Abstract
The NAC (NAM, ATAF, and CUC) family is one of the largest families of plant-specific transcription factors. It is involved in many plant growth and development processes, as well as abiotic/biotic stress responses. So far, little is known about the NAC family in Chenopodium quinoa. In the present study, a total of 90 NACs were identified in quinoa (named as CqNAC1-CqNAC90) and phylogenetically divided into 14 distinct subfamilies. Different subfamilies showed diversities in gene proportions, exon–intron structures, and motif compositions. In addition, 28 CqNAC duplication events were investigated, and a strong subfamily preference was found during the NAC expansion in quinoa, indicating that the duplication event was not random across NAC subfamilies during quinoa evolution. Moreover, the analysis of Ka/Ks (non-synonymous substitution rate/synonymous substitution rate) ratios suggested that the duplicated CqNACs might have mainly experienced purifying selection pressure with limited functional divergence. Additionally, 11 selected CqNACs showed significant tissue-specific expression patterns, and all the CqNACs were positively regulated in response to salt stress. The result provided evidence for selecting candidate genes for further characterization in tissue/organ specificity and their functional involvement in quinoa’s strong salinity tolerance.
1. Introduction
Quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd., 2n = 4× = 36) is an annual crop that originates from the Andean region of South America [1]. It is recognized as a crop of great value for its high nutritious content and high abiotic stress tolerance [2]. Quinoa produces nutritious grains, which are gluten-free, and have an exceptional balance between oil, essential amino acids, carbohydrates, minerals, vitamins, and dietary fibers [2,3]. Meanwhile, it has a good tolerance to high salinity, drought, and frost, which help it thrive under adverse climatic and soil conditions [4,5,6]. Due to its potential health benefits resulting from the outstanding nutritional value of seeds, and the great adaptability to adverse environments displayed, the emerging crop was recognized by the United Nations when 2013 was declared the International Year of Quinoa [7,8]. Until now, an increasing number of researchers have devoted themselves to the study of quinoa, and a draft of the C. quinoa genome sequence was recently reported [8,9], which provided insights into the mechanisms underlying agronomically important traits of quinoa and laid the foundation for accelerating the genetic improvement of other crops.
Transcription factors are a group of proteins which can regulate the expression of target genes to control plant biological processes. The NAC (NAM, ATAF, and CUC) family is one of the largest families of plant-specific transcription factors [10,11]. Members in the family are characterized by a highly conserved N-terminal region (NAC domain) and a relatively divergent C-terminal transcriptional activation region (TAR) [12,13]. The NAC domain is involved in DNA binding and can be further divided into five subdomains labeled from A to E, while the TAR region usually is related to the regulation of diversity, and may determine some specific functions [10]. The NAC family widely exists in various kinds of plants and is involved in many plant growth and development processes, including lateral root formation [14], leaf senescence [15], flower morphogenesis [16,17], fruit ripening [18], seed development [19], secondary wall synthesis [20], and hormonal signaling [21]. In particular, NAC genes respond to many abiotic/biotic stresses, such as high salinity [22], drought [23], temperature [24], and pathogen defense [25]. Thus, NAC genes are important for various plants to withstand adverse environmental conditions. Soil salinization is a major threat to agriculture and causes a substantial reduction in crop yield and quality. Since quinoa has been characterized as a highly salt-tolerant crop, the mechanism of tolerance has been studied, and novel genes which contribute to salinity tolerance were identified [4,26].
Members of the NAC family have been identified in various plant species, such as Arabidopsis [10,27], rice [28], foxtail millet [13], grape [29], potato [30], maize [31], Chinese cabbage [32], cassava [33], tomato [34], melon [35], switchgrass [36], woodland strawberry [37], cotton [12], and bread wheat [38]. However, genome-wide analysis of the NAC family in quinoa is lacking. With quinoa genome sequencing completed, an opportunity was opened to investigate gene families in quinoa, and a systematic research of the NAC family in quinoa is expected. In the present study, we identified putative NAC genes in quinoa and carried out a relatively detailed study of their phylogeny, genomic structures, conserved motifs, expansion patterns, and expression profiles. Our results will lay an important foundation for future research on the molecular evolution and biological function of the NAC family in quinoa.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Retrieval and Structural Analysis
The quinoa genome database (v1.0) was downloaded from Phytozome v12 (https://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html). The Arabidopsis NAC amino acid sequences were obtained from TAIR (http://www.arabidopsis.org) and were used as queries by searching against the quinoa genome database using the BLASTP program with default parameters [39]. Afterward, the conserved NAC domain of all the potential quinoa NACs were confirmed in the Conserved Domain Database in National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Finally, quinoa NAC sequences with at least four out of five conserved NAC subdomains were selected for the following analysis [10]. Primary and secondary protein structures were predicted with ProtParam (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/) and SOPMA (https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_sopma.html). The subcellular localization was inferred with PSORT (https://psort.hgc.jp/form.html) and Cello (http://cello.life.nctu.edu.tw/).
2.2. Phylogenetic Analysis, Gene Structure, and Protein Motif Prediction
All putative NAC sequences in this study were aligned using the ClustalW program [40]. The alignment file was then used to construct neighbor joining (NJ) phylogenetic trees by MEGA7 with 1000 bootstrap iterations [41]. The information of each NAC gene in quinoa was retrieved from the quinoa database, and the genomic schematic diagrams of the NACs were obtained by comparing the genomic sequences and their predicted coding sequences using the GSDS tool (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn/). The conserved motifs of the quinoa NAC proteins were identified using the MEME program (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme) with parameters set based on a previous study [42]. Sequence logos of the conserved domains were generated with the WebLogo program (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/).
2.3. Chromosomal Localization and Gene Duplication
The chromosomal positions of the quinoa NAC genes were searched from the quinoa database. Duplicated gene pairs were investigated as described in previous reports [43] and illustrated with the Circos program [44]. The Ka (non-synonymous substitution rate) and Ks (synonymous substitution rate) were estimated by DnaSP v5.0 software [45], and the selection pressure for each duplicated gene pair was calculated by the Ka/Ks ratio.
