Sex Chromosomes and Internal Telomeric Sequences in Dormitator latifrons (Richardson 1844) (Eleotridae: Eleotrinae): An Insight into Their Origin in the Genus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimens Collection and Identification
2.2. Cytogenetic Procedures
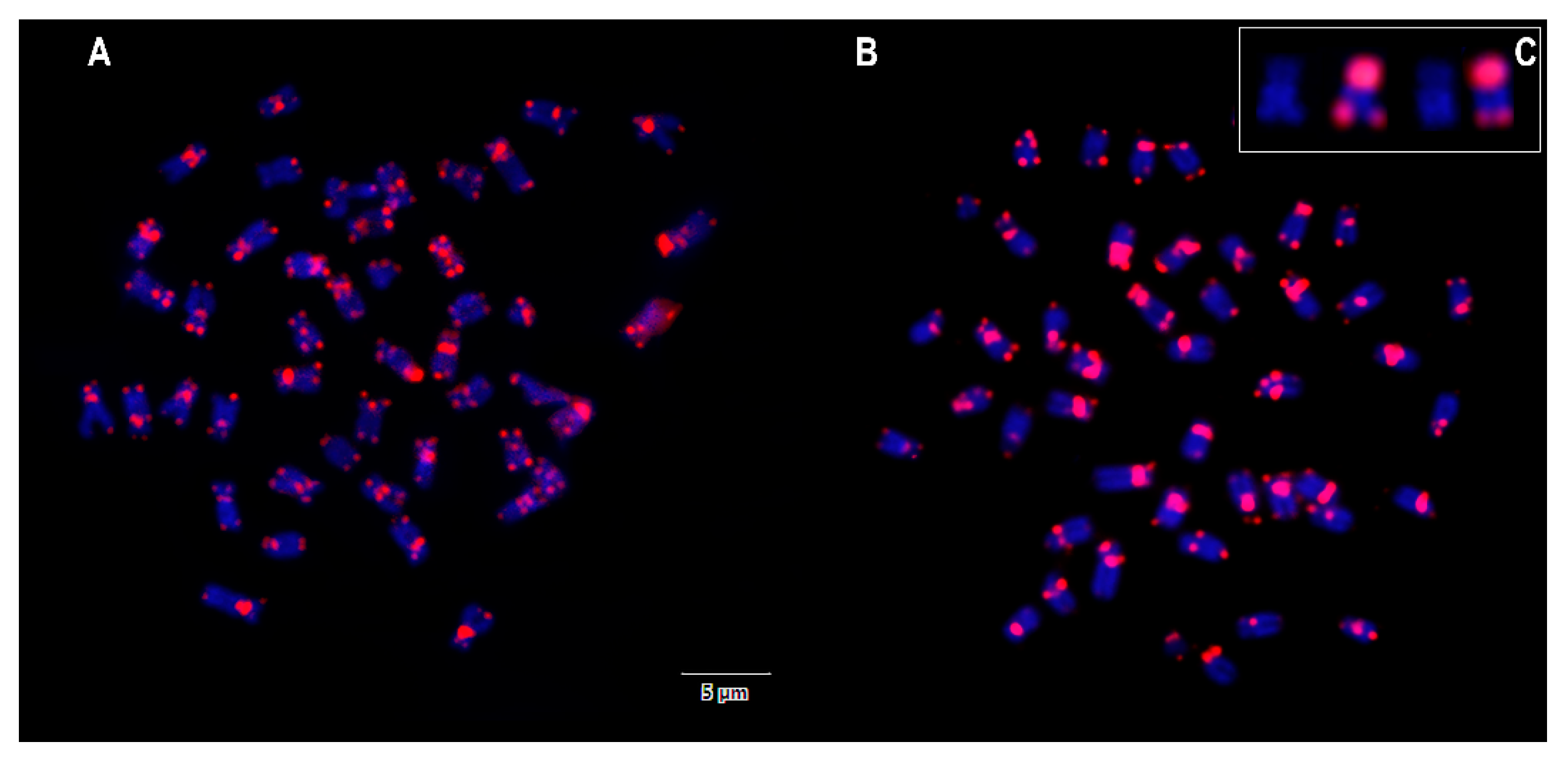
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gleick, P.H. Water resources. In Encyclopedia of Climate and Weather; Schneider, S.H., Ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Volume 2, pp. 817–823. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, J.S.; Grande, T.C.; Wilson, M.V.H. Fishes of the World, 5th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg, J.G.; Kottelat, M.; Smith, G.R.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; Gill, A.C. So many fishes, so little time: An overview of recent ichthyological discovery in continental waters. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2000, 87, 26–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussaint, A.; Charpin, N.; Brosse, S.; Villéger, S. Global functional diversity of freshwater fish is concentrated in the Neotropics while functional vulnerability is widespread. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, R.E.; Albert, J.S.; Di Dario, F.; Mincarone, M.M.; Petry, P.; Rocha, L.A. Fish biodiversity and conservation in South America. J. Fish Biol. 2016, 89, 12–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilsdorf, A.W.S.; Hallerman, E.M. Genetic Resources of Neotropical Fishes; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Nirchio, M.; Gaviria, J.I.; Siccha-Ramirez, Z.R.; Oliveira, C.; Foresti, F.; Milana, V.; Rossi, A.R. Chromosomal polymorphism and molecular variability in the pearly razorfish Xyrichtys novacula (Labriformes, Labridae): Taxonomic and biogeographic implications. Genetica 2019, 147, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Cioffi, B.M.; Wagner, F.M.; Ferreira, A.R.; Bertollo, L.A.C. Chromosomes as tools for discovering biodiversity–the case of erythrinidae fish family. Recent Trends Cytogenet. Stud. Methodol. Appl. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sember, A.; de Oliveira, E.A.; Ráb, P.; Bertollo, L.A.C.; de Freitas, N.L.; Viana, P.F.; Yano, C.F.; Hatanaka, T.; Marinho, M.M.F.; de Moraes, R.L.R.; et al. Centric Fusions behind the karyotype evolution of neotropical Nannostomus Pencilfishes (Characiforme, Lebiasinidae): First insights from a molecular cytogenetic perspective. Genes 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricke, R.; Eschmeyer, W.N.; Fong, J.D. Species by Family/Subfamily. Available online: http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/SpeciesByFamily.asp (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Froese, R.; Pauly, D. Eleotrinae Bonaparte. 1835. Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=267092 (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Patzner, R.; Van Tassell, J.L.; Kovacic, M.; Kapoor, B.G. The Biology of Gobies; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Galván-Quesada, S.; Doadrio, I.; Alda, F.; Perdices, A.; Reina, R.G.; García Varela, M.; Hernández, N.; Campos Mendoza, A.; Bermingham, E.; Domínguez-Domínguez, O. Molecular phylogeny and biogeography of the amphidromous fish genus Dormitator Gill 1861 (Teleostei: Eleotridae). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Tassell, J. Dormitator Latifrons. Available online: https://dx.doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-3.RLTS.T183257A8081686.en (accessed on 10 April 2020).
- Massay, S.; Mosquera, R. Presence of Chame Dormitator latifrons (Richardson, 1844) (Pisces: Eleotridae) in the Galapagos Islands, Ecuador. J. Fish Biol. 1992, 40, 815–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larumbe, E. Algunos aspectos biológicos de los popoyotes (Dormitator latifrons) en cautiverio. Panor. Acuícola 2002, 24–25. Available online: https://fis.com/panoramacuicola/noticias/noticia%203.htm (accessed on 15 May 2020).
