Structural Insight into the Mechanism of PALB2 Interaction with MRG15
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protein Expression and Purification
2.2. Pulldown Assay
2.3. Crystallization and Structure Determination
2.4. Binding and Competition Assays
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the MRG15-Binding Region of PALB2
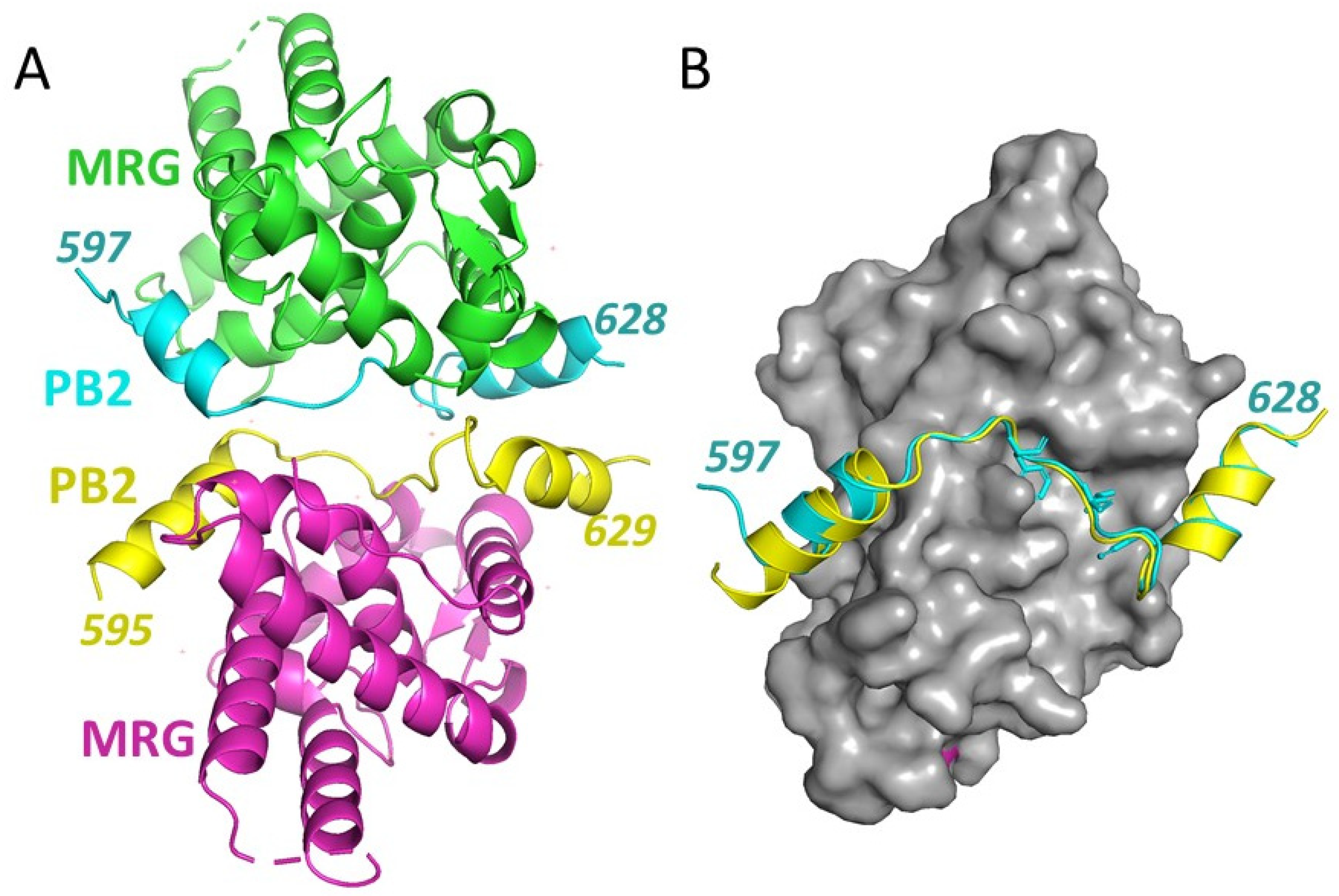
3.2. Crystal Structure of an MRG15 Complex with PALB2
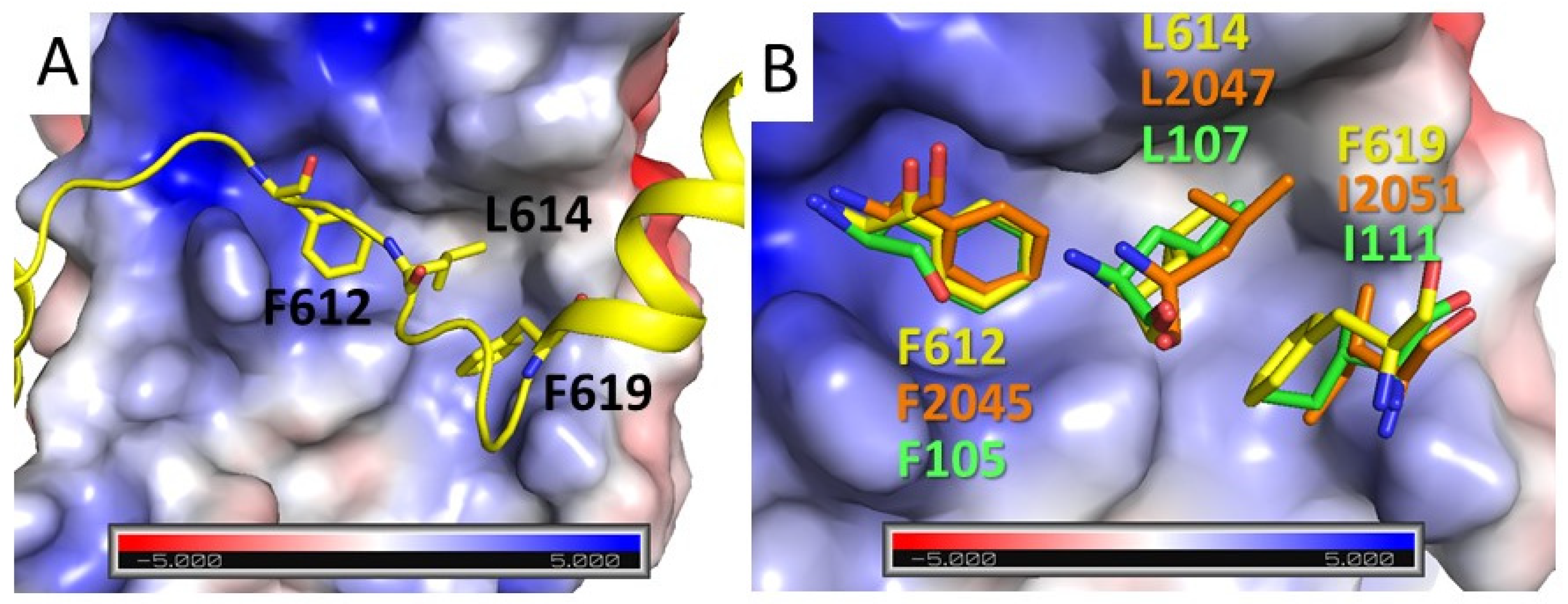
3.3. Contribution to MRG Binding of PALB2 Conserved Amino Acids and Amino Acids Mutated in Cancer Patients
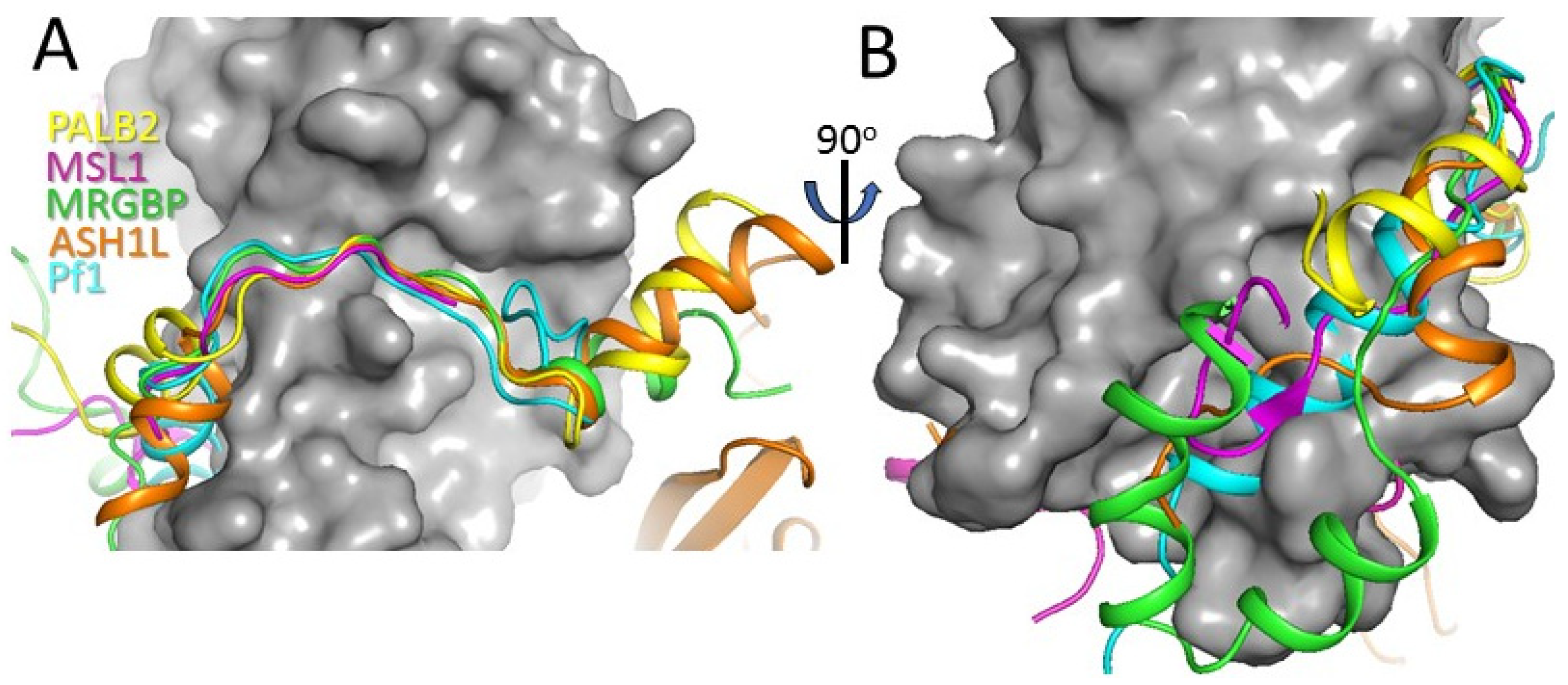
3.4. Comparison with Other MRG Complexes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Merrikh, H.; Zhang, Y.; Grossman, A.D.; Wang, J.D. Replication-transcription conflicts in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mortusewicz, O.; Herr, P.; Helleday, T. Early replication fragile sites: Where replication-transcription collisions cause genetic instability. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cox, M.M.; Goodman, M.F.; Kreuzer, K.N.; Sherratt, D.J.; Sandler, S.J.; Marians, K.J. The importance of repairing stalled replication forks. Nature 2000, 404, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawale, A.S.; Sung, P. Mechanism and significance of chromosome damage repair by homologous recombination. Essays Biochem. 2020, 64, 779–790. [Google Scholar]
- Venkitaraman, A.R. The breast cancer susceptibility gene, BRCA2: At the crossroads between DNA replication and recombination? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2000, 355, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scully, R.; Anderson, S.F.; Chao, D.M.; Wei, W.; Ye, L.; Young, R.A.; Livingston, D.M.; Parvin, J.D. BRCA1 is a component of the RNA polymerase II holoenzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5605–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wooster, R.; Bignell, G.; Lancaster, J.; Swift, S.; Seal, S.; Mangion, J.; Collins, N.; Gregory, S.; Gumbs, C.; Micklem, G. Identification of the breast cancer susceptibility gene BRCA2. Nature 1995, 378, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, B.; Sheng, Q.; Nakanishi, K.; Ohashi, A.; Wu, J.; Christ, N.; Liu, X.; Jasin, M.; Couch, F.J.; Livingston, D.M. Control of BRCA2 cellular and clinical functions by a nuclear partner, PALB2. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakash, R.