2.4. Plant Materials, RNA Extraction, and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Sterilized quinoa seeds were grown in a growth chamber at 24 °C/22 °C day/night with a photoperiod of 16 h. RNA samples were collected when seedlings were at the 4–5 leaf stage. Root, stem, leaf samples, and the root samples exposed to 300 mM NaCl (salt stress) for 0, 1, and 3 h, were harvested and were immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until RNA isolation. The root samples exposed to 300 mM NaCl for 0 h were selected as controls. Total RNA of each samples (100 mg) was extracted using the RNeasy Plant Mini Kit (QIAGEN), and cDNA was prepared using SuperScript™ III Reverse Transcriptase kit (Invitrogen). The quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) primers were designed (Table S5) and synthesized commercially (HUADA Gene, Beijing, China). The qRT-PCR analysis was performed in the ABI ViiA 7 Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, USA) by 2× QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR mix (QIAGEN), with the programme of 40 cycles and an annealing temperature of 60 °C. The quinoa Elongation Factor 1 alpha (EF1α) gene was used as an endogenous control. Relative gene expression levels were calculated using the 2−⊿⊿Ct method [46]. Each experiment was repeated in triplicate using independent RNA samples. The expression profiles of the NACs in quinoa were clustered using the Cluster 3.0 software [47].
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Identification of Putative NACs in Quinoa
In this study, we identified a total of 90 putative NAC genes in quinoa and designated them as CqNAC1–CqNAC90 (Table S1). The protein structures of CqNACs were highly diverse, the amino acid numbers of all identified CqNACs varied from 145 (CqNAC28) to 631 (CqNAC16), and molecular weight ranged between 16.9 (CqNAC28) and 70.2 kDa (CqNAC16). The isoelectric points ranged from 4.60 (CqNAC86 and CqNAC87) to 9.61 (CqNAC29).
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the NAC Family in Quinoa
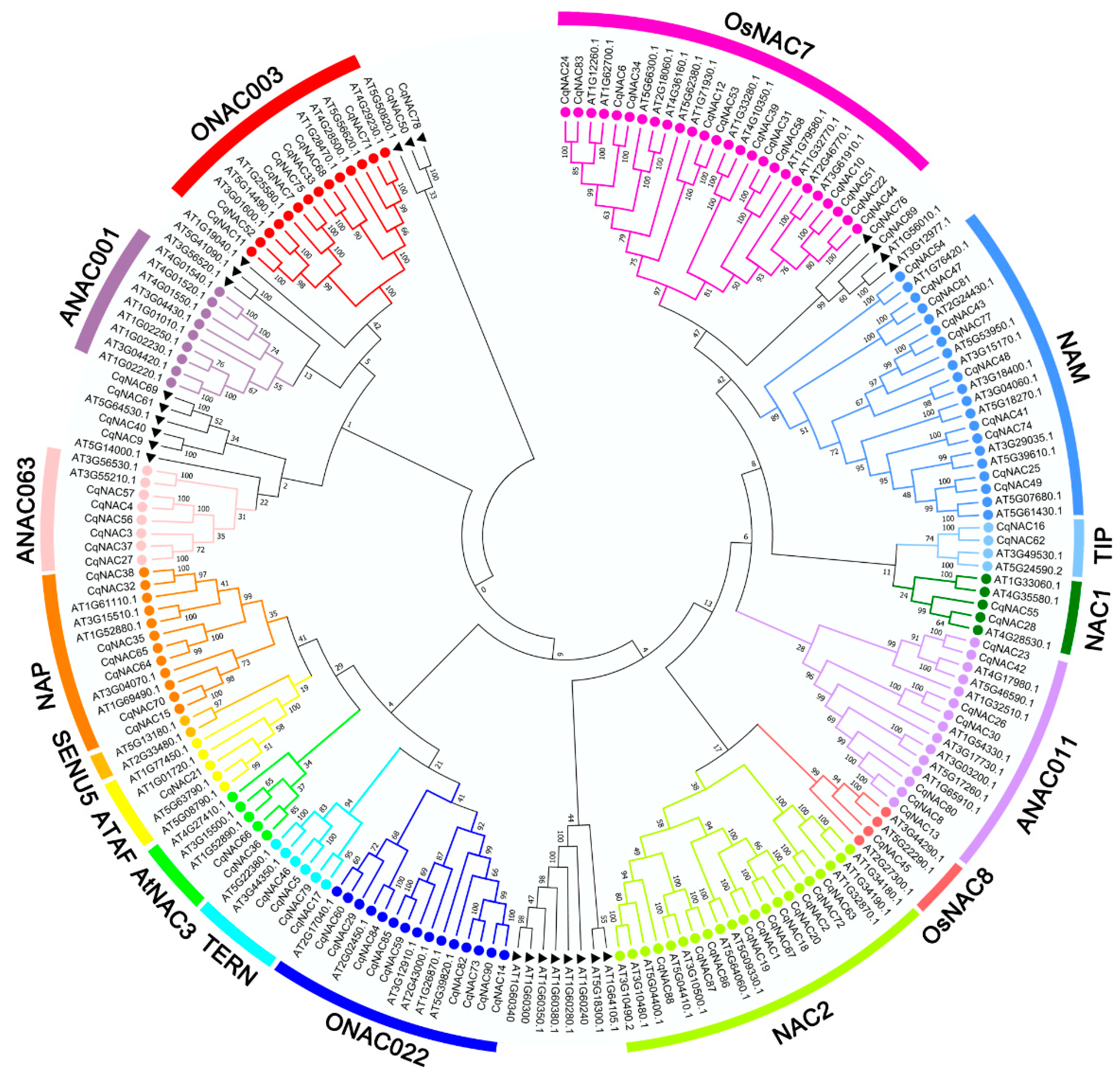
We performed the phylogenetic analysis of the identified CqNAC genes by using MEGA7 (Figure 1, Figure 2a, Table S2). The CqNAC subfamily was defined by a previous classification in the phylogenetic analysis [10]. In this study, the results indicated that 90 CqNACs can be divided into 14 subfamilies, each of which contained a different percentage of the gene members (Figure S1). The OsNAC7 subfamily (14%) contained the most members, followed by the NAC2 (12%) and NAM (11%) subfamilies. The least represented subfamilies were the OsNAC8 (1%) and ATAF (1%) subfamilies. Additionally, no CqNACs were found in the ANAC001 and SENU5 subfamilies, suggesting that they might have been lost in these subfamilies.
