PredLnc-GFStack: A Global Sequence Feature Based on a Stacked Ensemble Learning Method for Predicting lncRNAs from Transcripts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Datasets and Method
2.1. Datasets
2.2. Features Extraction
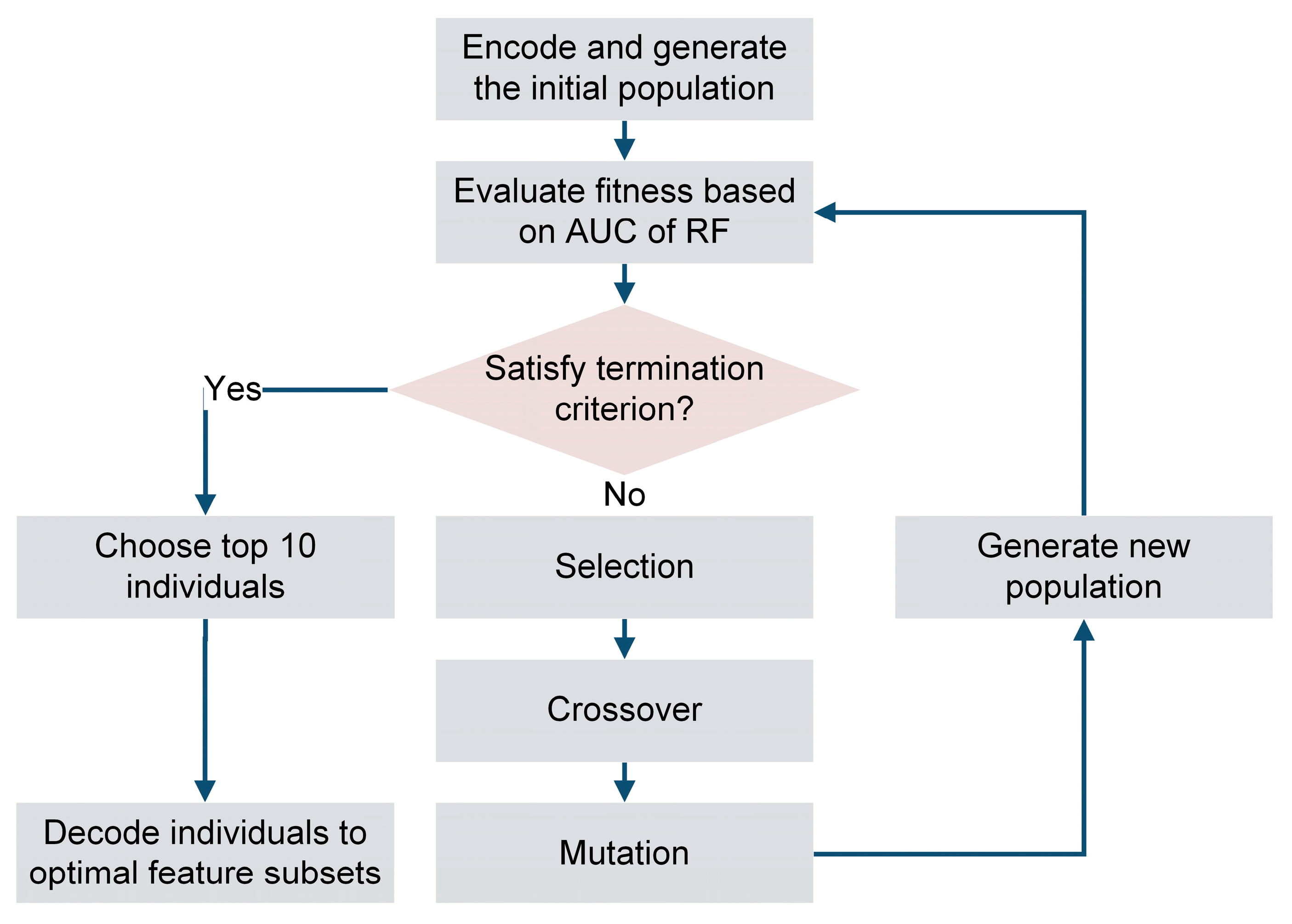
2.3. Feature Selection by Genetic Algorithm and Random Forest (GA-RF)
2.4. Stacked Ensemble Learning in PredLnc-GFStack
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance Evaluation
| (1) | |
| (2) | |
| (3) | |
| (4) | |
| (5) |
3.2. Evaluation of the Optimal Feature Subsets
3.3. Evaluation of PredLnc-GFStack on Different Datasets
3.4. Comparison with Other Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Rinn, J.L. Modular regulatory principles of large non-coding RNAs. Nature 2012, 482, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabili, M.N.; Trapnell, C.; Goff, L.; Koziol, M.; Tazon-Vega, B.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L. Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodrich, J.A.; Kugel, J.F. Non-coding-RNA regulators of RNA polymerase II transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 612–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Elsner, T.; Gou, D.; Kremmer, E.; Sauer, F. Noncoding RNAs of trithorax response elements recruit Drosophila Ash1 to Ultrabithorax. Science 2006, 311, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukiw, W.; Handley, P.; Wong, L.; McLachlan, D.C. BC200 RNA in normal human neocortex, non-Alzheimer dementia (NAD), and senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (AD). Neurochem. Res. 1992, 17, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Ravindranath, L.; Tran, N.; Petrovics, G.; Srivastava, S. Regulation of apoptosis by a prostate-specific and prostate cancer-associated noncoding gene, PCGEM1. Dna Cell Biol. 2006, 25, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prensner, J.R.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, G.; Yang, J.; Fan, X.; Gong, Y.; Xu, G.; Cui, Q.; Geng, B. Transcriptome analysis reveals distinct patterns of long noncoding RNAs in heart and plasma of mice with heart failure. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, P.J.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell 2013, 152, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.-Y.; Yedavalli, V.S.R.K.; Jeang, K.-T. NEAT1 long noncoding RNA and paraspeckle bodies modulate HIV-1 posttranscriptional expression. MBio 2013, 4, e00596-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jathar, S.; Kumar, V.; Srivastava, J.; Tripathi, V. Technological developments in lncRNA biology. In Long Non Coding RNA Biology; Rao, M.R.S., Ed.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2017; pp. 283–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Garcia, J.T.; Hung, T.; Flynn, R.A.; Shen, Y.; Qu, K.; Payumo, A.Y.; Peres-da-Silva, A.; Broz, D.K.; Baum, R.; et al. An inducible long noncoding RNA amplifies DNA damage signaling. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, C. Coding or noncoding, the converging concepts of RNAs. Front. Genet. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, W.; Li, M.; Zhao, K.; Liu, J.; Wu, F.-X.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J. LDAP: A web server for lncRNA-disease association prediction. Bioinformatics 2016, 33, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Qu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. The linear neighborhood propagation method for predicting long non-coding RNA–protein interactions. Neurocomputing 2018, 273, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yue, X.; Tang, G.; Wu, W.; Huang, F.; Zhang, X. SFPEL-LPI: Sequence-based feature projection ensemble learning for predicting LncRNA-protein interactions. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassett, A.R.; Akhtar, A.; Barlow, D.P.; Bird, A.P.; Brockdorff, N.; Duboule, D.; Ephrussi, A.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; Gingeras, T.R.; Haerty, W.; et al. Considerations when investigating lncRNA function in vivo. eLife 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, Z.