Network Protein Interaction in Parkinson’s Disease and Periodontitis Interplay: A Preliminary Bioinformatic Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
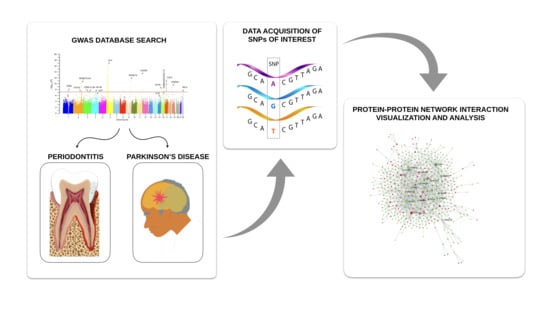
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Protein–Protein Interaction Networks Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.3. Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability Analysis
2.4. Data Management, Test Methods and Analysis
2.5. Protein Set Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
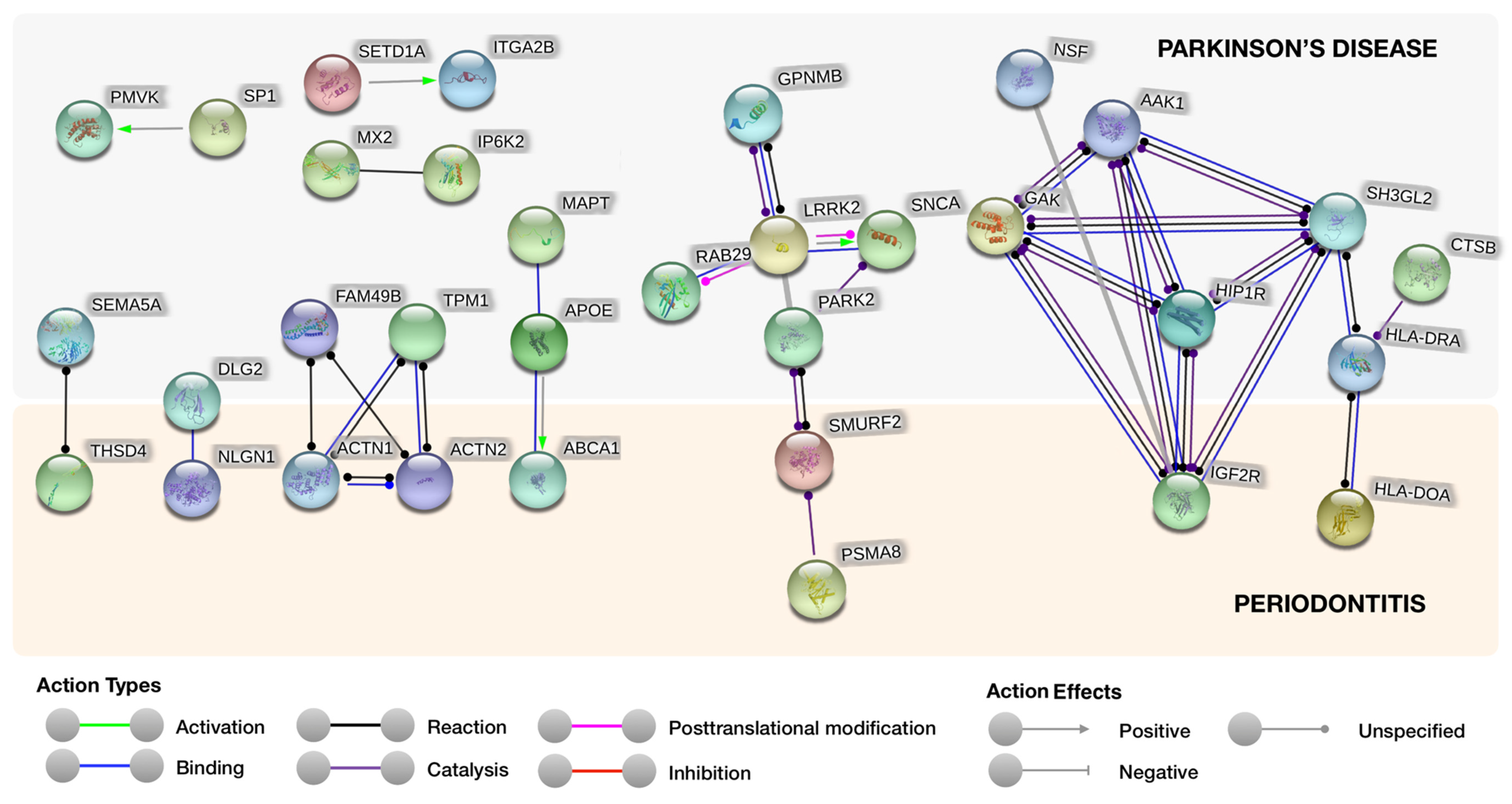
3.1. Protein–Protein Interaction Analysis
3.2. Hydrophobicity Levels of Proteins of Interest
3.3. Gene Enrichment Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tysnes, O.-B.; Storstein, A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foltynie, T.; Brayne, C.; Barker, R.A. The heterogeneity of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmeier, D.J.; Obeso, J.A.; Halliday, G.M. Selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrag, A.; Quinn, N.P.; Irving, R.J.; Oram, S.H.; Boyd, J.; Rutledge, P.; Mcrae, F.; Bloomfield, P. Cross sectional prevalence survey of idiopathic Parkinson’ s disease and parkinsonism in London Ten year audit of secondary prevention in coronary bypass patients. BMJ 2000, 321, 21–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alves, G.; Müller, B.; Herlofson, K.; HogenEsch, I.; Telstad, W.; Aarsland, D.; Tysnes, O.-B.; Larsen, J.P.; for the Norwegian ParkWest Study Group. Incidence of Parkinson’s disease in Norway: The Norwegian ParkWest study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noyce, A.J.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Kim, J.; Heilbron, K.; Kia, D.; Hemani, G.; Xue, A.; Lawlor, D.A.; Smith, G.D.; Duran, R.; et al. The Parkinson’s Disease Mendelian Randomization Research Portal. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1864–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, J.; Gan, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. C-Reactive Protein and Risk of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Cao, Z.; Liu, Q.; Cheng, Y. Cerebrospinal Fluid Inflammatory Cytokine Aberrations in Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tonetti, M.; Jepsen, S.; Jin, L.; Otomo-Corgel, J. Impact of the global burden of periodontal diseases on health, nutrition and wellbeing of mankind: A call for global action. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S149–S161. [Google Scholar]
- Caton, J.G.; Armitage, G.; Berglundh, T.; Chapple, I.L.C.; Jepsen, S.; Kornman, K.S.; Mealey, B.L.; Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Tonetti, M.S. A new classification scheme for periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions—Introduction and key changes from the 1999 classification. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S1–S8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Southerland, J.H.; Moss, K.; Taylor, G.W.; Beck, J.D.; Pankow, J.; Gangula, P.R.; Offenbacher, S. Periodontitis and diabetes associations with measures of atherosclerosis and CHD. Atherosclerosis 2012, 222, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, E.M.; Suvan, J.; Buti, J.; Czesnikiewicz-Guzik, M.; Ribeiro, A.B.; Orlandi, M.; Guzik, T.J.; Hingorani, A.D.; Nart, J.; D’Aiuto, F. Periodontitis is associated with hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Del Castillo, A.M.; Jepsen, S.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; D’Aiuto, F.; Bouchard, P.; Chapple, I.; Dietrich, T.; Gotsman, I.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis and cardiovascular diseases: Consensus report. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellesarian, S.V.; Malignaggi, V.R.; Kellesarian, T.V.; Al-Kheraif, A.A.; Alwageet, M.M.; Malmstrom, H.; Romanos, G.E.; Javed, F. Association between periodontal disease and polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2017, 29, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, V.; Escalda, C.; Proença, L.; Mendes, J.J.; Botelho, J. Is There a Bidirectional Association between Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and Periodontitis? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.B.; Botelho, J.; Machado, V.; Zehra, S.A.; Mendes, J.J.; Ciurtin, C.; Orlandi, M.; Aiuto, F.D. Is there a bidirectional association between rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominy, S.S.; Lynch, C.; Ermini, F.; Benedyk, M.; Marczyk, A.; Konradi, A.; Nguyen, M.; Haditsch, U.; Raha, D.; Griffin, C.; et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis in Alzheimer’s disease brains: Evidence for disease causation and treatment with small-molecule inhibitors. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashioka, S.; Inoue, K.; Miyaoka, T.; Hayashida, M.; Wake, R.; Oh-Nishi, A.; Inagaki, M. The Possible Causal Link of Periodontitis to Neuropsychiatric Disorders: More Than Psychosocial Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioguardi, M.; Crincoli, V.; Laino, L.; Alovisi, M.; Sovereto, D.; Mastrangelo, F.; Russo, L.L.; Muzio, L.L. The Role of Periodontitis and Periodontal Bacteria in the Onset and Progression of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, T.; Uppoor, A.; Naik, D. Parkinson’s disease and periodontitis—The missing link? A review. Gerodontology 2015, 33, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, P.; Machado, V.; Proença, L.; Domingos, J.; Godinho, C.; Mendes, J.J.; Botelho, J. Parkinson’s Disease, Periodontitis and Patient-Related Outcomes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2020, 56, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.; Heimhilger, E.; Storch, A. Increased periodontal pathology in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 608–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarsdóttir, E.R.; Gunnsteinsdóttir, H.; Hallsdóttir, M.H.; Sveinsson, S.; Jónsdóttir, S.R.; Olafsson, V.G.; Bragason, T.H.; Saemundsson, S.R.; Holbrook, W.P.; Sæmundsson, S.R. Dental health of patients with Parkinson’s disease in Iceland. Spéc. Care Dent. 2009, 29, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanaoka, A.; Kashihara, K. Increased frequencies of caries, periodontal disease and tooth loss in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 16, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, Y.; Washio, M.; Mori, M. Oral health conditions in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 14, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Stiphout, M.A.E.; Marinus, J.; Van Hilten, J.J.; Lobbezoo, F.; De Baat, C. Oral Health of Parkinson’s Disease Patients: A Case-Control Study. Park. Dis. 2018, 2018, 9315285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botelho, J.; Lyra, P.; Proença, L.; Godinho, C.; Mendes, J.J.; Machado, V. Relationship between Blood and Standard Biochemistry Levels with Periodontitis in Parkinson’s Disease Patients: Data from the NHANES 2011–2012. J. Pers. Med. 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-K.; Wu, Y.-T.; Chang, Y.-C. Periodontal inflammatory disease is associated with the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A population-based retrospective matched-cohort study. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salinas-Torres, V.M.; Gallardo-Blanco, H.L.; Salinas-Torres, R.A.; Cerda-Flores, R.M.; Lugo-Trampe, J.J.; Villarreal-Martínez, D.Z.; De Villarreal, L.E.M. Bioinformatic Analysis of Gene Variants from Gastroschisis Recurrence Identifies Multiple Novel Pathogenetic Pathways: Implication for the Closure of the Ventral Body Wall. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Ding, Z.; Liu, G.; Yu, P.; Jiang, G.; Yu, Z.; Yang, C.; Qian, J.; Jiang, H.; et al. Identification of a Common Different Gene Expression Signature in Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. Genes 2018, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salazar, C.; Ruiz-Hincapie, P.; Ruiz, L. The Interplay among PINK1/PARKIN/Dj-1 Network during Mitochondrial Quality Control in Cancer Biology: Protein Interaction Analysis. Cells 2018, 7, 154. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.K.; Quan, L.S. Biomarkers for ischemic stroke subtypes: A protein-protein interaction analysis. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 83, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhyan, S.B.; Zhao, L.; Wee, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M. Genetic links between endometriosis and cancers in women. PeerJ 2019, 7, e8135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, J.; Qi, F.-Z. Identification of key candidate genes and molecular pathways in white fat browning: An anti-obesity drug discovery based on computational biology. Hum. Genom. 2019, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ho, K.; Keaton, J.M.; Hartzel, D.N.; Day, F.; Justice, A.E.; Josyula, N.S.; Pendergrass, S.A.; Actkins, K.; Davis, L.K.; et al. A genome-wide association study of polycystic ovary syndrome identified from electronic health records. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHGRI-GWAS NHGRI-GWAS. Available online: https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas (accessed on 9 June 2020).