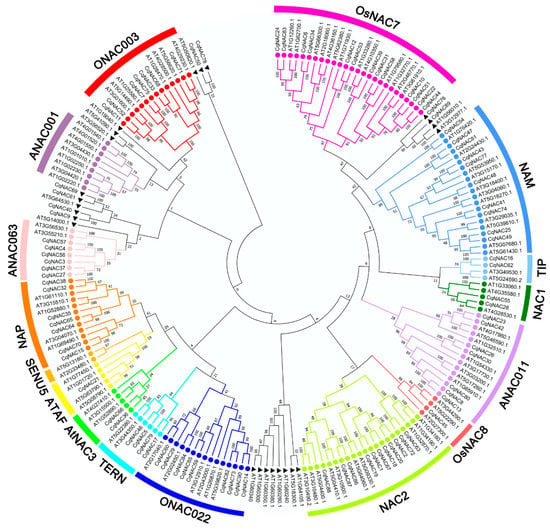
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic relationships of the NAC family in quinoa and Arabidopsis. Full-length amino acid sequences were aligned using ClustalW, and the phylogenetic tree was constructed using the MEGA7 method. The subfamilies are labeled and indicated with different colors. The NACs labeled with a black triangle indicate no group members. The numbers at the nodes represent bootstrap support values from 1000 replicates.
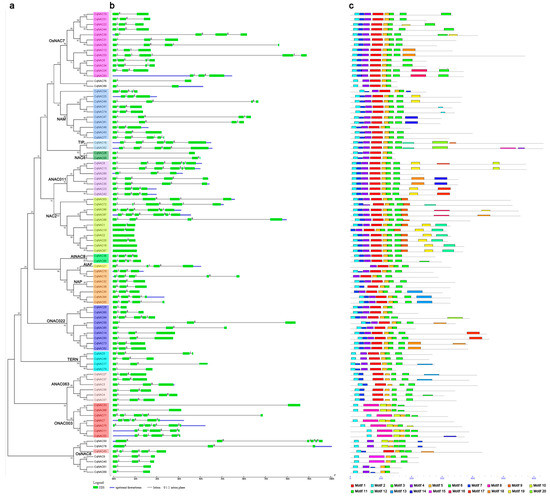
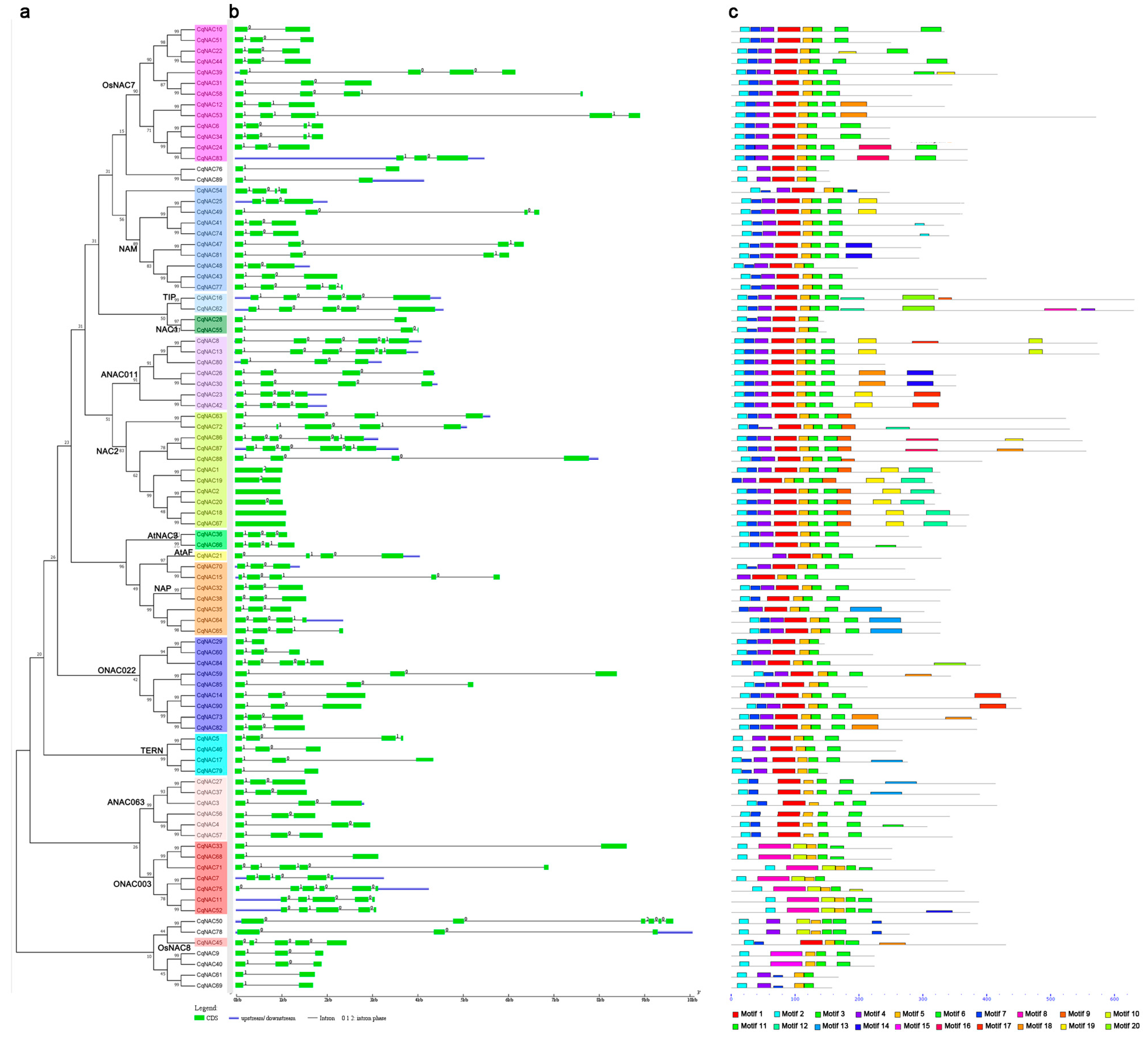
Figure 2.
The gene structures and conserved motifs of CqNAC genes according to the phylogenetic relationship. The phylogenetic tree (a) was generated using the MEGA7 method. Gene structures of CqNACs (b) were predicted with GSDS software. The exons are represented by green boxes, and the introns are indicated by black lines. The conserved motifs (c) were identified by the MEME web server. Each motif is indicated by a colored box numbered at the bottom. The location of each motif can be estimated using the scale at the bottom.
