MicroRNA 34a–AXL Axis Regulates Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Transfection
2.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.4. Western Blotting
2.5. Cell Migration Assay
2.6. Three-Dimensional Culture Assay
2.7. Transwell Invasion Assay
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression Levels of AXL are Associated with Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation In Vitro
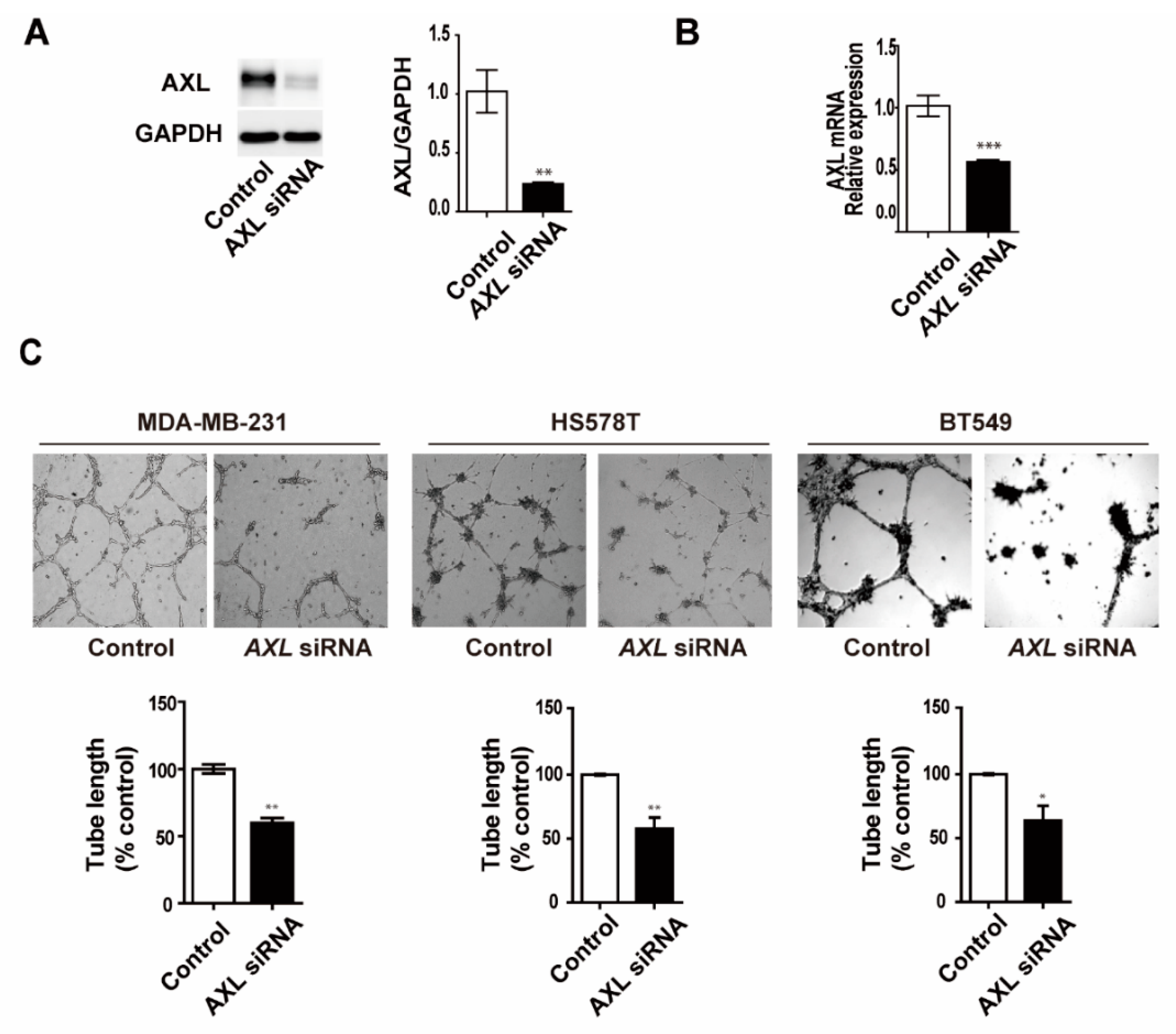
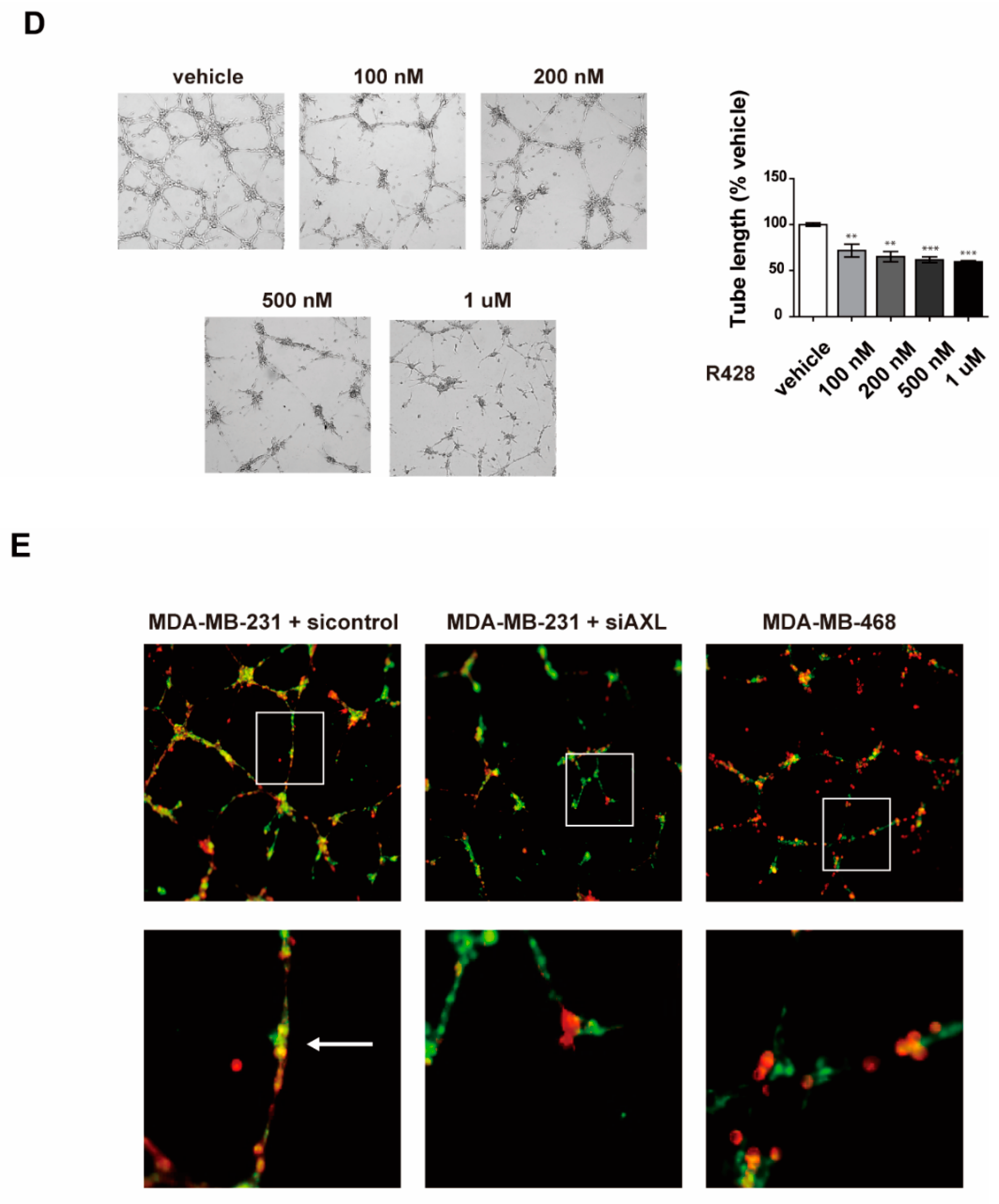
3.2. Inhibition of AXL Suppresses Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
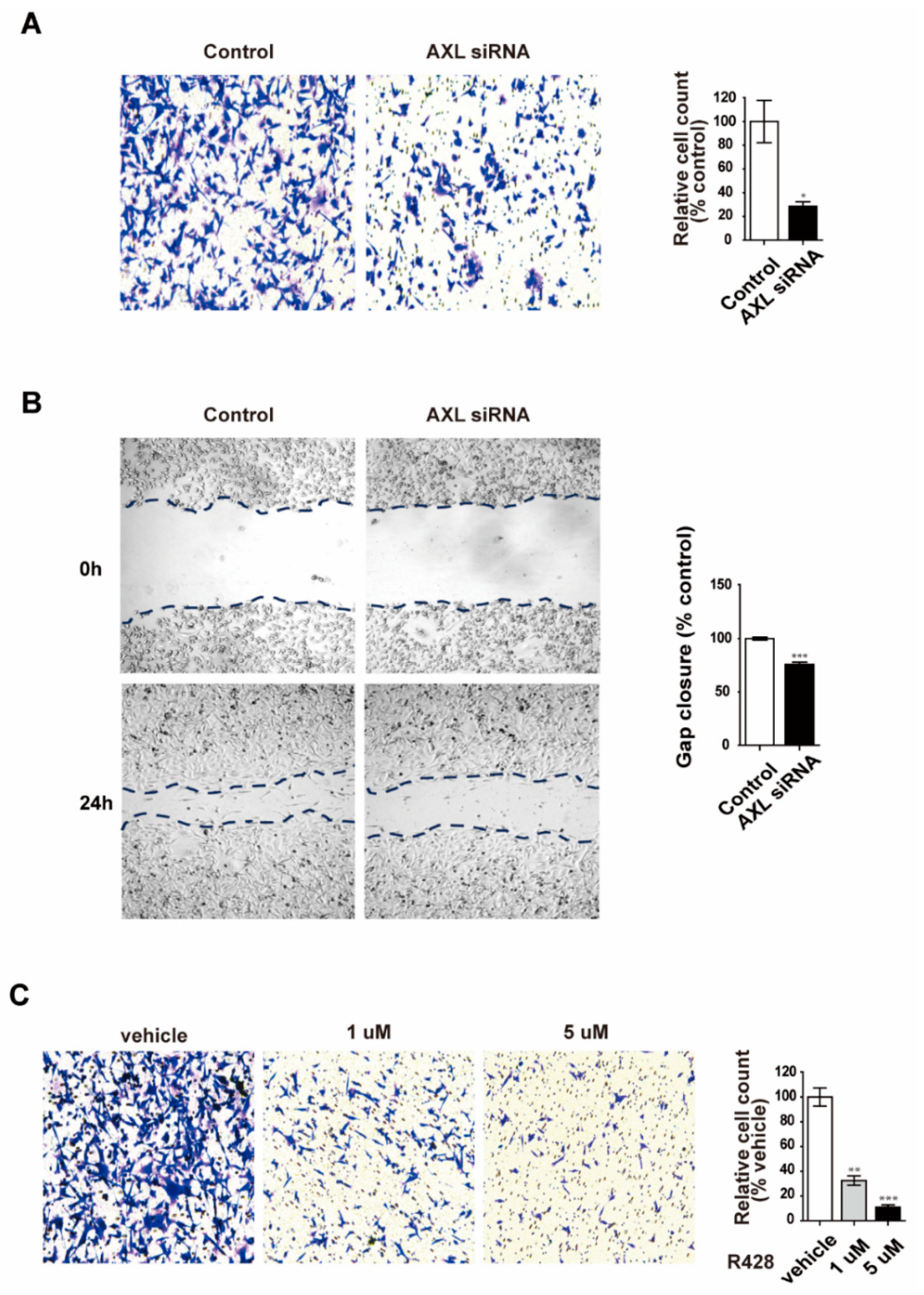
3.3. Inhibition of AXL Suppresses Cell Invasion and Migration in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
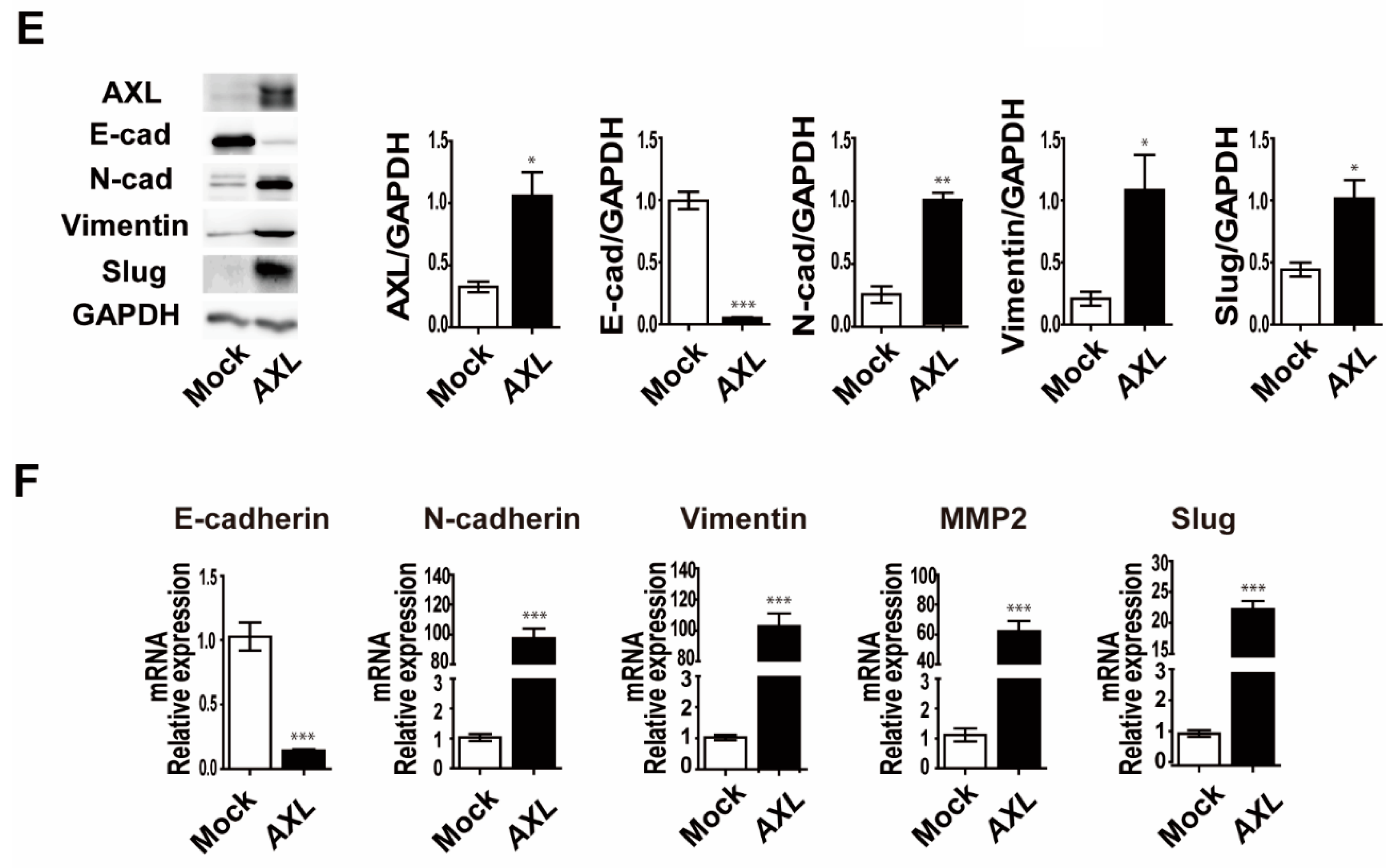
3.4. Overexpression of AXL Promotes Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation and Regulates Expression of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition Markers in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells
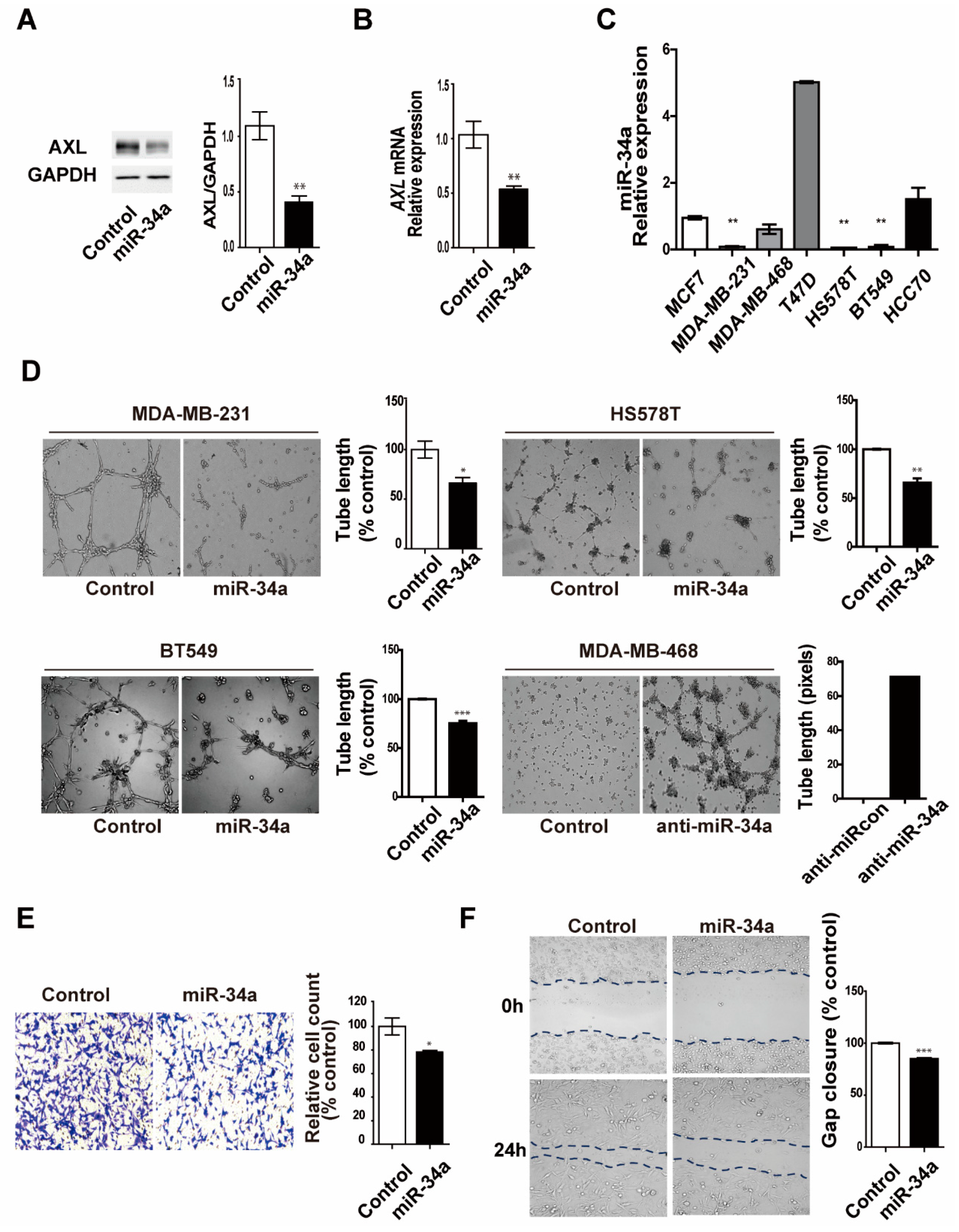
3.5. miR-34a Regulates AXL Expression and Reduces Cell Invasion, Migration, and Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akram, M.; Iqbal, M.; Daniyal, M.; Khan, A.U. Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer. Biol. Res. 2017, 50, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhan, J.R.; Andrechek, E.R. Triple-negative breast cancer and the potential for targeted therapy. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 1595–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Aggarwal, R. An overview of triple-negative breast cancer. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2016, 293, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, K.S. Regulation of post-translational modification in breast cancer treatment. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, R.; Trudeau, M.; Pritchard, K.I.; Hanna, W.M.; Kahn, H.K.; Sawka, C.A.; Lickley, L.A.; Rawlinson, E.; Sun, P.; Narod, S.A. Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4429–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, K.R.; Brown, M.; Cress, R.D.; Parise, C.A.; Caggiano, V. Descriptive analysis of estrogen receptor (ER)-negative, progesterone receptor (PR)-negative, and HER2-negative invasive breast cancer, the so-called triple-negative phenotype: A population-based study from the California cancer Registry. Cancer 2007, 109, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gucalp, A.; Traina, T.A. Targeting the androgen receptor in triple-negative breast cancer. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2016, 40, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seftor, R.E.; Hess, A.R.; Seftor, E.A.; Kirschmann, D.A.; Hardy, K.M.; Margaryan, N.V.; Hendrix, M.J. Tumor cell vasculogenic mimicry: From controversy to therapeutic promise. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 1115–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folberg, R.; Hendrix, M.J.; Maniotis, A.J. Vasculogenic mimicry and tumor angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kim, J. Regulation of IL-6 signaling by miR-125a and let-7e in endothelial cells controls vasculogenic mimicry formation of breast cancer cells. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, D.; Do, Y.; Kwon, B.S.; Chang, W.; Lee, M.S.; Kim, J.; Cho, J.G. Angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry as therapeutic targets in ovarian cancer. BMB Rep. 2020, 53, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrix, M.J.C.; Seftor, E.A.; Meltzer, P.S.; Gardner, L.M.G.; Hess, A.R.; Kirschmann, D.A.; Schatteman, G.C.; Seftor, R.E.B. Expression and functional significance of VE-cadherin in aggressive human melanoma cells: Role in