Complete Mitochondrial Genomes and Phylogenetic Positions of Two Longicorn Beetles, Anoplophora glabripennis and Demonax pseudonotabilis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection, DNA Extraction, and Mitogenome Sequencing
2.2. Mitogenome Assembly, Annotation, and Analyses
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses Methods
3. Results and Discussion
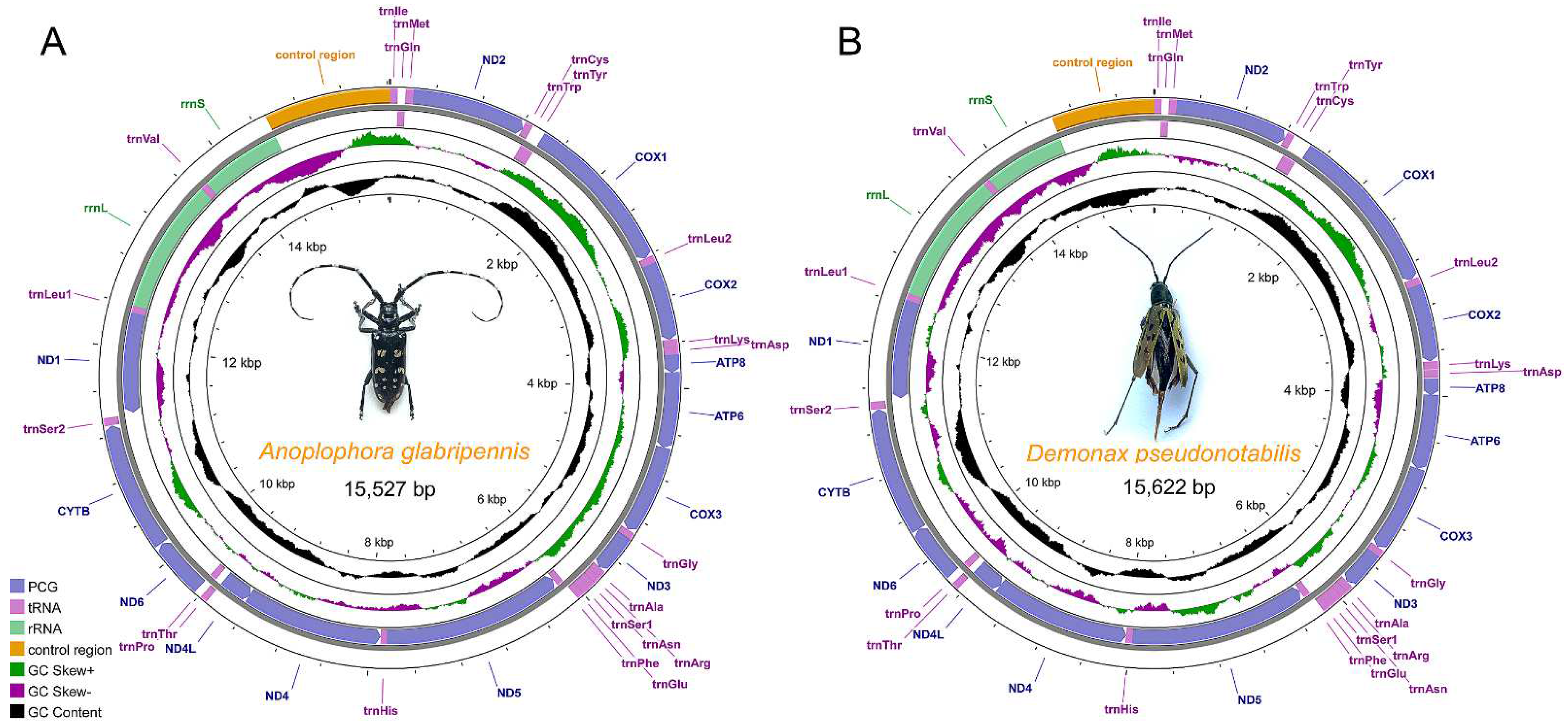
3.1. Genome Structure and Composition
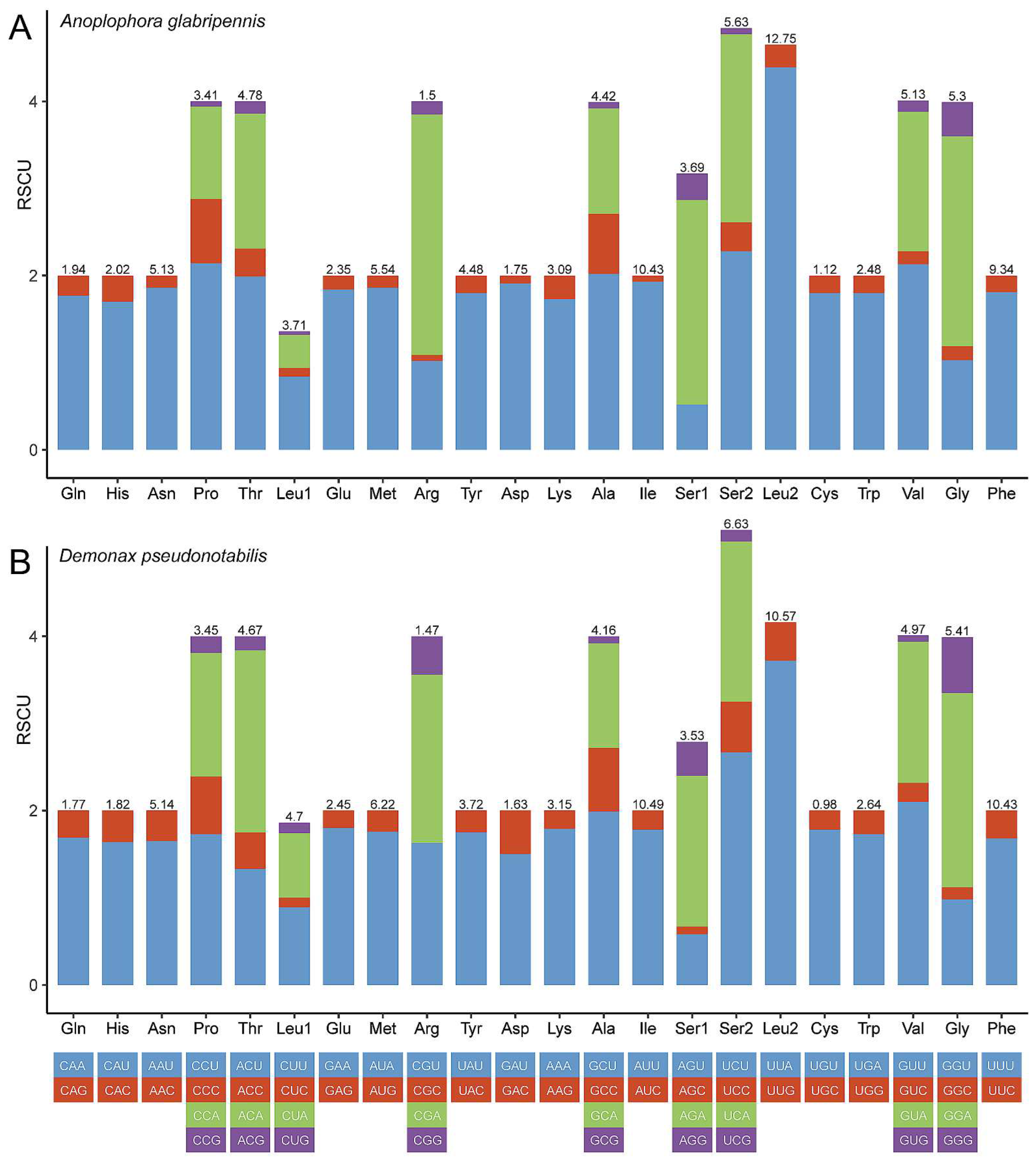
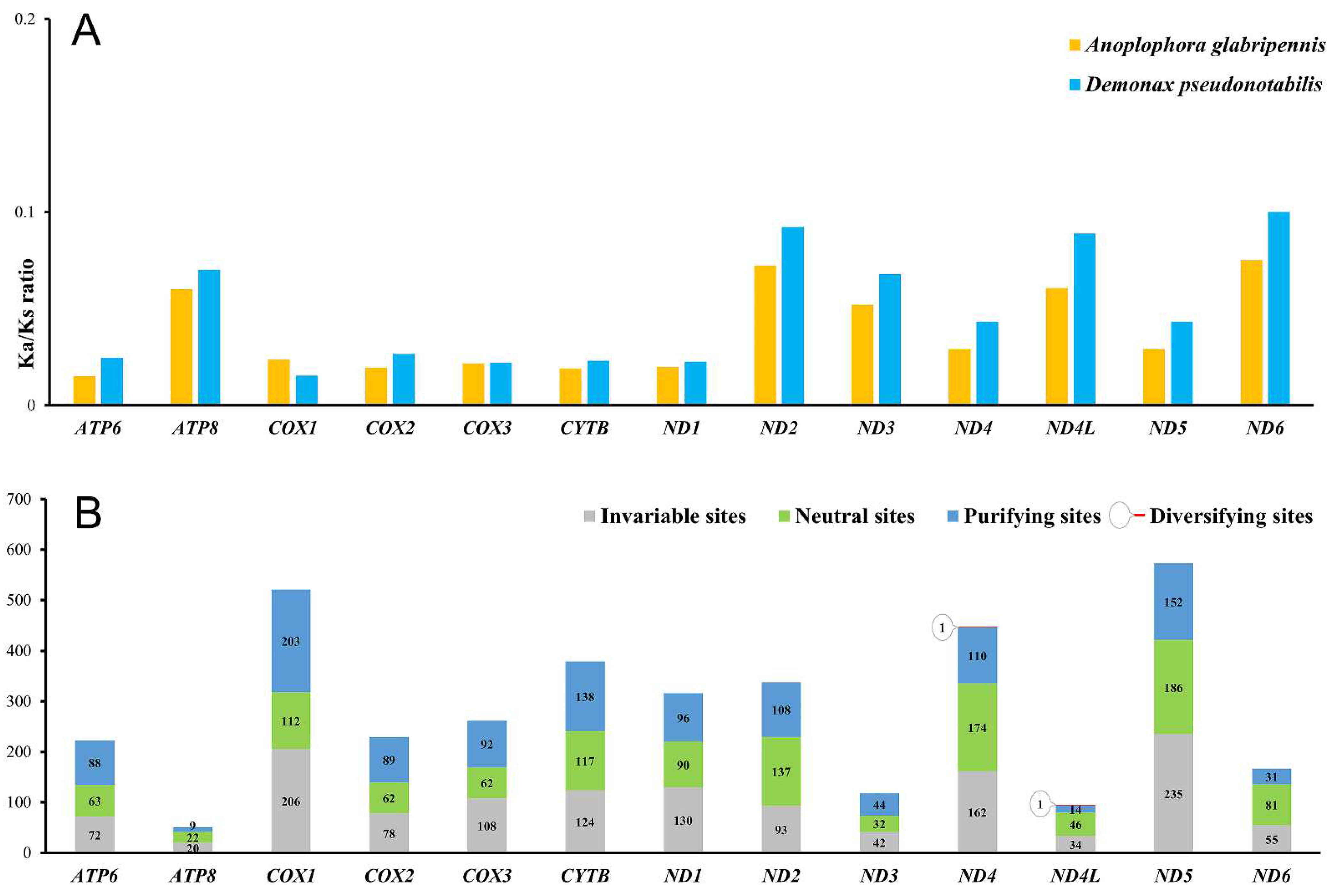
