Transcriptomic Profiling of DAF-7/TGFβ Pathway Mutants in C. elegans
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. C. elegans Strains and Maintenance
2.2. RNA Isolation
2.3. Next-Generation Sequencing on Illumina Platforms
2.4. Data Assessment
2.5. Data Visualization and Gene Ontology
2.6. Data Validation by qRT-PCR
3. Results
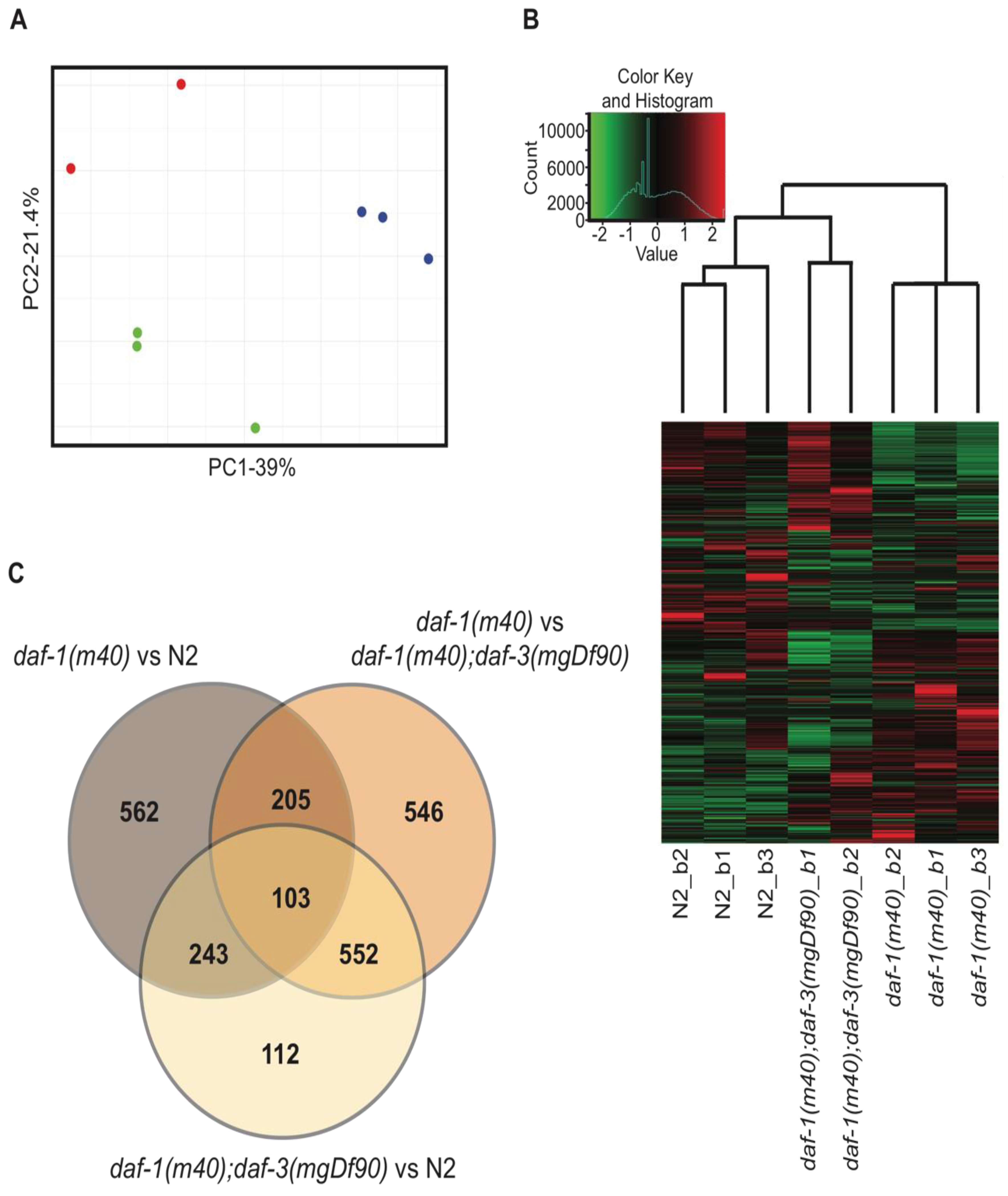
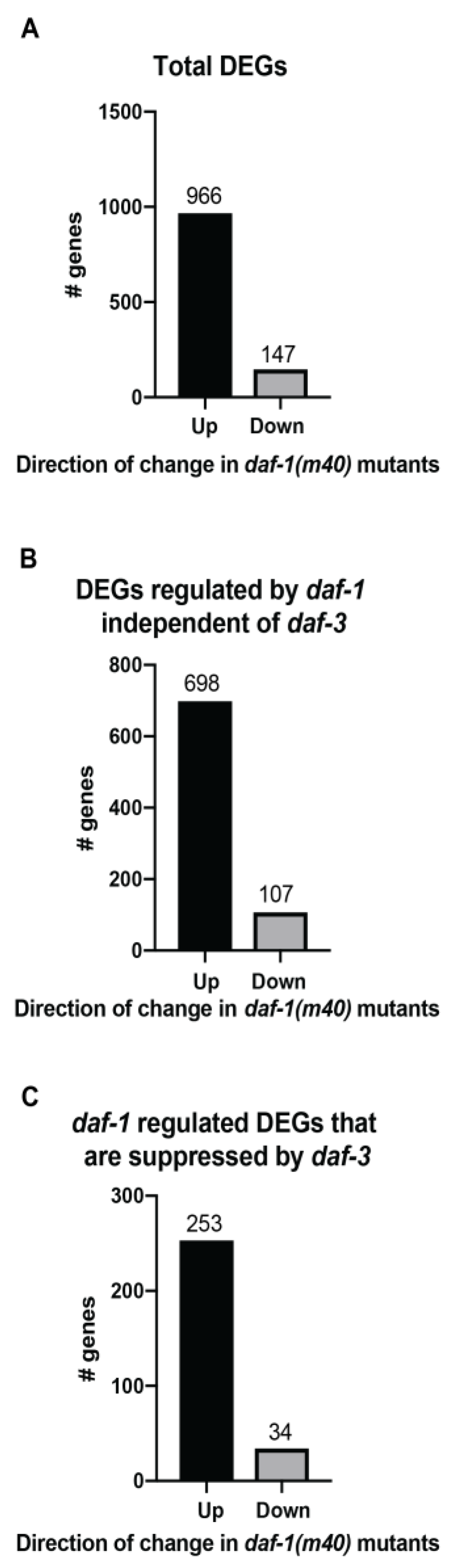
3.1. Overall Trends of the Wild-Type and TGFβ Mutant Transcriptomes
3.2. Functional Annotation of the Transcriptomic Data
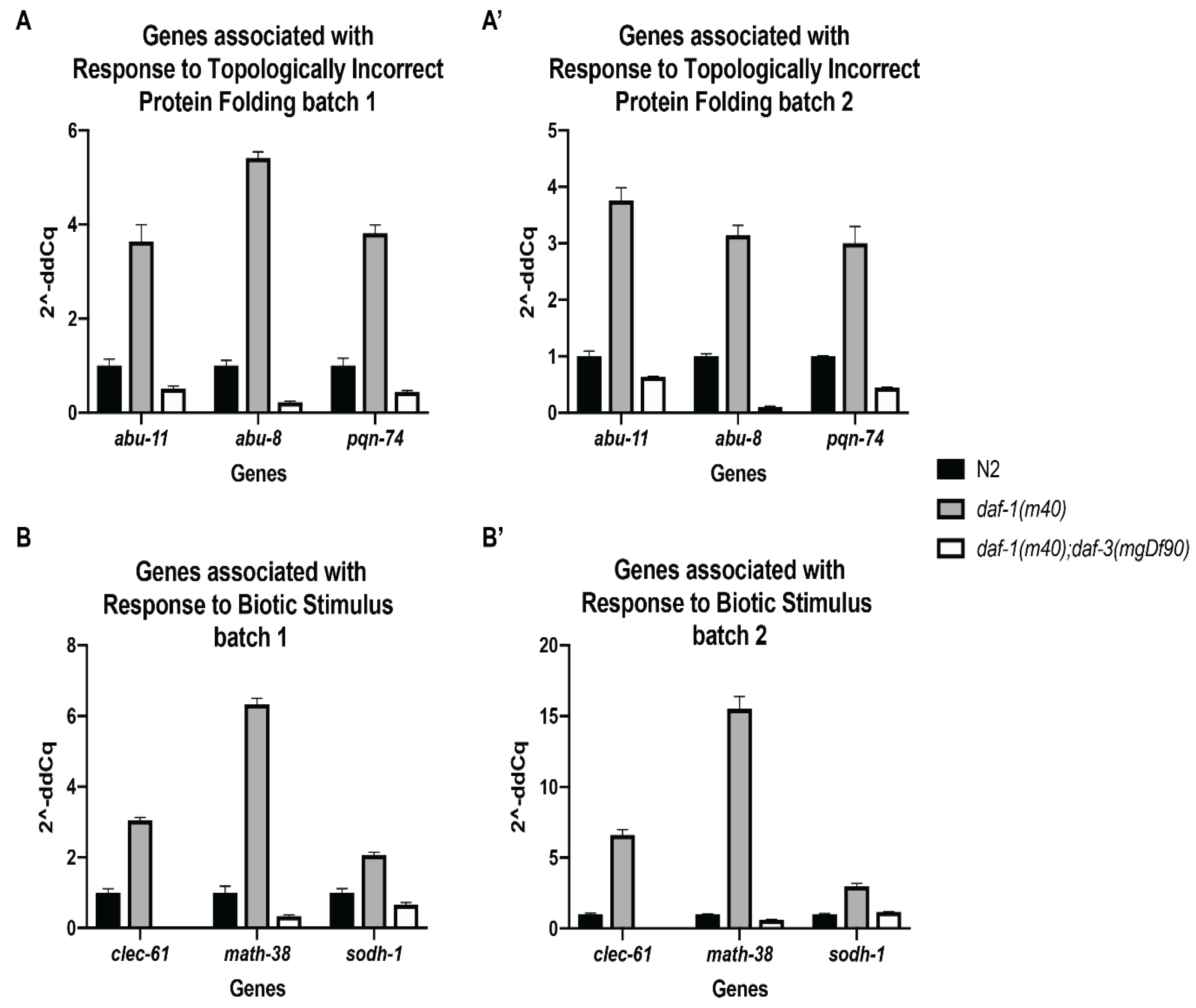
3.3. Validation of Select RNA-Sequencing Genes by Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Colak, S.; Ten Dijke, P. Targeting TGF-beta signaling in cancer. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, J.W.; Grobbelaar, A.O.; Rolfe, K.J. The role of the TGF-beta family in wound healing, burns and scarring: A review. Int. J. Burns Trauma 2012, 2, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sanjabi, S.; Oh, S.A.; Li, M.O. Regulation of the immune response by TGF-beta: From conception to autoimmunity and infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watabe, T.; Miyazono, K. Roles of TGF-beta family signaling in stem cell renewal and differentiation. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.Y.; Hill, C.S. TGF-beta superfamily signaling in embryonic development and homeostasis. Dev. Cell 2009, 16, 329–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimura, A.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Mori, T. Cellular and molecular basis for the regulation of inflammation by TGF-beta. J. Biochem. 2010, 147, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottinger, E.P.; Letterio, J.J.; Roberts, A.B. Biology of TGF-beta in knockout and transgenic mouse models. Kidney Int. 1997, 51, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumienny, T.L.; Savage-Dunn, C. TGF-beta signaling in C. elegans. WormBook 2013, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Moss-Taylor, L.; Kim, M.J.; Ghosh, A.C.; O’Connor, M.B. TGF-beta family signaling in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhury, A.; Howe, P.H. The tale of transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) signaling: A soigne enigma. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, K.M. Role of Ras and Mapks in TGFbeta signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000, 11, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petritsch, C.; Beug, H.; Balmain, A.; Oft, M. TGF-beta inhibits p70 S6 kinase via protein phosphatase 2A to induce G(1) arrest. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 3093–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soderberg, S.S.; Karlsson, G.; Karlsson, S. Complex and context dependent regulation of hematopoiesis by TGF-beta superfamily signaling. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2009, 1176, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scandura, J.M.; Boccuni, P.; Massague, J.; Nimer, S.D. Transforming growth factor beta-induced cell cycle arrest of human hematopoietic cells requires p57KIP2 up-regulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15231–15236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergeli, M.; mazzanti, B.; Ballerini, C.; Gran, B.; Amaducci, L.; Massacesi, L. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 inhibits the proliferation of rat astrocytes induced by serum and growth factors. J. Neurosci. Res. 1995, 40, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindholm, D.; Castren, E.; Kiefer, R.; Zafra, F.; Thoenen, H. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 in the rat brain: Increase after injury and inhibition of astrocyte proliferation. J. Cell Biol. 1992, 117, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; Serra, R. Deletion of Tgfbr2 in Prx1-cre expressing mesenchyme results in defects in development of the long bones and joints. Dev. Biol. 2007, 310, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, L.; Xu, X.; Li, C.; Huang, C.; Deng, C.X. TGF-beta/Smad3 signals repress chondrocyte hypertrophic differentiation and are required for maintaining articular cartilage. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Lim, C.S.; Johnsen, R.; Albert, P.S.; Pilgrim, D.; Riddle, D.L. Control of C. elegans larval development by neuronal expression of a TGF-beta homolog. Science 1996, 274, 1389–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schackwitz, W.S.; Inoue, T.; Thomas, J.H. Chemosensory neurons function in parallel to mediate a pheromone response in C. elegans. Neuron 1996, 17, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisel, J.D.; Panda, O.; Mahanti, P.; Schroeder, F.C.; Kim, D.H. Chemosensation of bacterial secondary metabolites modulates neuroendocrine signaling and behavior of C. elegans. Cell 2014, 159, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGehee, A.M.; Moss, B.J.; Juo, P. The DAF-7/TGF-beta signaling pathway regulates abundance of the Caenorhabditis elegans glutamate receptor GLR-1. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 67, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, K.M.; Sarafi-Reinach, T.R.; Horne, J.G.; Saffer, A.M.; Sengupta, P. The DAF-7 TGF-beta signaling pathway regulates chemosensory receptor gene expression in C. elegans. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 3061–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalfo, D.; Michaelson, D.; Hubbard, E.J. Sensory regulation of the C. elegans germline through TGF-beta-dependent signaling in the niche. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekar, O.; Ow, M.C.; Hui, K.Y.; Noyes, M.B.; Hall, S.E.; Hubbard, E.J.A. Linking the environment, DAF-7/TGFbeta signaling and LAG-2/DSL ligand expression in the germline stem cell niche. Development 2017, 144, 2896–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKnight, K.; Hoang, H.D.; Prasain, J.K.; Brown, N.; Vibbert, J.; Hollister, K.A.; Moore, R.; Ragains, J.R.; Reese, J.; Miller, M.A. Neurosensory perception of environmental cues modulates sperm motility critical for fertilization. Science 2014, 344, 754–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, W.M.; Luo, S.; Landis, J.; Ashraf, J.; Murphy, C.T. The C. elegans TGF-beta Dauer pathway regulates longevity via insulin signaling. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1635–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porta-de-la-Riva, M.; Fontrodona, L.; Villanueva, A.; Ceron, J. Basic Caenorhabditis elegans methods: Synchronization and observation. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, e4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Pachter, L.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Team, R. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Springer-Verlag New York: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Warnes, G.R.; Bolker, B.; Bonebakker, L.; Gentleman, R.; Andy Liaw, W.H.; Lumley, T.; Maechler, M.; Magnusson, A.; Moeller, S.; Schwartz, M.; et al. Gplots: Various R Programming Tools For Plotting Data, R package version 3.0. 1; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Angeles-Albores, D.L.; Lee, R.Y.; Chan, J.; Sternberg, P.W. Two new functions in the WormBase Enrichment Suite. Micropublication Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; UAB, Birmingham, AL, USA. Unpublished work. 2018.
- Greer, E.R.; Perez, C.L.; Van Gilst, M.R.; Lee, B.H.; Ashrafi, K. Neural and molecular dissection of a C. elegans sensory circuit that regulates fat and feeding. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, G.I.; Padgett, R.W. TGF beta-related pathways. Roles in Caenorhabditis elegans development. Trends Genet. 