- Schaefer, A.S.; Richter, G.M.; Nothnagel, M.; Manke, T.; Dommisch, H.; Jacobs, G.; Arlt, A.; Rosenstiel, P.; Noack, B.; Groessner-Schreiber, B.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies GLT6D1 as a susceptibility locus for periodontitis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 19, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divaris, K.; Monda, K.; North, K.; Olshan, A.; Lange, E.; Moss, K.; Barros, S.; Beck, J.; Offenbacher, S. Genome-wide Association Study of Periodontal Pathogen Colonization. J. Dent. Res. 2012, 91, S21–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Divaris, K.; Monda, K.L.; North, K.E.; Olshan, A.F.; Reynolds, L.M.; Hsueh, W.-C.; Lange, E.M.; Moss, K.; Barros, S.P.; Weyant, R.J.; et al. Exploring the genetic basis of chronic periodontitis: A genome-wide association study. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 2312–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teumer, A.; Holtfreter, B.; Völker, U.; Petersmann, A.; Nauck, M.; Biffar, R.; Völzke, H.; Kroemer, H.K.; Meisel, P.; Homuth, G.; et al. Genome-wide association study of chronic periodontitis in a general German population. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Wang, X.; Casado, P.L.; Küchler, E.C.; Deeley, K.; Noel, J.; Kimm, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Haas, A.N.; Quinelato, V.; et al. Genome wide association scan for chronic periodontitis implicates novel locus. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freitag-Wolf, S.; Dommisch, H.; Graetz, C.; Jockel-Schneider, Y.; Harks, I.; Staufenbiel, I.; Meyle, J.; Eickholz, P.; Noack, B.; Bruckmann, C.; et al. Genome-wide exploration identifies sex-specific genetic effects of alleles upstreamNPYto increase the risk of severe periodontitis in men. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag-Wolf, S.; Munz, M.; Wiehe, R.; Junge, O.; Graetz, C.; Jockel-Schneider, Y.; Staufenbiel, I.; Bruckmann, C.; Lieb, W.; Franke, A.; et al. Smoking Modifies the Genetic Risk for Early-Onset Periodontitis. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, J.R.; Polk, D.E.; Wang, X.; Feingold, E.; Weeks, D.E.; Lee, M.-K.; Cuenco, K.T.; Weyant, R.J.; Crout, R.J.; McNeil, D.W.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Periodontal Health Measured by Probing Depth in Adults Ages 18−49 years. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2014, 4, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shungin, D.; Haworth, S.; Divaris, K.; Agler, C.S.; Kamatani, Y.; Lee, M.K.; Grinde, K.; Hindy, G.; Alaraudanjoki, V.; Pesonen, P.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of dental caries and periodontitis combining clinical and self-reported data. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, S.; Momozawa, Y.; Takahashi, A.; Nagasawa, T.; Ashikawa, K.; Terada, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Tsuji, M.; Kubo, M.; et al. A Genome-wide Association Study of Periodontitis in a Japanese Population. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munz, M.; Willenborg, C.; Richter, G.M.; Jockel-Schneider, Y.; Graetz, C.; Staufenbiel, I.; Wellmann, J.; Berger, K.; Krone, B.; Hoffmann, P.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies nucleotide variants at SIGLEC5 and DEFA1A3 as risk loci for periodontitis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2577–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, L.; Navarra, C.O.; Pirastu, N.; Di Lenarda, R.; Gasparini, P.; Robino, A. A genome-wide association study identifies an association between variants in EFCAB4B gene and periodontal disease in an Italian isolated population. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munz, M.; Richter, G.M.; Loos, B.G.; Jepsen, S.; Divaris, K.; Offenbacher, S.; Teumer, A.; Holtfreter, B.; Kocher, T.; Bruckmann, C.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of aggressive and chronic periodontitis identifies two novel risk loci. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 27, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalls, M.A.; Keller, M.F.; Hernandez, D.G.; Chen, L.; Stone, D.J.; Singleton, A.B.; on behalf of the Parkinson’s Progression Marker Initiative (PPMI) investigators. Baseline genetic associations in the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI). Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernandez, D.G.; Nalls, M.A.; Ylikotila, P.; Keller, M.; Hardy, J.A.; Majamaa, K.; Singleton, A.B. Genome Wide Assessment of Young Onset Parkinson’s Disease from Finland. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallen, Z.D.; Chen, H.; Hill-Burns, E.M.; Factor, S.A.; Zabetian, C.P.; Payami, H. Plasticity-related gene 3 (LPPR1) and age at diagnosis of Parkinson disease. Neurol. Genet. 2018, 4, e271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fung, H.-C.; Scholz, S.; Matarin, M.; Simón-Sánchez, J.; Hernandez, D.; Britton, A.; Gibbs, J.R.; Langefeld, C.; Stiegert, M.L.; Schymick, J.; et al. Genome-wide genotyping in Parkinson’s disease and neurologically normal controls: First stage analysis and public release of data. Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraganore, D.M.; De Andrade, M.; Lesnick, T.G.; Strain, K.J.; Farrer, M.J.; Rocca, W.A.; Pant, P.V.K.; Frazer, K.A.; Cox, D.R.; Ballinger, D.G. High-Resolution Whole-Genome Association Study of Parkinson Disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pankratz, N.; Wilk, J.B.; Latourelle, J.C.; DeStefano, A.L.; Halter, C.; Pugh, E.W.; Doheny, K.F.; Gusella, J.F.; Nichols, W.C.; Foroud, T.; et al. Genomewide association study for susceptibility genes contributing to familial Parkinson disease. Qual. Life Res. 2009, 124, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, S.J.; Armasu, S.M.; Biernacka, J.M.; Anderson, K.J.; Lesnick, T.G.; Rider, D.N.; Cunningham, J.M.; Ahlskog, J.E.; Frigerio, R.; Maraganore, D.M. Genomic determinants of motor and cognitive outcomes in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biernacka, J.M.; Chung, S.J.; Armasu, S.M.; Anderson, K.S.; Lill, C.M.; Bertram, L.; Ahlskog, J.; Brighina, L.; Frigerio, R.; Maraganore, D.M. Genome-wide gene-environment interaction analysis of pesticide exposure and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 32, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hill-Burns, E.M.; Wissemann, W.T.; Hamza, T.H.; Factor, S.A.; Zabetian, C.P.; Payami, H. Identification of a novel Parkinson’s disease locus via stratified genome-wide association study. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simón-Sánchez, J.; Van Hilten, J.J.; Van De Warrenburg, B.C.; Post, B.; Berendse, H.W.; Arepalli, S.; Hernandez, D.G.; De Bie, R.M.A.; Velseboer, D.C.; Scheffer, H.; et al. Genome-wide association study confirms extant PD risk loci among the Dutch. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 19, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, R.; Verbitsky, M.; Kisselev, S.; Browne, A.; Mejia-Sanatana, H.; Louis, E.D.; Cote, L.J.; Andrews, H.F.; Waters, C.H.; et al. Genome-Wide association study identifies candidate genes for Parkinson’s disease in an Ashkenazi Jewish population. BMC Med. Genet. 2011, 12, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davis, M.F.; Cummings, A.C.; D’Aoust, L.N.; Jiang, L.; Edwards, D.R.V.; Laux, R.; Reinhart-Mercer, L.; Fuzzell, D.; Scott, W.K.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; et al. Parkinson disease loci in the mid-western Amish. Qual. Life Res. 2013, 132, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gan-Or, Z.; Amshalom, I.; Bar-Shira, A.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Mirelman, A.; Marder, K.; Bressman, S.; Giladi, N.; Orr-Urtreger, A. The Alzheimer disease BIN1 locus as a modifier of GBA-associated Parkinson disease. J. Neurol. 2015, 262, 2443–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill-Burns, E.M.; A Ross, O.; Wissemann, W.T.; Soto-Ortolaza, A.I.; Zareparsi, S.; Siuda, J.; Lynch, T.; Wszolek, Z.K.; Silburn, P.A.; Mellick, G.D.; et al. Identification of genetic modifiers of age-at-onset for familial Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 3849–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nalls, M.A.; Plagnol, V.; Hernandez, D.G.; Sharma, M.; Sheerin, U.