3.2. Protein-Coding Genes
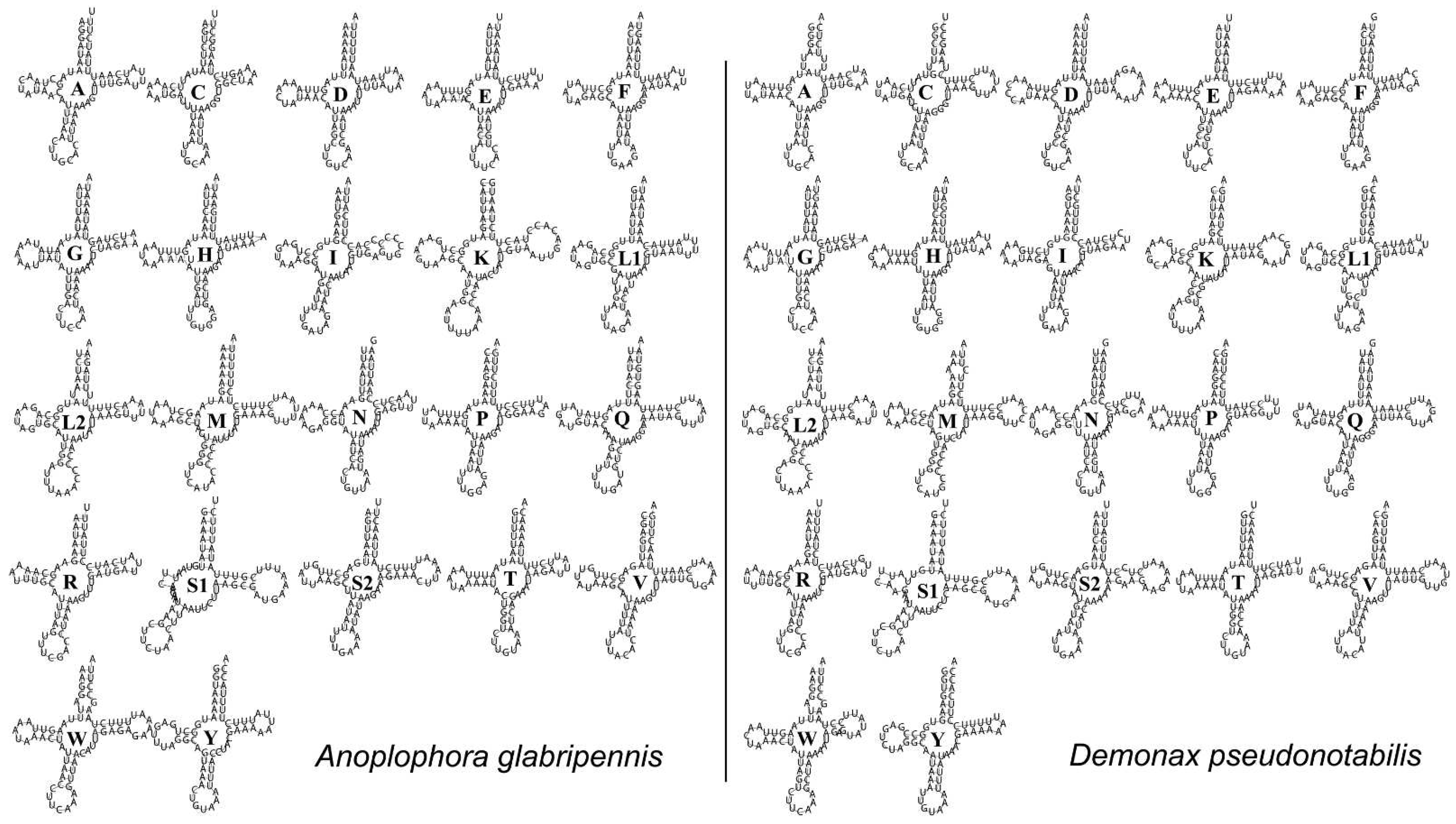
3.3. Transfer RNAs, Ribosomal RNAs, and Control Region
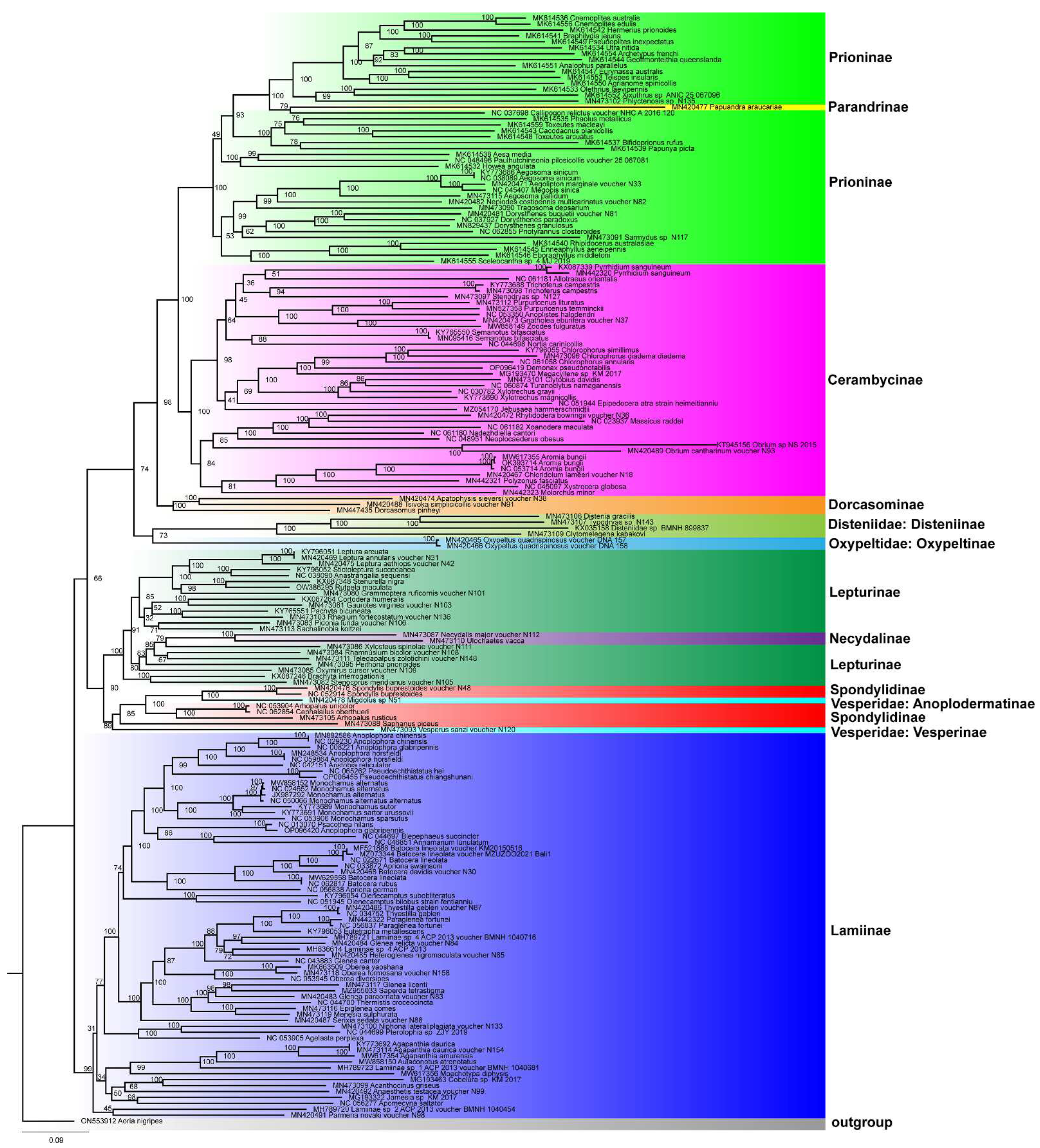
3.4. Phylogenetic Analyses
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Svacha, P.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, S.C. Larval morphology and biology of Philus antennatus and Heterophilus punctulatus, and systematic position of the Philinae (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae and Vesperidae). Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 1997, 33, 323–369. [Google Scholar]
- Sama, G.; Buse, J.; Orbach, E.; Friedman, A.; Rittner, O.; Chikatunov, V. A new catalogue of the Cerambycidae (Coleoptera) of Israel with notes on their distribution and host plants. Munis Entomol. Zool. 2010, 5, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakilian, G.L.; Chevillotte, H. Titan: Base de Données Internationales sur les Cerambycidae ou Longicornes. Version 4.0. Available online: http://titan.gbif.fr (accessed on 1 August 2022).