3.3. Exon/Intron Structures and Conserved Protein Motifs of CqNACs
Since the overall pattern of intron position acted as typical imprints of the evolution within some gene families [48,49], the gene structures and intron phases were investigated in the CqNAC family to obtain further insight into their evolutionary path (Figure 2b, Table S2). Results showed that most of the CqNACs (87 of 90 CqNACs) contained introns, the numbers of introns varied from 1 to 5, and the main gene structure was three exons and two introns (36 of 90 CqNACs). Three CqNACs (CqNAC2, CqNAC18, and CqNAC67) from the NAC2 subfamily had no intron, while CqNAC8 (ANAC011 subfamily), CqNAC13 (ANAC011 subfamily), CqNAC50 (No group), CqNAC75 (ONAC003 subfamily), CqNAC86 (NAC2 subfamily), and CqNAC87 (NAC2 subfamily) contained the maximum number of introns. The gains and losses of introns can result in diversity of gene structure. As shown in Figure 2b, some OsNAC7 and NAC2 subfamilies lost an intron between the first and second exons, and the ONAC022 subfamily lacked an intron between the second and third exons. A gain of an intron in the third exon was observed in OsNAC7, NAP, and NAM subfamilies. By contrast, no change was observed in the gene structure of the TIP and ANAC063 subfamilies.
To further investigate the structural diversity of putative NAC proteins in quinoa, 20 distinct conserved motifs were revealed by the MEME program. The motif distribution corresponding to the phylogenetic tree of the CqNAC family is shown in Figure 2c, and their multilevel consensus amino acid sequences of motifs are listed in Figure S2. Generally, NAC proteins that were clustered in the same subgroups shared similar motif composition. Motifs 3, and 5, which represented the highly conserved Subdomain D, were shared in the CqNAC family. Motifs 2, 4, 1, and 6, corresponding to Subdomains A, B, C, and E, also existed in most CqNACs. Meanwhile, a DNA-binding domain (DBD) existed in Subdomain C, and a nuclear localization signal (NLS) was found in Subdomain D (Figure S3). PSORT and Cello analysis showed that most of the NACs in quinoa are localized to the nucleus (Table S3).
3.4. Chromosomal Localization and Duplication of NACs in Quinoa
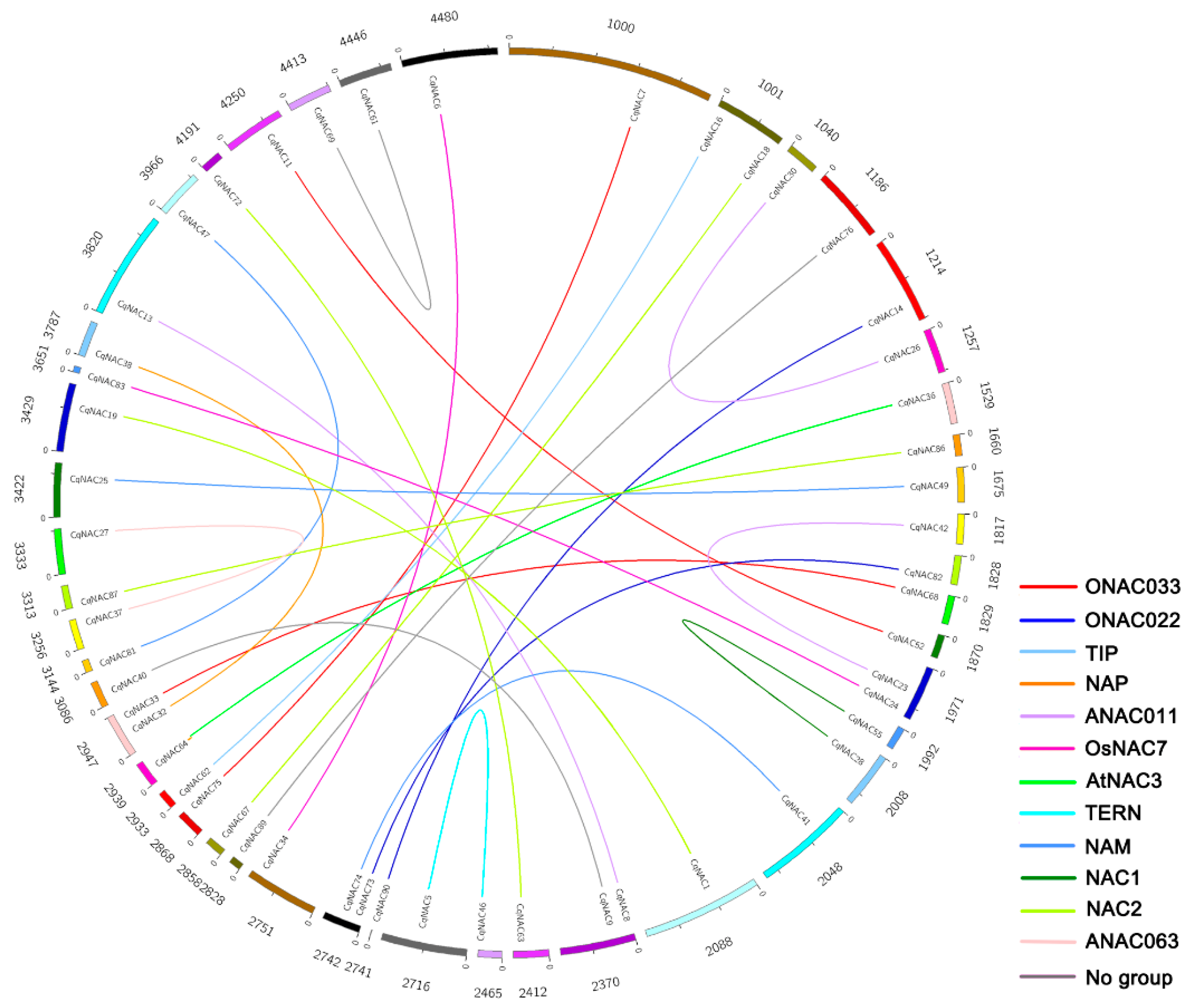
The genomic localization of CqNACs was displayed in Table S4. Gene duplication events were investigated to elucidate the expansion patterns of the NAC family in quinoa. In this study, 28 duplicated gene pairs were identified, and these gene pairs were concentrated in NAC2, ANAC011, NAM, and ONAC003 subfamilies (Figure 3, Table 1). In addition, the Ka/Ks ratio of each duplicated gene pair was calculated to assess the molecular evolutionary rates (Table 1). All of Ka/Ks ratios for the duplicated CqNACs were less than 1.
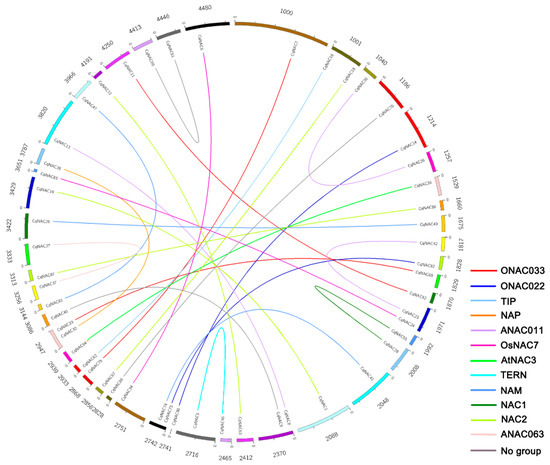
Figure 3.
