Identification of Genetic Susceptibility Factors Associated with Canine Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Cohort Characteristics
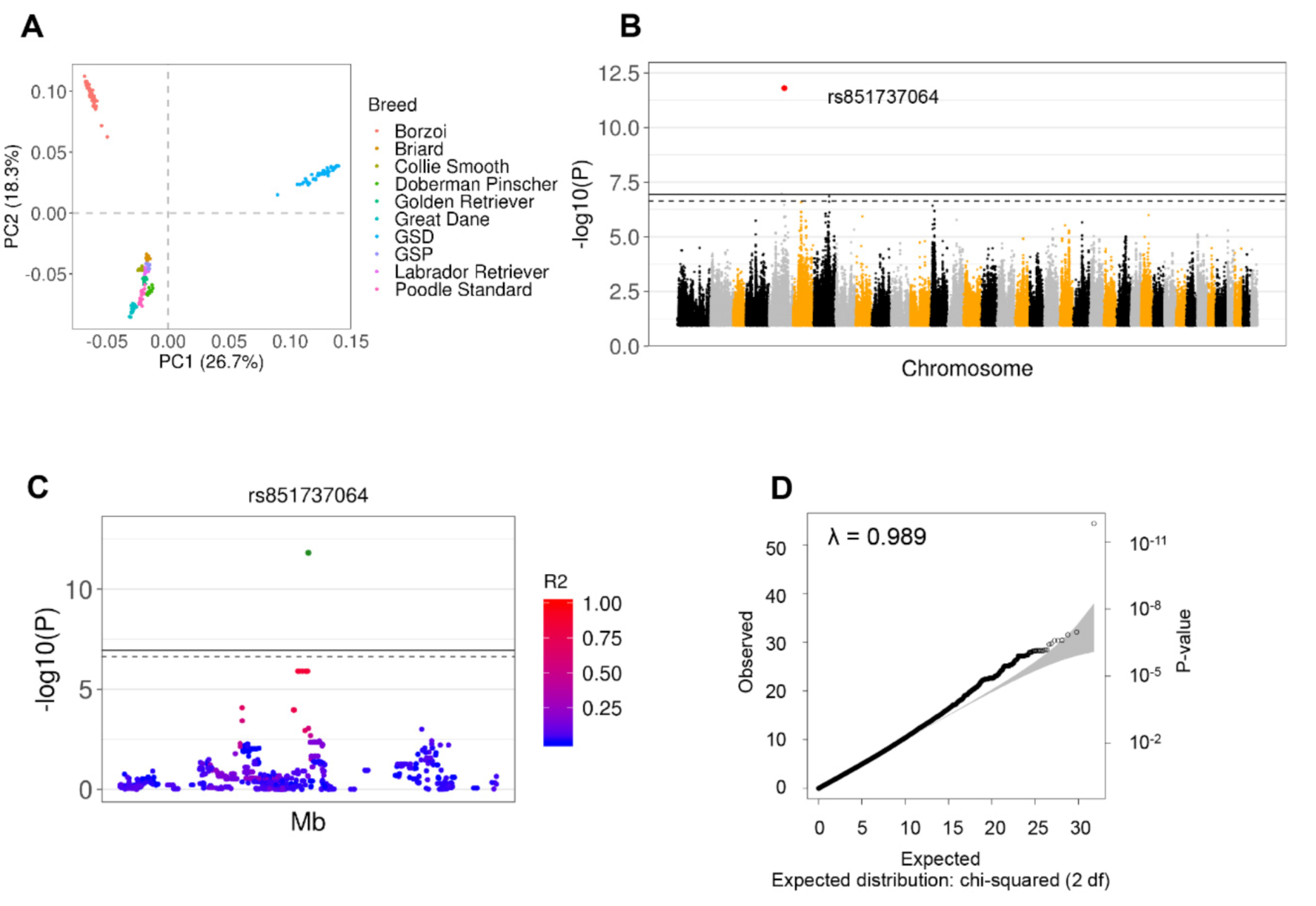
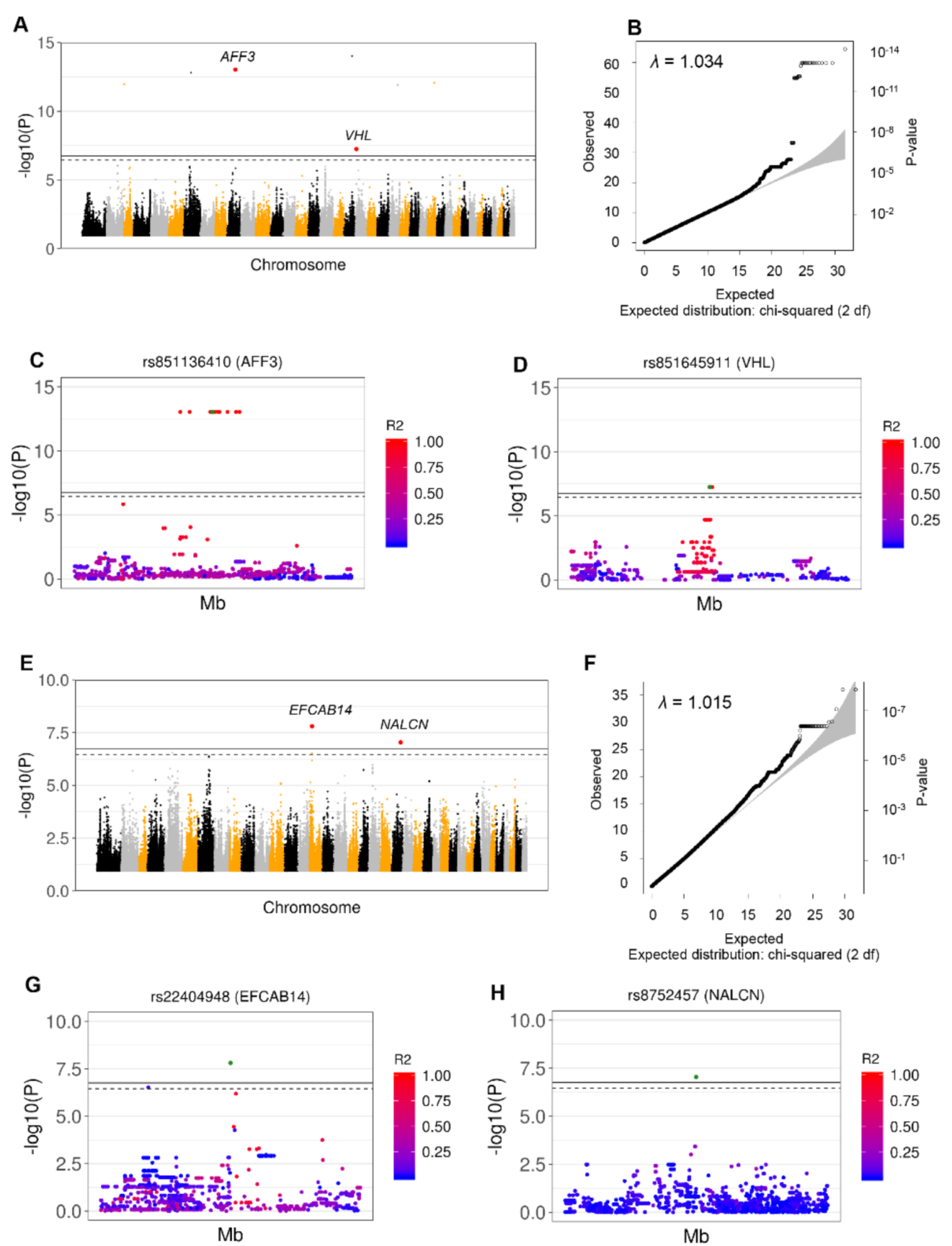
3.2. Identification of 26 Independent SNPs Associated with GDV through GWAS and Imputation from SNP Array Analysis
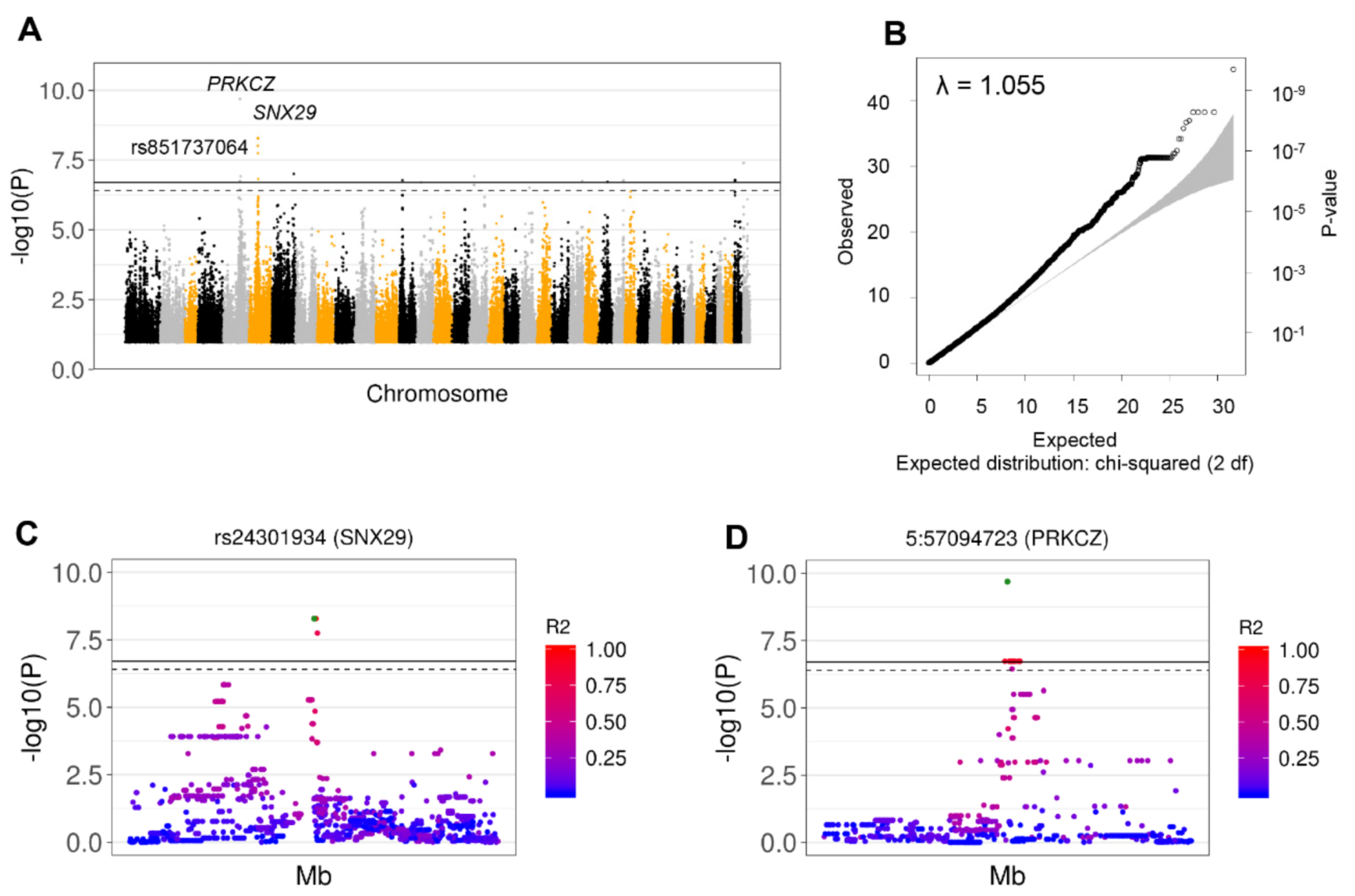
3.3. Nine Independent SNPs Associated with GDV Were Identified by GWAS from Whole Genome Sequencing Data
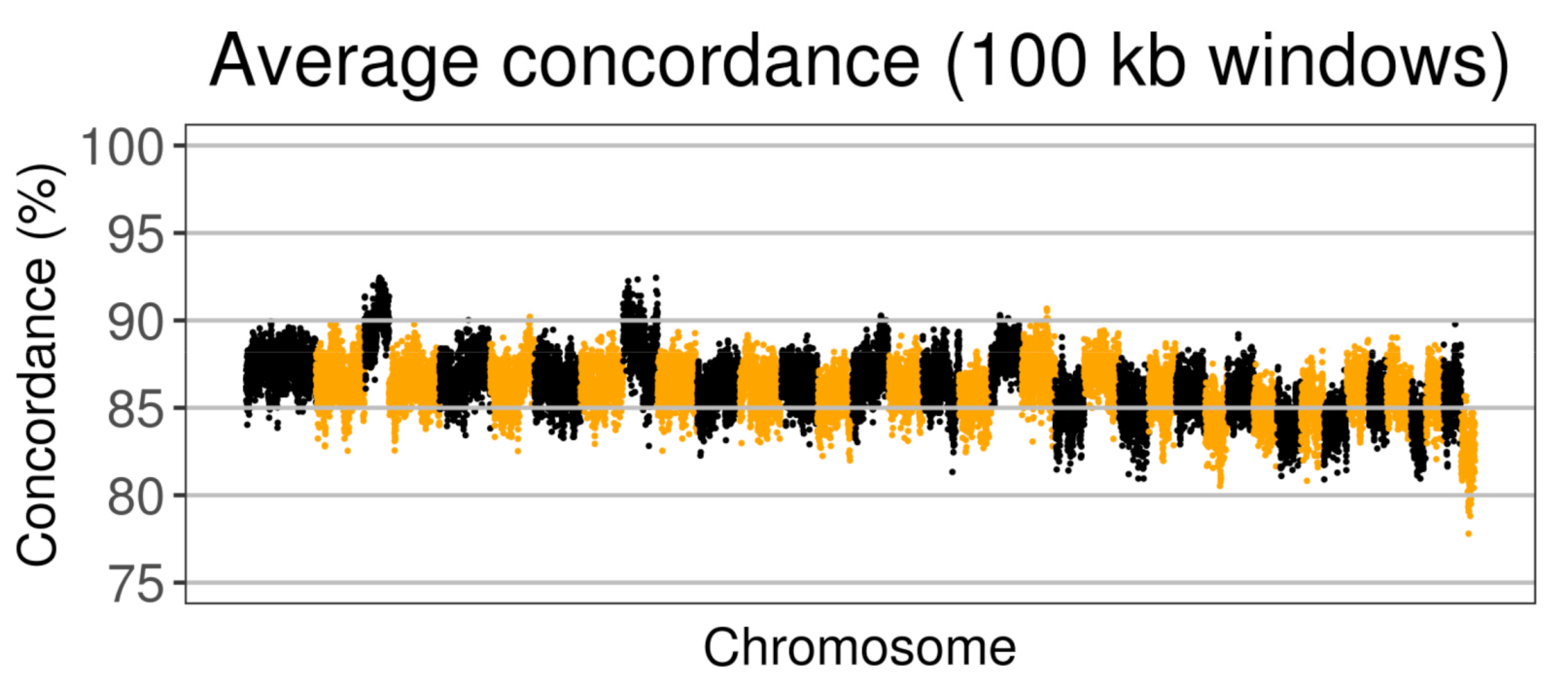
3.4. Concordance of Imputation and WGS Data
3.5. Identification of CNVs Associated with GDV Risk
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glickman, L.T.; Glickman, N.W.; Pérez, C.M.; Schellenberg, D.B.; Lantz, G.C. Analysis of risk factors for gastric dilatation and dilatation-volvulus in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1994, 204, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Przywara, J.F.; Abel, S.B.; Peacock, J.T.; Shott, S. Occurrence and recurrence of gastric dilatation with or without volvulus after incisional gastropexy. Can. Vet. J. 2014, 10, 981–984. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, D.G.; Case, J.; Boag, A.K.; Church, D.B.; McGreevy, P.D.; Thomson, P.C.; Brodbelt, D.C. Gastric dilation-volvulus in dogs attending UK emergency-care veterinary practices: Prevalence, risk factors and survival. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 58, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, P.; Paul, A. Gastropexy for Prevention of Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus in Dogs: History and Techniques. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2014, 29, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.J.; Thomas, T.M.; Hauptman, J.G.; Stanley, B.J. Investigation of potential risk factors for mesenteric volvulus in military working dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2018, 253, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leary, M.L.; Sinnott-Stutzman, V. Spontaneous gastric dilatation-volvulus in two cats. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2018, 28, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, T. A Case of Torsion of the Stomach in a Five-Year-Old Cat. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1968, 9, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formaggini, L.; Schmidt, K.; De Lorenzi, D. Gastric dilatation-volvulus associated with diaphragmatic hernia in three cats: Clinical presentation, surgical treatment and presumptive aetiology. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2008, 10, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nógrádi, A.L.; Cope, I.; Balogh, M.; Gál, J. Review of gastric torsion in eight Guinea pigs (Cavia Porcellus). Acta Vet. Hung. 2017, 65, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinton, J.D.; Aitken-Palmer, C.; Joyner, P.H.; Ware, L.; Walsh, T.F. Fatal gastric dilation in two adult black-footed ferrets (mustela nigripes). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2016, 47, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilsen, C.; Mans, C.; Colopy, S.A. Gastric Dilatation and Volvulus in a Red Panda (Ailurus fulgens). Vet. Surg. 2014, 38, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hinton, J.D.; Padilla, L.R.; Joyner, P.H.; Schnellbacher, R.; Walsh, T.F.; Aitken-Palmer, C. Gastric dilatation volvulus in adult maned wolves (chrysocyon brachyurus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2017, 48, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.S. Inherited and Predisposing Factors in the Development of Gastric Dilatation Volvulus in Dogs. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2014, 29, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, M.; Glickman, N.; McCabe, G.; Lantz, G.; Glickman, L.T. Diet-related risk factors for gastric dilatation-volvulus in dogs of high-risk breeds. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2004, 40, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schellenberg, D.; Yi, Q.; Glickman, N.W.; Glickman, L.T. Influence of Thoracic Conformation and Genetics on the Risk of Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus in Irish Setters. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1998, 34, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaible, R.H.; Ziech, J.; Glickman, N.W.; Schellenberg, D.; Yi, Q.; Glickman, L.T. Predisposition to Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus in Relation to Genetics of Thoracic Conformation in Irish Setters. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1997, 33, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.A.; Willer, R.L.; Seim, H.B.; Powers, B.E. Gross and histologic evaluation of hepatogastric ligaments in clinically normal dogs and dogs with gastric dilatation-volvulus. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1995, 56, 1611–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski, P.S.; Hallman, R.M. Diagnosis of chronic gastric instability using computed tomography in a Great Dane that progressed to gastric dilatation and volvulus: A literature review and case report. Open Vet. J. 2018, 8, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paris, J.K.; Yool, D.A.; Reed, N.; Ridyard, A.E.; Chandler, M.L.; Simpson, J.W. Chronic gastric instability and presumed incomplete volvulus in dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2011, 52, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theyse, L.F.H.; Van de Brom, W.E.; Van Sluijs, F.J. Small size of food particles and age as risk factors for gastric dilatation volvulus in great danes. Vet. Rec. 1998, 143, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, M.; Glickman, N.W.; Glickman, L.T. The effect of ingredients in dry dog foods on the risk of gastric dilatation-volvulus in dogs. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2006, 42, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberbauer, A.M.; Belanger, J.M.; Bellumori, T.; Bannasch, D.L.; Famula, T.R. Ten inherited disorders in purebred dogs by functional breed groupings. Canine Genet. Epidemiol. 2015, 2, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harkey, M.A.; Villagran, A.M.; Venkataraman, G.M.; Leisenring, W.M.; Hullar, M.A.J.; Torok-Storb, B.J. Associations between gastric dilatation-volvulus in great danes and specific alleles of the canine immune-system genes DLA88, DRB1, and TLR5. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 8, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keller, J.; Binnewies, U.; Rösch, M.; Juul Holst, J.; Beglinger, C.; Andresen, V.; Layer, P. Gastric emptying and disease activity in inflammatory bowel disease. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 45, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristinsson, J.O.; Hopman, W.P.M.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Drenth, J.P.H. Gastroparesis in patients with inactive Crohn’s disease: Case series. BMC Gastroenterol. 2007, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kathrani, A.; House, A.; Catchpole, B.; Murphy, A.; German, A.; Werling, D.; Allenspach, K. Polymorphisms in the Tlr4 and Tlr5 gene are significantly associated with inflammatory bowel disease in German shepherd dogs. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathrani, A.; Holder, A.; Catchpole, B.; Alvarez, L.; Simpson, K.; Werling, D.; Allenspach, K. TLR5 risk-associated haplotype for canine inflammatory bowel disease confers hyper-responsiveness to flagellin. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hullar, M.A.J.; Lampe, J.W.; Torok-Storb, B.J.; Harkey, M.A. The canine gut microbiome is associated with higher risk of gastric dilatation-volvulus and high risk genetic variants of the immune system. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeppner, M.P.; Lundquist, A.; Pirun, M.; Meadows, J.R.S.; Zamani, N.; Johnson, J.; Sundström, G.; Cook, A.; FitzGerald, M.G.; Swofford, R.; et al. An improved canine genome and a comprehensive catalogue of coding genes and non-coding transcripts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; Carneiro, M.O.; Hartl, C.; Poplin, R.; del Angel, G.; Levy-Moonshine, A.; Jordan, T.; Shakir, K.; Roazen, D.; Thibault, J.; et al. From fastQ data to high-confidence variant calls: The genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline. Curr. Protoc. Bioinforma. 2013, 43, 11.10.1–11.10.33. [Google Scholar]