2000, 16, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.J. Dauer. WormBook 2007, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, N.; Hashimoto, K.; Kitahara, M.; Okuda, H.; Ueda, E.; Watanabe, K.; Nakahara, M.; Sato, T.; Kinoshita, S.; Tourtas, T.; et al. Activation of TGF-beta signaling induces cell death via the unfolded protein response in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, N.; Malhi, H.; Shah, V.H.; Maiers, J.L. Transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta) cross-talk with the unfolded protein response is critical for hepatic stellate cell activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3137–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George-Raizen, J.B.; Shockley, K.R.; Trojanowski, N.F.; Lamb, A.L.; Raizen, D.M. Dynamically-expressed prion-like proteins form a cuticle in the pharynx of Caenorhabditis elegans. Biology Open 2014, 3, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Term | Expected | Observed | Enrichment Fold Change | p Value | q Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genes downregulated in daf-1(m40) mutants | |||||
| Biological Process GO Term | |||||
| Response to biotic stimulus GO:0009607 | 0.1 | 3 | 30 | 3.20 × 10−6 | 0.00041 |
| Genes upregulated in daf-1(m40) mutants | |||||
| Biological Process GO Terms | |||||
| Response to topologically incorrect protein GO:0035966 | 1.3 | 10 | 7.5 | 1.30 × 10−7 | 5.50 × 10−6 |
| IRE1-mediated unfolded protein response GO:0036498 | 0.81 | 4 | 5 | 0.0014 | 0.014 |
| Response to biotic stimulus GO:0009607 | 1.3 | 7 | 5.2 | 7.10 × 10−5 | 0.0015 |
| Molting cycle GO:0042303 | 0.77 | 5 | 6.5 | 0.00014 | 0.0022 |
| Cellular Component GO Terms | |||||
| Collagen trimer GO:0005581 | 1.2 | 30 | 26 | 1.10 × 10−34 | 7.10 × 10−33 |
| Extracellular region GO:0005576 | 3.9 | 16 | 4.1 | 5.50 × 10−7 | 1.70 × 10−5 |
| Extracellular space GO:0005615 | 2 | 7 | 3.4 | 0.0011 | 0.014 |
| Membrane GO:0016020 | 46 | 71 | 1.6 | 9.20 × 10−5 | 0.0017 |
| Intrinsic component of membrane GO:0031224 | 40 | 67 | 1.7 | 2.10 × 10−5 | 0.00054 |
| Molecular Function GO Terms | |||||
| Structural constituent of cuticle GO:0042302 | 1.1 | 32 | 28 | 4.60 × 10−38 | 5.90 × 10−36 |
| Passive transmembrane transporter activity GO:0022803 | 2.5 | 8 | 3.2 | 0.0011 | 0.014 |
| Substrate-specific channel activity GO:0022838 | 2.3 | 8 | 3.5 | 0.00052 | 0.0074 |
| Peptidase activity GO:0008233 | 3.1 | 9 | 2.9 | 0.0014 | 0.014 |
| Genes Upregulated in daf-1(m40) Mutants | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| GO Term: Response to Topologically Incorrect Protein Folding GO: 0035966 | |||
| Gene Name | RNAseq Fold Change | p Value | q Value |
| abu-1 | 6.6291588 | 0.00015 | 0.00184372 |
| * abu-8 | 2.3753599 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| abu-10 | 2.333622 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| * abu-11 | 2.7447639 | 0.0038 | 0.0237475 |