-Q.; Liu, X.-Q.; Zhao, S.-Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W345–W349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Luo, H.; Bu, D.; Zhao, G.; Yu, K.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, R.; Zhao, Y. Utilizing sequence intrinsic composition to classify protein-coding and long non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z. PLEK: A tool for predicting long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs based on an improved k-mer scheme. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Meng, J. lncRScan-SVM: A tool for predicting long non-coding RNAs using support vector machine. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-J.; Yang, D.-C.; Kong, L.; Hou, M.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC2: A fast and accurate coding potential calculator based on sequence intrinsic features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W12–W16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, H.W.; Raiol, T.; Brigido, M.M.; Walter, M.; Stadler, P.F. A support vector machine based method to distinguish long non-coding RNAs from protein coding transcripts. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Liu, S. CPPred: Coding potential prediction based on the global description of RNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random forest. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achawanantakun, R.; Chen, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y. LncRNA-ID: Long non-coding RNA IDentification using balanced random forests. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3897–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Xu, Z.; Hu, B.; Lu, Z.J. COME: A robust coding potential calculation tool for lncRNA identification and characterization based on multiple features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wucher, V.; Legeai, F.; Hedan, B.; Rizk, G.; Lagoutte, L.; Leeb, T.; Jagannathan, V.; Cadieu, E.; David, A.; Lohi, H.; et al. FEELnc: A tool for long non-coding RNA annotation and its application to the dog transcriptome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cristiano, F.; Veltri, P.; Prosperi, M.; Tradigo, G. On the identification of long non-coding rnas from RNA-Seq. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Shenzhen, China, 15–18 December 2016; pp. 1103–1106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Park, H.J.; Dasari, S.; Wang, S.; Kocher, J.P.; Li, W. CPAT: Coding-potential assessment tool using an alignment-free logistic regression model. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.-N.; Zhang, S.-W. LncRNA-MFDL: Identification of human long non-coding RNAs by fusing multiple features and using deep learning. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.; Lee, B.; Kwon, S.; Yoon, S. LncRNAnet: Long non-coding RNA identification using deep learning. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3889–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Yang, L.; Zhou, M.; Xie, H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, M.D.; Zhu, H. LncADeep: An ab initio lncRNA identification and functional annotation tool based on deep learning. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3825–3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Andrews, B. Distinguishing long non-coding RNAs from mRNAs using a two-layer structured classifier. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 7th International Conference on Computational Advances in Bio and Medical Sciences (ICCABS), Orlando, FL, USA, 19–21 October 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Simopoulos, C.M.A.; Weretilnyk, E.A.; Golding, G.B. Prediction of plant lncRNA by ensemble machine learning classifiers. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pian, C.; Zhang, G.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, L. LncRNApred: Classification of long non-coding RNAs and protein-coding transcripts by the ensemble algorithm with a new hybrid feature. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventola, G.M.; Noviello, T.M.; D’Aniello, S.; Spagnuolo, A.; Ceccarelli, M.; Cerulo, L. Identification of long non-coding transcripts with feature selection: A comparative study. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrow, J.; Frankish, A.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Tapanari, E.; Diekhans, M.; Kokocinski, F.; Aken, B.L.; Barrell, D.; Zadissa, A.; Searle, S. GENCODE: The reference human genome annotation for the ENCODE project. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curwen, V.; Eyras, E.; Andrews, T.D.; Clarke, L.; Mongin, E.; Searle, S.M.J.; Clamp, M. The ensembl automatic gene annotation system. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-hit: A fast program for clustering and comparing large sets of protein or nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilela, C.; McCarthy, J.E. Regulation of fungal gene expression via short open reading frames in the mRNA 5′ untranslated region. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubchak, I.; Muchnik, I.; Holbrook, S.R.; Kim, S.-H. Prediction of protein folding class using global description of amino acid sequence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8700–8704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, L. Handbook of Genetic Algorithms; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Blickle, T.; Thiele, L. A Mathematical analysis of tournament selection. In Proceedings of the ICGA, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1995; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble learning. In The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 2, pp. 110–125. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Ortiz, M.; Gutierrez, P.A.; Hervas-Martinez, C. Projection-based ensemble learning for ordinal regression. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jing, K.; Huang, F.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Li, J.; Gong, J. SFLLN: A sparse feature learning ensemble method with linear neighborhood regularization for predicting drug–drug interactions. Inf. Sci. 2019, 497, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, X.; Fu, Y.; Tsuji, J.; Weng, Z. Predicting human splicing branchpoints by combining sequence-derived features and multi-label learning methods. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Li, D.; Zhang, W.; Tu, S.; Zhu, X.; Tian, G. Accurate prediction of transposon-derived piRNAs by integrating various sequential and physicochemical features. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Luo, L.; Zhang, W.; Liu, F.; Luo, F. A genetic algorithm-based weighted ensemble method for predicting transposon-derived piRNAs. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Bagging predictors. Mach. Learn. 1996, 24, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, M. Thoughts on hypothesis boosting. Unpubl. Manuscr. 1988, 45, 105. [Google Scholar]
- Freund, Y.; Schapire, R.E. A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 1997, 55, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, M.; Li, Q. Predicting linear B-cell epitopes by using sequence-derived structural and physicochemical features. Int. J. Data Min. Bioinform. 2012, 6, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.H. Stochastic gradient boosting. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2002, 38, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Niu, Y.; Zou, H.; Luo, L.; Liu, Q.; Wu, W. Accurate prediction of immunogenic T-cell epitopes from epitope sequences using the genetic algorithm-based ensemble learning. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bühlmann, P.; Yu, B. Analyzing bagging. Ann. Stat. 2002, 30, 927–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Data Sources | Name | Coding RNAs | NcRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|
| GENCODE | Human-Main | 35760 | 20299 |
| Human-Independent | 1500 | 1500 | |
| Mouse-Main | 23987 | 11746 | |
| Mouse-Independent | 1500 | 1500 | |
| preprocess CPPred | Human-Testing | 8557 | 8241 |
| Mouse-Testing | 31102 | 19930 | |
| Zebrafish-Testing | 15594 | 10662 | |