- Danecek, P.; Auton, A.; Abecasis, G.; Albers, C.A.; Banks, E.; DePristo, M.A.; Handsaker, R.E.; Lunter, G.; Marth, G.T.; Sherry, S.T.; et al. The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2156–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, J.J.; White, M.E.; Boyle, M.; Shannon, L.M.; Casal, M.L.; Castelhano, M.G.; Center, S.A.; Meyers-Wallen, V.N.; Simpson, K.W.; Sutter, N.B.; et al. Imputation of canine genotype array data using 365 whole-genome sequences improves power of genome-wide association studies. PLOS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Browning, S.R.; Browning, B.L. Rapid and accurate haplotype phasing and missing-data inference for whole-genome association studies by use of localized haplotype clustering. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, C.L.; Bhérer, C.; Morrow, B.E.; Boyko, A.R.; Auton, A. A Pedigree-Based Map of Recombination in the Domestic Dog Genome. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2016, 6, 3517–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durinck, S.; Spellman, P.T.; Birney, E.; Huber, W. Mapping identifiers for the integration of genomic datasets with the R/Bioconductor package biomaRt. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plassais, J.; Kim, J.; Davis, B.W.; Karyadi, D.M.; Hogan, A.N.; Harris, A.C.; Decker, B.; Parker, H.G.; Ostrander, E.A. Whole genome sequencing of canids reveals genomic regions under selection and variants influencing morphology. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hadley, D.; Liu, R.; Glessner, J.; Grant, S.F.A.; Hakonarson, H.; Bucan, M. PennCNV: An integrated hidden Markov model designed for high-resolution copy number variation detection in whole-genome SNP genotyping data. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 1665–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Stephens, M. Genome-wide efficient mixed-model analysis for association studies. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Momozawa, Y.; Merveille, A.C.; Battaille, G.; Wiberg, M.; Koch, J.; Willesen, J.L.; Proschowsky, H.F.; Gouni, V.; Chetboul, V.; Tiret, L.; et al. Genome wide association study of 40 clinical measurements in eight dog breeds. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarviaho, R.; Hakosalo, O.; Tiira, K.; Sulkama, S.; Niskanen, J.E.; Hytönen, M.K.; Sillanpää, M.J.; Lohi, H. A novel genomic region on chromosome 11 associated with fearfulness in dogs. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, J.J.; Castelhano, M.G.; Oliveira, K.C.; Corey, E.; Balkman, C.; Baxter, T.L.; Casal, M.L.; Center, S.A.; Fang, M.; Garrison, S.J.; et al. Complex disease and phenotype mapping in the domestic dog. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, Y.; Sakai, Y.; Nobe, K.; Momose, K. Subcellular distribution of protein kinase C isoforms in gastric antrum smooth muscle of STZ-induced diabetic rats. Life Sci. 1999, 64, 1933–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.M.; Jang, H.J.; Han, S.J.; Ha, E.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, J.W.; Song, K.E.; Jung, S.H.; Ahn, S.M.; Choi, S.E.; et al. Classical PKC is not associated with defective insulin signaling in patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2009, 83, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollenweider, P.; Me, B.; Nicod, P. Insulin resistance, defective insulin receptor substrate 2-associated phosphatidylinositol-3’ kinase activation, and impaired atypical protein kinase C (zeta/lambda) activation in Myotubes From Obese Patients with Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.Y.; Ward, S.M.; Gerthoffer, W.T.; Sanders, K.M. PKC-ε translocation in enteric neurons and interstitial cells of Cajal in response to muscarinic stimulation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2003, 285, G593–G601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roy-Carson, S.; Natukunda, K.; Chou, H.C.; Pal, N.; Farris, C.; Schneider, S.Q.; Kuhlman, J.A. Defining the transcriptomic landscape of the developing enteric nervous system and its cellular environment. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razafinjatovo, C.; Bihr, S.; Mischo, A.; Vogl, U.; Schmidinger, M.; Moch, H.; Schraml, P. Characterization of VHL missense mutations in sporadic clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Hotspots, affected binding domains, functional impact on pVHL and therapeutic relevance. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maxwell, P.H.; Wlesener, M.S.; Chang, G.W.; Clifford, S.C.; Vaux, E.C.; Cockman, M.E.; Wykoff, C.C.; Pugh, C.W.; Maher, E.R.; Ratcliffe, P.J. The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 1999, 399, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimoto, K.; Makino, Y.; Pereira, T.; Poellinger, L. Mechanism of regulation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 4289–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leib, M.S.; Wingfield, W.E.; Twedt, D.C.; Bottoms, G.D. Plasma gastrin immunoreactivity in dogs with acute gastric dilatation-volvulus. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1984, 185, 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, T.; Maruyama, H.; Li, C.; Pastuhov, S.I.; Nix, P.; Bastiani, M.; Hisamoto, N.; Matsumoto, K. Axotomy-induced HIF-serotonin signalling axis promotes axon regeneration in C. elegans. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krejs, G.J. Physiological role of somatostatin in the digestive tract: Gastric acid secretion, intestinal absorption, and motility. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1986, 199, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikander, A.; Rana, S.V.; Prasad, K.K. Role of serotonin in gastrointestinal motility and irritable bowel syndrome. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 403, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Chang, I.Y.; Choi, S.; Jun, J.Y.; Jeon, J.H.; Xu, W.X.; Kwon, Y.K.; Ren, D.; So, I. Involvement of Na + -leak channel in substance P-induced depolarization of pacemaking activity in interstitial cells of Cajal. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forster, J.; Damjanov, I.; Lin, Z.; Sarosiek, I.; Wetzel, P.; McCallum, R.W. Absence of the interstitial cells of Cajal in patients with gastroparesis and correlation with clinical findings. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2005, 9, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zárate, N.; Mearin, F.; Wang, X.Y.; Hewlett, B.; Huizinga, J.D.; Malagelada, J.R. Severe idiopathic gastroparesis due to neuronal and interstitial cells of Cajal degeneration: Pathological findings and management. Gut 2003, 52, 966–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Sayed, M.D.; Al-Zaidan, H.; Albakheet, A.; Hakami, H.; Kenana, R.; Al-Yafee, Y.; Al-Dosary, M.; Qari, A.; Al-Sheddi, T.; Al-Muheiza, M.; et al. Mutations in NALCN cause an autosomal-recessive syndrome with severe hypotonia, speech impairment, and cognitive delay. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenehjem, K.K.; Schweigert, J.; Kumar, P. Atypical Presentation of Viral Gastroenteritis in a Three-year-old Child Due to a UNC80 Mutation. Cureus 2019, 11, e4395. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Noh, H.J.; Wang, D.; Sigurdsson, S.; Swofford, R.; Perloski, M.; Duxbury, M.; Patterson, E.E.; Albright, J.; Castelhano, M.; et al. Candidate genes and functional noncoding variants identified in a canine model of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yao, W.; Wu, H.; Ji, X.; Hu, Z.; Shen, H.; Fan, X.; Ni, C. Association analysis identifies new risk loci for coal workers’ pneumoconiosis in Han Chinese Men. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 163, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Breed | Technology | AF | UF | Informative SNPs | Independent SNPs ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Borzoi, Great Dane, GSD | WGS | 18 | 15 | 2,837,247 | 209,534 |
| Borzoi, Great Dane, GSD * | WGS | 18 | 7 | 2,794,769 | 198,090 |
| Borzoi, Great Dane, GSD | Imputed microarrays | 69 | 61 | 4,093,737 | 274,818 |
| Borzoi, Great Dane, GSD * | Imputed microarrays | 69 | 25 | 4,283,353 | 282,309 |
| All Breeds | Imputed microarrays | 125 | 90 | 4,139,410 | 399,810 |
| All Breeds * | Imputed microarrays | 125 | 45 | 4,519,848 | 434,516 |