-M.; Saad, M.H.F.; Simonsanchez, J.; Schulte, C.; Lesage, S.; Sveinbjornsdottir, S.; et al. Imputation of sequence variants for identification of genetic risks for Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies. Lancet 2011, 377, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saad, M.; Lesage, S.; Saint-Pierre, A.; Corvol, J.-C.; Zelenika, D.; Lambert, J.-C.; Vidailhet, M.; Mellick, G.D.; Lohmann, E.; Durif, F.; et al. Genome-wide association study confirms BST1 and suggests a locus on 12q24 as the risk loci for Parkinson’s disease in the European population. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 20, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, T.H.; Zabetian, C.P.; Tenesa, A.; Laederach, A.; Montimurro, J.; Yearout, D.; Kay, D.M.; Doheny, K.F.; Paschall, J.; Pugh, E.; et al. Common genetic variation in the HLA region is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, W.; Nakabayashi, Y.; Mizuta, I.; Hirota, Y.; Ito, C.; Kubo, M.; Kawaguchi, T.; Tsunoda, T.; Watanabe, M.; Takeda, A.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies common variants at four loci as genetic risk factors for Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, T.L.; Scott, W.K.; Almonte, C.; Burt, A.; Powell, E.H.; Beecham, G.W.; Wang, L.; Züchner, S.; Konidari, I.; Wang, G.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Confirms SNPs inSNCAand theMAPTRegion as Common Risk Factors for Parkinson Disease. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2010, 74, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Do, C.B.; Tung, J.Y.; Dorfman, E.; Kiefer, A.K.; Drabant, E.M.; Francke, U.; Mountain, J.L.; Goldman, S.M.; Tanner, C.M.; Langston, J.W.; et al. Web-Based Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Two Novel Loci and a Substantial Genetic Component for Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamza, T.H.; Chen, H.; Hill-Burns, E.M.; Rhodes, S.L.; Montimurro, J.; Kay, D.M.; Tenesa, A.; Kusel, V.I.; Sheehan, P.; Eaaswarkhanth, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Gene-Environment Study Identifies Glutamate Receptor Gene GRIN2A as a Parkinson’s Disease Modifier Gene via Interaction with Coffee. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacic, V.; Ozelius, L.J.; Clark, L.N.; Bar-Shira, A.; Gana-Weisz, M.; Gurevich, T.; Gusev, A.; Kedmi, M.; Kenny, E.E.; Liu, X.; et al. Genome-wide mapping of IBD segments in an Ashkenazi PD cohort identifies associated haplotypes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 4693–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Latourelle, J.C.; Pankratz, N.; Dumitriu, A.; Wilk, J.B.; Goldwurm, S.; Pezzoli, G.; Mariani, C.B.; DeStefano, A.L.; Halter, C.; Gusella, J.F.; et al. Genomewide association study for onset age in Parkinson disease. BMC Med Genet. 2009, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhang, J.; Fang, X.; Mei, P.; Cao, X.; Lin, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, R. A Pooling Genome-Wide Association Study Combining a Pathway Analysis for Typical Sporadic Parkinson’s Disease in the Han Population of Chinese Mainland. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 53, 4302–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pickrell, J.K.; Berisa, T.; Liu, J.Z.; Ségurel, L.; Tung, J.Y.; Hinds, D.A. Detection and interpretation of shared genetic influences on 42 human traits. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blauwendraat, C.; Heilbron, K.; Msc, C.L.V.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Von Coelln, R.; Pihlstrøm, L.; Simón-Sánchez, J.; Schulte, C.; Sharma, M.; Msc, L.K.; et al. Parkinson’s disease age at onset genome-wide association study: Defining heritability, genetic loci, and α-synuclein mechanisms. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blauwendraat, C.; Reed, X.; Krohn, L.; Heilbron, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Tan, M.M.; Gibbs, J.R.; Hernandez, D.G.; Kumaran, R.; Langston, R.; et al. Genetic modifiers of risk and age at onset in GBA associated Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body dementia. Brain 2020, 143, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beecham, G.W.; Dickson, D.W.; Scott, W.K.; Martin, E.R.; Schellenberg, G.; Nuytemans, K.; Larson, E.B.