| col-109 | 2.7839511 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| * pqn-74 | 2.3770804 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| fipr-24 | 6.4057217 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| T06E4.8 | 2.1258335 | 0.0002 | 0.00233793 |
| F41E6.11 | 2.7376684 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| clec-67 | 356.70377 | 0.0007 | 0.00656909 |
| GO Term: Response to Biotic Stimulus GO: 0009607 | |||
| Gene name | RNAseq Fold change | p value | q value |
| nlp-30 | 5.5977832 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| fipr-7 | Infinity | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| F20G2.5 | 4.2163742 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| *sodh-1 | 2.0632794 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| *clec-61 | 3.9058333 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| irg-1 | 4.981529 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| *math-38 | 8.2638921 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| GO Term: Molting Process GO 0042303 | |||
| Gene name | RNAseq Fold change | p value | q value |
| dpy-13 | 15.645535 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| nas-30 | 2.0286994 | 0.0002 | 0.00233793 |
| rol-6 | 8.4057641 | 0.0003 | 0.00330399 |
| sqt-1 | 12.831644 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| sqt-2 | 5.002505 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| Genes downregulated in daf-1(m40) mutants | |||
| GO Term: Response to Biotic Stimulus GO: 0009607 | |||
| Gene name | RNAseq Fold change | p value | q value |
| ilys-5 | 9.66785229 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| clec-218 | 5.85451214 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
| lys-4 | 9.58417075 | 5.00 × 10−5 | 0.00070927 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, M.; Crossman, D.; Prasain, J.K.; Miller, M.A.; Serra, R.A. Transcriptomic Profiling of DAF-7/TGFβ Pathway Mutants in C. elegans. Genes 2020, 11, 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030288
Hu M, Crossman D, Prasain JK, Miller MA, Serra RA. Transcriptomic Profiling of DAF-7/TGFβ Pathway Mutants in C. elegans. Genes. 2020; 11(3):288. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030288
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Muhan, David Crossman, Jeevan K. Prasain, Michael A. Miller, and Rosa A. Serra. 2020. "Transcriptomic Profiling of DAF-7/TGFβ Pathway Mutants in C. elegans" Genes 11, no. 3: 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030288
APA StyleHu, M., Crossman, D., Prasain, J. K., Miller, M. A., & Serra, R. A. (2020). Transcriptomic Profiling of DAF-7/TGFβ Pathway Mutants in C. elegans. Genes, 11(3), 288. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030288






