Genomic Analysis to Elucidate the Lignocellulose Degrading Capability of a New Halophile Robertkochia solimangrovi
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Whole Genome Sequencing, Assembly, and Annotation
2.2. Comparative Genomic Analysis
2.3. CAZyme Screening and Analysis of Lignocellulolytic Genes
2.4. Inoculum Preparation and Lignocellulolytic Enzyme Production
2.5. EFB Weight Loss Assessment and Lignocellulolytic Enzyme Activity Assays
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Genome Features of R. solimangrovi
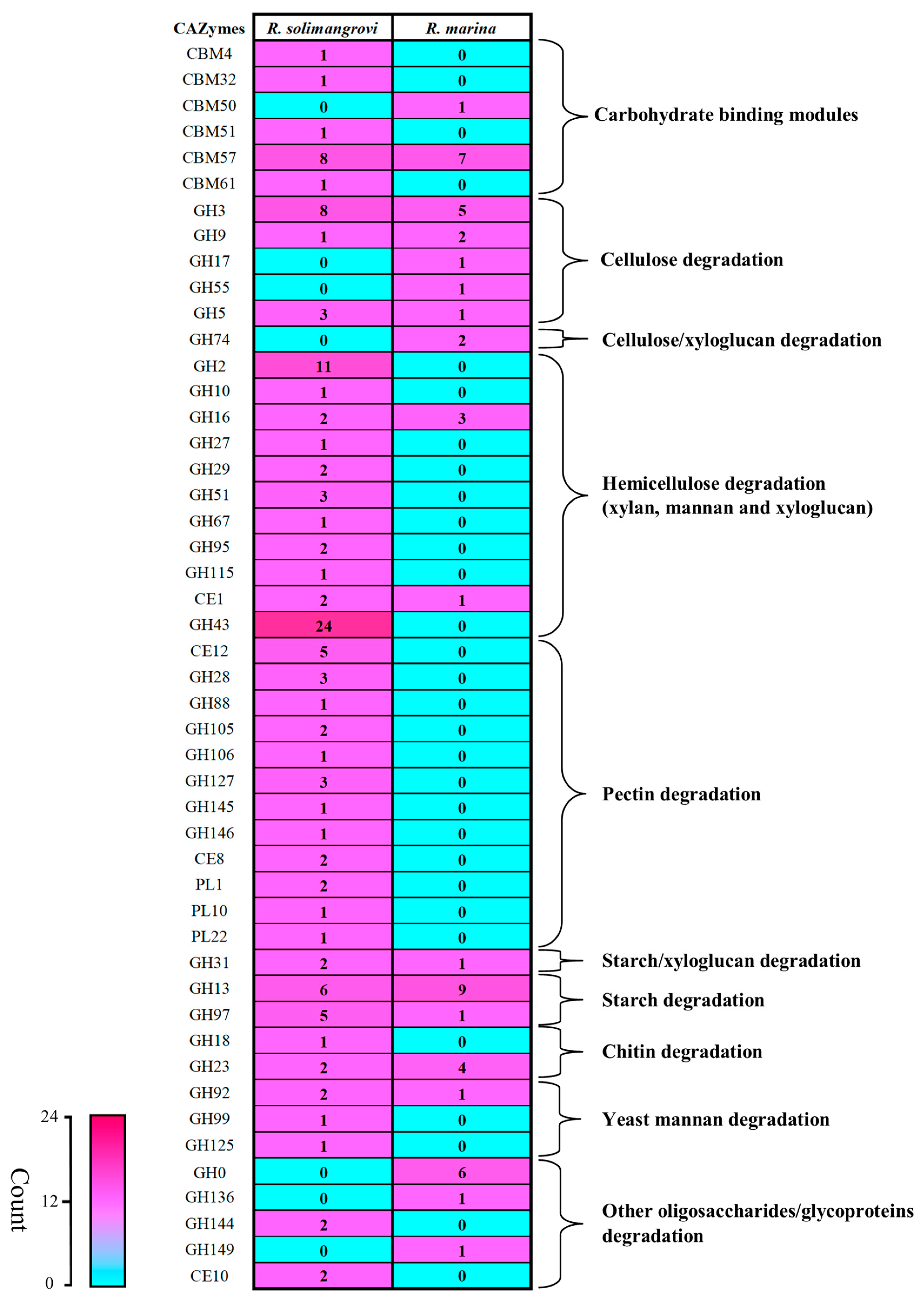
3.2. Genome Comparison: R. solimangrovi vs. R. marina
3.3. Mining and Analysis of Lignocellulolytic Enzymes of R. solimangrovi
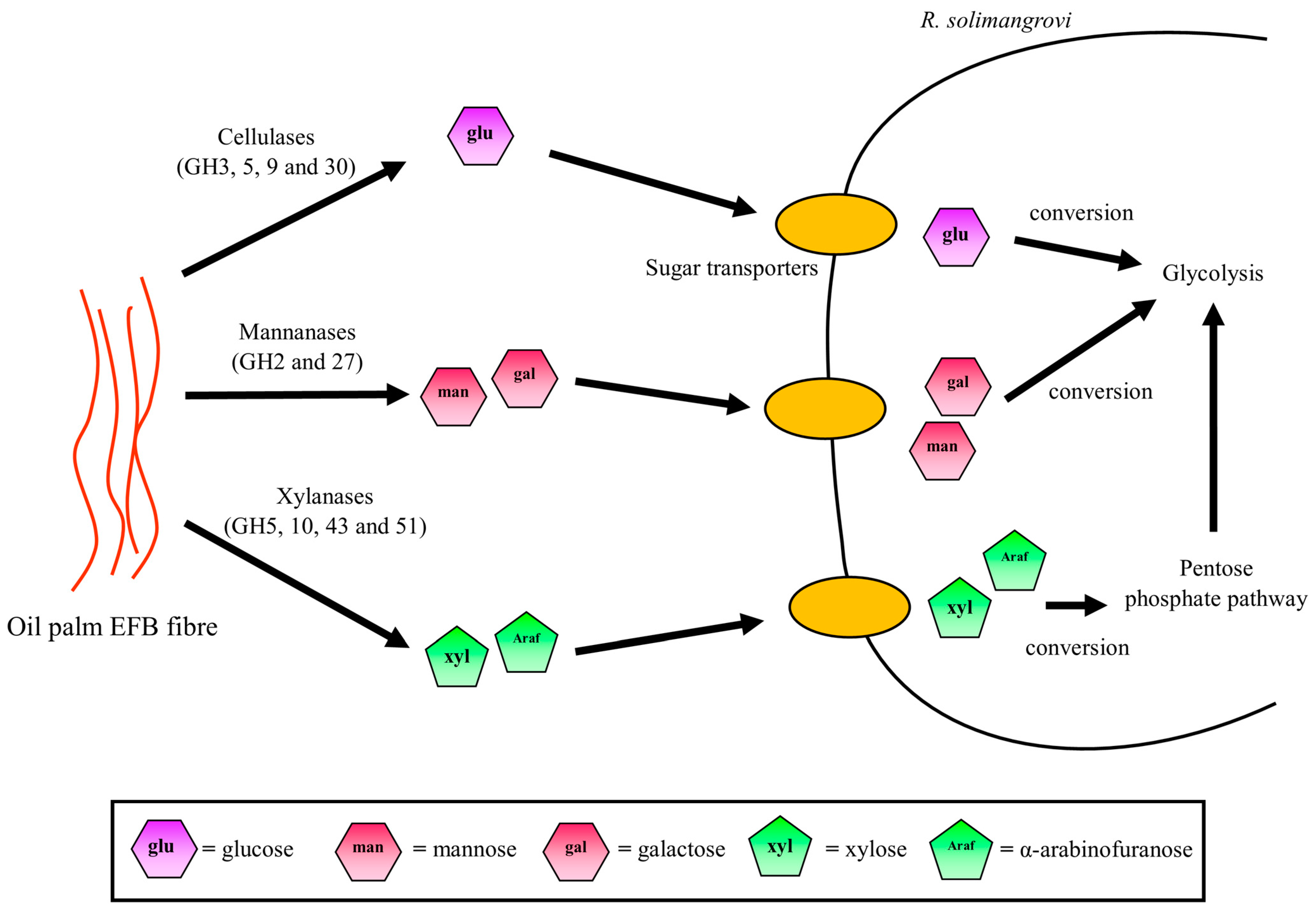
3.4. Capability of R. solimangrovi to Deconstruct Oil Palm Empty Fruit Bunch
3.5. Potential Sugar Uptake and Metabolic Pathway Taken by R. solimangrovi
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.; Baffoe, D.K.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G. Halophile, an essential platform for bioproduction. J. Microbiol. Methods 2019, 166, 105704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.H. Malignant hyperthermia: A runaway thermogenic futile cycle at the sodium channel level. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2014, 5, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokashe, N.; Chaudhari, B.; Patil, U. Operative utility of salt-stable proteases of halophilic and halotolerant bacteria in the biotechnology sector. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 493–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.Q.; Mut, N.N.N.; Thevarajoo, S.; Chen, S.J.; Selvaratnam, C.; Hussin, H.; Jamaluddin, H.; Chong, C.S. Characterization of detergent compatible protease from halophilic Virgibacillus sp. CD6. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevarajoo, S.; Selvaratnam, C.; Chan, K.-G.; Goh, K.M.; Chong, C.S. Draft genome sequence of Vitellibacter aquimaris D-24T isolated from seawater. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvaratnam, C.; Thevarajoo, S.; Ee, R.; Chan, K.-G.; Bennett, J.P.; Goh, K.M.; Chong, C.S. Genome sequence of Roseivirga sp. strain D-25 and its potential applications from the genomic aspect. Mar. Genom. 2016, 28, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Hetharua, B.; Lin, L.; Xu, H.; Zheng, T.; He, Z.; Tian, Y. Mangrove sediment microbiome: Adaptive microbial assemblages and their routed biogeochemical processes in Yunxiao mangrove national nature reserve, China. Microb. Ecol. 2019, 78, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmaso, G.Z.L.; Ferreira, D.; Vermelho, A.B. Marine extremophiles: A source of hydrolases for biotechnological applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 1925–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevarajoo, S.; Selvaratnam, C.; Goh, K.M.; Hong, K.W.; Chan, X.Y.; Chan, K.