| Borzoi | Imputed microarrays | 10 | 45 | 3,335,814 | 141,714 |
| Borzoi * | Imputed microarrays | 10 | 19 | 3,405,912 | 140,326 |
| Great Dane | Imputed microarrays | 22 | 6 | 3,612,725 | 164,347 |
| GSD | Imputed microarrays | 37 | 10 | 3,231,787 | 119,747 |
| Collie, GSP, Great Dane, | Imputed microarrays | 29 | 18 | 4,057,970 | 255,266 |
| Collie, GSP, Great Dane * | Imputed microarrays | 29 | 14 | 4,107,331 | 253,661 |
| All Breeds | Chr | bp | SNP ID | A1 | A2 | Gene | Entire Cohort | SC cohort | Concordance (Allelic Count) ** | ||
| Adj p | Model * | Adj p | Model * | ||||||||
| 5 | 57632433 | rs851737064 | G | A | - | 3.9 × 10−2 | B | 6.8 × 10−7 | A,B | - | |
| 5 | 63538480 | - | C | T | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| 7 | 43676279 | - | A | G | - | - | - | 2.1 × 10−2 | A | 0.800 (20) | |
| 7 | 43680845 | - | A | G | - | - | - | 2.1 × 10−2 | A | 0.800 (20) | |
| 7 | 43691688 | - | T | A | - | - | - | 2.1 × 10−2 | A | 0.800 (20) | |
| 7 | 43691953 | - | T | C | - | - | - | 2.1 × 10−2 | A | 0.800 (20) | |
| 7 | 43678127 | - | C | T | - | - | - | 3.2 × 10−2 | A | - | |
| 5 | 47125974 | - | A | G | - | - | - | 4.6 × 10−2 | B | - | |
| Collie, GSD, GD | 5 | 57094723 | - | G | A | - | 3.6 × 10−3 | A,B | 3.1 × 10−5 | A,B | - |
| 5 | 57632433 | - | G | A | - | 7.2 × 10−3 | A,B | 1.3 × 10−3 | A,B | - | |
| 38 | 2356822 | - | A | G | - | 8.2 × 10−3 | A,B | 6.6 × 10−3 | A,B | 0.833 (12) | |
| 6 | 29829315 | rs24300758 | C | A | - | 1.2 × 10−2 | A,B | 1.3 × 10−3 | A,B | 0.833 (12) | |
| 5 | 57091335 | rs24231711 | G | C | PRKCZ | 3.4 × 10−2 | A,B | 2.0 × 10−2 | A,B | 1.000 (12) | |
| 5 | 57097255 | - | T | C | - | 3.4 × 10−2 | A,B | 2.0 × 10−2 | A,B | 1.000 (12) | |
| 5 | 57097774 | - | T | C | - | 3.4 × 10−2 | A,B | 2.0 × 10−2 | A,B | 1.000 (12) | |
| 5 | 57099671 | rs24220585 | T | G | C1orf86-PRKCZ | 3.4 × 10−2 | A,B | 2.0 × 10−2 | A,B | 1.000 (12) | |
| 5 | 57099975 | - | T | G | - | 3.4 × 10−2 | A,B | 2.0 × 10−2 | A,B | 1.000 (12) | |
| 5 | 57100286 | - | G | T | - | 3.4 × 10−2 | A,B | 2.0 × 10−2 | A,B | 1.000 (12) | |
| Borzoi, GSD, GD | 15 | 13750111 | rs22404948 | G | A | EFCAB14 | - | - | 4.0 × 10−3 | A,B | 0.800 (10) |
| 15 | 13750230 | rs22404947 | A | G | EFCAB14 | - | - | 4.0 × 10−3 | A,B | 0.800 (10) | |
| 22 | 50824204 | rs8752457 | T | C | NALCN | - | - | 2.6 × 10−2 | A,B | 1.000 (14) | |
| 19 | 39848326 | - | C | A | - | 2.6 × 10−9 | A,B | - | - | 0.560 (16) | |
| 10 | 42896897 | - | C | T | - | 2.6 × 10−8 | A,B | - | - | - | |
| 10 | 42913666 | - | T | A | - | 2.6 × 10−8 | A,B | - | - | 0.961 (26) | |
| 10 | 42950857 | - | G | T | - | 2.6 × 10−8 | A,B | - | - | 0.961 (26) | |
| 10 | 42954164 | - | G | T | - | 2.6 × 10−8 | A,B | - | - | 0.961 (26) | |
| 10 | 42954515 | rs851136410 | T | C | AFF3 | 2.6 × 10−8 | A,B | - | - | 0.961 (26) | |
