CRISPR-Cas Diversity in Clinical Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Isolates from South Asian Countries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source and Assembly of the Genome Data
2.2. Detection of CRISPR Loci and Cas Genes
3. Results
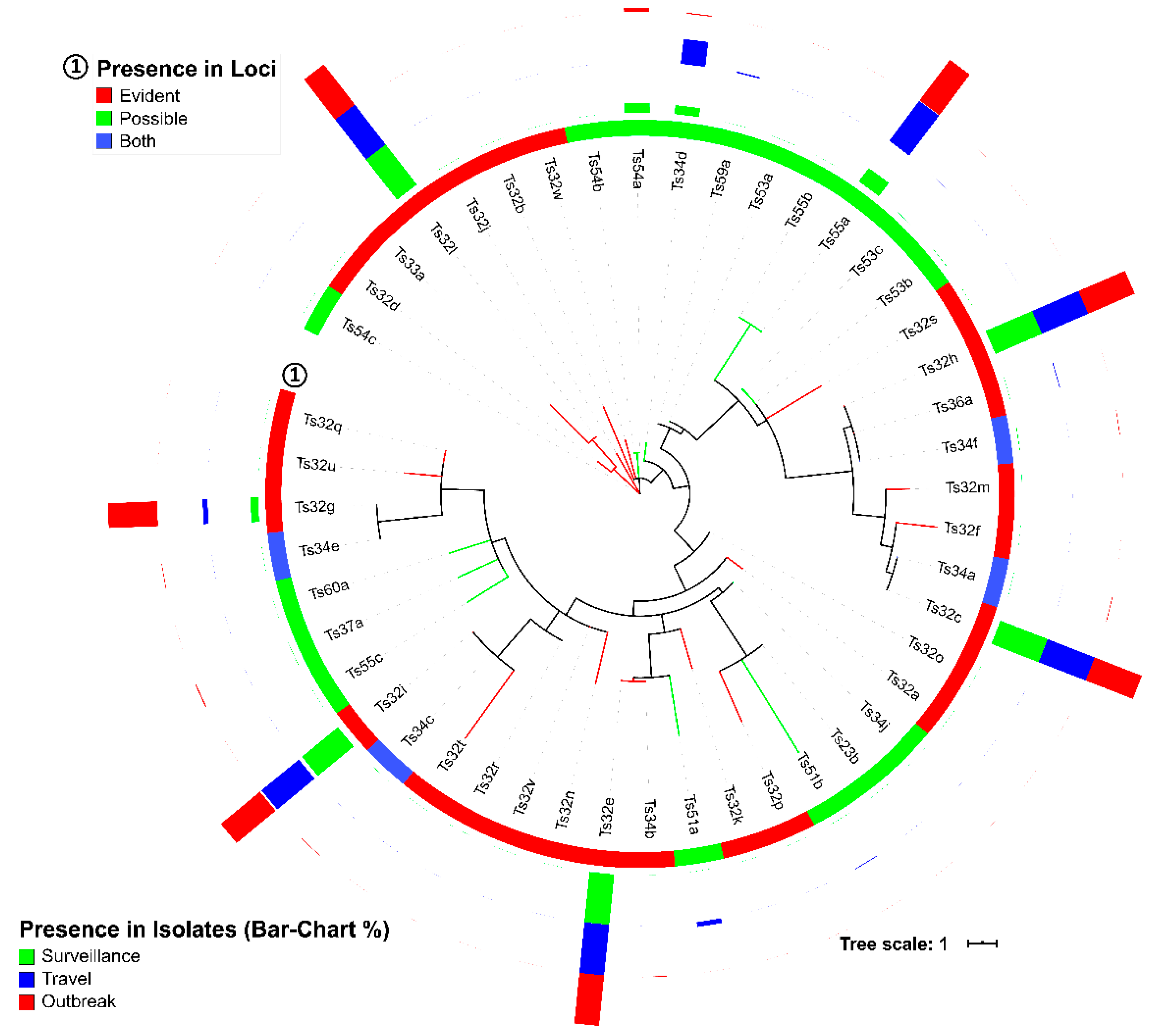
3.1. CRISPR Loci of S. Typhi Genomes
3.2. CRISPR Loci of S. Typhi Versus other Salmonella Species
3.3. Spacers and DRs of S. Typhi
3.4. Spacer Targets and PAM Identification
3.5. Cas Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Britto, C.D.; Wong, V.K.; Dougan, G.; Pollard, A.J. A systematic review of antimicrobial resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, the etiological agent of typhoid. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ong, S.Y.; Pratap, C.B.; Wan, X.; Hou, S.; Rahman, A.Y.A.; Saito, J.A.; Nath, G.; Alam, M. The Genomic Blueprint of Salmonella enterica subspecies enterica serovar Typhi P-stx-12. Stand. Genom. Sci. 2013, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stanaway, J.D.; Reiner, R.C.; Blacker, B.F.; Goldberg, E.M.; Khalil, I.A.; Troeger, C.E.; Andrews, J.R.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Crump, J.A.; Im, J. The global burden of typhoid and paratyphoid fevers: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crump, J.A. Progress in typhoid fever epidemiology. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 68, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanmoy, A.M.; Westeel, E.; De Bruyne, K.; Goris, J.; Rajoharison, A.; Sajib, M.S.I.; van Belkum, A.; Saha, S.K.; Komurian-Pradel, F.; Endtz, H.P. Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi in Bangladesh: Exploration of Genomic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance. mBio 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klemm, E.J.; Shakoor, S.; Page, A.J.; Qamar, F.N.; Judge, K.; Saeed, D.K.; Wong, V.K.; Dallman, T.J.; Nair, S.; Baker, S. Emergence of an Extensively Drug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Clone Harboring a Promiscuous Plasmid Encoding Resistance to Fluoroquinolones and Third-Generation Cephalosporins. mBio 2018, 9, e00105–e00118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, N.C.B.; Tanmoy, A.M.; Westeel, E.; de Almeida, L.G.P.; Rajoharison, A.; Islam, M.; Endtz, H.P.; Saha, S.K.; de Vasconcelos, A.T.R.; Komurian-Pradel, F. Analysis of isolates from Bangladesh highlights multiple ways to carry resistance genes in Salmonella Typhi. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hooda, Y.; Sajib, M.S.; Rahman, H.; Luby, S.P.; Bondy-Denomy, J.; Santosham, M.; Andrews, J.R.; Saha, S.K.; Saha, S. Molecular mechanism of azithromycin resistance among typhoidal Salmonella strains in Bangladesh identified through passive pediatric surveillance. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahsan, S.; Rahman, S. Azithromycin Resistance in Clinical Isolates of Salmonella enterica Serovars Typhi and Paratyphi in Bangladesh. Microb. Drug Resist. 2019, 25, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I. Evolutionary Genomics of Defense Systems in Archaea and Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 233–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, L.; Le Hello, S.; Roux, C.; Issenhuth-Jeanjean, S.; Weill, F.-X. CRISPR is an optimal target for the design of specific PCR assays for Salmonella enterica serotypes Typhi and Paratyphi A. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabre, L.; Zhang, J.; Guigon, G.; Le Hello, S.; Guibert, V.; Accou-Demartin, M.; De Romans, S.; Lim, C.; Roux, C.; Passet, V. CRISPR typing and subtyping for improved laboratory surveillance of Salmonella infections. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Aparicio, L.; Rebollar-Flores, J.; Gallego-Hernández, A.; Vázquez, A.; Olvera, L.; Gutiérrez-Ríos, R.; Calva, E.; Hernandez-Lucas, I. The CRISPR/Cas immune system is an operon regulated by LeuO, H-NS, and leucine-responsive regulatory protein in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 2396–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Medina-Aparicio, L.; Rebollar-Flores, J.E.; Beltrán-Luviano, A.A.; Vázquez, A.; Gutiérrez-Ríos, R.M.; Olvera, L.; Calva, E.; Hernández-Lucas, I. CRISPR-Cas system presents multiple transcriptional units including antisense RNAs that are expressed in minimal medium and upregulated by pH in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Microbiology 2017, 163, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourcel, C.; Touchon, M.; Villeriot, N.; Vernadet, J.-P.; Couvin, D.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Vergnaud, G. CRISPRCasdb a successor of CRISPRdb containing CRISPR arrays and cas genes from complete genome sequences, and tools to download and query lists of repeats and spacers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D535–D544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonin, E.V.; Makarova, K.S. Origins and evolution of CRISPR-Cas systems. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2019, 374, 20180087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. The Basic Building Blocks and Evolution of CRISPR–Cas Systems; Portland Press Limited: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Alkhnbashi, O.S.; Costa, F.; Shah, S.A.; Saunders, S.J.; Barrangou, R.; Brouns, S.J.; Charpentier, E.; Haft, D.H.; et al. An updated evolutionary classification of CRISPR-Cas systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deveau, H.; Barrangou, R.; Garneau, J.E.; Labonté, J.; Fremaux, C.; Boyaval, P.; Romero, D.A.; Horvath, P.; Moineau, S. Phage response to CRISPR-encoded resistance in Streptococcus thermophilus. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leenay, R.T.; Maksimchuk, K.R.; Slotkowski, R.A.; Agrawal, R.N.; Gomaa, A.A.; Briner, A.E.; Barrangou, R.; Beisel, C.L. Identifying and visualizing functional PAM diversity across CRISPR-Cas systems. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariat, N.; Timme, R.E.; Pettengill, J.B.; Barrangou, R.; Dudley, E.G. Characterization and evolution of Salmonella CRISPR-Cas systems. Microbiology 2015, 161, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touchon, M.; Rocha, E.P. The small, slow and specialized CRISPR and anti-CRISPR of Escherichia and Salmonella. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Louwen, R.; Staals, R.H.J.; Endtz, H.P.; van Baarlen, P.; van der Oost, J. The Role of CRISPR-Cas Systems in Virulence of Pathogenic Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sampson, T.R.; Napier, B.A.; Schroeder, M.R.; Louwen, R.; Zhao, J.; Chin, C.-Y.; Ratner, H.K.; Llewellyn, A.C.; Jones, C.L.; Laroui, H. A CRISPR-Cas system enhances envelope integrity mediating antibiotic resistance and inflammasome evasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11163–11168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Palmer, K.L.; Gilmore, M.S. Multidrug-resistant enterococci lack CRISPR-cas. MBio 2010, 1, e00227-10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Belkum, A.; Soriaga, L.B.; LaFave, M.C.; Akella, S.; Veyrieras, J.