- Svacha, P.; Lawrence, J.F. 2.1. Vesperidae Mulsant, 1839; 2.2 Oxypeltidae Lacordaire, 1868; 2.3 Disteniidae J. Thomson, 1861; 2.4 Cerambycidae Latreille, 1802. Handbook of Zoology, Band 4: Arthropoda: Insecta, Teilband/part 40 Coleoptera, Beetles. In Vol. 3: Morphology and Systematics (Phytophaga); Leschen, R.A.B., Beutel, R.G., Eds.; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 16–177. [Google Scholar]
- Haddad, S.; Shin, S.; Lemmon, A.R.; Lemmon, E.M.; Svacha, P.; Farrell, B.; Ślipiński, A.; Windsor, D.; McKenna, D.D. Anchored hybrid enrichment provides new insights into the phylogeny and evolution of longhorned beetles (Cerambycidae). Syst. Entomol. 2018, 43, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monné, M.L.; Monné, M.A.; Mermudes, J.R.M. Inventário das espécies de Cerambycinae (Insecta, Coleoptera, Cerambycidae) do Parque Nacional do Itatiaia, RJ, Brasil. Biota Neotrop. 2009, 9, 283–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepanov, A.I. Cerambycidae of Northern Asia (Prioninae, Disteniinae, Lepturinae, Aseminae); Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Švácha, P.; Danilevsky, M.L. Cerambycoid larvae of Europe and Soviet Union (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae). Part I. Acta Univ. Carol. Biol. 1986, 30, 1–176. [Google Scholar]
- Švácha, P.; Danilevsky, M.L. Cerambycoid larvae of Europe and Soviet Union (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae). Part II. Acta Univ. Carol. Biol. 1987, 31, 121–284. [Google Scholar]
- Švácha, P.; Danilevsky, M.L. Cerambycoid larvae of Europe and Soviet Union (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae). Part III. Acta Univ. Carol. Biol. 1988, 32, 1–205. [Google Scholar]
- Linsley, E.G. Ecology of Cerambycidae. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1959, 4, 99–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.J.; Pasek, J.E.; Sequeira, R.A.; Crane, D.E.; Mastro, V.C. Potential effect of Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) on urban trees in the United States. J. Econ. Entomol. 2001, 94, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S.; Mckenna, D.D. Phylogeny and evolution of the superfamily Chrysomeloidea (Coleoptera: Cucujiformia). Syst. Entomol. 2016, 41, 697–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, X.Y.; Xu, X.D.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Yu, D.N.; Storey, K.B.; Zhang, J.Y. The complete mitochondrial genomes of five longicorn beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) and phylogenetic relationships within Cerambycidae. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, R.; Vogler, A.P.; Yang, X.K.; Lin, M. Higher-level phylogeny of longhorn beetles (Coleoptera: Chrysomeloidea) inferred from mitochondrial genomes. Syst. Entomol. 2021, 46, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.L. Insect mitochondrial genomics: Implications for evolution and phylogeny. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, M.J.; Barton, C.; Haran, J.; Ahrens, D.; Culverwell, C.L.; Ollikainen, A.; Dodsworth, S.; Foster, P.G.; Bocak, L.; Vogler, A.P. Family-level sampling of mitochondrial genomes in Coleoptera: Compositional heterogeneity and phylogenetics. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linard, B.; Crampton-Platt, A.; Moriniere, J.; Timmermans, M.J.; Andújar, C.; Arribas, P.; Miller, K.E.; Lipecki, J.; Favreau, E.; Hunter, A.; et al. The contribution of mitochondrial metagenomics to large-scale data mining and phylogenetic analysis of Coleoptera. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2018, 128, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, M.J.; Lees, D.C.; Simonsen, T.J. Towards a mitogenomic phylogeny of Lepidoptera. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 79, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Leavengood, J.M., Jr.; Chapman, E.G.; Burkhardt, D.; Song, F.; Jiang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Cai, W. Mitochondrial phylogenomics of Hemiptera reveals adaptive innovations driving the diversification of true bugs. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2017, 284, 20171223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motschulsky, V. Diagnoses de Coléoptères nouveaux, trouvés par M. M. Tatarinoff et Gaschkéwitsh aux environs de Pékin. Etud. Ent. 1854, 2, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Gressitt, J.L.; Rondon, J.A.; von Breuning, S. Cerambycid-Beetles of Laos. Pacific Insects Monograph 24; Bishop Museum: Honolulu, HI, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.; Qian, L.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, B.; An, Y. The complete nucleotide sequence of the mitochondrial genome of the Asian longhorn beetle, Anoplophora glabripennis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Mitochondrial DNA Part A 2016, 27, 3299–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Chen, S.; Chen, Q.D.; Pu, D.Q.; Chen, Z.T.; Liu, Y.Y.; Liu, X. The first mitochondrial genomes of the family Haplodiplatyidae (Insecta: Dermaptera) reveal intraspecific variation and extensive gene rearrangement. Biology 2022, 11, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. Fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernt, M.; Donath, A.; Jühling, F.; Externbrink, F.; Florentz, C.; Fritzsch, G.; Pütz, J.; Middendorf, M.; Stadler, P.F. MITOS: Improved de novo metazoan mitochondrial genome annotation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 69, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, J.R.; Stothard, P. The CGView server: A comparative genomics tool for circular genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: A toolkit incorporating γ-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genom. Broteom. Bioinform. 