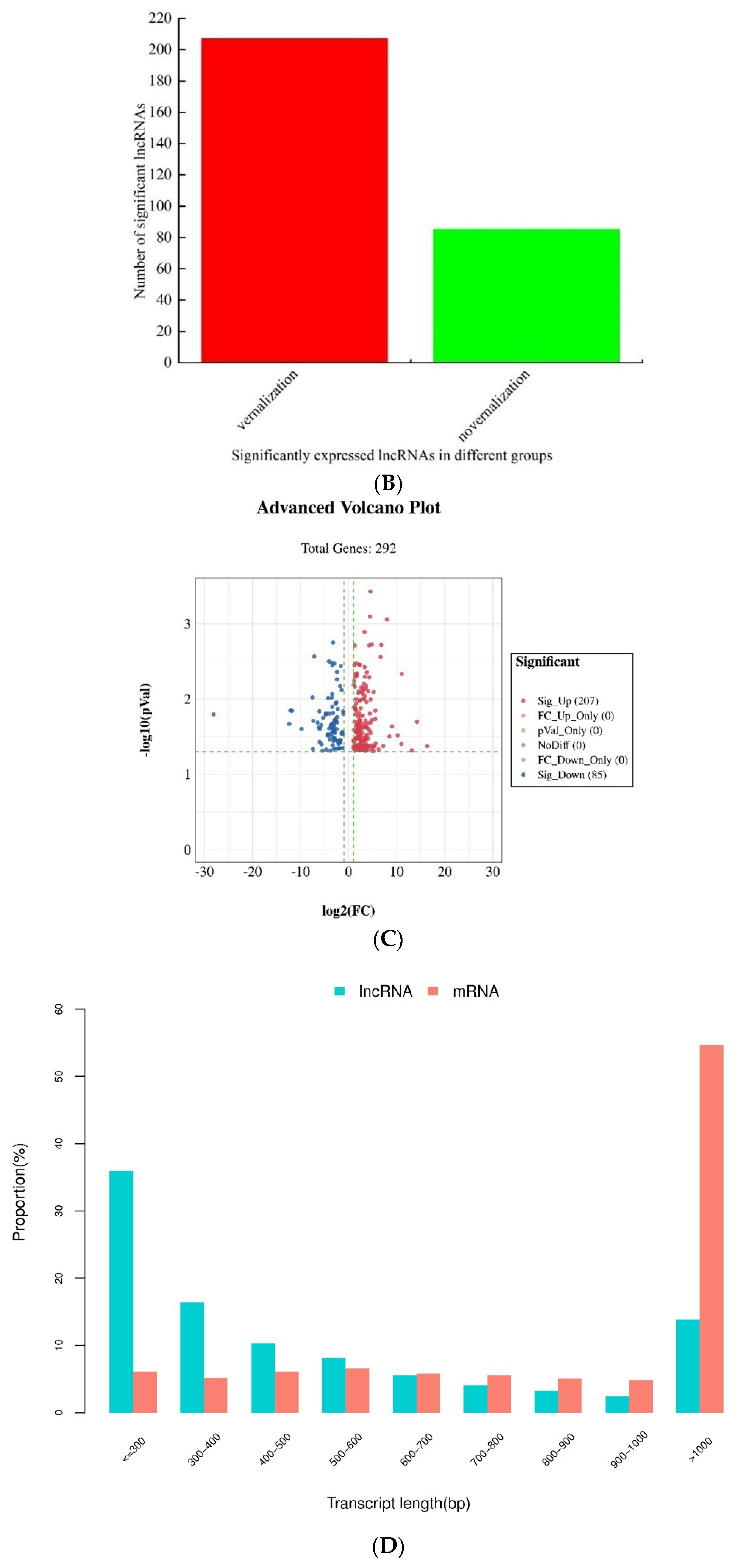
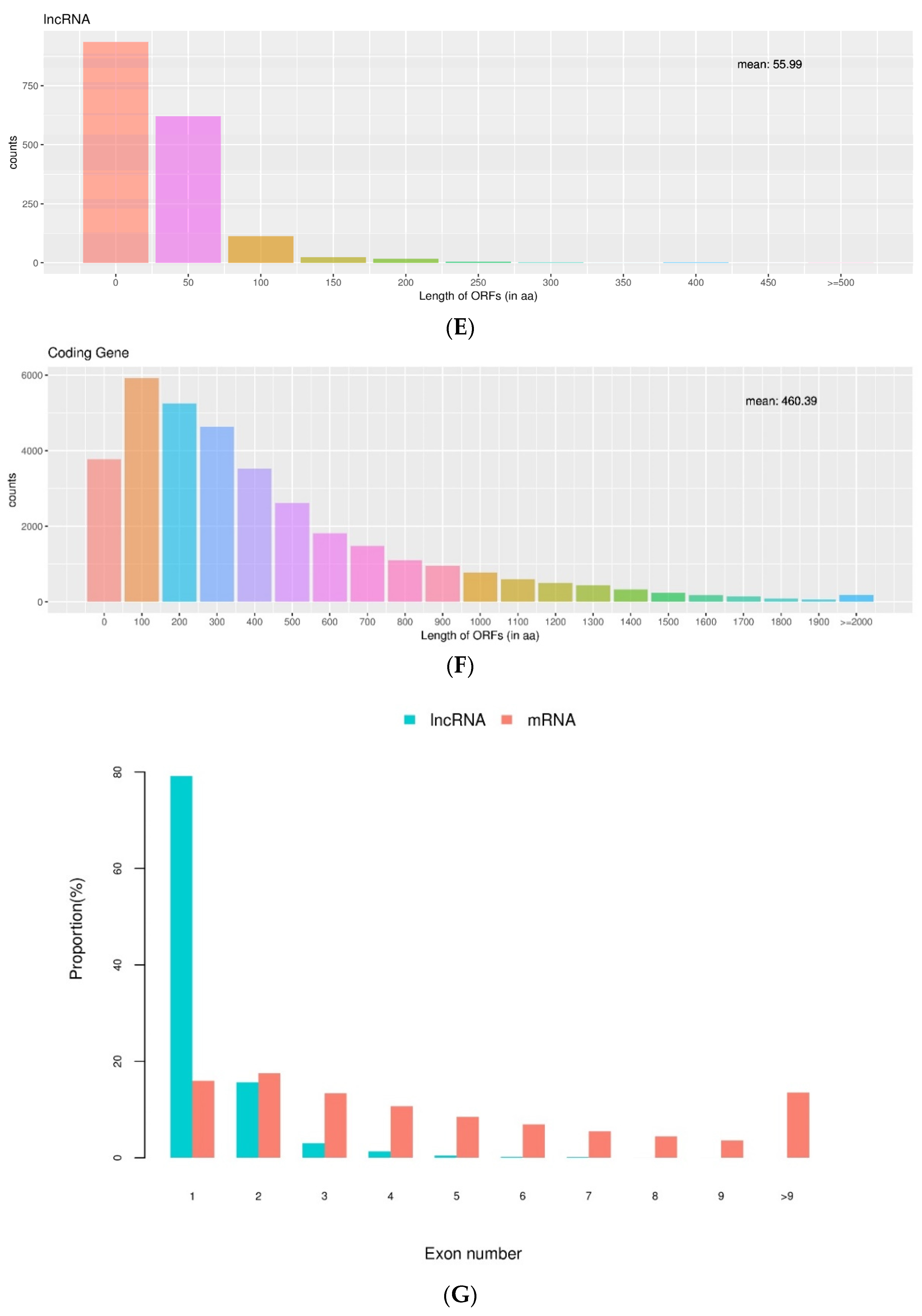
3.2. Identification and Analysis of Differentially Expressed lncRNAs between the Vernalized and Nonvernalized Samples
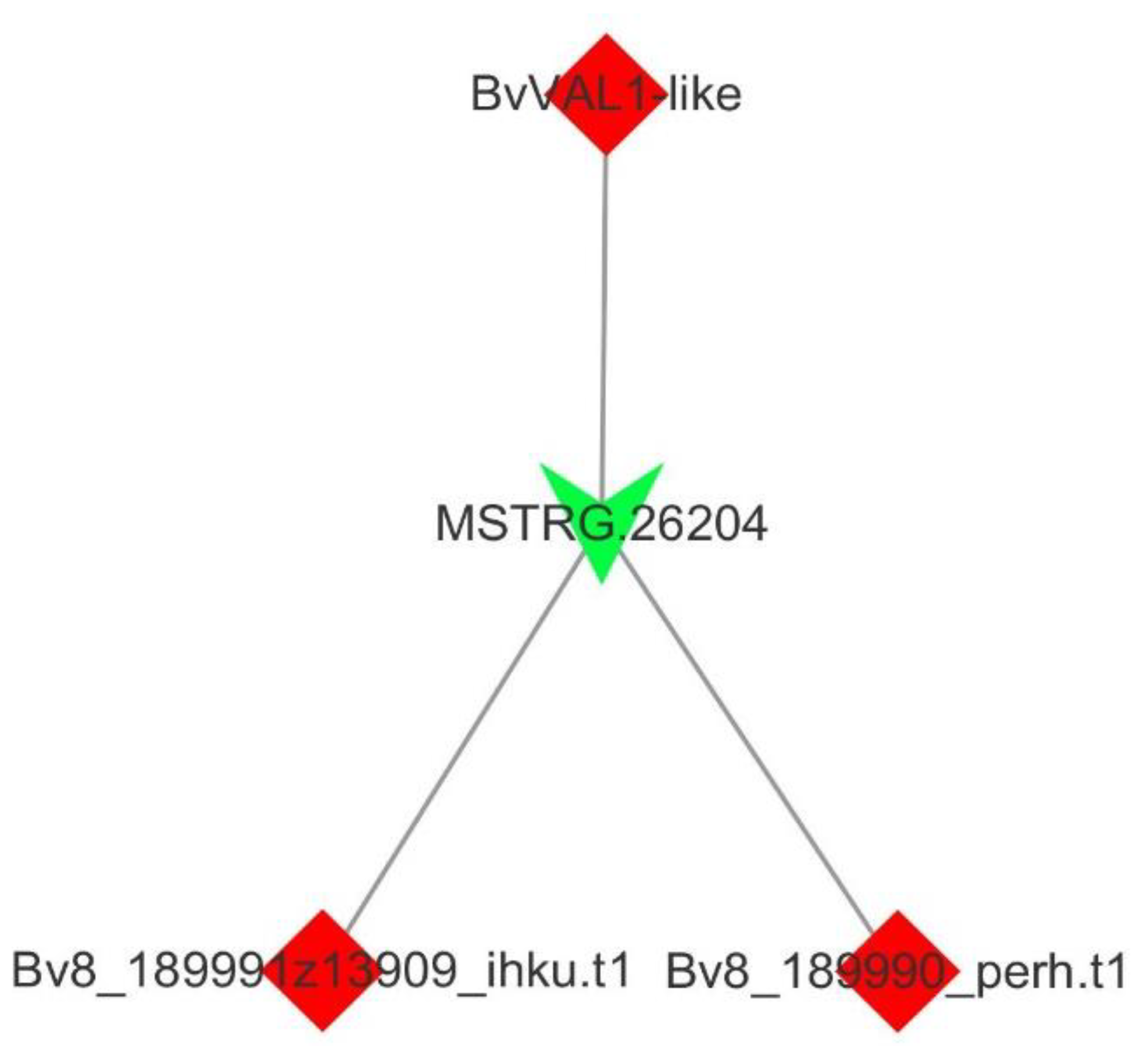
3.3. Target Gene Prediction of lncRNAs
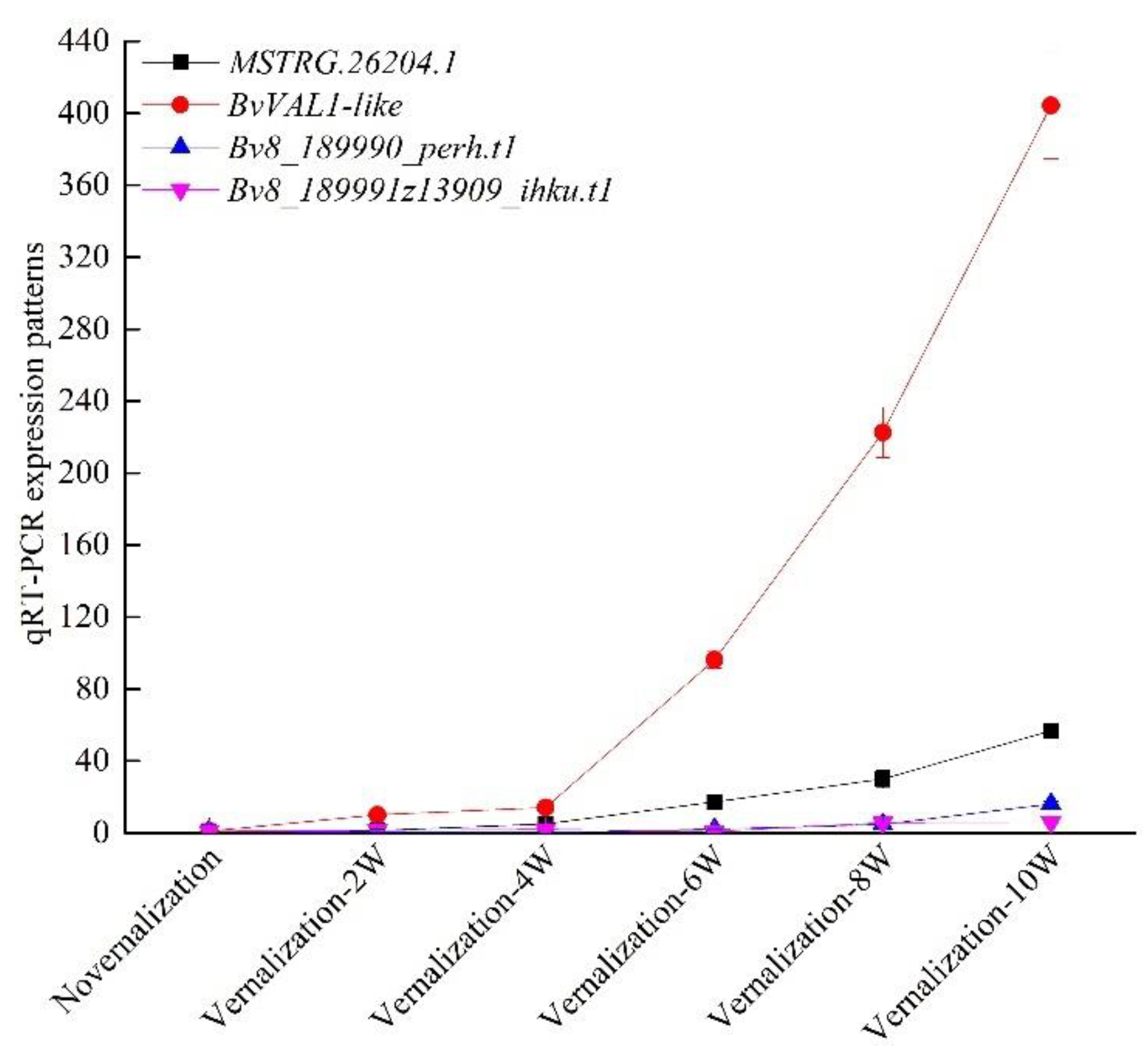
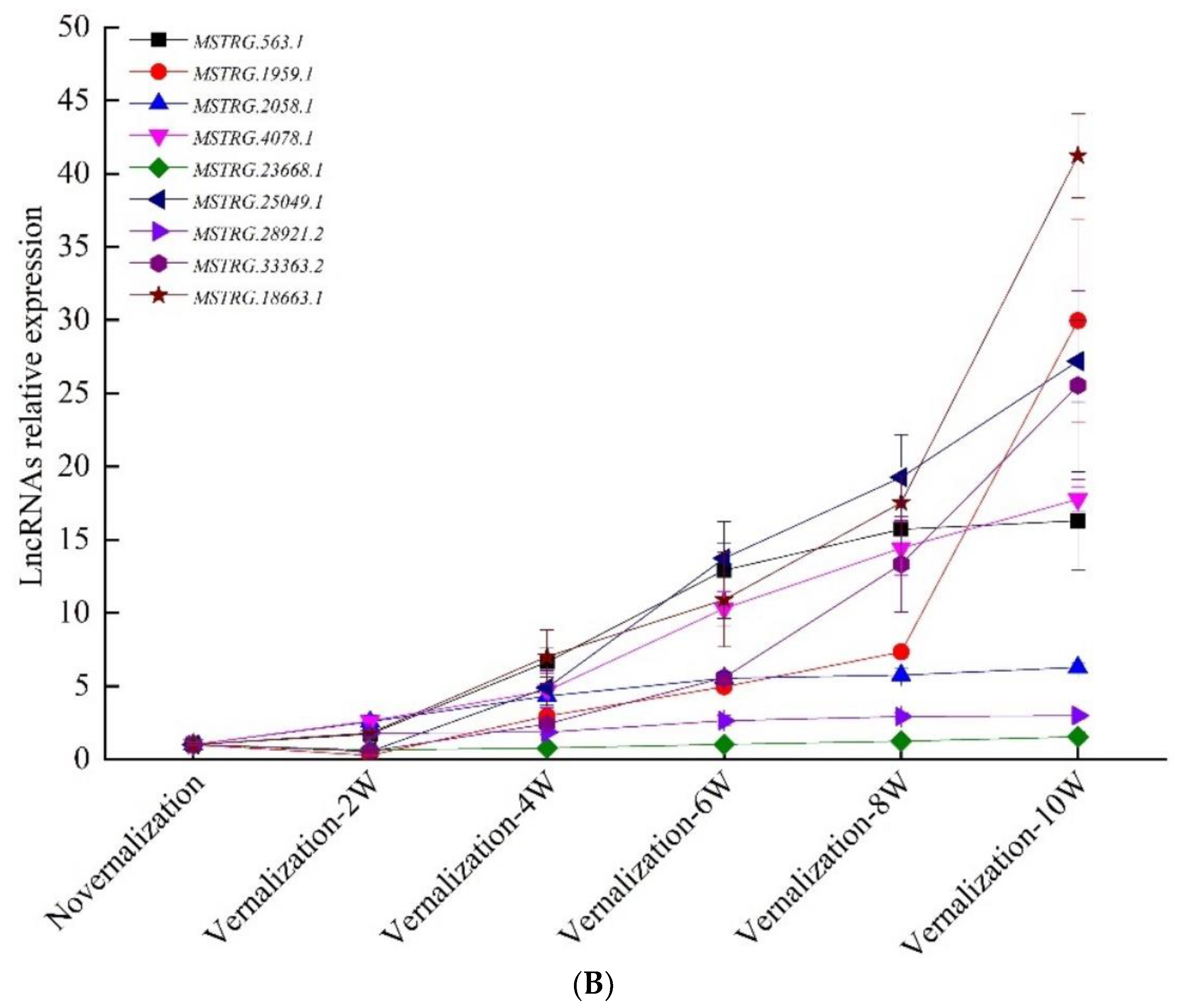
3.4. Verification of Vernalization-Related mRNAs and lncRNAs by qRT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helliwell, C.A.; Anderssen, R.S.; Robertson, M.; Finnegan, E.J. How is FLC repression initiated by cold? Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y. Transcriptome comparison reveals key candidate genes in response to vernalization of Oriental lily. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Pan, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, T.; Zhang, X. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis reveals distinct regulatory programs during vernalization and floral bud development of orchardgrass (Dactylis glomerata L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Bian, X.C.; Yang, F.; Chen, M.X.; Das, D.; Zhu, X.R.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cao, Y.Y.; Wu, C.F. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of faba bean in response to vernalization. Planta 2019, 251, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Li, G.; Yuan, L.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; Wang, C.; et al. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Gene Expression and Regulatory Characteristics Associated with Different Vernalization Periods in Brassica rapa. Genes 2020, 11, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendall, A.R.; Levy, Y.Y.; Wilson, A.; Dean, C. The VERNALIZATION 2 gene mediates the epigenetic regulation of vernalization in Arabidopsis. Cell 2001, 107, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhang, Y. The functions of E(Z)/EZH2-mediated methylation of lysine 27 in histone H3. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, D.; Primavesi, L.; Bishopp, A.; Roberts, G.; Doonan, J.; Jenuwein, T.; Goodrich, J. Silencing by plant Polycomb-group genes requires dispersed trimethylation of histone H3 at lysine 27. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4638–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, C.C.; Robertson, M.; Tanner, G.; Peacock, W.J.; Dennis, E.S.; Helliwell, C.A. The Arabidopsis thaliana vernalization response requires a polycomb-like protein complex that also includes VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 14631–14636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.M.; Dennis, E.S.; Pogson, B.J.; Finnegan, E.J. Histone acetylation, VERNALIZATION INSENSITIVE 3, FLOWERING LOCUS C, and the vernalization response. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finnegan, E.J.; Dennis, E.S. Vernalization-induced trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27 at FLC is not maintained in mitotically quiescent cells. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1978–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swiezewski, S.; Liu, F.; Magusin, A.; Dean, C. Cold-induced silencing by long antisense transcripts of an Arabidopsis Polycomb target. Nature 2009, 462, 799–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.B.; Sung, S. Vernalization-mediated epigenetic silencing by a long intronic noncoding RNA. Science 2011, 331, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Sung, S. Environmentally coordinated epigenetic silencing of FLC by protein and long noncoding RNA components. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2012, 15, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Tao, Z.; Dean, C. Phenotypic evolution through variation in splicing of the noncoding RNA COOLAIR. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Sung, S. Vernalization-Triggered Intragenic Chromatin Loop Formation by Long Noncoding RNAs. Dev. Cell 2017, 40, 302–312.e304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, F.; Wang, S.; Ji, X.; Xu, C.; He, Y.E.; Ding, Y. PRC2 recruitment and H3K27me3 deposition at FLC require FCA binding of COOLAIR. Science 2019, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, P.A.; He, Y.; Schmitz, R.J.; Amasino, R.M.; Panella, L.W.; Richards, C.M. Evolutionary Conservation of the FLOWERING LOCUS C-Mediated Vernalization Response: Evidence From the Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris). Genetics 2007, 176, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frerichmann, S.L.M.; Kirchhoff, M.; Müller, A.E.; Scheidig, A.J.; Jung, C.; Kopisch-Obuch, F.J. EcoTILLING in Beta vulgaris reveals polymorphisms in the FLC-like gene BvFL1 that are associated with annuality and winter hardiness. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutasa-Göttgens, E.S.; Joshi, A.; Holmes, H.F.; Hedden, P.; Göttgens, B. A new RNASeq-based reference transcriptome for sugar beet and its application in transcriptomescale analysis of vernalization and gibberellin responses. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcel, R.; Bustamante, A.; Ros, R.; Serrano, R.; Mulet Salort, J.M. BvCOLD1: A novel aquaporin from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) involved in boron homeostasis and abiotic stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 2844–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, N.G.; Cheng, D.Y.; Liu, Q.H.; Cui, J.; Luo, C.F. Difference of proteomics vernalization-induced in bolting and flowering transitions of Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.L.; Cui, J.; Dai, C.H.; Liu, T.J.; Cheng, D.Y.; Luo, C.F. Whole-Transcriptome RNA Sequencing Reveals the Global Molecular Responses and CeRNA Regulatory Network of mRNAs, lncRNAs, miRNAs and circRNAs in Response to Salt Stress in Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods. 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Sung, S. Coordination of the vernalization response through a VIN3 and FLC gene family regulatory network in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 454–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazee, A.C.; Pertea, G.; Jaffe, A.E.