-B.; Barbu, E.M.; Shortridge, D.; Blanc, B.; Hannum, G.; Zambardi, G.; et al. Phylogenetic distribution of CRISPR-Cas systems in antibiotic-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. mBio 2015, 6, e01796-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jaillard, M.; van Belkum, A.; Cady, K.C.; Creely, D.; Shortridge, D.; Blanc, B.; Barbu, E.M.; Dunne Jr, W.M.; Zambardi, G.; Enright, M. Correlation between phenotypic antibiotic susceptibility and the resistome in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 50, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, C.D.; Dyson, Z.A.; Duchene, S.; Carter, M.J.; Gurung, M.; Kelly, D.F.; Murdoch, D.R.; Ansari, I.; Thorson, S.; Shrestha, S.; et al. Laboratory and molecular surveillance of paediatric typhoidal Salmonella in Nepal: Antimicrobial resistance and implications for vaccine policy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.K.; Baker, S.; Pickard, D.J.; Parkhill, J.; Page, A.J.; Feasey, N.A.; Kingsley, R.A.; Thomson, N.R.; Keane, J.A.; Weill, F.-X. Phylogeographical analysis of the dominant multidrug-resistant H58 clade of Salmonella Typhi identifies inter-and intracontinental transmission events. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, V.K.; Baker, S.; Connor, T.R.; Pickard, D.; Page, A.J.; Dave, J.; Murphy, N.; Holliman, R.; Sefton, A.; Millar, M. An extended genotyping framework for Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi, the cause of human typhoid. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Couvin, D.; Bernheim, A.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Touchon, M.; Michalik, J.; Néron, B.; Rocha, C.; Eduardo, P.; Vergnaud, G.; Gautheret, D. CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W246–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Classification and nomenclature of CRISPR-Cas systems: Where from here? Cris. J. 2018, 1, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellner, M.J.; Koob, J.G.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Zhang, F. SHERLOCK: Nucleic acid detection with CRISPR nucleases. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2986–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Ma, E.; Harrington, L.B.; Da Costa, M.; Tian, X.; Palefsky, J.M.; Doudna, J.A. CRISPR-Cas12a target binding unleashes indiscriminate single-stranded DNase activity. Science 2018, 360, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatham-Stephens, K.; Medalla, F.; Hughes, M.; Appiah, G.D.; Aubert, R.D.; Caidi, H.; Angelo, K.M.; Walker, A.T.; Hatley, N.; Masani, S. Emergence of extensively drug-resistant Salmonella Typhi infections among travelers to or from Pakistan—United States, 2016–2018. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2019, 68, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Díez-Villaseñor, C.; Almendros, C.; García-Martínez, J.; Mojica, F.J. Diversity of CRISPR loci in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 2010, 156, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Li, P.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, G.; Xie, J.; Yi, S.; Wang, J.; Cui, X. Polymorphism of CRISPR shows separated natural groupings of Shigella subtypes and evidence of horizontal transfer of CRISPR. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louwen, R.; Horst-Kreft, D.; De Boer, A.; Van Der Graaf, L.; de Knegt, G.; Hamersma, M.; Heikema, A.; Timms, A.; Jacobs, B.; Wagenaar, J. A novel link between Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophage defence, virulence and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 32, 207–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garneau, J.E.; Dupuis, M.