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; et al. PARK10 is a major locus for sporadic neuropathologically confirmed Parkinson disease. Neurology 2015, 84, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lill, C.M.; Roehr, J.T.; McQueen, M.B.; Kavvoura, F.K.; Bagade, S.; Schjeide, B.-M.M.; Schjeide, L.M.; Meissner, E.; Zauft, U.; Allen, N.C.; et al. Comprehensive Research Synopsis and Systematic Meta-Analyses in Parkinson’s Disease Genetics: The PDGene Database. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spencer, C.C.A.; Plagnol, V.; Strange, A.; Gardner, M.; Paisan-Ruiz, C.; Band, G.; Barker, R.A.; Bellenguez, C.; Bhatia, K.; Blackburn, H.; et al. Dissection of the genetics of Parkinson’s disease identifies an additional association 5′ of SNCA and multiple associated haplotypes at 17q21. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Pankratz, N.; Beecham, G.W.; DeStefano, A.L.; Dawson, T.M.; Doheny, K.F.; Do, S.A.F.; Hamza, T.H.; Hung, A.Y.; Hyman, B.T.; Ivinson, A.J.; et al. Meta-analysis of Parkinson’s Disease: Identification of a novel locus, RIT2. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 71, 370–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foo, J.N.; Tan, L.C.; Irwan, I.D.; Au, W.-L.; Low, H.Q.; Prakash, K.-M.; Annuar, A.A.; Bei, J.; Chan, A.Y.; Chen, C.-M.; et al. Genome-wide association study of Parkinson’s disease in East Asians. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 26, 226–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foo, J.N.; Chew, E.G.Y.; Chung, S.J.; Peng, R.; Blauwendraat, C.; Nalls, M.A.; Mok, K.Y.; Satake, W.; Toda, T.; Chao, Y.; et al. Identification of Risk Loci for Parkinson Disease in Asians and Comparison of Risk Between Asians and Europeans. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.; Nalls, M.A.; Hallgrímsdóttir, I.B.; Hunkapiller, J.; Van Der Brug, M.; Cai, F.; Kerchner, G.A.; Ayalon, G.; Bingol, B.; Sheng, M.; et al. A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies identifies 17 new Parkinson’s disease risk loci. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandrés-Ciga, S.; Ahmed, S.; Sabir, M.S.; Blauwendraat, C.; Adarmes-Gómez, A.D.; Msc, I.B.; Msc, M.B.; Msc, D.B.; Carrillo, F.; Msc, M.C.; et al. The Genetic Architecture of Parkinson Disease in Spain: Characterizing Population-Specific Risk, Differential Haplotype Structures, and Providing Etiologic Insight. Mov. Disord. 2019, 34, 1851–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalls, M.A.; Pankratz, N.; Lill, C.M.; Do, C.B.; Hernandez, D.G.; Saad, M.; DeStefano, A.L.; Kara, E.; Bras, J.; Sharma, M.; et al. Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottier, C.; Zhou, X.; Perkerson, R.B.; Baker, M.; Jenkins, G.D.; Serie, D.J.; Ghidoni, R.; Benussi, L.; Binetti, G.; De Munain, A.L.; et al. Potential genetic modifiers of disease risk and age at onset in patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration and GRN mutations: A genome-wide association study. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trochet, H.; Pirinen, M.; Band, G.; Jostins, L.; McVean, G.; Spencer, C.C.A. Bayesian meta-analysis across genome-wide association studies of diverse phenotypes. Genet. Epidemiol. 2019, 43, 532–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Kuhn, M.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Minguez, P.; Doerks, T.; Stark, M.; Muller, J.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D561–D568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STRING—Functional Protein Association Networks. Available online: http://string-db.org/ (accessed on 28 March 2020).
- Uniprot Data Base. Available online: http://www.uniprot.org/ (accessed on 10 October 2012).
- Atlas, P. Protein Atlas. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Huang, X.; Ebert, D.; Mills, C.; Guo, X.; Thomas, P.D. Protocol Update for large-scale genome and gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system (v.14.0). Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonni, S.; Wang, H.-R.; Causing, C.G.; Kavsak, P.; Stroschein, S.L.; Luo, K.; Wrana, J.L. TGF-β induces assembly of a Smad2–Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase complex that targets SnoN for degradation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.W.; Ordureau, A.; Heo, J.M. Building and decoding ubiquitin hains for mitophagy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonello, F.; Hassoun, S.M.; Mouton-Liger, F.; Shin, Y.S.; Muscat, A.; Tesson, C.; Lesage, S.; Beart, P.M.; Brice, A.; Krupp, J.; et al. LRRK2 impairs PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy via its kinase activity: Pathologic insights into Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 1645–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, L.