| Fruit-fly-Testing | 17400 | 4098 | |
| S.cerevisiae-Testing | 6713 | 413 | |
| Integrate-Testing | 13903 | 13903 |
| Types | Features (Dimension) |
|---|---|
| codon-related features | stop codon count (1), stop codon frequency (1), stop codon frame score (1), stop codon frequency frame score (1), nucleotide position frequencies (4), Fickett TESTCODE score (1) |
| Open reading frame (ORF)-related features | the first ORF length (1), the longest ORF length (1), the ORF coverage (2), the ORF integrity (1), ORF frame score (1), the entropy density profiles (EDP) of ORF (16) |
| GC-related features | GC (1), GC1 (1), GC2 (1), GC3 (1), GC frame score (1), UTR GC content (2) |
| coding sequence-related features | Coding sequence (CDS) length (1), CDS percentage (1), coding potential of the transcripts (CDS score) (1) |
| transcript-related features | transcript length (1), k-mer (168), CTD (20), Hexamer score (1), Signal to noise ratio (SNR) (1), untranslated region (UTR) coverage (2), EDP (20) |
| structure-related features | Molecular weight (Mw) (1), isoelectric point (pI) (1), pI/Mw (1), pI/Mw frame score (1), Gravy (1), Instability index (1) |
| Optimal Feature Subset No. | Human | Mouse | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Number of Features | AUC | Number of Features | |
| 1 | 0.94979 | 134 | 0.96382 | 118 |
| 2 | 0.94946 | 137 | 0.96350 | 125 |
| 3 | 0.94940 | 131 | 0.96343 | 127 |
| 4 | 0.94934 | 136 | 0.96334 | 123 |
| 5 | 0.94929 | 138 | 0.96327 | 114 |
| 6 | 0.94929 | 134 | 0.96324 | 123 |
| 7 | 0.94923 | 129 | 0.96323 | 115 |
| 8 | 0.94916 | 127 | 0.96323 | 121 |
| 9 | 0.94913 | 137 | 0.96322 | 122 |
| 10 | 0.94910 | 128 | 0.96322 | 119 |
| Dataset | AUC | ACC | SN | SP | PRE | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human | 0.956 | 0.895 | 0.884 | 0.901 | 0.835 | 0.859 |
| Mouse | 0.969 | 0.914 | 0.875 | 0.933 | 0.865 | 0.870 |
| Training Dataset | Testing Dataset | AUC | ACC | SN | SP | PRE | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human-Main | Human-Testing | 0.995 | 0.968 | 0.962 | 0.974 | 0.973 | 0.967 |
| Mouse-Testing | 0.987 | 0.941 | 0.879 | 0.981 | 0.968 | 0.921 | |
| Integrated-Testing | 0.985 | 0.907 | 0.831 | 0.982 | 0.979 | 0.899 | |
| Zebrafish-Testing | 0.971 | 0.901 | 0.772 | 0.989 | 0.980 | 0.863 | |
| Fruit-fly-Testing | 0.992 | 0.940 | 0.714 | 0.993 | 0.962 | 0.819 | |
| S.cerevisiae-Testing | 0.983 | 0.960 | 0.828 | 0.969 | 0.621 | 0.710 | |
| Mouse-Main | Human-Testing | 0.977 | 0.887 | 0.807 | 0.964 | 0.955 | 0.875 |
| Mouse-Testing | 0.995 | 0.944 | 0.869 | 0.992 | 0.985 | 0.924 | |
| Integrated-Testing | 0.984 | 0.871 | 0.757 | 0.985 | 0.981 | 0.855 | |
| Zebrafish-Testing | 0.971 | 0.843 | 0.626 | 0.991 | 0.979 | 0.764 | |
| Fruit-fly-Testing | 0.990 | 0.917 | 0.593 | 0.994 | 0.957 | 0.733 | |
| S.cerevisiae-Testing | 0.964 | 0.942 | 0.382 | 0.976 | 0.500 | 0.433 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.; Liu, F.; Liu, S.; Zhang, W. PredLnc-GFStack: A Global Sequence Feature Based on a Stacked Ensemble Learning Method for Predicting lncRNAs from Transcripts. Genes 2019, 10, 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10090672
Liu S, Zhao X, Zhang G, Li W, Liu F, Liu S, Zhang W. PredLnc-GFStack: A Global Sequence Feature Based on a Stacked Ensemble Learning Method for Predicting lncRNAs from Transcripts. Genes. 2019; 10(9):672. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10090672
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuai, Xiaohan Zhao, Guangyan Zhang, Weiyang Li, Feng Liu, Shichao Liu, and Wen Zhang. 2019. "PredLnc-GFStack: A Global Sequence Feature Based on a Stacked Ensemble Learning Method for Predicting lncRNAs from Transcripts" Genes 10, no. 9: 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10090672
APA StyleLiu, S., Zhao, X., Zhang, G., Li, W., Liu, F., Liu, S., & Zhang, W. (2019). PredLnc-GFStack: A Global Sequence Feature Based on a Stacked Ensemble Learning Method for Predicting lncRNAs from Transcripts. Genes, 10(9), 672. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10090672