-È.; Villion, M.; Romero, D.A.; Barrangou, R.; Boyaval, P.; Fremaux, C.; Horvath, P.; Magadán, A.H.; Moineau, S. The CRISPR/Cas bacterial immune system cleaves bacteriophage and plasmid DNA. Nature 2010, 468, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Samai, P.; Marraffini, L.A. Degradation of Phage Transcripts by CRISPR-Associated RNases Enables Type III CRISPR-Cas Immunity. Cell 2016, 164, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marraffini, L.A.; Sontheimer, E.J. CRISPR Interference Limits Horizontal Gene Transfer in Staphylococci by Targeting DNA. Science 2008, 322, 1843–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mojica, F.J.; Díez-Villaseñor, C.; Soria, E.; Juez, G.J.M.M. Biological significance of a family of regularly spaced repeats in the genomes of Archaea, Bacteria and mitochondria. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 244–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almendros, C.; Guzmán, N.M.; García-Martínez, J.; Mojica, F.J.J.N.M. Anti-cas spacers in orphan CRISPR4 arrays prevent uptake of active CRISPR–Cas IF systems. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newire, E.; Aydin, A.; Juma, S.; Enne, V.; Roberts, A. Identification of a Type IV CRISPR-Cas system located exclusively on IncHI1B/ IncFIB plasmids in Enterobacteriaceae. bioRxiv 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makarova, K.S.; Anantharaman, V.; Grishin, N.V.; Koonin, E.V.; Aravind, L. CARF and WYL domains: Ligand-binding regulators of prokaryotic defense systems. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, K.S.; Koonin, E.V. Annotation and classification of CRISPR-Cas systems. In CRISPR; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 47–75. [Google Scholar]
- Makarova, K.S.; Haft, D.H.; Barrangou, R.; Brouns, S.J.; Charpentier, E.; Horvath, P.; Moineau, S.; Mojica, F.J.; Wolf, Y.I.; Yakunin, A.F. Evolution and classification of the CRISPR–Cas systems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Different Datapoints | Study Type | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surveillance | Outbreak | Travel | Total | |||||||||
| Country | Bangladesh | India | Nepal | Pakistan | Pakistan | Bangladesh | India | Nepal | Pakistan | - | ||
| Total number of Isolates | 536 | 131 | 198 | 20 | 100 | 38 | 22 | 1 | 13 | 1059 | ||
| Total number of CRISPR loci | 690 | 317 | 457 | 53 | 210 | 102 | 54 | 2 | 34 | 1919 | ||
| Range of CRISPR loci | 1–2 | 2–3 | 2–3 | 2–3 | 2–3 | 2–3 | 2–3 | 2-3 | 2-3 | 1–2 | ||
| Number of isolates and average CRISPR loci number by genotypes (genotypes with total ≥10 isolates) | 4.3.1 | No. of Isolates | 15 | 11 | 6 | 4 | 5 | - | 5 | - | 4 | 50 |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | 2–3 (2) | 2–3 (2) | 3 (3) | 2 (2) | - | 3–4 (3) | - | 2–3 (2.5) | 2–3 (2) | ||
| 4.3.1.1 | No. of Isolates | 223 | 24 | 15 | 7 | 4 | 19 | 2 | - | 4 | 298 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | 2 (2) | 2–3 (3) | 2–3 (3) | 2 (2) | 2–3 (3) | 2 (2) | - | 3 (3) | 1–2 (1) | ||
| 4.3.1.1.P1 | No. of Isolates | - | - | - | - | 88 | - | - | - | - | 88 | |
| Loci number | - | - | - | - | 2–3 (2) | - | - | - | - | 2–3 (2) | ||
| 4.3.1.2 | No. of Isolates | 4 | 59 | 133 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 213 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | 2–3 (3) | 2–3 (2) | 2 (2) | 2–3 (2.5) | 2 (2) | 2–3 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 (2) | 2–3 (2) | ||
| 4.3.1.3 | No. of Isolates | 53 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | 55 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | - | - | - | - | 3 (3) | - | - | - | 1–2 (1) | ||