-G.; Chong, C.S. Vitellibacter aquimaris sp. nov., a marine bacterium isolated from seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3662–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaratnam, C.; Thevarajoo, S.; Goh, K.M.; Chan, K.-G.; Chong, C.S. Proposal to reclassify Roseivirga ehrenbergii (Nedashkovskaya et al., 2008) as Roseivirga seohaensis comb. nov., description of Roseivirga seohaensis subsp. aquiponti subsp. nov. and emendation of the genus Roseivirga. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 5537–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D.M. Mangrove forests. In Blue Carbon: Coastal Sequestration for Climate Change Mitigation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 23–36. [Google Scholar]
- Alongi, D.M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.K. Contribution of mangroves to coastal carbon cycling in low latitude seas. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 213, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesen, S.D.; Dunn, C.; Freeman, C. Decomposition as a regulator of carbon accretion in mangroves: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 114, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alongi, D. Impact of global change on nutrient dynamics in mangrove forests. Forests 2018, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.C.; Flocco, C.G.; Costa, R.; Junca, H.; Vilchez, R.; Pieper, D.H.; Krögerrecklenfort, E.; Paranhos, R.; Mendonça-Hagler, L.C.; Smalla, K. Mangrove microniches determine the structural and functional diversity of enriched petroleum hydrocarbon-degrading consortia. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 74, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanakumar, K.; Rajendran, N.; Kathiresan, K.; Chen, J. Bioprospects of microbial enzymes from mangrove-associated fungi and bacteria. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Kim, S.-K., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 99–115. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, B.; Sethi, B.; Mishra, R.; Dutta, S.; Thatoi, H. Microbial cellulases–diversity & biotechnology with reference to mangrove environment: A review. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chukwuma, O.B.; Rafatullah, M.; Tajarudin, H.A.; Ismail, N. Lignocellulolytic enzymes in biotechnological and industrial processes: A review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombard, V.; Ramulu, H.G.; Drula, E.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B. The carbohydrate-active enzymes database (CAZy) in 2013. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D490–D495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juturu, V.; Wu, J.C. Microbial cellulases: Engineering, production and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 188–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juturu, V.; Wu, J.C. Microbial xylanases: Engineering, production and industrial applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malgas, S.; van Dyk, J.S.; Pletschke, B.I. A review of the enzymatic hydrolysis of mannans and synergistic interactions between β-mannanase, β-mannosidase and α-galactosidase. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gonzalo, G.; Colpa, D.I.; Habib, M.H.; Fraaije, M.W. Bacterial enzymes involved in lignin degradation. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 236, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, S.K. The potential of the Malaysian oil palm biomass as a renewable energy source. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 141, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.P.Q.; Lam, H.L.; Ng, F.Y.; Kamal, M.; Lim, J.H.E. Waste-to-wealth: Green potential from palm biomass in Malaysia. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 34, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.Q.; Vodovnik, M.; Zorec, M.; Chen, S.J.; Goh, K.M.; Yahya, A.; Salleh, M.M.; Ibrahim, Z.; Tokiman, L.; McQueen-Mason, S.J.; et al. Robertkochia solimangrovi sp. nov., isolated from mangrove soil, and emended description of the genus Robertkochia. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 1769–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, A.; Shahina, M.; Lin, S.-Y.; Lai, W.-A.; Liu, Y.-C.; Hsu, Y.-H.; Cheng, I.-C.; Young, C.-C. Robertkochia marina gen. nov., sp. nov., of the family Flavobacteriaceae, isolated from surface seawater, and emended descriptions of the genera Joostella and Galbibacter. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatusova, T.; DiCuccio, M.; Badretdin, A.; Chetvernin, V.; Nawrocki, E.P.; Zaslavsky, L.; Lomsadze, A.; Pruitt, K.D.; Borodovsky, M.; Ostell, J. NCBI prokaryotic genome annotation pipeline. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 6614–6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntemann, M.; Ivanova, N.N.; Mavromatis, K.; Tripp, H.J.; Paez-Espino, D.; Palaniappan, K.; Szeto, E.; Pillay, M.; Chen, I.M.A.; Pati, A.; et al. The standard operating procedure of the DOE-JGI Microbial Genome Annotation Pipeline (MGAP v.4). Stand. Genom. Sci. 2015, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Stærfeldt, H.-H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNAmmer: Consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.M.; Chan, P.P. tRNAscan-SE On-line: Integrating search and context for analysis of transfer RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W54–W57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, E.P.; Burge, S.W.; Bateman, A.; Daub, J.