Transcriptomic Analysis of the Chicken MDA5 Response Genes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus
2.2. Construction of Expression Vectors
2.3. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assays
2.4. RNA Sequencing
2.5. Transcriptome Analysis
2.6. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.7. Viral Infection and Titer Determination
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. ChMDA5 and Poly(I:C) Significantly Activated Chicken IFN-β Expression
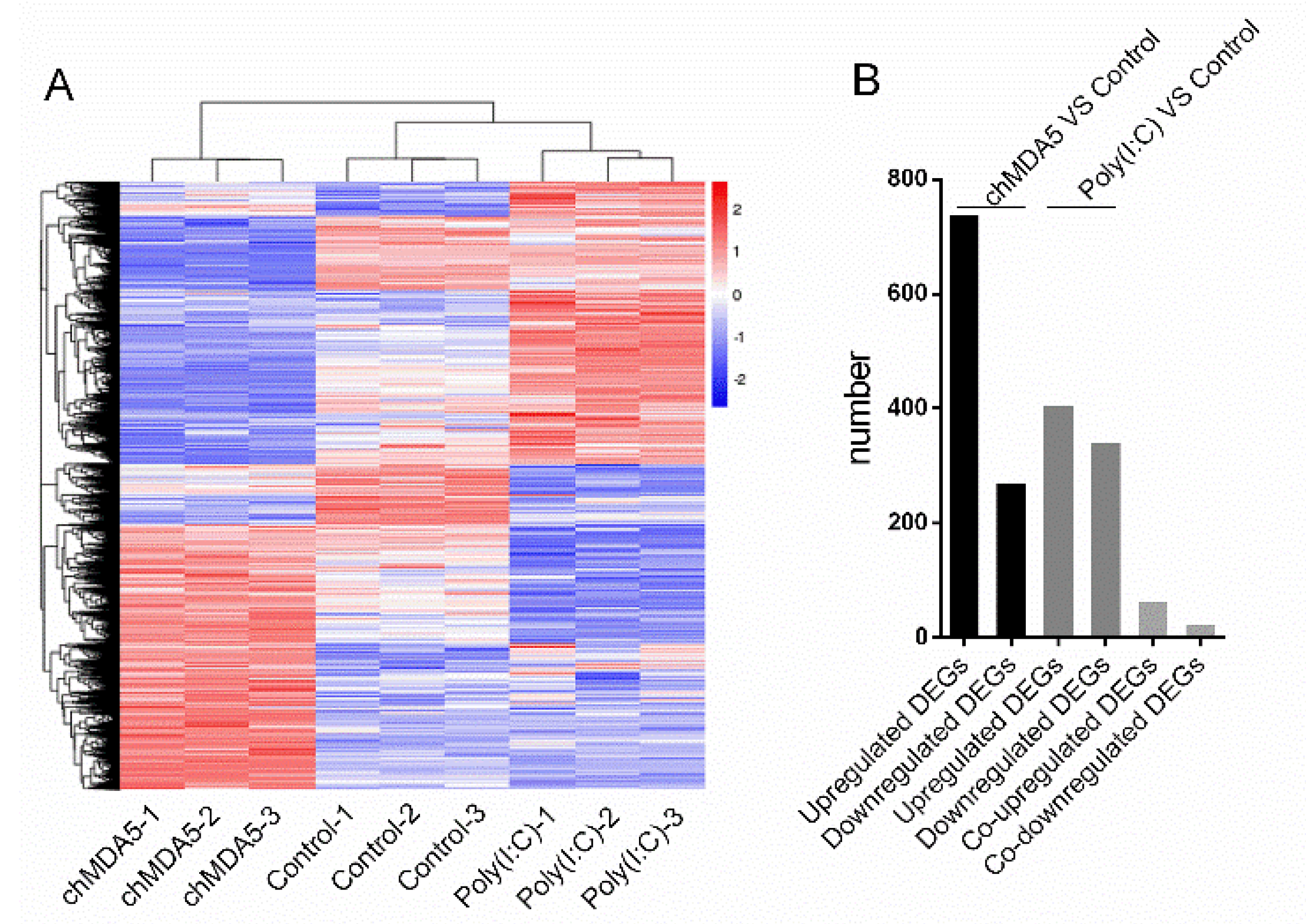
3.2. Host Response to ChMDA5 and Poly(I:C)
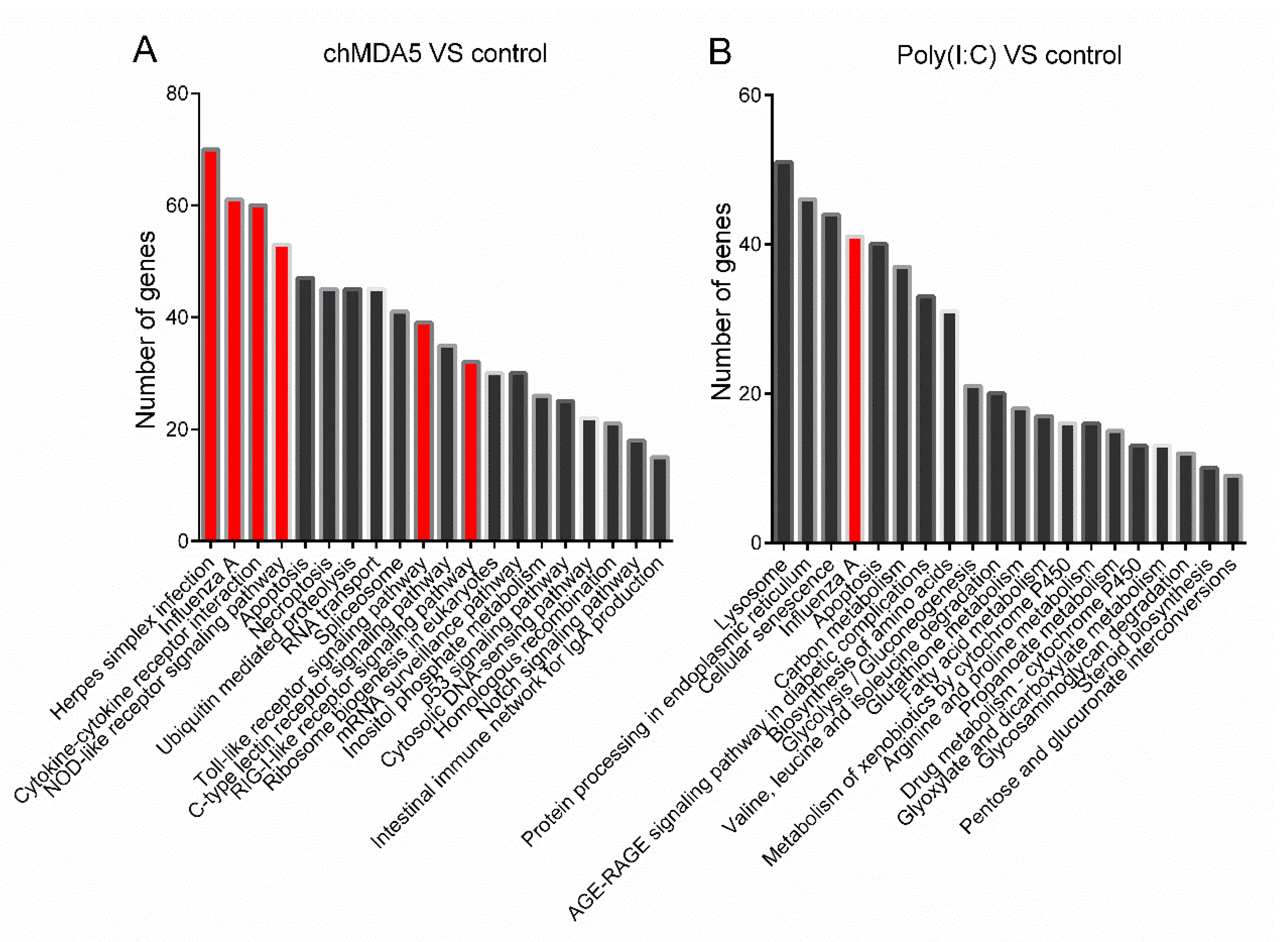
3.3. GO and KEGG Analysis
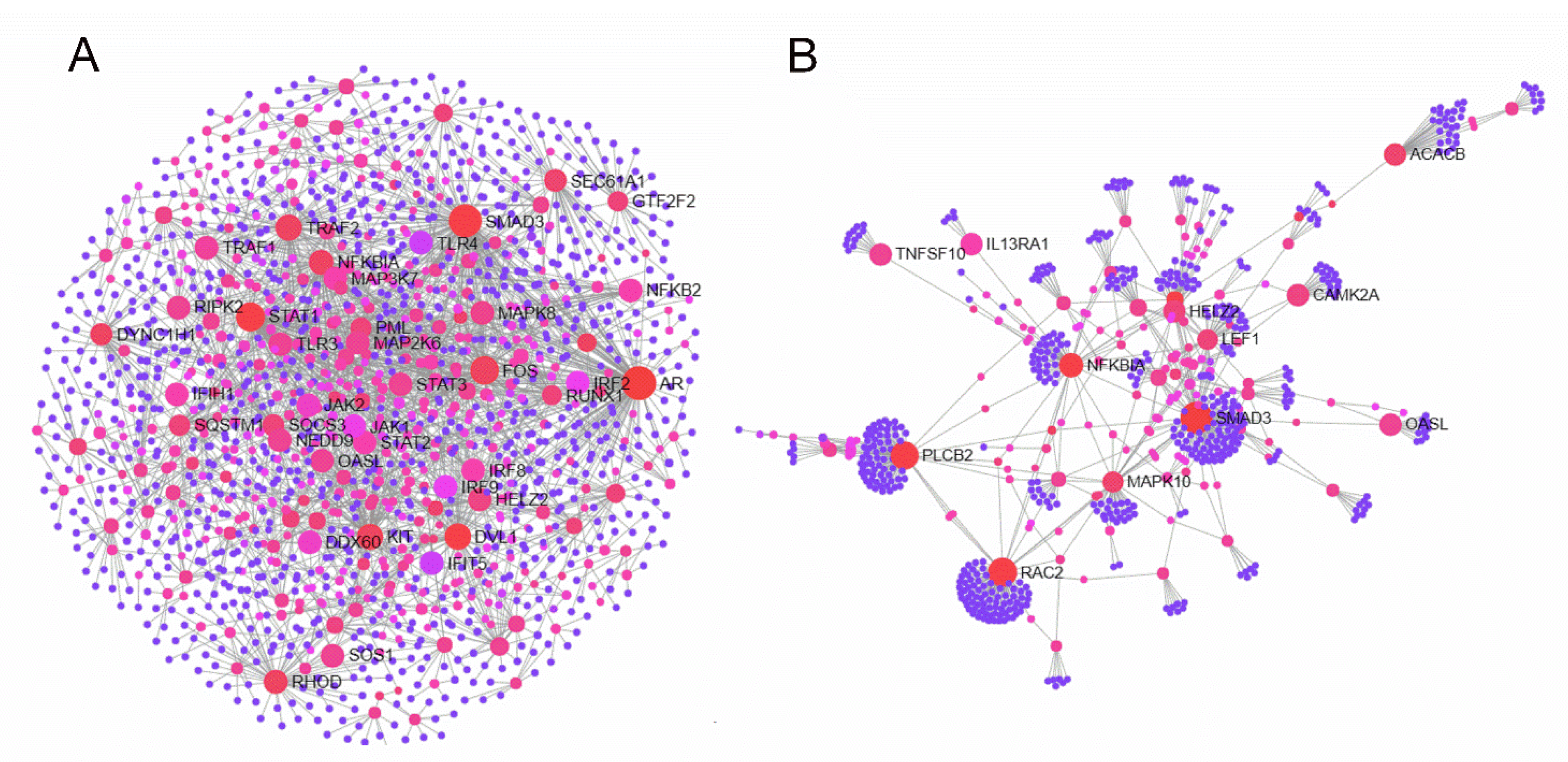
3.4. Network Analysis of the DEGs
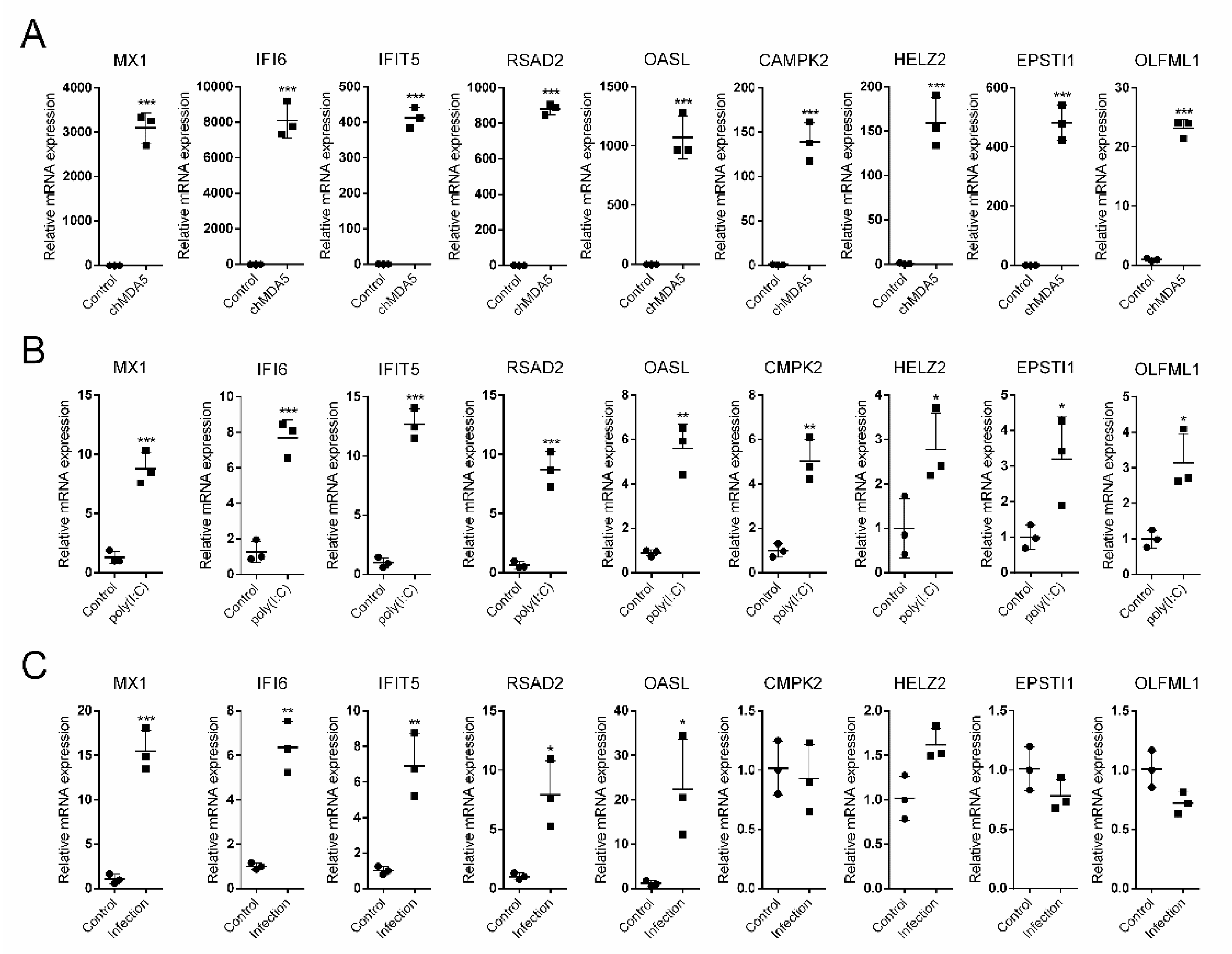
3.5. Validation of the Upregulated Genes in Both chMDA5 and poly(I:C) Groups
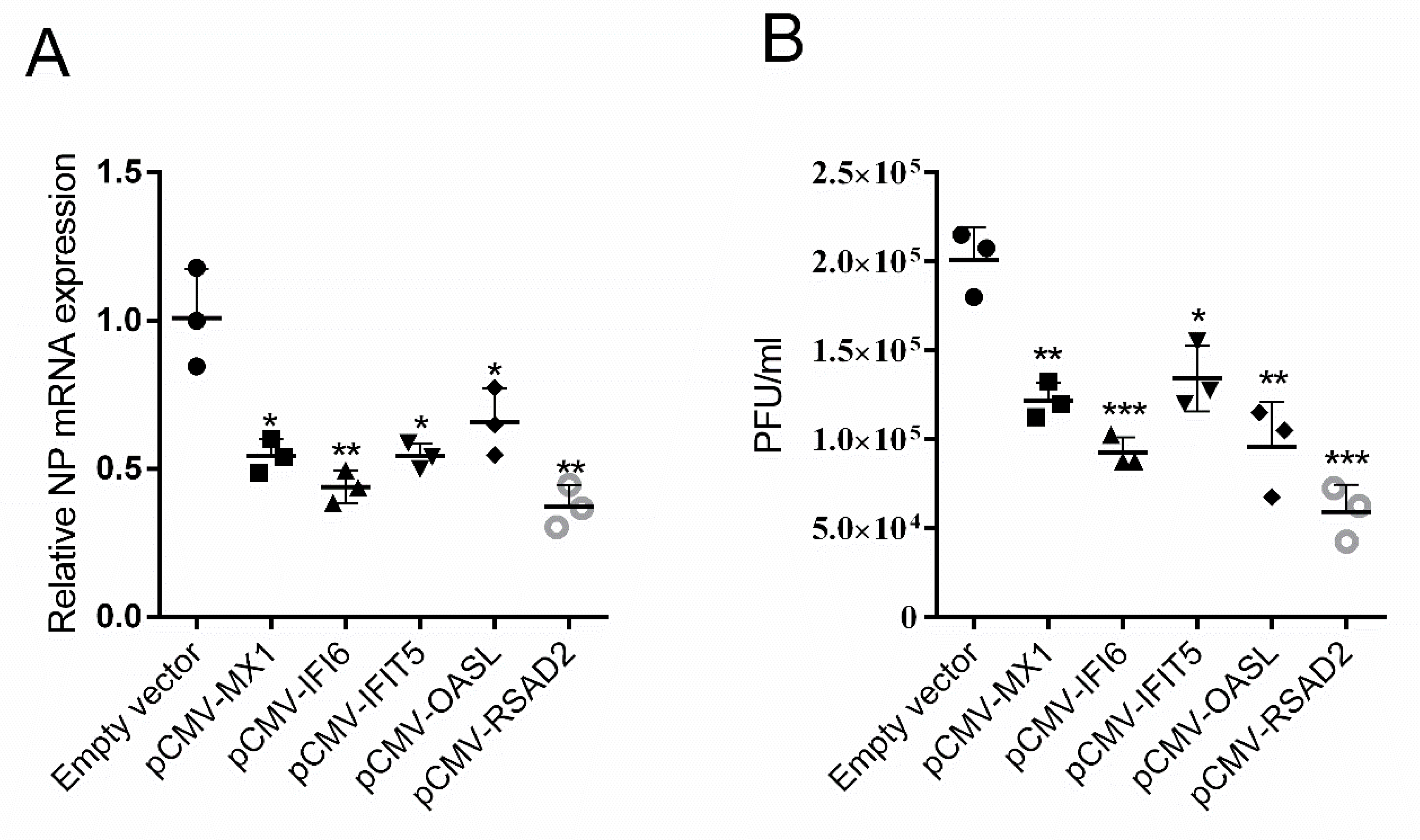
3.6. Chicken MX1, IFI6, IFIT5, RSAD2, and OASL Significantly Inhibited H5N6 Virus Infection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Recognition of viruses by innate immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 220, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Eisenächer, K.; Kirchhofer, A.; Brzózka, K.; Lammens, A.; Lammens, K.; Fujita, T.; Conzelmann, K.K.; Krug, A.; Hopfner, K.P. The C-terminal regulatory domain is the RNA 5′-triphosphate sensor of RIG-I. Mol. Cell 2008, 29, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Takahashi, K.; Sato, S.; Coban, C.; Kumar, H.; Kato, H.; Ishii, K.J.; Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. IPS-1, an adaptor triggering RIG-I- and Mda5-mediated type I interferon induction. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meylan, E.; Curran, J.; Hofmann, K.; Moradpour, D.; Binder, M.; Bartenschlager, R.; Tschopp, J. Cardif is an adaptor protein in the RIG-I antiviral pathway and is targeted by hepatitis C virus. Nature 2005, 437, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Imaizumi, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Taira, K.; Foy, E.; Loo, Y.M.; Gale, M., Jr.; Akira, S.; et al. Shared and unique functions of the DExD/H-box helicases RIG-I, MDA5, and LGP2 in antiviral innate immunity. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komuro, A.; Horvath, C.M. RNA- and virus-independent inhibition of antiviral signaling by RNA helicase LGP2. J. Virol. 2006, 80, 12332–12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenfusser, S.; Goutagny, N.; DiPerna, G.; Gong, M.; Monks, B.G.; Schoenemeyer, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Akira, S.; Fitzgerald, K.A. The RNA helicase Lgp2 inhibits TLR-independent sensing of viral Replication by retinoic acid-inducible gene-I. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5260–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, T.; Kato, H.; Kumagai, Y.; Yoneyama, M.; Sato, S.; Matsushita, K.; Tsujimura, T.; Fujita, T.; Akira, S.; Takeuchi, O. LGP2 is a positive regulator of RIG-I- and MDA5-mediated antiviral responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1512–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichlmair, A.; Schulz, O.; Tan, C.P.; Näslund, T.I.; Liljeström, P.; Weber, F.; Reis e Sousa, C. RIG-I-mediated antiviral responses to single-stranded RNA bearing 5′-phosphates. Science 2006, 314, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Mikamo-Satoh, E.; Hirai, R.; Kawai, T.; Matsushita, K.; Hiiragi, A.; Dermody, T.S.; Fujita, T.; Akira, S. Length-dependent recognition of double-stranded ribonucleic acids by retinoic acid-inducible gene-I and melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liniger, M.; Summerfield, A.; Zimmer, G.; McCullough, K.C.; Ruggli, N. Chicken cells sense influenza A virus infection through MDA5 and CARDIF signaling involving LGP2. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 705–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredericksen, B.L.; Keller, B.C.; Fornek, J.; Katze, M.G.; Gale, M. Establishment and maintenance of the innate antiviral response to West Nile Virus involves both RIG-I and MDA5 signaling through IPS-1. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitlin, L.; Benoit, L.; Song, C.; Cella, M.; Gilfillan, S.; Holtzman, M.J.; Colonna, M. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) is involved in the innate immune response to Paramyxoviridae infection in vivo. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1000734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Takeuchi, O.; Sato, S.; Yoneyama, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Matsui, K.; Uematsu, S.; Jung, A.; Kawai, T.; Ishii, K.J.; et al. Differential roles of MDA5 and RIG-I helicases in the recognition of RNA viruses. Nature 2006, 441, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, M.R.; Aldridge, J.R.; Webster, R.G.; Magor, K.E. Association of RIG-I with innate immunity of ducks to influenza. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5913–5918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Chang, M.; Nie, P.; Secombes, C.J. Origin and evolution of the RIG-I like RNA helicase gene family. BMC Evol. Biol. 2009, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.R.; Aldridge, J.R.; Fleming-Canepa, X.; Wang, Y.D.; Webster, R.G.; Magor, K.E. Identification of avian RIG-I responsive genes during influenza infection. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 54, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Jia, Y.; Ren, J.; Liu, H.; Adam, F.A.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. Insights into the chicken bursa of fabricius response to Newcastle disease virus at 48 and 72 hours post-infection through RNA-seq. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 236, 108389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpala, A.J.; Stewart, C.; McKay, J.; Lowenthal, J.W.; Bean, A.G. Characterization of chicken Mda5 activity: Regulation of IFN-beta in the absence of RIG-I functionality. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5397–5405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liniger, M.; Summerfield, A.; Ruggli, N. MDA5 can be exploited as efficacious genetic adjuvant for DNA vaccination against lethal H5N1 influenza virus infection in chickens. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cormican, P.; Lloyd, A.T.; Downing, T.; Connell, S.J.; Bradley, D.; O’Farrelly, C. The avian Toll-Like receptor pathway--subtle differences amidst general conformity. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2009, 33, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Zhou, H. Functional Analysis of Chicken IRF7 in Response to dsRNA Analog Poly(I:C) by Integrating Overexpression and Knockdown. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133450. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, P.J. The JAK-STAT signaling pathway: Input and output integration. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 2623–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, D.E.; Darnell, J.E. Stats: Transcriptional control and biological impact. Nature reviews. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 651–662. [Google Scholar]
- Kurokawa, C.; Iankov, I.D.; Galanis, E. A key anti-viral protein, RSAD2/VIPERIN, restricts the release of measles virus from infected cells. Virus Res. 2019, 263, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Zheng, C.; Sun, J.; Luo, D.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, H. Viperin Inhibits Enterovirus A71 Replication by Interacting with Viral 2C Protein. Viruses 2018, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hinson, E.R.; Cresswell, P. The interferon-inducible protein viperin inhibits influenza virus release by perturbing lipid rafts. Cell Host Microbe 2007, 2, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, O.G.; Sirma, H.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Haller, O. Mx1 GTPase accumulates in distinct nuclear domains and inhibits influenza A virus in cells that lack promyelocytic leukaemia protein nuclear bodies. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 2315–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumpey, T.M.; Szretter, K.J.; Van Hoeven, N.; Katz, J.M.; Kochs, G.; Haller, O.; García-Sastre, A.; Staeheli, P. The Mx1 gene protects mice against the pandemic 1918 and highly lethal human H5N1 influenza viruses. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 10818–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatsumi, R.; Hamada, K.; Sekiya, S.; Wakamatsu, M.; Namikawa, T.; Mizutani, M.; Sokawa, Y. 2′,5′-oligoadenylate synthetase gene in chicken: Gene structure, distribution of alleles and their expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1494, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, J.; Anwar, J.; Eskildsen-Larsen, S.; Rebouillat, D.; Paludan, S.R.; Sen, G.; Williams, B.R.; Hartmann, R. The p59 oligoadenylate synthetase-like protein possesses antiviral activity that requires the C-terminal ubiquitin-like domain. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 2767–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichlmair, A.; Lassnig, C.; Eberle, C.A.; Górna, M.W.; Baumann, C.L.; Burkard, T.R.; Bürckstümmer, T.; Stefanovic, A.; Krieger, S.; Bennett, K.L.; et al. IFIT1 is an antiviral protein that recognizes 5′-triphosphate RNA. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Diwany, R.; Soliman, M.; Sugawara, S.; Breitwieser, F.; Skaist, A.; Coggiano, C.; Sangal, N.; Chattergoon, M.; Bailey, J.R.; Siliciano, R.F.; et al. CMPK2 and BCL-G are associated with type 1 interferon-induced HIV restriction in humans. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat0843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, B.; Chen, L.; Yao, J.; Liu, J.; Kuang, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Elkady, G.; Lu, Y.; et al. Identification of fish CMPK2 as an interferon stimulated gene against SVCV infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 92, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Yang, D.; Yu, R.; Zhu, H. EPSTI1 Is Involved in IL-28A-Mediated Inhibition of HCV Infection. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 716315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguejiofor, C.F.; Cheng, Z.; Abudureyimu, A.; Anstaett, O.L.; Brownlie, J.; Fouladi-Nashta, A.A.; Wathes, D.C. Global transcriptomic profiling of bovine endometrial immune response in vitro. II. Effect of bovine viral diarrhea virus on the endometrial response to lipopolysaccharide. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 93, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, D.N.; Pratt, H.; Kandilas, S.; Cheon, S.S.; Lin, W.; Cronkite, D.A.; Basavappa, M.; Jeffrey, K.L.; Anselmo, A.; Sadreyev, R.; et al. HELZ2 Is an IFN Effector Mediating Suppression of Dengue Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, S.; Mao, H.; Jin, M.; Lin, X. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Chicken MDA5 Response Genes. Genes 2020, 11, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030308
Yu S, Mao H, Jin M, Lin X. Transcriptomic Analysis of the Chicken MDA5 Response Genes. Genes. 2020; 11(3):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030308
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Shiman, Haiying Mao, Meilin Jin, and Xian Lin. 2020. "Transcriptomic Analysis of the Chicken MDA5 Response Genes" Genes 11, no. 3: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030308
APA StyleYu, S., Mao, H., Jin, M., & Lin, X. (2020). Transcriptomic Analysis of the Chicken MDA5 Response Genes. Genes, 11(3), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030308