-S.; Li, L. Ubiquitin phosphorylation in Parkinson’s disease: Implications for pathogenesis and treatment. Transl. Neurodegener. 2016, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, S.; Zhu, S.; Xu, S.; Han, Y.; Liu, W.; Zuo, J. Molecular dynamics simulations of human E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 4561–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-S.; Kim, E.; Han, S.; Kang, K.L.; Heo, J.S. Evaluating the oxysterol combination of 22(S)-hydroxycholesterol and 20(S)-hydroxycholesterol in periodontal regeneration using periodontal ligament stem cells and alveolar bone healing models. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, L.; Nascimento, J.; Rêgo, J.; Canuto, K.; Crespo-López, M.E.; Leite, J.I.A.; Baysan, A.; Oriá, R.B. Apolipoprotein E, periodontal disease and the risk for atherosclerosis: A review. Arch. Oral Biol. 2019, 98, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fagan, E.S.; Pihlstrøm, L. Genetic risk factors for cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease: A review of the literature. Eur. J. Neurol. 2017, 24, 561-e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, P.C.; Poole, C. APOE-ε2 allele associated with higher pevalence of sporadic Parkinson disease. Neurology 2004, 62, 2198–2202. [Google Scholar]
- Clarimon, J.; Scholz, S.; Fung, H.-C.; Hardy, J.; Eerola, J.; Hellström, O.; Chen, C.-M.; Wu, Y.-R.; Tienari, P.J.; Singleton, A. Conflicting Results Regarding the Semaphorin Gene (SEMA5A) and the Risk for Parkinson Disease To. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 78, 1082–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Wang, F.; Ding, X.; Song, X.; Lu, X.; Zhang, K.; Xiao, H.; Ye, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Q. Association study of semaphorin 5A with risk of Parkinson’s disease in a Chinese Han population. Brain Res. 2008, 1245, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lesnick, T.G.; Maraganore, D.M.; Isacson, O. Axon guidance and synaptic maintenance: Preclinical markers for neurodegenerative disease and therapeutics. Trends Neurosci. 2009, 32, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; De Vos, R.A.; Steur, E.N.J.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, V.; Patel, N.; Turcotte, M.; Bossé, Y.; Paré, G.; Meyre, D. Benefits and limitations of genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
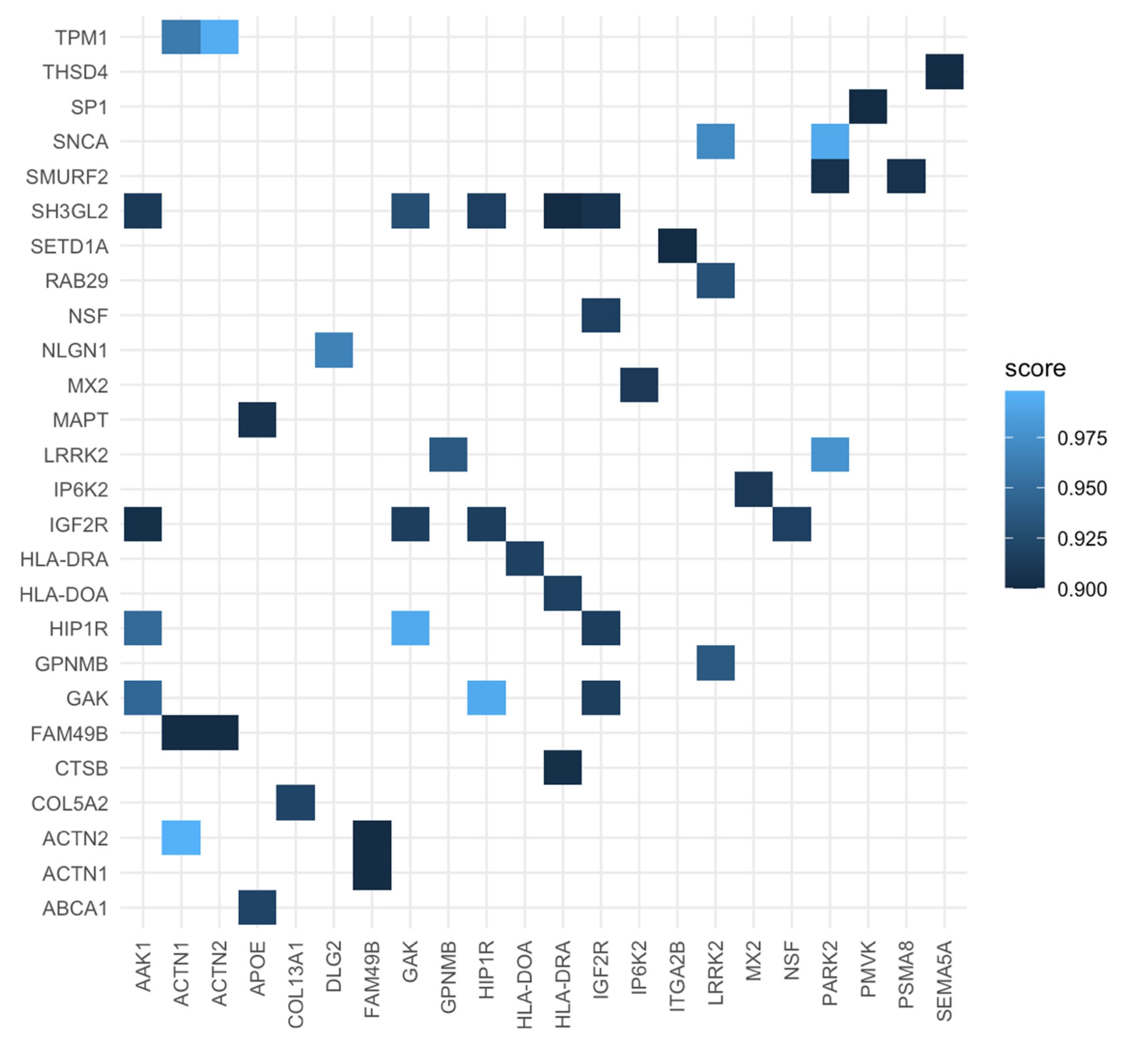

| Proteins for PD (Regulation) | Proteins for Periodontitis (Regulation) | Score |
|---|---|---|
| TPM1 | ACTN2 | 0.995 |
| DLG2 | NLGN1 | 0.966 |
| TPM1 | ACTN1 | 0.961 |
| APOE | ABCA1 | 0.921 |
| HLA-DRA | HLD-DOA | 0.918 |
| NSF | IGF2R | 0.917 |
| HIP1R | IGF2R | 0.916 |
| GAK | IGF2R | 0.916 |
| SH3GL2 | IGF2R | 0.907 |
| PARK2 | SMURF2 | 0.906 |
| AAK1 | IGF2R | 0.903 |
| SEMA5A | THSD4 | 0.902 |
| FAM49B | ACTN1 | 0.901 |
| FAM49B | ACTN2 | 0.901 |
| Protein Symbol | Name | Description | Localization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parkinson’s Disease | |||
| SEMA5A | Semaphorin-5A | Bifunctional axonal guidance signal via sulfated proteoglycans regulation. | - Plasma membrane - Extracellular exosome |
| FAM49B | Protein FAM49B | Family with sequence similarity 49 member B | - Mitochondrion |
| TPM1 | Tropomyosin α-1 chain | Tropomyosin 1 | - Cytoskeleton |
| APOE | Apolipoprotein E | Intermediates catabolic, link, and internalization processes of lipoprotein particles. | - Extracellular region or secreted |
| PARK2 | E3 ubiquitin–protein ligase parkin | Acts in a multiproteic complex (E3 ubiquitin ligase), catalyzing the link of proteins-ubiquitin moieties. Intervenes monoubiquitination as well as ’Lys-6′, ’Lys-11′, ’Lys-48′-linked and ’Lys-63′-linked polyubiquitination of substrates depending on the context. | - Mitochondrion - Nucleus - Cytosol - Endoplasmic reticulum |
| HIP1R | Huntingtin-interacting protein 1-related protein | Constituent of vesicles and pits coated by clathrin, that may bind the endocytic apparatus to the actin cytoskeleton. Binds 3-phosphoinositides (through the ENTH domain). May uphold cell survival via stabilization of tyrosine kinases receptor after endocytosis | - Perinuclear - Endomembrane system - Clathrin-coated vesicle membrane |