2010, 8, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baly, J.S. Descriptions of new genera and species of Eumolpidae. J. Entomol. 1860, 1, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, B.; Weaver, S.; Smith, M.D.; Wertheim, J.O.; Murrell, S.; Aylward, A.; Eren, K.; Pollner, T.; Martin, D.P.; Smith, D.M.; et al. Gene-wide identification of episodic selection. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, B.; Wertheim, J.O.; Moola, S.; Weighill, T.; Scheffler, K.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Detecting individual sites subject to episodic diversifying selection. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, G.; Lohman, D.J.; Meier, R. SequenceMatrix: Concatenation software for the fast assembly of multi-gene datasets with character set and codon information. Cladistics 2011, 27, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld., T.; Calcott., B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; Von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New models and efficient methods for phylogenetic inference in the genomic era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.; von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, S.; Dufayard, J.F.; Lefort, V.; Anisimova, M.; Hordijk, W.; Gascuel, O. New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: Assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 2010, 59, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 2003, 19, 1572–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, A. FigTree Version 1.4.4. 2019. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/fgtree/ (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Burla, H. Zur Kenntnis der Drosophiliden der Elfenbeinkuste (Franzosisch West-Afrika). Rev. Suisse Zool. 1954, 61, 1–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clary, D.O.; Wolstenholme, D.R. The ribosomal RNA genes of Drosophila mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985, 13, 4029–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojala, D.; Montoya, J.; Attardi, G. tRNA punctuation model of RNA processing in human mitochondria. Nature 1981, 290, 470–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Liu, L.; Huang, W.; Sang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Characterization of the complete mitogenome of Trachylophus sinensis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae: Cerambycinae), the type species of Trachylophus and its phylogenetic implications. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2022, 25, 101977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garey, J.R.; Wolstenholme, D.R. Platyhelminth mitochondrial DNA: Evidence for early evolutionary origin of a tRNAserAGN that contains a dihydrouridine arm replacement loop, and of serine-specifying AGA and AGG codons. J. Mol. Evol. 1989, 28, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.X.; Hewitt, G.M. Insect mitochondrial control region: A review of its structure, evolution and usefulness in evolutionary studies. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 1997, 25, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linsley, E.G.; Chemsak, J.A. The Cerambycidae of North America, part VI, no. 1. Taxonomy and classification of the subfamily Lepturinae. Univ. Calif. Publ. Entomol. 1972, 69, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Crowson, R.A. The Biology of the Coleoptera; Academic Press: London, UK, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Zurita, J.; Hunt, T.; Kopliku, F.; Vogler, A.P. Recalibrated tree of leaf beetles (Chrysomelidae) indicates independent diversification of angiosperms and their insect herbivores. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, T.; Bergsten, J.; Levkanicova, Z.; Papadopoulou, A.; John, O.S.; Wild, R.; Hammond, P.M.; Ahrens, D.; Balke, M.; Caterino, M.S.; et al. A comprehensive phylogeny of beetles reveals the evolutionary origins of a superradiation. Science 2007, 318, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.F.; Ślipiski, A.; Seago, A.E.; Thayer, M.K.; Newton, A.F.; Marvaldi, A.E. Phylogeny of the Coleoptera based on morphological characters of adults and larvae. Ann. Zool. 2011, 61, 1–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckenna, D.D.; Wild, A.L.; Kanda, K.; Bellamy, C.L.; Beutel, R.G.; Caterino, M.S.; Farnum, C.W.; Hawks, D.C.; Ivie, M.A.; Jameson, M.L.; et al. The beetle tree of life reveals Coleoptera survived end Permian mass extinction to diversify during the cretaceous terrestrial revolution. Syst. Entomol. 2015, 40, 835–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Ma, J.Y.; McKenna, D.D.; Yan, E.V.; Zhang, H.C.; Jarzembowski, E.A. The earliest known longhorn beetle (Cerambycidae: Prioninae) and implications for the early evolution of Chrysomeloidea. J. Syst. Palaeontol. 2014, 12, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.H.; Yin, X.M.; An, S.H.; Su, L.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.F. Molecular phylogenetic study of the higher taxa of the superfamily Cerambycoidea (Insecta: Coleoptera) based on the combined analysis of ribosomal DNA sequences. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2014, 57, 710–720. [Google Scholar]