| 4.3.1.3q1 | No. of Isolates | 55 | - | - | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 56 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | - | - | - | - | 3 (3) | - | - | - | 1–2 (1) | ||
| 2.0.0 | No. of Isolates | 18 | 1 | 1 | 3 | - | - | - | - | - | 23 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | 2 (2) | 2 (2) | 2–3 (2) | - | - | - | - | - | 1–2 (1) | ||
| 2.2.0 | No. of Isolates | 3 | 1 | 10 | - | - | - | - | - | 1 | 15 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | 2 (2) | 2 (2) | - | - | - | - | - | 3 (3) | 2 (2) | ||
| 2.3.3 | No. of Isolates | 18 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | 20 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | - | - | - | - | 2–3 (2.5) | - | - | - | 1–2 (1) | ||
| 3.2.2 | No. of Isolates | 61 | 2 | 6 | 1 | - | 2 | - | - | 1 | 73 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | 2–3 (2.5) | 2–3 (1) | 3 (3) | - | 3 (3) | - | - | 3 (3) | 1–2 (1) | ||
| 3.3 | No. of Isolates | 1 | 4 | 3 | 1 | - | - | - | - | 1 | 10 | |
| Loci number | 3 (3) | 2–3 (3) | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | - | - | - | - | 2 (2) | 2-3 (2) | ||
| 3.3.2 | No. of Isolates | 32 | 1 | 16 | - | - | 1 | - | - | - | 50 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | 4 (4) | 2-3 (2) | - | - | 3 (3) | - | - | - | 1–2 (1) | ||
| 3.3.2.Bd1 | No. of Isolates | 19 | - | - | - | - | 2 | - | - | - | 21 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | - | - | - | - | 2 (2) | - | - | - | 1–2 (1) | ||
| 3.3.2.Bd2 | No. of Isolates | 17 | - | - | - | - | 7 | - | - | - | 24 | |
| Loci number | 1–2 (1) | - | - | - | - | 2–3 (2) | - | - | - | 1–2 (2) | ||
| DR UniqueID | All | Surveillance (Bangladesh) | Surveillance (India, Nepal, Pakistan) | Surveillance (All) | Travel | Outbreak | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | |
| Td23a | 456 | 3 | 282 | 285 | 72 | 99 | ||||||
| Td28a | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Td29a | 1054 | 7 | 535 | 3 | 345 | 4 | 880 | 7 | 74 | 100 | ||
| Td29b | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||
| Td29c | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||
| Td34a | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Td35a | 192 | 6 | 148 | 154 | 36 | 2 | ||||||
| Td39a | 41 | 19 | 21 | 40 | 1 | |||||||
| Td39b | 139 | 117 | 16 | 133 | 6 | |||||||
| Td43a | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Td49a | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||
| Td55a | 8 | 1 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||
| Td55b | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||
| Td55c | 5 | 5 | 5 | |||||||||
| Td55d | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||
| Spacer UniqueID | All | Surveillance (Bangladesh) | Surveillance (India, Nepal, Pakistan) | Surveillance (All) | Travel | Outbreak | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | Group-A | Group-B | |
| Ts23b | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32a | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32b | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32c | 1050 | 3 | 531 | 345 | 3 | 876 | 3 | 74 | 100 | |||
| Ts32d | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32e | 1050 | 533 | 345 | 876 | 74 | 100 | ||||||
| Ts32f | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32g | 1052 | 2 | 533 | 2 | 345 | 878 | 2 | 74 | 100 | |||
| Ts32h | 1052 | 7 | 533 | 3 | 345 | 4 | 878 | 7 | 74 | 100 | ||
| Ts32i | 974 | 2 | 471 | 2 | 332 | 803 | 2 | 71 | 100 | |||
| Ts32j | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||
| Ts32k | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32l | 1047 | 533 | 342 | 875 | 73 | 99 | ||||||