| GAK | Cyclin-G-associated kinase | Is a serine/threonine kinase that links with CDK5 and cyclin G acting in the cell cycle and focal adhesion | - Golgi apparatus - Perinuclear region - Focal adhesion |
| AAK1 | AP2-associated protein kinase 1 | Regulates endocytosis mediated by clathrin-mediated via AP2M1/mu2 subunit phosphorylation of the adaptor protein complex 2 (AP-2) fostering high affinity binding of AP-2 to cargo membrane proteins during the initial stages of endocytosis. | - Plasma membrane - Clathrin-coated pit - Presynapse |
| SH3GL2 | Endophilin-A1 | Involved in the endocytosis of synaptic vesicles. | - Endosome - Cytoplasm - Membrane - Presynapse |
| CTSB | Cathepsin B | A Thiol protease that is implicated in intracellular degradation and proteins turnover. | - Lysosome - Plasma Membrane - Extracellular region |
| HLA-DRA | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR α chain | Binds antigens’ peptides that entree into the endocytic path of antigen presenting cells and bestows onto the cell surface for recognition by T-CD4 cells. | - Golgi apparatus - Lysosome - Plasma membrane - Endoplasmic reticulum - Endosome |
| NSF | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Involved in vesicle-mediated transport. Catalyzes the vesicles’ fusion with the Golgi cisternae. Acts as a fusion protein essential in the delivery of cargo proteins to the Golgi stack. | - Cytoplasm |
| Periodontitis | |||
| THSD4 | Thrombospondin type-1 domain-containing protein 4 | Promotes the assembly of a FBN1 matrix. Attenuates TGFB signaling. | - Extracellular Matrix |
| NLGN1 | Neuroligin-1 | Cell surface protein involved in synapses and synaptic signal transmission, and recruits and clusters other synaptic proteins. | - Extracellular Region - Plasma membrane - Post-synaptic density |
| ACTN1 | α-actinin-1 | Bundling protein of F-actin that anchors actin intracellularly. | - Plasma membrane - Cytoskeleton |
| ACTN2 | α-actinin-2 | Bundling protein of F-actin that anchors actin intracellularly. | - Z line |
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 1 | Anion transporter dependent on cAMP sensitive to sulfonylurea. | - Endosome - Plasma Membrane - Membrane |
| SMURF2 | E3 ubiquitin–protein ligase SMURF2 | Involved in the transfer of the ubiquitin to targeted substrates. Interacts with SMAD1 and SMAD7 triggering ubiquitination and degradation. | - Plasma Membrane - Nucleus - Cytoplasm - Membrane Raft |
| IGF2R | Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptor | Involved in the transport of phosphorylated lysosomal enzymes to lysosomes. | - Lysosome |
| HLA-DOA | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DO α chain | Modulates the HLA class II restricted antigen displaying path via the interaction with B-cells’ HLA-DM. Alters the peptide interchange activity of HLA-DM | - Lysosome - Endosome |
| Parkinson’s Disease and Periodontitis | |||
| DLG2 | Disks large homolog 2 | Acts in chronic pain perception via NMDA receptor signaling. Regulates the stability of cholinergic synapses. | - Plasma membrane Other locations: - Postsynaptic density - Synapse - Axon - Perikaryon |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Botelho, J.; Mascarenhas, P.; Mendes, J.J.; Machado, V. Network Protein Interaction in Parkinson’s Disease and Periodontitis Interplay: A Preliminary Bioinformatic Analysis. Genes 2020, 11, 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111385
Botelho J, Mascarenhas P, Mendes JJ, Machado V. Network Protein Interaction in Parkinson’s Disease and Periodontitis Interplay: A Preliminary Bioinformatic Analysis. Genes. 2020; 11(11):1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111385
Chicago/Turabian StyleBotelho, João, Paulo Mascarenhas, José João Mendes, and Vanessa Machado. 2020. "Network Protein Interaction in Parkinson’s Disease and Periodontitis Interplay: A Preliminary Bioinformatic Analysis" Genes 11, no. 11: 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111385
APA StyleBotelho, J., Mascarenhas, P., Mendes, J. J., & Machado, V. (2020). Network Protein Interaction in Parkinson’s Disease and Periodontitis Interplay: A Preliminary Bioinformatic Analysis. Genes, 11(11), 1385. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111385