vasculogenic mimicry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8018–8023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hess, A.R.; Seftor, E.A.; Gruman, L.M.; Kinch, M.S.; Seftor, R.E.B.; Hendrix, M.J.C. VE-cadherin regulates EphA2 in aggressive melanoma cells through a novel signaling pathway—Implications for vasculogenic mimicry. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2006, 5, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Qiao, L.; Liang, N.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J.; Deng, G.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J. The relationship between vasculogenic mimicry and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2016, 20, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, X.L.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, S.W.; Che, N.; Wang, X.H.; Du, J.; Liu, Y.X.; Sun, B.C. Expression and Functional Significance of Twist1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Its Role in Vasculogenic Mimicry. Hepatology 2010, 51, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lin, L.; Chen, X.; Sun, L.; Liao, Y.; Huang, N.; Liao, W. Metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 promotes vasculogenic mimicry in gastric cancer by upregulating TWIST1/2. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 11492–11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, D.J.; Chowdhury, S.; Stebbing, J. TAMing resistance to multi-targeted kinase inhibitors through Axl and Met inhibition. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2684–2686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.J.; Wei, Y.Q.; Wei, X.W. AXL receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising anti-cancer approach: Functions, molecular mechanisms and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankin, E.B.; Giaccia, A.J. The receptor tyrosine kinase axl in cancer