Distribution of 28 duplicated NAC gene pairs in quinoa. The numbers represent the scaffolds of quinoa which CqNACs are located in. The duplicated gene pairs are joined by colored lines. The differently colored lines represent the subfamilies within the CqNAC family.

Table 1.
Ka/Ks analysis for duplicated gene pairs of NACs in quinoa.
3.5. Expression Profiles of NACs in Quinoa
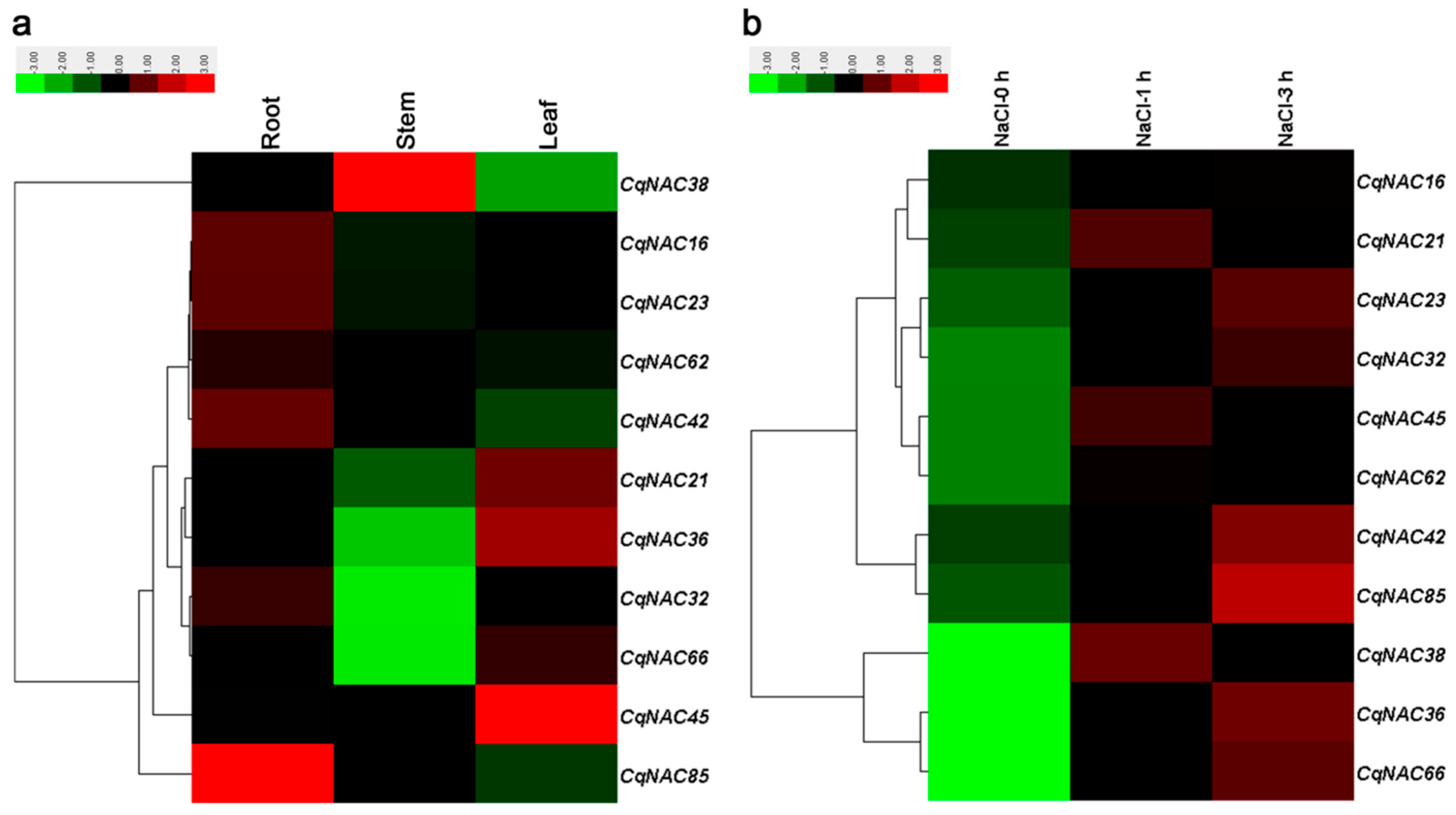
Previous studies have demonstrated that some NAC genes in Arabidopsis, such as ANAC019/AT1G52890 [50], RD26/AT4G27410 [50,51], ANAC2/AT3G15510 [21], NAC096/AT5G46590 [35], ATAF1/AT1G01720 [52], NTL6/AT3G49530 [53], NTL8/AT2G27300 [54], and ANAC042/AT2G43000 [55], played a role in plant responses to salt stress, as well as other abiotic stresses. In the current study, 11 CqNACs which showed high orthology to these AtNACs (Figure 1, Table S6) were selected, and the expression patterns of the 11 selected CqNACs were explored. As shown in Figure 4a, the expression patterns of these CqNACs varied significantly in different tissues. CqNAC38 was predominantly expressed in stems, while CqNAC45, CqNAC36, CqNAC21, and CqNAC66 expressed at a high level in leaves. Other genes, such as CqNAC85, CqNAC16, CqNAC23, CqNAC42, CqNAC62, and CqNAC32, shared a high expression level in roots. Additionally, to further confirm the salt stress response of CqNACs, the expression profiles of 11 CqNACs in the roots of seedlings under salt stress were investigated (Figure 4b). The result revealed that the expression of all 11 selected CqNACs were upregulated in response to salt stress. Among them, CqNAC36, CqNAC38, CqNAC66, and CqNAC85 showed a significant increase in expression levels after salt stress treatment. Moreover, the expression patterns of 4 duplicated CqNAC gene pairs were compared (Figure S4). Among them, 3 paired genes (CqNAC16/CqNAC62, CqNAC23/CqNAC42, and CqNAC32/CqNAC38) shared almost equivalent expression profiles in the tested tissues and root after salt treatment (Figure S4a–c,e–g), but this was not the case for CqNAC32/CqNAC38. The expression patterns of the duplicated gene pair were strongly divergent (Figure S4d,h).