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Floden, E.W.; Gardner, P.P.; Jones, T.A.; Tate, J.; et al. Rfam 12.0: Updates to the RNA families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D130–D137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodovsky, M.; Lomsadze, A. Gene identification in prokaryotic genomes, phages, metagenomes, and EST sequences with GeneMarkS suite. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2014, 32, 1E.7.1–1E.7.17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.-L.; Locascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriya, Y.; Itoh, M.; Okuda, S.; Yoshizawa, A.C.; Kanehisa, M. KAAS: An automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W182–W185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Li, W. WebMGA: A customizable web server for fast metagenomic sequence analysis. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, A.C.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple alignment of conserved genomic sequence with rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dong, Z.; Fang, L.; Luo, Y.; Wei, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, G.; Gu, Y.Q.; Coleman-Derr, D.; Xia, Q.; et al. OrthoVenn2: A web server for whole-genome comparison and annotation of orthologous clusters across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W52–W58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yohe, T.; Huang, L.; Entwistle, S.; Wu, P.; Yang, Z.; Busk, P.K.; Xu, Y.; Yin, Y. dbCAN2: A meta server for automated carbohydrate-active enzyme annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W95–W101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leadbeater, D.R.; Oates, N.C.; Bennett, J.P.; Li, Y.; Dowle, A.A.; Taylor, J.D.; Alponti, J.S.; Setchfield, A.T.; Alessi, A.M.; Helgason, T.; et al. Mechanistic strategies of microbial communities regulating lignocellulose deconstruction in a UK salt marsh. Microbiome 2021, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, J.; Gibrat, J.-F.; Robson, B. GOR method for predicting protein secondary structure from amino acid sequence. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 540–553. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, A.L.; Attwood, T.K.; Babbitt, P.C.; Blum, M.; Bork, P.; Bridge, A.; Brown, S.D.; Chang, H.-Y.; El-Gebali, S.; Fraser, M.I.; et al. InterPro in 2019: Improving coverage, classification and access to protein sequence annotations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D351–D360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.L. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 1959, 31, 426–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackebrandt, E.; Chertkov, O.; Lapidus, A.; Nolan, M.; Lucas, S.; Han, C.; Cheng, J.-F.; Tapia, R.; Goodwin, L.A.; Bruce, D.; et al. High-quality-draft genome sequence of the yellow-pigmented flavobacterium Joostella marina type strain En5T. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2013, 8, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lai, Q.; Li, C.; Shao, Z. Genome sequence of Galbibacter marinum type strain ck-I2-15. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Jin, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Jeon, C.O. Draft genome sequence of Zhouia amylolytica AD3, isolated from tidal flat sediment. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00316–e00327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, M.Q.; Oates, N.C.; Thevarajoo, S.; Tokiman, L.; Goh, K.M.; McQueen-Mason, S.J.; Bruce, N.C.; Chong, C.S. Genomic analysis of a lignocellulose degrading strain from the underexplored genus Meridianimaribacter. Genomics 2020, 112, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Brink, J.; de Vries, R.P. Fungal enzyme sets for plant polysaccharide degradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 91, 1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.-X.; Yendrek, C.R.; Caetano-Anolles, G.; Hartman, G.L. Genomic characterization of plant cell wall degrading enzymes and in silico analysis of xylanses and polygalacturonases of Fusarium virguliforme. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehemann, J.H.; Truong, L.V.; Unfried, F.; Welsch, N.; Kabisch, J.; Heiden, S.E.; Junker, S.; Becher, D.; Thürmer, A.; Daniel, R. Aquatic adaptation of a laterally acquired pectin degradation pathway in marine gammaproteobacterial. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2320–2333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Sczyrba, A.; Egan, R.; Kim, T.-W.; Chokhawala, H.; Schroth, G.; Luo, S.; Clark, D.S.; Chen, F.; Zhang, T. Metagenomic discovery of biomass-degrading genes and genomes from cow rumen. Science 2011, 331, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspeborg, H.; Coutinho, P.M.; Wang, Y.; Brumer, H.; Henrissat, B. Evolution, substrate specificity and subfamily classification of glycoside hydrolase family 5 (GH5). BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.B.; Cosgrove, D.J. Xyloglucan and its interactions with other components of the growing cell wall. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 180–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boraston, A.B.; Bolam, D.N.; Gilbert, H.J.; Davies, G.J. Carbohydrate-binding modules: Fine-tuning polysaccharide recognition. Biochem. J. 2004, 382, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lairson, L.L.; Henrissat, B.; Davies, G.J.; Withers, S.G. Glycosyltransferases: Structures, functions, and mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2008, 77, 521–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Z. Biotechnological aspects of salt-tolerant xylanases: A review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 8610–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rytioja, J.; Hildén, K.; Yuzon, J.; Hatakka, A.; de