progression. Cancers 2016, 8, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Liu, X.W.; Koul, S.; Lee, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; Halmos, B. AXL kinase as a novel target for cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 9546–9576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L. MicroRNA and metastasis. Adv. Cancer Res. 2016, 132, 165–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.M.; Zou, X.; Zhang, T.; Shen, J.; Yin, Y.X.; Xiang, J.Y. The role of miR-200a in vasculogenic mimicry and its clinical significance in ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 132, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.W.; Mu, L.Y.; Han, X.Z.; Li, Q.L.; Dong, B.J.; Li, H.L.; Liu, X.Q. MicroRNA-9 inhibits vasculogenic mimicry of glioma cell lines by suppressing Stathmin expression. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2013, 115, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudduluru, G.; Ceppi, P.; Kumarswamy, R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Papotti, M.; Allgayer, H. Regulation of Axl receptor tyrosine kinase expression by miR-34a and miR-199a/b in solid cancer. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2888–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Hermeking, H. miR-34a and miR-34b/c suppress intestinal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2746–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Jin, H.J.; Wang, N.; Fan, S.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.R.; Wei, L.; Tao, X.M.; Gu, D.S.; Zhao, F.Y.; et al. Gas6/Axl Axis contributes to chemoresistance and metastasis in breast cancer through Akt/GSK-3 β/β-catenin signaling. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1205–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, J.; Huang, R.Y. AXL-driven EMT state as a targetable conduit in cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3725–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Hu, L.; Li, J.; Fan, Z.; Wang, H.; Su, L.; Zhu, Z.; Li, C.; et al. CEACAM6 promotes tumor angiogenesis and vasculogenic mimicry in gastric cancer via FAK signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 1020–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Won, Y.J.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.; Hong, H.N.; Kim, B.S. Morphological characteristics of vasculogenic mimicry and its correlation with EphA2 expression in gastric adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, E.M.; Kendsersky, N.D.; Daniel, C.J.; Kuziel, G.M.; Pelz, C.; Murphy, K.M.; Capecchi, M.R.; Sears, R.C. ZEB1-repressed microRNAs inhibit autocrine signaling that promotes vascular mimicry of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, A.K.; Fletcher, M.S.; Zahn, C.M.; Gruman, L.M.; Coffin, J.E.; Seftor, E.A.; Hendrix, M.J. The clinical significance of tumor cell-lined vasculature in ovarian carcinoma: Implications for anti-vasculogenic therapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2002, 1, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.; Fan, G.; Li, Q. Molecular mechanisms and anticancer therapeutic strategies in vasculogenic mimicry. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 6327–6340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Zhu, B.; Wu, S.; Zhou, L.; Song, W.; Gong, X.; Wang, D. Evaluation of the correlation of vasculogenic mimicry, ALDH1, KiSS-1, and MACC1 in the prediction of metastasis and prognosis in ovarian carcinoma. Diagn. Pathol. 2017, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, X.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Huang, P.; Yan, S. Effect of AXL on the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Shi, X.; Ling, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, M. MiR-34a suppresses ovarian cancer proliferation and motility by targeting AXL. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 7277–7283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Ren, Z.J.; Tang, J.H. MicroRNA-34a: A potential therapeutic target in human cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesunloye, B.A.; Karzai, F.H.; Dahut, W.L. Angiogenesis inhibitors in the treatment of prostate cancer. Chem. Immunol. Allergy 2014, 99, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Saleem, A.F.; Zhao, X.; Sun, B. Vasculogenic mimicry: A new prognostic sign of gastric adenocarcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2010, 16, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D. Expression of Axl and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iderzorig, T.; Kellen, J.; Osude, C.; Singh, S.; Woodman, J.A.; Garcia, C.; Puri, N. Comparison of EMT mediated tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance in NSCLC. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerdrum, C.; Tiron, C.; Hoiby, T.; Stefansson, I.; Haugen, H.; Sandal, T.; Collett, K.; Li, S.; McCormack, E.; Gjertsen, B.T.; et al. Axl is an essential epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-induced regulator of breast cancer metastasis and patient survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, K.F.; Du, W.; Sorrelle, N.B.; Wnuk-Lipinska, K.; Topalovski, M.; Toombs, J.E.; Cruz, V.H.; Yabuuchi, S.; Rajeshkumar, N.V.; Maitra, A.; et al. Small-Molecule Inhibition of Axl Targets Tumor Immune Suppression and Enhances Chemotherapy in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 246–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Chen, M.; Nie, Q.; Hu, J.; Zhuo, Z.; Yiu, A.; Chen, H.; Xu, N.; Huang, M.; Ye, K.; et al. In vitro and in vivo antiangiogenic activity of desacetylvinblastine monohydrazide through inhibition of VEGFR2 and Axl pathways. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 843–858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plantamura, I.; Casalini, P.; Dugnani, E.; Sasso, M.; D’Ippolito, E.; Tortoreto, M.; Cacciatore, M.; Guarnotta, C.; Ghirelli, C.; Barajon, I.; et al. PDGFRbeta and FGFR2 mediate endothelial cell differentiation capability of triple negative breast carcinoma cells. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karroum, A.; Mirshahi, P.; Faussat, A.M.; Therwath, A.; Mirshahi, M.; Hatmi, M. Tubular network formation by adriamycin-resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cells is closely linked to MMP-9 and VEGFR-2/VEGFR-3 over-expressions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 685, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, M.D.; Lund, A.H. MicroRNA and cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 590–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misso, G.; Di Martino, M.T.; De Rosa, G.; Farooqi, A.A.; Lombardi, A.; Campani, V.; Zarone, M.R.; Gulla, A.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; et al. Mir-34: A new weapon against cancer? Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids 2014, 3, e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C.; Rack, B.; Muller, V.; Janni, W.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Circulating microRNAs as blood-based markers for patients with primary and metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Primers |
|---|---|
| Human 18s rRNA | Forward: 5′-ACCCGTTGAACCCCATTCGTGA-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-GCCTCACTAAACCATCCAATCGG-3′ | |
| Human AXL | Forward: 5′-AGGCTGAAGAAAGTCCCTTCG-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-CCCGGGCACCTGTGATATTC-3′ | |
| Human E-cadherin | Forward: 5′-GGACCTGGCAAGATGCAGAA-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-GCTGCTTGGCCTCAAAATCC-3′ | |