- Freire-Lascano, C.A. Experiencias en el manejo del Chame (Dormitator latifrons) en la Cuenca del Río Guayas, Ecuador. Rev. Electrónica Ing. Prod. Acuícola 2013, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- de Rodríguez-Montes Oca, G.A.; Medina-Hernández, E.A.; Velázquez-Sandoval, J.; López-López, V.V.; Román-Reyes, J.C.; Dabrowski, K.; Haws, M.C. Producción de larvas de Chame (Dormitator latifrons, Pisces: Eleotridae) usando GnRHa and LHRHa. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Pecu. 2012, 25, 422–429. [Google Scholar]
- Torell, E.; Tobey, J. Enterprise Strategies for Coastal and Marine Conservation: A Review of Best Practices and Lessons Learned; Coastal Resources Center, University of Rhode Island: Narragansett, RI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- López-Huerta, J.M.; Vega-Villasante, F.; Viana, M.T.; Carrillo-Farnés, O.; Badillo-Zapata, D. First report of nutritional quality of the native fish Dormitator latifrons (Richardson, 1844) (Perciformes: Eleotridae). Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2018, 46, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jácome, J.; Quezada Abad, C.; Sánchez Romero, O.; Pérez, J.E.; Nirchio, M. Tilapia en Ecuador: Paradoja entre la producción acuícola y la protección de la biodiversidad ecuatoriana. Rev. Peru. Biol. 2019, 26, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, A. Recent advancement in fish cytogenetics. J. Anim. Genet. 2005, 32, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorshkova, G. Practical use of cytogenetics in fish biology and aquaculture. Isr. J. Aquac. Bamidgeh 2006, 58, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Ocalewicz, K.; Jankun, M.; Luczynski, M. Cytogenetic characteristics of interspecific hybrids and chromosome set manipulated finfish. In Fish Cytogenetics; Pisano, E., Ozouf-Costaz, C., Foresti, F., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2007; pp. 289–332. [Google Scholar]
- Uribe-Alcocer, M.; Espinoza, J.A.; Padilla, A.T.; Pérez, A.C. Los cromosomas de Dormitator latifrons (Pisces: Gobiidae). An. Inst. Cienc. Mar Limnol. Univ. Nac. Auton. Mex. 1982, 10, 23–30. [Google Scholar]
- Uribe-Alcocer, M.; Ramirez-Escamilla, A. Comparación citogenética entre las especies del genero Dormitator (Pisces, Gobiidae). An. Inst. Cienc. Mar Limnol. Univ. Nac. Auton. Mex. 1989, 16, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado-Monroy, M.C.; Uribe-Alcocer, M. Karyotypical studies on Dormitator maculatus bloch and Gobiomorus dormitor Lacépède (Gobiidae: Perciformes). Cytologia 1985, 50, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, W.F. Intraspecific karyotypical diversity in brackish water fishes of the Eleotridae family (Pisces, Perciformes). Cytologia 2005, 70, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oliveira, C.; de Toledo, L.F.A. Evidence of an XX/XY sex chromosome system in the fish Dormitator maculatus (Teleostei, Eleotrididae). Genet. Mol. Biol. 2006, 29, 653–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, R. Fish Karyotypes: A Check List; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Uribe-Alcocer, M.; Díaz-Jaimes, P. Chromosome complements of Gobionellus microdon and Eleotris picta collected in Mexico. J. Fish Biol. 1996, 48, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocon-Stange, E.A. Caracterização cromossômica de Eleotris pisonis (Perciformes, Eleotrididae). In Proceedings of the IV Simpósio de Citogenética Evolutiva e Aplicada de Peixes Neotropicais, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 22–24 September 1992; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Masagca, J.T.; Sumantadinata, K. Chromosomal characters of the Indonesian sand goby, Oxyeleotris marmorata Blkr. 1874 (Eleotridae). Biotropia Southeast Asian J. Trop. Biol. 1994, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinthong, K.; Supiwong, W.; Tanomtong, A.; Hongsachart, P.; Phaengphairee, P.; Chantarangsee, M. A first karyological analysis of the sand goby, Oxyeleotris marmoratus (Teleostei, Eleotridae) in Thailand by Ag-NOR Staining Technique. Cytologia 2014, 79, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlesworth, B. Sex determination: Primitive Y chromosomes in fish. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, R745–R747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Takehana, Y.; Naruse, K.; Hamaguchi, S.; Sakaizumi, M. Evidence for different origins of sex chromosomes in closely related Oryzias fishes: Substitution of the master sex-determining gene. Genetics 2007, 177, 2075–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gornung, E. Twenty years of physical mapping of major ribosomal RNA genes across the Teleosts: A review of research. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2013, 141, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symonová, R.; Howell, W.M. Vertebrate genome evolution in the light of fish Cytogenomics and rDNAomics. Genes 2018, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, M.B.; Martins, C.; Bertollo, L.A.C. Chromosome spreading of associated transposable elements and ribosomal DNA in the fish Erythrinus erythrinus. Implications for genome change and karyoevolution in fish. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Prado, P.; Agruirre, W.; Moncayo, E.; Amaya, R.; Salazar, N.; Iván, F.; Rivera, J. Guía de Peces Para Aguas Continentales en la Vertiente Occidental del Ecuador; Pontificia Universidad Católica del Ecuador Sede Esmeraldas (PUCESE): Quito, Ecuador, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, R.; Ruiz Rejon, C.; Ruiz Rejon, M. A method for increasing the number of mitoses available for cytogenetic analysis in rainbow trout. Stain Technol. 1988, 63, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, S.L.; Underwood, W.; Anthony, R.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.; Poison, A.; Meyer, R. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals, 2013 ed.; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nirchio, M.; Oliveira, C. Citogenética de Peces; Universidad de Oriente: Cumaná, Venezuela, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Howell, W.M.; Black, D.A. Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: A 1-step method. Experientia 1980, 36, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, A.T. A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 1972, 75, 304–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinkel, D.; Straume, T.; Gray, J.W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 2934–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levan, A.; Fredga, K.; Sandberg, A.A. Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 1964, 52, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mank, J.E.; Avise, J.C. Phylogenetic conservation of chromosome numbers in Actinopterygiian fishes. Genetica 2006, 127, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kottler, V.A.; Schartl, M. The colorful sex chromosomes of Teleost fish. Genes 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, R.H.; Nagahama, Y. Sex determination and sex differentiation in fish: An overview of genetic, physiological, and environmental influences. Aquaculture 2002, 208, 191–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.; Almeida-Toledo, L.F.; Foresti, F. Karyotypic evolution in neotropical fishes. In Fish Cytogenetics; Pisano, E., Ozouf-Costaz, C., Foresti, F., Kapoor, B.G., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2007; pp. 111–164. [Google Scholar]
- Cioffi, M.B.; Camacho, J.P.M.; Bertollo, L.A.C. Repetitive DNAs and differentiation of sex chromosomes in neotropical fishes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2011, 132, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Cioffi, M.B.; Yano, C.F.; Sember, A.; Bertollo, L.A.C. Chromosomal evolution in lower Vertebrates: Sex chromosomes in Neotropical fishes. Genes 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitano, J.; Peichel, C.L. Turnover of sex chromosomes and speciation in fishes. Environ. Biol. Fishes 2012, 94, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, J.K.; Nordén, A.K.; Hansson, B. Sex chromosome evolution: Historical insights and future perspectives. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2017, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultheis, C.; Böhne, A.; Schartl, M.; Volff, J.N.; Galiana-Arnoux, D. Sex determination diversity and sex chromosome evolution in poeciliid fish. Sex Dev. 2009, 3, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalopin, D.; Volff, J.-N.; Galiana, D.; Anderson, J.L.; Schartl, M. Transposable elements and early evolution of sex chromosomes in fish. Chromosome Res. 2015, 23, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezaz, T.; Deakin, J.E. Repetitive sequence and sex chromosome evolution in Vertebrates. Adv. Evol. Biol. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.E.; Dean, R.; Zimmer, F.; Mank, J.E. How to make a sex chromosome. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crown, K.N.; Miller, D.E.; Sekelsky, J.; Hawley, R.S. Local inversion heterozygosity alters recombination throughout the genome. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, 2984–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.; Martinez, J.L.; Garcia-Vazquez, E.; Pendas, A.M. Sex chromosome linkage of 5S rDNA in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1996, 75, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scacchetti, P.C.; Utsunomia, R.; Pansonato-Alves, J.C.; Vicari, M.R.; Artoni, R.F.; Oliveira, C.; Foresti, F. Chromosomal mapping of repetitive DNAs in Characidium (Teleostei, Characiformes): Genomic organization and diversification of ZW sex chromosomes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 146, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.A.; Feldberg, E.; Carvalho, N.D.M.; Hernandez Rangel, S.M.; Schneider, C.H.; Carvalho-Zilse, G.A.; Da Silva, V.F.; Gross, M.C. Effects of environmental pollution on the rDNAomics of Amazonian fish. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 252, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Kobayashi, T. How do cells count multi-copy genes? “Musical Chair” model for preserving the number of rDNA copies. Curr. Genet. 2019, 65, 883–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolzán, A.D. Interstitial telomeric sequences in vertebrate chromosomes: Origin, function, instability and evolution. Mutat. Res. Mutat. Res. 2017, 773, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocalewicz, K.; Furgala-Selezniow, G.; Szmyt, M.; Lisboa, R.; Kucinski, M.; Lejk, A.M.; Jankun, M. Pericentromeric location of the telomeric DNA sequences on the European grayling chromosomes. Genetica 2013, 141, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrioli, M.; Bizzaro, D.; Manicardi, G.C.; Gionghi, D.; Bassoli, L.; Bianchi, U. Cytogenetic and molecular characterization of a highly repeated DNA sequence in the peach potato aphid Myzus persicae. Chromosoma 1999, 108, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Herrera, A.; Nergadze, S.G.; Santagostino, M.; Giulotto, E. Telomeric repeats far from the ends: Mechanisms of origin and role in evolution. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 122, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, S.; Deiana, A.; Elisabetta, C.; Floridia, G.; Rossi, E.; Zuffardi, O. Colocalization of (TTAGGG)n telomeric sequences and ribosomal genes in Atlantic eels. Chromosome Res. 1995, 3, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gornung, E.; Mannarelli, M.E.; Rossi, A.R.; Sola, L. Chromosomal evolution in Mugilidae (Pisces, Mugiliformes): FISH mapping of the (TTAGGG) telomeric repeat in the six Mediterranean mullets. Hereditas 2004, 140, 158–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.R.; Gornung, E.; Sola, L.; Nirchio, M. Comparative molecular cytogenetic analysis of two congeneric species, Mugil curema and M. liza (Pisces, Mugiliformes), characterized by significant karyotype diversity. Genetica 2005, 125, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libertini, A.; Vitturi, R.; Lannino, A.; Maone, M.C.; Franzoi, P.; Riccato, F.; Colomba, S. FISH mapping of 18S rDNA and (TTAGGG)n sequences in two pipefish species (Gasteroisteiformes: Syngnathidae). J. Genet. 