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, W.; Jasin, M. Homologous Recombination and Human Health: The Roles of BRCA1, BRCA2, and Associated Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a016600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quinet, A.; Vindigni, A. Superfast DNA replication causes damage in cancer cells. Nature 2018, 559, 186–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berti, M.; Vindigni, A. Replication stress: Getting back on track. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Ray Chaudhuri, A.; Lopes, M.; Costanzo, V. Rad51 protects nascent DNA from Mre11-dependent degradation and promotes continuous DNA synthesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ducy, M.; Sesma-Sanz, L.; Guitton-Sert, L.; Lashgari, A.; Gao, Y.; Brahiti, N.; Rodrigue, A.; Margaillan, G.; Caron, M.C.; Cote, J.; et al. The Tumor Suppressor PALB2: Inside Out. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanenberg, H.; Andreassen, P.R. PALB2 (partner and localizer of BRCA2). Atlas Genet. Cytogenet. Oncol. Haematol. 2018, 22, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, T.; Zhang, F.; Hayakawa, N.; Ohtani, Y.; Shinmyozu, K.; Nakayama, J.; Andreassen, P.R. MRG15 binds directly to PALB2 and stimulates homology-directed repair of chromosomal breaks. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sy, S.M.; Huen, M.S.; Chen, J. MRG15 is a novel PALB2-interacting factor involved in homologous recombination. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 21127–21131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Takano-Maruyama, M.; Pereira-Smith, O.M.; Gaufo, G.O.; Tominaga, K. MRG15, a component of HAT and HDAC complexes, is essential for proliferation and differentiation of neural precursor cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 1522–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleuyard, J.Y.; Fournier, M.; Nakato, R.; Couturier, A.M.; Katou, Y.; Ralf, C.; Hester, S.S.; Dominguez, D.; Rhodes, D.; Humphrey, T.C.; et al. MRG15-mediated tethering of PALB2 to unperturbed chromatin protects active genes from genotoxic stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 7671–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Pereira-Smith, O.M.; Tominaga, K. Loss of the chromatin regulator MRG15 limits neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation via increased expression of the p21 Cdk inhibitor. Stem Cell Res. 2011, 7, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doyon, Y.; Selleck, W.; Lane, W.S.; Tan, S.; Côté, J. Structural and functional conservation of the NuA4 histone acetyltransferase complex from yeast to humans. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 1884–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jelinic, P.; Pellegrino, J.; David, G. A novel mammalian complex containing Sin3B mitigates histone acetylation and RNA polymerase II progression within transcribed loci. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardo, P.S.; Leung, J.K.; Lucchesi, J.C.; Pereira-Smith, O.M. MRG15, a novel chromodomain protein, is present in two distinct multiprotein complexes involved in transcriptional activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 50860–50866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tominaga, K.; Kirtane, B.; Jackson, J.G.; Ikeno, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Hawks, C.; Smith, J.R.; Matzuk, M.M.; Pereira-Smith, O.M. MRG15 regulates embryonic development and cell proliferation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 2924–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yochum, G.S.; Ayer, D.E. Role for the mortality factors MORF4, MRGX, and MRG15 in transcriptional repression via associations with Pf1, mSin3A, and Transducin-Like Enhancer of Split. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 7868–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luco, R.F.; Pan, Q.; Tominaga, K.; Blencowe, B.J.; Pereira-Smith, O.M.; Misteli, T. Regulation of alternative splicing by histone modifications. Science 2010, 327, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrozza, M.J.; Li, B.; Florens, L.; Suganuma, T.; Swanson, S.K.; Lee, K.K.; Shia, W.J.; Anderson, S.; Yates, J.; Washburn, M.P.; et al. Histone H3 methylation by Set2 directs deacetylation of coding regions by Rpd3S to suppress spurious intragenic transcription. Cell 2005, 123, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doyon, Y.; Côté, J. The highly conserved and multifunctional NuA4 HAT complex. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, T.; Ohtani, Y.; Hayakawa, N.; Shinmyozu, K.; Saito, M.; Ishikawa, F.; Nakayama, J. RBP2 is an MRG15 complex component and down-regulates intragenic histone H3 lysine 4 methylation. Genes Cells 2007, 12, 811–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murr, R.; Loizou, J.I.; Yang, Y.G.; Cuenin, C.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.Q.; Herceg, Z. Histone acetylation by Trrap-Tip60 modulates loading of repair proteins and repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stols, L.; Gu, M.; Dieckman, L.; Raffen, R.; Collart, F.R.; Donnelly, M.I. A new vector for high-throughput, ligation-independent cloning encoding a tobacco etch virus protease cleavage site. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 25, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzymol. 1997, 276, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkoczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liebschner, D.; Afonine, P.V.; Baker, M.L.; Bunkoczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Croll, T.I.; Hintze, B.; Hung, L.W.; Jain, S.; McCoy, A.J.; et al. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: Recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. D Struct. Biol. 2019, 75, 861–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bowman, R.B.; Moure, M.C.; Kirtane, M.B.; Welschhans, L.R.; Tominaga, K.; Pereira-Smith, M.O.; Quiocho, A.F. Multipurpose MRG domain involved in cell senescence and proliferation exhibits structural homology to a DNA-interacting domain. Structure 2006, 14, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Graveline, R.; Kumar, G.S.; Zhang, Y.; Krishnan, A.; David, G.; Radhakrishnan, I. Structural basis for molecular interactions involving MRG domains: Implications in chromatin biology. Structure 2012, 20, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, T.; Zmyslowski, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Radhakrishnan, I. Structural Basis for Multi-specificity of MRG Domains. Structure 2015, 23, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, G.S.; Chang, W.; Xie, T.; Patel, A.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.G.; David, G.; Radhakrishnan, I. Sequence requirements for combinatorial recognition of histone H3 by the MRG15 and Pf1 subunits of the Rpd3S/Sin3S corepressor complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 422, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, G.S.; Xie, T.; Zhang, Y.; Radhakrishnan, I. Solution structure of the mSin3A PAH2-Pf1 SID1 complex: A Mad1/Mxd1-like interaction disrupted by MRG15 in the Rpd3S/Sin3S complex. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 408, 987–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, P.; Huang, C.; Liu, C.P.; Yang, N.; Yu, T.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, B.; Xu, R.M. Structural Insights into Stimulation of Ash1L’s H3K36 Methyltransferase Activity through Mrg15 Binding. Structure 2019, 27, 837–845.e833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, B.; Allen, J.; Luccarini, C.; Pooley, K.A.; Shah, M.; Bolla, M.K.; Wang, Q.; Ahmed, S.; Baynes, C.; Conroy, D.M.; et al. Rare, protein-truncating variants in ATM, CHEK2 and PALB2, but not XRCC2, are associated with increased breast cancer risks. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 54, 732–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hartley, T.; Cavallone, L.; Sabbaghian, N.; Silva-Smith, R.; Hamel, N.; Aleynikova, O.; Smith, E.; Hastings, V.; Pinto, P.; Tischkowitz, M.; et al. Mutation analysis of PALB2 in BRCA1 and BRCA2-negative breast and/or ovarian cancer families from Eastern Ontario, Canada. Hered Cancer Clin. Pract. 2014, 12, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leyton, Y.; Gonzalez-Hormazabal, P.; Blanco, R.; Bravo, T.; Fernandez-Ramires, R.; Morales, S.; Landeros, N.; Reyes, J.M.; Peralta, O.; Tapia, J.C.; et al. Association of PALB2 sequence variants with the risk of familial and early-onset breast cancer in a South-American population. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kadlec, J.; Hallacli, E.; Lipp, M.; Holz, H.; Sanchez-Weatherby, J.; Cusack, S.; Akhtar, A. Structural basis for MOF and MSL3 recruitment into the dosage compensation complex by MSL1. Nat. Struct Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belotserkovskaya, R.; Raga Gil, E.; Lawrence, N.; Butler, R.; Clifford, G.; Wilson, M.D.; Jackson, S.P. PALB2 chromatin recruitment restores homologous recombination in BRCA1-deficient cells depleted of 53BP1. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bleuyard, J.Y.; Buisson, R.; Masson, J.Y.; Esashi, F. ChAM, a novel motif that mediates PALB2 intrinsic chromatin binding and facilitates DNA repair. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zong, D.; Adam, S.; Wang, Y.; Sasanuma, H.; Callen, E.; Murga, M.; Day, A.; Kruhlak, M.J.; Wong, N.; Munro, M.; et al. BRCA1 Haploinsufficiency Is Masked by RNF168-Mediated Chromatin Ubiquitylation. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 1267–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porro, A.; Sartori, A.A. Context Matters: RNF168 Connects with PALB2 to Rewire Homologous Recombination in BRCA1 Haploinsufficiency. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 1089–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luijsterburg, M.S.; Typas, D.; Caron, M.C.; Wiegant, W.W.; van den Heuvel, D.; Boonen, R.A.; Couturier, A.M.; Mullenders, L.H.; Masson, J.Y.; van Attikum, H. A PALB2-interacting domain in RNF168 couples homologous recombination to DNA break-induced chromatin ubiquitylation. Elife 2017, 6, e20922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dray, E.; Etchin, J.; Wiese, C.; Saro, D.; Williams, G.J.; Hammel, M.; Yu, X.; Galkin, V.E.; Liu, D.; Tsai, M.S.; et al. Enhancement of RAD51 recombinase activity by the tumor suppressor PALB2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buisson, R.; Dion-Cote, A.M.; Coulombe, Y.; Launay, H.; Cai, H.; Stasiak, A.Z.; Stasiak, A.; Xia, B.; Masson, J.Y. Cooperation of breast cancer proteins PALB2 and piccolo BRCA2 in stimulating homologous recombination. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 1247–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deveryshetty, J.; Peterlini, T.; Ryzhikov, M.; Brahiti, N.; Dellaire, G.; Masson, J.Y.; Korolev, S. Novel RNA and DNA strand exchange activity of the PALB2 DNA binding domain and its critical role for DNA repair in cells. Elife 2019, 8, e44063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Wavelength (Å) | 1.54 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 30–2.7 |
| Space group | P 21 2 21 |
| Unit cell dimensions a, b, c (Å) a, b, g (Å) | 54.08; 60.16; 131.85 90.00; 90.00; 90.00 |
| Total reflections | 410,291 |
| Unique reflections | 12,298 (603) * |
| Multiplicity | 4.7 (4.6) |
| Completeness (%) | 98.7 (99.5) |
| Mean I/sigma (I) | 10.2 (1.7) |
| Wilson B-factor | 28.32 |
| R-merge | 0.077 (0.65) |
| R-pim | 0.065 |
| CC1/2 | 0.995 (0.675) |
| Refinement resolution range (Å) | 29.7–2.7 |
| Reflections used in refinement | 12,252 (1180) |
| Reflections used for R-free | 1228 (131) |
| R-work | 0.226 (0.289) |
| R-free | 0.297 (0.378) |
| Number of non-hydrogen atoms | 3153 |
| RMS (bonds) | 0.009 |
| RMS (angles) | 1.269 |
| Ramachandran favored (%) | 96.8 |
| Ramachandran allowed (%) | 3.2 |
| Ramachandran outliers (%) | 0.0 |
| Clashscore | 8.4 |
| Average B-factor | 33.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Redington, J.; Deveryshetty, J.; Kanikkannan, L.; Miller, I.; Korolev, S. Structural Insight into the Mechanism of PALB2 Interaction with MRG15. Genes 2021, 12, 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12122002
Redington J, Deveryshetty J, Kanikkannan L, Miller I, Korolev S. Structural Insight into the Mechanism of PALB2 Interaction with MRG15. Genes. 2021; 12(12):2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12122002
Chicago/Turabian StyleRedington, Jennifer, Jaigeeth Deveryshetty, Lakshmi Kanikkannan, Ian Miller, and Sergey Korolev. 2021. "Structural Insight into the Mechanism of PALB2 Interaction with MRG15" Genes 12, no. 12: 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12122002
APA StyleRedington, J., Deveryshetty, J., Kanikkannan, L., Miller, I., & Korolev, S. (2021). Structural Insight into the Mechanism of PALB2 Interaction with MRG15. Genes, 12(12), 2002. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12122002