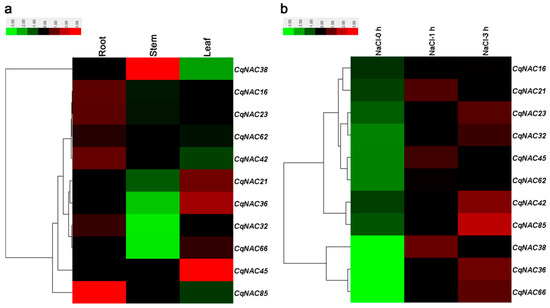
Figure 4.
Expression profiles of 11 CqNAC genes in different tissues (a) and in root under salt stress treatment (b). The color bar at the top of the heat map represents relative expression values.
4. Discussion
With quinoa being a highly stress-tolerant crop, sequencing of its genome facilitates our identification of resistant genes and genetic improvement of crops. The present research performed a genome-wide analysis of the NAC genes in the emerging crop quinoa.
In the present study, we identified a total of 90 NACs genes in quinoa (Table S1). The CqNACs varied substantially in the size, sequence, and the physicochemical properties of their encoded proteins, which were comparable with NACs from other plant species [12,31,33]. Through phylogenetic classification, 14 NAC subfamilies were clustered in quinoa (Figure 1, Figure 2a, Table S2). Among them, the OsNAC7 subfamily had the most CqNACs (14%), followed by the NAC2 (12%) and NAM (11%) subfamilies, whereas the OsNAC8 (1%) and ATAF (1%) subfamilies had the least genes (Figure S1) and a similar distribution of the NAC family was found in cassava [33] and cotton [12]. However, not all the subfamilies were present in quinoa. Compared with the NAC members in Arabidopsis, no CqNAC members were identified in ANAC001 and SENU5 subfamilies, suggesting that quinoa might have experienced gene loss in these subfamilies.
To investigate the structural features of CqNAC genes, gene structures and protein motifs were analyzed, and the distribution of introns/exons and conserved motifs confirmed the similar phylogenetic classification (Figure 2). In the present study, the number of introns of CqNACs varied from 0 to 5 (Figure 2b, Table S2). Most of CqNACs contained introns; only 3 of the CqNACs were intronless, and the predominant gene structure was three exons and two introns, indicating a similar gene structure diversity as NACs in other species [12,33]. The differences in gene structure of CqNAC genes result from the gains and losses of introns, and the diverse status of gene structure might be meaningful for CqNAC gene evolution and could thus facilitate evolutionary gene co-option for new functions to help plants adapt to environmental changes [12,31,33].
In this study, 20 distinct conserved motifs were identified and classified based on sequence similarity of the conserved motifs (Figure 2c, Figure S2). CqNAC proteins clustered in the same subfamilies shared similar motif composition, indicating functional similarities among members of the same subfamilies. Like NAC families in other species, the CqNAC family contained the NAC domain and TAR region, and Subdomains A, C, and D were highly conserved, while Subdomains B and E were relatively divergent (Figure 2c, Figure S3) [10,31]. In addition, a DNA binding domain (DBD) was identified in Subdomain C, which suggested that Subdomain C might be involved in DNA binding [56]. In addition, the putative NLS existed in Subdomain D, and most of the CqNACs were predicted to be nuclear proteins through PSORT and Cello analysis (Table S3). The result has been confirmed for some NACs through subcellular localization [17,23,57].
To elucidate the expanded mechanism of the NAC gene family in quinoa, gene duplication events were investigated (Figure 3, Table 1). We identified a total of 28 duplicated CqNAC gene pairs. The duplication events showed a strong expansion preference for some CqNAC subfamilies, including NAC2, ANAC011, NAM, and ONAC003 subfamilies (Figure 3, Table 1). Thus, the duplication event was not random across NAC subfamilies during quinoa evolution. Moreover, all of the Ka/Ks ratios for the duplicated CqNAC gene pairs were less than 1, suggesting that the CqNACs might have mainly experienced purifying selection (Table 1). As purifying selection apparently constrains the divergence of the duplicated genes, the results indicated that the duplicated CqNAC genes might have retained some essential functions during sequent evolution [42,43].
The analysis of gene expression profiles can provide crucial clues for functional assessment. The result in this study indicated the 11 selected CqNACs showed significant tissue-specific expression patterns (Figure 4a), suggesting that they might play diverse roles in quinoa plant growth and development. Moreover, NAC proteins are plant-specific TFs that have been shown to function in salt stress responses [21,22,23]. With the goal of identifying candidate salt stress-responsive CqNAC genes, we performed the analysis of expression patterns of selected CqNAC genes (Figure 4b). In this study, all the 11 CqNAC were positively regulated in response to salt stress. Among them, CqNAC36, CqNAC66 (orthologous to ANAC019 and RD26), CqNAC38 (orthologous to ANAC2), and CqNAC85 (orthologous to ANAC042) were significantly upregulated. These genes may play a role in the regulation of transcriptional reprogramming associated with plant responses to salt stress and contribute to the establishment of complex signaling networks in plant [58]. They can be selected as candidate genes for further characterization of their functional involvement in plant resistance to salt stress and provide an opportunity to further understand the mechanisms involved in quinoa’s strong salinity tolerance. Moreover, the expression profiles of duplicated CqNAC genes showed that 3 pairs of duplicated genes shared similar expression patterns (Figure S4). The result suggested that these duplicated genes might retain some essential functions during subsequent evolution, and the similar expression profiles might be related to their highly similar protein architecture, together with cis-regulatory elements [12,31]. However, the duplicated genes CqNAC32/CqNAC38 showed significant expression divergence, which might be caused by variation in gene regulation after the duplication events, and the differential expression patterns of duplicated CqNAC genes demonstrated that they might have experienced functionalization during the evolutionary process [31,59].