- Danilevsky, M.L. Morpho-Adaptive Ways of Evolution of the Larvae of Longhorn Beetles (Coleoptera, Cerambycidae) and Phylogenetic Relations of the Basic Groups of the Family. Insects Decomposing Wood and their Entomophages; Nauka: Moscow, Russia, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Napp, D.S. Phylogenetic relationships among the subfamilies of Cerambycidae (Coleoptera, Chrysomeloidea). Rev. Bras. Entomol. 1994, 28, 265–419. [Google Scholar]
- Reid, C.A.M. A cladistic analysis of subfamilial relationships in the Chrysomelidae sensu lato (Chrysomeloidea). In Biology, Phylogeny and Classification of Coleoptera: Papers Celebrating the 80th Birthday of Roy A. Crowson; Pakaluk, J., Slipinski, S.A., Eds.; Muzeum i Instytut Zoologii Polska Akademia Nauk: Warsaw, Poland, 1995; pp. 559–632. [Google Scholar]
- Bocak, L.; Barton, C.; Crampton-Platt, A.; Chesters, D.; Ahrens, D.; Vogler, A.P. Building the Coleoptera tree-of-life for >8000 species: Composition of public DNA data and fit with Linnaean classification. Syst. Entomol. 2014, 39, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Family | Subfamily | Species | Genome Size (bp) | GenBank No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cerambycidae s.s. | Cerambycinae | Allotraeus orientalis | 15,966 | NC_061181 |
| Anoplistes halodendri | 15,697 | NC_053350 | ||
| Aromia bungii | 15,652 | MW617355 | ||
| A. bungii | 15,760 | NC_053714 | ||
| A. bungii | 15,759 | OK393714 | ||
| Chloridolum lameeri | 15,731 | MN420467 | ||
| Chlorophorus annularis | 15,487 | NC_061058 | ||
| Chlorophorus diadema | 15,398 | MN473096 | ||
| Chlorophorus simillimus | 13,675 | KY796055 | ||
| Clytobius davidis | 15,571 | MN473101 | ||
| D. pseudonotabilis | 15,527 | OP096419 | ||
| Epipedocera atra | 15,662 | NC_051944 | ||
| Gnatholea eburifera | 15,281 | MN420473 | ||
| Jebusaea hammerschmidtii | 15,619 | MZ054170 | ||
| Massicus raddei | 15,858 | NC_023937 | ||
| Megacyllene sp. KM-2017 | 15,832 | MG193470 | ||
| Molorchus minor | 15,685 | MN442323 | ||
| Nadezhdiella cantori | 16,049 | NC_061180 | ||
| Neoplocaederus obesus | 15,683 | NC_048951 | ||
| Nortia carinicollis | 15,602 | NC_044698 | ||
| Obrium cantharinum | 15,632 | MN420489 | ||
| Obrium sp. NS-2015 | 15,680 | KT945156 | ||
| Polyzonus fasciatus | 15,804 | MN442321 | ||
| Purpuricenus lituratus | 15,744 | MN473112 | ||
| Purpuricenus temminckii | 15,689 | MN527358 | ||
| Pyrrhidium sanguineum | 16,203 | KX087339 | ||
| P. sanguineum | 15,748 | MN442320 | ||
| Rhytidodera bowringii | 15,278 | MN420472 | ||
| Semanotus bifasciatus | 13,837 | KY765550 | ||
| S. bifasciatus | 16,051 | MN095416 | ||
| Stenodryas sp. N127 | 15,333 | MN473097 | ||
| Trichoferus campestris | 13,696 | KY773688 | ||
| T. campestris | 15,737 | MN473098 | ||
| Turanoclytus namaganensis | 15,565 | NC_060874 | ||
| Xoanodera maculata | 15,767 | NC_061182 | ||
| Xylotrechus grayii | 15,540 | NC_030782 | ||
| Xylotrechus magnicollis | 13,692 | KY773690 | ||
| Xystrocera globosa | 15,707 | NC_045097 | ||
| Zoodes fulguratus | 15,885 | MW858149 | ||
| Dorcasominae | Apatophysis sieversi | 15,278 | MN420474 | |
| Dorcasomus pinheyi | 16,040 | MN447435 | ||
| Tsivoka simplicicollis | 16,700 | MN420488 | ||
| Lamiinae | Acanthocinus griseus | 15,600 | MN473099 | |
| Agapanthia amurensis | 15,512 | MW617354 | ||
| Agapanthia daurica | 14,282 | KY773692 | ||
| A. daurica | 17,153 | MN473114 | ||
| Agelasta perplexa | 15,552 | NC_053905 | ||
| Anaesthetis testacea | 15,169 | MN420492 | ||
| Annamanum lunulatum | 15,610 | NC_046851 | ||
| Anoplophora chinensis | 15,871 | MN882586 | ||
| A. chinensis | 15,805 | NC_029230 | ||
| A. glabripennis | 15,774 | NC_008221 | ||
| Anoplophora horsfieldi | 15,796 | MN248534 | ||
| A. horsfieldi | 15,837 | NC_059864 | ||
| A. glabripennis | 15,622 | OP096420 | ||
| Apomecyna saltator | 14,949 | NC_056277 | ||
| Apriona germarii | 14,858 | NC_056838 | ||
| Apriona swainsoni | 15,412 | NC_033872 | ||
| Aristobia reticulator | 15,838 | NC_042151 | ||
| Aulaconotus atronotatus | 14,491 | MW858150 | ||
| Batocera davidis | 15,554 | MN420468 | ||
| Batocera lineolata | 15,420 | MF521888 | ||
| B. lineolata | 16,158 | MW629558 | ||
| B. lineolata | 15,420 | MZ073344 | ||
| B. lineolata | 15,418 | NC_022671 | ||
| Batocera rubus | 16,158 | NC_062817 | ||
| Blepephaeus succinctor | 15,554 | NC_044697 | ||
| Cobelura sp. KM-2017 | 15,912 | MG193463 | ||
| Epiglenea comes | 15,213 | MN473116 | ||
| Eutetrapha metallescens | 15,072 | KY796053 | ||
| Glenea cantor | 15,514 | NC_043883 | ||
| Glenea licenti | 15,435 | MN473117 | ||
| Glenea paraornata | 15,510 | MN420483 | ||
| Glenea relicta | 15,486 | MN420484 | ||
| Heteroglenea nigromaculata | 15,502 | MN420485 | ||
| Jamesia sp. KM-2017 | 17,430 | MG193322 | ||
| Lamiinae sp. 1 ACP-2013 | 15,737 | MH789723 | ||
| Lamiinae sp. 2 ACP-2013 | 15,440 | MH789720 | ||
| Lamiinae sp. 4 ACP-2013 | 15,504 | MH789721 | ||
| Lamiinae sp. 4 ACP-2013 | 15,554 | MH836614 | ||
| Menesia sulphurata | 15,551 | MN473119 | ||
| Moechotypa diphysis | 15,493 | MW617356 | ||
| Monochamus alternatus | 14,649 | JX987292 | ||
| M. alternatus | 14,189 | MW858152 | ||
| M. alternatus | 15,874 | NC_024652 | ||
| M. alternatus | 15,880 | NC_050066 | ||
| Monochamus sartor urussovii | 14,359 | KY773691 | ||
| Monochamus sparsutus | 16,029 | NC_053906 | ||
| Monochamus sutor | 14,350 | KY773689 | ||