| 10 | 42954869 | - | T | C | - | 2.6 × 10−8 | A,B | - | - | 0.961 (26) | |
| Borzoi | 22 | 31689520 | - | G | C | - | - | - | 6.1 × 10−8 | A,B | 0.800 (10) |
| 22 | 32134106 | rs23055590 | C | G | - | - | - | 2.4 × 10−5 | A,B | 0.800 (10) | |
| 22 | 32134940 | rs23005916 | A | G | - | - | - | 2.4 × 10−5 | A,B | 0.700 (10) | |
| 22 | 33041052 | rs23063720 | C | T | - | - | - | 2.4 × 10−5 | A,B | 0.900 (10) | |
| 22 | 33045940 | - | G | T | - | - | - | 2.4 × 10−5 | A,B | 0.900 (10) | |
| 22 | 32424536 | - | A | G | - | - | - | 3.0 × 10−5 | A,B | 1.000 (10) | |
| 22 | 32424591 | - | C | T | - | - | - | 3.0 × 10−5 | A,B | 1.000 (10) | |
| 22 | 32424650 | - | G | A | - | - | - | 3.0 × 10−5 | A,B | 1.000 (10) | |
| 22 | 32425463 | rs23040592 | C | T | - | - | - | 3.0 × 10−5 | A,B | 0.800 (10) | |
| 22 | 32453864 | - | C | T | - | - | - | 3.0 × 10−5 | A,B | 1.000 (10) | |
| Borzoi, GSD, GD (WGS) *** | 7 | 60392183 | rs24461000 | A | G | - | - | - | 2.1 × 10−2 | A,B | - |
| 7 | 60392379 | rs24436905 | C | T | - | - | - | 2.1 × 10−2 | A,B | - | |
| 7 | 60392380 | rs24436906 | A | G | - | - | - | 2.1 × 10−2 | A,B | - | |
| 7 | 29089260 | - | A | G | - | - | - | 1.1 × 10−2 | B | - | |
| 7 | 29090352 | rs24427856 | A | G | SLC19A2 | - | - | 1.1 × 10−2 | B | - | |
| 7 | 29091216 | - | A | G | - | - | - | 1.1 × 10−2 | B | - | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piras, I.S.; Perdigones, N.; Zismann, V.; Briones, N.; Facista, S.; Rivera, J.L.; Rozanski, E.; London, C.A.; Hendricks, W.P.D. Identification of Genetic Susceptibility Factors Associated with Canine Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus. Genes 2020, 11, 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111313
Piras IS, Perdigones N, Zismann V, Briones N, Facista S, Rivera JL, Rozanski E, London CA, Hendricks WPD. Identification of Genetic Susceptibility Factors Associated with Canine Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus. Genes. 2020; 11(11):1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111313
Chicago/Turabian StylePiras, Ignazio S., Nieves Perdigones, Victoria Zismann, Natalia Briones, Salvatore Facista, José Luis Rivera, Elizabeth Rozanski, Cheryl A. London, and William P. D. Hendricks. 2020. "Identification of Genetic Susceptibility Factors Associated with Canine Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus" Genes 11, no. 11: 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111313
APA StylePiras, I. S., Perdigones, N., Zismann, V., Briones, N., Facista, S., Rivera, J. L., Rozanski, E., London, C. A., & Hendricks, W. P. D. (2020). Identification of Genetic Susceptibility Factors Associated with Canine Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus. Genes, 11(11), 1313. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11111313