In conclusion, we identified a total of 90 NAC genes in the quinoa genome and investigated the important features of the gene family, such as basic classification, expansion patterns, and expression profiles. These findings lay an important foundation for identification and molecular evolution of the NAC family in quinoa and provide gene resources for the functional characterization of CqNAC genes involved in salinity tolerance.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4425/10/7/500/s1, Figure S1: The percentage of members in each NAC subfamily in quinoa. Figure S2: Multilevel consensus sequence and their logo of CqNAC proteins as predicted by MEME web server. Figure S3: Conserved domain analysis of the CqNACs using the WebLogo program. Figure S4: Expression patterns of some duplicated CqNAC genes in different organs (a–d) and in root under salt stress treatment (e–h). Table S1: The structural analysis of NACs identified in this study. Table S2: The classification and gene structures of NACs in quinoa. Table S3: Subcellular localization of NAC proteins in quinoa. Table S4: Genomic location of NACs in quinoa. Table S5: PCR primers used for qRT-PCR in this study. Table S6: Orthology information of CqNACs and AtNACs from BLASTP.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.L. and R.W.; Data curation, F.L., X.G. and J.L.; Formal analysis, F.L., X.G., J.L., F.Z., J.W. and H.Z.; Funding acquisition, F.L., J.L. and R.W.; Investigation, F.L., X.G., J.L., F.Z. and W.L.; Project administration, F.L. and R.W.; Resources, R.W.; Software, F.L. and X.G.; Supervision, R.W.; Validation, F.L., X.G., J.W. and H.Z.; Writing—original draft, F.L.; Writing—review & editing, F.L., X.G., H.C., H.S. and R.W.
Funding
This research was funded by the Doctoral Scientific Research Foundation of Shanxi Datong University (2017-B-18), Key Research and Development Projects of Agricultural Science and Technology of Datong, Shanxi (2018042) and Shanxi Provincial Program on Key Basic Research Project (201603D221004-5).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hong, S.; Cheon, K.; Yoo, K.; Lee, H.; Cho, K.; Suh, J.; Kim, S.; Nam, J.; Sohn, H.; Kim, Y. Complete chloroplast genome sequences and comparative analysis of Chenopodium quinoa and C. album. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, Y.; Hirakawa, H.; Oikawa, T.; Toyoshima, M.; Matsuzaki, C.; Ueno, M.; Mizuno, N.; Nagatoshi, Y.; Imamura, T.; Miyago, M. Draft genome sequence of an inbred line of Chenopodium quinoa, an allotetraploid crop with great environmental adaptability and outstanding nutritional properties. DNA Res. 2016, 23, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, B.L.; Rojas Silva, P.; Rojo, L.E.; Delatorre Herrera, J.; Baldeón, M.E.; Raskin, I. Innovations in health value and functional food development of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 2015, 14, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolf, V.I.; Jacobsen, S.; Shabala, S. Salt tolerance mechanisms in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Environ. Exp. Bot. 2013, 92, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.; Monteros, C.; Corcuera, L.J.; Bravo, L.A.; Christiansen, J.L.; Mujica, A. Frost resistance mechanisms in quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Eur. J. Agron. 2007, 26, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A.; Zurita-Silva, A.; Maldonado, J.; Silva, H. Transcriptional responses of Chilean quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) under water deficit conditions uncovers ABA-independent expression patterns. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zurita-Silva, A.; Fuentes, F.; Zamora, P.; Jacobsen, S.; Schwember, A.R. Breeding quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.): Potential and perspectives. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, D.E.; Ho, Y.S.; Lightfoot, D.J.; Schmöckel, S.M.; Li, B.; Borm, T.J.; Ohyanagi, H.; Mineta, K.; Michell, C.T.; Saber, N. The genome of Chenopodium quinoa. Nature 2017, 542, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Chen, A.; Xiao, L.; Muller, H.M.; Ache, P.; Haberer, G.; Zhang, M.; Jia, W.; Deng, P.; Huang, R.; et al. A high-quality genome assembly of quinoa provides insights into the molecular basis of salt bladder-based salinity tolerance and the exceptional nutritional value. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooka, H.; Satoh, K.; Doi, K.; Nagata, T.; Otomo, Y.; Murakami, K.; Matsubara, K.; Osato, N.; Kawai, J.; Carninci, P. Comprehensive analysis of NAC family genes in Oryza sativa and Arabidopsis thaliana. DNA Res. 2003, 10, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.N.; Ernst, H.A.; Leggio, L.L.; Skriver, K. NAC transcription factors: Structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci. 2005, 10, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Li, F.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, W.; Cai, S.; Liu, J.; Lin, W. Asymmetric evolution and expansion of the NAC transcription factor in polyploidized cotton. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puranik, S.; Sahu, P.P.; Mandal, S.N.; Parida, S.K.; Prasad, M. Comprehensive genome-wide survey, genomic constitution and expression profiling of the NAC transcription factor family in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.J.; Wei, W.; Song, Q.X.; Chen, H.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, F.; Zou, H.F.; Lei, G.; Tian, A.G.; Zhang, W.K. Soybean NAC transcription factors promote abiotic stress tolerance and lateral root formation in transgenic plants. Plant J. 2011, 68, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Nam, H.G.; Lim, P.O. Regulatory network of NAC transcription factors in leaf senescence. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2016, 33, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sablowski, R.W.; Meyerowitz, E.M. A homolog of NO APICAL MERISTEM is an immediate target of the floral homeotic genes APETALA3/PISTILLATA. Cell 1998, 92, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Dai, S.; Singh, P.K.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Tan, J.L.; Wee, W.; Ito, T. A membrane-bound NAC-like transcription factor OsNTL5 represses the flowering in Oryza sativa. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, G.; Zhou, S.; Tu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, T.; Hu, Z. A new tomato NAC (NAM/ATAF1/2/CUC2) transcription factor, SlNAC4, functions as a positive regulator of fruit ripening and carotenoid accumulation. Plant Cell Physiol. 2013, 55, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, I.E.; Das, S.; Mahto, A.; Agarwal, P. Three rice NAC transcription factors heteromerize and are associated with seed size. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, R.; Demura, T.; Ye, Z. SND1, a NAC domain transcription factor, is a key regulator of secondary wall synthesis in fibers of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3158–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.J.; Mu, R.L.; Cao, W.H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Zhang, J.S.; Chen, S.Y. AtNAC2, a transcription factor downstream of ethylene and auxin signaling pathways, is involved in salt stress response and lateral root development. Plant J. 2005, 44, 903–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, H.; Guo, Q.; Chen, L.; Ren, F.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X. Two Brassica napus genes encoding NAC transcription factors are involved in response to high-salinity stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2012, 31, 1991–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Chen, B.; Lu, G.; Han, B. Overexpression of a NAC transcription factor enhances rice drought and salt tolerance. Biochem. Bioph. Res. Commun. 2009, 379, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Li, K.