| Niphona lateraliplagiata | 15,902 | MN473100 | ||
| Oberea diversipes | 15,499 | NC_053945 | ||
| Oberea formosana | 15,675 | MN473118 | ||
| Oberea yaoshana | 15,529 | MK863509 | ||
| Olenecamptus bilobus | 15,262 | NC_051945 | ||
| Olenecamptus subobliteratus | 13,854 | KY796054 | ||
| Paraglenea fortunei | 15,401 | MN442322 | ||
| P. fortunei | 15,496 | NC_056837 | ||
| Parmena novaki | 15,668 | MN420491 | ||
| Psacothea hilaris | 15,856 | NC_013070 | ||
| Pseudoechthistatus chiangshunani | 16,419 | OP006455 | ||
| Pseudoechthistatus hei | 16,103 | NC_065262 | ||
| Pterolophia sp. ZJY-2019 | 16,063 | NC_044699 | ||
| Saperda tetrastigma | 15,563 | MZ955033 | ||
| Serixia sedata | 14,714 | MN420487 | ||
| Thermistis croceocincta | 15,503 | NC_044700 | ||
| Thyestilla gebleri | 15,503 | MN420486 | ||
| T. gebleri | 15,505 | NC_034752 | ||
| Lepturinae | Anastrangalia sequensi | 16,269 | NC_038090 | |
| Brachyta interrogationis | 18,165 | KX087246 | ||
| Cortodera humeralis | 15,928 | KX087264 | ||
| Gaurotes virginea | 15,775 | MN473081 | ||
| Grammoptera ruficornis | 16,458 | MN473080 | ||
| Leptura aethiops | 15,690 | MN420475 | ||
| Leptura annularis | 16,530 | MN420469 | ||
| Leptura arcuata | 14,382 | KY796051 | ||
| Oxymirus cursor | 15,797 | MN473085 | ||
| Pachyta bicuneata | 13,894 | KY765551 | ||
| Peithona prionoides | 13,636 | MN473095 | ||
| Pidonia lurida | 15,668 | MN473083 | ||
| Rhagium fortecostatum | 16,274 | MN473103 | ||
| Rhamnusium bicolor | 15,527 | MN473084 | ||
| Rutpela maculata | 17,437 | OW386295 | ||
| Sachalinobia koltzei | 15,809 | MN473113 | ||
| Stenurella nigra | 16,504 | KX087348 | ||
| Stictoleptura succedanea | 14,381 | KY796052 | ||
| Teledapalpus zolotichini | 16,651 | MN473111 | ||
| Stenocorus meridianus | 16,227 | MN473082 | ||
| Xylosteus spinolae | 15,708 | MN473086 | ||
| Necydalinae | Necydalis major | 15,598 | MN473087 | |
| Ulochaetes vacca | 15,593 | MN473110 | ||
| Parandrinae | Papuandra araucariae | 15,475 | MN420477 | |
| Prioninae | Aegolipton marginale | 16,759 | MN420471 | |
| Aegosoma pallidum | 15,668 | MN473115 | ||
| Aegosoma sinicum | 15,658 | KY773686 | ||
| A. sinicum | 15,658 | NC_038089 | ||
| Aesa media | 15,714 | MK614538 | ||
| Agrianome spinicollis | 15,633 | MK614550 | ||
| Analophus parallelus | 15,722 | MK614551 | ||
| Archetypus frenchi | 16,156 | MK614554 | ||
| Bifidoprionus rufus | 15,590 | MK614537 | ||
| Brephilydia jejuna | 15,659 | MK614541 | ||
| Cacodacnus planicollis | 15,671 | MK614543 | ||
| Callipogon relictus | 15,742 | NC_037698 | ||
| Cnemoplites australis | 15,675 | MK614536 | ||
| Cnemoplites edulis | 13,161 | MK614556 | ||
| Dorysthenes buquetii | 15,778 | MN420481 | ||
| Dorysthenes granulosus | 15,858 | MN829437 | ||
| Dorysthenes paradoxus | 15,922 | NC_037927 | ||
| Eboraphyllus middletoni | 15,776 | MK614546 | ||
| Enneaphyllus aeneipennis | 16,505 | MK614545 | ||
| Eurynassa australis | 15,612 | MK614547 | ||
| Geoffmonteithia queenslanda | 15,628 | MK614544 | ||
| Hermerius prionoides | 13,696 | MK614542 | ||
| Howea angulata | 15,626 | MK614532 | ||
| Megopis sinica | 15,689 | NC_045407 | ||
| Nepiodes costipennis multicarinatus | 15,935 | MN420482 | ||
| Olethrius laevipennis | 15,690 | MK614533 | ||
| Papunya picta | 15,737 | MK614539 | ||
| Paulhutchinsonia pilosicollis | 15,846 | NC_048496 | ||
| Phaolus metallicus | 15,997 | MK614535 | ||
| Phlyctenosis sp. N135 | 15,000 | MN473102 | ||
| Priotyrannus closteroides | 15,854 | NC_062855 | ||
| Pseudoplites inexpectatus | 15,651 | MK614549 | ||
| Rhipidocerus australasiae | 15,721 | MK614540 | ||
| Sarmydus sp. N117 | 15,720 | MN473091 | ||
| Sceleocantha sp. 4 MJ-2019 | 15,804 | MK614555 | ||
| Teispes insularis | 15,632 | MK614553 | ||
| Toxeutes arcuatus | 15,859 | MK614548 | ||
| Toxeutes macleayi | 13,579 | MK614559 | ||
| Tragosoma depsarium | 15,712 | MN473090 | ||
| Utra nitida | 14,976 | MK614534 | ||
| Xixuthrus sp. ANIC_25-067096 | 15,523 | MK614552 | ||
| Spondylidinae | Arhopalus rusticus | 15,860 | MN473105 | |
| Arhopalus unicolor | 15,760 | NC_053904 | ||
| Cephalallus oberthueri | 15,763 | NC_062854 | ||
| Saphanus piceus | 15,832 | MN473088 | ||
| Spondylis buprestoides | 16,070 | MN420476 | ||
| S. buprestoides | 15,837 | NC_052914 | ||
| Disteniidae | Disteniinae | Clytomelegena kabakovi | 15,816 | MN473109 |
| Distenia gracilis | 15,704 | MN473106 | ||
| Disteniinae sp. BMNH 899837 | 15,598 | KX035158 | ||
| Typodryas sp. N143 | 15,647 | MN473107 | ||
| Oxypeltidae | Oxypeltinae | Oxypeltus quadrispinosus | 16,140 | MN420465 |
| O. quadrispinosus | 17,001 | MN420466 | ||
| Vesperidae | Anoplodermatinae | Migdolus sp. N51 | 14,931 | MN420478 |
| Vesperinae | Vesperus sanzi | 16,125 | MN473093 | |
| Chrysomelidae | A. nigripes | 17,306 | ON553912 |
| Gene | Position (bp) | Size (bp) | Direction | Intergenic Nucleotides | Anti− or Start/Stop Codons | A + T% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trnIle (I) | 1–67 | 67 | Forward | 0 | GAT | 61.2 |
| trnGln (Q) | 69–137 | 69 | Reverse | 1 | TTG | 78.3 |
| trnMet (M) | 137–205 | 69 | Forward | −1 | CAT | 72.5 |
| ND2 | 206–1216 | 1011 | Forward | 0 | ATT/TAA | 77.6 |
| trnTrp (W) | 1215–1282 | 68 | Forward | −2 | TCA | 76.5 |
| trnCys (C) | 1275–1336 | 62 | Reverse | −8 | GCA | 74.2 |
| trnTyr (Y) | 1338–1402 | 65 | Reverse | 1 | GTA | 69.2 |
| COX1 | 1403–2819 | 1417 | Forward | 0 | ATC/T | 68.1 |
| trnLeu2 (L2) | 2820–2884 | 65 | Forward | 0 | TAA | 73.8 |