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L.; Leek, J.T. Ballgown bridges the gap between transcriptome assembly and expression analysis. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, H.; Bu, D.; Zhao, G.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conesa, A.; Gotz, S.; Garcia-Gomez, J.M.; Terol, J.; Talon, M.; Robles, M. Blast2GO: A universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 3674–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, R.; Paul, S. Long non-coding RNAs: Fine-tuning the developmental responses in plants. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yu, Y.; Meyer, D.; Wu, C.; Shen, W.H. Prevention of early flowering by expression of FLOWERING LOCUS C requires methylation of histone H3 K36. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, A.; Soubigou-Taconnat, L.; Renou, J.P.; Steinmetz, A.; Shen, W.H. Di- and tri- but not monomethylation on histone H3 lysine 36 marks active transcription of genes involved in flowering time regulation and other processes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, P.; Shi, J.; Gao, X.; Shen, W.H.; Dong, A. H3K36 methylation is involved in promoting rice flowering. Mol. Plant. 2013, 6, 975–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Bernatavichute, Y.V.; Cokus, S.; Pellegrini, M.; Jacobsen, S.E. Genome-wide analysis of mono-, di- and trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 4 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome. Biol. 2009, 10, R62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiva-Eriksson, N.; Pin, P.A.; Kraft, T.; Dohm, J.C.; Minoche, A.E.; Himmelbauer, H.; Bulow, L. Differential expression patterns of non-symbiotic hemoglobins in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris ssp. vulgaris). Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Jia, J.; Yan, X.; Shi, H.; Han, Y. Arabidopsis KHZ1 and KHZ2, two novel non-tandem CCCH zinc-finger and K-homolog domain proteins, have redundant roles in the regulation of flowering and senescence. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 95, 549–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Kim, H.C.; Shin, S.; Kim, K.H.; Moon, J.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, B.M. Transcriptome Analysis of Flowering Time Genes under Drought Stress in Maize Leaves. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, B.; He, X.; Ruan, Y.; Jang, J.C.; Huang, Y. Genome-wide analysis and stress-responsive expression of CCCH zinc finger family genes in Brassica rapa. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Lin, W.; Yu, G.; Cheng, Q.; Xu, B.; Huang, B. Improved cold tolerance in switchgrass by a novel CCCH-type zinc finger transcription factor gene, PvC3H72, associated with ICE1-CBF-COR regulon and ABA-responsive genes. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2019, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, T.; Schultz, T.F.; Harmon, F.G.; Ho, L.A.; Kay, S.A. FKF1 F-Box Protein Mediates Cyclic Degradation of a Repressor of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Science 2005, 309, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, E.; Tan, Q.K.; Hill, T.A.; Irish, V.F. An Arabidopsis F-box protein acts as a transcriptional co-factor to regulate floral development. Development 2008, 135, 1235–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-Hamid, N.A.; Ahmad-Fauzi, M.I.; Zainal, Z.; Ismail, I. Diverse and dynamic roles of F-box proteins in plant biology. Planta 2020, 251, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Guo, J.; Zhou, F.; Singh, S.; Xu, X.; Xie, Q.; Yang, Z.; Huang, C.F. F-box protein RAE1 regulates the stability of the aluminum-resistance transcription factor STOP1 in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, V.; Virupapuram, V. Arabidopsis F-box protein At1g08710 interacts with transcriptional protein ADA2b and imparts drought stress tolerance by negatively regulating seedling growth. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 536, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, G.G. The autonomous pathway: Epigenetic and post-transcriptional gene regulation in the control of Arabidopsis flowering time. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2004, 7, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornyik, C.; Terzi, L.C.; Simpson, G.G. The spen family protein FPA controls alternative cleavage and polyadenylation of RNA. Dev. Cell. 2010, 18, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarillo, J.A.; Pineiro, M. Timing is everything in plant development. The central role of floral repressors. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, I.; Liu, C.C.; Ge, H.L.; Batool, K.; Yang, Y.Q.; Lu, Y.H. Genome wide survey, evolution and expression analysis of PHD finger genes reveal their diverse roles during the development and abiotic stress responses in Brassica rapa L. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponjavic, J.; Oliver, P.L.; Lunter, G.; Ponting, C.P. Genomic and transcriptional co-localization of protein-coding and long non-coding RNA pairs in the developing brain. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ohsumi, T.K.; Kung, J.T.; Ogawa, Y.; Grau, D.J.; Sarma, K.; Song, J.J.; Kingston, R.E.; Borowsky, M.; Lee, J.T. Genome-wide identification of polycomb-associated RNAs by RIP-seq. Mol. Cell. 2010, 40, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csorba, T.; Questa, J.I.; Sun, Q.; Dean, C. Antisense COOLAIR mediates the coordinated switching of chromatin states at FLC during vernalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16160–16165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qüesta, J.I.; Song, J.; Geraldo, N.; An, H.L.; Dean, C. Arabidopsis transcriptional repressor VAL1 triggers Polycomb silencing at FLC during vernalization. Science 2016, 353, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasnauskas, G.; Kauneckaite, K.; Siksnys, V. Structural basis of DNA target recognition by the B3 domain of Arabidopsis epigenome reader VAL1. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2018, 46, 4316–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Song, X.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Lei, Y.; Ruan, J.; Tan, B.; Liu, J.; Li, C. The transcriptional repressors VAL1 and VAL2 recruit PRC2 for genome-wide Polycomb silencing in Arabidopsis. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2021, 49, 98–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Guo, Q.; Lin, R. The B3-Domain Transcription Factor VAL1 Regulates the Floral Transition by Repressing FLOWERING LOCUS T. Plant Physiol. 2019, 181, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, Y.Y.; Mesnage, S.; Mylne, J.S.; Gendall, A.R.; Dean, C. Multiple roles of Arabidopsis VRN1 in vernalization and flowering time control. Science 2002, 297, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevaskis, B.; Bagnall, D.J.; Ellis, M.H.; Peacock, W.J.; Dennis, E.S. MADS box genes control vernalization-induced flowering in cereals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13099–13104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.J.; Chanson, A.H.; McCallum, E.J.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Byriel, K.; Hill, J.M.; Martin, J.L.; Mylne, J.S. The Arabidopsis B3 domain protein VERNALIZATION1 (VRN1) is involved in processes essential for development, with structural and mutational studies revealing its DNA-binding surface. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3198–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukoianov, A.; Yan, L.; Blechl, A.; Sanchez, A.; Dubcovsky, J. Regulation of VRN-1 vernalization genes in normal and transgenic polyploid wheat. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 2364–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, S.; Ogawa, T.; Kitagawa, S.; Suzuki, T.; Ikari, C.; Shitsukawa, N.; Abe, T.; Kawahigashi, H.; Kikuchi, R.; Handa, H.; et al. A genetic network of flowering-time genes in wheat leaves, in which an APETALA1/FRUITFULL-like gene, VRN1, is upstream of FLOWERING LOCUS T. Plant J. 2009, 58, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, M.; Su, S.; Liu, H.; Gan, J.; Ma, J. Structural insight into the role of VAL1 B3 domain for targeting to FLC locus in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 501, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Gong, X.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Liang, D.; Yuan, W. Interaction Analysis between the Arabidopsis Transcription Repressor VAL1 and Transcription Coregulators SIN3-LIKEs (SNLs). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Lecourieux, F.; Kuang, Y.; Xin, H.; Li, S.; Liang, Z. Characterization of Chromatin Accessibility and Gene Expression upon Cold Stress Reveals that the RAV1 Transcription Factor Functions in Cold Response in Vitis Amurensis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2021, 62, 1615–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, N.; Cheng, D.; Zhao, L.; Lu, H.; Xu, L.; Bi, Y. Identification of the Genes Encoding B3 Domain-Containing Proteins Related to Vernalization of Beta vulgaris. Genes 2022, 13, 2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122217
Liang N, Cheng D, Zhao L, Lu H, Xu L, Bi Y. Identification of the Genes Encoding B3 Domain-Containing Proteins Related to Vernalization of Beta vulgaris. Genes. 2022; 13(12):2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122217
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Naiguo, Dayou Cheng, Li Zhao, Hedong Lu, Lei Xu, and Yanhong Bi. 2022. "Identification of the Genes Encoding B3 Domain-Containing Proteins Related to Vernalization of Beta vulgaris" Genes 13, no. 12: 2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122217
APA StyleLiang, N., Cheng, D., Zhao, L., Lu, H., Xu, L., & Bi, Y. (2022). Identification of the Genes Encoding B3 Domain-Containing Proteins Related to Vernalization of Beta vulgaris. Genes, 13(12), 2217. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13122217