| Ts32m | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32n | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32o | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32p | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32q | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32r | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32s | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32t | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32u | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32v | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts32w | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts33a | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts34a | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | |||||||
| Ts34b | 1 | 1 | ||||||||||
| Ts34c | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| Ts34d | 192 | 6 | 148 | 154 | 36 | 2 | ||||||
| Ts34e | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |||||||
| Ts34f | 1 | 7 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 1 | ||||||
| Ts34j | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts36a | 4 | 3 | 3 | 1 | ||||||||
| Ts37a | 6 | 4 | 4 | 2 | ||||||||
| Ts51a | 8 | 1 | 1 | 7 | ||||||||
| Ts51b | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||||||||
| Ts53a | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||||||||
| Ts53b | 4 | 4 | 4 | |||||||||
| Ts53c | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts54a | 178 | 134 | 37 | 171 | 7 | |||||||
| Ts54b | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts54c | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts55a | 454 | 3 | 280 | 283 | 72 | 99 | ||||||
| Ts55b | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts55c | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Ts59a | 3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||
| Ts60a | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Loci Group | Pattern Names | Loci Length (bp) | DR | Spacer Arrangements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Group-A | a1 | 517 | Td29a | Ts32d, Ts32a, Ts32k, Ts32p, Ts32s, Ts32q, Ts32u, Ts32t |
| a2 * | 395, 421, 447, 499 | Td29a | Ts32h, Ts32c, Ts32l, Ts32e, Ts32i, Ts32g | |
| a3 | 579 | Td29a | Ts32m, Ts32o, Ts32r, Ts32b, Ts33a, Ts32w, Ts32n, Ts32f, Ts32v | |
| a4 * | 332, 356 | Td29a | Ts32h, Ts32c, Ts32e, Ts32i, Ts32g | |
| a5 | 360 | Td29a | Ts32g, Ts32e, Ts32l, Ts32c, Ts32h | |
| a6 | 421 | Td29a | Ts32g, Ts32i, Ts32e, Ts32l, Ts32j, Ts32h | |
| a7 * | 273, 299 | Td29a | Ts32g, Ts32l, Ts32c, Ts32h | |
| Group-B | b1 | 102 | Td23a | Ts55a |
| b2 | 102 | Td23a | Ts55b | |
| b3 | 102 | Td23a | Ts55c | |
| b4 | 89 | Td29a | Ts32h | |
| b5 | 80 | Td28a | Ts23b | |
| b6 | 96 | Td29b | Ts37a | |
| b7 | 96 | Td29c | Ts37a | |
| b8 | 129 | Td34a | Ts60a | |
| b9 | 105 | Td35a | Ts34d | |
| b10 | 133 | Td39a | Ts54a | |
| b11 | 133 | Td39a | Ts54c | |
| b12 | 133 | Td39b | Ts54a | |
| b13 | 133 | Td39b | Ts54b | |
| b14 | 121 | Td43a | Ts34j | |
| b15 | 158 | Td49a | Ts59a | |
| b16 | 162 | Td55a | Ts51a | |
| b17 | 164 | Td55b | Ts53a | |
| b18 | 164 | Td55c | Ts53b | |
| b19 | 164 | Td55c | Ts53c | |
| b20 | 162 | Td55d | Ts51b | |
| b21 | 150 | Td29a | Ts32c, Ts32h | |
| b22 | 211 | Td29a | Ts32g, Ts32i, Ts32h |
| DR Unique ID | Sequence | Presence in Number of Isolates | Presence in Group-B Loci | Length of Group-B Loci | CRISPRmap Findings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRISPRmap ID | Structural Motif | Sequence Family | Sub-Type | Superclass | |||||
| Td23a | GCTTCAGTGGCGAACGTCGTGAA | 456 | 456 | 101 | motif 11 | - | - | D | |
| Td28a | TTTTGATGTACTTTTGATGTAATTCTGT | 1 | 1 | 79 | - | - | - | ||