| COX2 | 2885–3572 | 688 | Forward | 0 | ATC/T | 72.1 |
| trnLys (K) | 3573–3641 | 69 | Forward | 0 | CTT | 68.1 |
| trnAsp (D) | 3642–3707 | 66 | Forward | 0 | GTC | 86.4 |
| ATP8 | 3708–3863 | 156 | Forward | 0 | ATT/TAG | 86.5 |
| ATP6 | 3860–4531 | 672 | Forward | −4 | ATA/TAA | 75.1 |
| COX3 | 4531–5319 | 789 | Forward | −1 | ATG/TAA | 70.6 |
| trnGly (G) | 5322–5385 | 64 | Forward | 2 | TCC | 85.9 |
| ND3 | 5383–5739 | 357 | Forward | −3 | ATA/TAG | 79.0 |
| trnAla (A) | 5738–5802 | 65 | Forward | −2 | TGC | 81.5 |
| trnArg (R) | 5803–5864 | 62 | Forward | 0 | TCG | 74.2 |
| trnAsn (N) | 5864–5927 | 64 | Forward | −1 | GTT | 75.0 |
| trnSer1 (S1) | 5928–5994 | 67 | Forward | 0 | GCT | 76.1 |
| trnGlu (E) | 5995–6057 | 63 | Forward | 0 | TTC | 87.3 |
| trnPhe (F) | 6060–6123 | 64 | Reverse | 2 | GAA | 82.8 |
| ND5 | 6124–7840 | 1717 | Reverse | 0 | ATT/T | 78.3 |
| trnHis (H) | 7841–7903 | 63 | Reverse | 0 | GTG | 84.1 |
| ND4 | 7904–9236 | 1333 | Reverse | 0 | ATG/T | 79.3 |
| ND4L | 9230–9517 | 288 | Reverse | −7 | ATG/TAA | 83.0 |
| trnThr (T) | 9520–9583 | 64 | Forward | 2 | TGT | 82.8 |
| trnPro (P) | 9584–9647 | 64 | Reverse | 0 | TGG | 78.1 |
| ND6 | 9650–10,153 | 504 | Forward | 2 | ATT/TAA | 85.1 |
| CYTB | 10,159–11,292 | 1134 | Forward | 5 | ATA/TAA | 72.2 |
| trnSer2 (S2) | 11,296–11,364 | 69 | Forward | 3 | TGA | 81.2 |
| ND1 | 11,382–12,332 | 951 | Reverse | 17 | TTG/TAG | 76.3 |
| trnLeu1 (L1) | 12,334–12,398 | 65 | Reverse | 1 | TAG | 78.5 |
| rrnL | 12,399–13,670 | 1272 | Reverse | 0 | 80.1 | |
| trnVal (V) | 13,671–13,739 | 69 | Reverse | 0 | TAC | 75.4 |
| rrnS | 13,740–14,518 | 779 | Reverse | 0 | 78.6 | |
| Control Region | 14,519–15,622 | 1104 | Forward | 0 | 79.3 |
| Gene | Position (bp) | Size (bp) | Direction | Intergenic Nucleotides | Anti− or Start/Stop Codons | A + T% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| trnIle (I) | 1–66 | 66 | Forward | 0 | GAT | 72.7 |
| trnGln (Q) | 64–132 | 69 | Reverse | −3 | TTG | 81.2 |
| trnMet (M) | 132–200 | 69 | Forward | −1 | CAT | 65.2 |
| ND2 | 201–1211 | 1011 | Forward | 0 | ATA/TAA | 76.2 |
| trnTrp (W) | 1210–1274 | 65 | Forward | −2 | TCA | 73.8 |
| trnCys (C) | 1274–1339 | 66 | Reverse | −1 | GCA | 72.7 |
| trnTyr (Y) | 1341–1405 | 65 | Reverse | 1 | GTA | 66.2 |
| COX1 | 1440–2940 | 1501 | Forward | 34 | ATT/T | 67.0 |
| trnLeu2 (L2) | 2941–3005 | 65 | Forward | 0 | TAA | 72.3 |
| COX2 | 3006–3692 | 687 | Forward | 0 | ATA/TAT | 70.7 |
| trnLys (K) | 3694–3764 | 71 | Forward | 1 | CTT | 70.4 |
| trnAsp (D) | 3768–3837 | 70 | Forward | 3 | GTC | 82.9 |
| ATP8 | 3847–3993 | 147 | Forward | 9 | ATA/TAG | 85.0 |
| ATP6 | 3990–4661 | 672 | Forward | −4 | ATA/TAA | 74.3 |
| COX3 | 4661–5447 | 787 | Forward | −1 | ATG/T | 69.5 |
| trnGly (G) | 5448–5510 | 63 | Forward | 0 | TCC | 84.1 |
| ND3 | 5511–5862 | 352 | Forward | 0 | ATT/T | 76.1 |
| trnAla (A) | 5863–5925 | 63 | Forward | 0 | TGC | 77.8 |
| trnArg (R) | 5925–5989 | 65 | Forward | −1 | TCG | 73.8 |
| trnAsn (N) | 5989–6053 | 65 | Forward | −1 | GTT | 73.8 |
| trnSer1 (S1) | 6054–6120 | 67 | Forward | 0 | GCT | 74.6 |
| trnGlu (E) | 6121–6186 | 66 | Forward | 0 | TTC | 86.4 |
| trnPhe (F) | 6190–6256 | 67 | Reverse | 3 | GAA | 79.1 |
| ND5 | 6257–7973 | 1717 | Reverse | 0 | ATT/T | 77.4 |
| trnHis (H) | 7974–8037 | 64 | Reverse | 0 | GTG | 84.4 |
| ND4 | 8037–9368 | 1332 | Reverse | −1 | ATA/TAA | 76.4 |
| ND4L | 9365–9643 | 279 | Reverse | −4 | ATG/TAA | 79.9 |
| trnThr (T) | 9646–9709 | 64 | Forward | 2 | TGT | 84.4 |
| trnPro (P) | 9709–9774 | 66 | Reverse | −1 | TGG | 75.8 |
| ND6 | 9776–10,273 | 498 | Forward | 1 | ATA/TAA | 81.7 |
| CYTB | 10,273–11,409 | 1137 | Forward | −1 | ATG/TAA | 68.1 |
| trnSer2 (S2) | 11,411–11,479 | 69 | Forward | 1 | TGA | 78.3 |
| ND1 | 11,497–12,447 | 951 | Reverse | 17 | TTG/TAG | 75.8 |
| trnLeu1 (L1) | 12,449–12,512 | 64 | Reverse | 1 | TAG | 75.0 |
| rrnL | 12,513–13,778 | 1266 | Reverse | 0 | 78.8 | |
| trnVal (V) | 13,779–13,846 | 68 | Reverse | 0 | TAC | 77.9 |
| rrnS | 13,847–14,620 | 774 | Reverse | 0 | 76.5 | |
| Control Region | 14,621–15,527 | 907 | Forward | 0 | 82.1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pu, D.-Q.; Liu, H.-L.; Wu, X.-L.; Chen, Z.-T. Complete Mitochondrial Genomes and Phylogenetic Positions of Two Longicorn Beetles, Anoplophora glabripennis and Demonax pseudonotabilis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Genes 2022, 13, 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101881
Pu D-Q, Liu H-L, Wu X-L, Chen Z-T. Complete Mitochondrial Genomes and Phylogenetic Positions of Two Longicorn Beetles, Anoplophora glabripennis and Demonax pseudonotabilis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Genes. 2022; 13(10):1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101881
Chicago/Turabian StylePu, De-Qiang, Hong-Ling Liu, Xing-Long Wu, and Zhi-Teng Chen. 2022. "Complete Mitochondrial Genomes and Phylogenetic Positions of Two Longicorn Beetles, Anoplophora glabripennis and Demonax pseudonotabilis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae)" Genes 13, no. 10: 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101881
APA StylePu, D.-Q., Liu, H.-L., Wu, X.-L., & Chen, Z.-T. (2022). Complete Mitochondrial Genomes and Phylogenetic Positions of Two Longicorn Beetles, Anoplophora glabripennis and Demonax pseudonotabilis (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae). Genes, 13(10), 1881. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13101881