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Hao, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S. A novel NAC transcription factor, PbeNAC1, of Pyrus betulifolia confers cold and drought tolerance via interacting with PbeDREBs and activating the expression of stress-responsive genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Huang, L.; Hong, Y.; Ding, X.S.; Nelson, R.S.; Zhou, X.; Song, F. Functions of rice NAC transcriptional factors, ONAC122 and ONAC131, in defense responses against Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Mol. Biol. 2013, 81, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmöckel, S.M.; Lightfoot, D.J.; Razali, R.; Tester, M.; Jarvis, D.E. Identification of putative transmembrane proteins involved in salinity tolerance in Chenopodium quinoa by integrating physiological data, RNAseq, and SNP analyses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.K.; Kjaersgaard, T.; Nielsen, M.M.; Galberg, P.; Petersen, K.; O’Shea, C.; Skriver, K. The Arabidopsis thaliana NAC transcription factor family: Structure-function relationships and determinants of ANAC019 stress signalling. Biochem. J. 2010, 426, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruzzaman, M.; Manimekalai, R.; Sharoni, A.M.; Satoh, K.; Kondoh, H.; Ooka, H.; Kikuchi, S. Genome-wide analysis of NAC transcription factor family in rice. Gene 2010, 465, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zheng, Y.; Xin, H.; Fang, L.; Li, S. Comprehensive analysis of NAC domain transcription factor gene family in Vitis vinifera. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Sharma, V.; Pal, A.K.; Acharya, V.; Ahuja, P.S. Genome-wide organization and expression profiling of the NAC transcription factor family in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). DNA Res. 2013, 20, 403–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Wang, M.; Miao, Y.; Ni, M.; Bibi, N.; Yuan, S.; Li, F.; Wang, X. Molecular evolution and expansion analysis of the NAC transcription factor in Zea mays. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Song, X.; Duan, W.; Huang, Z.; Liu, G.; Li, Y.; Hou, X. Genome-wide analysis and expression patterns of NAC transcription factor family under different developmental stages and abiotic stresses in Chinese cabbage. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wei, Y.; Xia, Z.; Yan, Y.; Hou, X.; Zou, M.; Lu, C.; Wang, W.; Peng, M. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in cassava. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e136993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Zhang, S.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, D.; Han, L. Genome-wide analysis of NAM-ATAF1, 2-CUC2 transcription factor family in Solanum lycopersicum. J. Plant Biochem. Biot. 2015, 24, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Gao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, X.; Huang, D. Genome-wide investigation of the NAC transcription factor family in melon (Cucumis melo L.) and their expression analysis under salt stress. Plant Cell Rep. 2016, 35, 1827–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, A.; Ye, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Wang, C.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, X.; Peng, Y. Genome-wide survey of switchgrass NACs family provides new insights into motif and structure arrangements and reveals stress-related and tissue-specific NACs. Sci. Rep. -UK 2017, 7, 3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Kang, H.; Su, C.; Qi, Y.; Liu, X.; Pu, J. Genome-wide identification and expression profile analysis of the NAC transcription factor family during abiotic and biotic stress in woodland strawberry. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e197892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guérin, C.; Roche, J.; Allard, V.; Ravel, C.; Mouzeyar, S.; Bouzidi, M.F. Genome-wide analysis, expansion and expression of the NAC family under drought and heat stresses in bread wheat (T. aestivum L.). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e213390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Madden, T.L.; Schäffer, A.A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Miller, W.; Lipman, D.J. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: A new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3389–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.D.; Higgins, D.G.; Gibson, T.J. CLUSTAL W: Improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4673–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Fan, K.; Ma, F.; Yue, E.; Bibi, N.; Wang, M.; Shen, H.; Hasan, M.M.; Wang, X. Genomic identification and comparative expansion analysis of the non-specific lipid transfer protein gene family in Gossypium. Sci. Rep. -UK 2016, 6, 38948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Li, W.; He, Q.; Daud, M.K.; Chen, J.; Zhu, S. Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of calcium-dependent protein kinase in Gossypium raimondii. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzywinski, M.I.; Schein, J.E.; Birol, I.; Connors, J.; Gascoyne, R.; Horsman, D.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A. Circos: An information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Hoon, M.J.; Imoto, S.; Nolan, J.; Miyano, S. Open source clustering software. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 1453–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogozin, I.B.; Sverdlov, A.V.; Babenko, V.N.; Koonin, E.V. Analysis of evolution of exon-intron structure of eukaryotic genes. Brief. Bioinform. 2005, 6, 118–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo, E.M.; Casano, L.M.; Barreno, E. Evolutionary implications of intron-exon distribution and the properties and sequences of the RPL10A gene in eukaryotes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 66, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, L.S.; Nakashima, K.; Sakuma, Y.; Simpson, S.D.; Fujita, Y.; Maruyama, K. Isolation and functional analysis of Arabidopsis stress inducible NAC transcription factors that bind to a drought responsive cis-element in the early responsive to dehydration stress 1 promoter. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 2481–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Fujita, Y.; Maruyama, K.; Seki, M.; Hiratsu, K.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Tran, L.P.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. A dehydration induced NAC protein, RD26, is involved in a novel ABA-dependent stress-signaling pathway. Plant J. 2004, 39, 863–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, Y. Arabidopsis ATAF1 enhances the tolerance to salt stress and ABA in transgenic rice. J. Plant Res. 2016, 129, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.J.; Park, M.J.; Seo, P.J.; Song, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, C.M. Controlled nuclear import of the transcription factor NTL6 reveals a cytoplasmic role of SnRK2. 8 in the drought-stress response. Biochem. J. 2012, 448, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.G.; Lee, A.K.; Yoon, H.K.; Park, C.M. A membrane-bound NAC transcription factor NTL8 regulates gibberellic acid-mediated salt signaling in Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant J. 2008, 55, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.; Allu, A.D.; Garapati, P.; Siddiqui, H.; Dortay, H.; Zanor, M.I.; Asensi-Fabado, M.A.; Munné-Bosch, S.; Antonio, C.; Tohge, T.; et al. JUNGBRUNNEN1, a reactive oxygen species–responsive NAC transcription factor, regulates longevity in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 482–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernst, H.A.; Olsen, A.N.; Skriver, K.; Larsen, S.; Leggio, L.L. Structure of the conserved domain of ANAC, a member of the NAC family of transcription factors. EMBO Rep. 2004, 5, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Bibi, N.; Gan, S.; Li, F.; Yuan, S.; Ni, M.; Wang, M.; Shen, H.; Wang, X. A novel NAP member GhNAP is involved in leaf senescence in Gossypium hirsutum. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 4669–4682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuruzzaman, M.; Sharoni, A.M.; Kikuchi, S. Roles of NAC transcription factors in the regulation of biotic and abiotic stress responses in plants. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, K.L. Evolution of duplicate gene expression in polyploid and hybrid plants. J. Hered. 2007, 98, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).