Vries, R.P.; Mäkelä, M.R. Plant-polysaccharide-degrading enzymes from Basidiomycetes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 614–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Furumichi, M.; Morishima, K.; Tanabe, M. New approach for understanding genome variations in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 47, D590–D595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Category | Number | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Number of contigs | 23 | - |
| Genome size (bp) | 4,407,290 | 100.00 |
| G + C content (%) | 1,794,772 | 40.72 |
| Total genes predicted | 3720 | 100.00 |
| Protein coding genes | 3669 | 98.63 |
| with COGs | 2840 | 77.41 |
| connected to KEGG pathway | 1325 | 36.11 |
| RNA genes | 51 | 1.37 |
| rRNA genes | 5 | 0.13 |
| 5S rRNA | 1 | 0.03 |
| 16S rRNA | 2 | 0.05 |
| 23S rRNA | 2 | 0.05 |
| tRNA | 42 | 1.13 |
| ncRNA | 4 | 0.11 |
| Pseudogenes | 25 | - |
| Horizontal transferred genes | 149 | 4.01 |
| Category | Annotation | CAZy Family | Number of Genes | NCBI Locus Tag Accession |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulase | Endoglucanase/ Exoglucanase | GH5 sub-family 46 | 1 | DMZ48_08160 |
| GH9 | 1 | DMZ48_13260 | ||
| β-glucosidase | GH3 | 7 | DMZ48_01605 DMZ48_08150 DMZ48_09610 DMZ48_13440 DMZ48_13560 DMZ48_14810 DMZ48_14815 | |
| GH30 | 2 | DMZ48_08155 DMZ48_08165 | ||
| Xylanase | 1,4-β-xylanase | GH5 sub-family 13 | 1 | DMZ48_12810 |
| GH10 | 1 | DMZ48_13420 | ||
| 1,4-β-xylanase/ α-arabinofuranosidase | GH43 sub-family 29 | 2 | DMZ48_01140 DMZ48_12865 | |
| β-xylosidase | GH43 | 2 | DMZ48_04615 DMZ48_15560 | |
| GH43 sub-family 31 | 2 | DMZ48_12790 DMZ48_12800 | ||
| β-xylosidase/ α-arabinofuranosidase | GH43 sub-family 1 | 1 | DMZ48_13400 | |
| GH43 sub-family 10 | 1 | DMZ48_09800 | ||
| GH43 sub-family 26 | 3 | DMZ48_12795 DMZ48_15550 DMZ48_18410 | ||
| α-arabinofuranosidase | GH43 | 1 | DMZ48_15515 | |
| GH43 sub-family 17 | 1 | DMZ48_15280 | ||
| GH43 sub-family 18 | 1 | DMZ48_12805 | ||
| GH43 sub-family 18 + CE10 | 1 | DMZ48_04720 | ||
| GH43 sub-family 19 | 1 | DMZ48_14390 | ||
| GH43 sub-family 19 + GH43 | 1 | DMZ48_07370 | ||
| GH51 | 3 | DMZ48_01125 DMZ48_01150 DMZ48_08775 | ||
| α-glucuronidase | GH67 | 1 | DMZ48_13435 | |
| GH115 | 1 | DMZ48_04675 | ||
| Uncharacterized xylanase | GH43 sub-family 28 | 2 | DMZ48_07195 DMZ48_17740 | |
| Acetyl xylan esterase | CE1 | 1 | DMZ48_16570 | |
| CE2 | 1 | DMZ48_07320 | ||
| CE4 | 1 | DMZ48_03780 | ||
| Mannanase | β-mannanase | GH113 | 1 | DMZ48_11390 |
| GH26 + GT2 sub-family 3 | 1 | DMZ48_06700 | ||
| α-galactosidase | GH27 with CBM51 | 1 | DMZ48_12870 | |
| Mannanase/Xyloglucanase | β-mannosidase/ β-galactosidase | GH2 | 11 | DMZ48_03505 DMZ48_04665 DMZ48_07180 DMZ48_07385 DMZ48_14580 DMZ48_14795 DMZ48_14865 DMZ48_15505 DMZ48_15590 DMZ48_16090 DMZ48_16435 |