| Human N-cadherin | Forward: 5′-CCTCCAGAGTTTACTGCCATGAC-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-GTAGGATCTCCGCCACTGATTC-3′ | |
| Human Vimentin | Forward: 5′-AGGCAAAGCAGGAGTCCACTGA-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-ATCTGGCGTTCCAGGGACTCAT-3′ | |
| Human MMP2 | Forward: 5′-AGCGAGTGGATGCCGCCTTTAA-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-CATTCCAGGCATCTGCGATGAG-3′ | |
| Human Slug | Forward: 5′-ATCTGCGGCAAGGCGTTTTCCA-3′ |
| Reverse: 5′-GAGCCCTCAGATTTGACCTGTC-3′ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, D.; Cho, J.G.; Yun, E.; Lee, A.; Ryu, H.-Y.; Lee, Y.J.; Yoon, S.; Chang, W.; Lee, M.-S.; Kwon, B.S.; et al. MicroRNA 34a–AXL Axis Regulates Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation in Breast Cancer Cells. Genes 2021, 12, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010009
Lim D, Cho JG, Yun E, Lee A, Ryu H-Y, Lee YJ, Yoon S, Chang W, Lee M-S, Kwon BS, et al. MicroRNA 34a–AXL Axis Regulates Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation in Breast Cancer Cells. Genes. 2021; 12(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010009
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Dansaem, Jin Gu Cho, Eunsik Yun, Aram Lee, Hong-Yeoul Ryu, Young Joo Lee, Sukjoon Yoon, Woochul Chang, Myeong-Sok Lee, Byung Su Kwon, and et al. 2021. "MicroRNA 34a–AXL Axis Regulates Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation in Breast Cancer Cells" Genes 12, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010009
APA StyleLim, D., Cho, J. G., Yun, E., Lee, A., Ryu, H.-Y., Lee, Y. J., Yoon, S., Chang, W., Lee, M.-S., Kwon, B. S., & Kim, J. (2021). MicroRNA 34a–AXL Axis Regulates Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation in Breast Cancer Cells. Genes, 12(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes12010009