| Td29a | GTGTTCCCCGCGCCAGCGGGGATAAACCG | 1059 | 7 | 88, 149, 210 | Crod_A_G_10_M1_F1 | motif 1 | family 1 | I-E | B |
| Td29b | GTGGGTGGACAGGCTGGACAAAGTGGACA | 3 | 3 | 95 | - | - | - | ||
| Td29c | TGTCCACTTTGTCCAGTCTGTCCACCCAC | 3 | 3 | 95 | - | - | - | ||
| Td34a | TATATTGGGTGATTACAACTCGTTGAAAAATAAG | 1 | 1 | 128 | - | - | F | ||
| Td35a | GTAGACCCTGATCCAGTAGACCCGGTTATCCCTGA | 192 | 192 | 104 | - | - | - | ||
| Td39a | CCAGCTTCTGAGCTGCGAATGCGCTGCTGACAGCGGTAC | 41 | 41 | 132 | motif 18 | - | - | ||
| Td39b | GTACCGCTGTCAGCAGCGCATTCGCAACTCAGAAGCTGG | 139 | 139 | 132 | motif 18 | - | - | ||
| Td43a | TGCGTACCCATCCACCTTTCAGTGCGTACCCATCCACCTTTCA | 1 | 1 | 120 | motif 11 | - | - | ||
| Database | Spacer Name | Genbank Accession | Description | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phage | Ts32a | KY006853.1 | Erythrobacter phage vB_EliS_R6L | 65,675 bp |
| Phage | Ts32g | KR052482.1 | Sinorhizobium phage phiN3 | 206,713 bp |
| Phage | Ts32i | MK268344.1 | Salmonella phage Munch | 350,103 bp |
| Phage | Ts32o | KY045851.1 | Pseudoalteromonas phage C5a | 35,209 bp |
| Phage | Ts32o | MG592431.1 | Vibrio phage 1.049.O._10N.286.54.B5 | 45,021 bp (partial genome) |
| Phage | Ts32o | MG592432.1 | Vibrio phage 1.050.O._10N.286.48.A6 | 45,285 bp (partial genome) |
| Plasmid | Ts34j | WP_128853136.1 | MULTISPECIES: hypothetical protein [Enterobacteriaceae] | 72 aa |
| Plasmid | Ts53a | WP_053521168.1 | hypothetical protein [Salmonella enterica] | 62 aa |
| Plasmid | Ts53a | WP_071785737.1 | hypothetical protein [Salmonella enterica] | 59 aa |
| Plasmid | Ts53a | WP_071790422.1 | hypothetical protein [Salmonella enterica] | 76 aa |
| Plasmid | Ts53b | WP_053521168.1 | hypothetical protein [Salmonella enterica] | 62 aa |
| Plasmid | Ts53b | WP_071785737.1 | hypothetical protein [Salmonella enterica] | 59 aa |
| Plasmid | Ts53c | WP_053521168.1 | hypothetical protein [Salmonella enterica] | 62 aa |
| Plasmid | Ts53c | WP_071785737.1 | hypothetical protein [Salmonella enterica] | 59 aa |
| Plasmid | Ts59a | WP_053521168.1 | hypothetical protein [Salmonella enterica] | 62 aa |
| Plasmid | Ts59a | WP_071785737.1 | hypothetical protein [Salmonella enterica] | 59 aa |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanmoy, A.M.; Saha, C.; Sajib, M.S.I.; Saha, S.; Komurian-Pradel, F.; van Belkum, A.; Louwen, R.; Saha, S.K.; Endtz, H.P. CRISPR-Cas Diversity in Clinical Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Isolates from South Asian Countries. Genes 2020, 11, 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111365
Tanmoy AM, Saha C, Sajib MSI, Saha S, Komurian-Pradel F, van Belkum A, Louwen R, Saha SK, Endtz HP. CRISPR-Cas Diversity in Clinical Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Isolates from South Asian Countries. Genes. 2020; 11(11):1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111365
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanmoy, Arif Mohammad, Chinmoy Saha, Mohammad Saiful Islam Sajib, Senjuti Saha, Florence Komurian-Pradel, Alex van Belkum, Rogier Louwen, Samir Kumar Saha, and Hubert P. Endtz. 2020. "CRISPR-Cas Diversity in Clinical Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Isolates from South Asian Countries" Genes 11, no. 11: 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111365
APA StyleTanmoy, A. M., Saha, C., Sajib, M. S. I., Saha, S., Komurian-Pradel, F., van Belkum, A., Louwen, R., Saha, S. K., & Endtz, H. P. (2020). CRISPR-Cas Diversity in Clinical Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhi Isolates from South Asian Countries. Genes, 11(11), 1365. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111365