| Xyloglucanase | Xyloglucan-specific endo-β-1,4-glucanase | GH5 sub-family 4 | 1 | DMZ48_14940 |
| GH16 | 2 | DMZ48_07400 DMZ48_16450 | ||
| α-fucosidase | GH29 | 1 | DMZ48_02920 | |
| GH29 with CBM32 | 1 | DMZ48_16630 | ||
| GH95 | 2 | DMZ48_14070 DMZ48_14845 | ||
| α-xylosidase | GH31 | 1 | DMZ48_14800 | |
| Pectinase | Endo/exo-polygalacturonase | GH28 | 3 | DMZ48_04685 DMZ48_04700 DMZ48_09805 |
| Endo-α-1,5-arabinanase | GH43 sub-family 4 | 1 | DMZ48_01145 | |
| Endo/exo-α-1,5-arabinanase | GH43 sub-family 5 | 1 | DMZ48_01135 | |
| GH43 sub-family 37 with CBM61 | 1 | DMZ48_08955 | ||
| β-1,4-endogalactanase | GH53 | 1 | DMZ48_07175 | |
| β-1,3-exogalactanase | GH43 sub-family 24 | 1 | DMZ48_07375 | |
| Unsaturated glucuronyl hydrolase | GH88 | 1 | DMZ48_16440 | |
| Unsaturated rhamnogalacturonyl hydrolase | GH105 | 2 | DMZ48_02835 DMZ48_04715 | |
| α-l-rhamnosidase | GH106 | 1 | DMZ48_04710 | |
| l-Rhα-α-1,4-GlcA α-rhamnohydrolase | GH145 | 1 | DMZ48_16445 | |
| β-arabinofuranosidase | GH127 | 3 | DMZ48_01130 DMZ48_14480 DMZ48_15545 | |
| GH146 | 1 | DMZ48_12780 | ||
| Rhamnogalacturonan acetylesterase | CE12 | 2 | DMZ48_02845 DMZ48_04660 | |
| CE12 + CE12 | 1 | DMZ48_04670 | ||
| CE12 + CE10 | 1 | DMZ48_09795 | ||
| Pectin lyase | PL1 sub-family 2 | 1 | DMZ48_09815 | |
| Pectin/pectate lyase with esterase | PL1 sub-family 2 + CE8 | 1 | DMZ48_09810 | |
| PL10 + CE8 | 1 | DMZ48_02840 | ||
| Oligogalacturonate/ oligogalacturonide lyase | PL22 | 1 | DMZ48_04705 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lam, M.Q.; Oates, N.C.; Leadbeater, D.R.; Goh, K.M.; Yahya, A.; Md Salleh, M.; Ibrahim, Z.; Bruce, N.C.; Chong, C.S. Genomic Analysis to Elucidate the Lignocellulose Degrading Capability of a New Halophile Robertkochia solimangrovi. Genes 2022, 13, 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112135
Lam MQ, Oates NC, Leadbeater DR, Goh KM, Yahya A, Md Salleh M, Ibrahim Z, Bruce NC, Chong CS. Genomic Analysis to Elucidate the Lignocellulose Degrading Capability of a New Halophile Robertkochia solimangrovi. Genes. 2022; 13(11):2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112135
Chicago/Turabian StyleLam, Ming Quan, Nicola C. Oates, Daniel R. Leadbeater, Kian Mau Goh, Adibah Yahya, Madihah Md Salleh, Zaharah Ibrahim, Neil C. Bruce, and Chun Shiong Chong. 2022. "Genomic Analysis to Elucidate the Lignocellulose Degrading Capability of a New Halophile Robertkochia solimangrovi" Genes 13, no. 11: 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112135
APA StyleLam, M. Q., Oates, N. C., Leadbeater, D. R., Goh, K. M., Yahya, A., Md Salleh, M., Ibrahim, Z., Bruce, N. C., & Chong, C. S. (2022). Genomic Analysis to Elucidate the Lignocellulose Degrading Capability of a New Halophile Robertkochia solimangrovi. Genes, 13(11), 2135. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13112135