2006, 85, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksenova, A.Y.; Mirkin, S.M. At the beginning of the end and in the middle of the beginning: Structure and maintenance of telomeric DNA repeats and interstitial telomeric sequences. Genes 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocalewicz, K. Telomeres in fishes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2013, 141, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, R.; Ráb, P. Chromosome evolution in the Salmonidae (Pisces): An update. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2001, 76, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slijepcevic, P. Telomeres and mechanisms of Robertsonian fusion. Chromosoma 1998, 107, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.G. Manipulation of chromosomes in fish: Review of various techniques and their implications in aquaculture. Bangladesh J. Fish. Res. 1998, 2, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Arai, K.; Fujimoto, T. Chromosome manipulation techniques and applications to aquaculture. In Sex Control in Aquaculture; Wang, H.-P., Piferrer, F., Chen, S.-H., Shen, Z.-G., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 137–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Long, J.; Tao, W.; Li, M.; Wang, D. Screening and characterization of sex-linked DNA markers and marker-assisted selection in the Southern catfish (Silurus meridionalis). Aquaculture 2020, 517, 734783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Species | 2n | Karyotype Composition | FN | Sampling Area | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eleotrinae | |||||
| D. latifrons | 46 | 44m/sm + 2st/a | 90 | Mexico | [25] |
| D. latifrons | 46 | 44m/sm + 2st/a | 90 | Mexico | [26] |
| D. latifrons | 46 | 42m/sm + 4a (♀) 41m/sm + 5a (♂) | 88/87 | Ecuador | This paper |
| D. maculatus | 46 | 44m/sm + 2st/a | 90 | Mexico | [26] |
| D. maculatus | 46 | 34m/sm + 12st/a | 80 | Brazil | [27] |
| D. maculatus | 46 | 40m/sm + 6st/a | 86 | Brazil | [28] |
| D. maculatus | 46 | 14m + 28sm + 2st + 2a (♀); 13m + 28sm + 3st + 2a (♂) | 90 | Brazil | [29] |
| Eleotris acanthopoma | 46 | 46st/a | 46 | Japan | [30] |
| Eleotris oxycephala | 46 | 46a | 46 | China | [30] |
| E. oxycephala | 46 | 46a | 46 | China | [30] |
| Eleotris picta | 52 | 52a | 52 | Mexico | [31] |
| E. pisonis | 46 | 2m/sm + 42st/a | 46 | Mexico | [31] |
| E. pisonis | 46 | 46a | 46 | Unknown | [32] |
| E. pisonis | 46 | 46a | 46 | Brazil | [28] |
| Gobiomorus dormitor | 48 | 6m/sm + 42a | 54 | Mexico | [27] |
| Hypseleotris cyprinoides | 48 | 48a | 48 | Japan | [30] |
| Mogurnda mogurnda | 46 | 6sm + 40st/a | 52 | Australia | [30] |
| Butinae | |||||
| Ophiocara porocephala | 48 | 48a | 48 | Thailand | [30] |
| Oxyeleotris marmorata | 46 | 2m + 2sm + 42a | 50 | Thailand | [30] |
| O. marmorata | 46 | 4sm + 42a | 50 | Indonesia | [33] |
| O. marmorata | 46 | 2m + 2sm+ 42a | 50 | Thailand | [34] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paim, F.G.; Nirchio, M.; Oliveira, C.; Rossi, A.R. Sex Chromosomes and Internal Telomeric Sequences in Dormitator latifrons (Richardson 1844) (Eleotridae: Eleotrinae): An Insight into Their Origin in the Genus. Genes 2020, 11, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060659
Paim FG, Nirchio M, Oliveira C, Rossi AR. Sex Chromosomes and Internal Telomeric Sequences in Dormitator latifrons (Richardson 1844) (Eleotridae: Eleotrinae): An Insight into Their Origin in the Genus. Genes. 2020; 11(6):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060659
Chicago/Turabian StylePaim, Fabilene Gomes, Mauro Nirchio, Claudio Oliveira, and Anna Rita Rossi. 2020. "Sex Chromosomes and Internal Telomeric Sequences in Dormitator latifrons (Richardson 1844) (Eleotridae: Eleotrinae): An Insight into Their Origin in the Genus" Genes 11, no. 6: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060659
APA StylePaim, F. G., Nirchio, M., Oliveira, C., & Rossi, A. R. (2020). Sex Chromosomes and Internal Telomeric Sequences in Dormitator latifrons (Richardson 1844) (Eleotridae: Eleotrinae): An Insight into Their Origin in the Genus. Genes, 11(6), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11060659






